1. Introduction
Millions of people worldwide are undernourished and affected by "hidden hunger", which is caused by a lack of essential minerals and micronutrients. Food items need to contain enough nutrients, whether processed or unprocessed so that these nutrients can be significant contributors to food and nutrition security [
1,
2]. The majority of consumers view food safety as being of the utmost importance [
3]. On the other hand, they are increasingly aware of nutrient uptake and seek to consume more foods that will benefit their health, well-being, and nutritional status. The increased consumption of fruit and vegetable-based products has been motivated by the potential health benefits based on the significant amounts of vitamins, nutrients, and bioactive compounds contained in these products [
4]. Several fruit and vegetable-based products are preferred in their fresh state. However, they have a high perishability and a short shelf life. This limits the amount of time for which they are available and safe for consumption. Processing techniques can increase food choices while increasing the length of time before a food product becomes unfit for consumption. In the manufacture of processed foods, the use of preservation strategies is unavoidable to suppress microbial or enzymatic and non-enzymatic spoilage and therefore, achieve an extended shelf life [
5].
Thermal processing has historically been one of the most extensively used and approved methods to prevent food-borne illnesses and ensure food safety through the inactivation of spoilage enzymes and the destruction of microbial contaminants (pathogenic and spoilage) in foods and beverages [
6]. The intensity of the heat treatment is dependent on the combination of temperature and treatment duration. From a microbiological perspective, intense heat treatment is preferable, but the employment of excessively high temperatures during prolonged times (severe heat treatments) can have deleterious consequences on the flavor, taste, and nutritive quality. Hence, a food product may be free of contaminants, comply with food safety standards and still be nutritionally poor [
7]. For instance, severe heat treatments degrade several heat-labile vitamins (e.g. vitamins A & C, and thiamin) and decrease the biological value (BV) of proteins by denaturing them and reducing their digestibility and bioavailability. The significance of nutrient degradation on nutrition security is determined by the eating habits and consumption frequency of a certain kind of food in the diet. Loss of nutritional value is thus more significant when there is a decrease in nutrients in nutritionally-rich and highly consumed food items that are sources of nutrients for a huge share of the population than in those foods that are either consumed in little quantities or have low nutritional contents [
8,
9].
Novel food processing methods are under investigation to address the loss of nutritional value due to thermal preservation [
10]. Food processors and scientists have been exploring more effective low-temperature technologies that enable high-quality retention to deliver safe food products with acceptable organoleptic and rich nutritional profiles [
7]. Non-thermal processing methods have been employed and among these, ultraviolet irradiation holds great promise as a food preservation technique for pathogen reduction and to minimize nutritional losses observed in heat-processed foods [
11,
12]. Ultraviolet radiation is divided into three categories in terms of wavelength range: UV-A (315-400 nm), UV-B (280-315 nm), UV-C (200-280 nm), and vacuum-UV (100-200 nm) [
13]. The UV-C range possesses great antimicrobial effectiveness which makes it useful for ensuring the microbial safety of foods. The genetic material (DNA or RNA) of microbes strongly absorbs UV photons within the UV-C range, with a wavelength around 260-265 nm corresponding to maximal UV absorption [
14]. The preferred alternative pasteurization and shelf-life extension method for beverages for the past two decades has been UV-C radiation at 253.7 nm [
15]. UV-C irradiation causes damage to the nucleic acids of microorganisms, mainly due to the formation of dimers of pyrimidine bases between adjacent pyrimidines in a DNA strand which prevents microbial replication and ultimately leads to cell death [
16,
17].
UV-C is a non-toxic and non-invasive method with numerous advantages that include the absence of chemical residues, no production of waste, cost-effectiveness (low installation and maintenance cost), simplicity to implement, eco-friendliness, low energy consumption, minimal impact on nutritional quality & organoleptic parameters, and good consumer perception [
11,
15,
18,
19]. The primary drawback of this technology is the poor penetration depth of UV-C, which limits its antibacterial efficacy [
20]. The microbial inactivation efficiency of UV-C is dependent on several factors like the UV-C dose (UV-C fluence), uniformity of UV-C dose distribution, UV-C sensitivity of the target microbial cells, the ability of the microorganisms to repair UV-induced damage, the physicochemical properties of the treated product (e.g. viscosity, density, soluble and suspended solids), and the optical properties of foods (e.g. transparency, absorption coefficient, scattering) [
16,
21,
22,
23]. This poses difficulties in the design of UV-C food treatment devices and for laboratory tests (experiments) that must guarantee a defined and consistent UV-C delivery while ensuring that all the food surfaces are exposed to the UV-C illumination [
22]. This paper provides a review of the impacts induced by ultraviolet pasteurization on the composition of nutrients and bioactive compounds on UV-C treated products. The regulatory standards, associated cost, consumer perception, and limitations of this emerging technology are equally discussed.
2. UV-C light: Principles and Mechanisms of Germicidal Action
Ultraviolet (UV) light has been used as a germicidal agent for over a century due to its ability to inactivate microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. UV-C light is a type of ultraviolet (UV) radiation with a wavelength range of 200-280 nanometers (nm). It is known for its germicidal properties and can be used to disinfect surfaces, air, and water [
21,
24]. The principle behind UV-C light's germicidal action is based on its ability to damage the DNA or RNA of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, through interaction between the UV photons and the genetic material of these microorganisms [
21]. In this sense, UV-C radiation, specifically the 253.7 nm electromagnetic wavelength, has been extensively studied and its germicidal properties are well-established [
21,
22]. When UV-C light penetrates the cell wall of a microorganism, it is absorbed by the DNA or RNA inside the cell. This disrupts the genetic material, which can lead to the formation of new bonds or the breakage of the existing ones. This alteration results in photodimerization, where two adjacent bases in the DNA/RNA sequence bind together. This genetic damage disrupts the affected cells' ability to replicate, rendering them unable to cause infection or pose a threat [
25].
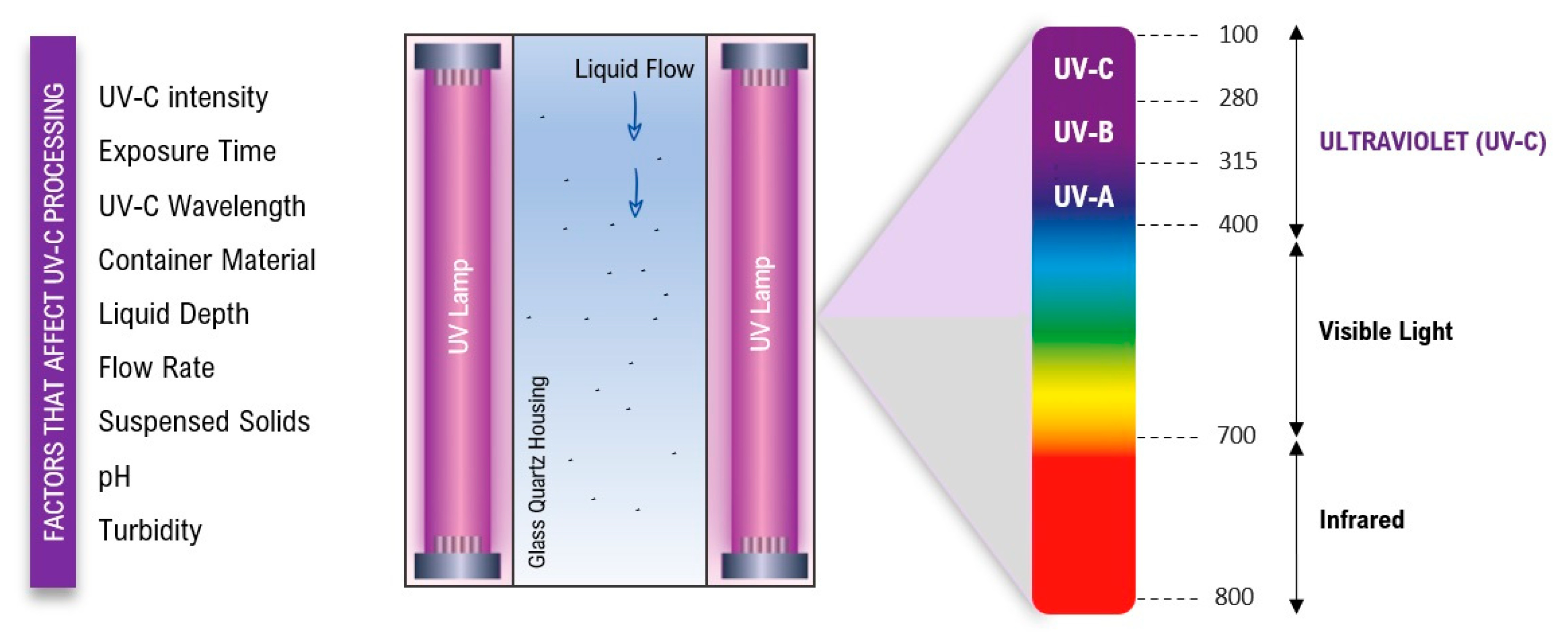
The mechanism of UV-C germicidal action involves several factors, including light intensity, exposure time, and the type of microorganism being targeted, which can vary depending on the specific application [
21,
26]. Furthermore, the germicidal effectiveness of UV-C light as a disinfectant is based on the dose-response relationship, microbial susceptibility, and the optical properties of the food matrices or treated surfaces [
27,
28]. In
Figure 1, the main factors that affect the success of UV-C processing are presented as well as a general representation of the reactor chamber.
