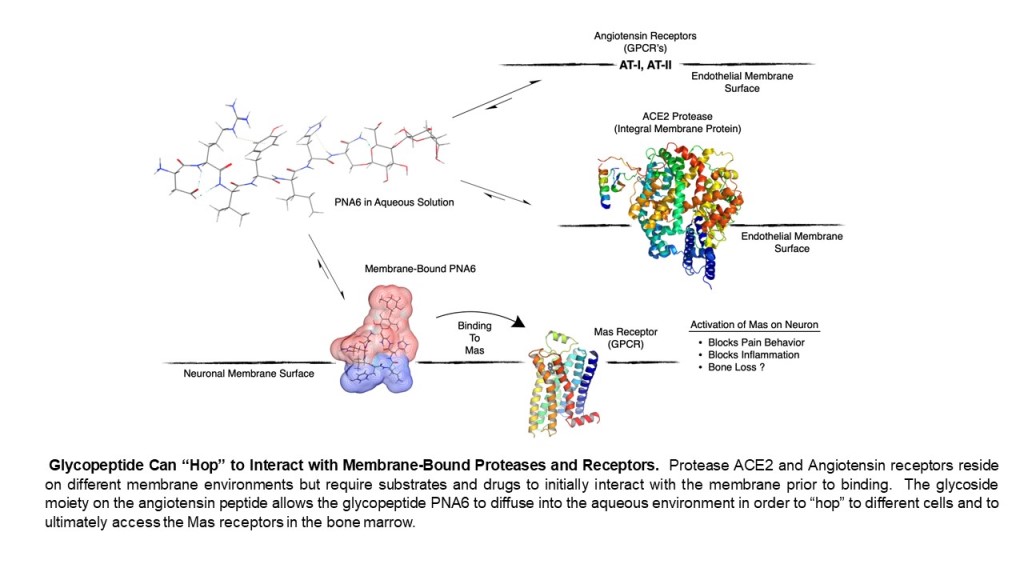
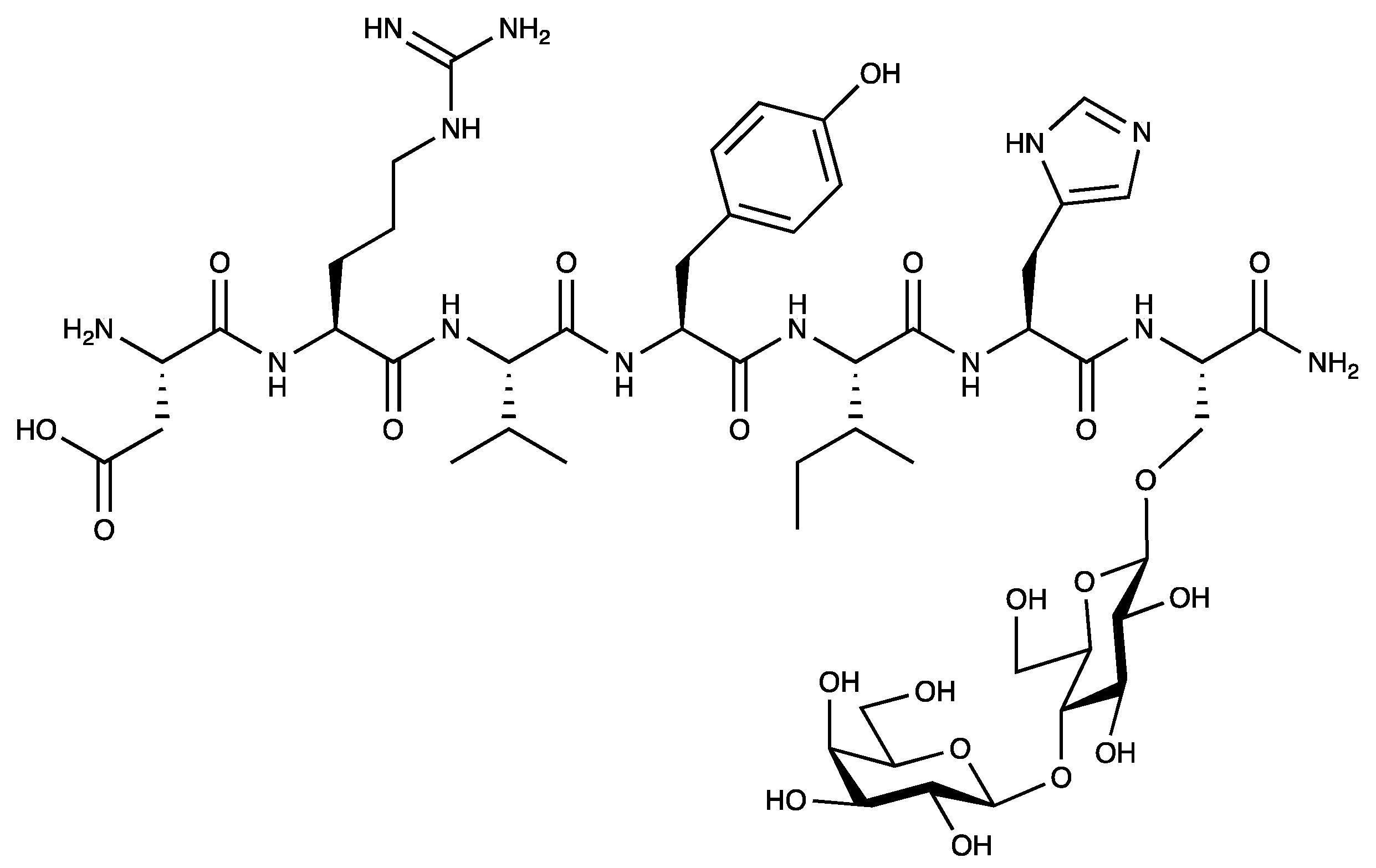
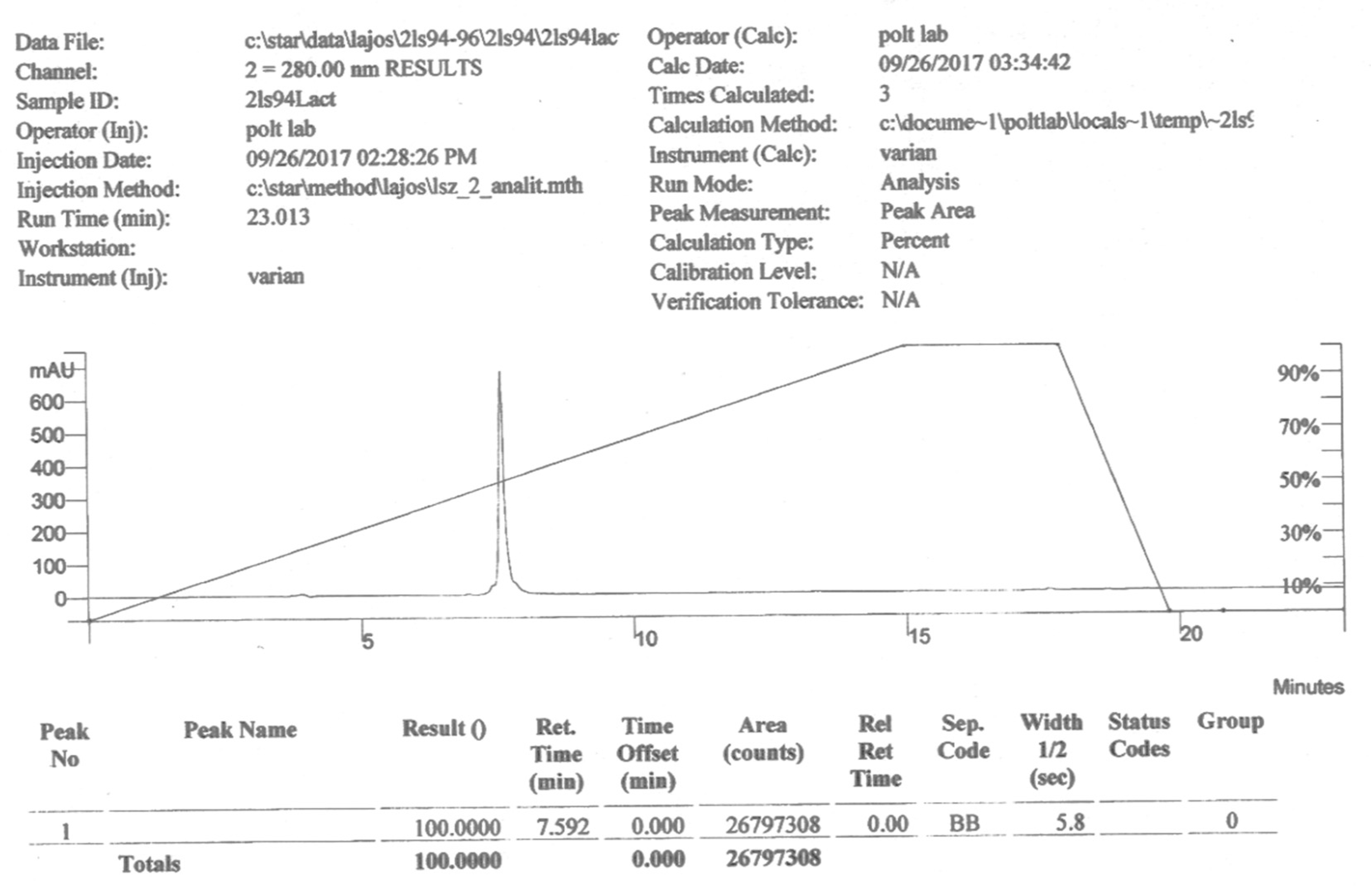
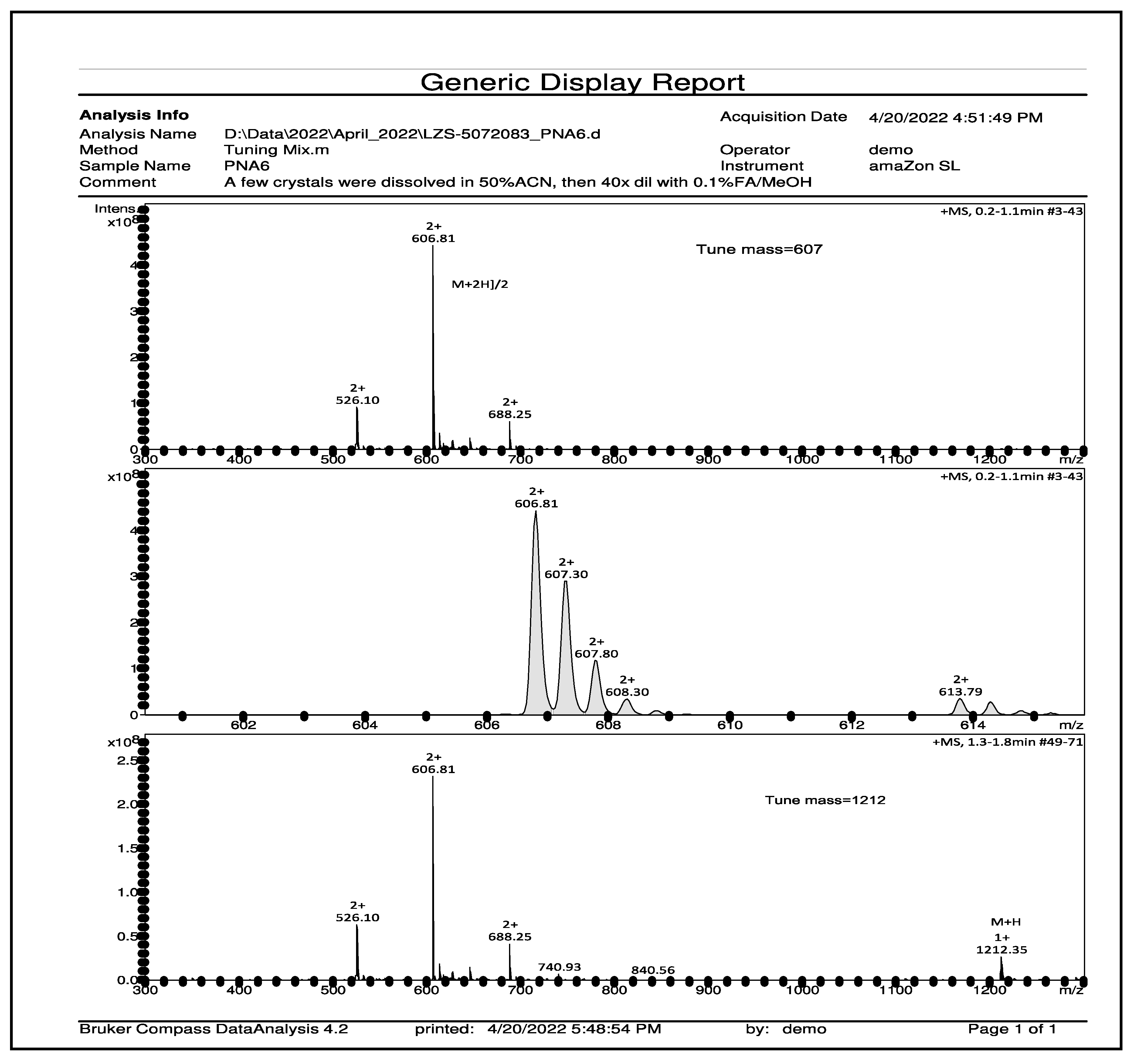
1. Introduction
Breast cancers are the most frequent malignant tumors in women of all racial and ethnic backgrounds in the United States and the second leading cause of death in women [
1]. More than 1.3 million women are diagnosed with breast cancer each year. In 2019, the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) reported 264,121 new cases of female breast cancer, with 42,280 deaths in total (CDC, 2019). Breast cancer can also occur in men, although men represent 1% of all breast cancer cases [
2].
Of the patients who die from breast cancer, greater than 90% have been associated with the progression of metastatic breast cancer [
3]. The brain, lungs, liver, and bone are the most common loci for breast tumor metastasis. Clinically, bone metastasis represents 60-70% of all breast cancer metastasis [
4,
5]. Over 50% of individuals with advanced breast cancer have bone metastasis, and about 70% of women who die from breast cancer develop bone metastases [
6,
7,
8]. Typical complications of bone metastasis are pathological fracture, spinal compression, hypercalcemia, and persistent pain [
9]. These complications lead to a massive reduction in the survival rate and decreased quality of life.
Pain is the most significant impairment and debilitating challenge for patients with bone metastasis. Therefore, the primary objective of current therapy is to mitigate and prevent the persistence of pain. Cancer-induced bone pain can be intermittent but progresses rapidly into continuous pain exacerbated by episodes of breakthrough pain. Thus, cancer-induced bone pain is characterized as a complex pain comprising inflammatory, neuropathic, and mechanical components [
5,
10,
11]. In addition to cancer-induced pain, chemotherapy often results in long-lasting neuropathic pain that can last well after treatment [
12]. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a progressive, durable, and often irreversible side effect of various antineoplastic medications. Thus, interventions that can alleviate both cancers induced, and chemotherapy-related neuropathic pain are highly desirable.
One class of antineoplastic drugs associated with CIPN is platinum-based drugs, such as oxaliplatin is frequently implicated in peripheral neurotoxicity, leads to triggering abnormal sensations like tingling, numbness, pressure, persistent pain, and heightened temperature sensitivity, causing significant suffering [
13]. These symptoms usually manifest during the second or third treatment cycle and last 2-4 days after the drug infusion. The exact mechanisms underlying CIPN remain incompletely understood, and practical strategies for its prevention and treatment remain unresolved challenges in medicine [
14]. Nevertheless, numerous drugs have been employed over the past few decades to intervene in CIPN, and their effects have been evaluated. In addition, various compounds have been developed to prevent or treat CIPN by targeting ion channels, inflammatory cytokines, and oxidative stress [
13].
The RAS is a crucial player in regulating blood pressure and fluid homeostasis [
