1. Introduction
With the rapid development of industry, heavy metal pollution caused by mining, waste incineration, heavy use of pesticides and fertilizers has become increasingly serious [
1]. Cadmium is a type of harmful and non-essential toxic heavy metal for plants, and once absorbed, it inhibits plant growth and development, resulting in slower root development, curled or chlorotic and etiolated leaves, and in severe cases, plant death [
2,
3]. Cadmium inhibits plant growth by affecting physiological processes such as photosynthesis, oxidative damage and mineral nutrition, resulting in growth retardation, leaf yellowing and biomass reduction. Some studies have shown that the chloroplast granule and thylakoid lamellar structure of wheat were disrupted under cadmium stress, and the efficiency of light capture and photosynthetic electron transport were significantly reduced [
4,
5]. Many studies have reported that active oxygen species and membrane peroxidation of rapeseed and Arabidopsis thaliana increased under cadmium stress [
6,
7]. At the same time, cadmium stress can inhibit the absorption, transport and distribution of many mineral elements in plants [
8,
9]. Studies in barley, tomato and other plants have shown that cadmium stress significantly inhibits the uptake of K, Mg, Fe, Ca, Zn and Mn, resulting in stagnation of plant growth [
10,
11]. In addition, cadmium not only affects plant growth and development, but also has a negative impact on human health when it accumulates in plants and enters the food chain. Therefore, agricultural and environmental researchers have focused on finding a method that can effectively mitigate cadmium stress on crops.
In recent years, the exogenous application of plant growth regulators has become an important way of reducing cadmium damage to plants and even reducing cadmium uptake. It has been reported that external foliar application of fulvic acid can reduce cadmium toxicity in lettuce [
12] and ascorbic acid can reduce cadmium toxicity and absorption in maize [
13]. During plant growth, tolerance to abiotic stress increased after selenium application [
14,
15]. Studies have shown that selenium can counteract and reverse the harmful effects of cadmium on plants, improve plant photosynthesis, regulate the balance of plant mineral elements, reduce cadmium levels in plants and increase plant antioxidant capacity to alleviate cadmium stress in plants. FILEK et al. found that cadmium stress caused chloroplast membrane degradation in rapeseed, whereas exogenous selenium application resulted in ultrastructural reconstruction of the chloroplast, recombination of thylakoid and stromal lamellar structure, increased fatty acid unsaturation of chloroplast size and fluidity of the plasma membrane [
16]. Zhang et al. found that surface application of selenium increased photosystem II and electron transfer rate of Brassica napus leaves under cadmium stress, while root application of selenium increased photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, transpiration rate and stomatal threshold under cadmium stress [
17]. The study on the effect of selenium on the absorption of mineral nutrients under cadmium stress showed that with the increase of cadmium concentration, the absorption of trace elements in plants was unbalanced, while the low concentration of selenium increased the content of Ca, Cu in the stem and Fe, Cu and Zn in the leaves, which effectively alleviated the toxic effect of cadmium and restored the normal growth of plants [
18].Selenium can enhance the capacity of plant antioxidant defense system, reduce membrane lipid peroxidation and increase resistance to oxidative stress by scavenging intracellular free radicals, increasing antioxidant oxidase activity and non-enzymatic antioxidant content [
19]. Research has shown that selenium can reduce the level of cadmium in the cell by increasing the retention of cadmium in the cell wall, and selenium can increase the synthesis of pectin, cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in the cell wall of plant roots to trap more cadmium in the cell wall to reduce cadmium stress [
20].
Cabbage (
Brassica oleracea L. var.
capitata), is an annual or biennial herb of the Brassica genus in the cruciferous family, originating from the Mediterranean region, with high adaptability, easy storage and transport resistance, and high yield and occupies a very important position in the national annual vegetable supply and export trade. As a cruciferous plant, cabbage usually has a strong ability to absorb and accumulate heavy metals [
21], and the increased cadmium content in the soil and farmland led to a significant reduction in yield and quality. Therefore, it is a matter of concern to reduce the accumulation of cadmium in cabbage. This study aimed to investigate the protective mechanism of exogenous selenium on cadmium stress in cabbage seedlings, that is, exogenous selenium may improve the growth, photosynthesis and gas exchange ability of cabbage to protect the chloroplast ultrastructure of leaves, prevent oxidative damage by enhancing antioxidant activity, and mediate the absorption and transport of cadmium to enhance the tolerance of plants to cadmium. This study provides new insights into the potential physiological mechanism of exogenous selenium application in alleviating cadmium stress in cabbage seedlings, and certain indications for promoting yield and resistance to cadmium stress in cabbage seedlings.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Handling
The cabbage variety ‘Fuer’ was provided by the College of Horticulture, Northwest A&F University. Seeds were soaked in 5% sodium hypochlorite for 5 min, rinsed twice with distilled water and then germinated for 24 hours in the dark at 25°C.
Seedlings were transplanted into a cavity dish with a soil: vermiculite ratio of 3:1 and grown in an incubator at 25/20°C(day/night), with a 14h/10h(day/night) photoperiod, 150μmol·m-2·s-1 light intensity and 70-80% relative humidity. Seedlings were transplanted into plastic POTS (25 cm × 20 cm × 10 cm; six plants per pot). To ensure normal growth of the cabbage, the cadmium and selenium concentration tests were carried out after 2 days of slow germination in Hogland’s nutrient solution, and the nutrient solution was renewed every 5 days.
The experiment was a completely randomized block design with four treatments: T1: Hoagland solution; T2: Hoagland solution +10μMol/L selenium; T3: Hoagland’s solution+25μMol/L cadmium; T4: Hoagland solution +25μMol/L cadmium+10μMol/L selenium, where the concentration of cadmium (25μMol/L) was chosen according to the previous study. After 14 days of cadmium stress, samples were collected and immediately cryopreserved in -80 °C liquid nitrogen for further analysis.
2.2. Measurement of Growth Parameters
Fresh and dry weight of cabbage leaves and roots, stem diameter, plant height and root length were measured after 10 days of cadmium treatment. Stem diameter, plant height and root length of cabbage were measured with calipers. Fresh weight was determined after washing the seedlings in distilled water, and dry weight was determined by drying the plants to constant weight at 65 °C.
2.3. Determination of Root Activity
Root activity determination was performed according to the method described by Luo et al. [
24]. Briefly, 0.5 g of root sample and 5 mL of phosphate buffer (60 mM, pH 7.0) were added to the tube and reacted at 37°C for 2.5 h, then 2 mL of 1M sulfuric acid was added to the tube to stop the chemical reaction. Grind the roots in 3-4 mL of ethyl acetate with a mortar and pestle, transfer the red grinding liquid to the test tube, make up to 10 mL with ethyl acetate and record the absorbance at 485 nm.
2.4. Determination of Chlorophyll Content
The leaf sample (0.5 g) was placed in 10 mL of 95% ethanol at room temperature, extracted in the dark for 24 h and the supernatant centrifuged at 5000× g for 10 min. Absorbance values were measured with a spectrophotometer at 649 nm and 665 nm to calculate the contents according to the method of Wintermans and De-Mots [
25].
2.5. Determination and Analysis of Leaf Stomata Parameters
Three cabbage seedlings were randomly selected for each treatment, and the stomatal exchange parameters of the fourth fully expanded leaf were determined from 9:00 to 10:00 using the Plant Photosynthesis Analyzer 6800 (LI-6800, LI-COR Corporation of the United States). The parameters were set as follows: photosynthetic photon density (PPFD) 1000 μmol m-2 s-1, leaf temperature (25°C), CO2 concentration (400 μmol CO2 mol-1).
2.6. Determination and Analysis of Leaf Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters
We randomly selected three cabbage seedlings from each treatment and measured the relevant parameters of the fourth fully unfolded leaf using a portable modulated chlorophyll fluorescence analyzer (PAM2500, WALZ, Germany), including maximum photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm), actual photochemical efficiency Y(II), non-photochemical quenching (NPQ) and the quantum yield for the regulation of energy dissipation in photochemical quenching (qP).
