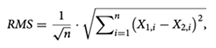1. Introduction
The use of digital technology in dentistry has been increased in recent years [
1], thanks to different computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD-CAM) systems being used to fabricate different types of prostheses [
2] and to intraoral scanners (IOSs) that allow to obtain a full digital workflow from the impression to the delivery.
In a completely digital workflow, an accurate IOS is an essential aspect to ensure long term results, since the fitting of the future restoration is largely depending on the quality of the IOS [
5].
Recently the IOS clinically acceptable results were shown on the fabrication of crowns and fixed partial dentures (FPDs) [
3,
4,
5], with higher time efficiency and better patient acceptance compared with those of conventional impression methods [
6,
7]. As reported in the glossary of digital terms [
8], the accuracy of a digital scanner is the closeness of agreement between a measured result and a reference value. It is described by trueness and precision. Trueness is the closeness between the test object and the reference object, whereas precision is the variability of repeated measurements of the object [
9,
10]. Differences in accuracy have reported between IOSs and laboratory scanners [
11], and among different IOSs [
12,
13], Additionally, the accuracy of a IOS can be affected by clinical circumstances as scanning protocol [
14], presence of blood or saliva [
15], limited spacing between abutments and adjacent teeth [
16], and edentulous span length [
17]. One of the most critical steps during impression taking, both conventional and digital, is detecting the finish line, in particular subgingival tooth margins. For both traditional or digital impression technique the detection of the finish line relies on a clean, healthy gingival sulcus, proper soft tissue displacement, and clear visibility of the prepared tooth anatomy. However, the preparation of an abutment for a digital impression must consider limitations due to the digital impression device [
18]. To date only fews studies [
15,
19,
20,
21,
22] evaluated the reliability of intraoral scanners in detecting subgingival vertical preparations (VP)[
15,
20,
21]. So the aim of this in vitro study was to evaluate the trueness and precision of four IOS devices (Trios 3, 3Shape A/S), (Medit I700), (Vivascan,Ivoclar) and (Experimental IOS, GC) used in standardized conditions, on complete crowns abutments with subgingival VP finishing line. The following null hypothess were tested: 1) there are no differences in term of trueness and precision among the different IOSs for the abutment surface and for marginal areas 2) there are no differences in terms of accuracy comparing full abutment surface and marginal area.
2. Materials and Methods
A reference maxillary typodont (MT) mounted on a simulator phantom head, was fabricated by performing a vertical preparation for full coverage on resin abutments on maxillary right first molar #16 and left first incisor #21. Teeth preparations were performed with the following protocol: mesio-distal preparation with flame bur 012 (Komet, Lemgo, Germany) preparation of the occlusal surface following the angle of the cusps using a conical burr (Komet, Lemgo, Germany); and axial reduction above the buccal and palatal cemento-enamel junction with the 012C flame diamond burr. Thus, a circumferential tooth reduction was obtained using a flame bur 012C vertically below the cemento-enamel junction until the preparation is rectified with the axial plane. In order to standardize the scanning condition, the preparation was performed at least 2 mm around the gingival margin to ensure the overcome clinical limit and was confirmed with a periodontal probe (CP 15 UNC; HU-Friedy, CHI, USA).
The MT was scanned with a laboratory scanner (Aadva lab scanner, GC, Tokyo, Japan) to obtain a digital maxillary typodont (dMT) in standard tessellation language .stl format.
Subsequently, 40 digital casts (dIOC) were obtained by scanning the MT 10 times by each of the four different IOSs (Trios 3, 3Shape A/S), (I700, Medit), (Vivascan, Ivoclar), (Experimental IOS, GC). The scanning procedure was conducted starting from the right maxillary quadrant and ending at the left one and then continuing on the palatal side and finally on the palatal vault with a clockwise movement. All the scans were done under the same light conditions and by the same operator with an interval of 10 minutes to rest and allow the IOS to cool. The numbers of images per scan varied between 743 and 1126, and the scanning time was between 1 and 2 minutes. All the excess areas were removed by using CAD software (Meshmixer; Autodesk, San Rafael, USA) so that the acquired test models were standardized and ready for superimposition. The two groups of .stl files dMT and dIOC were imported into an inspection software program (Geomagic Control X; 3D SYSTEMS) to be superimposed, indicating the dMT “as reference data” in the software program, to calculate trueness. The dMT .stl file was superimposed with each dIOC .stl file in the software program by activating the function “initial alignment” and then the function “best-fit alignment,” which aligned the 2 digital casts with a minimal distance between the superimposed surfaces [
23]. 3D analysis was performed on the prepared teeth #16 and #21 (all regions above the finish line of abutment), and marginal region (the region up to 1,5 mm on the gingival margin) of the abutment.
