1. Introduction
Heart failure is a global health problem, and an estimated 64.3 million people are living with heart failure worldwide. More than 50% of them suffer from heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) which contribute to increasing healthcare costs worldwide. However, in most cases, HFpEF is still underdiagnosed in clinical practices because of the variety of diagnostic capabilities and limited clinical signs and symptoms, which often manifest late [
1]. Consequently, failure to diagnose and treat HFpEF early will further increase the total cost [
2].
In heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction is caused by myocardial fibrosis [
3]. Initially, mature cardiac tissue consists of cardiomyocytes and non-cardiogenic cells, which are mainly fibroblasts. Fibroblasts provide structural and paracrine support to nearby cardiomyocytes. During myocardial injury, fibroblasts will be active and migrate to the site of injury to maintain the structural integrity of the heart by inducing fibrosis. This leaves non-contractile areas in the heart, which result in worsened ventricular function and contribute to remodeling and increased stiffness of the heart [
4].
MicroRNA (miRNA) plays an important role in cardiovascular disease, including heart failure. MicroRNA is a non-coding (non-coding) RNA that works at the post-transcriptional stage by degrading or inhibiting target messenger RNA (mRNA) translation, which results in the modification of gene expression [
4]. MicroRNA is also detected in the circulation and is stable, meaning it has the potential to be used as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in HFpEF patients [
5]. Several studies have reported that some miRNAs are involved in the development of myocardial fibrosis event [
6,
7]. The miRNAs with the most prominent roles in cardiac myocardial fibrosis include miR-1, miR-30, miR-133, miR-21, and miR-29 [
8,
9].
Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) is the preferable and superior method to diagnose myocardial fibrosis. However, its lack of disease-specific cut-off values for reference still limits its introduction into the decision-making algorithms of everyday clinical practice. Meanwhile, left ventricular global longitudinal strain (LV GLS) with speckle tracking echocardiography (STE) can be an alternative for measuring myocardial fibrosis non-invasively, and it could be used as a more sensitive method of measuring myocardial function that correlates and predicts the extent of the condition [
10]. LV GLS can also show direct visualization of the fibrotic wall, which can sometimes be seen as hyper-refringent on ultrasounds [
11].
This study aimed to investigate the diagnostic potential of circulating microRNAs (miR-1, miR-21, and miR-29) for detecting the early development of myocardial fibrosis. It also aimed to analyze the relationship between those microRNA levels with NTproBNP examination and global longitudinal strain with STE in myocardial fibrosis in HFpEF patients.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was an observational study with a case-control research design. The population of this study were cardiac patients who sought treatment at the Cardiac Polyclinic of Dr. Soetomo Surabaya General Academic Hospital. The sample was collected from 50 consecutive sampling patients from January-March 2023, and they were grouped into a control group and a myocardial fibrosis group by GLS examination. Then, all the subjects had their HFpEF status determined, and they were evaluated through risk factor, clinical manifestation, echocardiography, and laboratory findings. Inclusion criteria were male or female patients aged 18-70 years old with normal ejection fraction who were willing to follow the research procedures by signing informed consent forms. Meanwhile, exclusion criteria were patients with LV regional wall motion abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, comorbid cancer, and renal failure, patients with mental disabilities, and patients with poor echo windows.
2.1. Variables and Outcome
The independent variables were the concentrations of plasma miR-1, miR-21, and miR-29, which were measured using the reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) method, and they were expressed by CT value level. The mature miRNA sequences were 5' UAGCUUAUCAGACUGAUGUUGA 3' (assay ID 000397), 5' UAGCACCAUCUGAAAUCGGUUA 3' (assay ID 002112), and 5' UGGAAUGUAAAGAAGUAUGUAU 3' (assay ID 002222) for miR-21, miR-29, and miR-1, respectively.
The dependent variable was myocardial fibrosis by GLS examination. GLS was performed using speckle tracking software (GE Vivid V7) on 17 segments from three standard apical views (3-chamber, 4-chamber, and 2-chamber). The endocardial boundary was then tracked automatically by the software. Three cardiac cycles from each view were recorded. The graphical display of the deformity parameters then appeared automatically. The cut-off value for fibrosis was -15%. Other left ventricular parameters were also assessed for baseline characteristics, namely ejection fraction (EF) using Simpson’s biplane method, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD), left ventricular end-systolic diameter (LVESD), and right ventricular function parameter tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE).
Baseline characteristics were taken from clinical data, including NTproBNP levels. ELISA was used to evaluate NTproBNP levels from the serum sample. Mouse antihuman monoclonal antibody (ABCAM) was used.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
The data obtained were analyzed using SPSS 25.0 software. After going through the coding, entry, cleaning, and editing process, the data were analyzed and presented in descriptive statistics. The independent samples T-test would be conducted if the sample was normally distributed. The Mann-Whitney test would be conducted if the data distribution was not normal. In addition, the data would also be analyzed using Pearson’s correlation test if the data were normally distributed. Spearman's correlation test analysis would be performed if the data were not normally distributed. ROC curve analysis was used to determine the discrimination power of miR-1, miR-21, and miR-19 toward myocardial fibrosis and to determine the best cut-off for each miRNA. Results were declared statistically significant if p was smaller than 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Study Subjects
The baseline characteristics of the study subjects included demographic data consisting of age, gender, NT Pro-BNP, and echocardiographic parameters such as LV GLS, LVEF, lVIDD, LVIDS, IVSD, and IVSS. This study’s data were tested for normality with Saphiro-Wilk. If the data were normally distributed, the parameters would be presented as mean ± standard deviation. If the data were not normally distributed, it would be presented in the form of a median (minimum value - maximum value).
