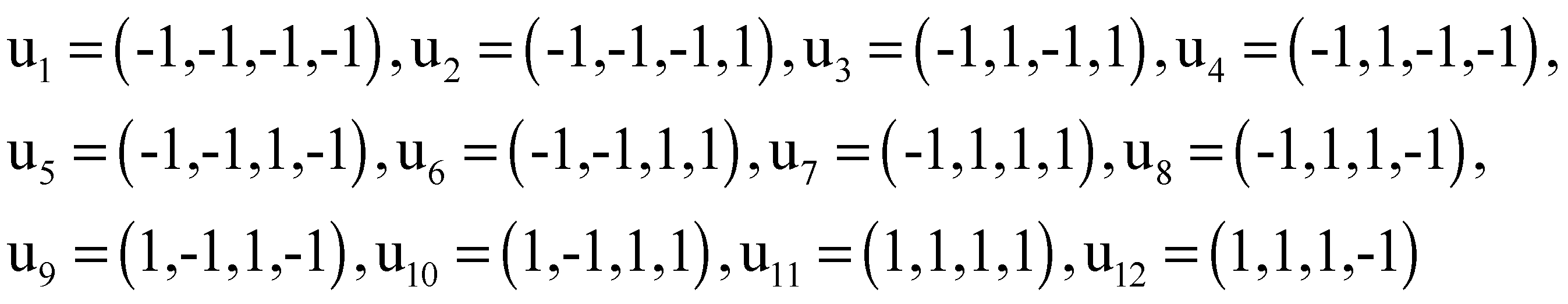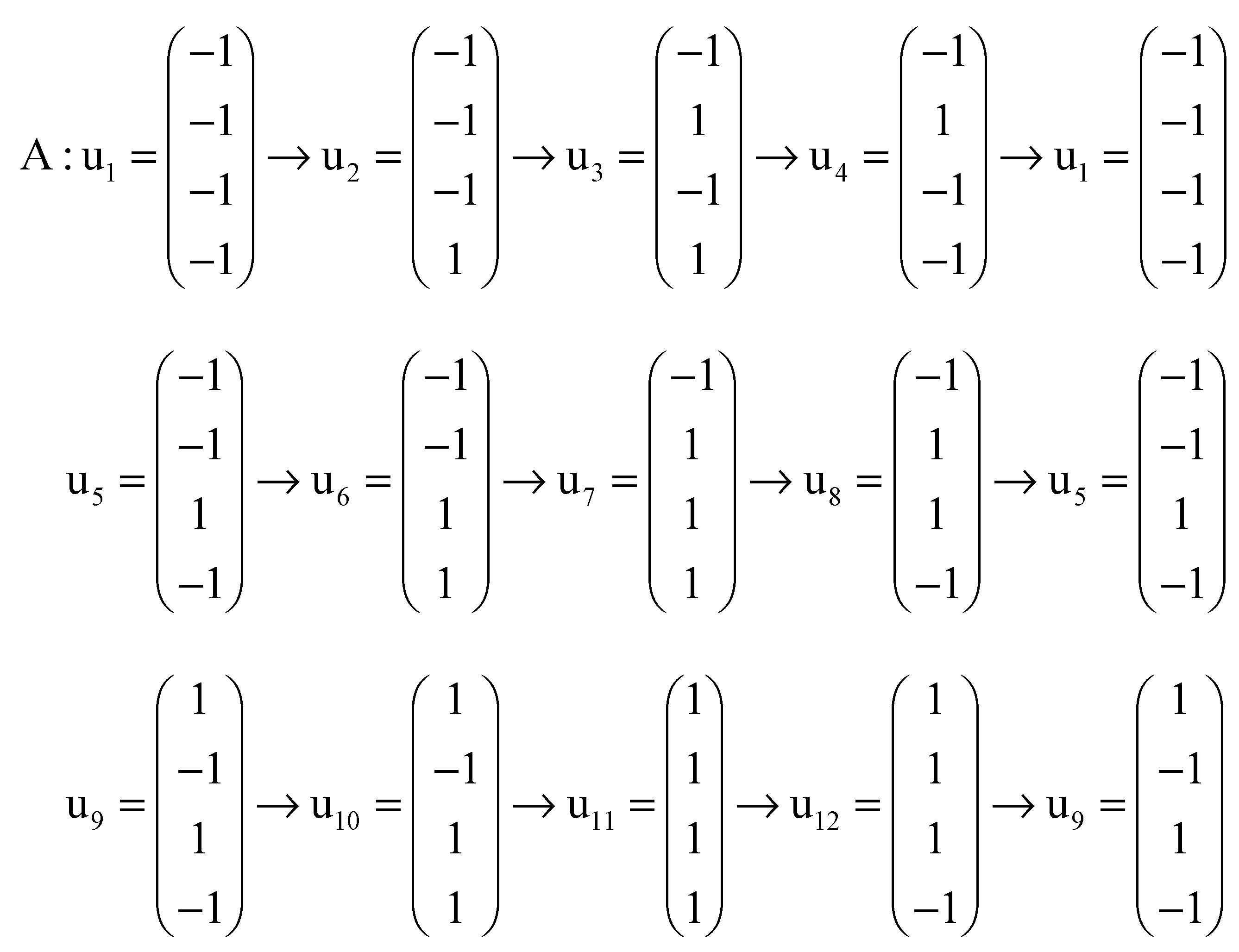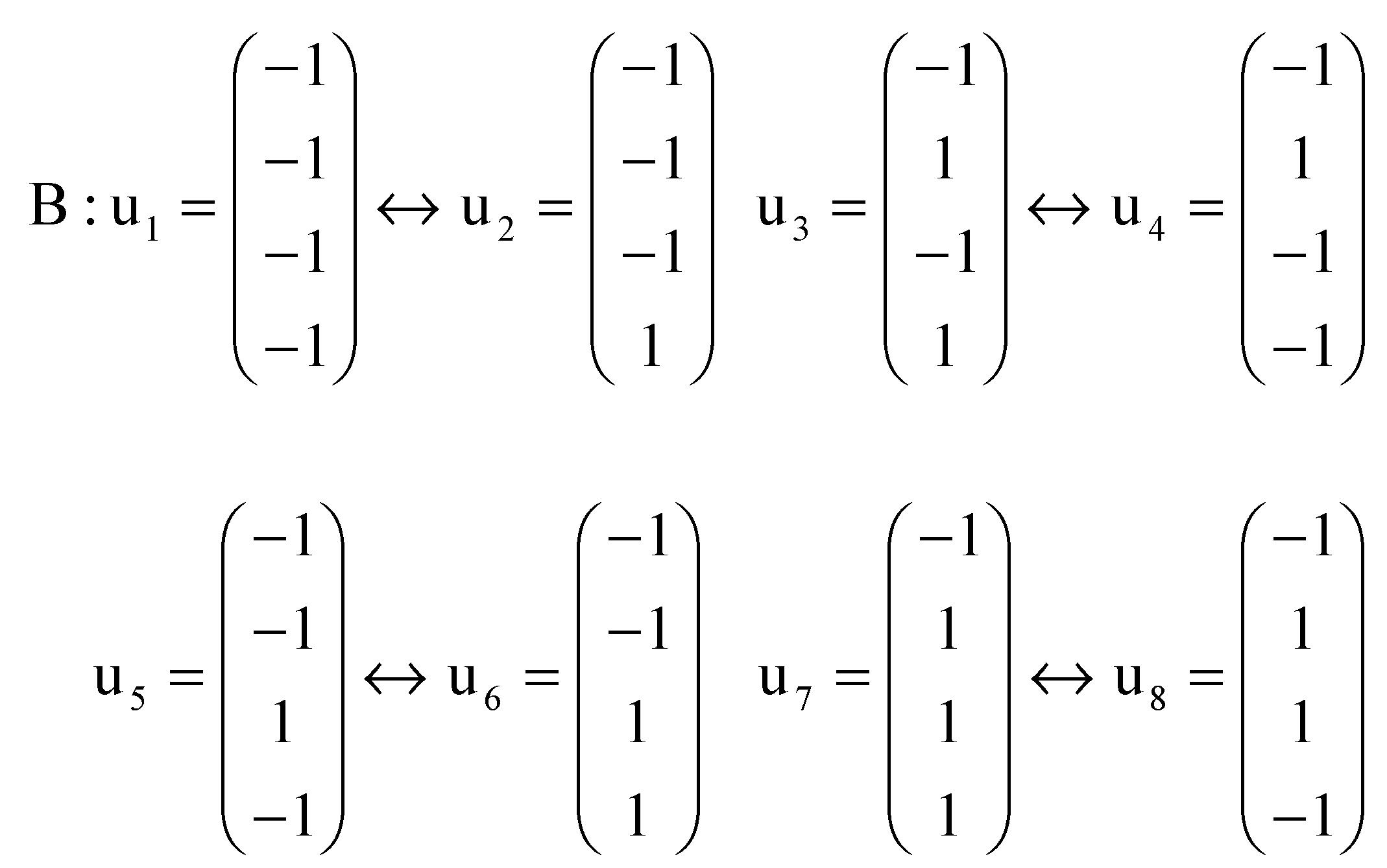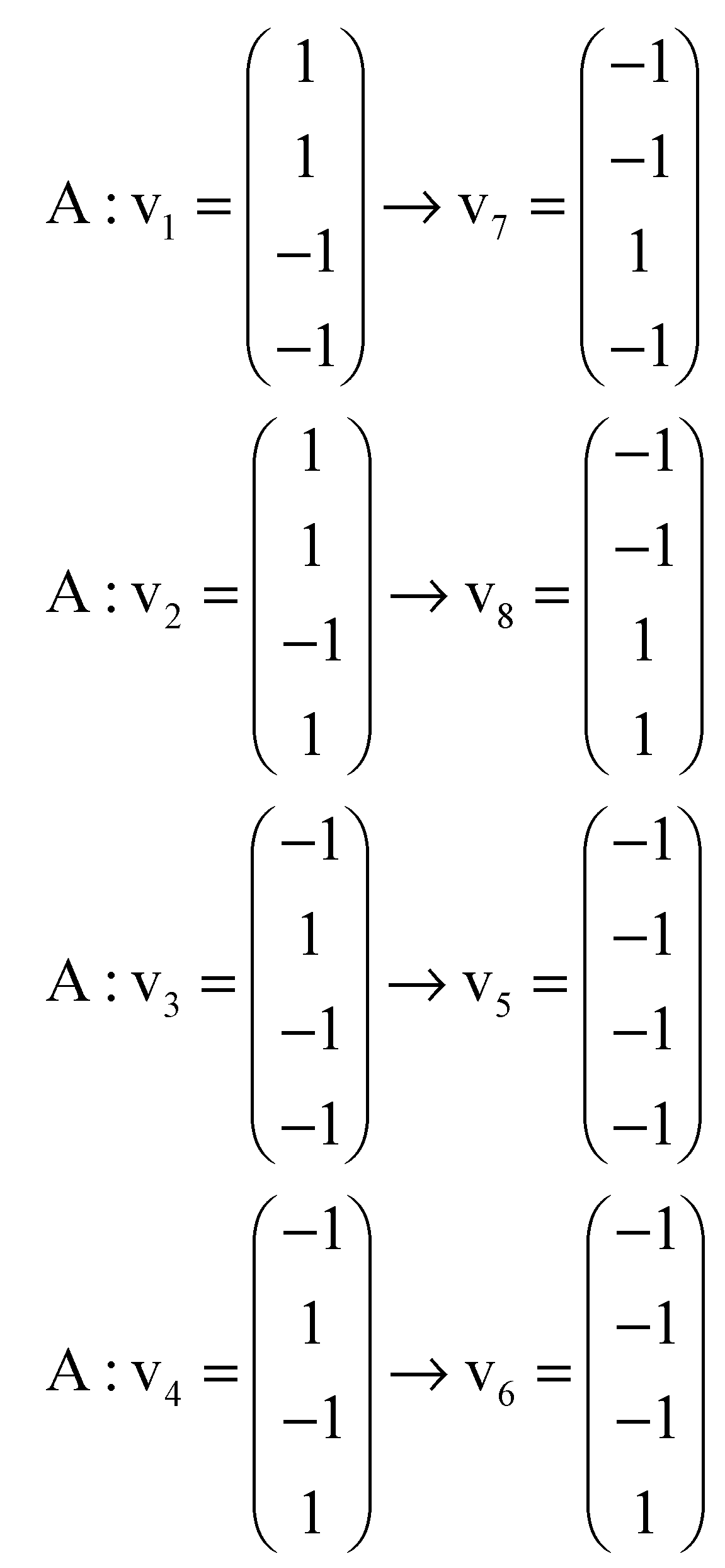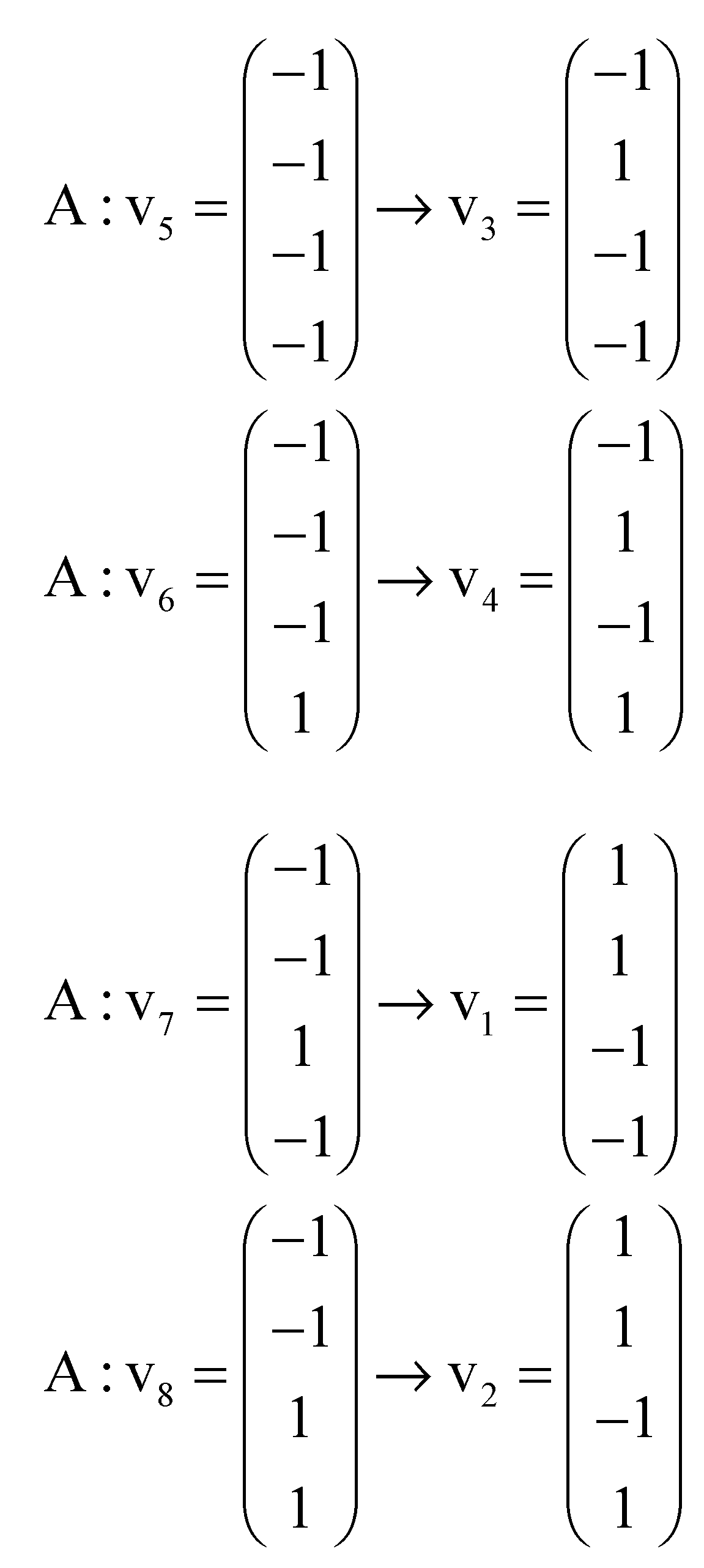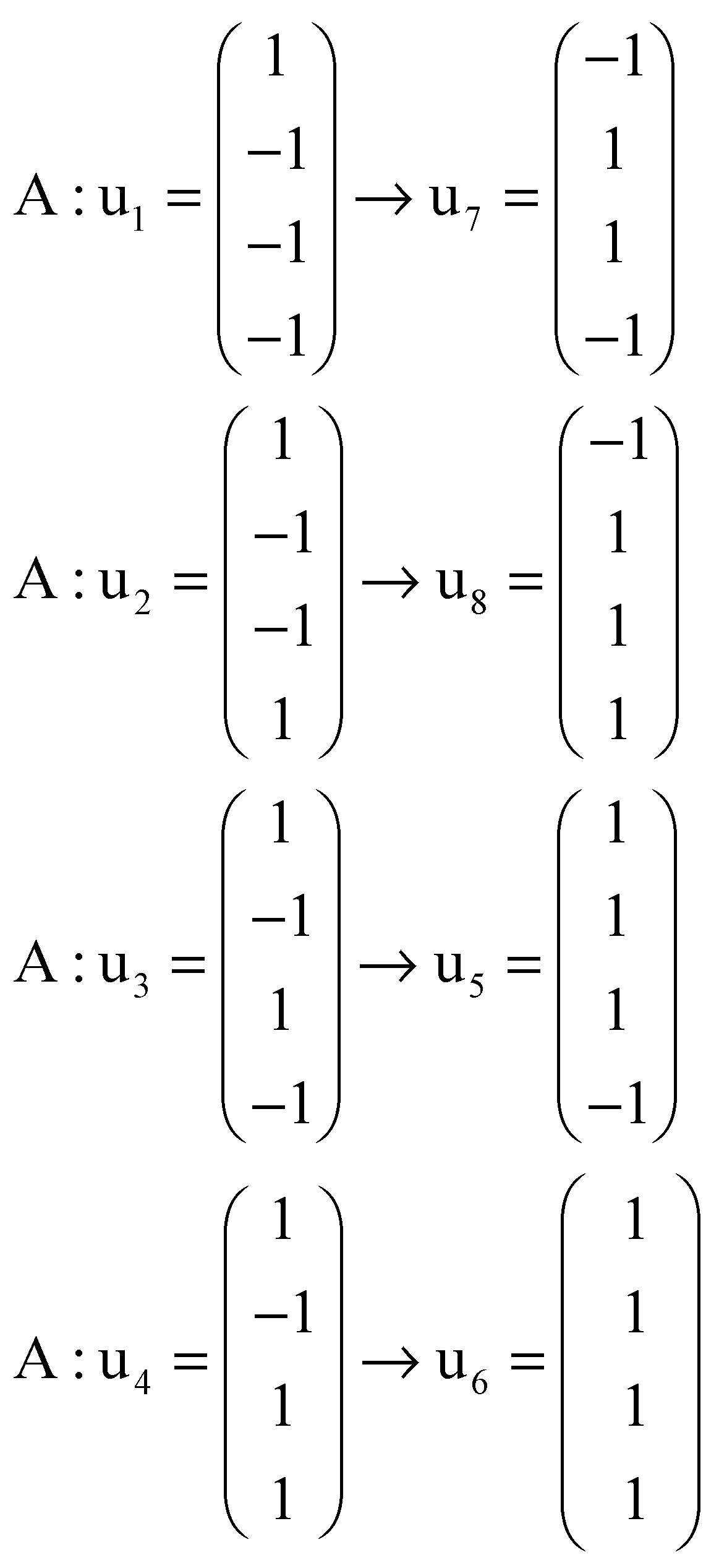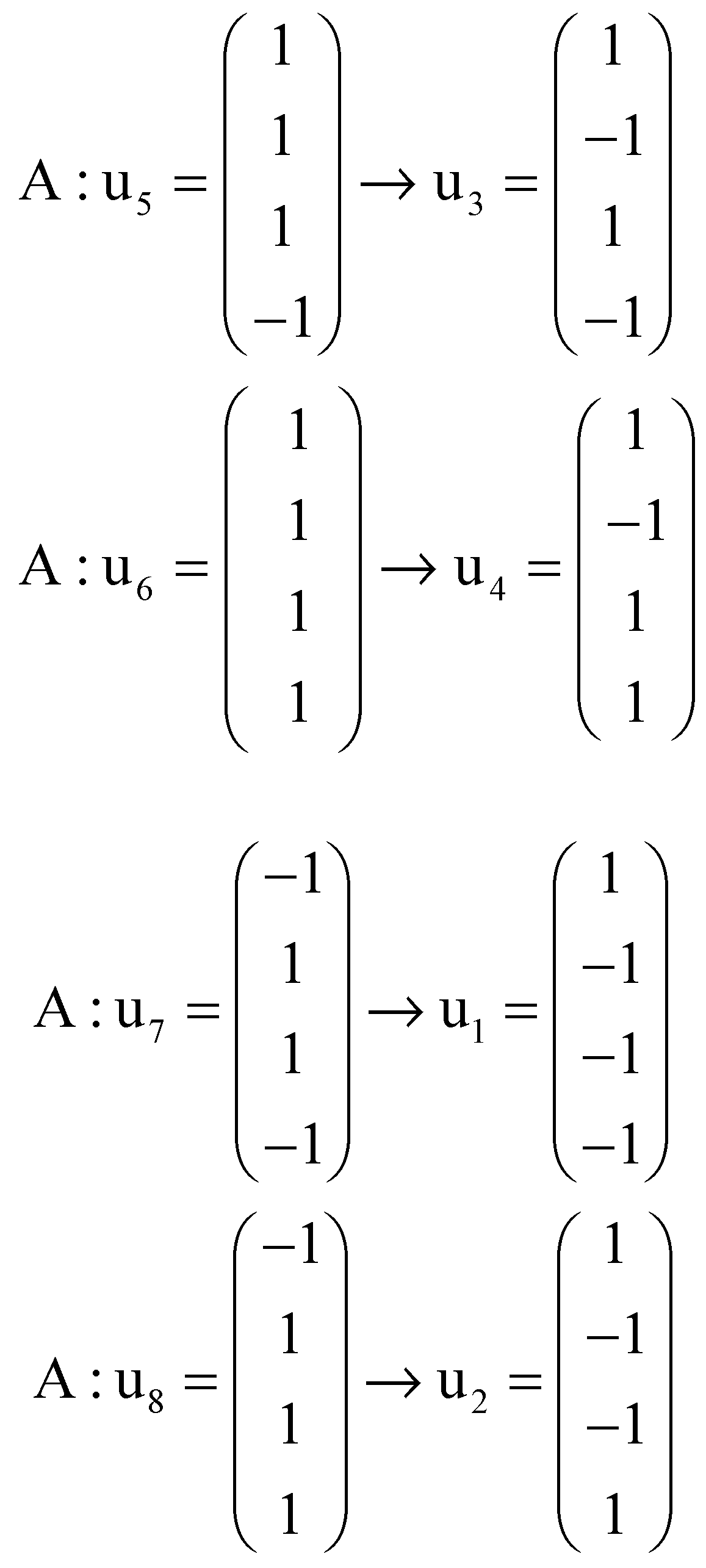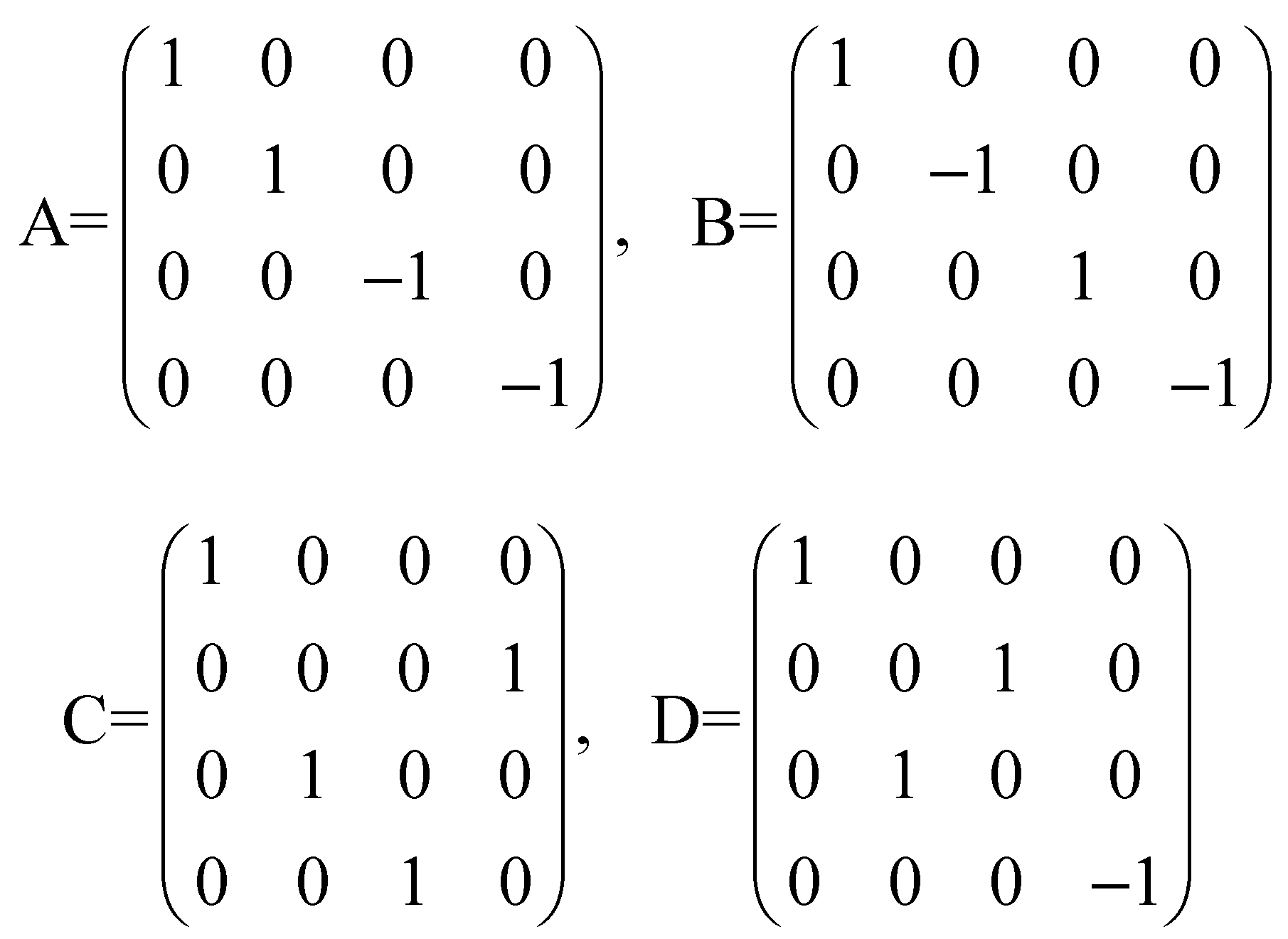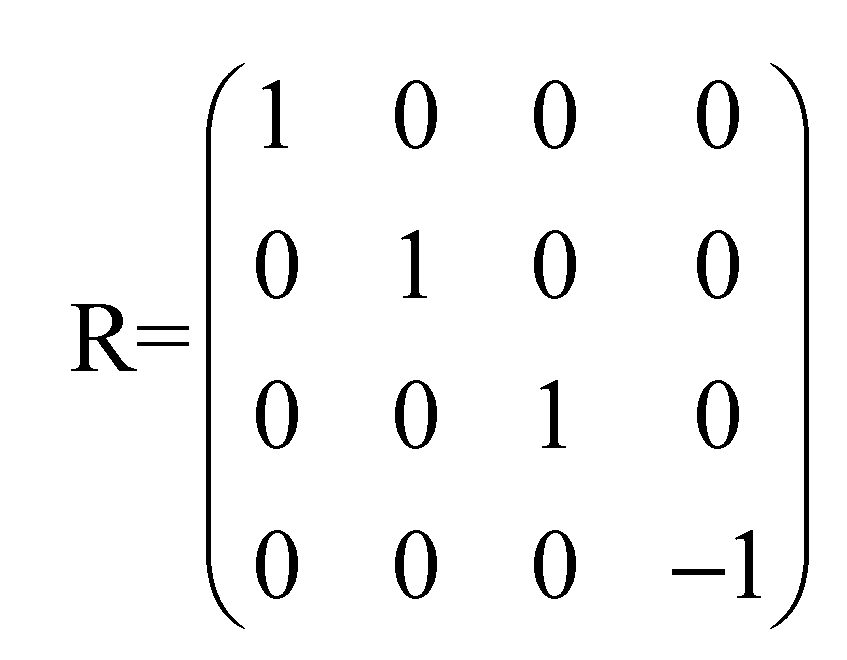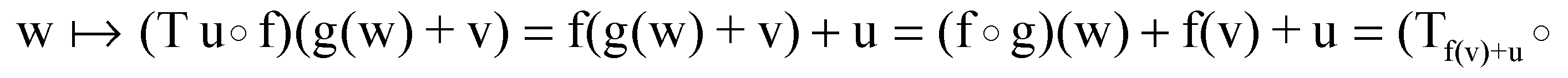Appendix A
Mathematical background
The Euclidean n-dimensional −space, ( , +, *) being the field of real numbers, has a basis the so-called canonical basis, where, for each with 1 in the place and 0 in the remainders.
A remarkable observation: The n-dimensional vector space ( , +, *) is a generalization of the ordinary 3-dimensional −space, ( , +, *) where every triplet represents a point of the space, endowed with a system of axis and pairwise orthogonal or perpendicular, intercepted in a
common point denoted as O and called the
origin of coordinates, represented by the triplet (0,0,0). Usually, every point P is identified with the triplet that represents it, as they were the same object. So, the equality is admitted. The axis are right lines defined as The addition of two points and is defined as . This operation, so defined, is associative, has a neutral element, and for every point its additive inverse exists, such that P + (−P) = O. Then, the ordered pair (, +) is a group. As the addition + is also commutative, it is an Abelian group. The product of a real number by a point is defined as . This external operation, of a real number by a point, has the following algebraic properties:
1. for (Mixed associativity).
2. 1 * P = P, for every (Existence of an external neutral element).