The correspondence between dMT and dIOC was evaluated by using the 3D comparison function. The root mean square value (RMS) was calculated based on all cloud points of dMT by using the following formula:
where X1,i indicates a measurement point at ith in dMT and X2,i indicates a measurement point at ith in dIOC. n is the number of all points evaluated. Therefore, the RMS value is the absolute average distance of all cloud points and means the degree of agreement between dMT and dIOC, so this value was used to evaluate the trueness.
For each experimental group, the trueness was calculated taking the RMS value resulting from the superimposition of each dIOC .stl and the dRT .stl. The precision was evaluated as the RMS values recorded after the superimposition between each dIOC and the cast that recorded the best result of trueness in the same group. Therefore, all the scans from the same scanner group were superimposed onto this selected cast, whose trueness corresponded to the actual reference value for precision.
In order to evaluate the difference in marginal surface area, it was selected the single prepared abutments models for 16 and 21 as reported in
Figure 1.
The 3D comparison was performed as previously reported after the alignment of the abutment model with the 10 different scans obtained per each group.
All RMS data were statistically analyzed to evaluate trueness and precision. The homogeneity and normality of distributions were tested by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov. The nonparametric Kruskal- Wallis test was performed to compare the trueness and precision differences among the scanner groups (α = 0.05) All statistical analyses were performed by using a statistical software program (IBM SPSS Statistics, v22.0; IBM Corp).