15]. The octapeptide, Angiotensin II, is the first significant end product. Angiotensin II binds strongly to G-coupled protein receptors (GPCRs), Angiotensin receptor type 1 (AT1) to produce vasoconstriction, sodium-water retention, inflammation, and fibrosis; and binds weakly to Angiotensin II receptor type II (AT2), which produces vasodilation and angiogenesis [
16]. Angiotensin II is cleaved by Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) to yield the heptapeptide, Ang-(1—7), which has a greater affinity for AT2 than AT1 [
17]. Ang-(1—7), a biologically active heptapeptide, binds to the GPCR, Mas receptor (MasR1; Kd = 0.83 nM) with 60- to 100-fold greater selectivity over the AT1 and AT2 receptors, respectively [
18,
19].
Ang-(1—7) at Mas receptors (MasR1) has been reported to prevent cognitive impairment in cardiovascular disease [
20,
21], reduce cognitive decline in Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) [
22], and attenuate cancer-induced bone pain (CIBP) [
23]. However, Ang-(1—7) is degraded rapidly by enzymes and has a short half-life in vivo. On the other hand, the glycopeptide PNA6, an O-linked lactoside analogue of Ang-(1—7), has been shown to have a half-life of over 1.5 hours and good penetration into the CNS. Furthermore, it significantly decreases spontaneous, evoked pain behavior in CIBP mice and significantly reverses CIPN in mice.
Permanent pain relief has not been achieved with the current therapies. Cancer-induced bone pain has become an increasing challenge, as new treatments are needed to maximize effectiveness while reducing adverse events; in this study, we established the efficacy of the MasR1 agonist, PNA6, in attenuating pain induced by inflammation, cancer-induced bone pain, and CIPN in mice.
3. Discussion
Despite the improvement of therapeutic techniques to reduce cancer mortality, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgery, and bio-chemotherapy, no new developments have targeted the number one complaint, chronic pain, and chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. Recent studies demonstrate RAS's role in developing and invasiveness of several types of cancers. Ang-(1—7), an essential component of the RAS system, demonstrated an implication in metastatic disease and pain [
25,
26,
27], yet no studies have investigated whether PNA6/MasR1 was active in murine models of inflammation, CIBP or CIPN. Evidence shows that mRNA and protein expression of the Mas receptor (MasR1) is upregulated in DRG after chronic constriction injury to the sciatic nerve, and Ang-(1—7) significantly inhibits neuropathic pain in chronic constriction injury [
28]. Since cancer-induced bone pain (CIBP) and chemotherapy-induced neuropathy displays characteristics of ongoing neuropathic and inflammatory pain [
10], we chose to investigate the utility of PNA6, a Lactosyl Ang-(1—7) analog with a longer half-life and good CNS penetration, in murine models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. We tested both acute and chronic systemic administration of PNA6 to attenuate the spontaneous pain behaviors induced by carrageenan-induced inflammation, breast cancer confined to the long bones, and oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in mice.