3. for all (Distributivity of the product with respect to the addition of points, also called distributivity at the left).
4. for all (Distributivity of the product with respect to the addition of numbers, also called distributivity at the right.)
The condition of Abelian group for the addition and the four properties of the external operation, completes the structure of a vector space over the field ( , +, ×) of the real numbers, in the set of all the points of the space.
The concept of vector: Given two different points we call the vector of origin and extreme to the oriented segment of right line that joins with It is denoted as We define the addition of two vectors and with common origin P as the vector such that S = R + Q − P If the points and are not collinear the four points are the vertexes of a plane parallelogram. It means that the lines and are parallel. If the null point the function: where for is defined as a vector whose initial and final points coincide, is a bijective function between the set of all the triplets or points of the space, and the set of all the vectors with origin This correspondence induces over the set the operations + and * of addition and product of numbers by vectors and is endowed the structure of a vector space over the field of the real numbers.
Euclidean norm
The Euclidean norm, module, or length, of a vector v = (x1,x2,…,xn) is defined as the non-negative square root of the sum of the squares of its components.
Main properties of the Euclidean norm
N1) For every v, and it is =0 if, and only if, v = 0 the null vector O = (0, 0, 0, …, 0) (Positivity of the norms for all the non-null vectors)
N2) For and , (The norm module, or absolute value, of the real number is the positive of the couple and, for
From N2 we have that for every .
N3) For all (Triangle inequality).
The Euclidean Distance between vectors
For the Euclidean distance between their extremes, is defined as
Main properties of the Euclidean distance
D1) For every v, being the null vector = (0, 0, …, 0) (Positivity of the distance to the origin for all the final points of the non-null vectors).
D2) For all (Symmetry).
D3) For all (Triangle inequality).
With this distance the set of vectors, is a metric space and the vector space is called the n-dimensional Euclidean Vector Space.
Linear transformations
A function f: is called a linear transformation, or linear endomorphism, if it has the following property:
For all and , the equality holds.
Note: The latter condition is equivalent to the two conditions:
L1) f(u+v) = f(u) + f(v), for all . (This means that f is a group homomorphism of the additive group ( , +) onto itself).
L2) f(α*u) = α*f(u) for all and
If the function f is bijective, the linear transformation is a linear isomorphism, and it is called a linear automorphism of the vector space.
Matrix representation of a linear transformation
For every endomorphism f there is a unique square matrix such that for every j, being the j-th column of Then, is a matrix whose columns are the column matrixes associated of the vector images of the canonical unitary vectors. It is called the matrix of f with respect to the canonical basis. It will be denoted as A = [f] In the case of an automorphism the matrix is a non-singular or invertible matrix, hence, its determinant is different from 0.
For every vector v = (x1,x2,…,xn) the column matrix is taken as the matrix representation of It is well known that the matrix representation of the image vector is the matrix product Conversely, every square matrix defines an endomorphism f, whose matrix representation [f] is
Translations
For any vector the translation defined by is the function such that, for all For every u, is a bijective function that preserves the norm of each vector and the distance between different vectors of the space. Hence, it is an isometry of the Euclidean vector space. For two translations and the composition is equal to the translations The correspondence between and the set T, of all the translations, is a bijective function, that induces over T the structure of a n-dimensional vector space, isomorphic to the Euclidean n-space ( , +, *)
The concept of affine transformation
An affine transformation is a function that is a composition of a linear endomorphism f, followed by a translation It acts over every vector as The affine transformation is bijective if, and only if, its linear part f is an automorphism. The set of all the affine transformations of the vector space ( , +, *) will be denoted as . The composition of two affine transformations and acts over a vector in the form:
Then, the composition is the affine transformation . Hence, we have the equality
We see that the composition of two affine transformations is an affine transformation. Then, the composition is an inner operation in the set . As the operation is associative and its neutral element, the identity function I, is the affine transformation the ordered pair ( ) is a monoid, or semigroup with neutral element.