3. Results
3.1. RMS Evaluations
The mean RMS values and standard deviations of each group regarding the trueness and precision on the prepared abutments were reported in
Table 1.
On #16 abutment, Experimental IOS, GC performed the best trueness result (55,4±5,6µm), but not statistically significant differences were found in comparison to the other tested groups. On #21 abutment, Vivascan (56,0 ±12,1µm) and Experimental IOS, GC (59,2±2,7µm) performed statistically better than the other two devices for trueness. Regarding precision, Experimental IOS, GC (10,7 ± 2,1µm) and I700 (15,8±2,7µm) showed statistically better results than the other two groups on the molar #16, while on the incisor abutment #21 the ones that reported statistically better results were Experimental IOS, GC (16,9±13,8µm) and Trios 3 (29,8 ± 3,7µm).
The RMS mean values and standard deviations of each scanner at the marginal level of the prepared abutments are reported in the
Table 2.
3.2. Accuracy at the Marginal Level
I700 reported the highest accuracy at marginal level on the #16 (96,3 ± 0,13). The I700 and Experimental IOS, GC scanners obtained statistically difference and better results than Trios 3 and Vivascan any marginal level for the 21.
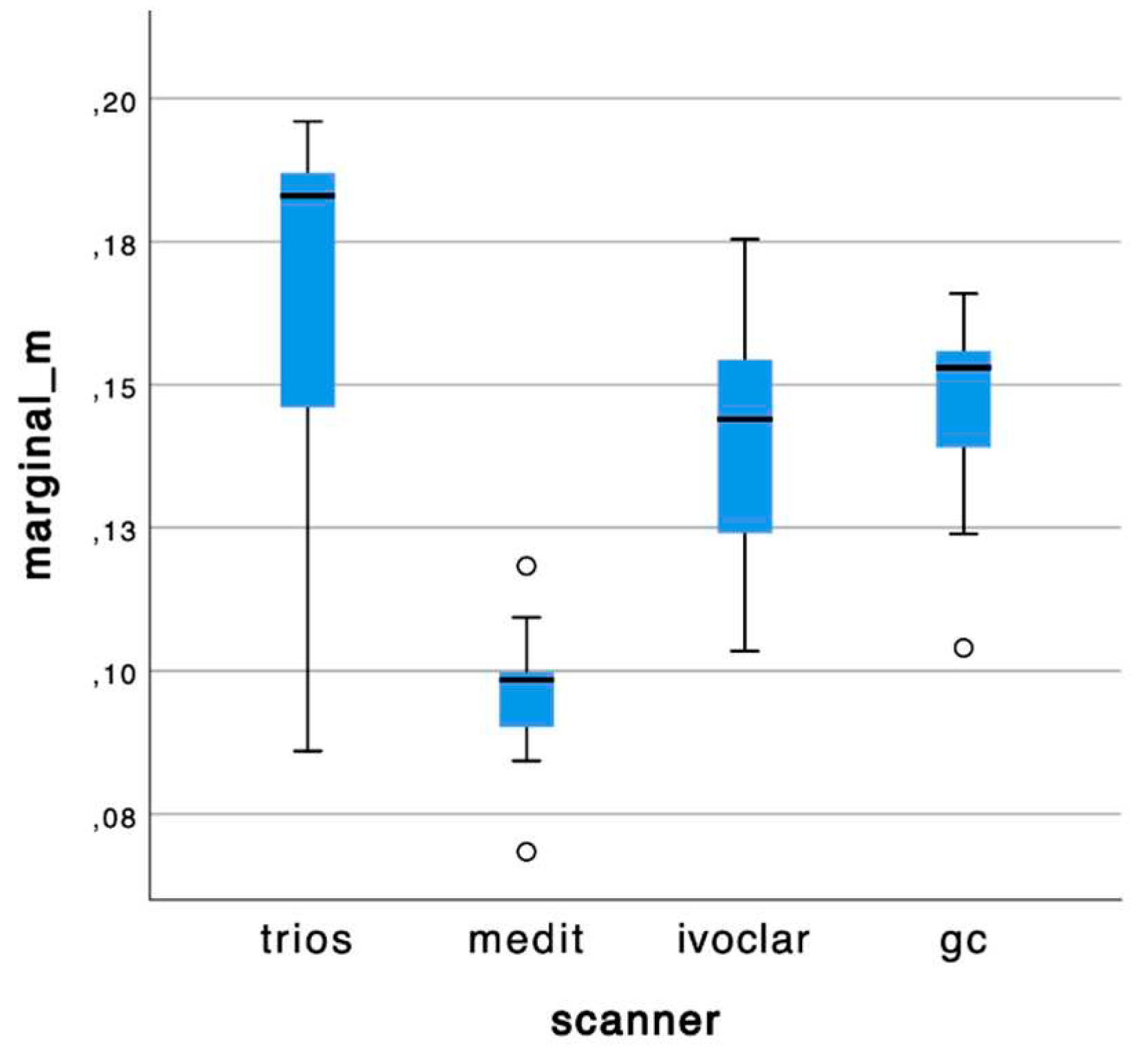
The boxplots of mean values for each group are reported in Graph 1 and 2.
Graph 1.
Box plots of mean values at marginal level of the molar #16.
Graph 1.
Box plots of mean values at marginal level of the molar #16.
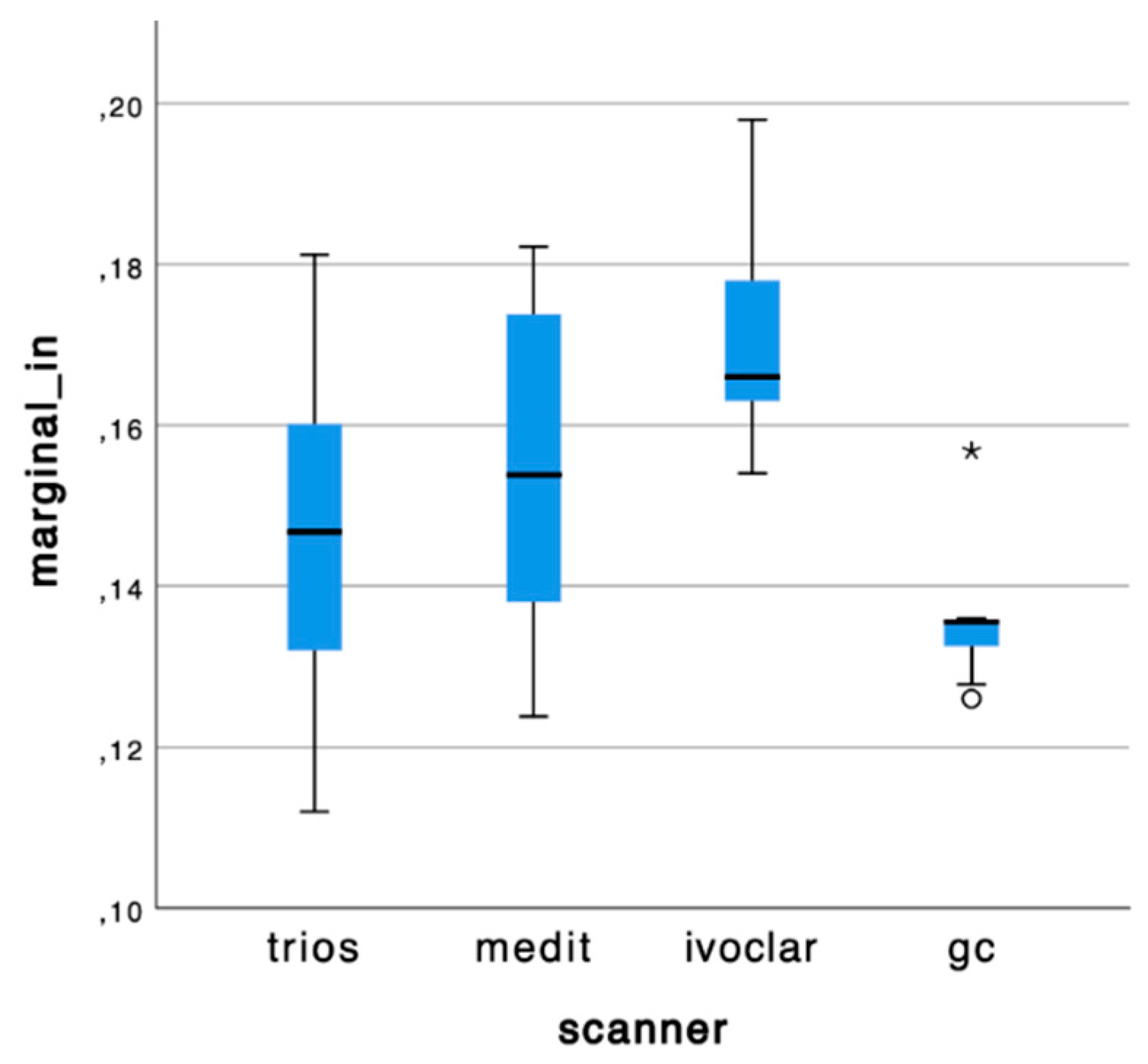
Graph 2.