Native peptides are known for their inherent instability in vivo, with short half-lives of the biologically active peptide and low permeability across biological membranes. Therefore, several strategies have been applied to improve the native peptides’ stability, safety, circulation time, efficacy, biodistribution, etc. These strategies are PEGylation, lipidation, conjugation to antibodies, and stapled peptides [
29]. One promising strategy to synthesize our compound of interest here (PNA6) is glycosylation. Glycosylation is a synthetic method introducing carbohydrate moieties to peptides [
30]. Some advantages of peptide glycosylation include protecting amino acids’ side chain from oxidation, increasing metabolic stability, enhancing the penetration through biological membranes, targeting specific organs, improving the biodistribution in tissues, lowering the clearance rate, enhancing receptor-binding, and stabilizing the physical properties of peptides [
31,
32,
33,
34]. As Ang-(1—7) is a native bioactive peptide with all the above-mentioned therapeutic potential, our group developed derivatives of it via the glycosylation strategy. One of these derivatives is PNA6, successfully synthesized using the SPPS strategy [
35] with high purity by the glycosylation of Ang-(1—7) (DRVYIHP) replacing the seventh residue (proline) with serine. A lactoside was attached to the hydroxyl group of the serine, and the C-terminus was acetamidate, resulting in Ang-1-6-Ser-(β-O-Lact)-CONH2 (PNA6). This synthesis approach is like the one performed to synthesize the ser-glucoside derivative of Ang-(1—7) (PNA5) [
36] PNA6 is an amphipathic glycopeptide that contains a carbohydrate moiety. As mentioned above, sugar moiety affects its interaction with the biological membrane and increases its aqueous solubility. In general, glycopeptides have relatively lipophilic backbones and hydrophilic sugar moieties; this allows O-glycopeptide to interact with both the membrane surface and the aqueous compartment in a “hopping” motion, which promotes transport of the drug throughout the body in vivo, improves bioavailability, shows more stability, less degradation by enzymes and improves half-life [
37,
38,
39]. The modification of peptides demonstrates potential in the design of novel therapeutics that tend to have high efficacy while lacking unwanted side effects [
40].
Our findings demonstrating that PNA6 had long-acting efficacy when given acutely as well as chronically suggest that a modified natural peptide may be helpful in reducing CIBP. Since some drugs can cause paralysis or decrease limb use resulting in the misinterpretation of antinociceptive effects, we demonstrated that PNA6 had no significant effect on the motor movement of the limbs using a rotarod. Our data indicate that the mechanism of action through which PNA6 inhibits pain involves its interaction with the MasR1, a G-protein coupled receptor, within either the tumor-peripheral nociceptor and/or the CNS. Our data indicate that PNA6 directly targets nociceptive activation rather than exerting its effects through the tumor-bone environment. This is supported by the finding that PNA6 did not significantly alter tumor-induced bone degradation, as demonstrated by many compounds that alter such an environment and have an influence on osteoclast activity [
41]. Unlike compounds that modulate bone wasting and may influence pain through osteoclast activity, our chronic studies with PNA6 did not result in significant bone loss. An additional explanation of PNA6’s ability to inhibit CIBN would be the potential slowing of tumor proliferation, yet the chronic administration of PNA6 did not have a substantial impact on tumor burden, further suggesting that its analgesic effect is primarily mediated by inhibiting nociceptive activation. These findings shed light on the specific mechanism by which PNA6 attenuates pain and highlight its potential as a targeted therapeutic approach for pain management in the context of the tumor-nociceptor microenvironment.
One may anticipate alterations in MasR1 expression within the nociceptive circuit and/or the bone-tumor microenvironment if MasR1 is a viable therapeutic target for CIBP and the site of action for PNA6. Our Previous data confirms that MasR1 is expressed in the DRG of naive mice, and cancer cell inoculation significantly increased the expression of MasR1 in the ipsilateral femur extrudate, in accordance with a previous report of inflammatory pain, The study utilized a rat model of chronic nerve injury to demonstrate that MasR1 expression in DRG neurons is induced over time [
42]. The increased MasR1 expression was observed at both the mRNA and protein levels, leading to enhanced MasR1-ligand binding on DRG neuron membranes. Our Behavioral tests confirmed that MASR1 activation improved pain symptoms, while MASR1 inhibition attenuated the effects of PNA6.
Metastatic cancer is most often treated with chemotherapy [
43]. Such types of treatments are becoming more successful with patients living longer but with more unwanted side effects induced by the treatment. One such side effect that can often result in the diminution of treatment is chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) [
44]. CIPN is a debilitating and persistent side effect of several antineoplastic agents that often results in sensory abnormalities such as tingling, numbness, pressure, persistent pain, and thermal pain hyperalgesia [
45]. The pathogenesis of CIPN remains largely unknown, and its prevention and treatment are ongoing challenges in medicine. CIPN is commonly associated with platinum-based drugs such as oxaliplatin [
46]. Numerous drugs have been developed and evaluated over the years to try and prevent or treat CIPN, including targeting ion channels, inflammatory cytokines, and oxidative stress, yet no new treatment is available for CIPN.
The idea of significantly attenuating CIPN by pretreatment with PNA6 to reduce the incidence and/or severity of CIPN would be optimal and allow for proper chemotherapy dosing to overcome metastatic cancer.
The findings from studies conducted on both human neuropathic pain and animal models have provided clear evidence that the activation of glial cells and the subsequent release of pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as IL-1b, IL-6, and TNF-a) [
47] and chemokines (such as CCLs, CX3CL1, and CXCL12) [
48] play a role in chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. The release of cytokines triggered by chemotherapy agents may be attributed to their ability to activate Toll-like receptors (TLRs), particularly TLR4. In knockout mice lacking this specific receptor, the pain behavior induced by cisplatin was notably reduced [
49]. Interestingly, a recent study identified this same target, TLR4, as a mechanism of chronic morphine-induced pain in a murine model of bone cancer pain [
41], potentially limiting opioids as a treatment for CIPN. Pro-inflammatory cytokines have been shown to sensitize nociceptors by modulating ion channel properties, as evidenced by the research conducted by Jin et al. [
50]. Oxaliplatin can increase the level of the CCL-2 chemokine, primarily released from astrocytes, and the level of CCL-2 is correlated with the degree of hyperalgesia observed in rats [
51]. Other studies have confirmed the role of chemokine CXCL12 [
52] and chemokine CX3CL1 signaling in oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy [
53]. The role of Ang-(1—7) in reducing inflammation in animal models has been previously reported; however, the role of this protective peptide hormone in treating CIPN has not been described.
Ang-(1—7) exhibits anti-inflammatory properties that have been observed in various studies. Ang-(1—7) acts on MasR1, resulting in a significant reduction in the levels of proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, and IL-6. At the same time, it stimulates the production of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. These effects contribute to the overall suppression of inflammation in the body [
54].
In Conclusions: Our findings suggest that PNA6 may be a promising therapeutic agent for the treatment of CIBP and CIPN. Notably, PNA6 was effective in mitigating pain without altering tumor growth or bone loss, unlike what has been reported with the use of opioids which are current clinical practices [
41]. This indicates that patients with bone cancer pain may still receive chemotherapeutic intervention, which is often halted or reduced due to CIPN, while being treated with PNA6, further eradicating the metastasis proliferation while having pain relief. Further studies are needed to evaluate the efficacy of PNA6 in human subjects and to further evaluate its mechanism of action in treating CIPN. Overall, our results suggest that PNA6 may have therapeutic potential for managing CIPN, a significant challenge in oncology care. Moving forward, further investigations are warranted to unravel the precise molecular pathways through which PNA6 exerts its antinociceptive effects. Understanding the specific inflammatory and pain pathways modulated by PNA6 will provide valuable insights for the development of novel therapeutic strategies for pain management in cancer patients. Additionally, the potential of PNA6 or similar glycosylated derivatives as a viable treatment option for neuronal damage and PNS to CNS inflammation warrants comprehensive exploration in preclinical and clinical studies. These advancements hold promise for addressing the unmet needs of cancer patients suffering from chronic and neuropathic pain, ultimately improving their quality of life during treatment.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS)
The reagents used for SPPS were: Rink amide MBHA resin (100−200 mesh, 0.83 mmol/g), 6-chloro-1-hydroxybenzotriazole (Cl-HOBt), Fmoc-L-His(Trt)-OH, Fmoc-L-Ile-OH, Fmoc-L-Tyr(tBu)-OH, Fmoc-L-Val-OH, Fmoc-L-Arg(Pbf)-OH, N, N-Methylmorpholine (NMM), and 1,8-Diazabicyclo [5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU) were obtained from Chem-Impex INT’L INC (Wood Dale, IL, USA). Fmoc-Pro-OH, Fmoc-Asp (OtBu)-OH, and 2-(1H-benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate (HBTU), and N, N-diisopropylcarbodiimide (DIC), as well as Fmoc-L-Ser(β-O-LactAc7)-OH were obtained from AAPPTec (Louisville, KY, USA). Anisole was obtained from Aldrich Chemical CO., INC (Milwaukee, WI, USA). N, N-Diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich, Co (St. Louis, MO). N-methyl pyrrolidone (NMP) was obtained from VWR Chemicals BDH® (Radnor, PA, USA). Dichloromethane (DCM) was obtained from Fisher Chemical (Geel, Belgium). N, N-Dimethylformamide (DMF). Piperidine and Hydrazine monohydrates were obtained from Alfa Aesar (Ward Hill, MA). Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) and Triethylsilane (TES) were obtained from Oakwood Chemical (Columbia, South Carolina). Ether Anhydrous was obtained from Avantor–J.T.Baker® (Radnor, PA).
The PNA6 drug candidate (
Figure 1, Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Ser(β-O-Lact)) was assembled using standard Fmoc-based solid-phase peptide synthesis on Rink amide-MBHA resin (loading: 0.83 mol/g). First, the coupling of Fmoc-Ser(β-O-LactAc7)-OH (1.3 eq) was done manually using Cl-HOBt (1.3 eq) and DIC (1.3 eq) in NMP, capping of unused sites on the resin was accomplished with 10% acetic anhydride and 10% DIPEA in DCM. Then, the coupling of the Fmoc–protected amino acids was performed on a PreludeTM automated synthesizer. Coupling was accomplished with 2.5 eq Fmoc-AA and HBTU (3.0 eq) and 12 eq of NMM in DMF.