Matrix representation
The matrix representation of the affine transformation is given by the composition being the matrix of which acts over the matrix of a vector as
The conjugated of a translation by a linear automorphism
The conjugated acts over any vector as Then The latter means that the group of translations ( ) is a normal subgroup of the group being the set of all the invertible affine transformations, and the group of all the linear automorphisms of the space ( , +, *) The group that is called the affine group of the space ( , +, *) is a subgroup of the group of all the bijective transformation of the set It contains as a normal subgroup, the group ( ) of all the translations. In fact, it is the semidirect product of the group ( ) with the group of all the linear automorphisms. (A group is semidirect product of its subgroups and if and is a normal subgroup of The semidirect product will be denoted as Then, The affine group is the group of invertible elements of the monoid ( ).
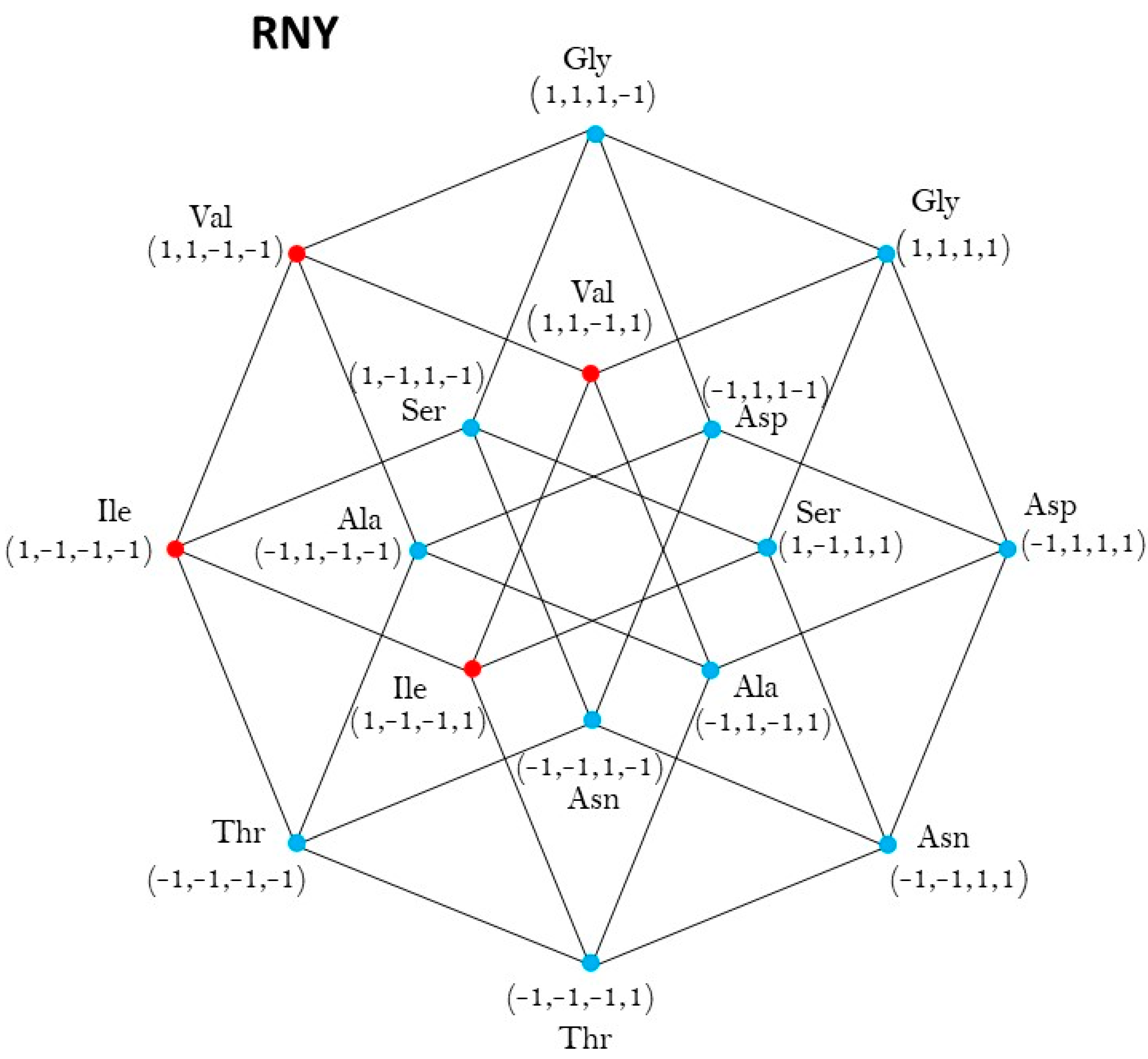
The n-dimensional binary hypercube.
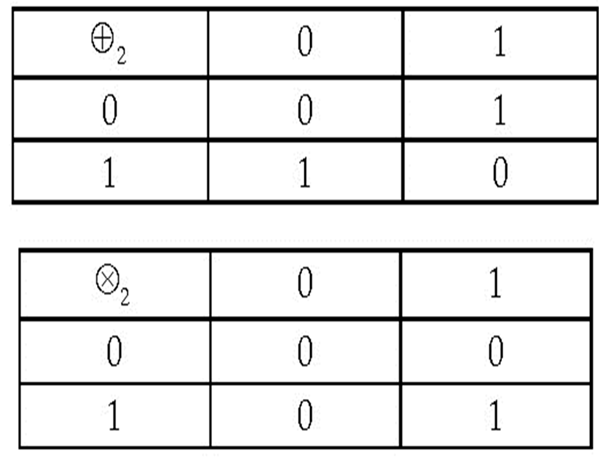
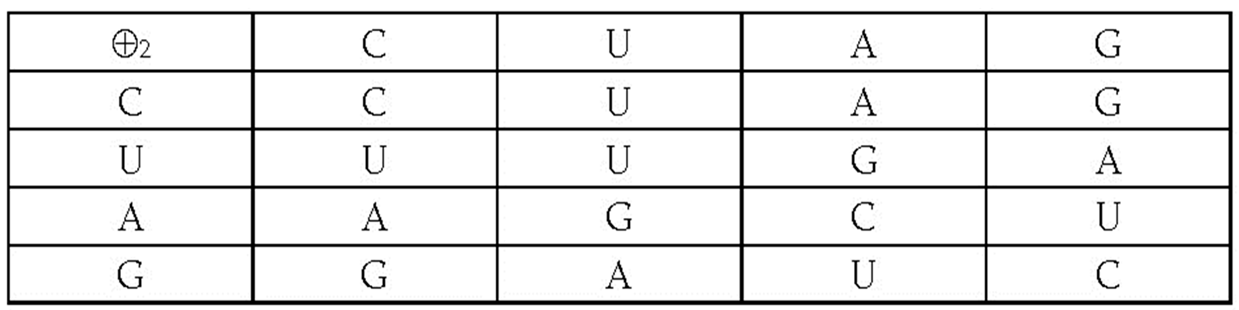
The binary vector space vector space over the binary field is also called the n-dimensional binary hypercube. Its set of vertexes coincides with the set {0,1}n of the n-tuples of zeros and ones. This set is a subset of the set of all the n-tuples of the whole numbers. The set determines the Abelian group ( , +) subgroup of the additive group of the n-dimensional Euclidean n-space .
The n-dimensional hypercube, whose vertexes are the elements of the set {0,1}n is defined as the convex closure [0,1]n of the set Here, denotes the closed interval of the real numbers between 0 and 1. The convex closure of a set is the minimal convex set that contains it.
A convex set is a set that, for two different elements a and of the segment that joins them is entirely contained in C.