Box plots of mean values at marginal level on the incisor #21.
Graph 2.
Box plots of mean values at marginal level on the incisor #21.
The comparisons between trueness on 16 and 21 and their respectively marginal area reported a statistically difference in all the IOS groups.
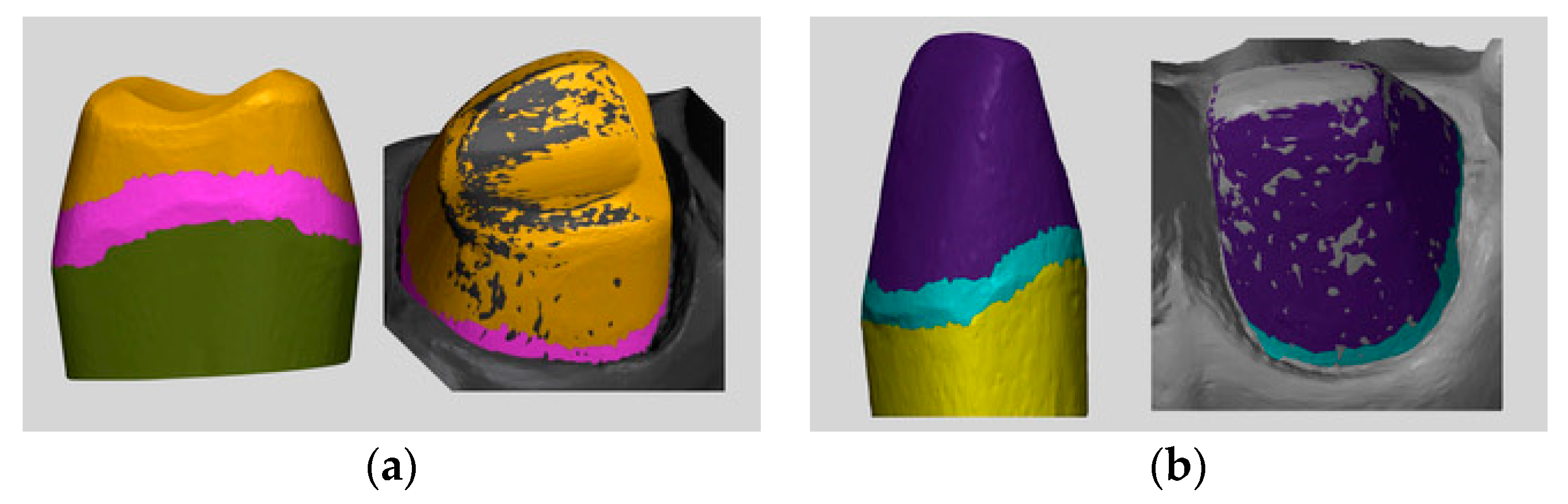
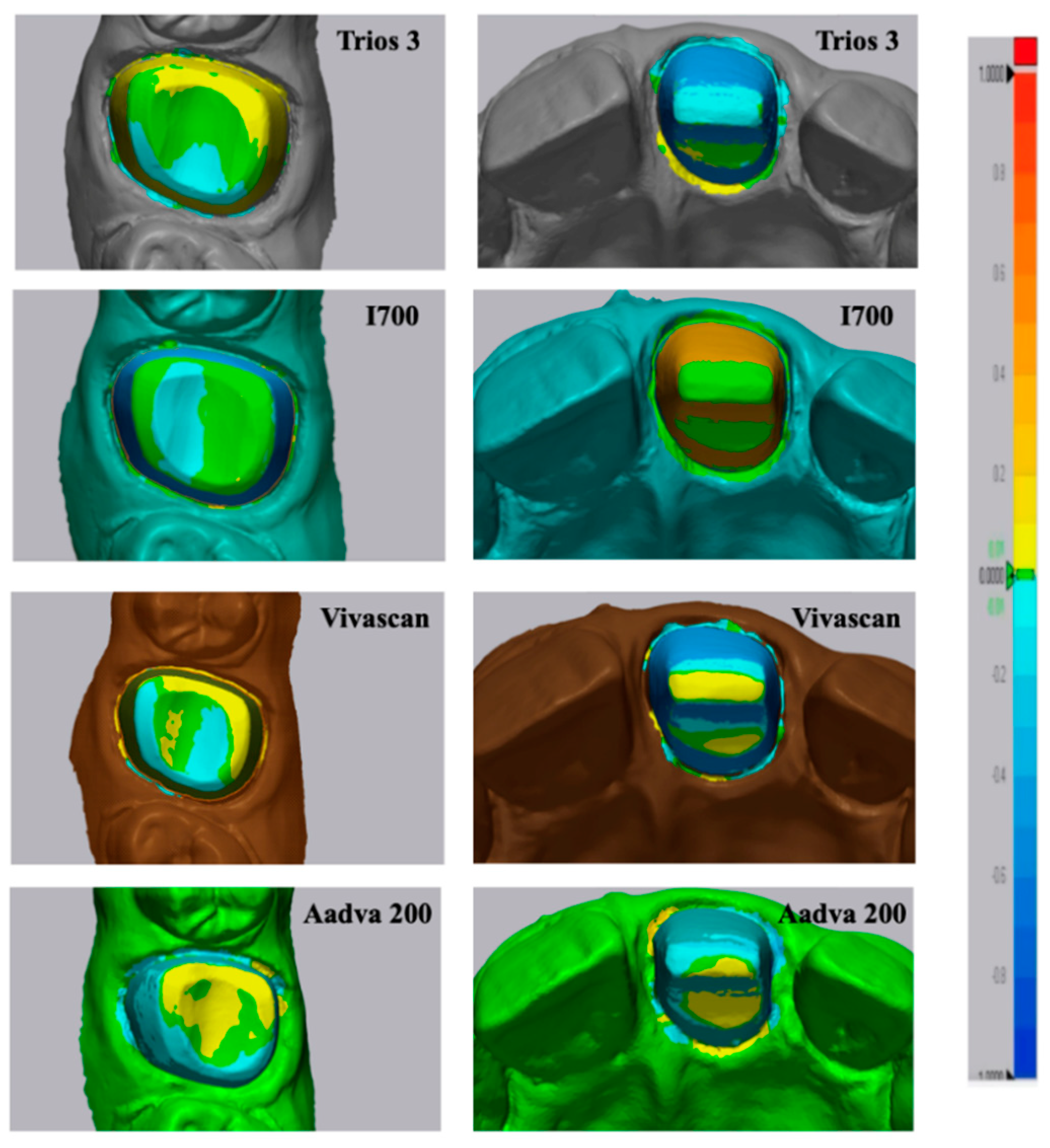
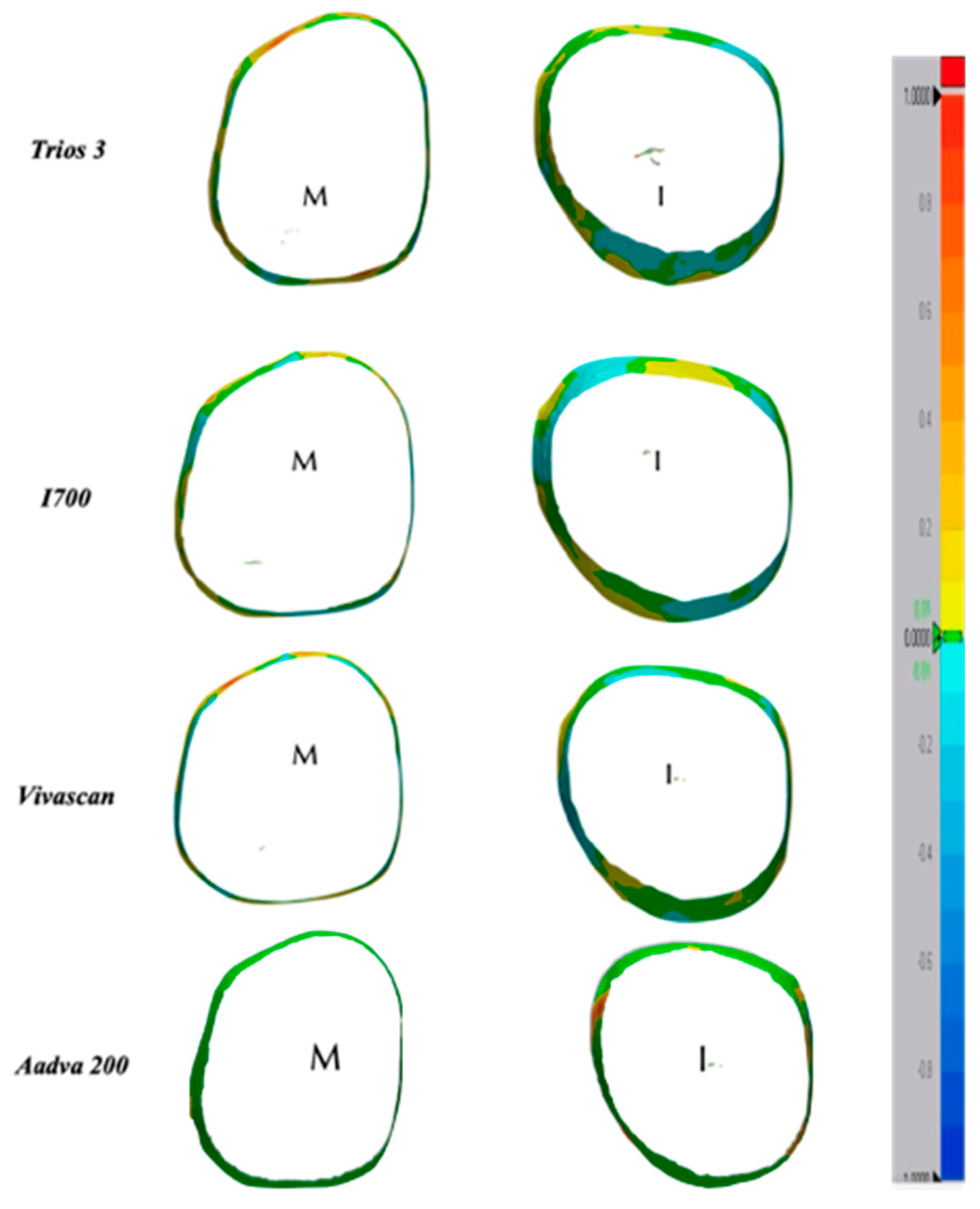
3.3. Color Map Evaluations
A color map was created to visualize the displacement between the superimposed IOS to MT for the whole abutment area as shown in
Figure 2 and for the sub gingival margin as shown in
Figure 3.
4. Discussion
In the digital workflow, the accuracy of the cast obtained by IOS becomes fundamental for long term results [
5] in order to achieve good marginal and internal fit of the restoration [
24,
25].
Internal fit of the restoration, if incongruous, can lead to precontacts between the restoration’s material and some areas of the abutment, a thick thickness of cement along the surface and ultimately an exposition of cement at