2.7. Determination of Selenium and Cadmium Contents
The root and leaf tissues were dried at 65°C until the sample reached constant weight, then the dried plant samples (0.5 g) were ground to powder, mixed with nitric acid/perchloric acid (4:1, v/v) and boiled at 220°C until clear and used for constant volume determination. The cadmium content was determined by flame atomic absorption spectrophotometer and the selenium content by liquid phase atomic fluorescence photometer.
2.8. Chloroplast Ultrastructure Analysis
The fourth fully expanded leaf (approximately 1 mm
2) of cabbage from each treatment was fixed in 2.5% (v/v) glutaraldehyde (0.1M phosphate buffer, pH 7.2) overnight, soaked in 1% (v/v) osmic acid and washed with 0. 1M PBS (pH 7.4) after 1-2 h. Then the sample was dehydrated in 30%-50%-70%-80%-95%-100% alcohol sequentially, dehydrated in 100% ethanol for 15 min 3 times and immersed in Epon-812 epoxy resin at 60°C overnight. Finally, the samples were semi-sectioned, stained, rinsed with dye solution, fixed in copper mesh, scanned by transmission electron microscopy, and photographed for observation [
26].
2.9. Determination and Analysis of Relative Water Content
The fourth fully unfolded leaf of the seedling under each treatment was selected to determine the electrical conductivity and the specific measurement method was taken from Bajji. [
27].
2.10. Pro Content Determination and Analysis
0.5 g of cabbage leaves were weighed and pulverized with liquid nitrogen, 7.5 mL of 3% sulfosalicylic acid was added to regrind completely and then centrifuged at 4°C for 20 min (11000×g). 2 mL of the supernatant was removed and mixed by adding 2 mL of ninhydrin and 2 mL of 3.5% acetic acid, and the mixed solution was boiled at 100°C for 1 h. After cooling, 4 mL of toluene was added to the reaction mixture, and the absorbance value was measured at 520 nm [
28].
2.11. MDA Content Determination and Analysis
Weigh 0.5 g of cabbage leaves, add 5 mL of 0.1 % trichloroacetic acid (TCA), crush completely in a pre-cooled mortar and centrifuge at 4000 × g for 15 min at 4 °C. The supernatant is the liquid to be measured. The supernatant was the liquid to be determined. 1 mL of the supernatant was absorbed and 4 mL of a 20 % TCA mixture containing 0.65 % (w/v) TBA was added. The mixture was reacted in boiling water for 15 min, immediately cooled and centrifuged again to determine light absorption at 450, 532 and 660 nm.
2.12. Analysis of O2− and H2O2 Contents
Tissue from 0.5 g of fresh leaves was taken and 5 mL of 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.8) was added. Take 0.5 g of fresh leaf tissue, ground with 5mL of 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.8), and the mixture centrifuged at 10,000×g for 20 min. The O2- content was measured in the supernatant and calculated from the standard curve based on sodium nitrite, expressed as μmol·g−1·min−1 FW. To determine H2O2 content, 0.5 g of fresh leaf tissue was ground in an ice bath with 5 mL 100% cold water acetone, centrifuged at 10,000×g 4°C for 20 min and the supernatant was collected immediately for H2O2 analysis. The concentration of H2O2 was measured according to the standard curve and expressed as μmol·g−1 FW.
2.13. H2O2 and O2- Histochemical Staining
The nitrogen blue tetrazole (NBT) method was used for O2- staining analysis of cabbage leaves: The leaves were soaked in 0.5 mg·mL-1 NBT solution (pH 7.8) in the dark for 1 h, then removed, rinsed 3 times with distilled water and then heated with 95% ethanol for 10 min for decolorizations. The blue spots on the leaves indicated the production of O2-. The 3, 3-diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining method was used to stain the tissue of cabbage leaves for H2O2: The leaves were soaked in 1 mg·mL-1 DAB solution (pH 7.8) at 25 °C for 5 h, then decolored with 95% (v/v) ethanol every 20 min at 80 °C until the green background was completely removed from the leaves. Red-brown spots on the leaves indicate H2O2 production.
2.14. Determination and Analysis of GSH
The level of GSH was determined using the Solarbio BC1175 kit for the content of reduced glutathione.
2.15. APX Determination and Analysis
The determination was carried out by means of the Solarbio BCO220 Ascorbate Peroxidase Kit.
2.16. Antioxidant Enzyme System Determination and Analysis
The 0.5 g leaf sample was weighed and ground to a homogenate with 3 mL of phosphate buffer consisting of 0.2 mM EDTA and 2% (w/v) PVP. The homogenate was centrifuged at 4°C for 20 min at 13,000×g, and the supernatant was the enzyme liquid to be measured, which was used for the determination of SOD and POD enzyme activities. APX assay: 3 mL of the reaction mixture contained 50 mM PBS (pH 7.0), 9 mM ASA, 12.5 mM H2O2, and 100μL of enzyme solution, and the enzyme activity was calculated based on the change in absorbance at 290 nm every 1 min.
2.17. Statistical Analysis
All data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan multiple range tests. P value < 0.05 was considered significant. Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) of at least three independent experiments with three replicates for each treatment (P ≤ 0.05).
4. Discussion
Heavy metal contamination of soil is a global problem and poses a serious threat to public health [
27,
28,
29]. Cadmium is highly toxic to plants [
30], and the accumulation of cadmium in edible parts of crops is one of the main threats to human health. Reducing the damage of abiotic stress to plants by applying exogenous substances has gradually become the focus of research [
31]. As one of the essential elements for animals and humans, selenium has been proven to reduce the toxicity of cadmium, lead Pb and arsenic As to plants [
32,
33,
34]. Therefore, the application of exogenous selenium to alleviate cadmium stress in cabbage seedlings is of great significance for agricultural production.