The average age of the study subjects was 56 years old, and 58% of them were female. Based on echocardiographic assessment, our study subjects had a mean LVEF value of 63%, with a mean LV GLS value of -14.72. The results of these baseline characteristics were presented to show the difference between the incidence of fibrosis compared to the control group. There were no significant differences in age, gender, or LVEF. Meanwhile, the mean NT pro-BNP level in the myocardial fibrosis group was higher than that in the non-fibrosis group with a significant difference (1.502 vs 1.186; p = 0.001). In addition, it was found that the incidence of HFpEF was significantly higher in the myocardial fibrosis group. Data on overall baseline characteristics are presented in
Table 1.
3.2. MicroRNA Changes in Myocardial Fibrosis
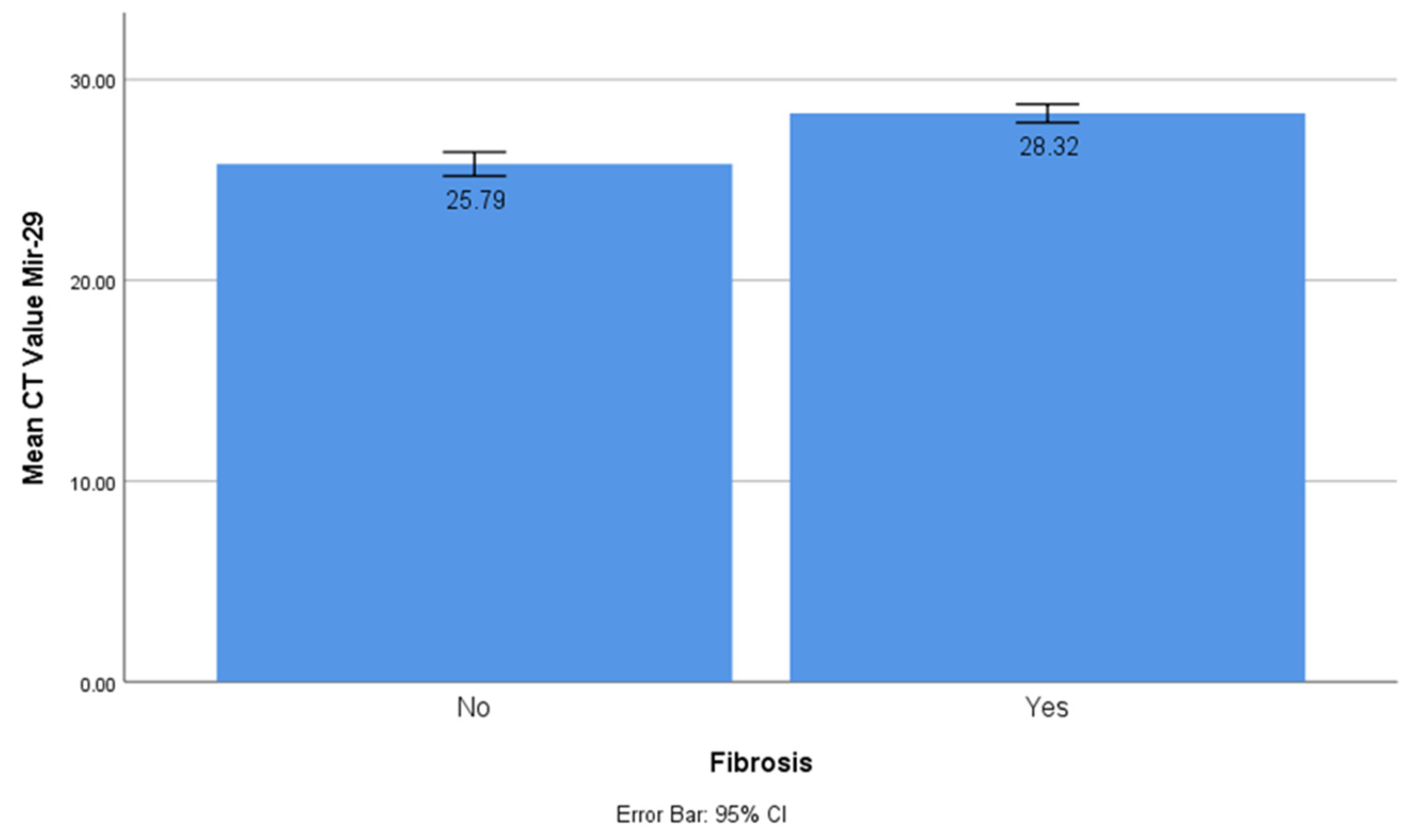
The CT values of miR-1 and mir-21 were significantly lower in the myocardial fibrosis group compared to the control group with CT values of 37.15 ± 0.27 vs 35.2 ± 0.511 and 26.25 vs 25.09, respectively (t-test, p < 0.001). This showed that miR-1 and mir-21 had significantly higher concentrations in the myocardial fibrosis group, and they had a prominent role in the myocardial fibrosis process. On the other hand, the CT value of miR-29 was significantly higher in the myocardial fibrosis group (CT value 25.72 ± 1.56 vs 27.94 ± 1.38; t-test, p < 0.001). This showed that miR-29 had a significantly lower concentration in myocardial fibrosis and acted as a protective factor (
Figure 1).
