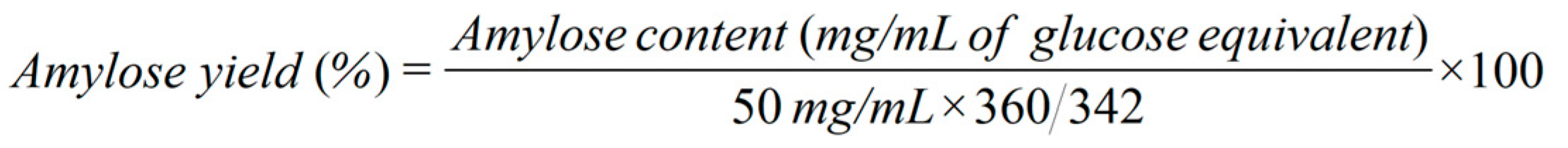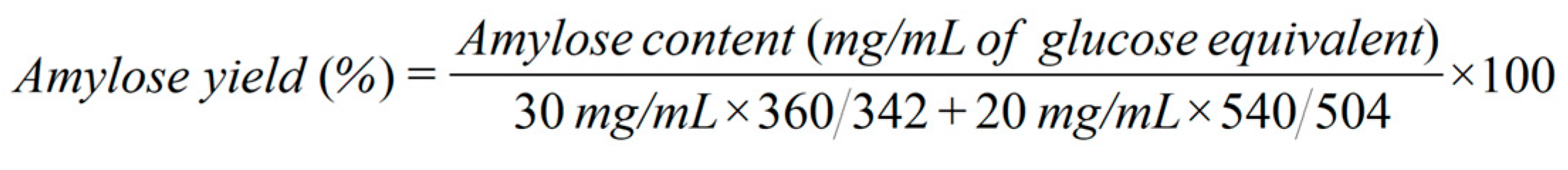1. Introduction
Cellobiose phosphorylase (CBP, EC 2.4.1.20) catalyzes the reversible phosphorolysis of cellobiose into α-glucose 1-phosphate (G-1-P) and glucose. CBPs identified so far are all from anaerobic bacteria, such as
Clostridium thermocellum [
1],
Cellvibrio gilvus [
2],
Fomes annosus [
3],
Clostridium stercorarium [
4],
Thermotoga neapolitana [
5],
Cellulomonas uda [
6],
Ruminococcus albus [
7], and so on. Since G-1-P produced through phosphorolysis pathway in vivo can be converted to G-6-P by a mutase and then enter the glycolytic pathway without activation by a kinase, CBPs confer host bacteria with more energy advantage in utilizing cellobiose compared to hydrolysis pathway by a β-glucosidase.
CBPs play important roles in lignocellulosic biomass biorefinery. CBP, along with a cellodextrin transporter, was employed to construct an engineered
Saccharomyces cerevisiae which could directly assimilate cellobiose to produce ethanol. Moreover, it was proved that the strains using cellobiose in the phosphorolytic pathway had higher biomass and ethanol yields compared to the strains using cellobiose in the hydrolytic pathway [
8]. Taking advantage of high energy product G-1-P generated by CBPs, we previously established an
in vitro enzymatic pathway transforming cellulose to amylose [
9]. In this one-pot transformation system, pretreated cellulose was first partially hydrolyzed to cellobiose by selected cellulases, and then cellobiose was catalyzed by CBP from
Clostridium thermocellum (CtCBP) to form G-1-P, which was then added to maltodextrin primers by potato alpha-glucan phosphorylase (PGP) to finally form amylose. This
in vitro starch synthesis process did not require any ATP or GTP consumption, therefore it is easy to be scaled up.
For the reason that CBP dominantly acts on cellobiose with little activity on cellodextrins with a degree of polymerization (DP) ≥3, the composition of cellulose hydrolysate in the above system needs to be optimized towards high content of cellobiose. Since only half of the glucose units in cellobiose were transformed into amylose, the theoretical conversion rate of cellulose to starch is only 50% given that cellulose is thoroughly degraded into cellobiose. Actually, a real partially-degraded cellulose hydrolysate contains not only cellobiose, but also other cellodextrins such as cellotriose. A modified CBP with broadened substrate specificity is more desirable for full use of cellodextrin components in the hydrolysate. Furthermore, the so-modified CBP could produce more G-1-P from cellotriose or cellotetraose than from cellobiose (2 molecules of G-1-P from cellotriose and 3 from cellotetraose), and thus increase the conversion rate of cellulose to starch. Assuming that cellulose can be degraded exactly into cellobiose and cellotriose with a mole ratio of 1:1, then the theoretical conversion rate of cellulose to starch would be raised to 60%. This theoretical calculation helps to illustrate the benefits of the modified CBP not only in the process of cellulose to starch but also in the construction of a yeast capable of producing ethanol from cellodextrin.
Based on this envisage, here we have identified a variant of CtCBP with a broadened substrate specificity, and its ability to convert cellodextrin into starch has been investigated.