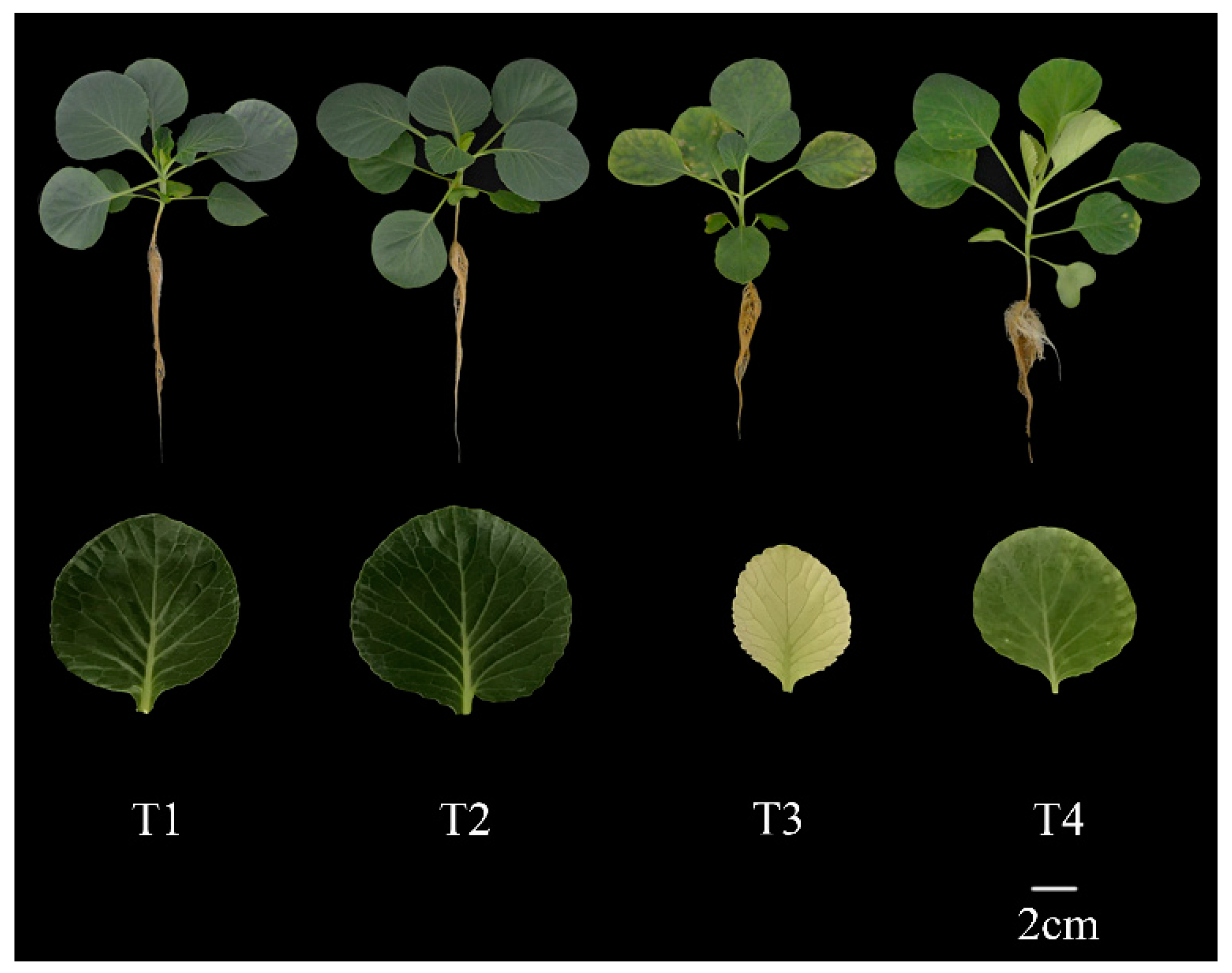
In this study, we analyzed the physiological and biochemical parameters of cabbage seedlings regulated by exogenous selenium application under cadmium stress. Under cadmium stress, cabbage plants showed obvious symptoms such as leaf rolling, yellowing, inhibition of root elongation and reduction of biomass (
Figure 1), which was consistent with studies in Brassica napus, mustard, tomato and cucumber [
35,
36,
37,
38]. On the contrary, exogenous application of selenium could alleviate these phenomena, and exogenous application of selenium promoted the growth of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress, which was reflected in the increase of plant height, stem diameter and biomass (
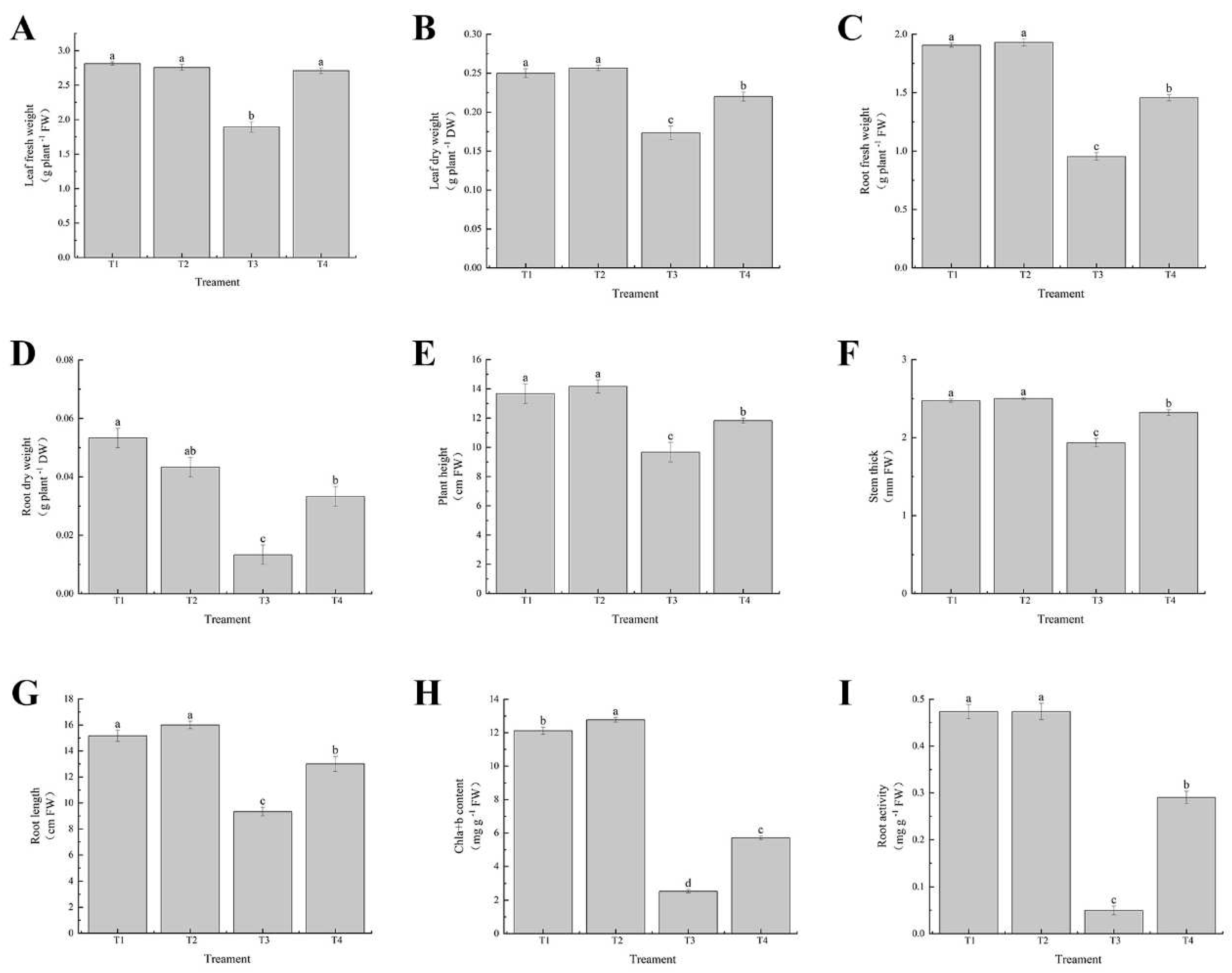
Figure 2A-G). This was consistent with the research results of Filek M and Qi W. [
39,
40], which indicated that selenium could reduce the growth inhibition of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress(
Figure 2I). The root activity may reflect the growth status of plants, and the activities of roots treated with cadmium alone were significantly reduced, while they were apparently restored after exogenous application of Se, which was consistent with the results of Jiang J ‘s study [
41]. These results indicated that selenium could enhance root vitality by improving the efficiency of root water and nutrient uptake to promote plant growth under cadmium stress.