3.3. MicroRNA Changes in HFpEF
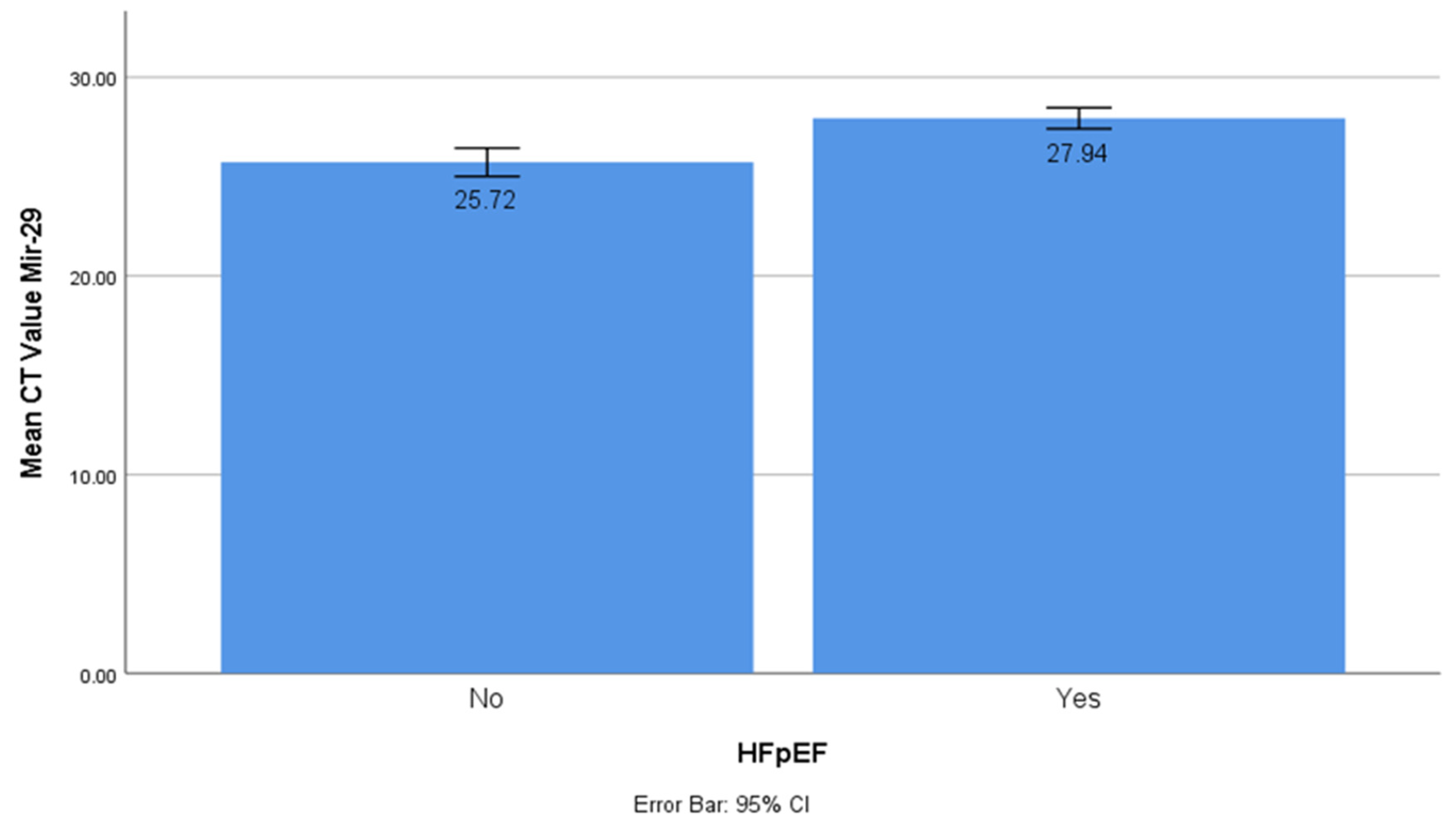
The CT values of miR-1 and mir-21 were significantly lower in the HFpEF group (t-test, p < 0.001). This showed that miR-1 and mir-21 had significantly higher concentrations in HfpEF. The CT value of miR-29 was significantly higher in the HFpEF group (t-test, p < 0.001), which was different from the miR-1 and mir-21 results. This showed that miR-29 had a significantly lower concentration in HFpEF (
Figure 2).
3.4. NT Pro BNP Increasing in Myocardial Fibrosis and Correlated with GLS
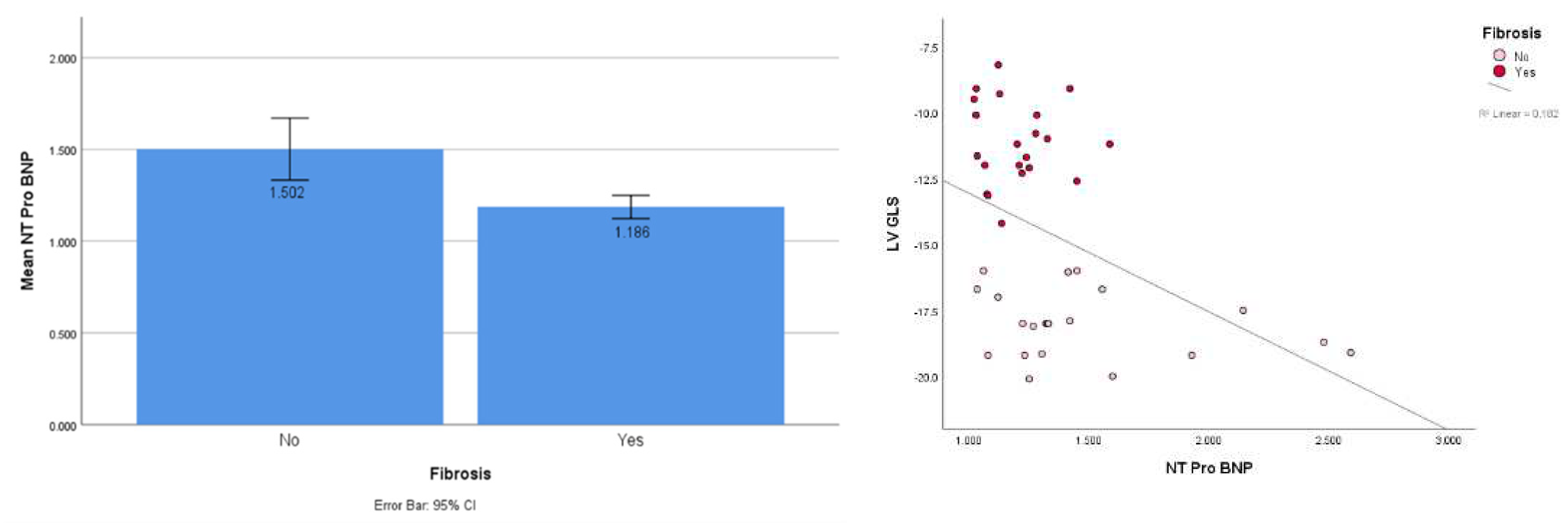
This study showed a significantly higher NT ProBNP in the fibrosis group (mean 1.502 vs 1.186; t-test, p < 0.001). Spearman’s rho correlation test also showed a significant correlation between NTproBNP and GLS at an r-value of 0.536 and a p-value of 0.000 (
Figure 3a,b).