2. Results
2.1. Modification of the Catalytic Loop of CtCBP
Considering cellodextrin phosphorylase (CDP) catalyzes the same reactions with CBP except that it acts on cellodextrins with DP ≥ 3, the structure of CDP is a good template for CBP’s substrate specificity modification. Both CDP and CBP belong to glycoside hydrolase family 94 and show high similarity in structure: both are homodimers with each subunit containing an N-terminal β-sandwich domain, a helical linker, an (α/α)
6-barrel catalytic domain, and a C-terminal jelly roll domain [10, 11]. O’Neill et al. [
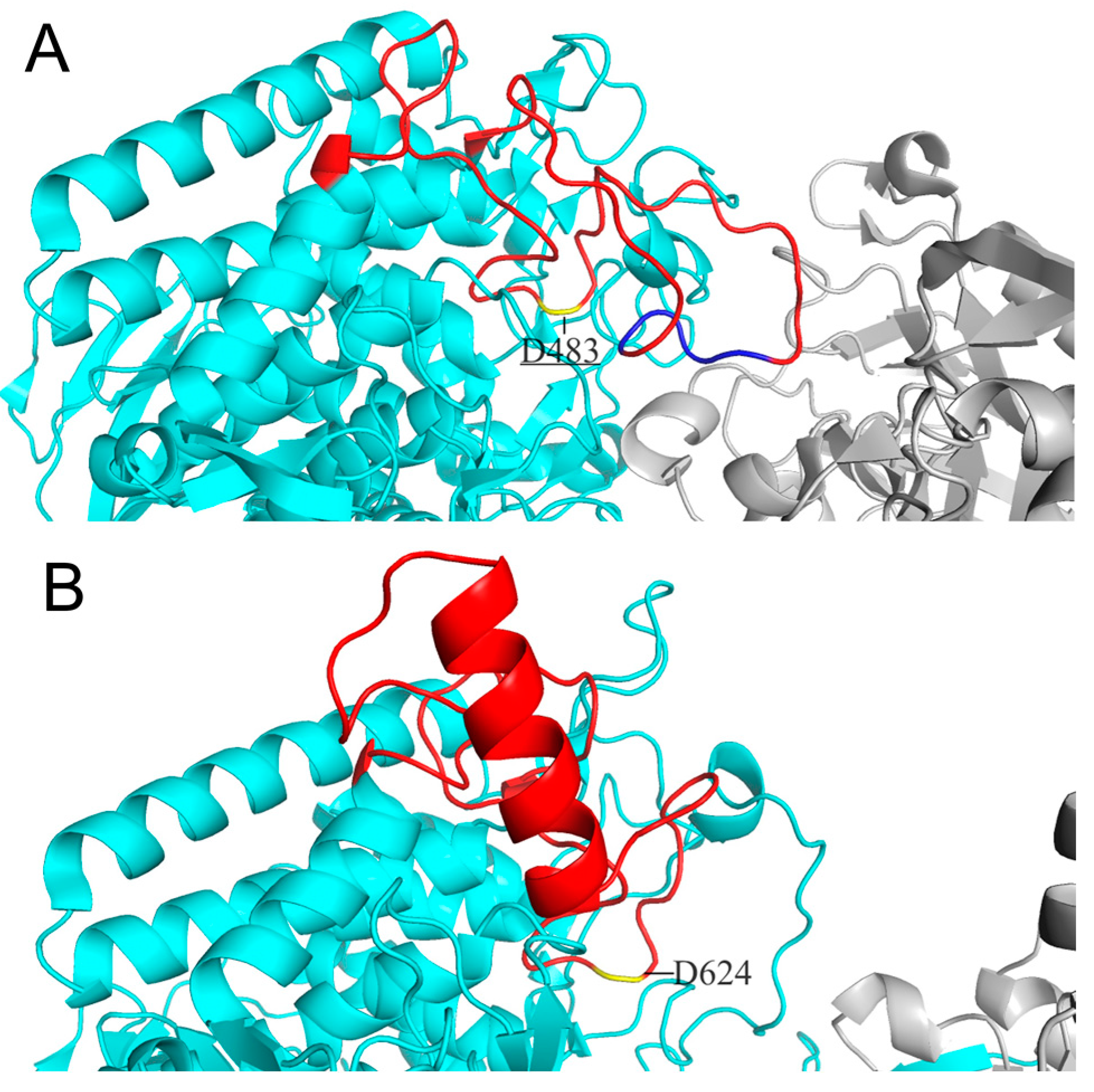
11] revealed the structure features accounting for CBP’s more enclosed active site compared to that of CDP. The difference in the catalytic loop of the two enzymes was proposed to be the main factor: the catalytic loop of CBP from
Cellovibrio gilvus (CgCBP) is fully ordered with the C-terminal portion folded over the active site pocket, while the catalytic loop of CDP from
Clostridium thermocellum (CtCDP) forms a helix after the catalytic Asp624, going away from the active site, thereby making a relatively open dimer interface. We have also aligned the structure of CtCBP and CtCDP and found the same differences in conformation of the catalytic loops as those found in CgCBP and CtCDP (
Figure 1). We then speculate that substitution of the catalytic loop of CtCDP for that of CtCBP may broaden the dimer interface of CtCBP and hence enable CtCBP to accept longer cellodextrins as substrates.
The modification of CtCBP started with replacing the whole portion of the catalytic loop of CtCBP (residue 465-510) with the whole portion of the catalytic loop of CtCDP (residue 606-663), generating the variant designated as CBP-Δ1. Unfortunately, CBP-Δ1 lost its natural CBP activity and meanwhile did not show any CDP activity, estimated by reversed synthetic reactions using xylose and cellobiose as glycosyl acceptor, respectively. To decrease the disturbance of catalytic loop substitution on CtCBP’s conformation, we narrowed step by step the portion of catalytic loop needed to be replaced in CtCBP, and generated 4 other variants as shown in
Table 1. It was found that CBP-Δ5 with only 4 residues replaced had a best improved activity on cellobiose with a 2-fold specific activity of that of wild type (WT), however, its natural CBP activity decreased to not more than 10% of that of wild type.
Since the catalytic loop substitution did not work as expected, we turned to modify the key portion of the catalytic loop of CtCBP. It was found that residues 496-499 (ESFQ) fell into the active site pocket and the side chains might hinder the access of the bigger substrates. Therefore, mutations were made on this portion in the hopes of eliminating its hindrance to the active site entrance. However, when all 4 residues were changed to glycine (named CBP-GGGG variant) or alanine (named CBP-AAAA variant), its activity on xylose was almost completely destroyed (
Table 2) indicating that residues 496-497 were essential to the activity. As E496 is a charged residue which may have interactions with the catalytic residue D483, we then started single-site mutations at S497 and fortunately found the mutant S497G which displayed a 1.3-fold higher activity on xylose and meanwhile a 2.3-fold higher activity on cellobiose compared to wild type, indicating a broadened substrate specificity without compromising its natural activity.
