1. Introduction
One of the main issues facing the modern civilized world is the global energy crisis and the threats posed by climate change. The primary identified causes of the aforementioned concern are the depletion of fossil fuel reserves and the release of greenhouse gases. Solar, wind, and tidal energy are examples of renewable energy sources (RES) that are the solution to these problems. Solar energy is one of these RES that is considered to have the potential to resolve the crisis because it is abundant and cost-free [
1,
2]. Due to its emergency qualities and affordability, solar power has emerged as among the world’s primary sustainable power sources. In order to combat energy shortages, solar energy has also emerged as a substitute source. The key benefits of solar energy are that it is pollution-free, abundant, clean in nature, and requires less maintenance [
3]. Solar energy is transformed into controlled electrical energy using photovoltaic (PV) cells and a power electronics converter. These PV solar cells have nonlinear properties, The reliability of solar PV is dramatically decreased because of the indiscriminate properties of solar power and environmental circumstances [
4]. As a result, the solar PV system’s maximum power output varies according to changes in irradiance and weather. In different climatic conditions, such as partial shade, the characteristics of solar cells grow more complex [
5,
6]. These problems make it necessary for researchers to enhance the power output of solar PV cells under fluctuating atmospheric conditions. The writers of [
7,
8] have thoroughly detailed several optimum power tracking approaches to attain maximum power. A charge controller-equipped battery charger is also essential for maximizing the transmission of electricity from solar PV to the battery bank.
A charger for batteries with a charge controller’s primary job is to i) It aids to extract the maximum available energy from the solar panel and operate the panel at possible maximum voltage and current conditions by adjusting the duty ratio in the charging algorithm. ii). It shortened the battery charge duration and supported the photovoltaic arrays. Moreover, it prevents the battery from being overcharged and discharged, extending its life. By taking into account the key benefits of the charge controller used in this article, the authors are concerned with building an appropriate charge controller that enhances the charging ability and effectively extends battery exitance with optimal charging speed. Also, a comparative analysis has been done by contrasting the charge regulators suggested by the different authors in the existing compositions. A PV charge controller’s algorithm controls the efficiency of PV array usage and battery charging, enhancing the system’s capacity to fulfill the demand for electrical load. Charge controllers in series, shunt, PWM, and MPPT are the varieties of charge controllers for solar PV that are most frequently employed. [
9] The series controller uses a control component that connects the batteries and a solar panel in a series. Due to the existing limits of shunt controllers, this charge regulator is frequently employed with compact PV systems and can be employed for effective systems. The shunt regulator controls the battery charging using the solar panel by impeding the PV array inward to the regulator. This charge controller is primarily employed to control current or voltage to prevent storage batteries from being overcharged and deeply discharged, which might harm the batteries [
9]. The sluggish charging period of distributed battery cells has been acknowledged as a drawback, and a quick and effective solution is the pulse-based charging approach.The pulse frequency for controlling the battery charge duration will be dynamically changed within a specific range to inject the maximum charge current into the battery cells. To furnish the battery pack with a long-life cycle, we designed a quick method for charging batteries according to the recommended frequency and workload cycle while defending against over-voltage or overheating situations for battery cells.
1.1. Background and Motivation
PV is One of the energy resources that can generate electricity without relying on fossil fuels like coal and petroleum. The main issue with solar energy is that it has lower conversion efficiency and higher installation costs. Research is focused on this area to create an effective control mechanism and optimum control. So, the overall fitting charges of the photovoltaic charging systems are minimized. The demanding research work in this area is the motive behind the research work. Most “12 volts” panels generate around 16 to 20 volts; Thus, if there is no regulation, overcharging will cause harm to the batteries [