It is important to note that these factors are interconnected and should be considered collectively during the design and implementation of UV-C treatment processes for developing shelf-stable food. Higher intensity levels of UV-C radiation generally lead to better microbial inactivation [
29]. However, the duration of UV-C exposure should be optimized to achieve microbial reduction without compromising food quality [
30,
31]. UV-C radiation within the 200-280 nm wavelength range is effective for damaging the DNA and RNA of microorganisms [
32]. Furthermore, the choice of the UV-C wavelength should be based on the target microorganisms and the food product [
25]. The material of the product’s container can affect UV-C treatment, with transparent materials allowing better penetration, as well as the depth of the liquid and flow rate through the UV-C system should be considered for uniform exposure [
33,
34]. At the same time, suspended solids can reduce the effectiveness of UV-C treatment, requiring pre-treatment methods [
24,
26]. The pH and turbidity of the liquid also impact treatment efficiency, and maintaining optimal ranges enhances the effectiveness of UV-C treatment [
26]. From the understanding of these principles, UV-C light technology has been used effectively not only for disinfection and sterilization in various applications, such as healthcare settings, and water treatment, but also in the food industry and more recently as a neutralizing agent of infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 [
22,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39]. Some factors that influence UV-C efficacy are described below.
2.1. Dose-response relationship
The dose-response relationship of UV-C light germicidal action follows a pattern where the effectiveness of killing microorganisms increases with higher doses or intensities of UV-C light [
40,
41]. At lower doses, the light exposure may not be sufficient to cause significant damage to the microorganisms, allowing some of them to survive or repair the damage [
12,
41,
42]. As the dose of UV-C light increases, the likelihood of DNA and RNA damage also increases, leading to a higher rate of microorganism inactivation [
43].
It's important to note that there is an optimal range of UV-C light intensity for germicidal action. [
21] reported that the sensitivity of microbes to UV light varies depending on the wavelength. However, the strong absorption of ultraviolet light by water at wavelengths below 230 nm is a limiting factor for the germicidal effect. Beyond this range, increasing the dose may not significantly enhance the killing efficacy and may even result in diminishing returns. Additionally, excessively high doses of UV-C light can harm human health and damage materials or surfaces [
38,
44]. In this sense, it is crucial to use UV-C light within safe and recommended exposure limits to balance its germicidal efficacy with potential risks.
2.2. Microbial susceptibility
The susceptibility of microorganisms to UV-C light varies depending on their structure and genetic makeup [
24]. UV susceptibility of microorganisms can differ considerably due to differences in cellular elements like cell wall thickness, composition, nucleic acid structure, type of proteins within the cell, photoproducts, the physiological condition of the microbe, and the cell's capacity for repairing damage caused by ultraviolet radiation [
19]. However, it is worth mentioning that the effectiveness of UV-C light as a microbial inactivation method depends on other factors, including exposure time, distance from the UV-C source, and the presence of any physical barriers or shadows that may shield microorganisms from direct UV-C exposure. UV-C light affects microorganisms mainly through the damage caused to their genetic material, either DNA or RNA [
43]. Different microorganisms have varying levels of sensitivity to UV-C-induced DNA/RNA damage. In this sense, viruses with RNA genomes are more susceptible to UV-C light than viruses with DNA genomes [
45]. Another important factor is the cell wall structure. Microorganisms with more robust and resistant cell walls may be more resistant to germicidal UV-C light. Viruses and fungi, on the other hand, may be more susceptible to UV-C light due to their fragile cell walls. Gram-negative bacteria, in general, are more sensitive to UV-C light than Gram-positive bacteria due to their thinner cell walls [
46].
2.3. Optical properties of surfaces
The optical properties of surfaces refer to how they interact with light. These properties can include reflection, absorption, transmission, and scattering of light [
21,
34]. When it comes to UV-C light, the optical properties of surfaces that host microorganisms can affect the effectiveness of UV-C light. For example, Surfaces that are rough or uneven may scatter UV-C light, potentially reducing the intensity of UV-C radiation in a particular direction [
34], and if they are porous, UV-C light can be absorbed. Reflective surfaces can also scatter and absorb UV-C light [
22,
38]. When compared to smooth surfaces, some of these surfaces require roughly two orders of magnitude greater UV-C doses to adequately inactivate microorganisms [
38,
47]. Normally, light transmission refers to the passage of UV-C light through materials. Materials, like certain types of glass, can allow UV-C light to pass through with minimal attenuation, while others may block or attenuate UV-C light, reducing its transmission. [
33,
34].
3. Current Applications of UV-C Light in the Food Industry
The recent consumer demands for safe food with high-quality nutritional (e.g. Vitamins, protein) and sensory (mainly color, flavor, and texture) attributes have challenged the scientific community and the food industry to develop and implement nonthermal technologies to process/manufacture foods while minimizing changes to these attributes [
48,
49,
50]. In this sense, UV-C light has been a promising technology for improving food safety and reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses in the food industry [
21,
24]. In the last decades, the food industry has used this versatile tool for surface decontamination, air, and water treatment, to prevent the spread of microorganisms and ensure food safety and preservation.
3.1. Air Purification and Surface Disinfection
UV-C light is used to purify air in food processing facilities. UV-C lamps can be installed in air handling units to sterilize the air as it circulates through the facility, reducing the risk of airborne contamination [
36]. Air disinfection can be accomplished by irradiating only the upper parts of the room or by irradiating the entire air, either in an empty room or using an air conditioner [
51]. UV-C light is also used to disinfect surfaces following routine cleaning procedures in food processing facilities, including food preparation areas, packaging areas, and equipment. UV-C light can effectively kill bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms that may contaminate surfaces and cause foodborne illness [
36,
52,
53]. Low-pressure mercury lamps are ideal for controlling surface microorganisms in the food industry since 90% of the emitted light is at 253.7 nm wavelength [
54].
3.2. Water Treatment and Food Preservation
UV-C light can be used to sanitize water used in food processing and production as well as to help preventing the growth of harmful bacteria and other microorganisms in municipal water supply systems [
53,
55]. Additionally, UV-C light has been used to extend the shelf life of fresh, minimally processed, and liquid foods by reducing the microbial load, and helping to prevent spoilage [
12,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60].
3.3. Retention of Bioactive Compounds
While UV-C light technology is commonly used for its antimicrobial properties in the food industry, there is also research indicating that it can be used to improve and/or preserve the nutritional properties of fruit and vegetables [
24,
60,
61,
62,
63]. When exposed to UV-C light, certain compounds in foods can be activated or transformed resulting in the production of bioactive compounds that may have health benefits [
64,
65,
66]. Bhat & Stamminger (2014) reported that exposure to UV-C light has been shown to increase the levels of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity in strawberries juice [
48]. In the same way, UV-C light exposure has been shown to increase the levels of certain phytochemicals in plant produce [
67].
Győrfi et al. (2011) identified the capacity of UV-C light to increase the production of vitamin D in mushrooms. When exposed to UV-C light, the ergosterol in mushrooms is converted to vitamin D2, increasing the vitamin D content [
68]. Overall, UV-C light can be a useful tool for producing bioactive compounds in foods, which can enhance their nutritional value and potential health benefits. However, it is important to carefully evaluate the safety and efficacy of these compounds before incorporating them into food products.
4. Ultraviolet light for the preservation of Fruit and Vegetable-based non-Solid Foods
There is a growing demand for fresh foods such as fruits and vegetables that are ready to eat, nutritious, safe, free of additives, and can be included in a healthy diet. However, the convenience and attractiveness of these high-in-demand fresh foods and beverages are affected by rapid spoilage and short shelf life due to changes that can be physical, chemical, microbiological, and enzymatic [
69]. Frequent outbreaks of foodborne pathogens are associated with fresh produce and fruit juices. The addition of chemical preservatives to liquid foods and beverages to extend their shelf life and protect against foodborne pathogens is eliciting negative consumer acceptance. UV irradiation has been used mainly for microbial load reduction in liquid foods and beverages, such as milk, juices, ciders, liquid eggs, beverages, and honey [
19]. In terms of plant-based products, UV has been applied as a non-thermal method to improve the safety and shelf life of products such as vegetables, fruits, cold-pressed juices, plant-derived milk alternatives, and nectars [
26,
70,
71,
72].