2.2. Catalytic Properties of CtCBP Variant S497G
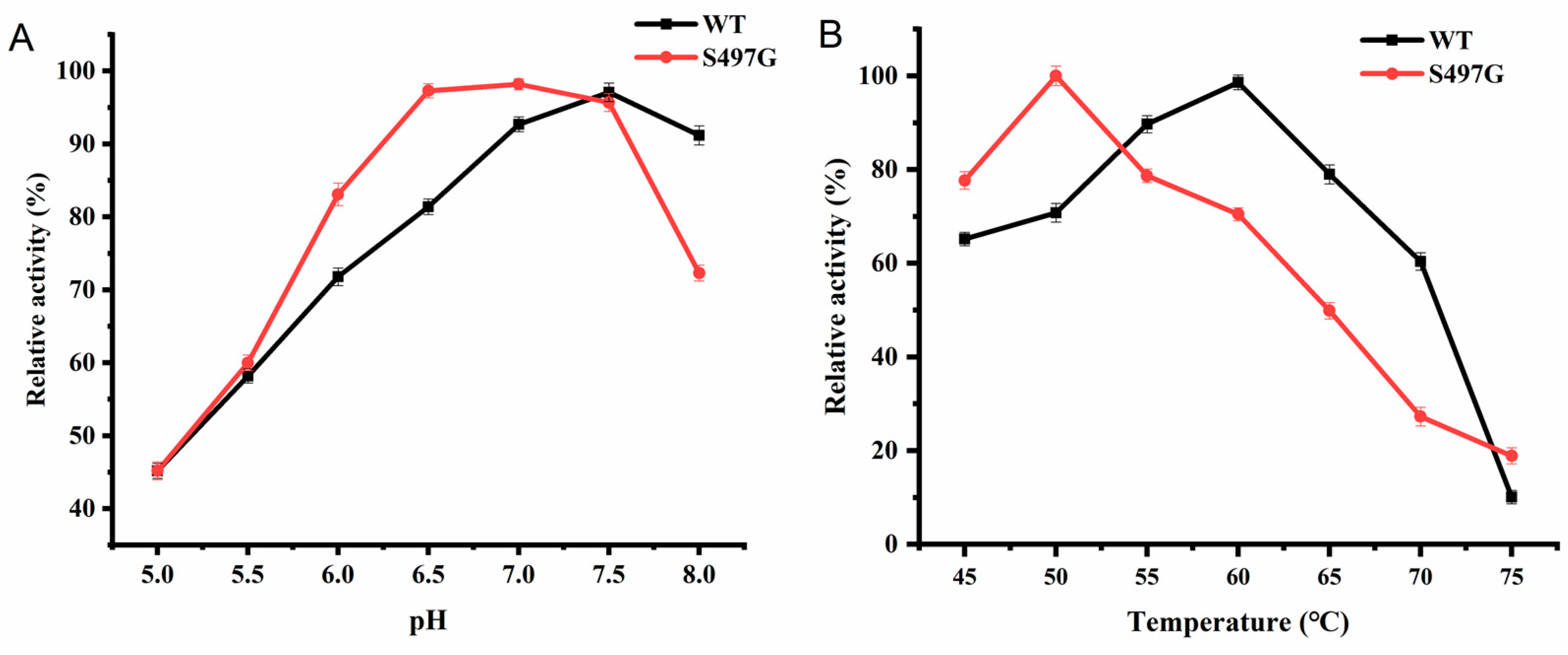
S497G variant showed an optimal pH of 7.0, slightly lower than that of wild type (pH 7.5), and the optimal temperature was found to be 50 ℃, lower than that of wild type (60 ℃) (
Figure 2). It is surprising that one site mutation markedly decreased the enzyme’s thermostability although the enzyme was stable under 50 ℃ with 80% of initial activity remained after 50-min incubation. From an application perspective, 50 ℃ could satisfy much of application scenarios CBPs involved. Therefore, the deceased optimal temperature may not affect S497G’s application.
Concerning the kinetic properties of S497G variant, the Michaelis-Menten constant (
Km) and turnover number (
kcat) were determined in both synthetic reaction and phosphorolytic reaction. In synthetic reaction, different concentrations of xylose or cellobiose were used as substrates. The results showed that S497G had a higher affinity and meanwhile a higher
kcat for both xylose and cellobiose compared to wild type, demonstrating its higher catalytic efficiency than wild type (
Table 3). In phosphorolytic reaction, when cellobiose was the substrate, S497G showed a slightly higher
kcat and catalytic efficiency compared to wild type, while when cellotriose was the substrate, S497G had a 2.3-fold higher
kcat and a 5.7-fold higher catalytic efficiency compared to wild type (
Table 4). These changes would enable variant S497G superior to wild type under the circumstances where cellodextrins of both cellobiose and cellotriose needed to be phosphorolyzed.