3.5. Correlation between MicroRNA and Global Longitudinal Strain
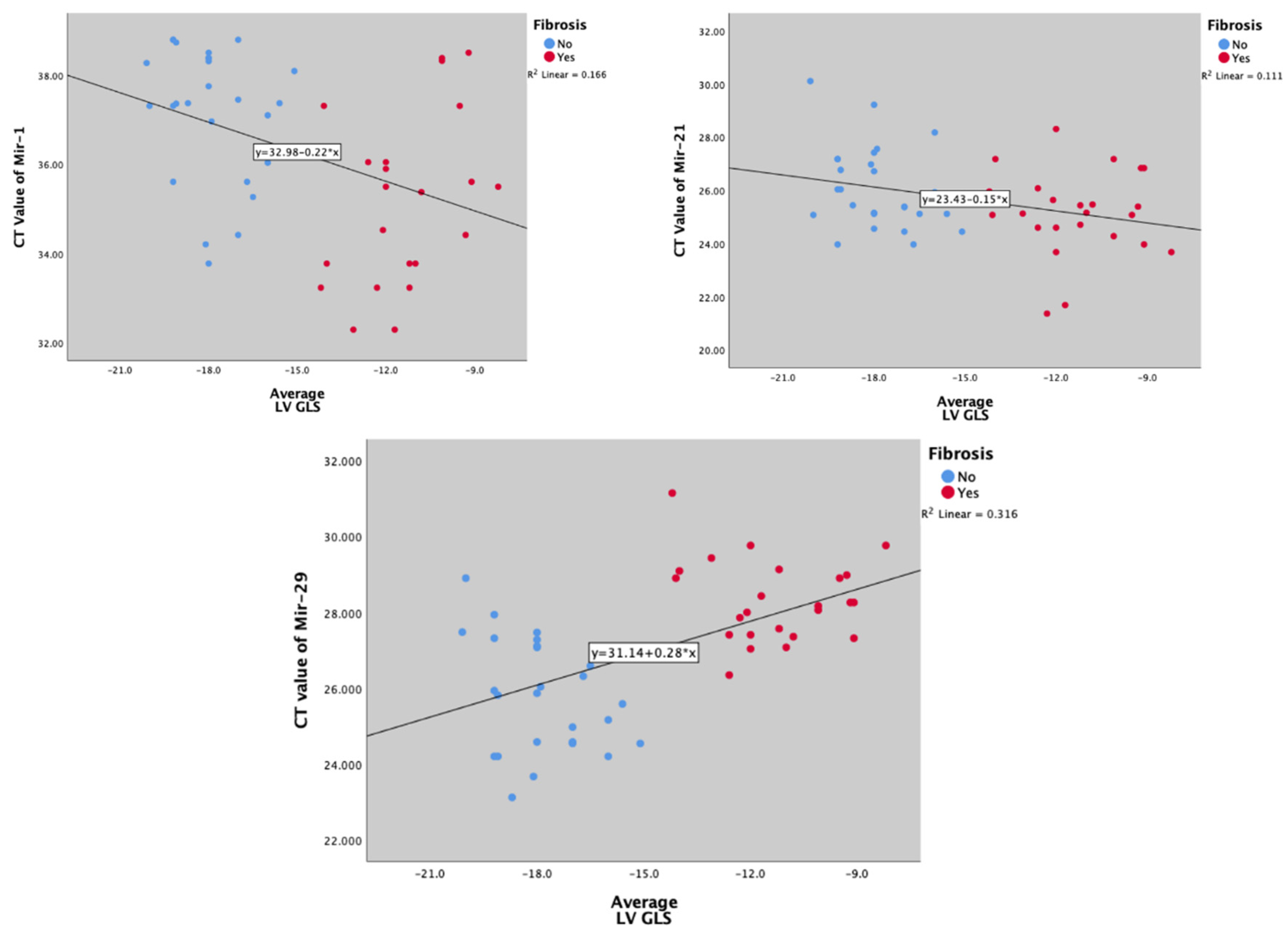
miR-1 and mir-21's CT values were inversely and significantly correlated with myocardial fibrosis (marked with GLS) (Spearman’s Rro r = -0.404, p = 0.004; and r = -0.300, p = 0.035, respectively) (
Figure 4a,b), while mir-29 was positively correlated (Spearman’s rho r = -0.540; p < 0.001) (
Figure 4c).