10]. The primary role of a charge regulator is to sustain the battery at the maximum potential energy state. Charge-controller device preserves the battery from overcharging and detaches the load to obstruct the deep discharge. The ideal scenario is for the charge controller to directly regulate the battery’s condition, equivalent to constant potential charging [
10]. In the absence of a charge controller, depending on the irradiance, power from the PV module will flow into a battery, whether or if the battery has to be charged. Uncontrolled charging will result in an extremely high battery voltage if the battery is fully charged, which hastens grid corrosion, electrolyte loss, internal heating, and severe gassing [
11,
12]. The charge controller maintains the battery in good condition and increases its lifespan.
The charge controller adjusts charge rates depending on battery capacity and monitors battery temperature to prevent overheating[
12,
13]. The charge controller uses the PWM technique to generate pulses to the battery with multiple duty ratios. In essence, it performs the function of an intelligent switch between solar cells and batteries, managing the voltage and current flowing into the batteries. The benefits of PWM charge regulators are as follows:(i) increased battery life, (ii) increased recharge effectiveness, (iii) lessens the battery’s stress and (iv) battery overheating is less frequent, (v) the capacity of a battery can be restored. Here The charge controller acts as a switch that connects the battery with the PV panel through PWM operation. When the switch is closed, the battery and panel will be at almost the matching voltage.
The PWM protocol algorithm integrated with the solar charge controller improves the amount of current from the PV module into the battery. In order to precisely match the PV module to the battery, the PWM charge regulator is a DC/DC adapter that accepts DC as input from the solar module, turns it to AC, and then changes it to stabilize to a different DC potential and current. Solar charge controllers benefit standalone PV systems, solar housing systems, off-grid PV power systems, and some rural places [
15,
16]. It extracts the maximum accessible energy from the PV component by composing them to run at the most effective voltage. It inspects the yield of the PV component, compares it to the battery voltage, and then finalizes the admirable power that the PV module can initiate to charge the battery and change it to the best voltage to get the utmost ampers into the battery.
Additionally, it can power a DC load that is straitly attached to the battery. MPPT is most effective when the weather is cold, cloudy, or foggy and when the battery is thoroughly discharged. The benefits of MPPT in this kind of system would be substantially lower. However, there would be no drawbacks to utilizing an MPPT regulator on a solar module with a voltage nearby the battery potentiality [
17,
18].
1.2. Pulse Mode Technique
In this state, the battery receives a pulse current or voltage and has low impedance during the relaxation intervals of these pulses. This low impedance enhances power transfer by enabling the subsequent charge pulse to enter the battery more effectively and prevents overheating and overvoltage gassing [
19,
20].The increased discharge capacity of the pulse-charged battery shows that the pulse technique may effectively utilize the battery’s active components without overcharging while still providing long cycling existence [
19,
21]. The effect of the pulse method charging on the cycle period of Li-ion batteries was investigated, and it proved that the pulse technique enhanced the lifespan of batteries as to dc imposing techniques [
19,
22]. Although there has been much research on battery charging, there is still a need to optimize battery charging performance.
2. Materials and Methods
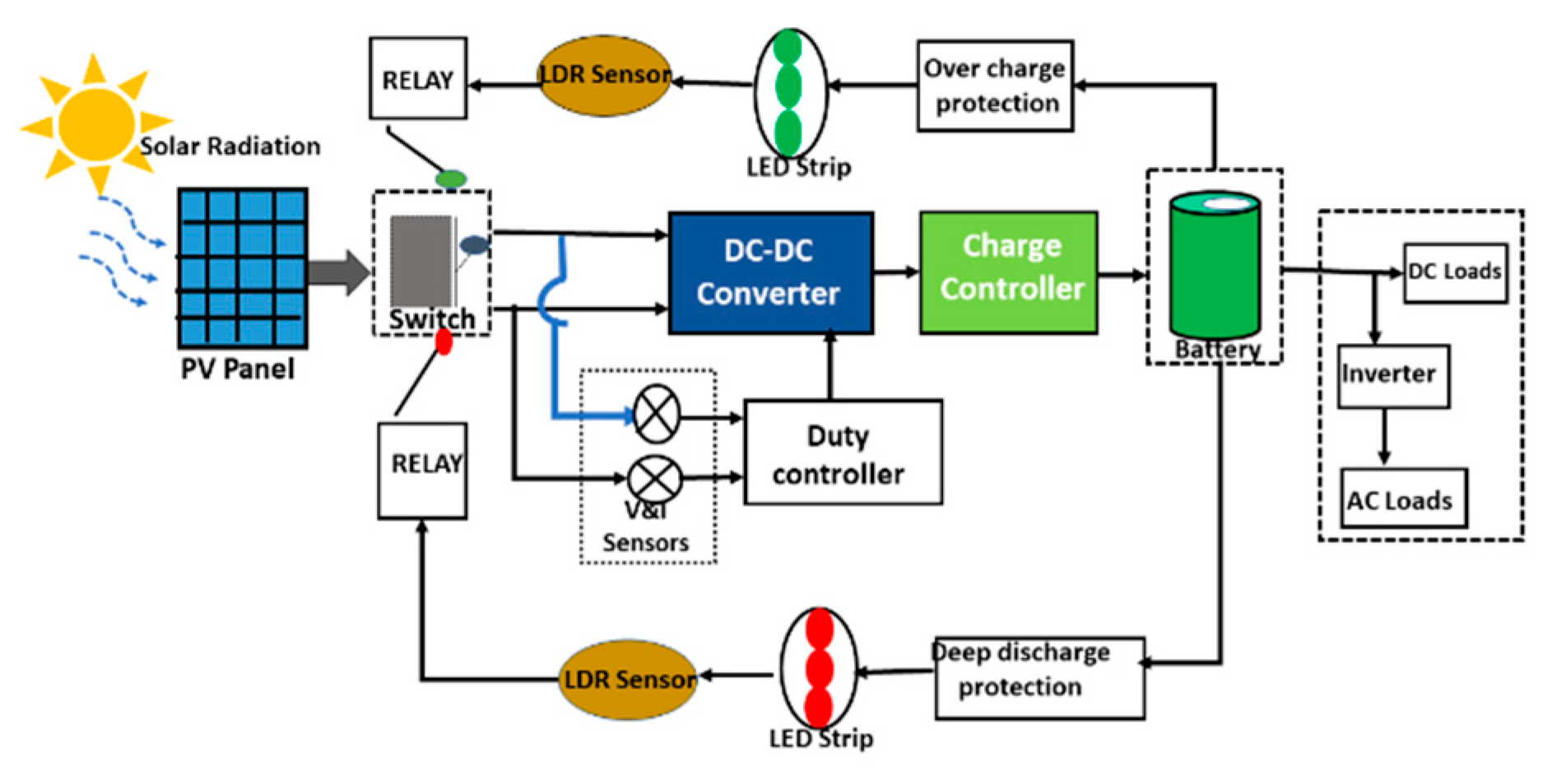
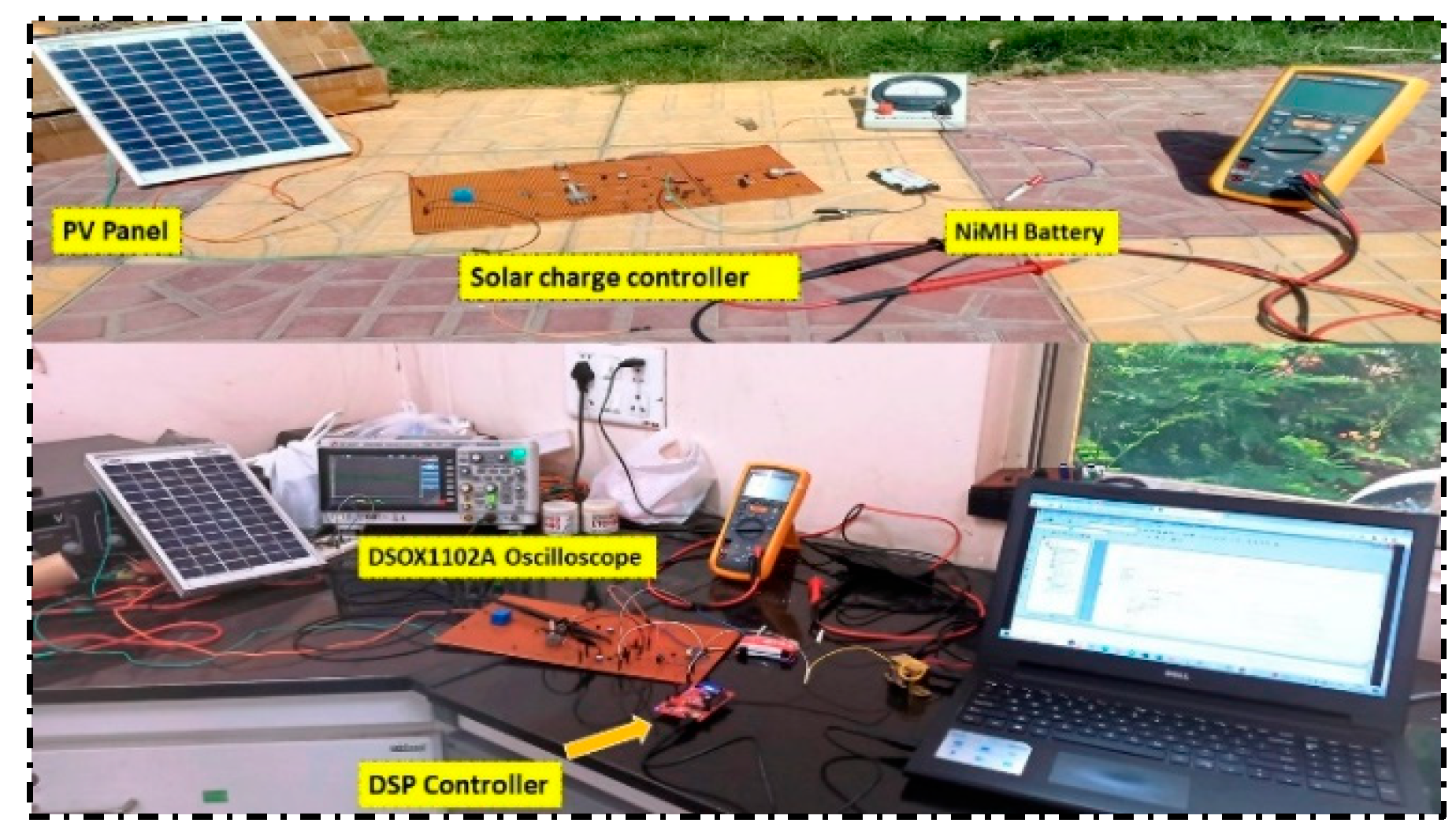