2.3. Transformation of Cellodextrin to Amylose
To test whether S497G could really show advantages in the transformation system of cellodextrin to amylose, a mixed cellodextrin (3% (w/v) cellobiose + 2% (w/v) cellotriose), simulating the composition of a partially-degraded cellulose hydrolysate, was used as the substrate, meanwhile a 5% (w/v)-cellobiose system was used as a reference. All reaction conditions were kept the same between the groups with S497G variant and the groups with wild type CtCBP. It could be seen that in cellobiose system S497G variant showed a slightly increased amylose yield (15.0% vs 13.5%) with a 11% increase in amylose yield compared to wild type, whereas in mixed cellodextrin system S497G variant produced a significant higher amylose yield (16.2% vs 11.7%), with a 38% increase compared to wild type (
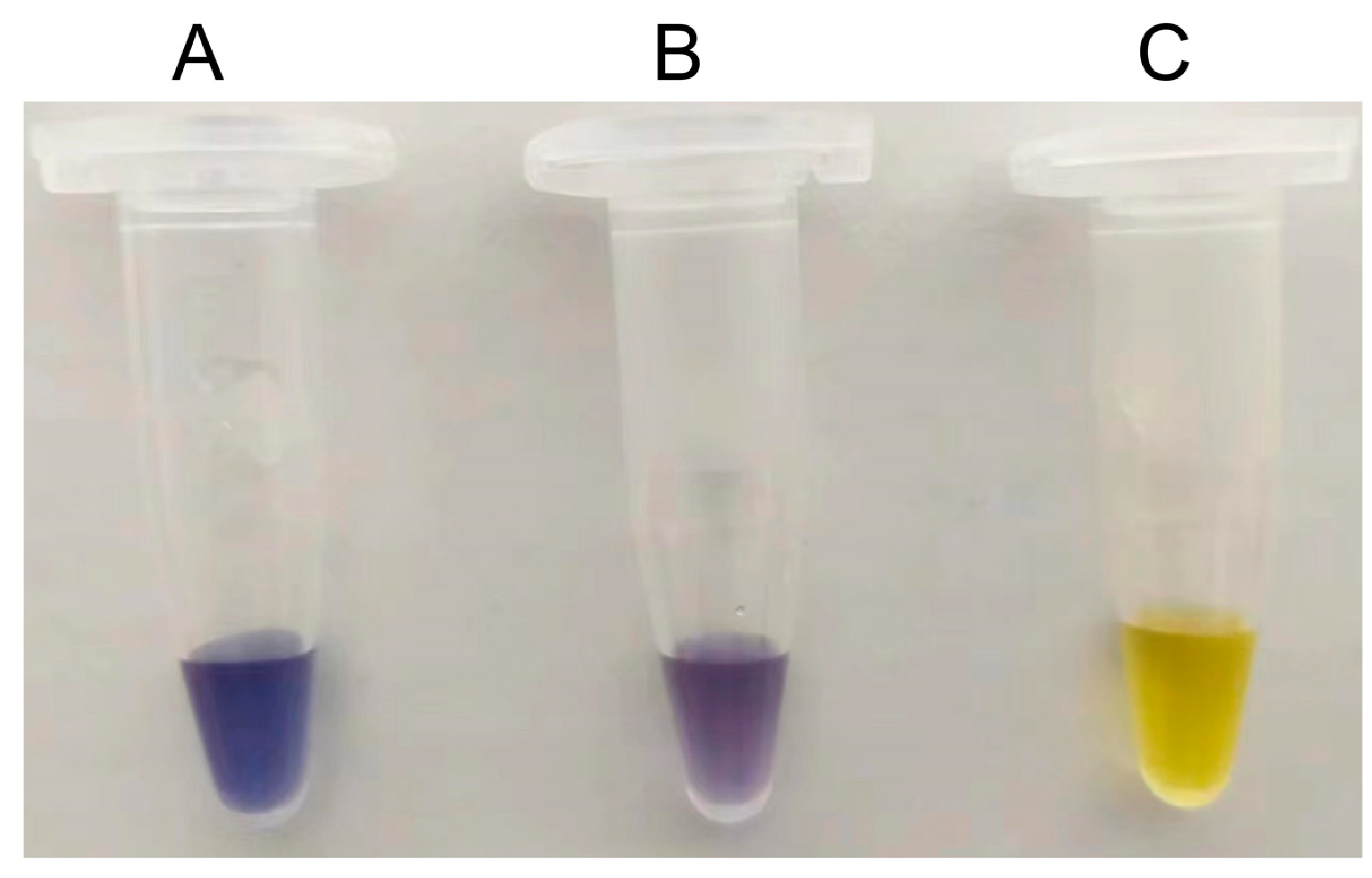
Table 5). The increase in amylose yield brought by S497G variant compared to wild type in mixed cellodextrin system could also be observed by a darker blue appeared when adding iodide solution to the reaction sample (
Figure 3). The difference of amylose yields between S497G variant and wild type is larger in mixed cellodextrin system than in cellobiose system, indicating that in mixed cellodextrin system S497G must have converted more cellotriose to amylose than wild type. The performance of S497G in the transformation system of cellodextrin to amylose confirmed that S497G possessed a broadened substrate specificity.
It is worth noting that wild type CtCBP in mixed cellodextrin system generated a lower amylose yield than in cellobiose system (11.7% vs 13.5%), which is reasonable due to a decreased concentration of CtCBP’s natural substrate cellobiose in mixed cellodextrin system. In contrast, S497G variant in mixed cellodextrin system generated a modest higher amylose yield than in cellobise system (16.2% vs 15.0%), demonstrating that the variant could use cellotriose as substrate, and moreover the advantage of cellotriose as substrate to synthesize amylose is displayed.
