Submitted:
16 August 2023
Posted:
17 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
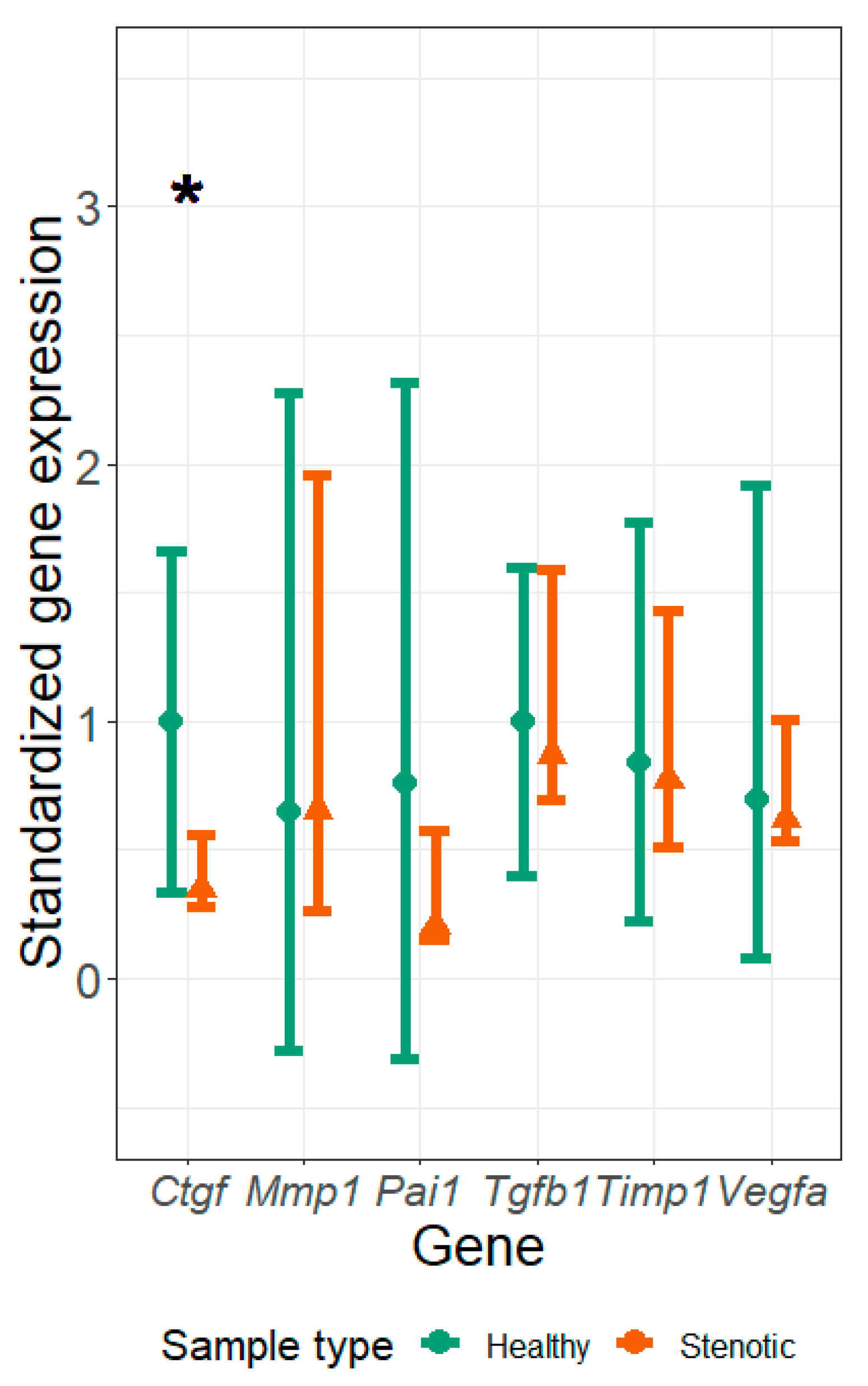
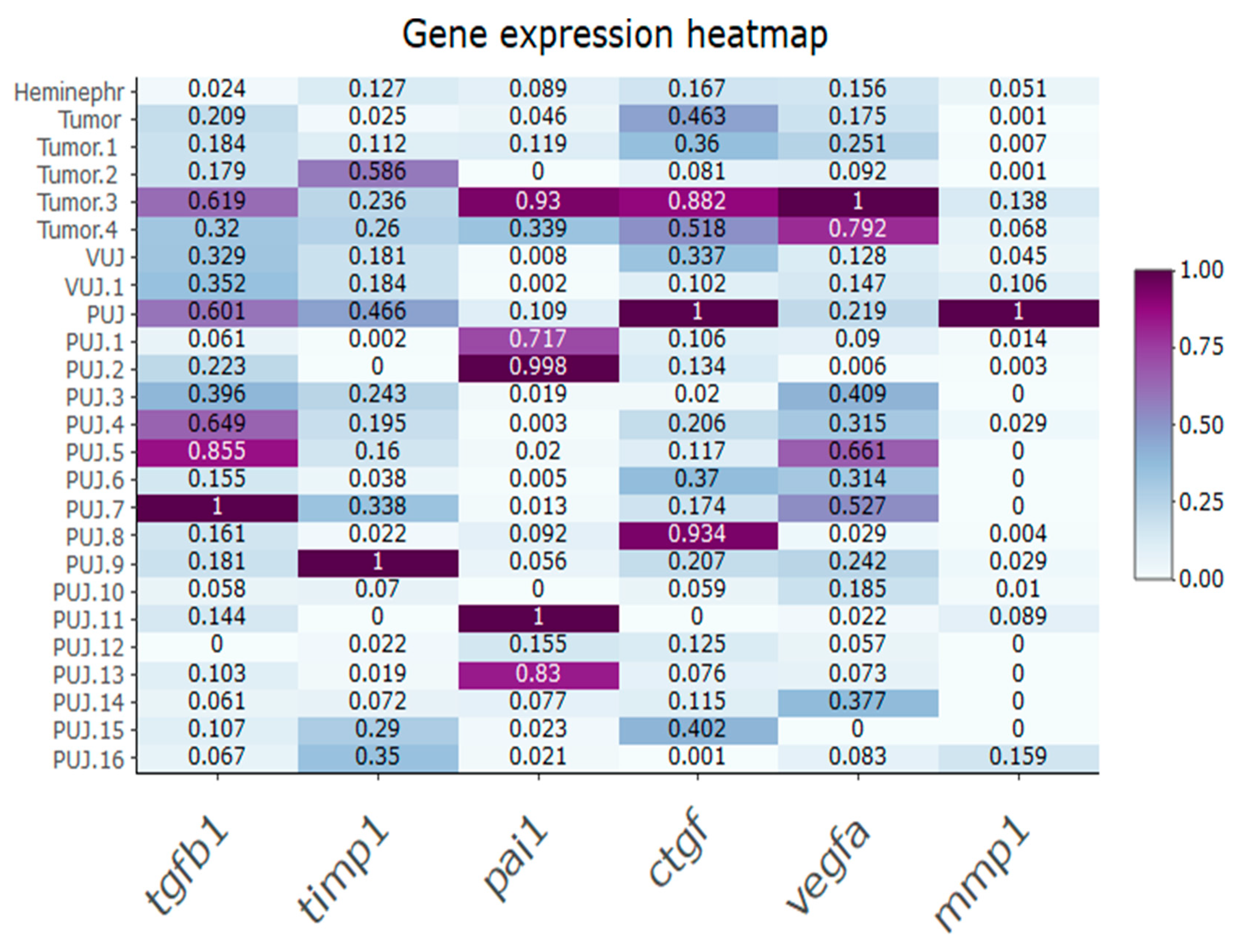
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UB | ureteric bud; |
| PUJO | obstructed pyeloureteric junction; |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor; |
| AT1R | angiotensin type 1 receptor; |
| AT2R | angiotensin type 2 receptor; |
| UVJO | ureterovesical junction obstruction; |
| ChKD | chronic kidney disease; |
| ESRD | end stage renal disease; |
| LTBP | latent TGFβ binding proteins |
References
- Zhao, S.; Li, W.; Yu, W.; Rao, T.; Li, H.; Ruan, Y.; Yuan, R.; Li, C.; Ning, J.; Li, S.; et al. Exosomal miR-21 from tubular cells contributes to renal fibrosis by activating fibroblasts via targeting PTEN in obstructed kidneys. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8660–8673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, I.Y.; Kim, J.N.; Jun, J.Y.; You, H.J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Park, K.-S.; Yoon, S.P. Repression of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease by p53-dependent apoptosis in hydronephrosis-induced rat kidney. Free. Radic. Res. 2011, 45, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.-F.; Chu, H.; Peng, B.; Liu, X.; Cao, Y.-S. Outcome analysis of early surgery and conservative treatment in neonates and infants with severe hydronephrosis. J. Int. Med Res. 2021, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isali, I.; McClellan, P.; Wong. , T.R.; Gupta, S.; Woo, L. A systematic review of underlying genetic factors associated with ureteropelvic junction obstruction in stenotic human tissue. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2022, 18, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkul, T.; Kucukodaci, Z.; Iseri, C.; Karademir, K.; Erden, D.; Baloglu, H.; Narin, Y. The Smooth Muscle Ratio at the Renal Pelvis in Adults: Does It Predict Surgical Outcome? Urol. Int. 2004, 73, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajbafzadeh, A.