The center of the hypercube [0,1]n is the point obtained by the sum of the 2n vertexes divided by 2n. That is so because, for every place i of the n-tuples, 2n−1 of them, that is, the half, have 1, and the other 2n−1 have 0. Then, for each place i, the quotient is
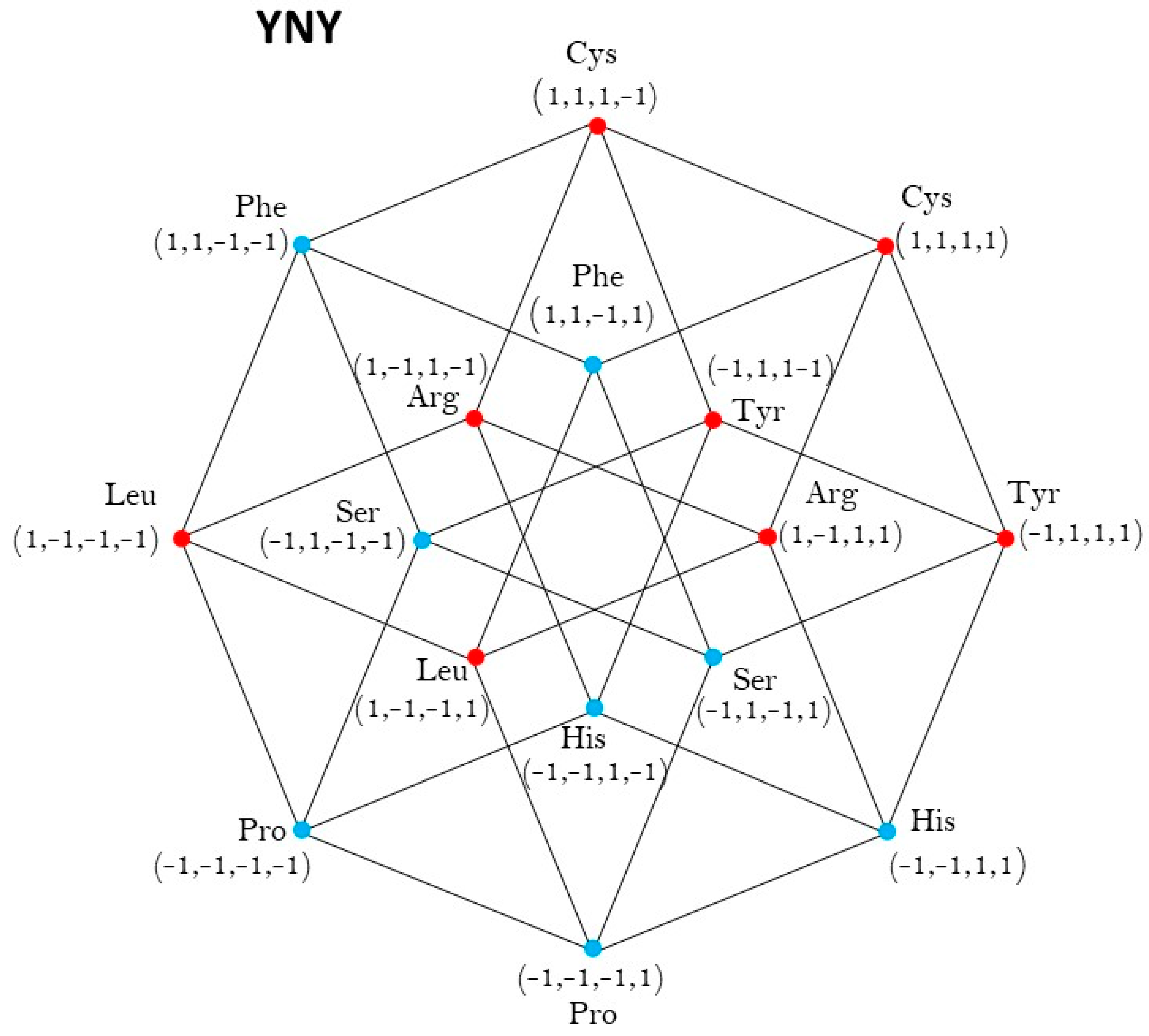
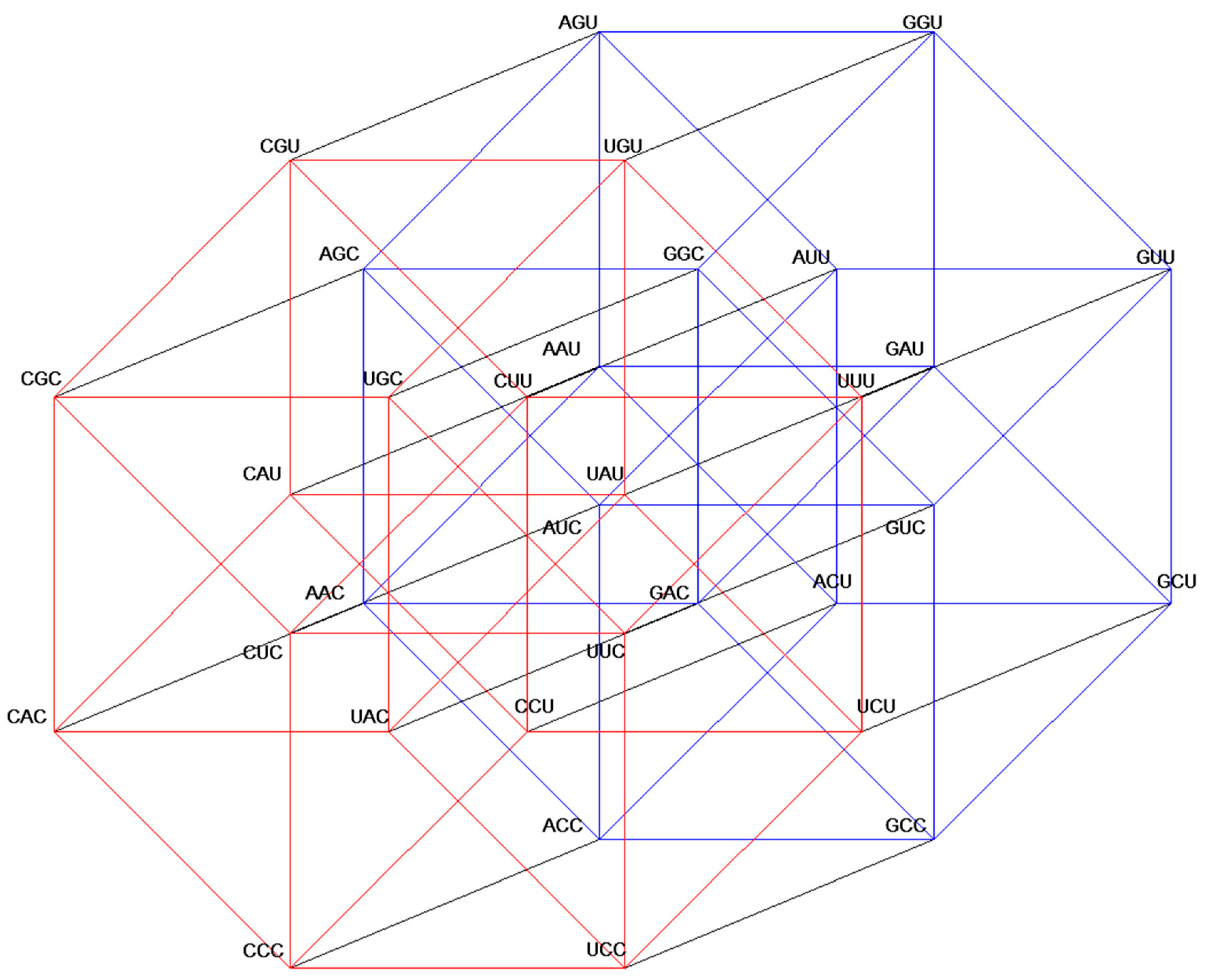
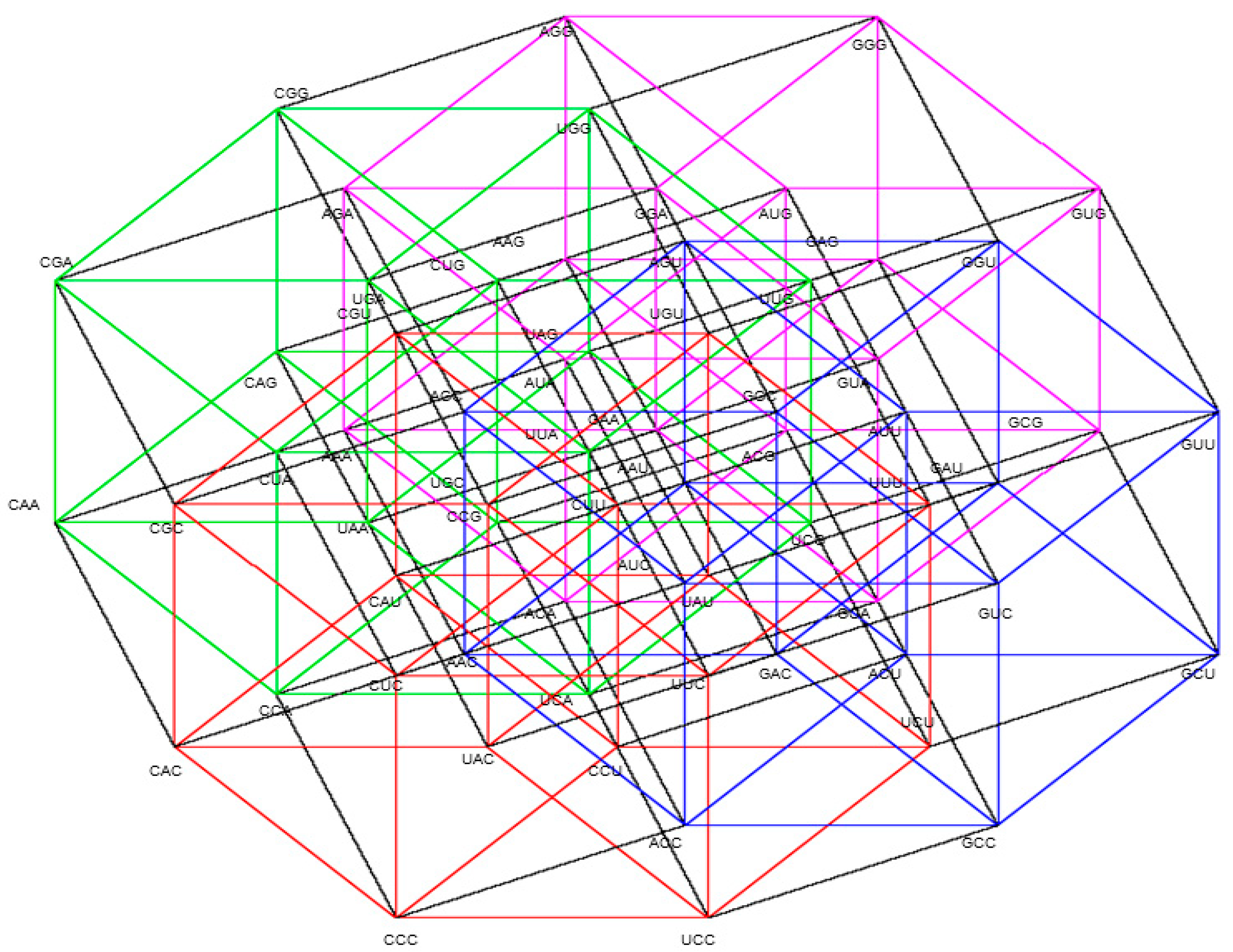
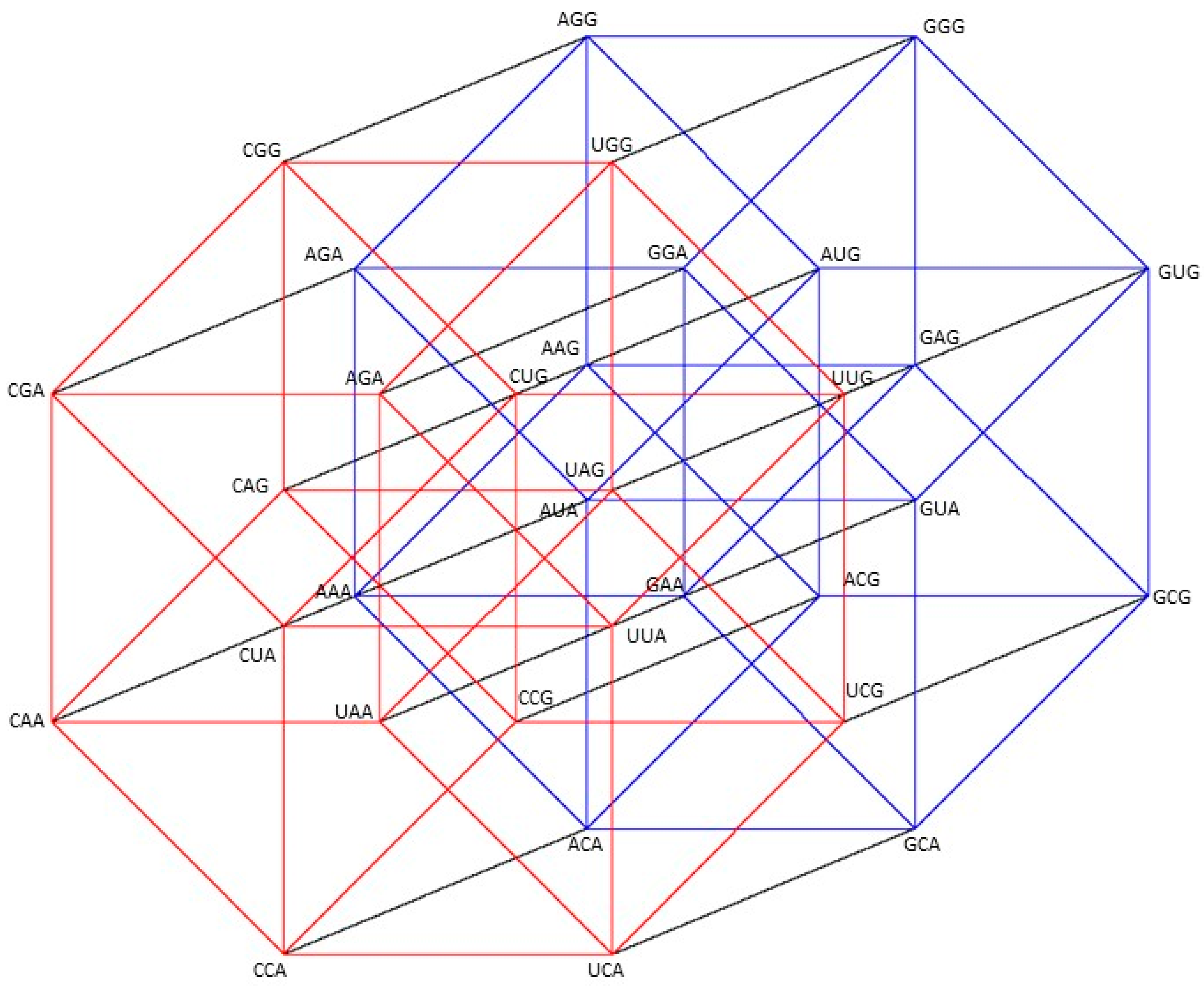
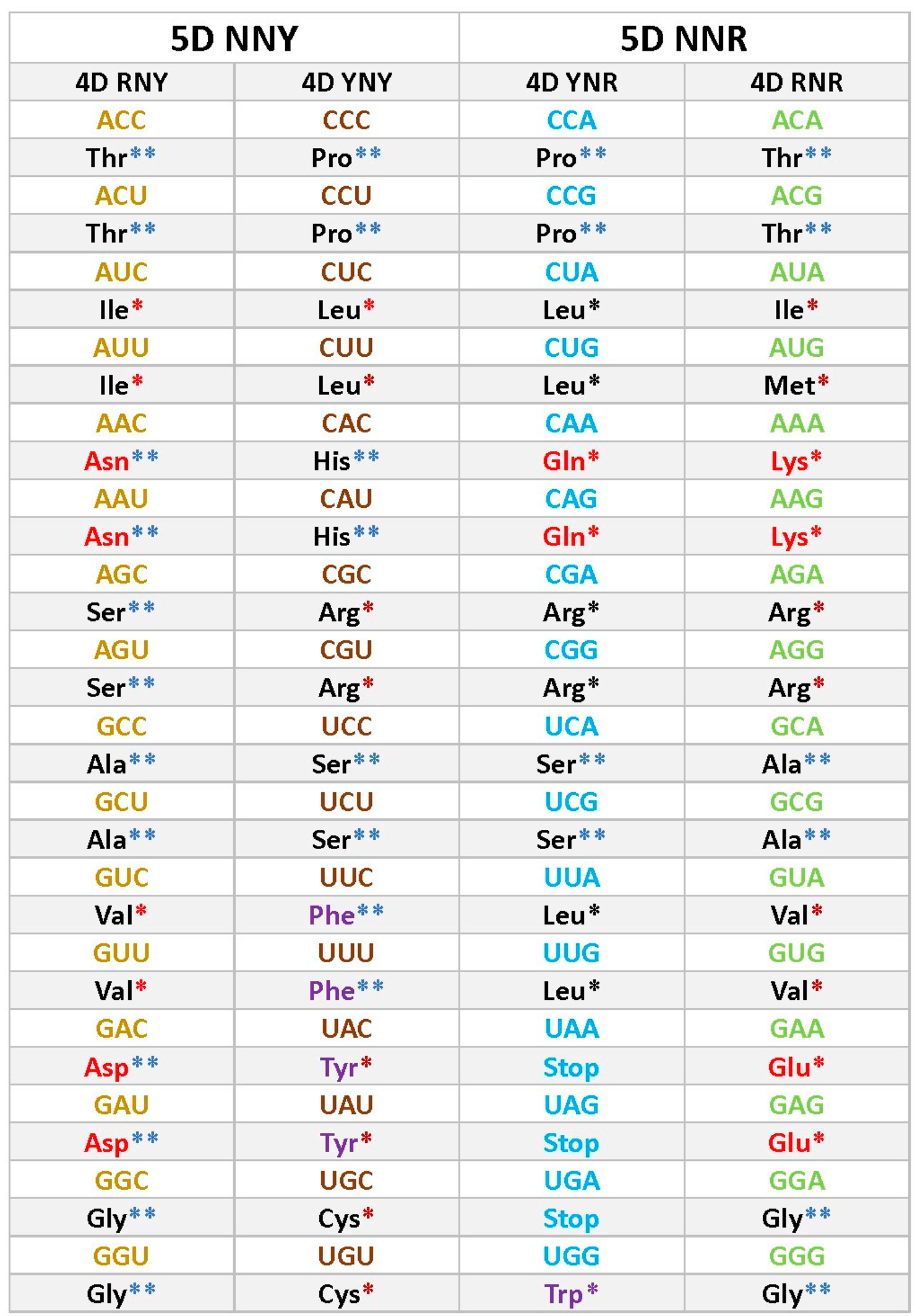
Figure A1.