2.4. Structure Basis for Properties of S497G Variant
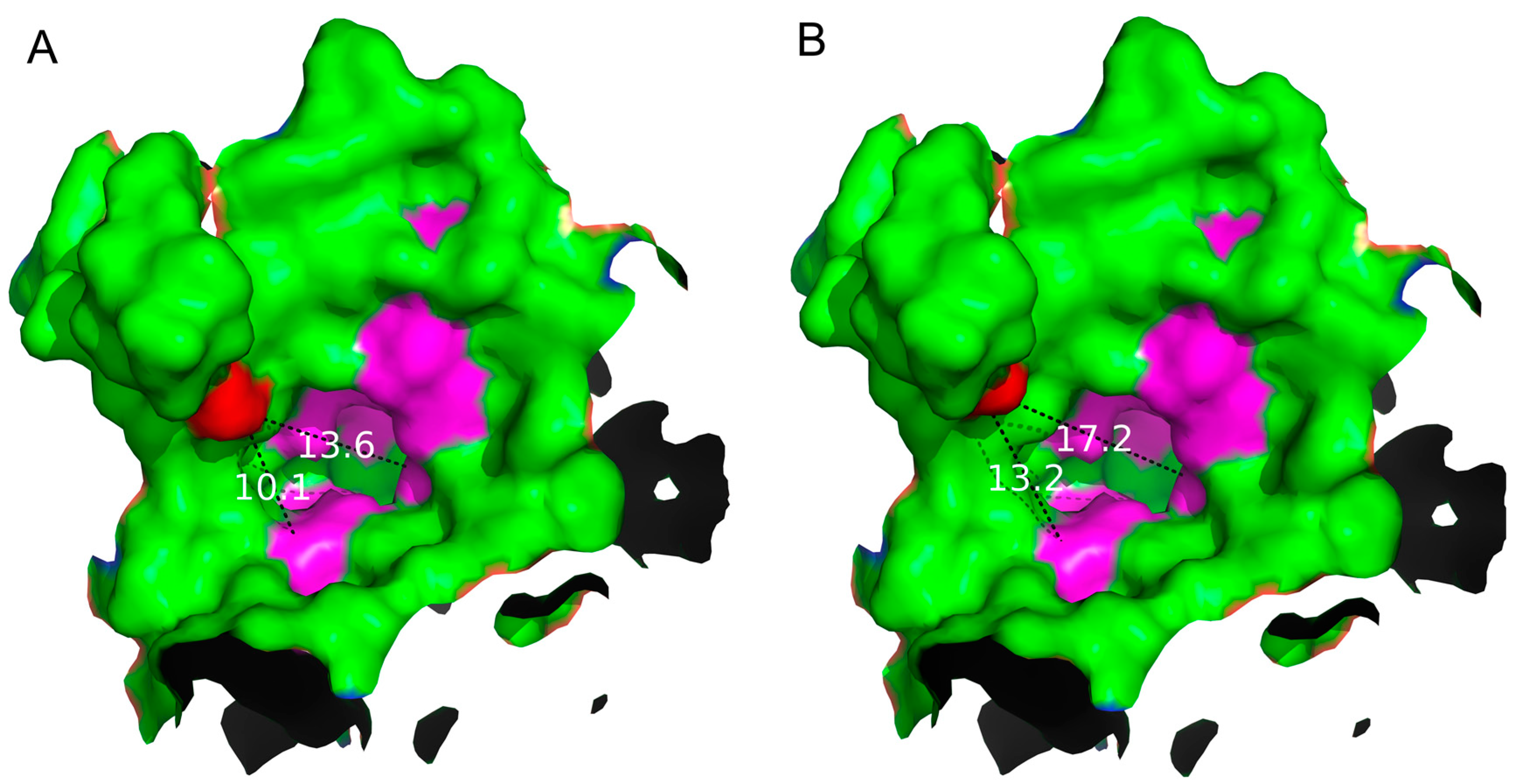
By analyzing the structure of S497G variant, especially the entrance shape and size, it can be seen that the entrance of the S497G variant was expanded compared to that of wild type CtCBP due to the mutation (
Figure 4). The entrance of the substrate binding pocket of the wild type enzyme had a diameter of 13.6 Å, while that of S497G variant was expended to 17.2 Å, thereby expanding the size of the entrance of the substrate-binding pocket, which might contribute to bulky substrate entry, resulting in the S497G variant having higher catalytic activity toward cellotriose.
Regarding protein’s stability, glycine substitution generally enhances conformational flexibility of the protein [
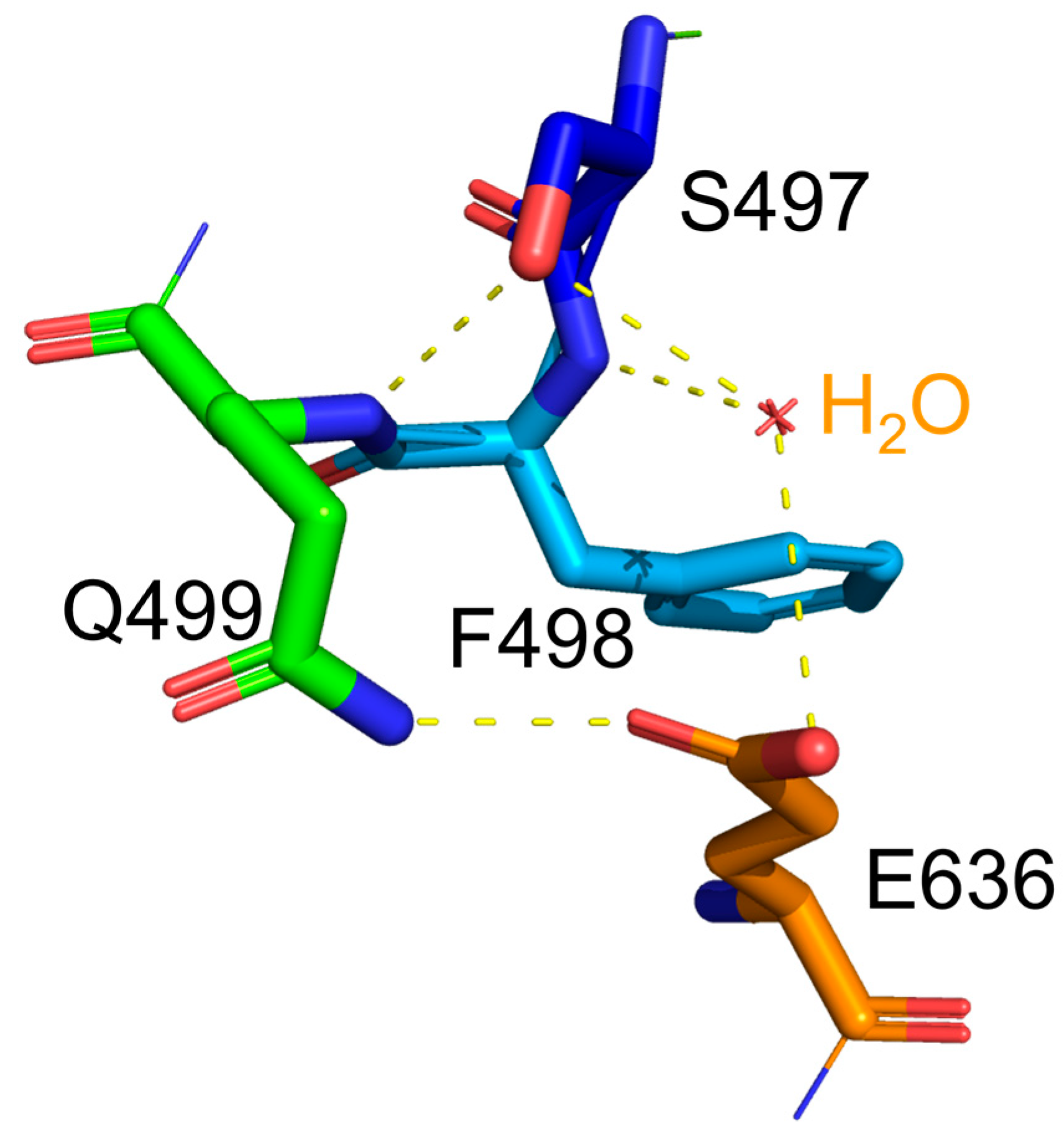
12], which corresponds to the lower stability of the protein. Indeed, S497G variant exhibited a lower thermostability in terms of its decreased optimal temperature (50 ℃). In S497G variant, the 3 hydrogen bonds occurring at the hydroxyl group of serine residue in wild type CtCBP (as shown in
Figure 5) did not exist, which could make its structure not as compact as that of the wild type. It turned out that the structure change caused by S497G mutation was favorable to bulky substrate entry, but not to enzyme stability.
3. Discussion
The phosphorolytic cleavage of cellobiose by CBP was needed in the process of constructing
S. cerevisiae with capacity to assimilate cellobiose as well as in the conversion of cellulose to starch. In these two applications, a CBP with ability to phosphorolyze cellodextrin with DP greater than 2 would be more desirable for higher efficiency of cellulose utilization. This work focused on the modification of CBP towards broadened substrate specificity. Another approach to solving the problem of longer cellodextrin’s utilization is to add enzyme CDP to the system besides CBP. It seems reasonable despite the extra cost caused by more enzymes used. However, Ha et al. [
8] demonstrated that when the engineered yeasts with a cellodextrin transporter as well as with CDP (from
C. lentocellum or
C. thermocellum or
A. cellulolyticus) grew on YP medium containing cellobiose, cellotriose or cellotetraose, only CDP from
C. lentocellum showed slight cell growth increase compared to the control, and the other two did not confer any growth increase on the host. Consequently, the authors chose to use CBP to construct the engineered yeast. Actually we also added CDP from