the margin. Marginal fit is one of the main factors in the success of the restoration because any discrepancy leads to marginal gap and, subsequently, to possible microleakage, cement dissolution by oral fluids, and biofilm accumulation, with consequences such as caries or endodontic and periodontal problems [
26,
27]
In a previous in vitro study Verniani et al.l. [
28] evaluated the marginal fit of crowns fabricated with a completely digital workflow of vertical preparation. It was reported that the obtained crowns had good adaptation to the abutment independently from the two tested iOS, however it was not evaluated the accuracy at the subgigngival finish line.
To date only few studies have evaluated the accuracy of IOSs depending on the the finishing line location and the difficulties in acquiring subgingival margins, and they compared only few devices [
19,
20,
21,
22].
Due to the lack of evidence in the evaluation of the IOS behaviors in vertical preparation, the aim of the present study was to assess the accuracy of different IOSs on complete abutment surface and on sub gingival area in vertical prepared abutments. The evaluated IOSs devices reported statistically different results for trueness on #21 and precision for both #16 and #21 at marginal level, thus the null hypotheses were rejected.
Regarding the level of accuracy of complete abutments, all the reported values were largely lower than 100 µm, that was indicated in previous clinical trials studies as the clinically acceptable margins and consequently the recommended scan accuracy [
29,
30]. The result of this study suggest that while for the trueness in the molar area no statistically significant difference was shown between the tested iOS, when the incisor abutment was evaluated, the Vivascan and the Experimental IOS, GC showed statistically significative better results compared to the other tested intraoral scanner.
It can be supposed that, the proximity of the molar abutment to the adjacent teeth in the posterior area, can acts as a confounding factor that can modify the performances of the IOSs [
16].