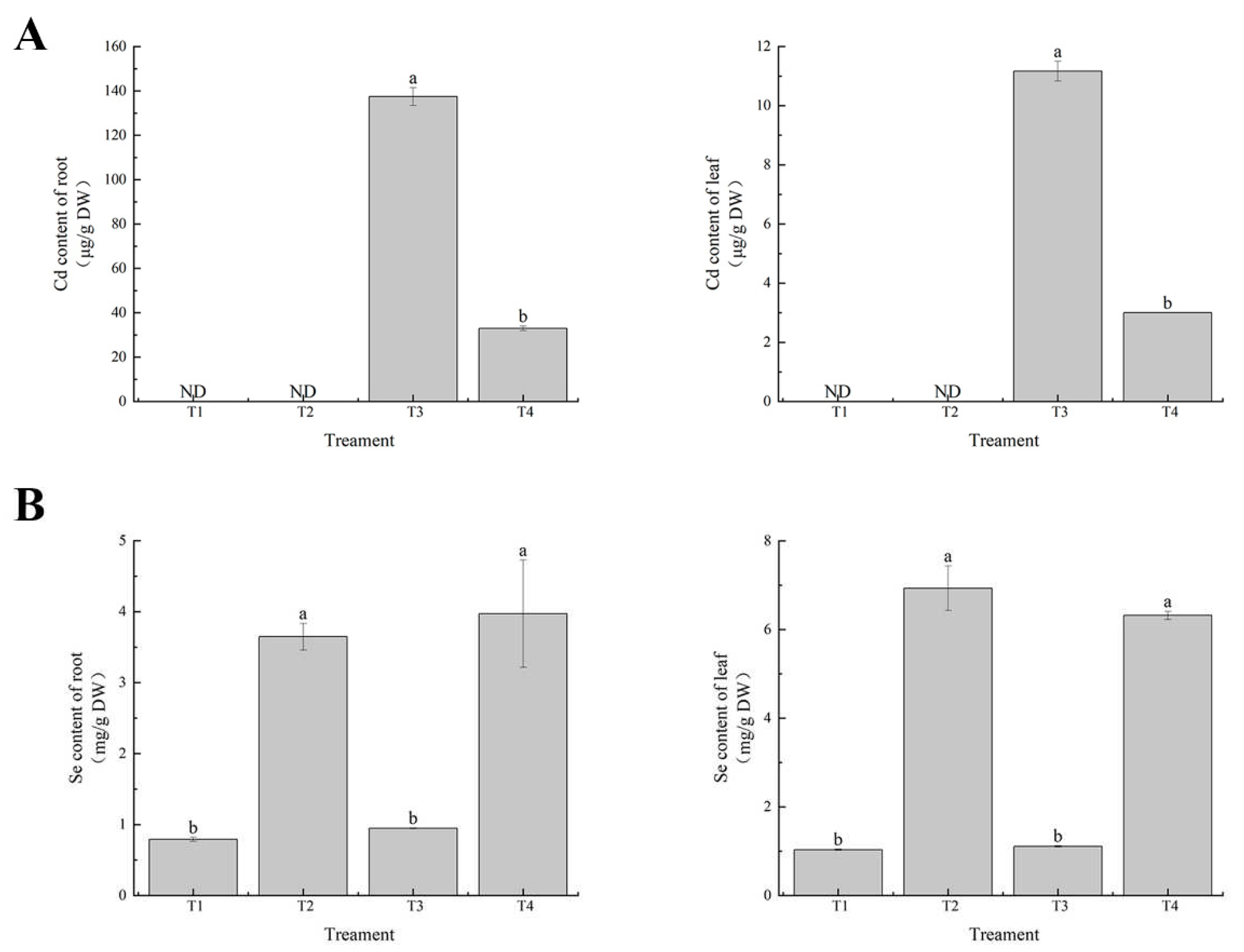
Our research showed that the cadmium content in leaves and roots of cabbage seedlings was significantly increased under cadmium stress, and was higher in roots than in leaves (
Figure 5A), indicating that cadmium is trapped in the roots and a small amount is subsequently transported to the leaves. The results are consistent with those of previous studies that cadmium accumulates more in roots than in leaves. However, the cadmium content in leaves and roots was reduced after exogenous selenium application, which is similar to the results of the study by Li L et al. in mustard. In conclusion, exogenous selenium application has a positive effect on reducing cadmium content in cabbage seedlings, and the difference in the positive effect of selenium on different plant parts may be related to the accumulation of cadmium in the upper part of the plant.
Cadmium stress can lead to a decrease in photosynthetic pigment content in plants, which has been reported in cabbage, broccoli, pepper and other plants [
41,
42,
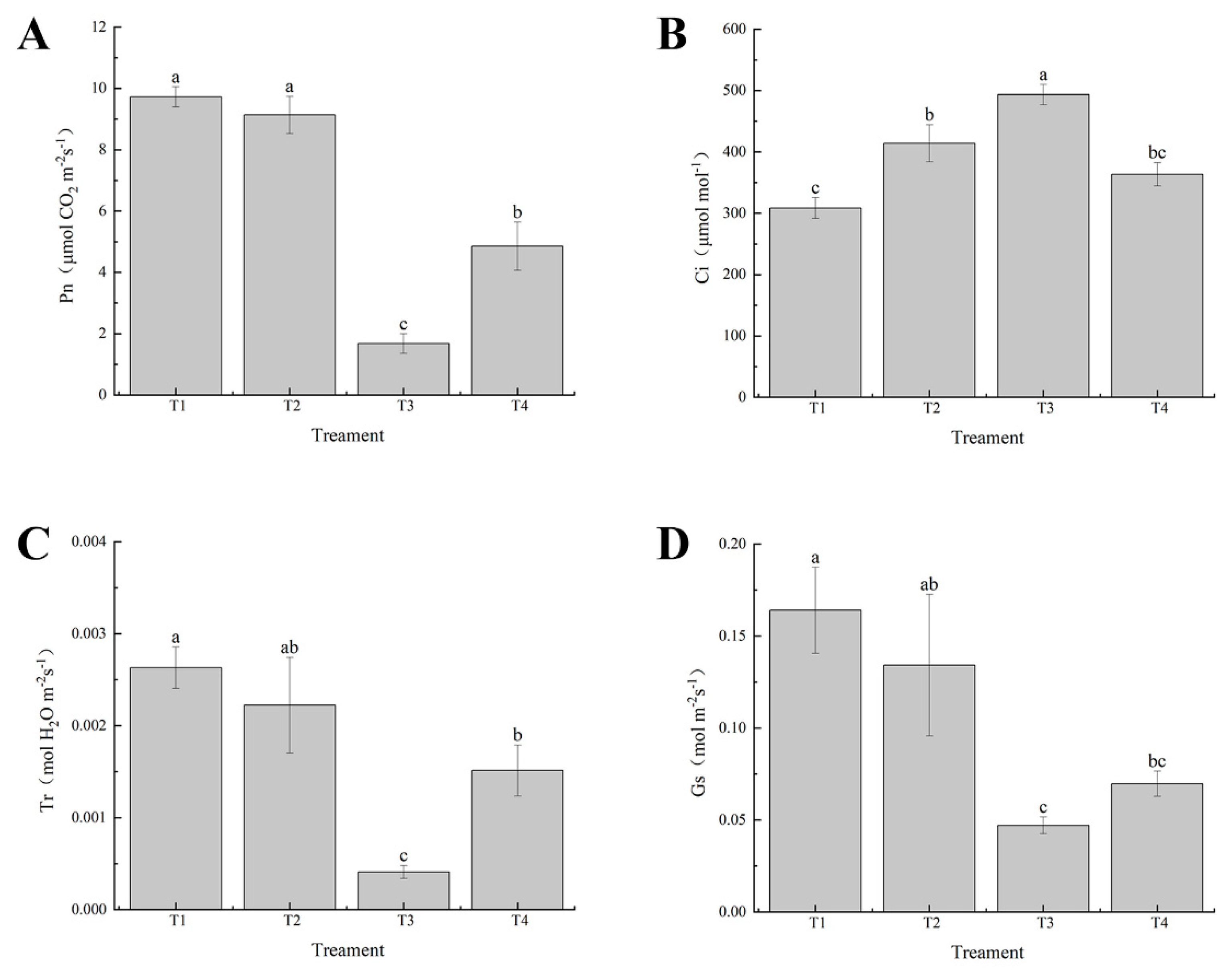
43]. Our results showed that cadmium treatment alone resulted in a significant decrease in total chlorophyll content, and at the same time, cadmium stress also significantly decreased gas exchange characteristics such as Pn, Gs and Tr and increased Ci (
Figure 3A,
Figure 3D,
Figure 3C,
Figure 3B). We speculated that cadmium stress led to stomatal closure, reduced mesophyll conductance and CO
2 fixation, and ultimately photoinhibition. selenium can promote growth and development of plants under various abiotic stresses. In this study, exogenous selenium application effectively alleviated the cadmium induced decrease in chlorophyll content and photosynthetic characteristics, which was consistent with previous studies [
44].