C. thermocellum (CtCDP) along with CtCBP when we were establishing the in vitro enzymatic pathway of cellulose to amylose, in the hopes of phosphorolyzing longer cellodextrins. But unexpectedly, the oligomer finally formed was the cellulose instead of the amylose, as long as CtCDP was added to the system. The reason should be that the relatively low concentration of longer cellodextrins is not enough to drive CtCDP’s phosphorolytic reaction, on the contrary, CtCDP easily takes newly generated G-1-P as a glycosyl donor to synthesize cellulosic oligomer which will become insoluble once DP reaches 9 [
13], and this insoluble product’s formation would further drive the proceeding of synthetic reaction catalyzed by CtCDP. Under these circumstances, broadening the substrate specificity of CBP would be an essential way to enhance cellodextrin’s conversion.
Regarding modification of CBP towards broadened substrate specificity, De Groeve et al [
14] created a variant OCP2 of
Cellulomonas uda CBP which showed activity towards various alkyl β-glucosides, methyl α-glucoside, and cellobiose, the activity beneficial to the synthesis of cellobiosides and other glycosides. Variant OCP2 carried 5 mutations at sites N156/N163/T508/E649/N667 involving residues at substrate binding pocket as well as residues on the route towards the active site entrance. With OCP2 as a starting template, Ubiparip et al. [
15] identified a new variant OCP2_M52R which further improved its activity towards cellobiose with a higher cellotriose yield compared to OCP2. Both of these variants were screened out in terms of their higher ability to use larger or anomerically substituted substrates in synthetic reaction. Their ability to use larger substrates in phosphorolytic reaction has not been evaluated. In present work, the significant difference between the catalytic loop of CtCBP and that of CtCDP drew our attention. Although replacing the catalytic loop of CtCBP with the corresponding fragment of CtCDP did not create desired variants, the residue S497 at the special portion of the catalytic loop was finally found to greatly influence CtCBP’s substrate specificity. The variant S497G was especially evaluated by its ability to use larger substrates in phosphorolytic reation and this improved ability has been validated in the conversion of mixed cellodextrin to amylose. It is notable that the residue S497 of CtCBP identified here to be related to the substrate specificity is not overlapped with those found in
C. uda CBP based on alignment between the two CBPs.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
Cellobiose, maltodextrin (DE 4.0-7.0), phosphoglucomutase (PGM), glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, USA). Cellotriose was purchased from Megazyme Company (Bray, Ireland). Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase and Dpn1 restriction enzyme were purchased from New England BioLabs (Beijing) LTD.