Figure 2 demonstrates some possible outcomes from the application of UV-C in the fruit and vegetable sector.
The application of ultraviolet light in developing minimally processed plant-based products holds considerable promise thanks to the excellent germicidal properties of UV-C light for inactivating a wide range of microbial pathogens (e.g. bacteria, fungi, yeasts, molds and viruses) [
26]. As a physical method, irradiation with ultraviolet light has a positive image among consumers and is of interest to the food industry as a low-cost non-thermal preservation method [
21]. Furthermore, the use of UV for processing liquid fruit and vegetable-based foods continues to grow in popularity since it is non-thermal and chemically inert [
73].
4.1. Microbial Inactivating Effect
Liquid food products have a diverse range of physical (e.g. viscosity and density), chemical, and optical properties. Each group of properties must be properly evaluated to design the preservation process and optimize the performance of the UV reactor. The physical properties influence the effectiveness of the fluid momentum transfer and the flow pattern. Optical properties are the main factors affecting UV light transmission and hence microbial inactivation in liquid foods. Chemical composition, pH, dissolved solids (°Brix), and water activity are considered obstacles that can modify the effectiveness of UV inactivation [
21]. The sensitivity of microorganisms to ultraviolet radiation varies significantly due to differences in cellular components, such as cell wall structure, thickness, composition, nucleic acid structure, type of cellular proteins, photoproducts, physiological state of the microorganism, and the ability of the cell to repair the damage caused by ultraviolet radiation [
19].
Numerous applications of UV treatment in plant-based non-solid foods have been recorded. In a study conducted by Caminiti et al. (2010), reconstituted apple juice was exposed to UV light in a continuous laboratory scale system with doses ranging from 2.66 to 53.10 J/cm
2, altering the exposure time. The treated and untreated juices were evaluated for microbial count and selected physical and chemical attributes. Microbiological analysis was performed by inoculating apple juice with
Escherichia coli K12 and
Listeria innocua and the bacterial count was estimated before and after processing. Overall, this study demonstrated that UV technology applied for short periods can represent a valid alternative to the heat treatment of reconstituted apple juice by reducing
E. coli and
L. innocua counts below detection limits [
74]. Mango nectar was UV-C-treated at varying flow rates of 0.073 and 0.451 liter/min and analyzed for yeast and total microbial counts during storage a 3 °C. The highest log reduction obtained from the UV-C exposure at 0.451 liter/min for 30 minutes was 2.71 CFU/ml for the total microbial count and 2.94 CFU/ml for the yeast count [
71].
Table 1 shows some examples of how UV-C light has been used to reduce microbial load in non-solid fruit and vegetable-based foods.
4.2. Preservation of the biological activities of foods
Regarding the use of UV treatments, preventing the loss of nutritional quality and bioactive compounds is the aspect that has received the most attention, after microbial control. Bioactive compounds are extra-nutritional constituents, available mainly in fruits and vegetables, that confer additional health benefits to humans [
81]. A few examples of bioactive components include phytosterols, phytoestrogens, glucosinolates, polyphenols, taurine, carotenoids, flavonoids, carnitine, choline, coenzyme Q, and dithiolthiones. Vitamins and minerals possess pharmacological activity and can also be classified as bioactive compounds for this reason. The majority of biologically active compounds contain antimicrobial, anticarcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant activities [
82]. In contrast to the major nutrients, bioactive substances are neither officially recommended nor listed by governmental organizations to [
83].
The antioxidant potential is one of the most important properties that protects against harmful free radicals known to contribute to the occurrence of chronic conditions such as cancer and age-related degenerative diseases. Moreover, antioxidants are a good predictor of the biological activity and health-protective properties of foods since they are known to inhibit oxidative damage in organisms [
51,
81,
84]. Living plant tissues (e.g. peppers and blueberries) frequently experience hermetic reactions from UV-C light, which stimulates the production of secondary metabolites and raises their antioxidant capacity [
85]. Likewise, UV-C light can induce the formation of phenolic compounds, which have gained popularity as anti-cancer agents. [
86,
87]. On the other hand, UV-C exposure has been shown to cause oxidation in several fruit and vegetable juices and purees. For example, after being exposed to UV-C radiation, the total phenolic and vitamin C content of apple juice dropped considerably, and this deterioration was accelerated in clarified apple juice. Clarification increases light transmittance and removes the intrinsic protective compounds enhancing UV-C's effect on food components. Also, a decrease in the antioxidant activity of UV-C treated horchata beverage against DPPH radical was reported_ [
85].
Pala & Toklucu (2011) conducted a study where they exposed apple juice to UV radiation to preserve the main quality characteristics, such as anthocyanins, polymeric color, antioxidant activity, and total phenols content. The obtained results were compared with the control, i.e., the untreated juice, and a better preservation of the studied parameters was obtained with UV-C [
88]. After being exposed to UV-C for durations ranging from 5 to 25 minutes, blueberry and raspberry nectars were reported to contain more total monomeric anthocyanins [
89].
Table 2 shows some examples of how UV-C light has been used to produce, increase, or retain bioactive compounds in liquid foods, but the benefits are proven to be extended to solid foods.
4.3. Modelling the Kinetics of Preservation of bioactive compounds and nutrients
Kinetic models are often used for objective assessment and economic evaluation of food safety. Kinetic modeling can also be used for predicting the influence of processing on critical quality parameters. Knowledge of the kinetics of food quality degradation, including reaction order and half-life is critical for predicting the of food quality loss during storage and preservation processes. One of the crucial factors to consider in processing is compositional changes due to nutrient loss. Therefore, kinetic studies are essential to minimize unwanted variation and optimize the quality of specific foods [
98].
Considering that the kinetics of nutrient changes in fruits and vegetables usually follows either a zero-order or a first-order model, eq. (1)-(4) [
99].
where
k is the nutrient rate constant,
n is the reaction order and
P is the parameter of the nutrient to be estimated with a variable time,
t. In the zero-order reaction kinetic model, the nutrient parameters are usually independent of the reaction rate, as shown in eq. 2:
Integrating eq. (2) yields eq. 3:
where
P0 is the value of the nutrient parameter at time zero and ± would typically signify the increase or degradation of the nutrient parameter. When the reaction rate is dependent on the nutrient parameter, the solution of a first-order reaction rate eq. 1 is expressed by eq. 4:
4.4. The combined use of UV-C With Other Preservation Technologies
The limited microbial lethality of UV light in food matrices with a high absorption coefficient and turbidity, such as non-transparent liquid foods, promotes the emergence of combined processes and hurdle technology. UV technology can be combined with conventional and other non-thermal processes to increase the lethal effects of UV light on microorganisms. The germicidal degree of combined treatments can result from an additive or synergistic effect. Synergistic lethal effects are preferable in the design of combination processes because a specific level of inactivity can be achieved by reducing energy consumption and treatment intensity/severity [
100].
Several studies have investigated the effectiveness of UV irradiation treatment in combination with other treatments. In one research study, UV irradiation combined with laser irradiation was effective against
Bacillus cereus, compared to UV irradiation or laser irradiation alone [
19]. The combination of ultraviolet-C radiation and ultrasonic technology as a barrier approach provides increased efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and reduced processing time without compromising quality. These are widely accepted and are continually being evaluated as alternatives to conventional thermal techniques for decontaminating fruits, vegetables, and derived products. However, studies in these areas have presented challenges related to quality, safety, limited capacity, and energy cost [
101]. According to Gayán et al. (2014), the simultaneous application of UV light with gentle heating, oxidizing agents or cell membrane fluidizing compounds can result in successful inactivation treatments [
102]. The application of UV-C pulsed radiation in combination with thermosonication at 90 °C resulted in a 3 log reduction of the heat-resistant and radiation-resistant cells of the vegetable contaminants,
Enterococcus faecalis and
Deinococcus radiodurans, surpassing the industrial requirement of 2 log reduction [
12].
Table 3 demonstrates some examples of how UV-C light combined with other treatments has been used to reduce the microbial load in non-solid fruit and vegetable-based foods.
5. Ultraviolet reactors for non-solid food pasteurization
UV-C irradiation in liquid foods can be performed in equipment that either uses batch or continuous operation modes. In batch processing, the product is placed in a glass container within a UV-C irradiation chamber. The product is then irradiated for a predetermined amount of time at a given UV-C dose. Continuous operation mode involves pumping the product into a high-permittivity UV light tube, coiled tube, or jacketed reactor that contains lamps that emit UV-C light. In continuous systems, UV-C exposure is performed for minutes to hours during which the product flows around the lamps with or without recirculation [
102,
106,
107]. Continuous UV-C is preferable for industrial applications because it could present advantages over batch processing, such as increased productivity [
107].