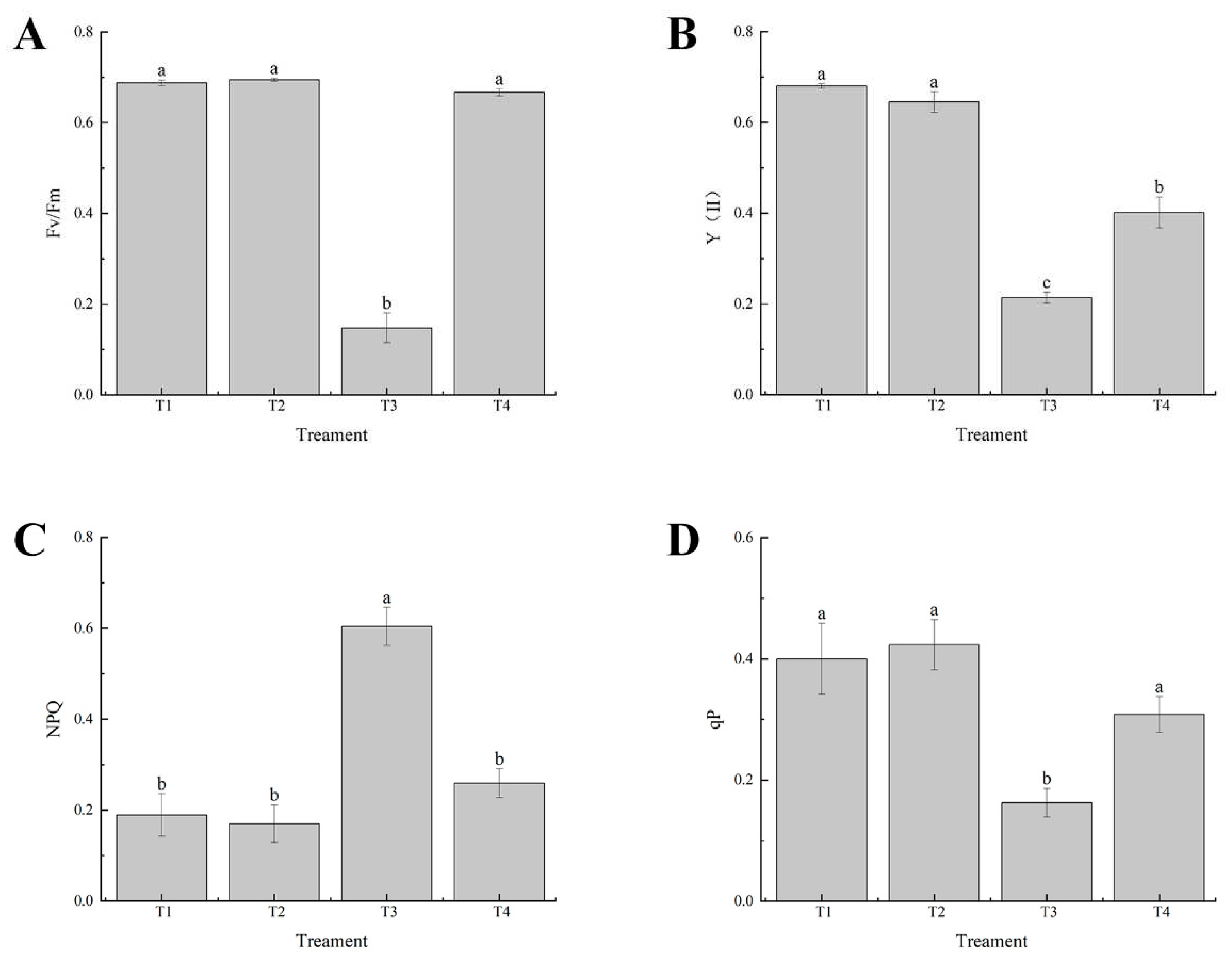
Chlorophyll fluorescence can reflect the photosynthetic efficiency and photosynthetic inhibition of plants under heavy metal stress. In this study [
45], cadmium treatment significantly reduced Fv/Fm, Y(II) and qP parameters, but increased NPQ value (
Figure 4A-D), indicating that PSII under cadmium stress had an imbalance between light energy absorption and photosynthetic electron transfer [
46,
47]. However, exogenous selenium can significantly increase chlorophyll content and photosynthetic capacity and reduce cadmium stress-induced photoinhibition by increasing Fv/Fm, Y(II) and qP [
48,
49].
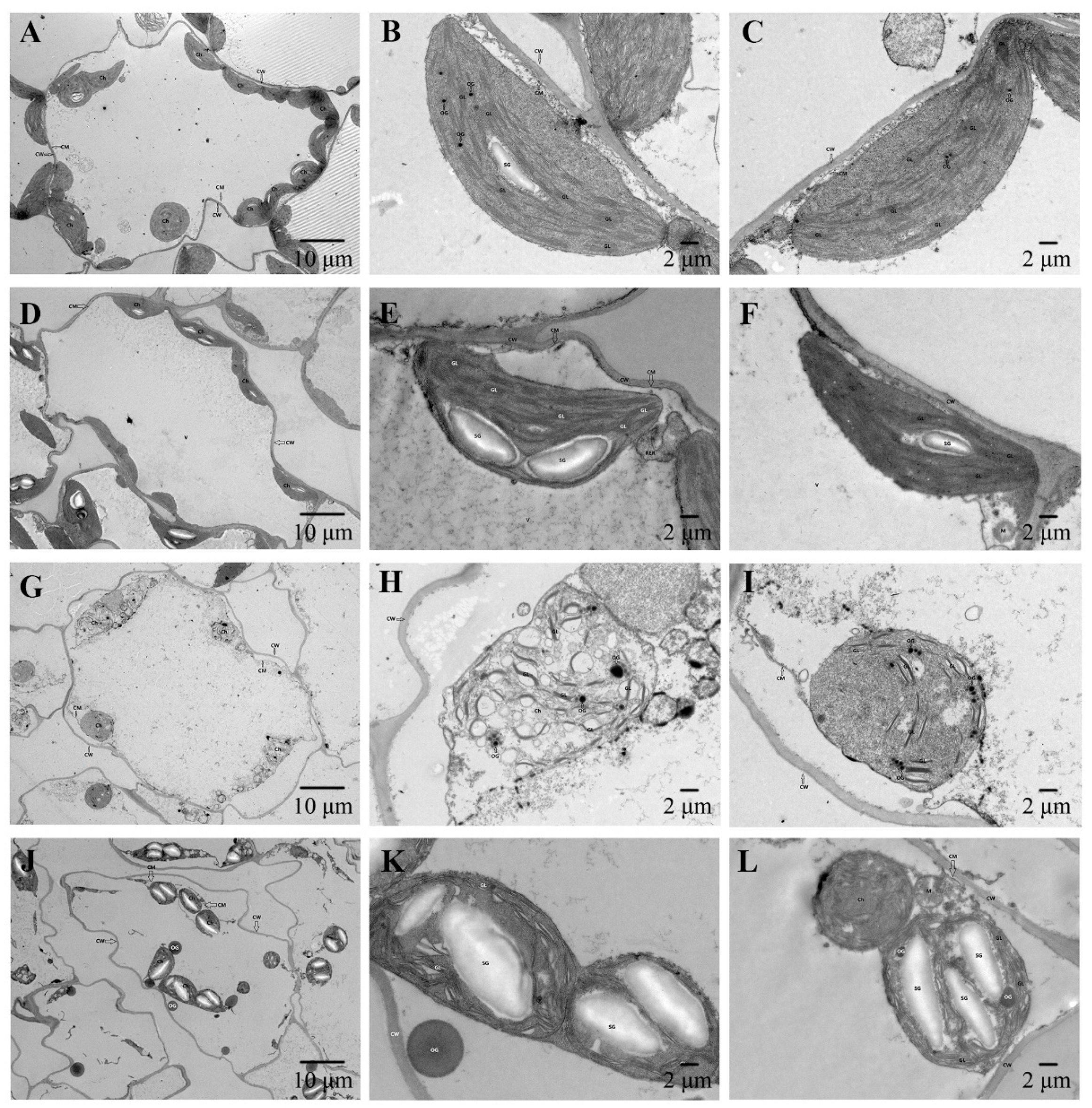
Chloroplasts, as the sites of photosynthesis in plants, are involved in the regulation of various physiological responses and are also organelles sensitive to cadmium stress. In this study, the ultrastructure of leaf mesophyll cells of cabbage seedlings was significantly damaged under cadmium stress, as shown by chloroplast deformation and damage, poor lamellar arrangement, reduction of starch granules and appearance of osmophilic particles, which was consistent with previous studies [
50,
51]. The results showed that cadmium stress significantly decreased the photosynthetic rate, chlorophyll content and starch granule accumulation in cabbage chloroplasts, which was consistent with the results of H. Y. Sun et al. Therefore, we speculate that the structural changes in chloroplasts under cadmium stress may be the direct cause of damage to the photosynthetic system and chlorophyll degradation, which ultimately leads to the inhibition of photosynthesis.