On the other hand in the incisor area, thanks to the increased interproximal space among the abutment and adjacent the teeth, the effect of this confounding factor can be reduced, thus some statistical differences were found in the RMS obtained valued
Regarding precision Experimental IOS, GC reported statistically lower results than the others IOS devices in both molar and incisor abutments revealing the closure scans in between each the same group, thus resulting as the most repeatable reliable IOSs. Instead Vivascan reported the biggest standard deviations or precision.
All our data about sub gingival marginal region reported increased values of trueness and precision compared to full abutment. The mean values for trueness and precision are all above the level of clinical acceptability according to Shim et al.l. [
30] except for i700 on marginal M.
As it can be evaluated in the color map images in
Figure 2 and
Figure 3, the prevalence of cold colors at marginal level revealed as the IOS abutment surface did not penetrate in the reference scan surface. Thus, it seems that the IOS was not able to record the true abutment surface into the sulcus when, at marginal level, it was closer to the tissue surface. A possible explanation of this finding is related to the continuous surface generated in the software by “joining the dots” according to the “stitching” algorithm.
This behavior of IOS was confirmed by recent papers. Son et al. [
21] reported that the trueness of the marginal region at the location of the subgingival finish line (0.5-mm below the level of the gingival) was the worst. In another study [
20], the two IOSs tested showed clinically acceptable scan trueness at a depth of up to 0.25-mm of subgingival finish line without gingival displacement cord but showed clinically acceptable scan trueness at a depth of up to 1-mm when the gingival displacement cord was used. Additionally, they found out that with the increase of the subgingival finish line depth without gingival displacement cord, the surface area of the abutment decreased but they limited the study only to two different types of intraoral scanners.
Our data confirm also the results obtained by Ferrari Cagidiaco et al.l. [
19], that digital impression is not recommended when crowns’ margins are positioned deep (1.5–2 mm) into the sulcus.
However further studies could be conducted in order to understand what the vertical limit for each IOSs is to obtain an acceptable scan in terms of accuracy at marginal level.
Additionally, the present study has some limitations like the absence of saliva, blood, limited mouth opening and movements of the patient, [
31], those factors could be considered in an in vivo experimental design.
Also, it must consider that three devices were using a software already available, while the Experimental IOS, GC was an experimental software not available into the market yet.
5. Conclusions
Based on the findings of this in vitro study, the following conclusions can be drawn:
The trueness deviations of the analyzed scanners were consistent and with no major differences on the molar, instead significant difference was found on the incisor.
At marginal level the accuracy results were not clinically acceptable for all the IOS probably due to the “joining the dots” effect.
More studies are required to validate the behavior of IOS in vertical preparations
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.F. and A.C.; methodology, A.C.; software, R.H.; validation, A.C., G.V. and M.F.; formal analysis, F.M.; investigation, R.H.; resources, G.V.; data curation, N.M.R.; writing—original draft preparation, R.H. and G.V.; writing—review and editing, G.V. and C.C.; visualization, M.F.; supervision, A.C.; project administration, F.M.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Richert, R.; Goujat, A.; Venet, L.; Viguie, G.; Viennot, S.; Robinson, P.; et al. Intraoral scanner technologies: a review to make a successful impression. J Healthc Eng 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghazzawi, T.F. ; Advancements in CAD/CAM technology: options for practical implementation. J Prosthodont Res 2016, 60, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memari, Y.; Mohajerfar, M.; Armin, A.; Kamalian, F.; Rezayani, V.; Beyabanaki, E. ; Marginal adaptation of CAD/CAM all-ceramic crowns made by different impression methods: a literature review. J Prosthodont 2019, 28, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, K.; Beuer, F.; Stimmelmayr, M.; Erdelt, K.; Keul, C.; Güth, J.F. ; Fit of 4-unit FDPs from CoCr and zirconia after conventional and digital impressions. Clin Oral Investig 2016, 20, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chochlidakis, K.M.; Papaspyridakos, P.; Geminiani, A.; Chen, C.J.; Feng, I.J.; Ercoli, C. ; Digital versus conventional impressions for fixed prosthodontics: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Prosthet Dent 2016, 116, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlholm, P.; Sipilä, K.; Vallittu, P.; Jakonen, M.; Kotiranta, U. Digital versus conventional impressions in fixed prosthodontics: a review. J Prosthodont 2018, 27, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuzbasioglu, E.; Kurt, H.; Turunc, R.; Bilir, H. Comparison of digital and conventional impression techniques: evaluation of patients’ perception, treatment comfort, effectiveness and clinical outcomes. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glossary of Digital Dental Terms, 2nd Edition: American College of Prosthodontists and ACP Education Foundation. J Prosthodont. 2021, 30, 172–181. [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 5725-1. Accuracy (trueness and precision) of measurement methods and results. Part 1: general principles and definitions. Berlin: International Organization for Standardization; 1994. Available at: http://www.iso.org/iso/home.html.