A variety of UV light sources have been used in UV-disinfection systems, including pulsed-light (PL), excimer lamps, low-pressure mercury (LPM), medium-pressure mercury (MPM), low-pressure high output mercury lamp-amalgam type, mercury-free amalgam lamps and so on [
108]. LPM lamps currently serve as radiation sources in the majority of UV-based disinfection systems for the treatment of non-solid foods and beverages [
109]. More recently, ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (UV-LEDs) have been employed in treating juices and beverages in continuous reactors [
110]. There are various types of UV-C reactors with various flow patterns. The flow pattern in the reactor has a major impact on the UV-C dose required for the inactivation of undesirable microorganisms. Hence, to maximize the homogeneity of UV-C treatment, it is necessary to enhance the flow conditions [
111]. In general, four flow types can be identified as follows: Taylor-Couette flow, Dean-Vortex flow, laminar and turbulent flow. Various reactor designs or systems are often utilized for achieving the aforementioned flow characteristics [
112].
5.1. Laminar and Turbulent Flow Reactors
Laminar flow is a flow type where the fluid travels smoothly or through regular paths, as opposed to turbulent flow where the fluid experiences unstable fluctuations and mixing [
113]. The low radial mixing in laminar flow systems reduces their efficiency in facilitating a uniform UV dose distribution [
114]. Turbulent flow systems, on the other hand, use higher flow rates to increase turbulence within a UV reactor, thereby enabling close contact between the UV-C light and the product’s constituents during treatment and overcoming product turbidity which interferes with UV penetration. The turbulent flow mechanism efficiently mixes the fluid, allowing for a more uniform UV-C dose distribution [
115,
116]. Laminar and turbulent flow were previously used in thin film reactors. The intended effect of thin film reactors is to shorten the path of UV radiation to maximize the UV-C radiation delivery to the food or beverage, thus providing a solution to inadequate penetration of UV photons [
117]. Using laminar and turbulent flow in continuous thin film reactors, Koutchma et al. (2004) investigated the effectiveness of UV radiation to inactivate
E. coli K-12 in apple juice. They observed that the inactivation of
E. coli in apple juice increased under turbulent flow conditions due to enhanced mixing [
118]. In another study, turbulent flow conditions in an ultra-thin film annular reactor produced better UV dose distribution and higher microbial inactivation rate compared to a laminar flow regime. The microbial inactivation rates were found to increase as the flow rate increased due to greater turbulence intensity [
119].
5.2. Taylor Couette reactors
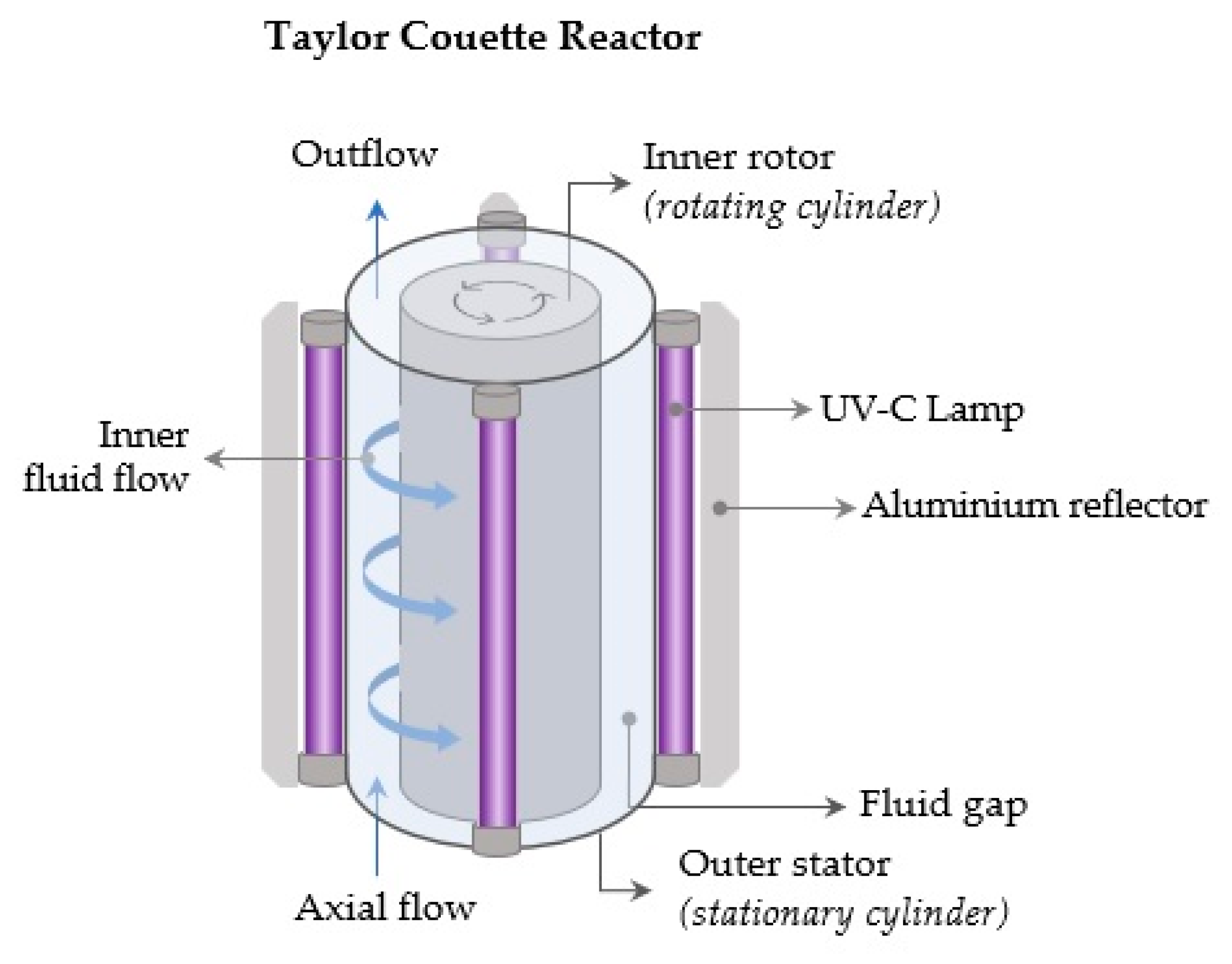
The flow between two coaxial cylinders with an inner rotating cylinder is referred to as Taylor-Couette flow [
120,
121]. The Taylor-Couette ultraviolet unit is made up of two concentric cylinders: an outer stator (outer stationary cylinder) and an inner rotor (inner rotating cylinder). The fluid product is pumped through the annular space between the cylinders and subjected to UV-C irradiation that originates from lamps positioned around the outer cylinder. The rotation of the inner cylinder creates a Taylor-Couette flow [
52]. The vortices produced in the Taylor-Couette UV reactors have the potential to deliver effective radial and axial mixing. Furthermore, the thickness of the fluid boundary layer between the fluid and the UV lamps is minimized, resulting in prolonged UV exposure times for the undesired microorganisms and uniform radiation intensities [
122]. Several flow regimes can be obtained under different flow and rotation rates in a Taylor-Couette system [
120]. Ye et al. (2008) demonstrated that higher log reduction levels of
Escherichia coli K12 (ATCC 25253) and
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis can be achieved with laminar Taylor-Couette flow as opposed to turbulent or laminar Poiseuille flow. The authors concluded that the Taylor-Couette UV-C reactors are appropriate for the preservation of a variety of juices, particularly those with high absorption coefficients [
123]. Similarly, a study by Orlowska et al. (2014) highlighted that the Taylor-Couette UV unit offered effective mixing that could overcome the limited UV-C penetration depth in opaque beverages like carrot juice [
124].
Figure 3.
Taylor-Couette UV-C Reactor.
Figure 3.
Taylor-Couette UV-C Reactor.