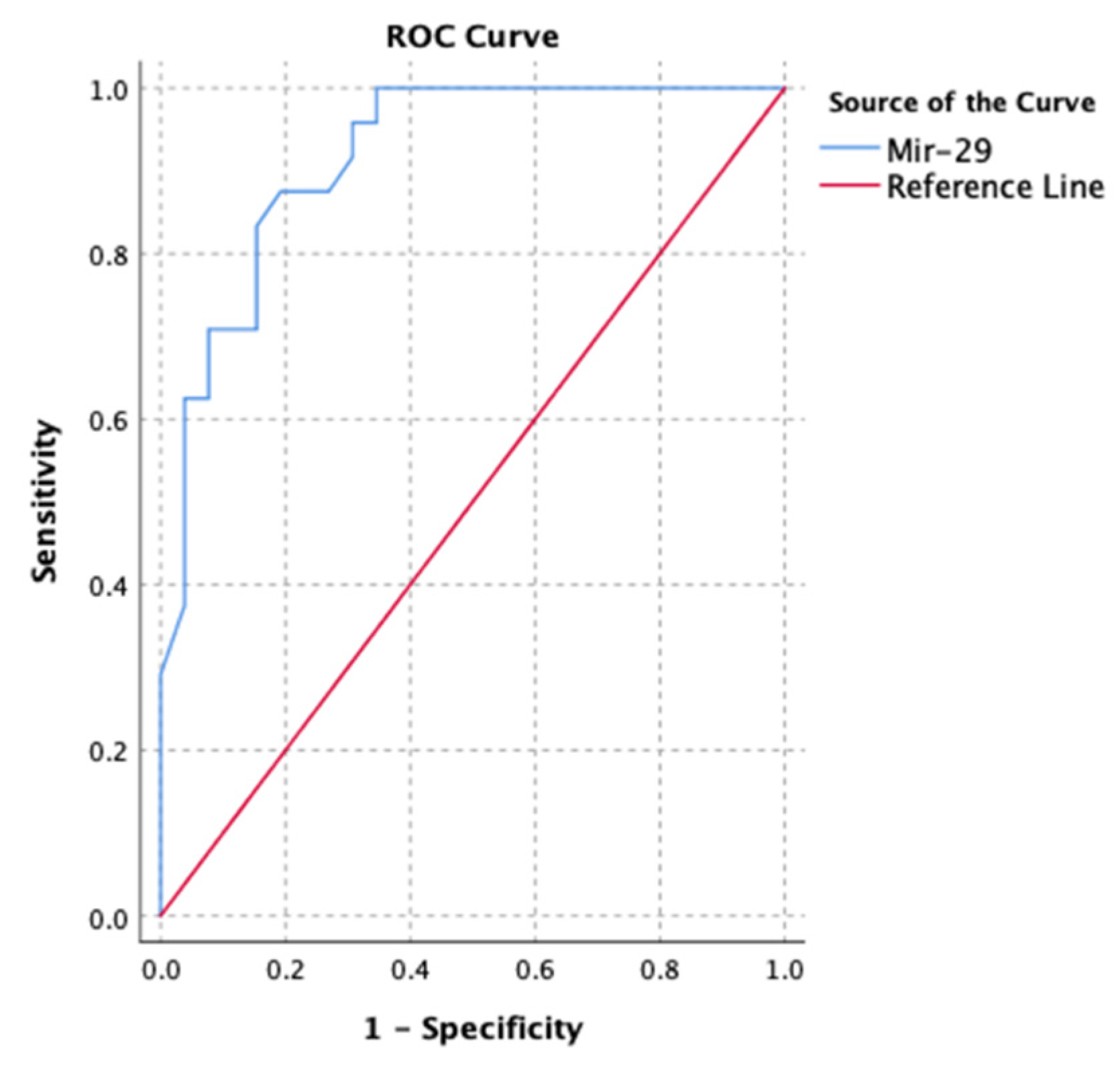
3.6. MicroRNA Ability to Predict Myocardial Fibrosis
The receiver operating curve was used to assess the performance of microRNAs to predict myocardial fibrosis. Micro RNA-1, 21, and 29 were all individually capable of predicting myocardial fibrosis (based on GLS) (ROC area under the curve = 0.782; p < 0.001). Micro RNA-29 seemed to be superior (
Figure 5).
3.7. MicroRNA Changes and Its Diagnostic Capabilities
The receiver operating curve was used to assess the performance of microRNAs in acute heart failure. Micro RNA-1, 21, and 29 were all individually capable of predicting acute heart failure (based on ejection fraction), yet micro-RNA-1 seemed to be superior (
Figure 6).
4. Discussion
4.1. Increased Circulating MicroRNA-1 and MicroRNA-21 Consistent with Myocardial Injury Model
The research conducted by Pan et al. (2012) revealed that overexpression of miR-1 worsened myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, leading to increased infarct size, apoptosis, caspase-3 expression, and elevated levels of LDH and CK in the heart. However, treatment with LNA-anti-miR-1 attenuated I/R injury [
12]. Similarly, inhibiting miR-1 was shown to protect rat H9c2 cardiomyocytes against apoptosis induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R), potentially through targeting Bcl-2 [
12,
13]. Inhibition of miR-1 also demonstrated protective effects against cardiac I/R injury in rats, possibly by promoting the MAPK3/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [
7,
12,
13,
14]. Moreover, miR-1 was found to be released from heart tissue to circulating under ischemic conditions or post-myocardial infarction (MI), suggesting it may serve as an adaptive mechanism to ischemia. Elevated levels of miR-1, however, exacerbate myocardial damage caused by I/R [
7].