Figure 1, depicts the structural illustration of the preferred system, in which PV panel output current and voltage are sensed and provided to the microcontroller. The microcontroller is set up to carry out the Pulse width modulation operation to maintain the system operating at the highest power level to extract the total power from the PV source. The DSP controller produces pulses, whose frequency changes to monitor the solar panel’s maximum voltage point, and the MOSFET switch of the dc-to-dc converter receives this pulse. ACS712 module is utilized here as a current sensor, while the LM358 op-amp is used as a voltage sensor, and the DSP TMS32028027F is for regulating. The power generated by the dc converter is given to the solar charge controller. The proposed system comprises three circuits: a front-end dc-dc converter, isolation circuits, an intermediate battery charging circuit, and a sensor and control circuit. AC loads are connected to the battery through inverting output.
The size of the PV panel is 36 cells 12V/5W has been used to charge two cells in a series of 1200mAh ratings for a wide selection of input voltages from 5 to 22V. The final accepted charging current is limited to 250mA. For longer battery life, it also has overcharge and reverses polarity protections.
2.1. PV Equivalent Circuit Analysis
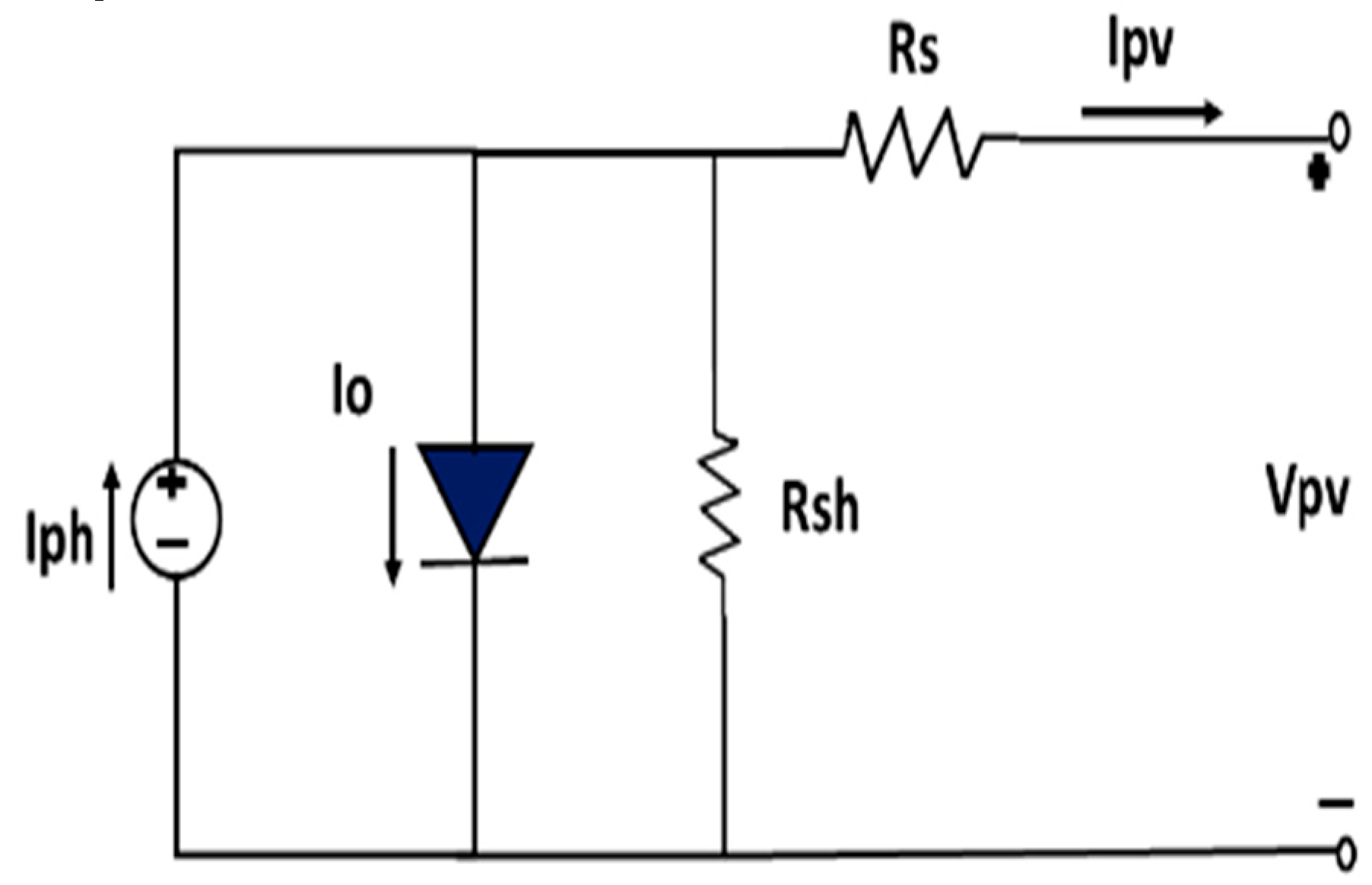
Generally, a current source and a reverse diode analogous can represent a solar cell. It has its own internal parallel and series resistance. Parallel resistance is caused by leakage current, while series resistance is caused by obstructions in the movement of electrons from the N to P union. When irradiance strikes its surface, an electrical field is created inside the solar PV cell [
23,
25]. This development can generate power for an outermost circuit when an electric field is present. The strength of the incident radiation affects the produced current. More electrons can be released from the surface at higher light intensities, which results in a more significant current generation [
24,
25,
26]. The source current I
pv indicates the unit photocurrent and R
sh is used to indicate the solar unit’s intrinsic shunt and series resistance, respectively. Generally, R
sh and R
S have very high and low values; therefore, it is feasible to omit them to simplify the analysis. PV array is simplified by using mathematical eqn (i)-(iv) and pv characteristics are shown in
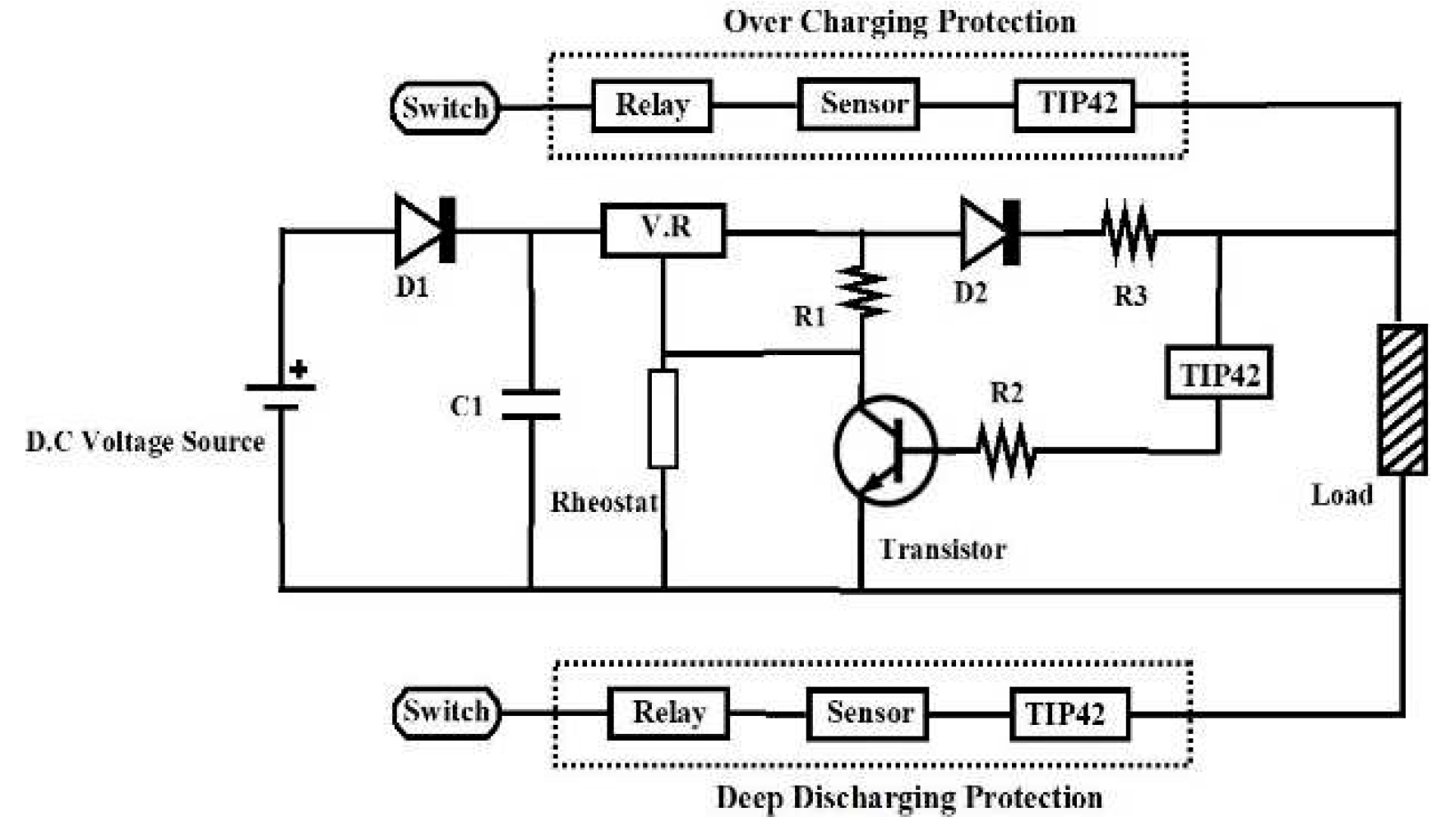
Table 2. An equivalent circuit model of the proposed charge controlled is shown in
Figure 2. It is the composition of advanced protection circuits using sensors and TIP42C is used to discharge the high currents to the grounds. A current source connected simultaneously to a diode simulates the ideal PV cell. Resistances in series and shunt are added to the model, as shown in
Figure 3 because no solar cell is perfect.
Figure 1.
Proposed charge controller detailed block diagram.
Figure 1.
Proposed charge controller detailed block diagram.
Figure 2.
Equivalent circuitdiagram.
Figure 2.
Equivalent circuitdiagram.
Figure 4.
DC-DC converter equivalent circuit diagram.
Figure 4.
DC-DC converter equivalent circuit diagram.
Here Io is the PV module’s current.
PV module voltage is Vo.
The reference temperature in Kelvin is Trk.
Tak is the operating temperature in Kelvin.
1.380649
10-
23 J/k is the Boltzmann constant [
27]
Electron charge (q)= 1.602
10-
19 C [
28]
Rs is a PV module’s series resistance.
The short-circuit and current temperature co-efficient (Ki) at Iscr is defined as Iscr, the PV module short-circuit current at 250C, and 1000W/m2 = 2.55A.
Table 1.
Electrical Characteristics of Data of JIGHISOL System Pvt Limited: 12V5W, Model No:0117003479.
Table 1.
Electrical Characteristics of Data of JIGHISOL System Pvt Limited: 12V5W, Model No:0117003479.
| PV Module Electrical Parameters and Ratings:5W/12V |
|---|
| Maximum Power (MPmax) |
5W/12V |
| Potential at Ultimate. Power (Vmp) |
17.40V |
| Current at Optimum Power (Imp) |
0.26A |
| The voltage at Open Circuit (Voc) |
21.50V |
| Panel current at short circuit (Isc) |
0.32A |
| Tolerance |
+5% |
| Specifications are at STC 1000W/m Irradiance AM 1.5, Cell Temp 25oC |
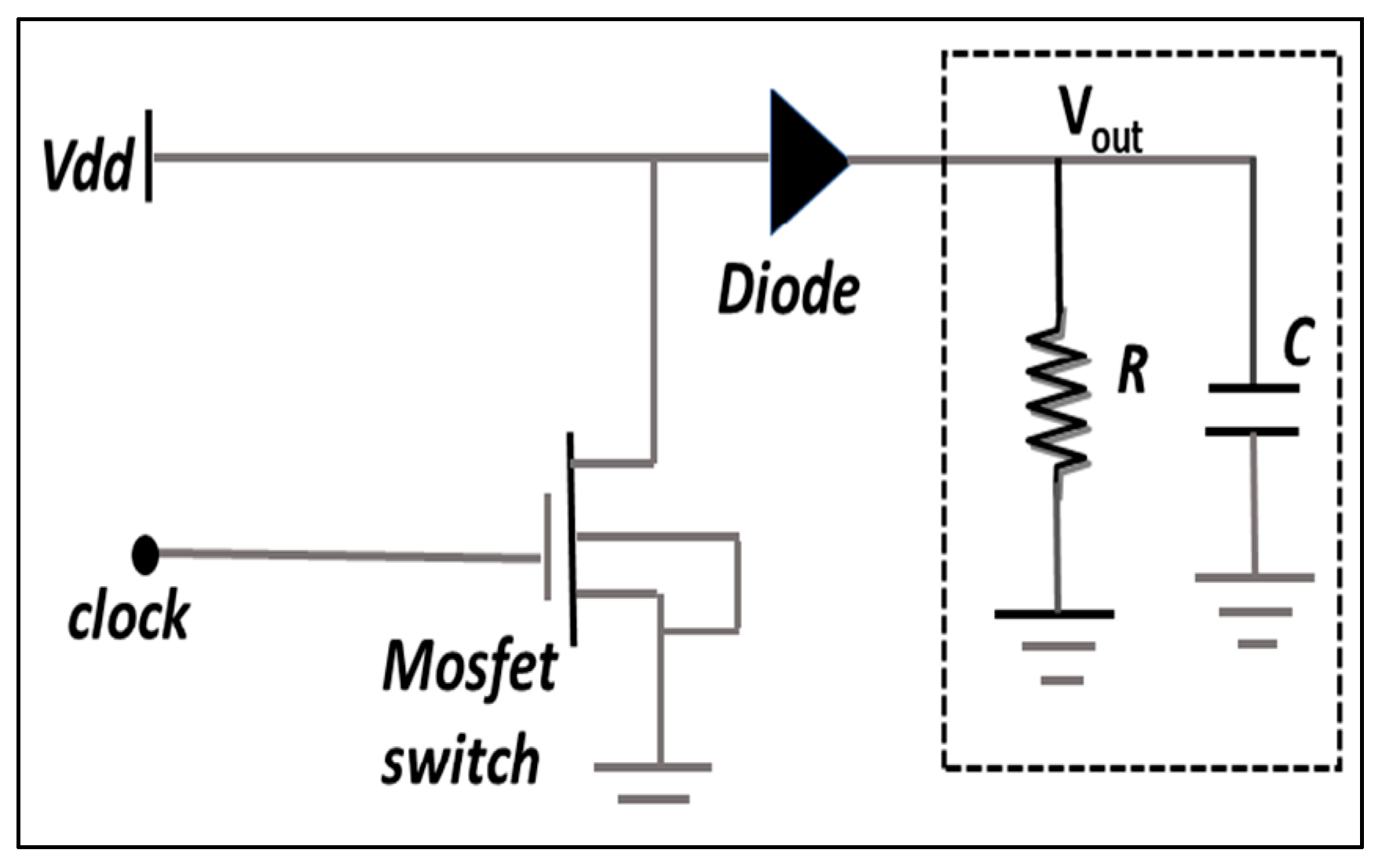
2.2. Converter for dc-dc
By adjusting the duty period (D) of the converter, the switching regulator is used to match the maximum power and voltages (VMPP) at all climatic circumstances with the load voltage (VPV) seen by the PV panel. The load is connected to the module by a dc-to-dc converter through a charge controller that facilitates the delivery of the PV module’s maximum possible power to the load. This chopper circuit is controlled with a pulse width modulation technique using a DSP TMS32028027F [
27]. The equivalent circuit model of the chopper converter is shown in the
Figure 4.
The control circuit’s time ratio is the proportion of a switch’s on-pulse to the duration of one full course.
Here, Ii denotes the input current, and Io denotes the output current.TON stands for turn-on time, TOFF for turn-off time, and Ts for total switching time.