4.2. Mutagenesis of CtCBP
The cellobiose phosphorylase gene from
Clostridium thermocellum (
ctcbp, GenBank accession no. AAL67138.1) was originally obtained by PCR from
C. thermocellum ATCC 27405 genomic DNA [
9] and cloned to plasmid pET28a. The gene of cellodextrin phosphorylase from
C. thermocellum (CtCDP) (GenBank accession no: BAA22081.1) was used as the reference sequence.
For replacement of CtCBP catalytic loop, first, the plasmid pET28a-ctcbp was linearized by inverse PCR with removal of the fragment needed to be replaced; second, the fragment of CtCDP catalytic loop needed to be introduced was synthesized and flanked by the two 20-bp homologous sequences of 5′ end and 3′ end of the linearized plasmid; third, the above linearized plasmid and the fragment with homologous sequences were recombined using ClonExpress® II One Step Cloning Kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China) and then transformed into Escherichia coli competent cells for positive selection.
For site-directed mutation of CtCBP, inverse PCR was used to construct a mutant plasmid. All DNA synthesis and sequencing were performed by Genewiz Inc. (Suzhou, China).
4.3. Expression and Purification
Potato alpha-glucan phosphorylase gene from
Solanum tuberosum (
pgp, GenBank accession no. D00520.1) was codon-optimized for
E. coli and synthesized. The codon-optimized
pgp sequence was deposited in GenBank under the accession number MZ821655. Both
ctcbp and
pgp were expressed in
E. coli BL21(DE3) through plasmid pET28a with an N-terminal and a C-terminal 6×His tag. The recombinant CtCBP, PGP as well as CtCBP variants were purified by affinity chromatography using Ni-NTA resin as described in our previous work [
16]. The protein concentration was determined using Bradford method [
17] with bovine serum albumin as the standard.
4.4. Enzyme Assays
In synthetic reaction of CtCBP and its variants, the activity was assayed by measuring the amount of phosphate liberated from glycosyl donor G-1-P. For CBP activity, D-xylose was used as the glycosyl acceptor. A reaction mixture of 200 μL contained 50 μL appropriately diluted enzyme, 40 mM G-1-P, 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 10 mM D-xylose, and 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.5). The mixture was incubated for 20 min at 45 ℃ and then the reaction was terminated by the addition of 2 mL of the molybdate reagent containing 15 mM ammonium molybdate, 100 mM zinc acetate (pH 5.0), and 500 μL of ascorbic acid reagent (10% [w/v], pH 5.0) was then added to the mixture. This mixture was incubated at 30 ℃ for 15 min, and the absorbance was measured at 850 nm. For CDP activity, all assay procedures were the same as above except that 10 mM cellobiose was used as the glycosyl acceptor and the incubation time for reaction was 6 h.
In phosphorolytic reaction of CtCBP and its variants, the activity was assayed by measuring the formation of G-1-P from cellobiose for CBP activity or cellotriose for CDP activity [
18]. A reaction mixture containing 10 mM cellobiose or cellotriose, 5 mM MgCl
2, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 100 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.5), and appropriate enzyme was incubated for 15 min at 50 ℃. The reaction was stopped by boiling for 10 min, and the amount of G-1-P produced was determined by a coupled enzyme assay measuring the formation of NADPH at 340 nm. The reaction mixture for G-1-P measurement contained phosphoglucomutase (4.0 U/mL), glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (2.0 U/mL), and 3 mM NADP+ in 80 mM triethanolamine buffer (pH 7.5) containing 4.4 mM MgCl
2. The mixture was incubated at 30 ℃ for 10 min followed by spectrophotometric analysis at 340 nm.
4.5. Kinetic Analysis
For determining kinetic parameters in synthetic reaction, different concentrations of D-xylose or cellobiose (1 mM, 5 mM, 10 mM, 20 mM, 30 mM, and 40 mM) were used as substrates and the initial reaction rates at each concentration of substrate were determined under the aforementioned conditions, except that reaction was carried out at 50 ℃ for 10 min. For phosphorolytic reaction, different concentrations of cellobiose or cellotriose (0.5 mM, 1 mM, 2 mM, 4 mM, 5 mM, and 10 mM) were used as substrates and the initial reaction rates at each concentration of substrate were determined under the aforementioned conditions except that reaction time was 10 min. Km and kcat values were calculated based on Hannes-Woolf plots. Each value was an average of the data from three independent determinations.
4.6. Transformation of Cellodextrin to Amylose
In transformation of cellodextrin to amylose, two reaction systems were conducted: one was with 5% (w/v) cellobiose as the substrate and the other was with 5% (w/v) mixed cellodextrin (3% (w/v) cellobiose + 2% (w/v) cellotriose) as the substrate. In both systems, 500 µL of reaction mixture contained 50 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.5), 20 mM Na
2HPO
4, 75 µM maltodextrin, 30 µg/mL of CBP or S497G, and 30 µg/mL of PGP. The mixture was incubated at 45 ℃ for 16 h followed by 10-min water boiling to terminate reaction and denature enzymes. After centrifugation the supernatant was collected for measurement of amylose content. To qualitatively detect amylose, 100 μL of the supernatant was mixed with 10 μL of iodine/potassium iodide solution to observe the appearance of blue color. To determine the amylose yield, two volumes of 100% ethanol were added to the supernatant to precipitate amylose. Then the precipitated amylose was separated and re-dissolved with 400 μL of deionized water. The content of amylose was determined by phenol sulfuric acid method [
9] in terms of glucose equivalent content. The amylose yield was calculated based on equation (1) for the cellobiose system and equation (2) for the mixed cellodextrin system. All reactions were performed in triplicate.