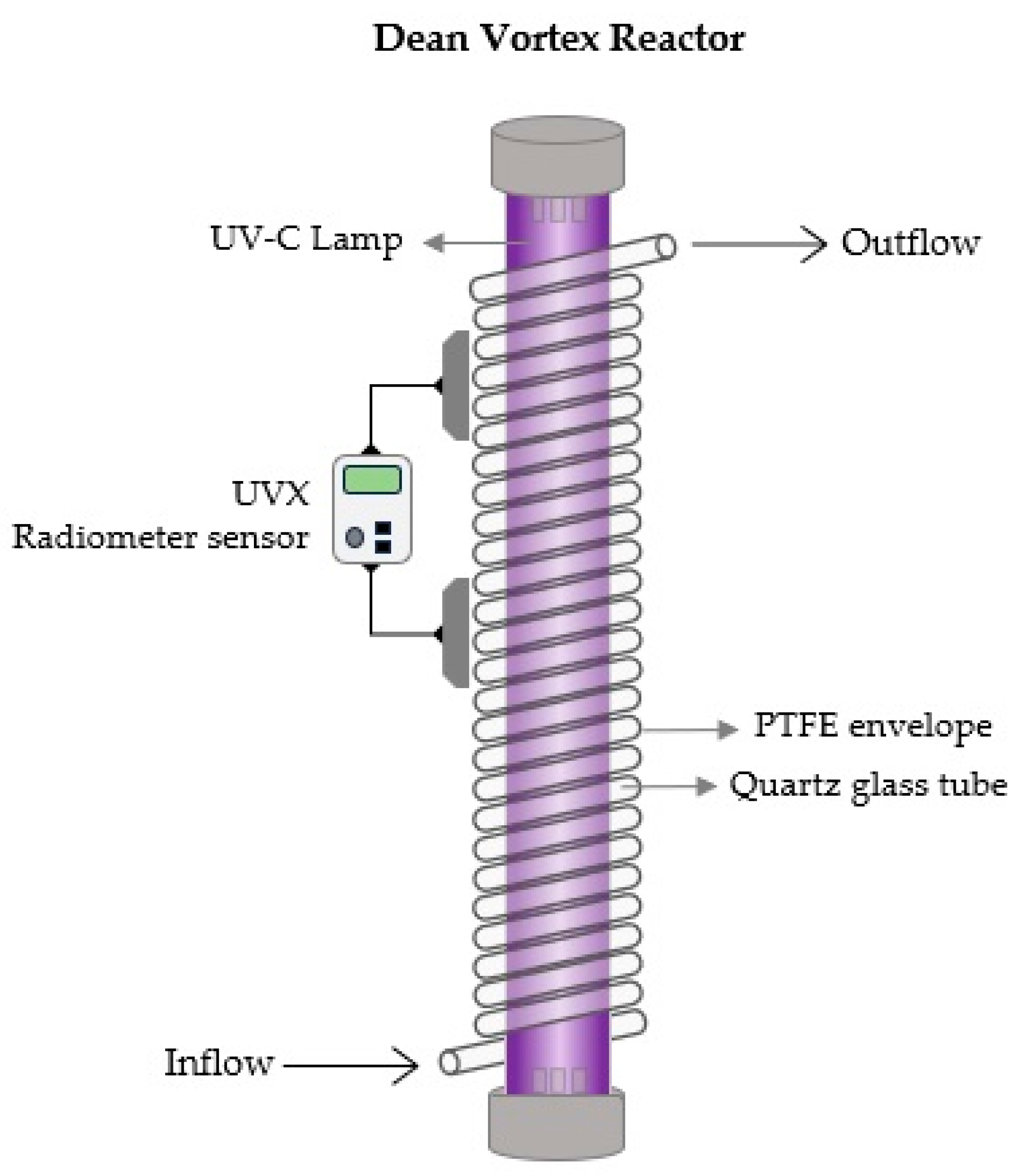
5.3. Dean Vortex-based reactors
A Dean flow system is characterized by secondary flow vortices (also known as Dean vortices) with the primary forward flow caused by the coiled flow channel in coiled tube reactors. The Dean vortices form as a result of centrifugal forces acting on the fluid volume during rotation. This generates effective radial mixing as well as more homogeneity of velocity and residence time distribution (RTD) of the liquid products due to higher Reynold numbers and turbulent conditions, resulting in more uniform treatment conditions [
125,
126]. The fluid product in these reactors passes through a highly UV-transparent fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) tube that is coiled in a helix pattern around one or more UV-C lamps [
102]. A Dean flow system consisting of a module made up of a PTFE envelope with a helically coiled tube tightly fitted to a quartz glass cylinder that houses the UV-C light source was previously used to investigate the formation of toxic compounds in UV-C treated cloudy apple juices. No quantifiable alterations were found in the cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of UV-C treated apple juices [
127]. The UVivatec Dean-Vortex reactor was used to treat
Lactobacillus plantarum BFE 5092 in orange juice. The authors found that increasing the Reynolds number from 86 to 696 led to an increase in the inactivation rate by roughly 2.5 log
10 cfu/ml [
126]. Barut Gök (2021) exposed apple and grape juice to low doses of UV-C in a dean vortex-based reactor. This study demonstrated the potential of this technology to eliminate relevant microorganisms in opaque fruit juice such as
Lactobacillus plantarum NRIC1749 and
Saccharomyces cerevisiae NCIB4932 [
128]. Orange juice was treated using a modified UV-C reactor based on Dean vortex flow. The results indicated that UV-C treatment would be a helpful way to remove or reduce the content of 5-(hydroxymethyl)furfural in orange juice. Additionally, no furan formation was found, and there was no significant alteration in the appearance and color of the juice following UV-C treatment [
129]. Cranberry flavored water was previously treated in a continuous UV-C reactor under a laminar flow regime combined with dean vortices to ensure suitable mixing and the treatment enabled a 5-log reduction (99.999%) of
Escherichia coli ATCC 700728 and
Salmonella enterica ser. Muenchen ATCC BAA 1764 with a UV-C fluence of 12 mJ·cm
−2 and 16 mJ·cm
−2, respectively. In addition, there was no formation of cytotoxic substances up to a UV-C dose of 120 mJ·cm
−2 [
130].
Figure 4.
Dean-Vortex UV-C Reactor.
Figure 4.
Dean-Vortex UV-C Reactor.
Some examples of commercially available UV-C pasteurizers with their flow types are provided in
Table 4.
6. Cost Implications, Market Potential, and Consumer Perception
UV-C radiation sources are readily available at affordable costs. This decontamination method is rapid and can be easily integrated into existing food processing systems with low initial investment [
134]. The cost of a UV-irradiation unit costs between
$10,000-15,000 making it more affordable than a heat pasteurization unit which costs between
$20,000- 30,000. The cost of production using UV-C pasteurization may be cheaper than thermal pasteurization. It costs 0.895 Malaysian Ringgit (RM) (
$0.20) to produce UV-C treated pineapple juice in a 320 mL container, while thermally pasteurized pineapple juice costs RM 0.900 (
$0.20) [
15]. Similarly, UV-C decontamination costs about RM 1.60 (
$0.35) per 100 liters for apple cider, while thermal treatment costs about RM 4.00 (
$0.88). Furthermore, food producers with limited financial resources are likely to benefit from the low initial cost of UV reactors and the low requirement for safety equipment [
134].
Compared to other technologies, food, and beverage preservation using UV-C is a more sustainable option offering additional cost-saving opportunities due to its lower electricity consumption. In comparison to heat pasteurization, it has been found that a UV system can consume approximately 10,000 times less energy. Additionally, compared to other emergent food processing technologies like pulsed electric fields (PEF), high-pressure processing (HPP), and membrane filtering (MF), UV also consumes less specific energy when considering an achievement of 5 log reduction in apple juice [
135]. The number and kind of UV light sources, the flow rate and pattern, the effectiveness of mixing the UV reactor, and the type/characteristics of the food to be treated (UV light attenuation coefficient, composition of the product, and viscosity) all impact the energy-efficiency of the UV system, and will ultimately influence its operational cost [
18].
The operational cost of UV-C food processing is further influenced by a variety of factors, including size/quantity of the food product to be treated, the level of microbial reduction required, the design and capacity of the UV-C equipment, maintenance costs, regulatory compliance, and quality standards. The operational cost of UV-C food processing is between
$0.01 and
$0.05 per liter for liquid foods and
$0.02 to
$0.10 per kilogram for solid goods. In the years to come, the market potential for UV-C food processing is anticipated to increase dramatically as consumers desire food products that are fresher, safer, and processed minimally. UV-C is a more sustainable food processing option. The market for UV disinfection equipment was valued at
$1.3 billion in 2019 and is anticipated to rise to
$5.7 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.1% from 2020 to 2027. Main factors responsible for propelling the market growth are the environmental and financial benefits of UV-C over conventional technologies and the advent of novel UV-C applications in the food and beverage industries [
136]. It is a potential green alternative for processes such as drying of fresh produce, microbial decontamination of food products (blanching pasteurization and sterilization), post-lethality sanitization of meat, disinfection of food contact surfaces, decontamination of food packaging materials, and fresh produce shelf-life extension [
36,
137,
138].