However, exogenous application of selenium restored the damage to the chloroplast structure, increased the number of starch granules in cabbage leaves, and effectively improved the stability and integrity of the chloroplast structure (
Figure 6), indicating that selenium could protect the growth of cabbage seedlings and alleviate the damage to the chloroplast structure under cadmium stress, thus promoting photosynthesis, which played a key role in alleviating cadmium stress in cabbage seedlings.
To investigate the effect of exogenous selenium application on the scavenging of ROS in seedling leaves, we examined the levels of O
2- and H
2O
2 in leaves of cabbage seedlings. The results showed that cadmium caused a significant increase in the production of O
2- and H
2O
2, resulting in excessive ROS production (
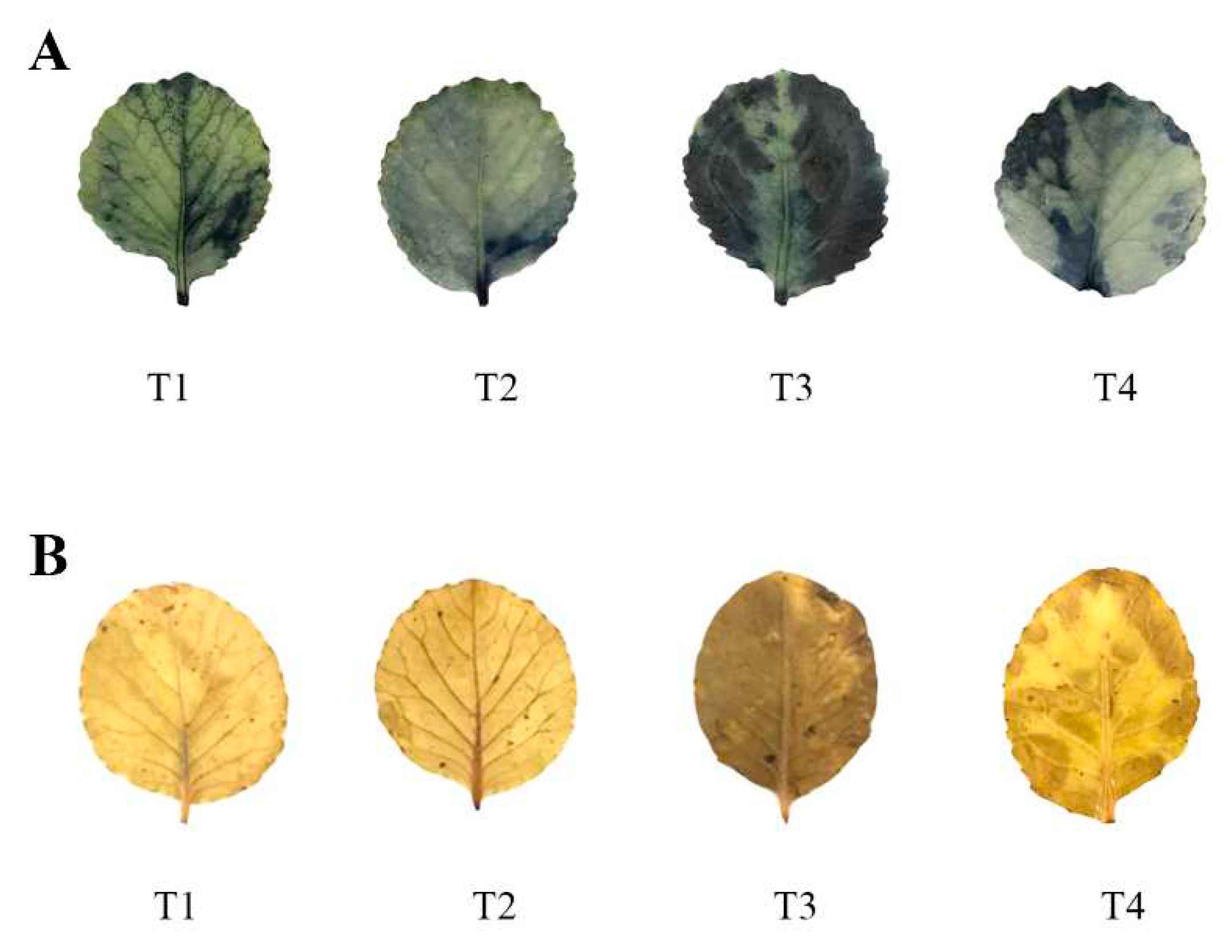
Figure 7,
Figure 8), which was consistent with the results of He S et al. [
52]. However, exogenous application of selenium minimized the production of ROS induced by cadmium stress, possibly due to its function of protecting cells from cadmium-induced oxidative damage.
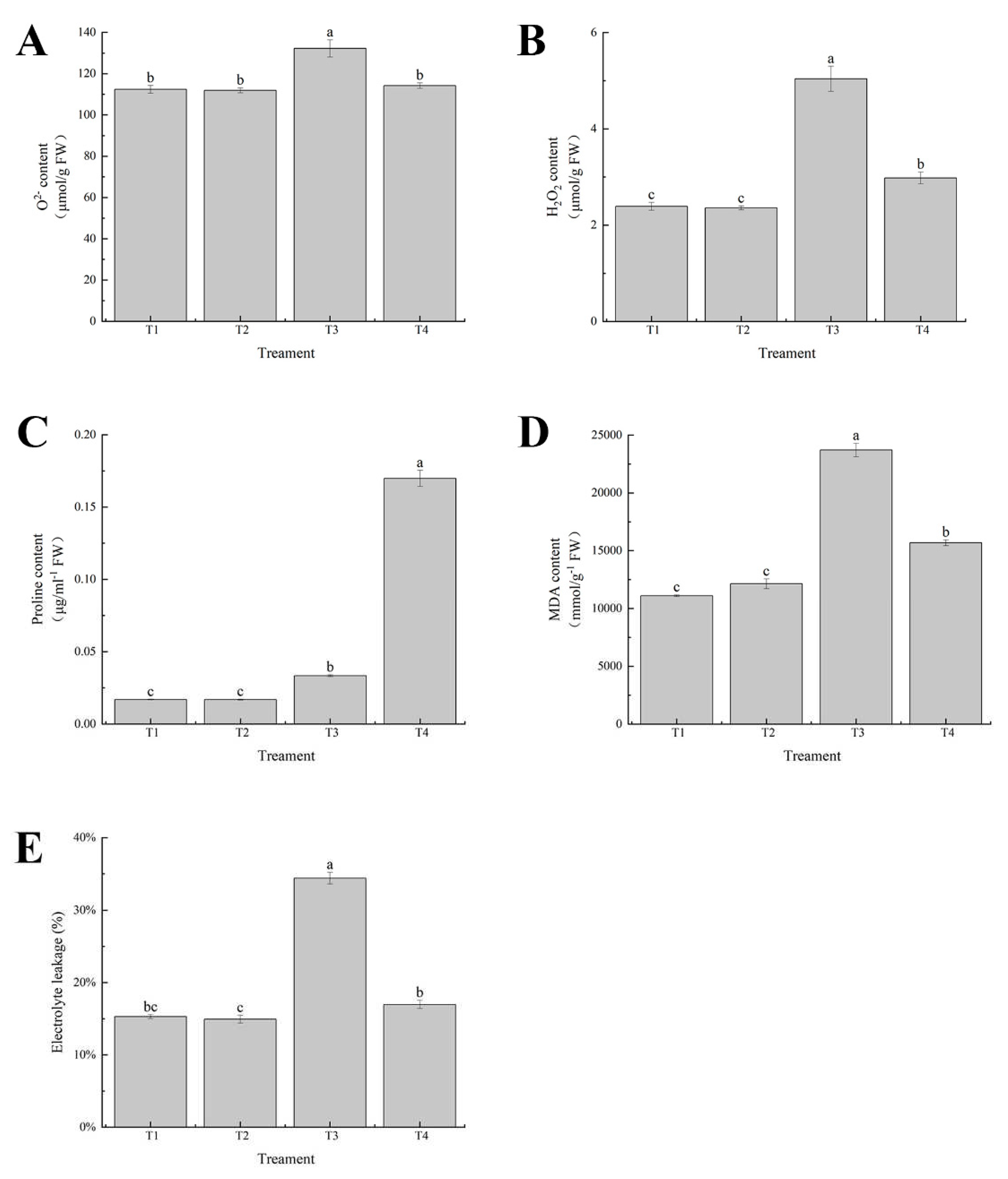
At the same time, the levels of MDA, proline and electrolyte leakage are used as important indicators of lipid peroxidation in plants to reflect the degree of membrane damage [
53]. Our results showed that cadmium treatment significantly increased the generation of MDA, proline and electrolyte leakage in leaf tissues compared to the control (
Figure 8D). According to the histochemical detection, the staining degree of leaves of cabbage seedlings treated with cadmium alone was higher, indicating that cadmium stress caused severe cellular REDOX imbalance and oxidative damage, increased lipid peroxidation and excessive ROS accumulation. It can be concluded that the oxidative damage caused by cadmium in plants is the reason for the destruction of cell membrane, inhibition of nutrient absorption and enhanced lipid peroxidation [
54].