4.7. Homology Modeling and Structure Comparison
CtCBP structure (PDB code 3qde) and CtCDP structure (PDB code 5NZ7) were extracted from the PDB database (
http://www. rcsb.org/). The structure of S497G variant was generated with wild-type CtCBP as a reference in PyMOL (
http://www.pymol.org). The substrate binding pockets of CtCBP and S497G variant were visualized using PyMOL v2.5. The size of the entrance of the substrate binding pocket (between site 497 and Gln699, site 497 and Arg355) was measured by PyMOL.
5. Conclusions
A CBP with broadened substrate specificity will be more desirable when used in transforming cellulose to amylose as well as in constructing a yeast with the ability to use cellodextrin to produce ethanol. In present work, we engineered CBP from C. thermocellum and identified a variant S497G which showed a 5.7-fold higher catalytic efficiency towards cellotriose in phosphorolytic reaction direction compared to wild type, without any loss of catalytic efficiency on its natural substrate cellobiose. When S497G variant was used in the transformation of mixed cellodextrin (cellobiose + cellotriose) to amylose, a significant increase in amylose yield was achieved confirming its promising feature favorable to those application scenarios involving cellodextrin’s phosphorolysis. Therefore, S497G variant is a useful catalyst for the conversion of lignocellulose biomass to value-added bioproducts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.C.; methodology, G.M. and X.L.; investigation, Y.Z., Y.L. and X.L.; formal analysis, H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.C. and Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, H.C. and Y.Z.; supervision, H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2022YFC3401700).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data produced in this study have been included in this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tanaka, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Imada, Y.; Ooi, T.; Arai, M. Purification and properties of cellobiose phosphorylase from Clostridium thermocellum. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1995, 79, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doudoroff, M. Disaccharide Phosphorylases. Enzymes 1955, 1, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Hüttermann, A.; Volger, C. Cellobiose phosphorylase in Fomes annosus. Nature: New Biol. 1973, 245, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichenbecher, M.; Lottspeich, F.; Bronnenmeier, K. Purification and properties of a cellobiose phosphorylase (CepA) and a cellodextrin phosphorylase (CepB) from the cellulolytic thermophile Clostridium stercorarium. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 247, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yernool, D.A.; Mccarthy, J.K.; Eveleigh, D.E.; Bok, J.D. Cloning and characterization of the glucooligosaccharide catabolic pathway beta-glucan glucohydrolase and cellobiose phosphorylase in the marine hyperthermophile Thermotoga neapolitana. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 5172–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nidetzky, B.; Eis, C.; Albert, M. Role of non-covalent enzyme-substrate interactions in the reaction catalysed by cellobiose phosphorylase from Cellulomonas uda. Biochem. J. 2000, 351, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamura, K.; Saburi, W.; Abe, S.; Morimoto, N.; Taguchi, H.; Mori, H.; Matsui, H. Enzymatic Characteristics of Cellobiose Phosphorylase from Ruminococcus albus NE1 and Kinetic Mechanism of Unusual Substrate Inhibition in Reverse Phosphorolysis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 76, 812–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.J.; Galazka, J.M.; Oh, E.J.; Kordić, V.; Kim, H.; Jin, Y.S.; Cate, J.H.D. Energetic benefits and rapid cellobiose fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing cellobiose phosphorylase and mutant cellodextrin transporters. Metab. Eng. 2013, 15, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, C.; Chen, H.G.; Myung, S.; Sathitsuksanoh, N.; Ma, H.; Zhang, X.Z.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.-H.P. Enzymatic transformation of nonfood biomass to starch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7182–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchetti, C.M.; Elsen, N.L.; Fox, B.G.; Phillips, G.N. Jr. Structure of cellobiose phosphorylase from Clostridium thermocellum in complex with phosphate. Acta Crystallogr. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2011, 67, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Neill, E.C.; Pergolizzi, G.; Stevenson, C.E.M.; Lawson, D.M.; Nepogodiev, S.A.; Field, R.A. Cellodextrin phosphorylase from Ruminiclostridium thermocellum: X-ray crystal structure and substrate specificity analysis. Carbohydr. Res. 2017, 451, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, A.; Watanabe, G.; Oshikawa, M.; Ajioka, I.; Muraoka, T. Glycine Substitution Effects on the Supramolecular Morphology and Rigidity of Cell-Adhesive Amphiphilic Peptides. Chemistry 2019, 25, 13523–13530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraishi, M.; Igarashi, K.; Kimura, S.; Wada, M.; Kitaoka, M.; Samejima, M. Synthesis of highly ordered cellulose II in vitro using cellodextrin phosphorylase. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 2468–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groeve, M.R.M.; Remmery, L.; Van Hoorebeke, A.; Stout, J.; Desmet, T.; Savvides, S.N.; Soetaert, W. Construction of cellobiose phosphorylase variants with broadened acceptor specificity towards anomerically substituted glucosides. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 107, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubiparip, Z.; Moreno, D.S.; Beerens, K.; Desmet, T. Engineering of cellobiose phosphorylase for the defined synthesis of cellotriose. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 8327–8337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; Hou, H.W.; Li, Y.P.; Yang, S.; Lin, H.; Chen, H.G. Fusion of cellobiose phosphorylase and potato alpha-glucan phosphorylase facilitates substrate channeling for enzymatic conversion of cellobiose to starch. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 52, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Mao, G.T.; Fan, H.Y.; Song, A.D.; Zhang, Y.-H.P.; Chen, H.G. Biochemical properties of GH94 cellodextrin phosphorylase THA_1941 from a thermophilic eubacterium Thermosipho africanus TCF52B with cellobiose phosphorylase activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).