UV preservation technologies have a good consumer perception due to their numerous benefits, including microbial inactivation (including spores), and deactivation of spoilage enzymes and mycotoxins [
59,
139]. In comparison to high-temperature short-time, PEF, and HPP treatment, continuous UV-C radiation has reduced machinery and electricity cost. However, low-pressure vapor mercury lamps, which are extensively used, present a health risk due to mercury exposure. [
140]. In a 2022 survey, all consumers perceived UV-treated food products as safe for consumption, but they also expressed health-related concerns, primarily due to radiophobia, because numerous consumers still connect radiation with radioactivity and nuclear energy. Furthermore, younger people proved to be more pessimistic, which might be explained by rising health consciousness among this group of respondents, implying that extra efforts will be required for efficient communication to successfully introduce UV-processed foods into the market [
141]. The consumer acceptance of UV-treated foods can be increased by omitting the word “radiation” from the label information and adding phrases/terms such as “food safety”, “no radioactivity”, “elimination of microorganisms”, “minimal changes to food”, “absence of residues and toxic effects”, besides the fact that UV preservation is more affordable and energy-efficient than other preservation techniques [
141,
142].
7. International standards and regulations for the UV-C Pasteurization of beverages foods
UV-C has been used for a long time in the global industry as a viable alternative to thermal pasteurization where its application must guarantee no toxicity to the product, and its use must be allowed by component authorities. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved under regulation 21CFR179.39 the use of UV-C to reduce human pathogens and other microorganisms in juices, surface microorganisms’ control in food and food products, and sterilization of water used in food production [
143]. The technology is considered germicidal as it effectively inactivates bacteria and viruses with safe use at 253.7 nm, where the preferred UV source for food treatment is the low-pressure mercury lamps emitting 90% of emission at a wavelength of 254 nm. However, FDA does not specify any minimum/maximum UV dose levels, where this should be determined on a case-by-case basis, considering good manufacturing practices and situational factors [
143]. According to 21CFR179.41, it is approved the application of pulsed light technology for food treatment to remove surface microorganisms with a regulated dose below 12 J/cm
2. The FDA does not have specific regulations or guidance addressed to labeling requirements for foods treated with UV irradiation [
144].
The European Union (EU) Novel Food Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2015/2283) is responsible for the authorization and safety assessment of UV-treated foods in the EU, as these are considered novel foods [
145]. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), covered by the regulation in EC n° 258/97, approved the safe use of UV radiation for milk processing post pasteurization aiming for the extension of shelf life and to increase the vitamin D content [
146]. The intended use of the foods that contain vitamin D resulting from ultraviolet treatment and the specific wavelength ranges allowed for different food (200-800 nm for mushrooms, 240-315 nm for bread, 200-310 nm for milk, not specified for baker’s yeast) were provided by the European Commission (EC). The EU Regulation also covered the novel foods that need to be authorized before entry into the market in Great Britain since their approach is based on EU processes [
147].
The scientific committee of the Food Safety Authority of Ireland published a report in 2020 focusing on the evaluation of emergent food processing technologies (including UV-C) as well as the safety and associated changes in the nutritional content of products treated using emergent technologies in comparison to conventional preservation processes [
148]. An evaluation template of novel food processing methods is provided in this report to protect public health and facilitate the development of innovative technologies in the Irish food sector [
149]. In Israel, food derived from new production processes, like UV-treated milk was approved by The National Food Service at the Ministry of Health to be safely used, where the Israeli food legislation and standardization are under European standards [
150]. The regulation requires the product label as “UV-treated” [
147].
In Canada, the Novel Foods Regulation of Health Canada regulates UV-light-treated foods and guarantees the safe use of CiderSure 3500 equipment to achieve at least a 5-log reduction of
E. coli O157:H7 in unpasteurized and unfermented apple cider and juice [
151]. The scientific committee of the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) approved raw milk and other dairy products treated with the SurePure UV system with the status “Process Approval” [
152].
The knowledge of specific guidelines and regulations regarding UV treatment in each country opens new opportunities for further development and commercialization of UV-treated products at an industrial scale.
8. Current Limitations and Future Trends of UV-C Food Processing
UV-C light is a non-thermal process technology applied in plant-based non-solid foods as a viable alternative to traditional pasteurization in the food industry. UV radiation extends the food products' shelf life due to a germicidal effect, inactivating microorganisms, and maintaining the freshness, flavor, and nutritional content of foods, whereas some current limitations need to be considered. The biggest obstacle to the commercial use of UV-C technology is its poor penetrating power [
153]. The composition and type of food, influence UV-C penetration capabilities, being necessary to study foods and beverages case by case to obtain information regarding microbial disinfection and determine the optimal UV-C dosage. This is because the optical and physicochemical characteristics of liquid foods could cause interferences in the target microbe’s exposure to the radiation, which can lessen the efficiency of UV-C radiation [
154,
155]. For instance, UV-C radiation penetrates easily through transparent or clear liquids. In contrast, because UV-C light can be readily absorbed by opaque matrices, its penetrating potential in opaque foods is quite limited [
156]. Additionally, the color and viscosity of the liquid products as well as the presence of natural pigments, organic solutes, and suspended solids limit the penetration of UV photons, lowering the efficacy of UV radiation in inactivating microbes [
137,
157]. The physicochemical characteristics of treated foods and beverages should be closely monitored because UV-C at high doses may cause the production of hazardous chemicals [
158].
Microbial species can have different degrees of susceptibility and resistance, which can affect the efficacy of UV-C penetration. As such, higher doses of UV-C light will be required for the most resistant species to be inactivated. Because UV-C has a shallow penetration depth, microorganisms need to be directly exposed to it to be inactivated. Hence, a major technical difficulty in commercial UV-C applications is how to guarantee that all the product surfaces are exposed to UV-C radiation uniformly to allow a regular dose delivery and complete microbial exposure [
153]. However, altering the flow rate improves its efficiency to inactivate microbes. Another strategy is employing turbulent flow to guarantee the success of the liquid treatment [
117]. Also, UV-C can be combined with other low-intensity preservation technologies such as ultrasound, high-pressure processing, and even mild temperatures enhancing overall food safety and quality [
159]. However, these combined treatments and hurdle technology should be conducted properly before large-scale implementation to guarantee that the microbiological permissible limits and quality requirements are attained through effective control of the dose and exposure of UV-C [
15].
Recently, pulsed ultraviolet (PUV) treatment has been studied for the decontamination of non-solid foods. PUV has some benefits over continuous UV-C technology: it is rich in UV-C germicidal radiation (200–280 nm) and comprises UV-B and UV-A ranges (280–400 nm band), it has a higher intensity, and shorter treatment duration [
31]. Xenon lamps are common light sources in pulsed ultraviolet application having the advantage of being mercury-free, yet, their high installation and maintenance cost limits their use in PUV treatments, albeit this can be offset by their cheap operating costs and long lastingness [
140]. UVC radiation from pulsed xenon lamps therefore offers a safe alternative to traditional UV-C food preservation technologies and provides a solution to the low energy output of UV-C radiation through the emission of very high intensity light compared to conventional UV-C light sources such as mercury lamps [
26,
160]. Nevertheless, the current regulations and guidelines for UV-C application are not standardized in various countries and information is missing in terms of exposure times, permissible doses, and labeling requirements, this leads to variability of standards, presenting an obstacle for food manufacturers in their food processing operations (see section 8). Conducting supplemental research and validation studies are a strategic key to optimizing the process and minimizing any negative effects on the safety, sensory quality, physicochemical properties, and nutritional attributes of foods.
9. Concluding Remarks
UV-C technology is an environmentally friendly, energy-efficient, and cost-effective process having appreciable germicidal properties that can inactivate a variety of microbiological pathogens, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses to efficiently prevent foodborne diseases and extend the shelf life of food through microbial load reduction without compromising the food's quality by ensuring minimal alterations to the food's nutritional value. Numerous food safety applications of UV-C technology exist in the manufacturing of non-solid foods, ranging from the popular pasteurization of juices to the less common treatment of opaque liquid and semi-liquid plant-based foods that needs more investigation.
The efficacy of UV-C to preserve nutrients in foods has been discussed extensively, however, the potential contributions of its nutrient retention ability with respect to nutrition insecurity is lacking in the literature. Instances of nutrition insecurity, where individuals do not obtain sufficient nutrients from foods will inevitably lead to hidden hunger (micronutrient deficiencies). The pasteurization of plant-based non-solid food has been studied in various UV-C reactor types and this technology has proven its abilities to reduce the microbial load while causing minimal degradation of nutrients and health-promoting bioactive compounds in foods. Thanks to this, employing UV-C technology in food production processes can help to tackle hidden hunger and have a positive effect on nutrition security. Consequently, UV-C could be employed as a tool in food design strategies targeting hidden hunger. Thereby providing a solution to tackle this global challenge affecting the lives of millions of people.