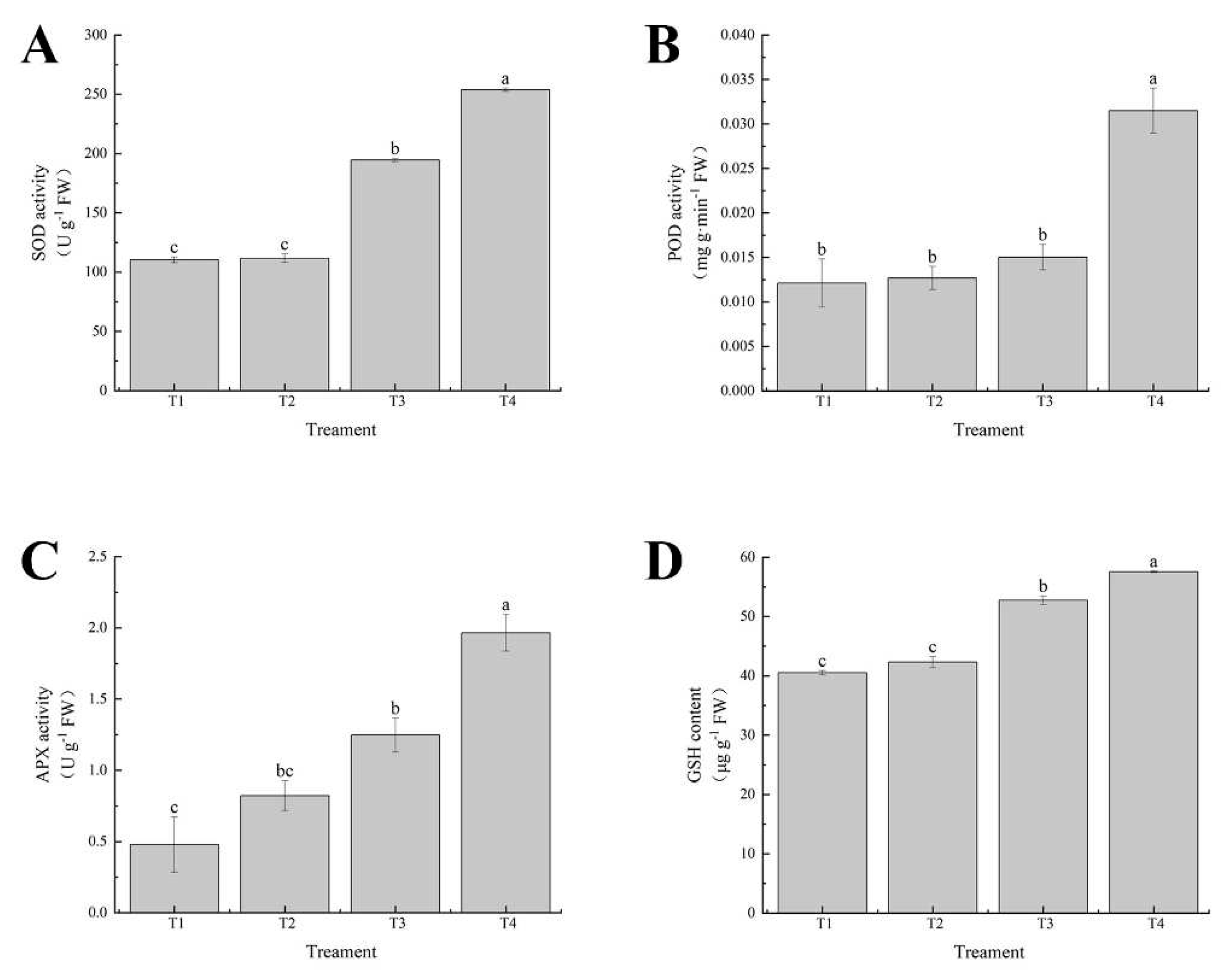
Plants induce resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses by producing antioxidant enzymes, and oxidative damage is closely related to antioxidant defense mechanisms. The results showed that the activities of SOD, POD, APX and GSH of cabbage seedlings were increased under cadmium stress, while the exogenous application of selenium further improved the activity of cabbage seedling leaves (
Figure 9), indicating that selenium could significantly reduce the oxidative damage caused by cadmium stress by enhancing the antioxidant response. Our results were consistent with those of Qi W et al. who confirmed that Cadmium-stressed Brassica napus plants could enhance the activity of antioxidant enzymes, and the enzyme activity was further improved after selenium application, and antioxidant enzymes were closely related to cadmium tolerance [
40]. These results suggest that exogenous selenium may induce REDOX homeostasis by activating both enzyme-supported and non-enzyme-supported antioxidant systems, thereby protecting cabbage seedlings from cadmium stress.