Post-MI cardiac remodeling was characterized by the development of fibrosis in the heart tissue, and miR-21 had been implicated in this process. In mouse’s hearts exposed to acute MI, miR-21 levels were elevated in the infarct zone and contributed to myocardial fibrosis post-MI. Treatment with transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) enhanced miR-21 expression in cardiac fibroblasts, while overexpression of miR-21 promoted fibroblast activation induced by TGF-β1. This activation was evidenced by increased expression of Collagen-1, alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), and F-actin. Conversely, inhibiting miR-21 attenuated the fibrotic process. The study also identified Smad7 as a direct target of miR-21, suggesting that miR-21 may play a crucial role in cardiac fibrosis post-MI through the TGF-β/Smad7 signaling pathway [
7,
15].
In this study, it was observed that the CT values of miR-1 and miR-2 were significantly lower in the myocardial fibrosis group, indicating higher levels of these microRNAs in myocardial fibrosis. These findings support the hypothesis that miR-1 and miR-2 are associated with upregulation and pathological processes in the myocardium.
4.2. Downregulation of Serum MicroRNA-29 in Myocardial Injury Model
Researchers have identified that at least 16 genes of miR-29 targets are involved in the extracellular matrix (ECM), such as collagens, lamins, and integrins [
16]. Studies have shown that both mutations and specific knockdown of miR-29 promote the occurrence and progression of myocardial fibrosis (MF) [
17]. The TGF-β/Smad pathway is considered a primary mechanism in MF, and recent research has documented miR-29 as a novel therapeutic target that interacts with this pathway. It is suggested that miR-29 may silence c-Fos to block the downstream TGF-β/Smad pathway, thus attenuating MF [
18,
19]. Modulating miR-29 levels, such as down-regulation using anti-miRs, induces collagen expression, while over-expression of miR-29 in fibroblasts reduces collagen expression [
20].
The miR-21 plasma CT value in the myocardial fibrosis group in this study was significantly lower than in the group without myocardial fibrosis. This showed that plasma miR-21 levels in the myocardial fibrosis group were higher than in the group without myocardial fibrosis. The microRNA-21 is a miRNA that may have a special role in the regulation of the pathological process of myocardial fibrosis.
4.3. Changes in Micro RNA-1, 21, and 29 Expression Altering Protein Expression Involved in Myocardial Fibrosis
MicroRNAs, including miR-1, miR-21, and miR-29, target certain genes (such as AZIN1 and JNK1) that contribute to the fibrotic properties observed in MF. JNK1 is targeted by miR-21 and miR-29 and is considered a potential regulator of cardiac fibrosis. AZIN1 and JNK1 are targeted by miRNAs in cardiac fibroblasts, influencing fibroblast proliferation and myofibroblast differentiation. Reduced expression of AZIN1 activates TGFβ/Smad3 signaling in cardiac fibroblasts, while decreased JNK levels increase the phosphorylation of ERK, P38 kinase, and Smad3, thereby promoting fibroblast proliferation and differentiation into myofibroblasts [
21].
The regulation of MF by miR-29 involves a complex interconnected network of pathways, including TGF-β/Smad, MAPK, Wnt, Notch, SH2B3, AMPK, and DNA methylation. The TGF-β-dependent pathway serves as the core of this network, triggering both the Smad-dependent and MAPK pathways. The crosstalk between these two pathways depends on the inhibition of Smad4 by ERK. Furthermore, Smad3 reduces miR-29 expression by binding to its promoter, while miR-29 directly targets TGF-β and c-Fos to inactivate the TGF-β/Smad pathway. Additionally, miR-29 may attenuate MF by blocking the ERK/MAPK and p38/JNK/MAPK pathways although the exact mechanism remains unclear. One possible explanation is that miR-29 inhibits the MAPK pathway by silencing TGF-β and DNMT, where DNMT upregulates ERK1/2 signaling and is regulated by TGF-β [
19]
4.4. Superior Diagnostic Capability of MicroRNA-1 in Acute Heart Failure
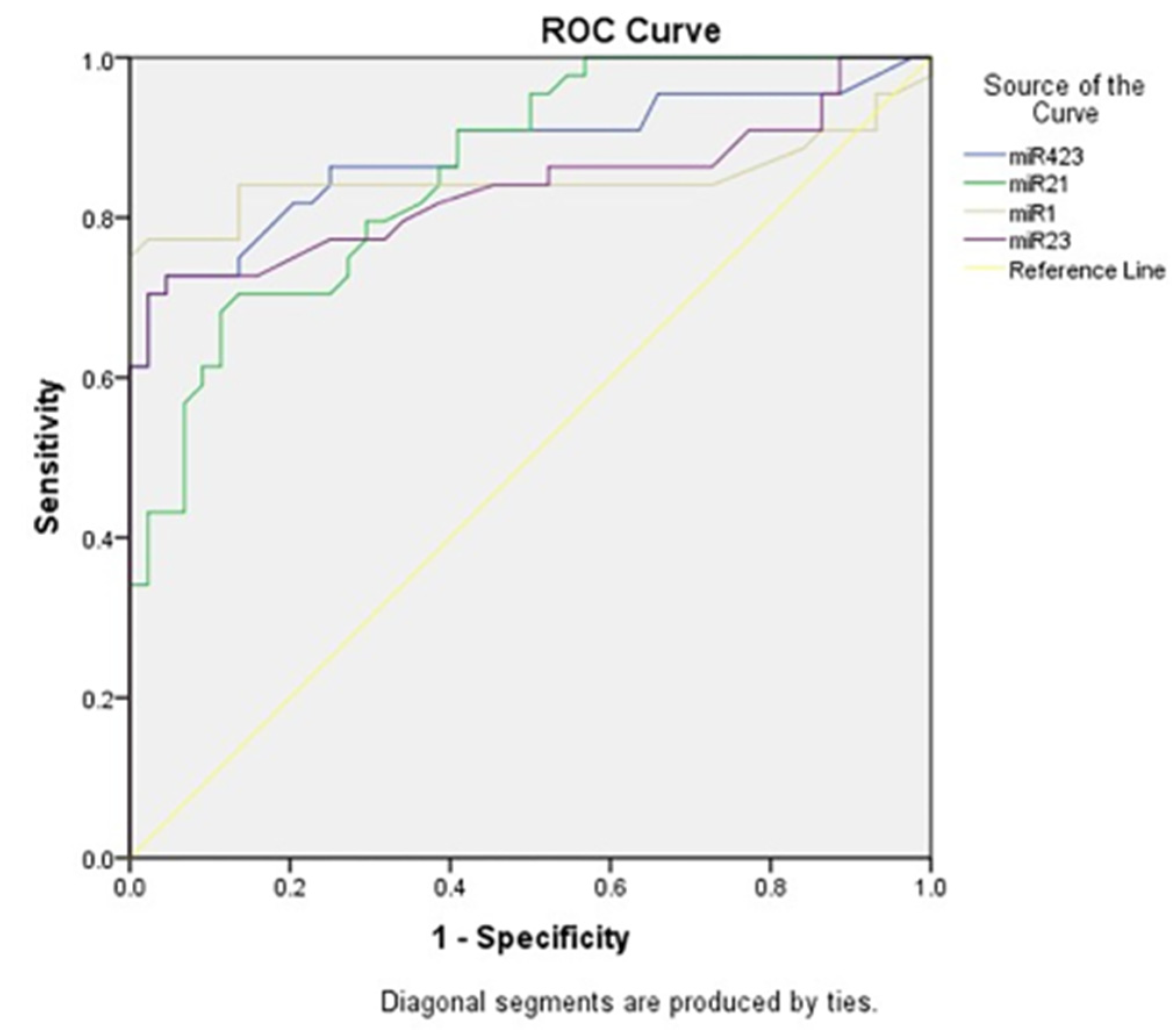