The Fmoc groups were removed using a mixture of 2% piperidine and 2% DBU in DMF for 12 min with argon bubbling as agitation. Next, the acetyl-protecting groups of the sugar moiety were removed by a 1:1 mixture of hydrazine monohydrate in NMP (H2NNH2•H2O: NMP) with argon agitation for four h. Finally, the PNA6 was cleaved from the resin with a peptide cleavage cocktail consisting of 89% TFA, 10% DCM, 0.25% TES, 0.25% water, and 0.5% Anisole for 1 hr at room temperature, which simultaneously removed the side chain protecting groups.
For the HPLC purification and characterization of PNA6, the crude was precipitated in cold ether, dissolved in a minimal amount of distilled water, and then lyophilized. First, the crude material was purified by RP-HPLC Gilson system on a semi-preparative C18 Phenomenex column (5 µm, 100 Å, 250 mm × 50 mm) using gradient program mobile phase of (A: 5–80% ACN) vs. (B: 0.1% TFA in H2O) over 60 min to give the compound in a pure form. Then, assessing the purity by analytical HPLC (Inspire C18 5 μm 250 mm × 4.6 mm column) on a Varian LC with a diode array detector system (at 280 nm) employing the same mobile gradient phase program for 15 min. The pure fractions obtained from preparative HPLC purification were frozen at −80C and then lyophilized to afford pure PNA6 as a white and fluffy solid. The same analytical RP-HPLC was used to evaluate the purity of the compound after lyophilization. Finally, the mass measurements of pure synthetic PNA6 were performed and characterized using mass spectrometry (Bruker AmaZon ion trap mass spectrometer via infusion, Analytical & Biological Mass Spectrometry, Core Facility in BIO5 Keating Bioresearch Building, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA).
4.2. In Vitro
4.2.1. Cell Culture
E0771 breast adenocarcinoma cells were gifted by Kathryn Visser at the Olivia Newton-John Cancer Research Institute Metastasis Research Institute (Victoria, Australia). 8 x 104 E0771 breast adenocarcinoma cells (P10-20) suspended in 5uL volume of OPTI-MEM were injected into the medullary cavity into the right femur of female C57BLK/6J wild-type mice to induce cancer-induced bone pain (CIBP). Cancer Cells were cultured in DMEM–Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 1% penicillin /streptomycin (P/S), and 25 mM HEPES buffer. The E0771 cells were plated in T-75 tissue culture flasks and allowed to grow exponentially in an incubator at 37˚C and 5% CO2. Cells were passaged every four days or as needed, and cells used for all experiments were in the 10-20 passage range.
4.2.2. Cell Viability Assay
We assessed the effect of PNA6 on the viability and performance of the E0771 adenocarcinoma cells. First, E0771 adenocarcinoma cancer cells were thawed and resuspended in growth media, then plated in T-75 tissue culture flasks, allowing them to grow in the incubator at 37 ˚C with 5% CO2. Next, the cancer cells were inoculated in a flat-bottom 96-well microtiter plate at a concertation of 1x106/ well in serum media (determined from the pre-optimized procedure) and placed in the incubator for 24 hrs. After 24 hours, the media was removed using a suction pipette; the cells were treated with respective pharmacological treatments in serum-free media. The treatments utilized were serum-free media alone, cells with media, and different doses of PNA6 (0.01, 0.1, 1, 10 µM) for another 24 hrs. Cell viability to the different drug doses was assessed after 24 hrs. with the tetrazolium salt XTT cell proliferation assay according to the manufacturer protocol (catalog number 30-1011K; ATCC, Manassas, VA).
4.3. In Vivo
4.3.1. Animals
All procedures were approved by the University of Arizona Animal Care and Use Committee and conformed to the National Institutes of Health Guidelines and the International Association for the Study of Pain. Male CD1 mice (n=44) 18-20g (7-8 weeks) were used for the inflammatory model study. Adult female C57BLK/6J wild-type mice between 15 and 20 g (7-8 weeks) were used in the cancer study (n=10-12 mice per treatment group) for the syngeneic implant of E0771 cells. In addition, 24 adult female C57BLK/6J wild-type mice were used in the CIPN study. Mice were housed in a climate control room on a 12-hour light-dark cycle and allowed food and water ad libitum. Animals were monitored on days 0, 7, 10, and 13 of the study for clinical signs of rapid weight loss (less than 20% in 1 week) and anxiety symptoms. All mice were euthanized utilizing an IACUC-approved CO2 procedure.
4.3.2. Drug Treatment
Animals received PNA6, a lactosyl Ang-(1—7) analog, or vehicle (saline) in the absence or presence of the MasR1 antagonist A-779 (Abcam, Cambridge, MA). All injections were made by the intraperitoneal (i.p.) route at a dose of 1mg/kg (10ml/kg). In the antagonist studies, A-779 (1 mg/kg, i.p.) was administered 30 minutes before PNA6 administration. Therefore, only one PNA6 injection (1mg/kg i.p.) or vehicle (saline) was given on day seven of post-cancer cells femur inoculation for the acute inflammatory study. For the chronic study, administration of PNA6 or vehicle (saline) was started on day seven post-cancer cell femur inoculation and continued once-daily injections of PNA6 (1mg/kg, i.p) or vehicle for seven consecutive days. Dosing was performed regularly at 9:00 am. Lastly, for the CIPN study, Oxaliplatin (4mg/kg i.p.) (Tocris Bioscience a Bio-Techne Brand, 61825-94-4, catalog No.: 2623) was prepared daily in a vehicle of sterile 5% dextrose solution distilled water and prepared each day. Systemic administration of PNA6 (1mg/kg, i.p) or vehicle was started on day one and continued once-daily injection for 14 consecutive days.
4.3.3. Induction of Inflammatory Model of Pain
Behavioral assays (mechanical allodynia) using von Frey testing were performed as a baseline measurement of mechanical thresholds of the right hind-paw (details described below). Male CD1 mice (n=40) were anesthetized using nose-cone isoflurane/O2, and acute inflammatory pain was induced by injecting 50μl of 2% λ-Carrageenan or saline subcutaneously into the plantar surface of the right paw subcutaneously (s.c.). After 3hrs, redness and swelling signs and symptoms of inflammation appeared in the right paw ipsilateral to the site of 2% λ-Carrageenan injection. Mechanical allodynia was reassessed by application of von Frey filaments was performed 3 hours after a 2% λ-Carrageenan injection. Mice were then injected with PNA6 (1mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle (i.p.). Mechanical allodynia testing was carried out in a blinded-to-treatment manner, at intervals of every 30 minutes (30, 60, 90, 120, and 180 minutes) post-drug or vehicle administration over a 3-hour time course or until their pain behaviors returned to baseline.
4.3.4. Intramedullary Implantation of E0771 Cells into Mouse Femur
Intramedullary implantation of E0771(murine breast cancer cells) into the right femur of C57BLK/6J wild-type female mice was performed as previously described [
55]. On day 0, mice were anesthetized with ketamine/ xylazine (9mg/kg: 1mg/ml, i.p.). The area of the surgery (right hind leg) was shaved and then cleaned with antiseptic chlorhexidine three times, then exposed the thigh muscle by lateral incision over the femur. An arthrotomy was performed, and the condyles of the right distal femur were exposed. A hole was drilled at the intercondylar space to access the medullary cavity of the right distal femur. 80,000 E0771 cells were suspended in 5µLvolume of OPTI-MEM, then breast adenocarcinoma cells were injected into the medullary cavity using an injection cannula affixed via plastic tubing to a 10µL Hamilton syringe; sham animals received only OPTI-MEM. The femur was then sealed using bone cement, and the muscular compartment was closed using a 5-0 vinyl suture. The skin was closed using wound clips. Gentamicin (8 mg/kg, 10 mL/kg volume) and Normal Saline (3 ml, s.c.) were given to all mice after surgery to prevent infection and dehydration. The mice were monitored D1, D2, and D3 to check the presence of clips and monitored clinical signs of paralysis. Animals were allowed seven days to recover, and clips were removed. Any animal showing signs of illness (loss of significant weight, lack of regular motor movement, etc.) or animals with radiographic signs of fracture before day 14 post-surgery were removed from the study, and their data was not included in the analysis.
4.3.5. Induction of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice
Oxaliplatin (4 mg/ kg) was prepared daily in a vehicle of sterile 5% dextrose solution. Animals received systemic intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of vehicle or dose (4mg/kg-dose) Oxaliplatin for two consecutive days, followed by five days of rest, followed by a second cycle of two daily i.p. injections, followed by five days of rest. The total cumulative doses of oxaliplatin over the course of four injections was 16 mg/kg. The dose of the drug was selected based on the literature evidence, which indicates its effectiveness in inducing neuropathic pain without unspecific systemic toxicity [
56]. Moreover, the dose used in this study is relevant to clinical dosing. The highest recommended dose of oxaliplatin patients is 110 mg/m2 (2.97 mg/kg) [
57]. The total human equivalent dose (THED) of oxaliplatin daily dosing ranges in mice is 0.04–10.0 mg/kg/day, and the cumulative 3.0–30.0 mg/kg (0.24–2.4 mg/kg THED) [
58]. Mechanical allodynia of the right hind paw was determined using manual von Frey filaments. After habituation to the test environment and baseline measurements of pain sensitivity, mice were randomized to two treatment groups of either PNA6 (1mg/kg) or vehicle. Mice were treated with daily intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections for 14 consecutive days. Mechanical hypersensitivity thresholds were assessed every day at the same time for 14 days after 1 hour of PNA6 or vehicle injection. Mechanical allodynia testing was carried out in a blinded-to-treatment manner.