-M.; Payabvash, S.; Salmasi, A.H.; Monajemzadeh, M.; Tavangar, S.M. Smooth Muscle Cell Apoptosis and Defective Neural Development in Congenital Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction. J. Urol. 2006, 176, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishahi M. et al., “SMOOTH MUSCLE CELLS AND COLLAGEN FIBRES ARCHITECTURE IN EQUIVO-CAL URETEROPELVIC JUNCTION OBSTRUCTION: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY STUDY WITH CLINI-CAL CORRELATION IN ADULT EGYPTIANS,” 2020.
- Hinz, B. The extracellular matrix and transforming growth factor-β1: Tale of a strained relationship. Matrix Biol. 2015, 47, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Lipson, K.; Wong, C.; Teng, Y.; Spong, S. CTGF is a central mediator of tissue remodeling and fibrosis and its inhibition can reverse the process of fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2012, 5, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; He, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yu, D.; Sun, L.; Cheng, G.; Liu, D.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, Z. miR-15a-5p suppresses inflammation and fibrosis of peritoneal mesothelial cells induced by peritoneal dialysis via targeting VEGFA. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 9746–9755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.-H.; Duan, G.-R.; Luo, X.-D.; Xie, Y.-M.; Luo, H.; Zhou, Y.-X.; Pan, B.-R. Expression of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in rats with hepatic fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Vaughan, D.E. PAI-1 in tissue fibrosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.; Bakir, A.S.; Shabana, S.S. Serum TGF-β, Serum MMP-1, and HOMA-IR as non-invasive predictors of fibrosis in Egyptian patients with NAFLD. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladouceur, M.; Baron, S.; Nivet-Antoine, V.; Maruani, G.; Soulat, G.; Pereira, H.; Blanchard, A.; Boutouyrie, P.; Paul, J.L.; Mousseaux, E. Role of myocardial collagen degradation and fibrosis in right ventricle dysfunction in transposition of the great arteries after atrial switch. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 258, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganger, M.T.; Dietz, G.D.; Ewing, S.J. A common base method for analysis of qPCR data and the application of simple blocking in qPCR experiments. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horbelt, D.; Denkis, A.; Knaus, P. A portrait of Transforming Growth Factor β superfamily signalling: Background matters. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarakoon, R.; Overstreet, J.M.; Higgins, P.J. TGF-β signaling in tissue fibrosis: Redox controls, target genes and therapeutic opportunities. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Gao, H.; Ji, S.J.; Wang, C. The expression of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta1 in the stenotic tissue of congenital pelvi-ureteric junction obstruction in children. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2003, 38, 1656–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, O.; Kaya, C.; Ozturk, M.I.; Gunes, M.; Gumrukcu, G.; Karaman, M.I. Analysis of expression of TNF-alpha and TGF-beta3 in intrinsic ureteropelvic junction obstruction. Bratisl. Med J. 2013, 114, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seremetis, G.M.; Maizels, M. TGF-beta mRNA expression in the renal pelvis after experimental and clinical ureteropelvic junction obstruction. J. Urol. 1996, 156, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duymelinck, C.; Dauwe, S.E.; De Greef, K.E.; Ysebaert, D.K.; Verpooten, G.A.; De Broe, M.E. TIMP-1 gene expression and PAI-1 antigen after unilateral ureteral obstruction in the adult male rat. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, 1186–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.E.; Lazos, S.A.; Tong, K. Angiotensin II regulates the expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cultured endothelial cells. A potential link between the renin-angiotensin system and thrombosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Vaughan, D.E. PAI-1 in tissue fibrosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görbe. ; Magyar, Z.; Schönleber, J.; Romics, M.; Hruby, E.; Nagy, B.; Sulya, B.; Beke, A.; Harmath,.; Jeager, J.; et al. Expression of VEGF in Neonatal Urinary Obstruction: Does Expression of VEGF Predict Hydronephrosis? Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 1319–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickelhaupt, S.; Erbel, C.; Timke, C.; Wirkner, U.; Dadrich, M.; Flechsig, P.; Tietz, A.; Pföhler, J.; Gross, W.; Peschke, P.; et al. Effects of CTGF Blockade on Attenuation and Reversal of Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle-Tenney, R.; Rebolledo, D.L.; Lipson, K.E.; Brandan, E. Role of hypoxia in skeletal muscle fibrosis: Synergism between hypoxia and TGF-β signaling upregulates CCN2/CTGF expression specifically in muscle fibers. Matrix Biol. 2020, 87, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roestenberg, P.; van Nieuwenhoven, F.A.; Joles, J.A.; Trischberger, C.; Martens, P.P.; Oliver, N.; Aten, J.; Höppener, J.W.; Goldschmeding, R. Temporal expression profile and distribution pattern indicate a role of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN-2) in diabetic nephropathy in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2006, 290, F1344–F1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang X. and Cretoiu D., “Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 913 Telocytes Connecting Cells.” [Online]. Available online: http://www.springer.com/series/5584.
- Huang, B.-L.; Brugger, S.M.; Lyons, K.M. Stage-specific Control of Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CTGF/CCN2) Expression in Chondrocytes by Sox9 and β-Catenin*. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 27702–27712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airik, R.; Trowe, M.-O.; Foik, A.; Farin, H.F.; Petry, M.; Schuster-Gossler, K.; Schweizer, M.; Scherer, G.; Kist, R.; Kispert, A. Hydroureternephrosis due to loss of Sox9-regulated smooth muscle cell differentiation of the ureteric mesenchyme. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 4918–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampawong, S.; Klincomhum, A.; Likitsuntonwong, W.; Singha, O.; Ketjareon, T.; Panavechkijkul, Y.; Zaw, K.-M.; Kengkoom, K. Expression of Aquaporin-1, -2 and -4 in Mice with a Spontaneous Mutation Leading to Hydronephrosis. J. Comp. Pathol. 2012, 146, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paces-Fessy, M.; Fabre, M.; Lesaulnier, C.; Cereghini, S. Hnf1b and Pax2 cooperate to control different pathways in kidney and ureter morphogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 3143–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