Although UV-C has limited capacity to penetrate dense and opaque fluids, technological advancements have been made to circumvent the high opacity and high turbidity of some plant-based non-solid products that lower the UV-C photon penetration of such as the use of thin-film systems and the use of equipment that improve flow pattern using turbulent or Dean vortex flow [
128]. Several difficulties and limitations associated with this technique remain, including the need for adequate reactor design, appropriate selection of processing parameters, and safety precautions. In addition, legislation and standards governing UV-C technology applications in the food industry differ from countries to countries.
Depending on the specific conditions and requirements of each application, incur different operating expenses. UV-C food processing equipment may incur different operating expenses. A feasibility assessment and a cost-benefit analysis are therefore necessary, before introducing UV-C food processing in a food production plant Although scientists and food professionals know about the advantages and risks of foods processed by UV-C technology, consumers are less informed. An increase in public awareness about this decontamination technology is therefore needed. Additionally, the right labelling can be used to encourage consumers to adopt UV-irradiated food products as rich sources of beneficial nutrients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.D.T.; writing—original draft preparation, R.D.T. A.R.L., A.C.Q., N.L.C., and M.C.V.; writing—review and editing, R.D.T., A.R.L., and M.C.V.; supervision, M.C.V.; funding acquisition, M.C.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is part of the Partnership for Research and Innovation in the Mediterranean Area (PRIMA) program, grant number 2032, supported by the European Union. R.D.T. is funded by the European’s Union Horizon 2020 Functionalized Tomato Products (FunTomP) project. A.C.Q. is supported by the grant UIDB/05183/2020. A.R.L. and N.L.C. are supported by national funds through FCT PhD grants (SFRH/BD/149398/2019) and (SFRH/BD/149395/2019), respectively.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ingram, J. Nutrition Security Is More than Food Security. Nat Food 2020, 1, 2–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talens, C.; Garcia-Fontanals, L.; Fabregat, P.; Ibargüen, M. Rational Food Design Targeting Micronutrient Deficiencies in Adolescents: Nutritional, Acoustic-Mechanical and Sensory Properties of Chickpea-Rice Biscuits. Foods 2023, 12, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlowska, M.; Koutchma, T.; Grapperhaus, M.; Gallagher, J.; Schaefer, R.; Defelice, C. Continuous and Pulsed Ultraviolet Light for Nonthermal Treatment of Liquid Foods. Part 1: Effects on Quality of Fructose Solution, Apple Juice, and Milk. Food Bioprocess Technol 2013, 6, 1580–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, M.; Livne, D. Novel Industrial UV-C System for Preservation of Fruit and Vegetable Juices. 5.
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, D.; Burton-Freeman, B.M.; Edirisinghe, I. Chemical Changes of Bioactive Phytochemicals during Thermal Processing. In Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier, 2016 ISBN 978-0-08-100596-5.
- Soni, A.; Bremer, P.; Brightwell, G. A Comprehensive Review of Variability in the Thermal Resistance (D-Values) of Food-Borne Pathogens—A Challenge for Thermal Validation Trials. Foods 2022, 11, 4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadini, C.C.; Gut, J.A.W. The Importance of Heating Unit Operations in the Food Industry to Obtain Safe and High-Quality Products. Front Nutr 2022, 9, 853638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellows, P.J. 1 - Properties of Food and Principles of Processing. In Food Processing Technology (Fourth Edition); Fellows, P.J., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing, 2017; pp. 3–200 ISBN 978-0-08-101907-8.
- Lešková, E.; Kubíková, J.; Kováčiková, E.; Košická, M.; Porubská, J.; Holčíková, K. Vitamin Losses: Retention during Heat Treatment and Continual Changes Expressed by Mathematical Models. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2006, 19, 252–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R.M.S.; Vieira, M.C.; Silva, C.L.M. Effect of Heat and Thermosonication Treatments on Watercress (Nasturtium Officinale) Vitamin C Degradation Kinetics. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 2008, 9, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fundo, J.F.; Miller, F.A.; Mandro, G.F.; Tremarin, A.; Brandão, T.R.S.; Silva, C.L.M. UV-C Light Processing of Cantaloupe Melon Juice: Evaluation of the Impact on Microbiological, and Some Quality Characteristics, during Refrigerated Storage. LWT 2019, 103, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, F.I.G.; Silva, C.L.M.; Vieira, M.C. Combined Pre-Treatments Effects on Zucchini (Cucurbita Pepo L.) Squash Microbial Load Reduction. Int J Food Microbiol 2019, 305, 108257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Avci, P.; Dai, T.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Hamblin, M.R. Ultraviolet Radiation in Wound Care: Sterilization and Stimulation. Advances in Wound Care 2013, 2, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.; Popović, V.; Warriner, K.; Koutchma, T. The Efficacy of UVC LEDs and Low Pressure Mercury Lamps for the Reduction of Escherichia Coli O157:H7 and Listeria Monocytogenes on Produce. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 2020, 64, 102410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Karim Shah, N.; Shamsudin, R.; Abdul Rahman, R.; Adzahan, N. Fruit Juice Production Using Ultraviolet Pasteurization: A Review. Beverages 2016, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taze, B.H.; Akgun, M.P.; Yildiz, S.; Kaya, Z.; Unluturk, S. 2.18 - UV Processing and Storage of Liquid and Solid Foods: Quality, Microbial, Enzymatic, Nutritional, Organoleptic, Composition and Properties Effects. In Innovative Food Processing Technologies; Knoerzer, K., Muthukumarappan, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, 2021; ISBN 978-0-12-815782-4. [Google Scholar]
- Banaś, A.K.; Zgłobicki, P.; Kowalska, E.; Bażant, A.; Dziga, D.; Strzałka, W. All You Need Is Light. Photorepair of UV-Induced Pyrimidine Dimers. Genes (Basel) 2020, 11, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme, M.M.; Guimarães, J.T.; Coutinho, N.M.; Balthazar, C.F.; Rocha, R.S.; Silva, R.; Margalho, L.P.; Pimentel, T.C.; Silva, M.C.; Freitas, M.Q.; et al. Ultraviolet Radiation: An Interesting Technology to Preserve Quality and Safety of Milk and Dairy Foods. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2020, 102, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemmireddy, V.; Adhikari, A.; Moreira, J. Effect of Ultraviolet Light Treatment on Microbiological Safety and Quality of Fresh Produce: An Overview. Frontiers in Nutrition 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Hernández, K.; Ramírez-Rojas, N.Z.; Meza-Plaza, E.F.; García-Mosqueda, C.; Jauregui-Vázquez, D.; Rojas-Laguna, R.; Sosa-Morales, M.E. UV-C Treatments against Salmonella Typhimurium ATCC 14028 in Inoculated Peanuts and Almonds. Food Eng Rev 2021, 13, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutchma, T. Advances in Ultraviolet Light Technology for Non-Thermal Processing of Liquid Foods. Food Bioprocess Technol 2009, 2, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunter-Ward, D.M.; Patras, A.; S. Bhullar, M.; Kilonzo-Nthenge, A.; Pokharel, B.; Sasges, M. Efficacy of Ultraviolet (UV-C) Light in Reducing Foodborne Pathogens and Model Viruses in Skim Milk. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 2018, 42, e13485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atilgan, M.R.; Yildiz, S.; Kaya, Z.; Unluturk, S. Kinetic and Process Modeling of UV-C Irradiation of Foods. In Innovative Food Processing Technologies; Elsevier, 2021; pp. 227–255 ISBN 978-0-12-815782-4.