4.3.6. Measurement of Mechanical Allodynia
Mechanical allodynia was measured according to the method described previously [
59]. Paw withdrawal threshold of the ipsilateral paw (to the injury site) to assess mechanical hypersensitivity utilized a series of calibrated von Frey filaments (0.04–4.0 g). Mice were tested for preinjury baseline mechanical hypersensitivity and after 3hrs (baseline after injury), as well as after 30, 60,90, 120, and 180 mins post PNA6 i.p. injection. The mice, after placement in a plexiglass cage with mesh metal flooring, were acclimated to the environment for 30±5 minutes. After test cage acclimation, von Frey filaments of 0.16, 0.4, 0.6, 1, 1.4, and 2 g were applied perpendicularly at the plantar surface in the middle of the large right hind paw of the mice using the up and down method. Each filament was used with a force that caused slight bending and was held at the same force for 2–3 seconds. The filament of 0.6 g was applied as a starting filament to the paw of the mice kept in mesh metal flooring. In the absence of a hind paw withdrawal response to the selected filament, a higher force filament matching a stronger stimulus was applied; a filament of lighter force was chosen in the event of paw withdrawal response. The same procedure was repeated for five consecutive readings, and the average value of five scores was calculated using a Dixon nonparametric test and expressed as the mean withdrawal threshold. A 2 g force was selected as the cut-off force.
4.3.7. Acute and Chronic Behavioral Testing of Spontaneous Pain
Flinching, guarding, and limb use are spontaneous pain-related behaviors that accurately measure ongoing pain in the cancer-bearing limb. Flinching is lifting and rapid flicking of the hind paw ipsilateral to the cancer inoculation limb not associated with walking or other movements. However, if the mouse shook its foot while walking, this was also counted as a flinch; this behavior test counted how many times the mice flinched over 2 min. Guarding is characterized by fully retracting the ipsilateral hind paw under the torso. Time spent guarding the tumor-bearing limb over a 2-min period was quantified using a stopwatch. Limb-use was tested by allowing mice were to move freely in a plexiglass cage individually while the gait of each mouse was observed and scored as follows: 4: Normal use of the affected limb, 3: Limping, 2: Limp and guard, 1: Partial non-use, and 0: complete lack of use of the affected limb. Mice were allowed to acclimate for 30 minutes before testing. All mice were baselined for these behaviors at day 0 before surgery. Animals were then re-examined for pain behaviors on days 7, 10, and 13 post-surgery. Behaviors were analyzed by treatment-blind examiners.
4.3.7.1. Acute Behavioral Testing
Each animal was observed for 2 minutes. Flinching, guarding, and limb use was evaluated at baseline day 0 (before surgery). Behavioral testing was repeated on day seven post-femur-cancer inoculation. Mice were separated into groups; each group had 10-12 mice and consisted of; Sham- PNA6 (1mg/kg), Sham- Saline, Cancer- PNA6 (1mg/kg), and Cancer- Saline, mice received a single dose of PNA6 or saline. Spontaneous pain behavior was assessed at 30, 60, 90, and 120 mins after administration of PNA6 (i.p.) or saline (i.p.). An acute time-response curve was generated on day 7. Behaviors were analyzed by treatment-blind examiners.
4.3.7.2. Chronic Behavioral Testing
Spontaneous pain behaviors were assessed before surgery (baseline) and on day seven post-surgery as a new injured CIBP baseline. Mice then received treatment at the same time each day (9:00 am 30 min) from days 7 to 13. Spontaneous pain behaviors were measured 1 hour after treatment on days 7, 10, and 13 based on the time of peak effect determined by the acute studies. Mice were grouped as follows Sham-PNA6 (1mg/kg, i.p.), Sham-Saline, Cancer-PNA6 (1mg/kg, i.p.), and Cancer-Saline with 10-12 mice in each group. Behaviors were analyzed by treatment-blind examiners.
4.3.8. The Rotarod Test
The rotarod test is widely used to evaluate the motor coordination of rodents, and we used it to determine the motor effect of PNA6 to prevent interpretation of behavior as a false positive. Four days before testing, naïve mice were trained to acclimate to the rotating rod (LE8505 Rota-Rod, Panlab Harvard Apparatus, Spain) at a constant speed of 10 rpm. A maximal cut-off time of 180 seconds was used to prevent exhaustion. On the day of testing, mice were baselined and reevaluated at 30, 60,90, and 120 min after treatment.
4.3.9. Radiographic Analysis
A digital Faxitron machine (Ultrafocus; Faxitron Bioptics) was used to image the femurs of all mice (all groups in chronic studies) on days 0 (baseline), 7, 10, and 14 post-surgery to determine an average bone score and to exclude the data for any mice with full cortical fracture before day 14. Two blinded observers evaluated the images using a 5-point bone rating scale. Mice were anesthetized with ketamine/xylazine on day 0 before the surgery, D7, D10, D14, and radiographs were acquired. The bone scoring scale was as follows: 0 = normal bone, 1 = 1-3 lesions with no fracture, 2 = 4+ lesions with no fracture, 3 = uni-cortical, full thickness fracture, 4 = bicortical, full thickness fracture. Animals with bicortical, full fractures were euthanized as our IACUC protocol measures dictated.
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical significance for all data was analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc correction or an ordinary repeated measure two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc correction, depending on the experimental design. Data were reported as mean ± SEM for n=10-12 mice /treatment group. Power analyses were performed on cumulated data using G* Power 3.1 software to estimate the required number; we found adequate statistical separation for each group to detect 80% between groups at alpha ˂ 0.05. Data were expressed with data analysis performed using GraphPad Prism 7.0 (Graph pad INC., San Diego, CA, USA). All experiments performed with treatment blinded observers’ drug vs. vehicle treatment to increase rigor and data collection responsibility.
Figure 1.
The chemical structure of PNA6.
Figure 1.
The chemical structure of PNA6.
Figure 2.
Analytical HPLC chromatogram of pure PNA6.
Figure 2.
Analytical HPLC chromatogram of pure PNA6.
Figure 3.
Mass spectroscopy spectrum of pure PNA6 shows single charged ion ([M+H] + 1212.35) and double charged ion ([M+2H]2+ 606.81).
Figure 3.
Mass spectroscopy spectrum of pure PNA6 shows single charged ion ([M+H] + 1212.35) and double charged ion ([M+2H]2+ 606.81).
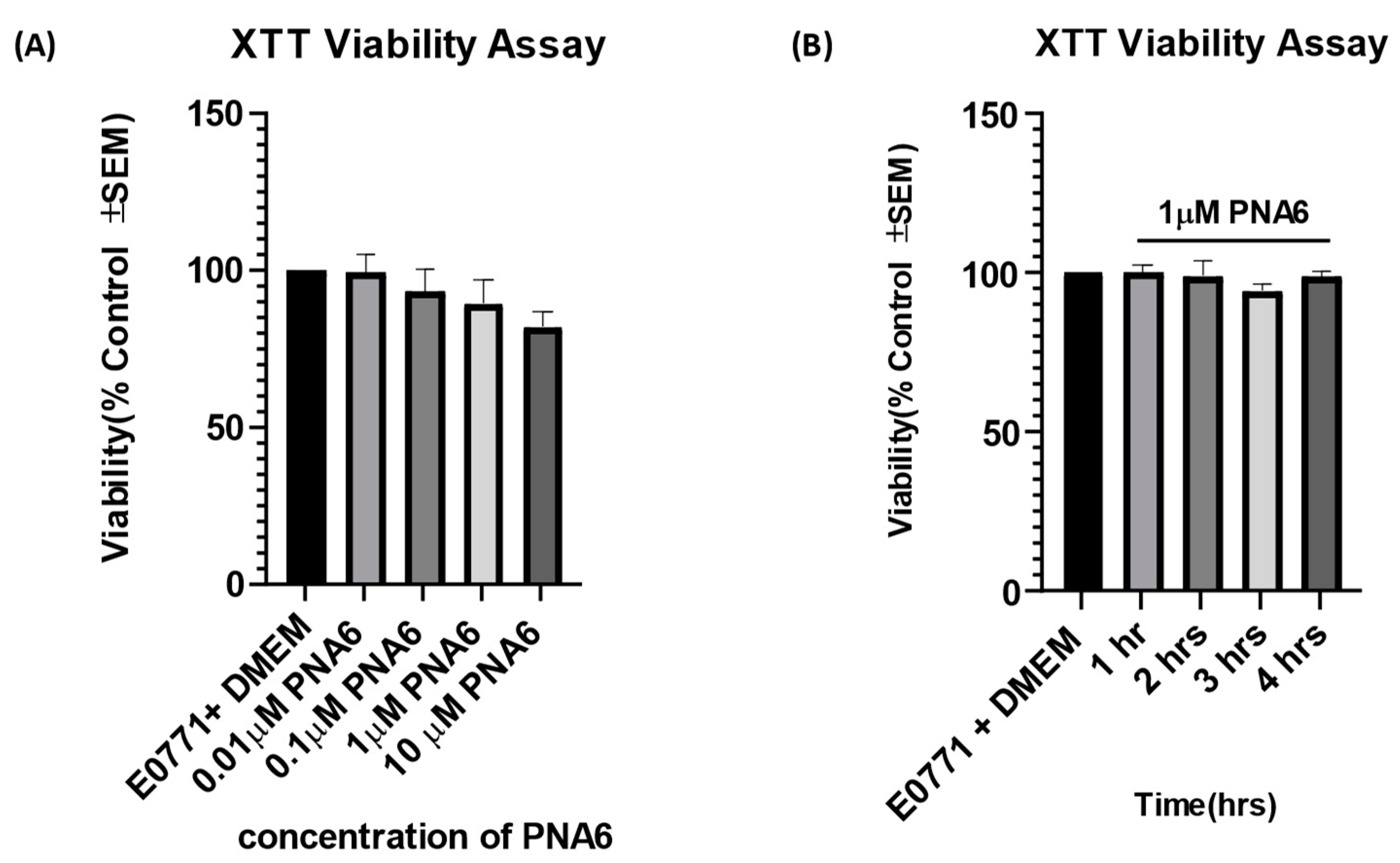
Figure 4.