2.3. Control system based on PID
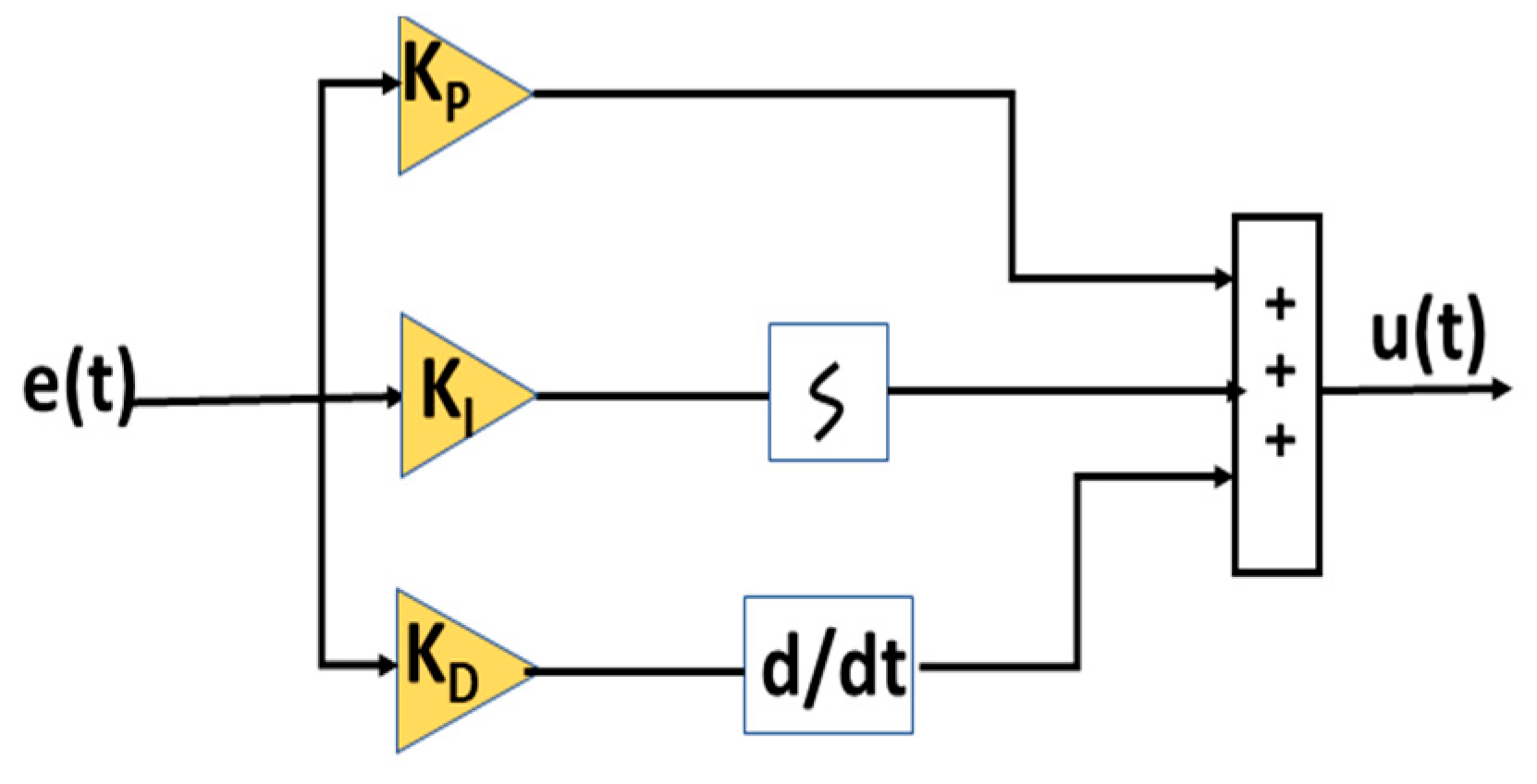
The main objective of the PID controller is tuning the converter circuit to track the total amount of energy from the PV source, is Considering the potential and current of the PV array. The PID controller receives the error waveform produced by comparing the quoted potential with the output potential of the switching regulator. The switch’s gate pulse is activated using the PID controller’s output to increase the solar cell’s power.
Figure 5, illustrates the PID controller’s construction, which may be written as equation (9).
e(t) = controller input, u(t) = regulator output
Potential Gain is Kp.
Integral gain = Ki.
Derivative gain is Kd.
2.4. Solar charge regulator
A charge monitor, further known as a charge regulator, controls the current and voltage to prevent batteries from overcharging. It controls the solar panels’ voltage and current as they feed the battery [
28]. Shunt and series regulation are the two fundamental techniques for managing or regulating battery charging [
10,
29]. Although both techniques are helpful, each may include several variants that change its fundamental functionality and usefulness. The controller is a series type when the MOSFET IC (integrated circuit) component is linked sequentially with the PV layout and the battery. It is referred to as Shunt form when combined in parallel over the PV array or the battery. When the battery is fully charged, the MOSFET switch is kept open in the series type. During this time, the PV Array stops delivering current. When the battery is completely charged, the MOSFET IC is kept shut in the shunt type to shunt (switch) the entire PV array short circuit current away from the battery [
29].
2.5. LDR Sensors
Implementing sensors in the proposed solar charge controller is crucial to achieving the system’s desired functionality. Both voltage and current sensors in the proposed charge controller are the components that will be in charge of observing and reporting to the microcontroller everything that occurs in the system. In addition to these sensors, two light-dependent resistance (LDR) sensors [
30] will also be included to access the system. These two sensors will monitor the battery condition and alert the relay circuit to control the charging process. These sensors must be effective and respond well to the relay switches.
3. Assessment of the experiment and test results
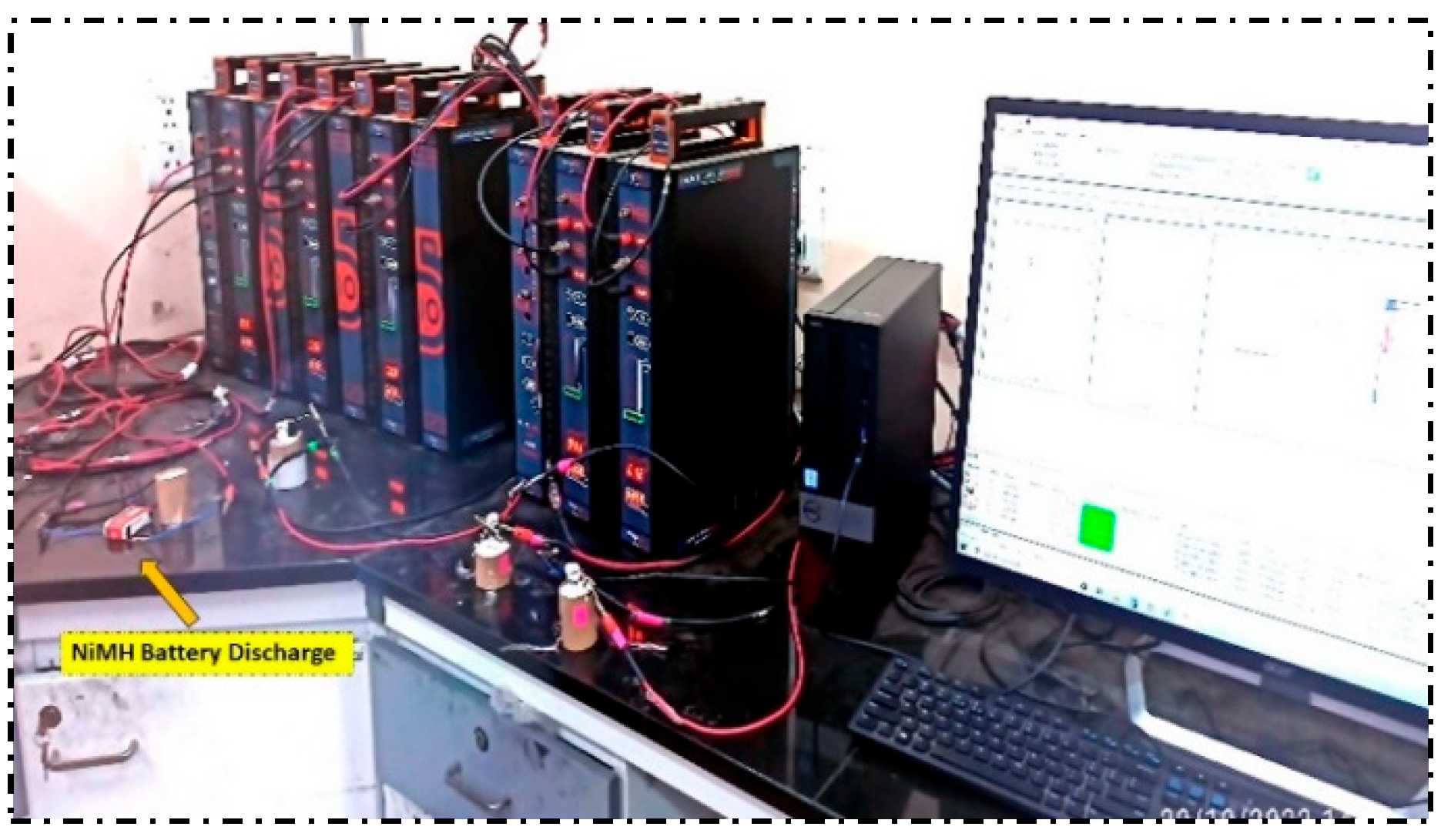
To comprehend and research how well the proposed charge controller, Nickel metal hydride (NiMH) batteries employed for charge-discharge investigations, was the type of battery used in this research. The tested battery cells’ specifications are 1.2V,600mAh, an anode composed of hydrogen-absorbing alloys (MH), a cathode made of nickel hydroxide (Ni (OH)2), and an electrolyte made of caustic Potash (KOH) made up NiMH batteries [
31]. The test was conducted over a while and examined with both charging methods. These batteries are all fully charged using constant amperage and constant voltage [
32] by utilizing a charge controller board. The PV panel, filter capacitor, and voltage regulator make up the charger circuit, LDR sensors, and relay coils, as depicted in
Figure 6. The solar panel is the primary power source linked to the charge controller circuit by a dc-to-dc converter.