Acute heart failure (AHF), a life-threatening and burden some cardiovascular disease (CVD), requires a timely and accurate diagnosis. It should be distinguished from chronic heart failure (CHF). The current obstacle is the difficulty of making a definite diagnosis based on anamnesis, physical examination, and echocardiogram. Current biomarkers such as B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP) have their limitations as reliable indicators. Other conditions and comorbidities such as older age, renal disease, atrial fibrillation, and thromboembolic events influence the level of serum biomarkers BNP/NT-proBNP, which may obscure the diagnosis. This condition signifies the importance of a novel biomarker. This study showed that miR-1 had 83.3% sensitivity and 70.8% specificity for the detection of myocardial fibrosis based on GLS findings. They also had a sensitivity of 81% and specificity of 74.1% for the detection of HFpEF. Sadat-Ebrahimi et al. documented that miR-1 had a 77% sensitivity and 97.7% specificity for the detection of acute heart failure, which is the highest of all miR (miR-1, miR-21, miR-23, and miR-423-5p) for a value above 1.22. As they play a pathophysiological role in cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and apoptosis before overt clinical signs, miRNAs may predict the development of HF at an earlier stage. In this manner, a screening test may be the primary application of miR in the diagnosis of HF. MiR-1 is considered a muscle-specific miR reported to be closely associated with CVD [
7,
22]
4.5. Limitation: GLS for Fibrosis
The gold standard of fibrosis is CMR, and the use of GLS can be justified with the limitations of the tool. GLS is also operator- and image-dependent; therefore, it is necessary to consider re-evaluation in the future [
10]. However, research also compared the usage of GLS and LV fibrosis microscopically and showed a strong correlation. CMR comparison also showed that GLS>15 was related to myocardial fibrosis [
23].
5. Conclusions
Increasing microRNA-1 and microRNA-21 followed by decreasing microRNA-29 in HFpEF patients suggest early myocardial fibrosis. Detection of those biomarkers can be beneficial for early myocardial fibrosis diagnosis, early aggressive HFpEF treatment, and targeted miRNA silencing therapy to prevent worsening HFpEF.
Author Contributions
A is the principal investigator, conceived the ideas and supervised the project. MJAF helped project administration. MGA, RRJ, OWF analyzed and interpreted the patient data. REI performed the statistical analysis. ANF and MST contributed for writing the manuscript. IGRS, MA, NDR, BSP helped supervised the project. RAN visualization of the software. All authors read and approved the final manuscript
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of UNIVERSITAS AIRLANGGA (Ref Number: 551 / KEPK / XI / 2022) for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper” if applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Acknowledgments
Authors gratefully thank Mrs. Sri Redjeki, Mrs. Fita Triastuti, Mr. Kurniadi Doni and Mrs. Yunanda for their excellent administrative support during the experiment. Authors would also like to acknowledge Prof. Delvac Oceandy for his assistance in verifying the statistical approach used in our study. Finally, authors would like to dedicate this manuscript to all staff and resident from Department of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Airlangga - Dr. Soetomo Academic General Hospital.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mentz, R.J.; Kelly, J.P.; von Lueder, T.G.; Voors, A.A.; Lam, C.S.; Cowie, M.R.; Kjeldsen, K.; Jankowska, E.A.; Atar, D.; Butler, J.; et al. Noncardiac Comorbidities in Heart Failure With Reduced Versus Preserved Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 64, 2281–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarese, G.; Becher, P.M.; Lund, L.H.; Seferovic, P.; Rosano, G.M.C.; Coats, A.J.S. Global burden of heart failure: a comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 3272–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González A, Schelbert EB, Díez J, Butler J. Myocardial Interstitial Fibrosis in Heart Failure: Biological and Translational Perspectives. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Apr 17;71(15):1696–706.