Effects of PNA6 on E0771 cancer cell viability in vitro. (A) E0771 adenocarcinoma cells do not have a significant change in viability when treated with varying concentrations of PNA6 for 24 h; the cell viability was tested by using the XTT assay. One-Way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc correction. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p< 0.001 (n=5). (B) Timeline of 1, 2, 3, and 4 hrs post PNAS application at 1µM utilizing the XTT assay. There was no significant effect on the cell viability of E0771 cells in the presence of PNA6 from 1 to 4 hours.
Figure 4.
Effects of PNA6 on E0771 cancer cell viability in vitro. (A) E0771 adenocarcinoma cells do not have a significant change in viability when treated with varying concentrations of PNA6 for 24 h; the cell viability was tested by using the XTT assay. One-Way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc correction. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p< 0.001 (n=5). (B) Timeline of 1, 2, 3, and 4 hrs post PNAS application at 1µM utilizing the XTT assay. There was no significant effect on the cell viability of E0771 cells in the presence of PNA6 from 1 to 4 hours.
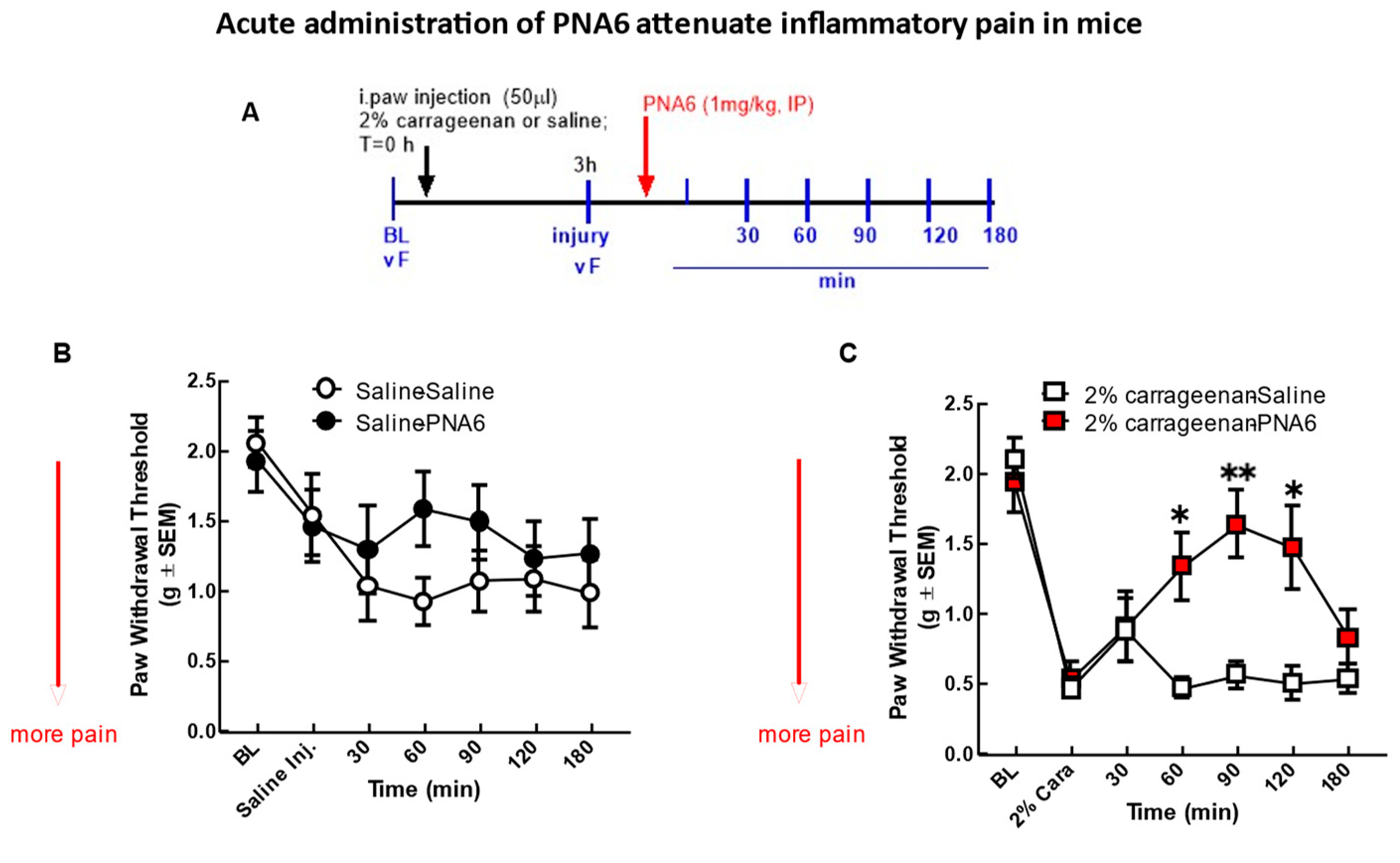
Figure 5.
Acute model of inflammatory pain. Significant mechanical allodynia was detected after 2%λ- Carrageenan injection. (A) Timeline of experiment. (B) mice injected i.paw with saline control didn’t show a significant decrease in mechanical thresholds in the ipsilateral hind paw. Neither PNA6 nor saline given intraperitoneally 3 hrs post i-paw injection resulted in a significant change over the 3-hour testing period. (C) 2%λ- Carrageenan injection significantly decreased hind-paw thresholds 3 hours post-injection. PNA6 (1 mg/kg i.p.) significantly reversed the mechanical hypersensitivity induced by carrageenan in the ipsilateral hind paw at 60, 90, and 120 minutes (n=10-12) mice in each group * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01). Saline (1 ml/kg, i.p.) did not significantly affect carrageenan-induced mechanical hypersensitivity. Results were analyzed by RM2- ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test.
Figure 5.
Acute model of inflammatory pain. Significant mechanical allodynia was detected after 2%λ- Carrageenan injection. (A) Timeline of experiment. (B) mice injected i.paw with saline control didn’t show a significant decrease in mechanical thresholds in the ipsilateral hind paw. Neither PNA6 nor saline given intraperitoneally 3 hrs post i-paw injection resulted in a significant change over the 3-hour testing period. (C) 2%λ- Carrageenan injection significantly decreased hind-paw thresholds 3 hours post-injection. PNA6 (1 mg/kg i.p.) significantly reversed the mechanical hypersensitivity induced by carrageenan in the ipsilateral hind paw at 60, 90, and 120 minutes (n=10-12) mice in each group * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01). Saline (1 ml/kg, i.p.) did not significantly affect carrageenan-induced mechanical hypersensitivity. Results were analyzed by RM2- ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test.
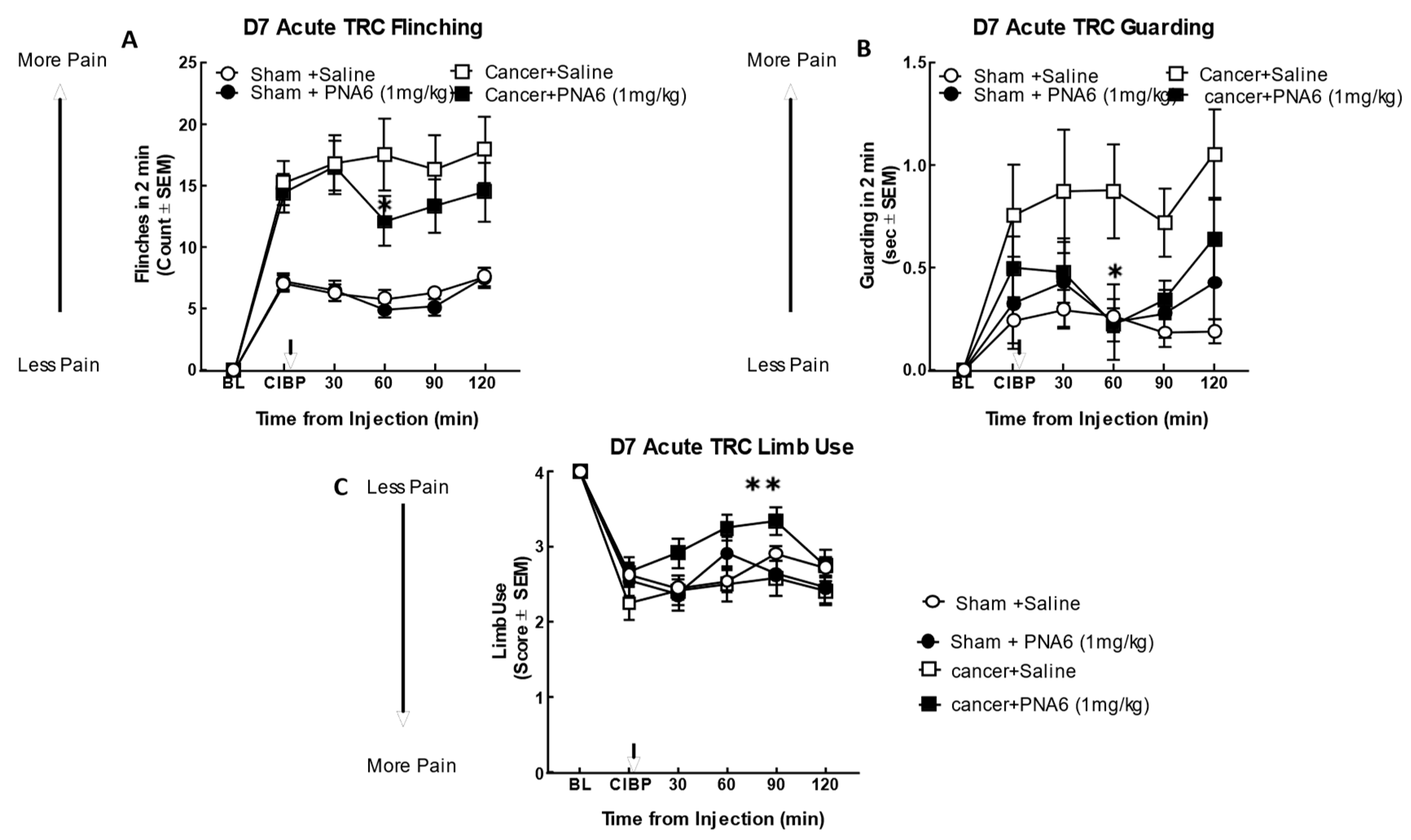
Figure 6.