The optocoupler (PC817), a crucial component of the power regulation circuit and a source of 5V input for the DSP TMS32028027F, receives a 12V supply from the 12V regulator. The voltage controller IC, which continues the voltage stability and provides a continual DC potential, is connected to the capacitor’s power output. The 78xx category includes the voltage regulators that are utilized. The regulator code number might change conditional on the utilization and needed potentiality. For instance, the regulator utilized is 7812 if the controller supply voltage requirement is 12V. The power circuit is made up of the specified components put together. According to
Figure 6, the power control circuit consists of an Opto-isolator (PC817), a DSP TMS32028027F, and an isolation circuit.
In a short circuit over the semiconductor switch, the optocouplers serve as safety circuits to the PWM controller and power circuit. The optocoupler’s collector is connected to a 12V regulated dc. The gate terminal of the semiconductor switch and the photocoupler emitter pins are interconnected. These can be employed as shifting resistors and have the specified values of 48 ohms and 1.5 k ohms in the circuit. The DSP controller manages the timing of the gate signals. The triggering pulse for the power switch is provided by a selected output pin grounded to the earth plane. The proposed controller circuit is forged and proven with a NiMH battery group of cells. By stepping down the battery potential to the requisite voltage proportion and rectification, this charging circuit is also used for electrical circuits for AC. Then it is right away connected to the charging circuit. We must employ an amp meter and potentiometer to adjust stable voltage and current during this charging procedure and keep track of voltage and current fluctuations. The charger circuit receives power directly from the solar panel, and the duty proportion, which is configured in the Code Composer Studio software, controls the output voltage [
33]; here, NiMH battery pack P and Q are charged using a 60-mA steady current approach, then drained using origalysis electrochemical work station with 50-mA load as shown in the
Figure 7.
Table 3 displays the prototype outcome (charge; discharge) and battery cell capability for pairing pulse and traditional methods. Currently, the TL431 is used as a variable selector; it operates critically combined to divert the over currents to the common ground and guard against the continually charged battery.
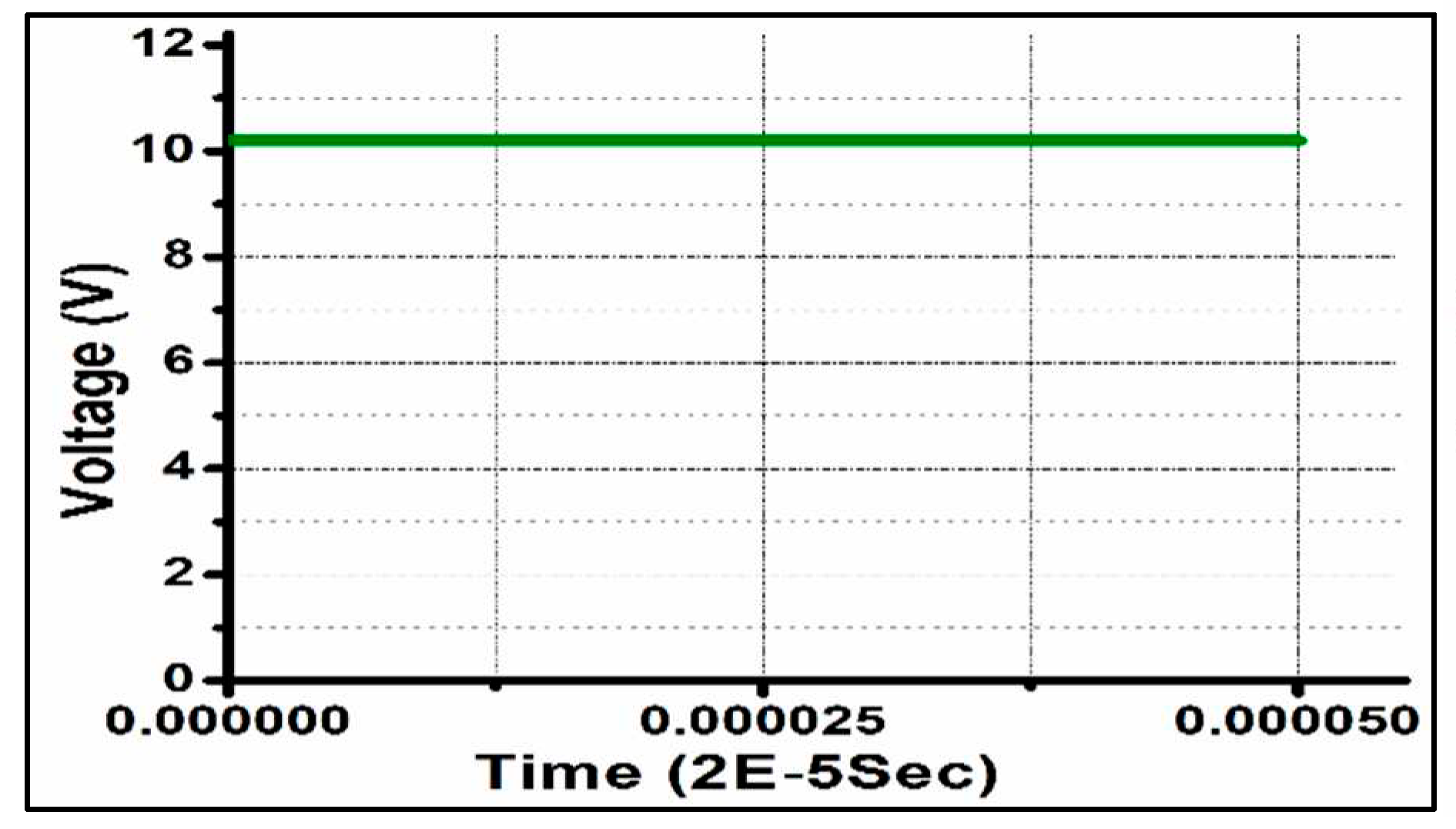
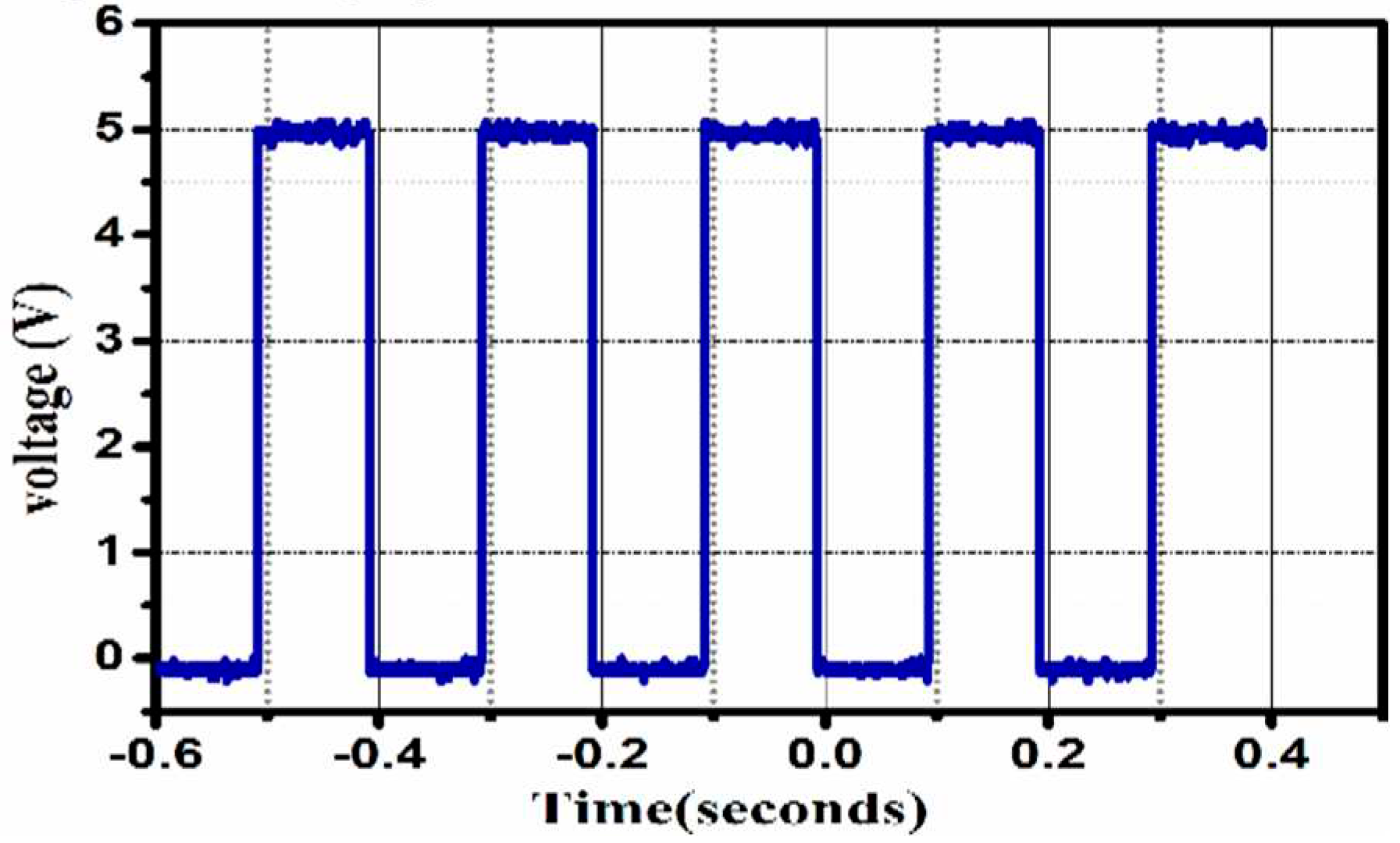
Figure 8 &
Figure 9 indicates input voltage firing pulses to the semiconductor switch.
Figure 6.
Charge controller prototype design.
Figure 6.
Charge controller prototype design.
Figure 7.
Origalysis electrochemical workstation.
Figure 7.
Origalysis electrochemical workstation.
Figure 10.
Output Pulse Burst.
Figure 10.
Output Pulse Burst.