- Sim, J.Y.; Jang, Y.; Kim, W.C.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.H. Comparing the accuracy (trueness and precision) of models of fixed dental prostheses fabricated by digital and conventional workflows. Journal of prosthodontic research 2019, 63, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesemann, C.; Muallah, J.; Mah, J.; Bumann, A. Accuracy and efficiency of full-arch digitalization and 3D printing: A comparison between desktop model scanners, an intraoral scanner, a CBCT model scan, and stereolithographic 3D printing. Quintessence international 2017 48, 41–50.
- Amornvit, P.; Rokaya, D.; Sanohkan, S. Comparison of Accuracy of Current Ten Intraoral Scanners. BioMed research international 2021, 2673040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedelcu, R.G.; Persson, A.S. Scanning accuracy and precision in 4 intraoral scanners: an in vitro comparison based on 3-dimensional analysis. J Prosthet Dent 2014, 112, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latham, J.; Ludlow, M.; Mennito, A.; Kelly, A.; Evans, Z.; Renne, W. Effect of scan pattern on complete-arch scans with 4 digital scanners. J Prosthet Dent 2020, 123, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Mickesh, G.J.; Cho, D.; Sorensen, J.A. ; Effect of finish line location and saliva contamination on the accuracy of crown finish line scanning. J Prosthodont. 2023, 10, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeling, A.; Wu, J.; Ferrari, M. Confounding factors affecting the marginal quality of an intra-oral scan. J Dent. 2017, 59, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukazawa, S.; Odaira, C.; Kondo, H. Investigation of accuracy and reproducibility of abutment position by intraoral scanners. J Prosthodont Res 2017, 61, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, J.F.; Keul, C.; Stimmelmayr, M.; Beuer, F.; Edelhoff, D. Accuracy of digital models obtained by direct and indirect data
capturing. Clin. Oral Invest. 2013, 17, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari Cagidiaco, E.; Zarone, F.; Discepoli, N.; Joda, T.; Ferrari, M. ; Analysis of The Reproducibility of Subgingival Vertical Margins Using Intraoral Optical Scanning (IOS): A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. J Clin Med. 2021, 10, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.T.; Son, K.; Lee, K.B. Trueness of intraoral scanners according to subgingival depth of abutment for fixed prosthesis. Sci Rep. 2022, 12, 20786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, K.; Lee, K.B. ; Effect of finish line locations of tooth preparation on the accuracy of intraoral scanners. Int J Comput Dent. 2021, 24, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- García-Gil, I.; Perez de la Calle, C.; Lopez-Suarez, C.; Pontevedra, P.; Suarez, M.J. Comparative analysis of trueness between conventional and digital impression in dental-supported fixed dental prosthesis with vertical preparation. Journal of clinical and experimental dentistry 2020, 12, e896–e901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marani, R.; Reno, V.; Nitti, M.; D’Orazio, T.; Stella, E. A modified iterative closest point algorithm for 3D point cloud registration. Comput Aided Civil Infrastruct Eng 2016, 31, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, S. The fit of Procera titanium crowns. An in vitro and clinical study. Acta Odontol Scand 1993, 51, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, FM. Margins of complete crowns--literature review. J Prosthet Dent 1982, 48, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, J.W.; Von Fraunhofer, J.A. The estimation of cement film thickness by an in vivo technique. Br Dent J 1971, 131, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, J.D.; Rozier, R.G.; McFall, W.T. Jr; Ramsey, D.L. Effect of crown margins on periodontal conditions in regularly attending patients. J Prosthet Dent 1991, 65, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verniani, G.; Ferrari Cagidiaco, E.; Marruganti, C.; Kamposiora, P.; Ferrari, M. Comparison of marginal fit and sealing ability of luted lithium disilicate crowns fabricated with CAD/CAM technology using two different intraoral scanners. J Osseointegr 2021, 13, S299–S304. [Google Scholar]
- Brawek, P.K.; Wolfart, S.; Endres, L.; Kirsten, A.; Reich, S. The clinical accuracy of single crowns exclusively fabricated by digital workflow—the comparison of two systems. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2013, 17, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, Y.J.; Shin, S.W.; Ryu, J.J. Effect of software version and parameter settings on the marginal and internal adaptation of crowns fabricated with the CAD/CAM system. Journal of applied oral science 2015, 23, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduo, J.; Elseyoufi, M. Accuracy of Intraoral Scanners: A Systematic Review of Influencing Factors. The European journal of prosthodontics and restorative dentistry 2018, 26, 101–121. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).