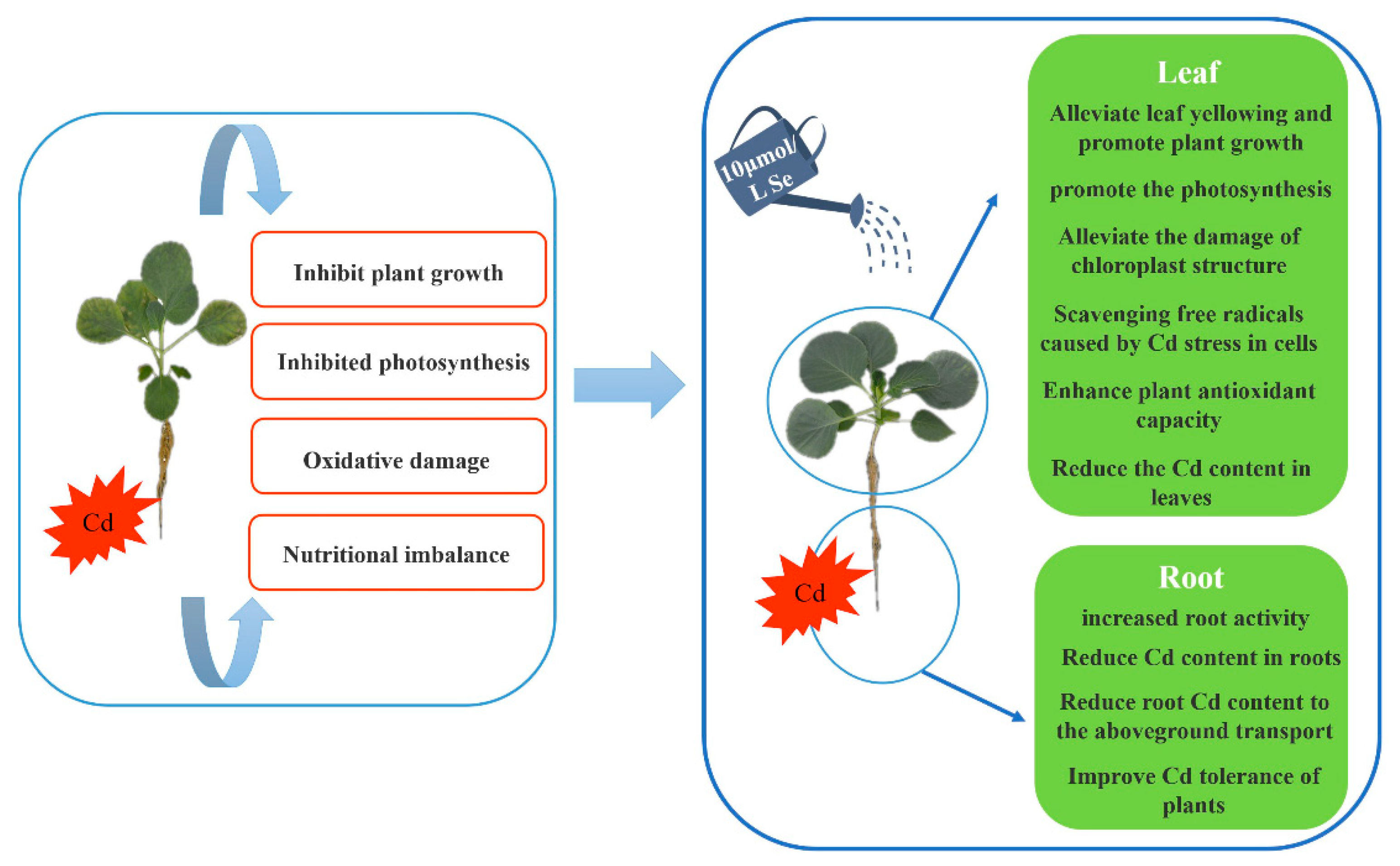
5. Conclusions
In this study, we found that exogenous selenium can effectively alleviate the stress of cadmium on the growth and physiological and biochemical characteristics of cabbage seedlings, inhibit the transport of cadmium from root to leaf, and restore the negative effect of cadmium stress. Exogenous selenium application is an important way to alleviate cadmium stress.
Cadmium stress severely inhibited the growth and photosynthesis of cabbage seedlings, increased the levels of O
2-, H
2O
2, MDA, electrolyte leakage and proline, decreased the antioxidant capacity of SOD, POD, APX and GSH, and disturbed the nutrient balance. However, exogenous application of selenium increased the biomass and photosynthetic efficiency of cabbage seedlings and decreased the concentration of cadmium, which was conducive to maintaining the growth of cabbage seedlings and eliminating excess ROS by upregulating antioxidant enzymes to protect the ultrastructure of chloroplasts. Therefore, the results confirmed the ameliorative effect of exogenous selenium application on cadmium stress in cabbage seedlings, which laid the foundation for the study of exogenous selenium application to reduce cadmium stress in cabbage (
Figure 10).
In conclusion, this study elucidates the role and regulatory mechanism of selenium under cadmium stress in cabbage, which is helpful for the application of selenium under cadmium stress in agricultural production to promote plant growth and increase yield.
Figure 1.
Effect of exogenous selenium on plant and leaf morphology of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress.
Figure 1.
Effect of exogenous selenium on plant and leaf morphology of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress.
Figure 2.
Effect of exogenous selenium on the growth of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress. (A) leaf fresh weight, (B) leaf dry weight, (C) root fresh weight, (D) root dry weight, (E) plant height, (F) stem thick, (G) root length, (H) Chla+b content, and (I) root activity. Values are means of three replicates ± SD. Different letters indicate significant difference at P ≤ 0.05.
Figure 2.
Effect of exogenous selenium on the growth of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress. (A) leaf fresh weight, (B) leaf dry weight, (C) root fresh weight, (D) root dry weight, (E) plant height, (F) stem thick, (G) root length, (H) Chla+b content, and (I) root activity. Values are means of three replicates ± SD. Different letters indicate significant difference at P ≤ 0.05.
Figure 3.
Effects of exogenous selenium on stomatal parameters of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress. (A) Pn, (B) Ci, (C) Tr, (D) Gs. Values are means of three replicates ± SD. Different letters indicate significant difference at P ≤ 0.05.
Figure 3.
Effects of exogenous selenium on stomatal parameters of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress. (A) Pn, (B) Ci, (C) Tr, (D) Gs. Values are means of three replicates ± SD. Different letters indicate significant difference at P ≤ 0.05.
Figure 4.
Effects of exogenous selenium on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress. (A) Fv/Fm, (B) Y (Ⅱ), (C) Tr, (D) qP. Values are means of three replicates ± SD. Different letters indicate significant difference at P ≤ 0.05.
Figure 4.
Effects of exogenous selenium on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress. (A) Fv/Fm, (B) Y (Ⅱ), (C) Tr, (D) qP. Values are means of three replicates ± SD. Different letters indicate significant difference at P ≤ 0.05.
Figure 5.
Effects of exogenous selenium on tolerance of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress. (A) Cd content (B) Se content. Values are means of three replicates ± SD. Different letters indicate significant difference at P ≤ 0.05.
Figure 5.
Effects of exogenous selenium on tolerance of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress. (A) Cd content (B) Se content. Values are means of three replicates ± SD. Different letters indicate significant difference at P ≤ 0.05.
Figure 6.
Observation on chloroplast ultrastructure of cabbage seedling leaves. T1. (A–C), T2. (D–F), T3. (G–I), T4. (J–L). Abbreviation: CW, cell wall. CM, cell membrane. Ch, chloroplast. OG, osmiophilic globule. GL, grana lamellae. M, mitochondria. V, vacuole. SG, starch granules.
Figure 6.
Observation on chloroplast ultrastructure of cabbage seedling leaves. T1. (A–C), T2. (D–F), T3. (G–I), T4. (J–L). Abbreviation: CW, cell wall. CM, cell membrane. Ch, chloroplast. OG, osmiophilic globule. GL, grana lamellae. M, mitochondria. V, vacuole. SG, starch granules.
Figure 7.
Effects of exogenous selenium on DAB and NBT staining of leaves of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress (A,B).
Figure 7.
Effects of exogenous selenium on DAB and NBT staining of leaves of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress (A,B).
Figure 8.
Effects of exogenous selenium onO2- content, H2O2 content, Proline content, MDA content, Electrolyte leakage of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress (A–E). Values are means of three replicates ± SD. Different letters indicate significant difference at P ≤ 0.05.
Figure 8.
Effects of exogenous selenium onO2- content, H2O2 content, Proline content, MDA content, Electrolyte leakage of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress (A–E). Values are means of three replicates ± SD. Different letters indicate significant difference at P ≤ 0.05.
Figure 9.
Effects of exogenous selenium on antioxidant enzyme activities of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress. (A) SOD activity, (B) POD activity, (C) APX activity, (D) GSH content. Values are means of three replicates ± SD. Different letters indicate significant difference at P ≤ 0.05.
Figure 9.
Effects of exogenous selenium on antioxidant enzyme activities of cabbage seedlings under cadmium stress. (A) SOD activity, (B) POD activity, (C) APX activity, (D) GSH content. Values are means of three replicates ± SD. Different letters indicate significant difference at P ≤ 0.05.
Figure 10.
Exogenous selenium has an alleviating effect on the physiological mechanism of cabbage seedlings.
Figure 10.
Exogenous selenium has an alleviating effect on the physiological mechanism of cabbage seedlings.