3.1. Traditional Charging Strategy
First, a common technique for charging energy storage devices is Constant Currents Constant Voltage (CCCV). Charges are carried out in constant current mode until the terminal voltage crosses the threshold. With the constant current mode, as V
oc rises, the terminal voltage gradually rises until it exceeds the voltage limit. The charger then changes to constant-voltage mode to fix the terminal voltage and cut down the amplitude of the current. This is due to the internal potential, V
oc, rising when energy is charged, and it is advised for battery safety during charging. The charger must make sure the charging current is less than the highest charging current the battery can tolerate. Due to this technique, chargers disperse energy inequitably, unbalance energy distribution, and experience a higher capacity decrease. The battery charger switches to CV mode from CC mode, where the moving charge rapidly drops [
34,
35]. The result of the current and terminal force is the injected power. As a result, changing the charging strategy to accommodate a continuous power supply is essential because the increase in injected power in the CC mode is noticeable.
3.2. Proposed efficient pulse charging protocol
Pulse magnitude modulation (PMM) and pulse width modulation (PWM) are two alternative ways that the pulse approach can be used [
36]. The pulsed current’s duration is changeable while its amplitude is constant in the PWM mode, as depicted in
Figure 10. The proposed pulse charging approach is the constant current with the relaxation time, as illustrated in
Figure 9&
Figure 10 In contrast, in the PMM mode, the length of the pulsed current is constant, but the pulsed current amplitude is varied. The high-frequency current pulse’s amplitude is constant, and during the relaxation period, the current is zero. The following formula calculates the current pulse’s frequency: T being the pulse period, f = 1 /T. Ton is the current pulse’s duration, and Toff is the relaxation time. Equation no. 7 can be used to calculate the duty cycle of the given pulse. Several factors, including frequency, duty cycle, and ambient temperature, were considered when analyzing pulse mode charging. According to the results of the experiments, pulse mode charging can increase battery capacity and extend battery life by increasing the number of cycles when compared to CC-CV charging. The optimal conditions for pulse mode charging are f
Zmin (around 25 kHz), 50% duty cycle, and 28 °C ambient temperature. Moreover, the charging speed can be improved by 24% compared to the CC-CV charging.
4. Comparative Evaluation and Results with Discussions
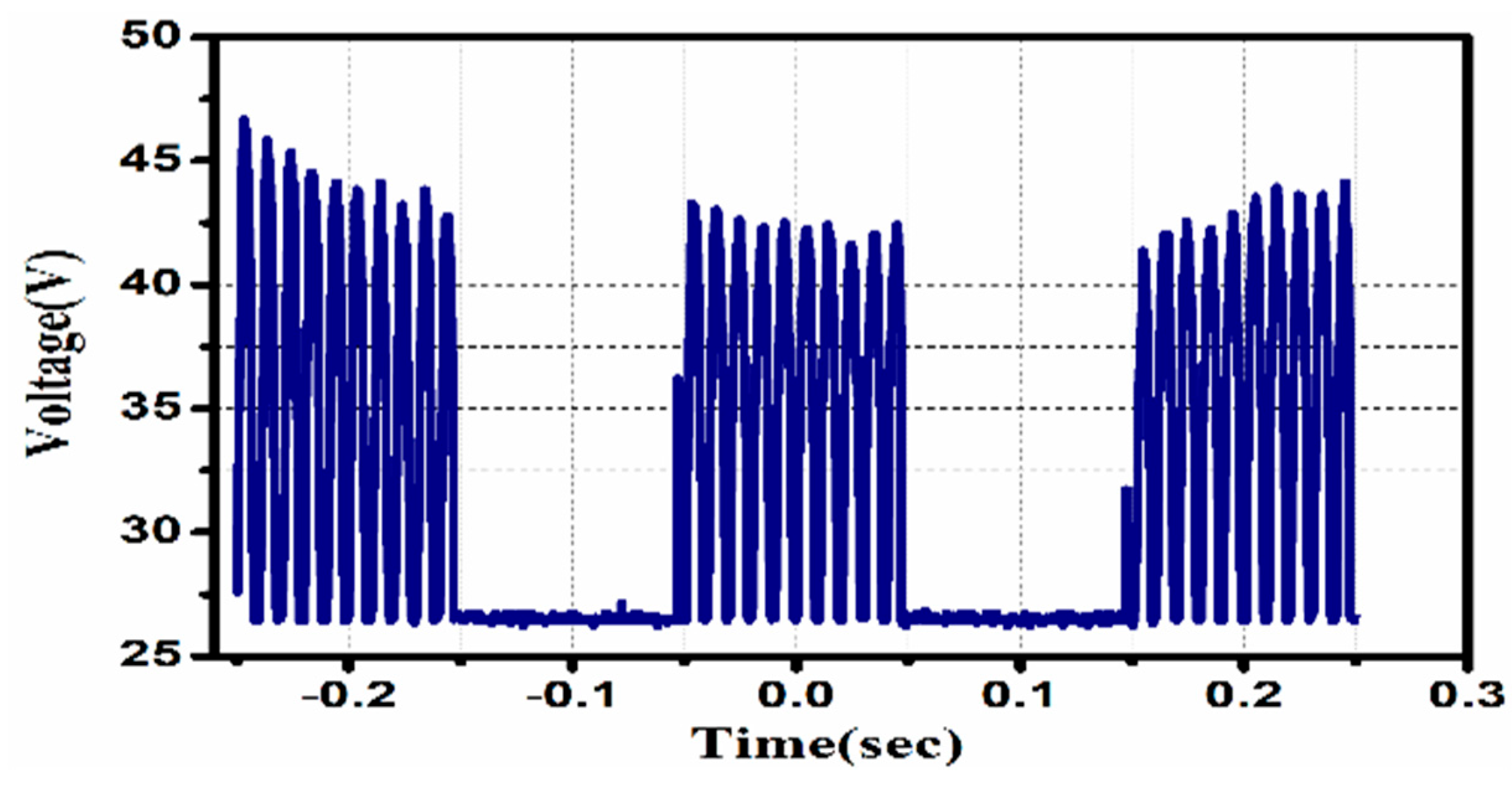
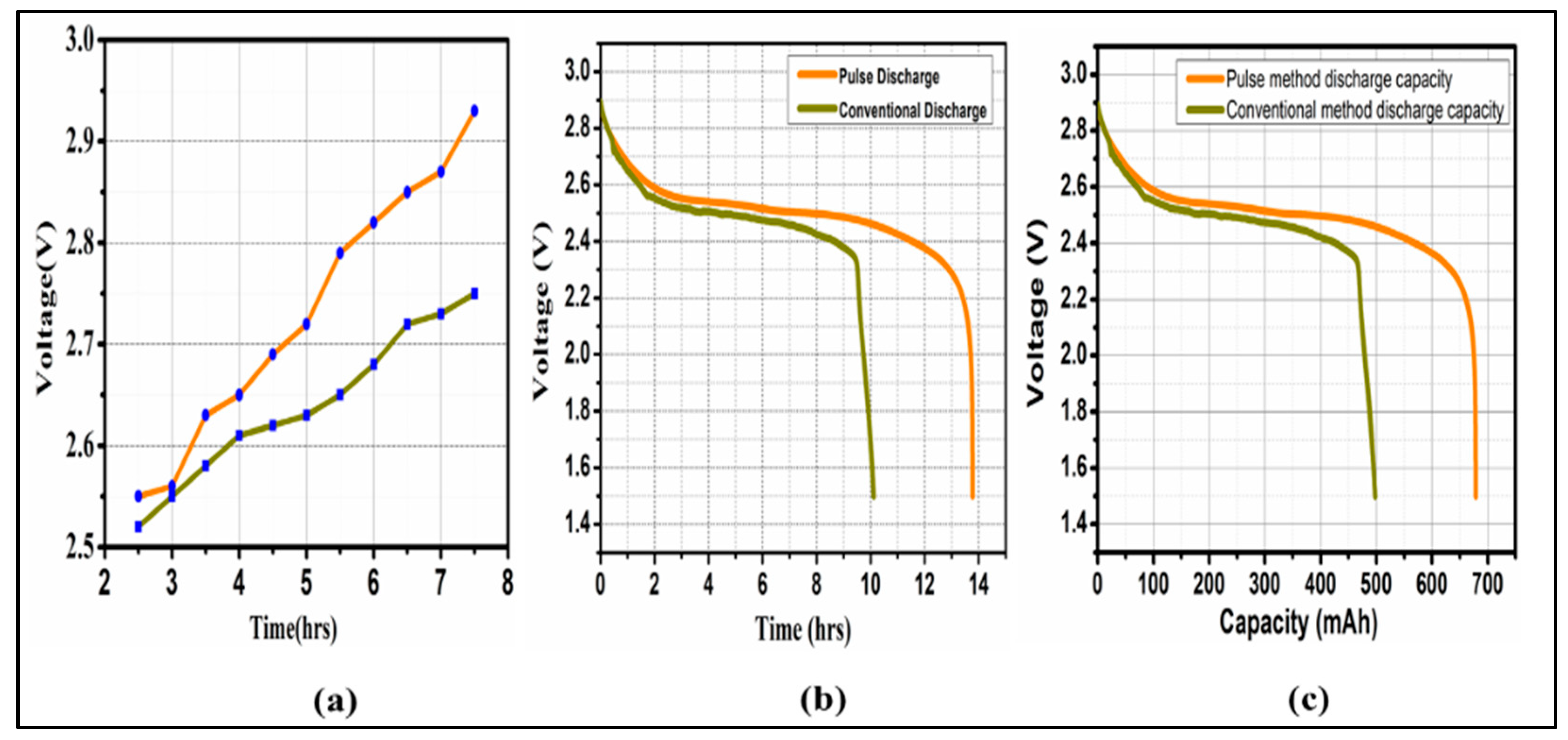
In this part, a comparison between the CC-CV and the fixed pulse (duty cycle of 50%, frequency of 25 KHz) was made. In both methods, the total charging duration is 7:30 hours maximum, based on solar sunlight availability daily. With a total discharge capacity of 498mAh, the CC-CV technique uses 60mA constant current charging that lasts for 10:06 hours as shown in
Figure 10(a&b). The proposed charging method fed to the battery with the same C-rate as the CC-CV method and lasted 13:45h with discharging capacity of 678mAh, as shown in
Figure 10(c). This demonstrates that continuous current in the CC stage keeps the charging process and capacity gains from being sped up.Meanwhile, increasing the parameters of battery impedance and temperature as shown in the thermal and impedance analysis section. The proposed pulse charging current, with optimum performance characteristics, is manifested in
Table 3. The research findings demonstrate that the suggested charge technique accomplishes rapid charging at operational temperature. This is particularly appropriate for the charge of PV-powered batteries and EVs or PHEVs from 15% SOC to 82% SOC levels [
37].