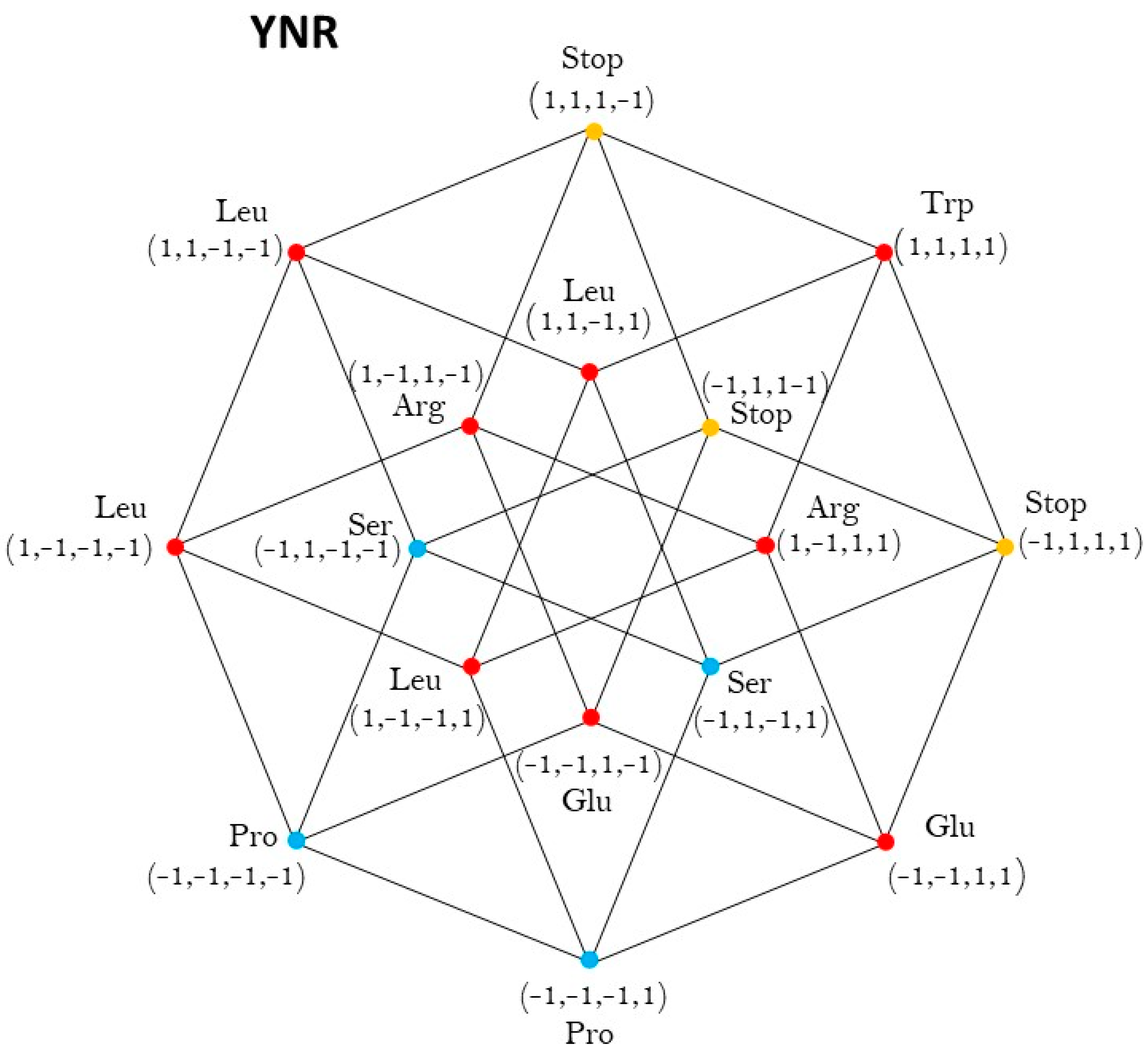
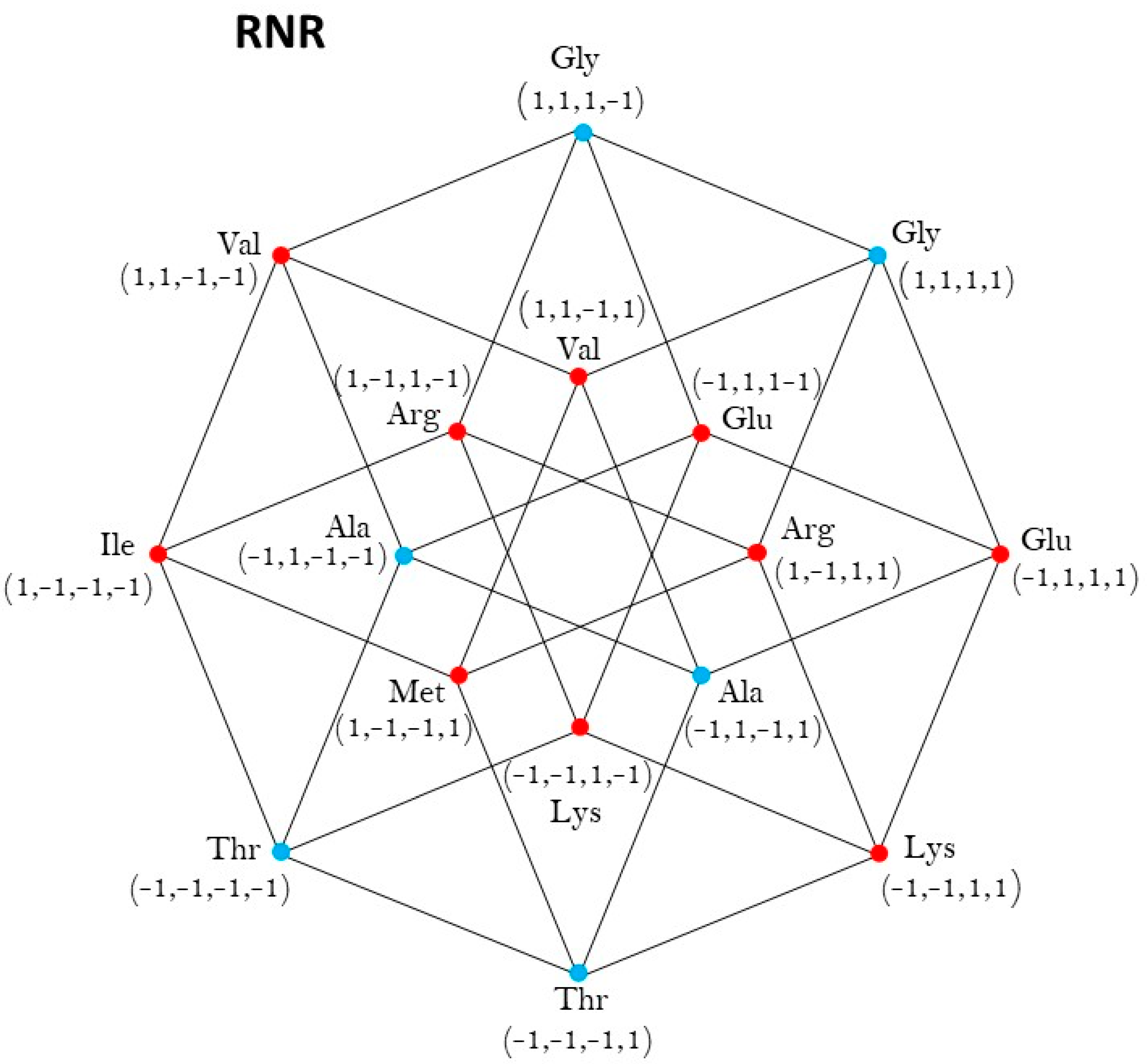
Five-dimensional hypercube NNR Figure 5. The five-dimensional hypercube of triplets which is the union of the 4-dimensional hypercubes and
Figure A1.
Five-dimensional hypercube NNR Figure 5. The five-dimensional hypercube of triplets which is the union of the 4-dimensional hypercubes and