Acute administration of PNA6 in established cancer-induced bone pain attenuates spontaneous pain behavior in CIBP. Animals display no pain behavior before surgery (BL=baseline). Instead, animals demonstrate increased flinching, guarding, and decreased limb use post-cancer surgery inoculation (CIBP). (A) Time response curve of flinching behavior after PNA6 1 mg/kg at time = 30, 60, 90, 120 min on day seven after surgery. (B) Guarding behavior time response curve after 1mg/kg at times 30, 60, 90, and 120 min on day seven after surgery. (C) Time response curve of Limb use at 30, 60, 90, and 120 min on day seven after surgery. Saline had no significant effect on all three behaviors. The time of peak effect for PNA6 was 60 minutes after administration. n=10-12 mice in each group * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 Results were analyzed by RM, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test.
Figure 6.
Acute administration of PNA6 in established cancer-induced bone pain attenuates spontaneous pain behavior in CIBP. Animals display no pain behavior before surgery (BL=baseline). Instead, animals demonstrate increased flinching, guarding, and decreased limb use post-cancer surgery inoculation (CIBP). (A) Time response curve of flinching behavior after PNA6 1 mg/kg at time = 30, 60, 90, 120 min on day seven after surgery. (B) Guarding behavior time response curve after 1mg/kg at times 30, 60, 90, and 120 min on day seven after surgery. (C) Time response curve of Limb use at 30, 60, 90, and 120 min on day seven after surgery. Saline had no significant effect on all three behaviors. The time of peak effect for PNA6 was 60 minutes after administration. n=10-12 mice in each group * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 Results were analyzed by RM, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test.
Figure 7.
Sustained administration of PNA6 attenuates cancer pain in the murine model of cancer-induced bone pain. Spontaneous pain behavior (A) flinching (B) guarding (C) limb use measured before and at the regular interval following cancer inoculation in female C57BL/6J mice. At D7 post-surgery, animals inoculated with E0771 breast adenocarcinoma cells had significantly elevated spontaneous pain behavior in mice inoculated with E0771 adenocarcinoma cells in comparison to the sham mice group. PNA6 at D7, 10, and 13 significantly attenuated flinchings and guarding in mice with cancer compared to saline-treated mice (A,B). PNA6 at D7 and 10 significantly increased limb use in mice with cancer compared to saline-treated mice (C). MasR1 antagonist, A779, Reverse the Antinociception of PNA6 in the Murine Model of Cancer-Induced Bone Pain. To investigate receptor dependence, animals were dosed post-surgery days 7- 13 with A779 1mg/ kg 30 minutes before administration of PNA6. Spontaneous pain behaviors Flinching (D), guarding (E), and limb use (F) were recorded as previously described. Daily administration of A779 reversed the effect of PNA6 in the CIBP model. In all behavioral tests, n=10-12 mice in each group * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 Results were analyzed by RM2- ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. Limb Use Scale: 0=complete lack of use, 1=partial non-use, 2=limp with guard, 3=limping, 4=Normal.
Figure 7.