Figure 11.
Charge-discharge studies of NiMHbatteries using pulse and conventional methods (a)Total charge time (b)Total discharge time (c) Total discharge capacity.
Figure 11.
Charge-discharge studies of NiMHbatteries using pulse and conventional methods (a)Total charge time (b)Total discharge time (c) Total discharge capacity.
4.1. Impedance Study
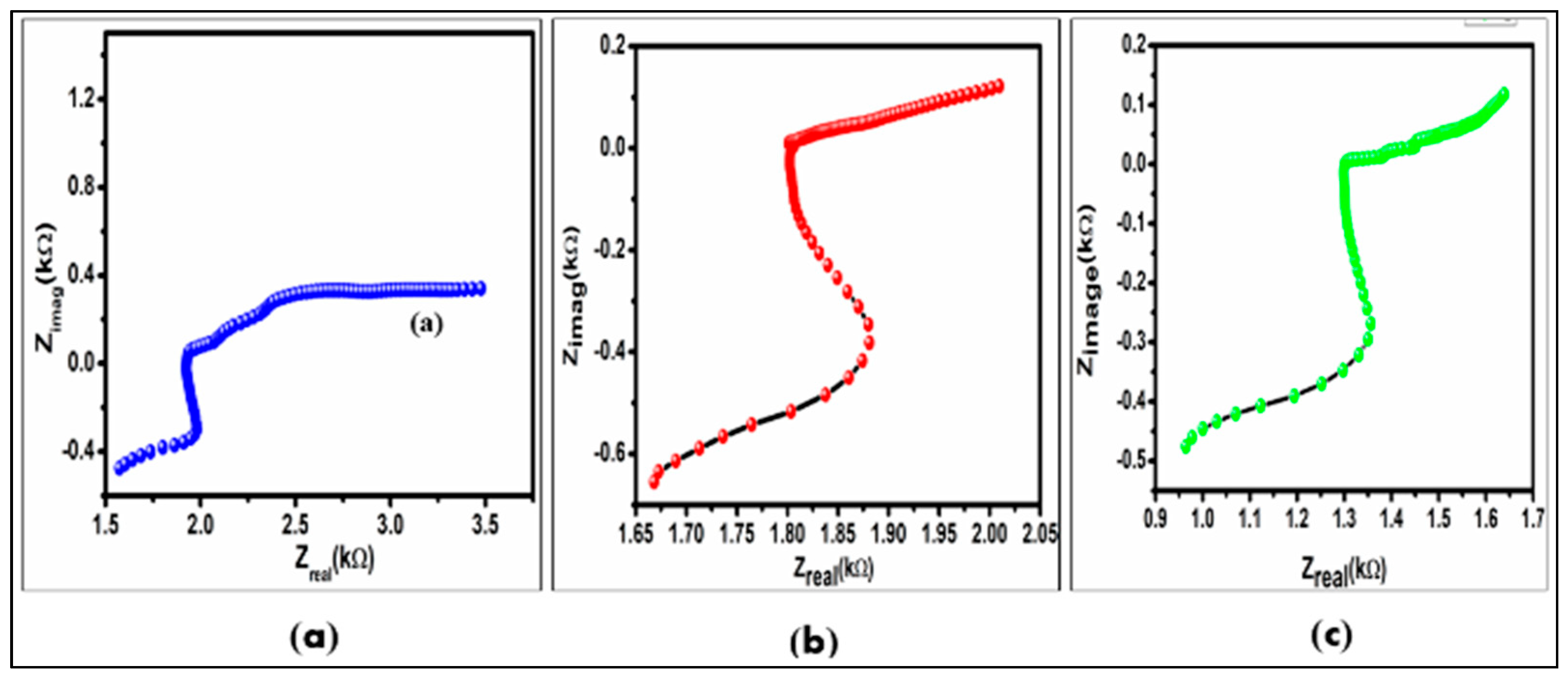
Here the impedance study was done by using dynamic EIS (electrochemical spectroscopy) and we measured the overall impedance by applying an AC of 5mA root mean square (RMS) at a frequency range of 20 kHz to 100mHz, using an electrochemical measurement unit (origamaster-OGFEIS). Connecting a tiny amount of alternating potential, evaluating the current, and gently spreading through a range of frequencies—mostly from a few Hz (or mHz) to thousands of kHz—are the usual methods for obtaining EIS spectra (or MHz).The output data can be mapped in different ways. The highest popular methods are Nyquist plots, which show a comparison of the imaginary and actual impedances (Zimag and Zreal), The advantage of the Nyquist plot, despite being more complicated, is that the charge transfer impedance, time constants, and Warburg impedance, can all be precisely calculated.
Figure 12 shows the impedance studies of NimH battery with different charging protocols and subsequent A Nyquist plot of an EIS, overall impedance before charging was reported as 1.6k Ώ as shown in plot
Figure 12(a), and impedance with conventional charging, i.e.,1.66k Ώ as shown in plot
Figure 12(b), impedance reported with pulse charging, i.e., 0.99k Ώ
Figure 12(c). The electrochemical cell’s charge transfer resistance (R
ct) rises due to the decreased electron transport. The Nyquist plot demonstrates the growth in R
ct with an increment in the boundary of the curve’s semicircle.
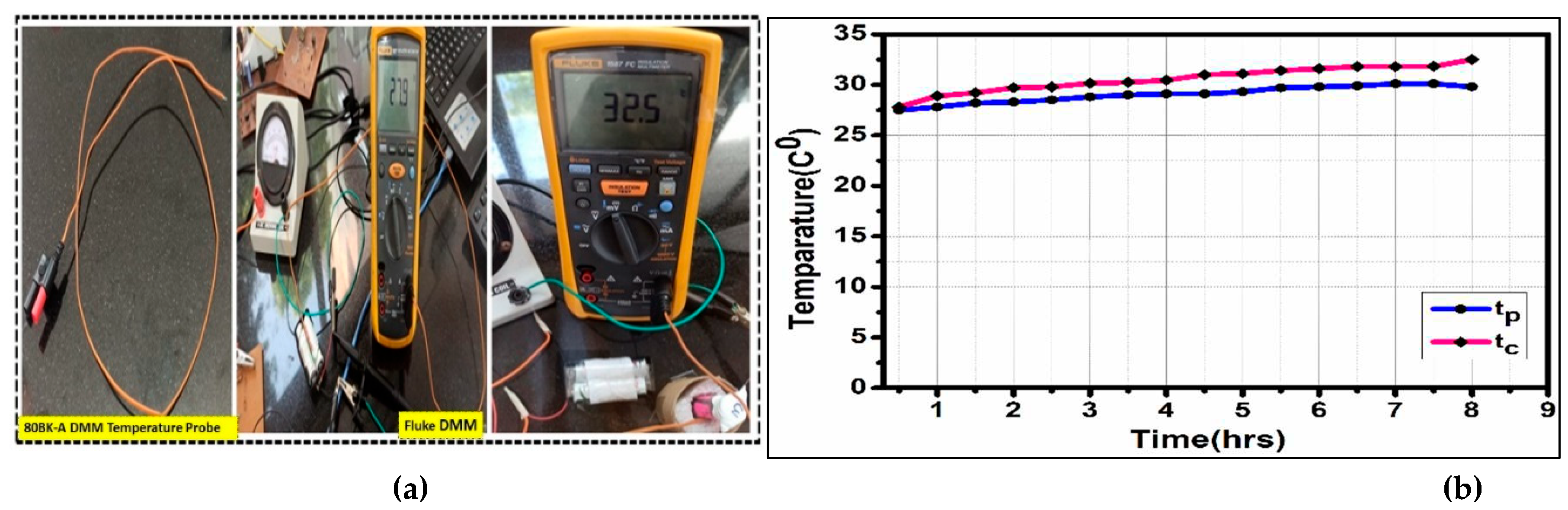
4.2. Thermal Study
To examine the battery’s thermal behavior [
38] during charging and discharge cycles, we use 80BK-A Integrated DMM Temperature Probe to monitor the surface body temperature in both charging methods.
Figure 13(a) shows the experimental comparison of the two methods. The thermal study was conducted at room temperature, i.e. t
r 26
oc and the temperature reported in both the charging methods is t
p =29
oc, tc= 32.5
oc as depicted in
Figure 13(b).
Figure 12.
A Nyquist graph of an EIS study with NiMH battery (a) battery impedance before charging (b) impedance with conventional charging. (c) impedance with pulse charging.
Figure 12.
A Nyquist graph of an EIS study with NiMH battery (a) battery impedance before charging (b) impedance with conventional charging. (c) impedance with pulse charging.
Figure 13.
Thermal analysis of NiMH battery (a) Temperature measurements using sensor probe (b) Temperature variations in both the charging methods (tc & tp).
Figure 13.
Thermal analysis of NiMH battery (a) Temperature measurements using sensor probe (b) Temperature variations in both the charging methods (tc & tp).
Table 2.
Solar charge controller circuit design parameters.
Table 2.
Solar charge controller circuit design parameters.
| Circuit parameters for a prototype solar charge controller |
| Steady Input voltage |
16.5V |
| Input current |
65mA |
| Output voltage |
14.3V |
| Output stable current |
50mA |
| Resistors |
100,180,470,1k ohms |
| Diode |
IN4007 |
| Rheostats |
1k,2k,5k ohms |
Switching Frequency
LDR
Relays
Transistors |
25KHz
6
1
BC 541, TL431, TIP42C |
Table 3.
NiMH Battery charge-discharge study with 60mA CC &50mA load.
Table 3.