- Andrianto; Pikir, B. S.; Ferdiansyah; Pristianto, T.; Hermawan, H.O.; Zaini, B.S.I.; Muhammad, A.R. Efficiency Comparison of Direct Reprogramming CD34+ Cells into Cardiomyocytes Using Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Medium vs MicroRNA-1. Cell. Reprogramming 2022, 24, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ransom, J.F.; Li, A.; Vedantham, V.; von Drehle, M.; Muth, A.N.; Tsuchihashi, T.; McManus, M.T.; Schwartz, R.J.; Srivastava, D. Dysregulation of Cardiogenesis, Cardiac Conduction, and Cell Cycle in Mice Lacking miRNA-1-2. Cell 2007, 129, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Khanna, S.; Hussain, S.-R.A.; Biswas, S.; Azad, A.; Rink, C.; Gnyawali, S.; Shilo, S.; Nuovo, G.J.; Sen, C.K. MicroRNA expression in response to murine myocardial infarction: miR-21 regulates fibroblast metalloprotease-2 via phosphatase and tensin homologue. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 82, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kura, B.; Kalocayova, B.; Devaux, Y.; Bartekova, M. Potential Clinical Implications of miR-1 and miR-21 in Heart Disease and Cardioprotection †. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duisters RF, Tijsen AJ, Schroen B, Leenders JJ, Lentink V, van der Made I, et al. miR-133 and miR-30 regulate connective tissue growth factor: implications for a role of microRNAs in myocardial matrix remodeling. Circ Res. 2009 Jan 30;104(2):170–8, 6p following 178. [CrossRef]
- Thum, T.; Gross, C.; Fiedler, J.; Fischer, T.; Kissler, S.; Bussen, M.; Galuppo, P.; Just, S.; Rottbauer, W.; Frantz, S.; et al. MicroRNA-21 contributes to myocardial disease by stimulating MAP kinase signalling in fibroblasts. Nature 2008, 456, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameli, M.; Mondillo, S.; Righini, F.M.; Lisi, M.; Dokollari, A.; Lindqvist, P.; Maccherini, M.; Henein, M. Left Ventricular Deformation and Myocardial Fibrosis in Patients With Advanced Heart Failure Requiring Transplantation. J. Card. Fail. 2016, 22, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandoli, G.E.; D'Ascenzi, F.; Vinco, G.; Benfari, G.; Ricci, F.; Focardi, M.; Cavigli, L.; Pastore, M.C.; Sisti, N.; De Vivo, O.; et al. Novel Approaches in Cardiac Imaging for Non-invasive Assessment of Left Heart Myocardial Fibrosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Sun, X.; Ren, J.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. miR-1 Exacerbates Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Mouse Models. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e50515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, C.; Tang, G.; Peng, L.; Hu, H.; Qian, G.; Wang, S.; Yao, J.; Zhang, X.; Fang, Y.; Yang, S.; et al. Inhibition of microRNA-1 attenuates hypoxia/re-oxygenation-induced apoptosis of cardiomyocytes by directly targeting Bcl-2 but not GADD45Beta. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 1952–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuwabara, Y.; Ono, K.; Horie, T.; Nishi, H.; Nagao, K.; Kinoshita, M.; Watanabe, S.; Baba, O.; Kojima, Y.; Shizuta, S.; et al. Increased MicroRNA-1 and MicroRNA-133a Levels in Serum of Patients With Cardiovascular Disease Indicate Myocardial Damage. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2011, 4, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, H.; Ge, D.; Xu, Y.; Xu, H.; Yang, Y.; Gu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ge, T.; et al. Mir-21 Promotes Cardiac Fibrosis After Myocardial Infarction Via Targeting Smad7. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegel, A.J.; Liu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Ding, X.; Liang, M.; Padmanabhan, S.; Joe, B.; Paterson, M.R.; Drummond, C.A.; Alexander, L.E.C.; et al. The miR-29 family: genomics, cell biology, and relevance to renal and cardiovascular injury. Physiol. Genom. 2012, 44, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue H, Zhang G, Geurts AM, Usa K, Jensen DM, Liu Y, et al. Tissue-specific effects of targeted mutation of Mir29b1 in rats. EBioMedicine. 2018 Sep;35:260–9. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.-R.; Wei, L.-H.; Chung, A.C.; Yu, C.-M.; Lan, H.-Y. miR-29b as a Therapeutic Agent for Angiotensin II-induced Cardiac Fibrosis by Targeting TGF-β/Smad3 signaling. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, N.; Rao, P.; Wang, L.; Lu, D.; Sun, L. Role of the microRNA-29 family in myocardial fibrosis. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 77, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooij, E.; Sutherland, L.B.; Thatcher, J.E.; DiMaio, J.M.; Naseem, R.H.; Marshall, W.S.; Hill, J.A.; Olson, E.N. Dysregulation of microRNAs after myocardial infarction reveals a role of miR-29 in cardiac fibrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13027–13032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, J.Y.Y.; Bernardo, B.C.; McMullen, J.R. Therapeutic potential of targeting microRNAs to regulate cardiac fibrosis: miR-433 a new fibrotic player. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 548–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat-Ebrahimi SR, Rezabakhsh A, Aslanabadi N, Asadi M, Zafari V, Shanebandi D, et al. Novel diagnostic potential of miR-1 in patients with acute heart failure. PLoS One. 2022 Sep 23;17(9):e0275019. [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Ji, M.; He, Q.; Xie, M.; Li, Y. Clinical Utility of Strain Imaging in Assessment of Myocardial Fibrosis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).