Sustained administration of PNA6 attenuates cancer pain in the murine model of cancer-induced bone pain. Spontaneous pain behavior (A) flinching (B) guarding (C) limb use measured before and at the regular interval following cancer inoculation in female C57BL/6J mice. At D7 post-surgery, animals inoculated with E0771 breast adenocarcinoma cells had significantly elevated spontaneous pain behavior in mice inoculated with E0771 adenocarcinoma cells in comparison to the sham mice group. PNA6 at D7, 10, and 13 significantly attenuated flinchings and guarding in mice with cancer compared to saline-treated mice (A,B). PNA6 at D7 and 10 significantly increased limb use in mice with cancer compared to saline-treated mice (C). MasR1 antagonist, A779, Reverse the Antinociception of PNA6 in the Murine Model of Cancer-Induced Bone Pain. To investigate receptor dependence, animals were dosed post-surgery days 7- 13 with A779 1mg/ kg 30 minutes before administration of PNA6. Spontaneous pain behaviors Flinching (D), guarding (E), and limb use (F) were recorded as previously described. Daily administration of A779 reversed the effect of PNA6 in the CIBP model. In all behavioral tests, n=10-12 mice in each group * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 Results were analyzed by RM2- ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. Limb Use Scale: 0=complete lack of use, 1=partial non-use, 2=limp with guard, 3=limping, 4=Normal.
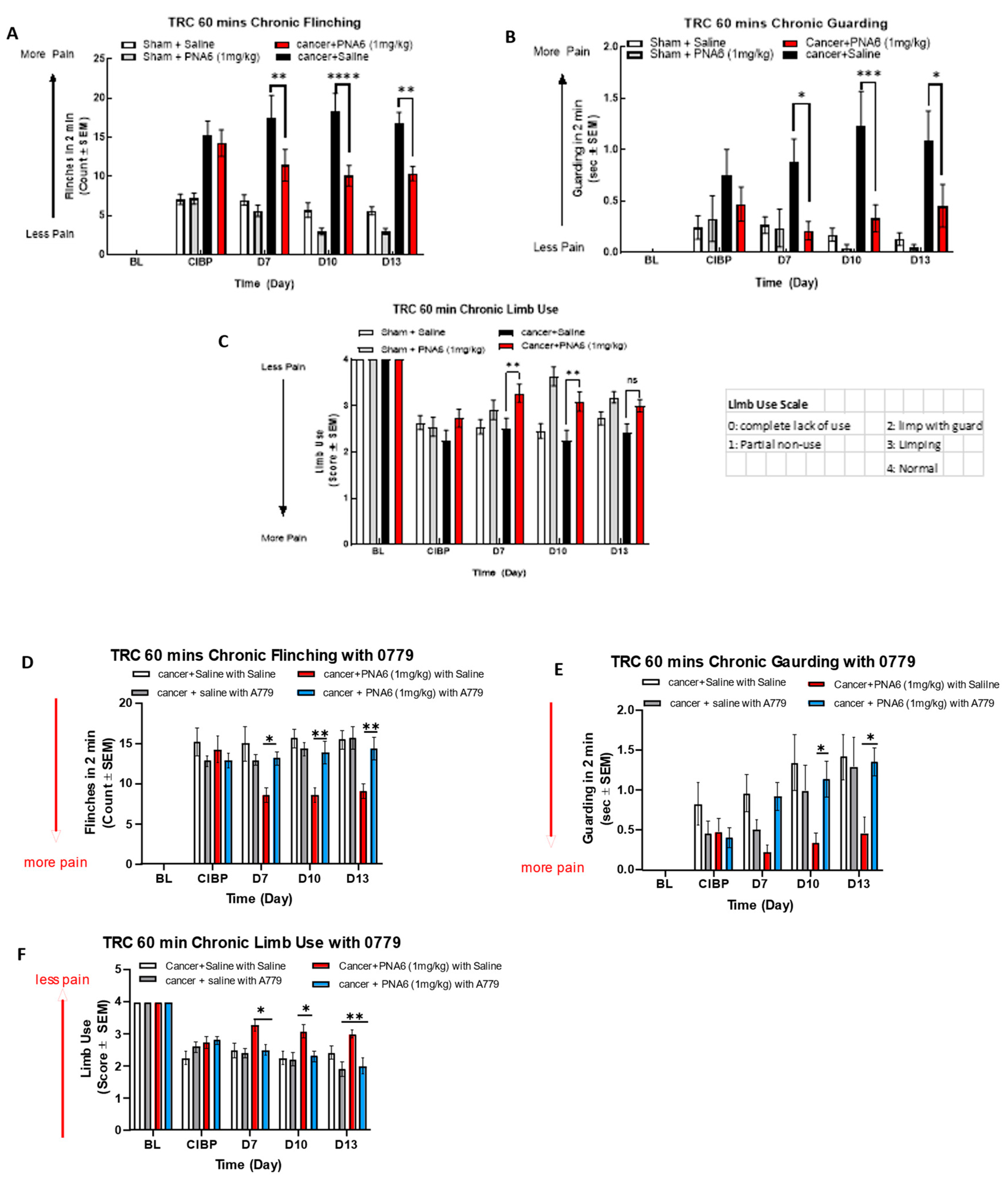
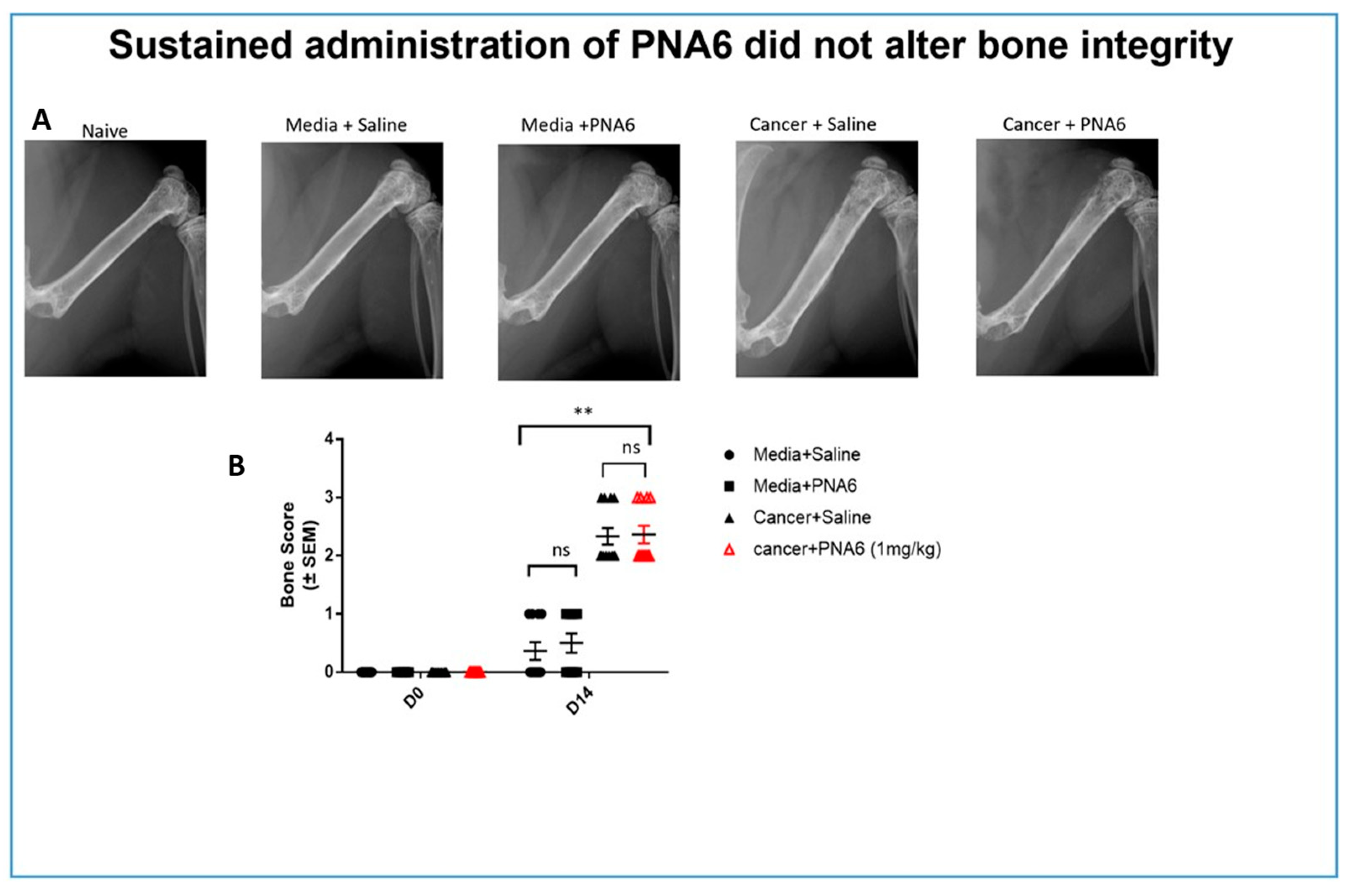
Figure 8.
Sustained administration of PNA6 did not alter bone integrity. (A) Representative radiograph of the right femur of mice D14 post-surgery. Radiographs were obtained before surgery and at D14 post-surgery to monitor cancer-induced lesions. (B) Quantification of bone scores (n=10-12/treatment groups). Bone scores were determined on a 5-point scale by blinded observers. The scoring system was as follows: 0 = normal bone, 1 = 1-3 lesions with no fracture, 2 = 4-6 lesions with no fracture, 3 = uni-cortical, full thickness fracture, 4 = bi-cortical, full thickness fracture. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (One- way ANOVA, Tukey’s HSD post-hoc).
Figure 8.
Sustained administration of PNA6 did not alter bone integrity. (A) Representative radiograph of the right femur of mice D14 post-surgery. Radiographs were obtained before surgery and at D14 post-surgery to monitor cancer-induced lesions. (B) Quantification of bone scores (n=10-12/treatment groups). Bone scores were determined on a 5-point scale by blinded observers. The scoring system was as follows: 0 = normal bone, 1 = 1-3 lesions with no fracture, 2 = 4-6 lesions with no fracture, 3 = uni-cortical, full thickness fracture, 4 = bi-cortical, full thickness fracture. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (One- way ANOVA, Tukey’s HSD post-hoc).
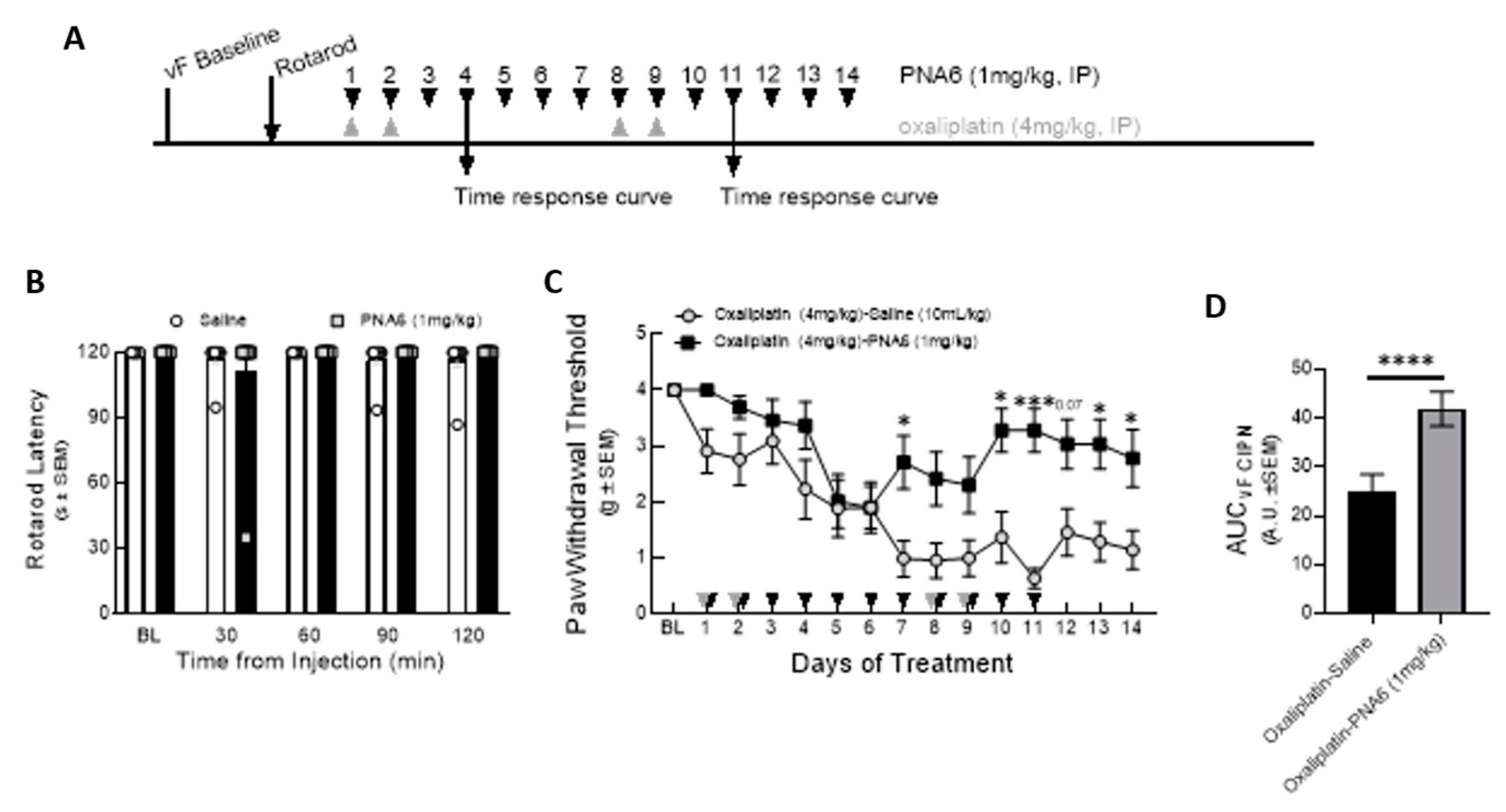
Figure 9.
Chronic effect of PNA6 on CIPN. Timeline of experiment (A). PNA6 does not impair animal locomotion at all testing times (B). Animals experienced a significant decrease in mechanical thresholds due to the treatment of oxaliplatin (4 mg/kg i.p on days 1, 2, 8, 9). Animals with oxaliplatin demonstrated a significant increase in the paw withdrawal thresholds on days 7, 10, 11, 13, and 14 after PNA6 (1 mg/kg i.p.) treatment for 14 consecutive days (C). The area under the curve was calculated, demonstrating significant inhibition of CIPN by PNA6 (D). Values represent mean ± SEM, n = 12 per group * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Results were analyzed by RM2- ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test.
Figure 9.
Chronic effect of PNA6 on CIPN. Timeline of experiment (A). PNA6 does not impair animal locomotion at all testing times (B). Animals experienced a significant decrease in mechanical thresholds due to the treatment of oxaliplatin (4 mg/kg i.p on days 1, 2, 8, 9). Animals with oxaliplatin demonstrated a significant increase in the paw withdrawal thresholds on days 7, 10, 11, 13, and 14 after PNA6 (1 mg/kg i.p.) treatment for 14 consecutive days (C). The area under the curve was calculated, demonstrating significant inhibition of CIPN by PNA6 (D). Values represent mean ± SEM, n = 12 per group * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Results were analyzed by RM2- ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test.