NiMH Battery charge-discharge study with 60mA CC &50mA load.
| Battery Specifications |
Traditional Mode Charging |
Pulse Charging |
| Total charging period(hrs.) |
7:30 |
7:30 |
| Total discharging period(hrs.) |
10:06 |
13:45 |
Battery Capacity(mAh)
Battery Cell Voltage (V) |
498
2.7 |
678
2.9 |
5. Conclusions
In this article, the performance and analysis of the solar charge controller with the proposed charging protocol were studied; the system is tested with two charging protocols: the conventional CC-CV method and the proposed pulse protocol. Using two charging methods, dynamic frequency control can minimize impedance while maximizing discharge capacity and time. The duty cycle is carefully managed to maintain the concentration of polarization at a manageable quantity. This ensures the most significant charge speed without causing damage to the battery by causing the charging current to conform to the polarization arc to feed ideal charging currents into the battery cells. The solar charge controller circuit’s lab model is put into practice. NiMH battery cells are used as the load to evaluate the charge controller circuit. The experimental outcomes reported in this study, the NiMH cell’s charge and discharge potential are substantially increased with pulse charging compared to the traditional charging technique; simultaneously, it delivers a more extended discharge period. Graphically
Figure 11(c) and hand-held reading observation can show this. The proposed method utilizes a somewhat sophisticated algorithm and pulse control circuit compared to conventional methods. The implementation of this may be challenging. A significant variation in the charging current can occur, particularly when the charging time and rest period are abruptly switched. Thus, ignoring how the charger affects the power grid is impossible. The CC mode is selected because it has no supply current ripple, which results in much lower RMS currents against the switch and less electromagnetic noise. The results of the experiments indicate that the suggested approach may end up to nearly 70% of its final capacity in roughly 13.45 hours with a battery temperature decrease of roughly 3
0C, and this technique will provide a low impedance during charging.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Dr. Vatsala, and Y. Shyam.; Methodology, Dr. Vatsala, and Y. Shyam.; Software, Y. Shyam, VK Awaar, M eskandar.; validation, Y. Shyam, VK Awaar. and Dr. Vatsala.; formal analysis, Y. Shyam.; investigation, Y. Shyam; resources, Dr. Vatsala.; data curation, Y. Shyam, VK Awaar.; writing—original draft preparation, Y. Shyam, VK Awaar; writing—review and editing, Y. Shyam, VK Awaar.; supervision, Dr. Vatsala, M eskandar.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Please add: “This research received no external funding”
Acknowledgments
The author acknowledges CSIR for providing a research fellowship and is also thankful to Director, CSIR-IICT (Manuscript No. IICT/Pubs./2023/077), for providing all the required facilities to carry out the work. The author gratefully thanks Dr. Pratyay Basak for his valuable suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
Declare conflicts of interest or state “The authors declare no conflict of interest.”
References
- Haque, A. Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) Scheme for Solar Photovoltaic System. Energy Technol. Policy 2014, 1, 115–122, . [CrossRef]
- Solanki, Chetan Singh.; Solar photovoltaics: fundamentals, technologies and applications. Phi learning pvt. Ltd., 2015.
- Bull, S.R. Renewable energy today and tomorrow. Proc. IEEE 2001, 89, 1216–1226.
- Sharma, Swedika.; Modeling and Performance of Solar Photovoltaic Module. 8th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS). 2022 Vol. 1. IEEE, 2022.
- Bouselham, L.; Hajji, M.; Hajji, B.; Bouali, H. A New MPPT-based ANN for Photovoltaic System under Partial Shading Conditions. Energy Procedia 2017, 111, 924–933, . [CrossRef]
- Chhipa, A.A.; Kumar, V.; Joshi, R.R.; Chakrabarti, P.; Jasinski, M.; Burgio, A.; Leonowicz, Z.; Jasinska, E.; Soni, R.; Chakrabarti, T. Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System-Based Maximum Power Tracking Controller for Variable Speed WECS. Energies 2021, 14, 6275, . [CrossRef]
- Alzayed, M.; Chaoui, H.; Farajpour, Y. Maximum Power Tracking for a Wind Energy Conversion System Using Cascade-Forward Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2021, 12, 2367–2377, . [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Chau, K.T.; Liu, W.; Pang, H.; Lee, C.H.T. Maximum Power Tracking for Magnetic Field Editing-Based Omnidirectional Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 12901–12912, . [CrossRef]
- LokeshReddy, M.; Kumar, P.P.; Chandra, S.A.M.; Babu, T.S.; Rajasekar, N. Comparative study on charge controller techniques for solar PV system. Energy Procedia 2017, 117, 1070–1077, . [CrossRef]
- Osaretin, C. A., and F. O. Edeko.; Design and implementation of a solar charge controller with variable output. Electrical and electronic engineering. 2015: 12.2 40-50.
- Koehler, Uwe.; General overview of non-lithium battery systems and their safety issues. Electrochemical Power Sources: Fundamentals, Systems, and Applications 2019: 21-46.
- Eskandari, Mohsen, et al.; Battery energy storage systems (BESSs) and the economy-dynamics of microgrids: Review, analysis, and classification for standardization of BESSs applications. Journal of Energy Storage. 2022: 55 105627.
- Chao, K.-H.; Huang, B.-Z. Quantitative Design for the Battery Equalizing Charge/Discharge Controller of the Photovoltaic Energy Storage System. Batteries 2022, 8, 278, . [CrossRef]
- Di Yin, M.; Cho, J.; Park, D. Pulse-Based Fast Battery IoT Charger Using Dynamic Frequency and Duty Control Techniques Based on Multi-Sensing of Polarization Curve. Energies 2016, 9, 209, . [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, Binayak, et al.; A novel off-grid hybrid power system comprised of solar photovoltaic, wind, and hydro energy sources. Applied Energy. 2014: 133 236-242.
- Taslimi, Melika Sadat, et al.; Assessment and multi-objective optimization of an off-grid solar based energy system for a Conex. Energy Equipment and Systems. 2021: 9.2 127-143.
- Eltawil, M.A.; Zhao, Z. MPPT techniques for photovoltaic applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 25, 793–813, . [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Tian, S.; Cheng, Y.; Bai, L. An Improved MPPT Controller for Photovoltaic System Under Partial Shading Condition. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 5, 978–985, . [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Murphy, E.; Winnick, J.; A Kohl, P. The effects of pulse charging on cycling characteristics of commercial lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2001, 102, 302–309, . [CrossRef]
- Goldammer, E.; Kowal, J. Determination of the Distribution of Relaxation Times by Means of Pulse Evaluation for Offline and Online Diagnosis of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Batteries 2021, 7, 36, . [CrossRef]
- Yadasu, S.; Jetti, V.R.; Awaar, V.K.; Gorle, M. Development of Novel Pulse Charger for Next-Generation Batteries. Energy Technol. 2023, 11, 2200894 . [CrossRef]
- Amanor-Boadu, J.M.; Guiseppi-Elie, A.; Sánchez-Sinencio, E. The Impact of Pulse Charging Parameters on the Life Cycle of Lithium-Ion Polymer Batteries. Energies 2018, 11, 2162, . [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Mu, G.; Tang, X.; Chen, M. Mid-IR Intraband Photodetectors with Colloidal Quantum Dots. Coatings 2022, 12, 467, . [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, M.; Laudani, A.; Lozito, G.M.; Mancilla-David, F.; Fulginei, F.R.; Salvini, A. Low-Cost Solar Irradiance Sensing for PV Systems. Energies 2017, 10, 998, . [CrossRef]
- Al-Ezzi, A.S.; Ansari, M.N.M. Photovoltaic Solar Cells: A Review. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2022, 5, 67, . [CrossRef]
- Bayod-Rújula, Angel Antonio.; Solar photovoltaics (PV). Solar Hydrogen Production. Academic Press. 2019. 237-295.
- Zhang, Ting, et al.; Design and control of a multisensory five-finger prosthetic hand. Proceeding of the 11th world congress on intelligent control and automation. IEEE, 2014.
- Abu Eldahab, Y.E.; Saad, N.H.; Zekry, A. Enhancing the design of battery charging controllers for photovoltaic systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 646–655, . [CrossRef]
- Al-Quraan, A.; Al-Qaisi, M. Modelling, Design and Control of a Standalone Hybrid PV-Wind Micro-Grid System. Energies 2021, 14, 4849, . [CrossRef]
- Marinho, F.; Carvalho, C.M.; Apolinário, F.; Paulucci, L. Measuring light with light-dependent resistors: an easy approach for optics experiments. Eur. J. Phys. 2019, 40, 035801, . [CrossRef]
- Fetcenko, M.; Ovshinsky, S.; Reichman, B.; Young, K.; Fierro, C.; Koch, J.; Zallen, A.; Mays, W.; Ouchi, T. Recent advances in NiMH battery technology. J. Power Sources 2007, 165, 544–551, . [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Wang, S.; Fernandez, C.; Yu, C.; Zou, C.; Jiang, C. A novel practical state of charge estimation method: an adaptive improved ampere-hour method based on composite correction factor. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 11385–11404, . [CrossRef]
- Nichols, Daniel.; Arduino-based data acquisition into Excel, LabVIEW, and MATLAB. The Physics Teacher. 2017:55.4 226-227.
- Lin, C.-H.; Chen, C.-L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Wang, S.-J.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Huang, H.-W.; Chen, K.-H. Fast charging technique for Li-Ion battery charger. 2008 15th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems - (ICECS 2008). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, MaltaDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 618–621.
- Berliner, M.D.; Jiang, B.; Cogswell, D.A.; Bazant, M.Z.; Braatz, R.D. Fast Charging of Lithium-ion Batteries by Mathematical Reformulation as Mixed Continuous-Discrete Simulation. 2022 American Control Conference (ACC). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, United StatesDATE OF CONFERENCE; .
- Tolbert, Leon M., Fang Zheng Peng, and Thomas G. Habetler.; Multilevel PWM methods at low modulation indices. IEEE Transactions on power electronics. 2000: 15.4 719-725.
- Tushar, W.; Yuen, C.; Huang, S.; Smith, D.B.; Poor, H.V. Cost Minimization of Charging Stations With Photovoltaics: An Approach With EV Classification. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2015, 17, 156–169, . [CrossRef]
- Khan, Mohammad Rezwan, Maciej Jozef Swierczynski, and Søren Knudsen Kær.; Towards an ultimate battery thermal management system: A review. Batteries. 2017: 3.1 9.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).