- Bevilacqua, A.; Petruzzi, L.; Perricone, M.; Speranza, B.; Campaniello, D.; Sinigaglia, M.; Corbo, M.R. Nonthermal Technologies for Fruit and Vegetable Juices and Beverages: Overview and Advances. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety 2018, 17, 2–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allai, F.M.; Azad, Z.R.A.A.; Mir, N.A.; Gul, K. Recent Advances in Non-Thermal Processing Technologies for Enhancing Shelf Life and Improving Food Safety. Applied Food Research 2023, 3, 100258–100258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Khatri, M.; Kim, K.-H.; Bhardwaj, N. UVC Radiation for Food Safety: An Emerging Technology for the Microbial Disinfection of Food Products. Chemical Engineering Journal 2021, 417, 128084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouma, M.; Gayán, E.; Raso, J.; Condón, S.; Álvarez, I. UV-Heat Treatments for the Control of Foodborne Microbial Pathogens in Chicken Broth. BioMed Research International 2015, 2015, e436030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Said, M.; Khefacha, S.; Maalej, L.; Daly, I.; Hassen, A. Effect of Ultraviolet, Electromagnetic Radiation Subtype C (UV-C) Dose on Biofilm Formation by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. African Journal of Microbiology Research 2011, 5, 4353–4358. [Google Scholar]
- Liltved, H.; Landfald, B. Effects of High Intensity Light on Ultraviolet-Irradiated and Non-Irradiated Fish Pathogenic Bacteria. Water Research 2000, 34, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopisetty, V.V.S.; Patras, A.; Kilonzo-Nthenge, A.; Yannam, S.; Bansode, R.R.; Sasges, M.; Burns, S.M.; Vergne, M.J.; Pan, C.; Xiao, H. Impact of UV-C Irradiation on the Quality, Safety, and Cytotoxicity of Cranberry-Flavored Water Using a Novel Continuous Flow UV System. Lwt 2018, 95, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutchma, T. Advances in UV-C Light Technology Improve Safety and Quality Attributes of Juices, Beverages, and Milk Products. Food Safety Magazine 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Duering, H.; Westerhoff, T.; Kipp, F.; Stein, C. Short-Wave Ultraviolet-Light-Based Disinfection of Surface Environment Using Light-Emitting Diodes: A New Approach to Prevent Health-Care-Associated Infections. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, I.; Rotter, A.; Malvestiti, A.; Silva, M. The Role of Glass as a Barrier against the Transmission of Ultraviolet Radiation: An Experimental Study. Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine 2009, 25, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodling, S.E.; Moraru, C. Influence of Surface Topography on the Effectiveness of Pulsed Light Treatment for the Reduction of Listeria Innocua on Stainless Steel Surfaces. J. Food Sci 2005, 70, 245–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasin, M.; Strizzi, S.; Bianco, A.; Macchi, A.; Utyro, O.; Pareschi, G.; Loffreda, A.; Cavalleri, A.; Lualdi, M.; Trabattoni, D.; et al. UV and Violet Light Can Neutralize SARS-CoV-2 Infectivity. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology 2022, 10, 100107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, A.; Lobacz, A.; Tarapata, J.; Zulewska, J. UV Light Application as a Mean for Disinfection Applied in the Dairy Industry. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lah, E.F.C.; Musa, R.N.A.R.; Ming, H.T. Effect of Germicidal UV-C Light(254 Nm) on Eggs and Adult of House Dustmites, Dermatophagoides Pteronyssinus and Dermatophagoides Farinae (Astigmata: Pyroglyhidae). Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine 2012, 2, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeiszadeh, M.; Adeli, B. A Critical Review on Ultraviolet Disinfection Systems against COVID-19 Outbreak: Applicability, Validation, and Safety Considerations. ACS Photonics 2020, 7, 2941–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.; Beck, S.; Boczek, L.; Carlson, K.; Brinkman, N.; Linden, K.; Lawal, O.; Hayes, S.; Ryu, H. Efficacy of Inactivation of Human Enteroviruses by Dual-Wavelength Germicidal Ultraviolet (UV-C) Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). Water 2019, 11, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, W. Ultraviolet Germicidal Irradiation Handbook: UVGI for Air and Surface Disinfection; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2009; ISBN 978-3-642-01998-2. [Google Scholar]
- Templeton, M.R.; Antonakaki, M.; Rogers, M. UV Dose–Response of Acinetobacter Baumannii in Water. Environmental Engineering Science 2009, 26, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-F.; Zhang, R.-J.; Huang, S.-B.; Shao, J.-H.; Cui, B.; Du, Z.-L.; Xue, L.; Zhou, N.; Hou, B.; Lin, C. UV Dose Effects on the Revival Characteristics of Microorganisms in Darkness after UV Disinfection: Evidence from a Pilot Study. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 713, 136582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.P.; Häder, D.-P. UV-Induced DNA Damage and Repair: A Review. Photochem Photobiol Sci 2002, 1, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessling, M.; Haag, R.; Sieber, N.; Vatter, P. The Impact of Far-UVC Radiation (200-230 Nm) on Pathogens, Cells, Skin, and Eyes - a Collection and Analysis of a Hundred Years of Data. GMS Hyg Infect Control 2021, 16, Doc07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Dong, J. Effect of Inactivating RNA Viruses by Coupled UVC and UVA LEDs Evaluated by a Viral Surrogate Commonly Used as a Genetic Vector. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutchma, T. Basic Principles of UV Light Generation. Food Plant Safety 2014, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadnum, J.L.; Li, D.; Redmond, S.N.; John, A.R.; Pearlmutter, B.; Donskey, C. Effectiveness of Ultraviolet-C Light and a High-Level Disinfection Cabinet for Decontamination of N95 Respirators. PAI 2020, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, R.; Stamminger, R. Impact of Ultraviolet Radiation Treatments on the Physicochemical Properties, Antioxidants, Enzyme Activity and Microbial Load in Freshly Prepared Hand Pressed Strawberry Juice. Food Science and Technology International 2014, 21, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Sánchez, C.; Lozano-Sánchez, J.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. Alternatives to Conventional Thermal Treatments in Fruit-Juice Processing. Part 1: Techniques and Applications. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 2017, 57, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutchma, T.; Popović, V.; Ros-Polski, V.; Popielarz, A. Effects of Ultraviolet Light and High-Pressure Processing on Quality and Health-Related Constituents of Fresh Juice Products: UV & HPP Effects on Juice Quality…. COMPREHENSIVE REVIEWS IN FOOD SCIENCE AND FOOD SAFETY 2016, 15, 844–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darré, M.; Vicente, A.R.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Artés-Hernández, F. Postharvest Ultraviolet Radiation in Fruit and Vegetables: Applications and Factors Modulating Its Efficacy on Bioactive Compounds and Microbial Growth. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio-Gutiérrez, O.T.; López-Díaz, A.S.; López-Malo, A.; Palou, E.; Ramírez-Corona, N. 7 - UV-C Light for Processing Beverages: Principles, Applications, and Future Trends. In Processing and Sustainability of Beverages; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing, 2019; pp. 205–234 ISBN 978-0-12-815259-1.
- Bintsis, T.; Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E.; Robinson, R.K. Existing and Potential Applications of Ultraviolet Light in the Food Industry - a Critical Review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jildeh, Z.B.; Wagner, P.H.; Schöning, M.J. Sterilization of Objects, Products, and Packaging Surfaces and Their Characterization in Different Fields of Industry: The Status in 2020. physica status solidi (a) 2021, 218, 2000732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Parraga Estrada, K.J.; Chhetri, V.S.; Janes, M.; Fontenot, K.; Beaulieu, J.C. Evaluation of Ultraviolet (UV-C) Light Treatment for Microbial Inactivation in Agricultural Waters with Different Levels of Turbidity. Food Science and Nutrition 2020, 8, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guneser, O.; Karagul Yuceer, Y. Effect of Ultraviolet Light on Water- and Fat-Soluble Vitamins in Cow and Goat Milk. Journal of Dairy Science 2012, 95, 6230–6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, A.; Gatica, I.; Bustamante, A.; Cárdenas, D.; Escalona, V. Effect of the Combined Treatment of UV-C Light and Modified Atmosphere Packaging on the Inactivation of Escherichia Coli Inoculated Watercress. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 2015, 39, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Solà, J.; Valero, A.; Abadias, M.; Nicolau-Lapeña, I.; Viñas, I. Evaluation of Water-Assisted UV-C Light and Its Additive Effect with Peracetic Acid for the Inactivation of Listeria Monocytogenes, Salmonella Enterica and Murine Norovirus on Whole and Fresh-Cut Strawberries during Shelf-Life. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 2022, 102, 5660–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R.M.S.; Godinho, A.I.A.; Aslan, D.; Koçak, N.F.; Vieira, M.C. Modeling the Kinetics of Peroxidase Inactivation, Colour and Texture Changes of Portuguese Cabbage (Brassica Oleracea L. Var. Costata DC) during UV-C Light and Heat Blanching. International Journal of Food Studies 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.R.; Cristofoli, N.L.; Veneral, J.G.; Fritz, A.R.M.; Vieira, M.C. Optimization Conditions of UV-C Radiation Combined with Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Cherry Tomato (Lycopersicon Esculentum) Lycopene Extract. International Journal of Food Studies 2019, 8, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Aguilar, G.A.; Villegas-Ochoa, M.A.; Martínez-Téllez, M.A.; Gardea, A.A.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F. Improving Antioxidant Capacity of Fresh-Cut Mangoes Treated with UV-C. J Food Science 2007, 72, S197–S202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modesto Junior, E.N.; Martins, M.G.; Pereira, G.A.; Chisté, R.C.; Pena, R.D.S. Stability Kinetics of Anthocyanins of Grumixama Berries (Eugenia Brasiliensis Lam.) during Thermal and Light Treatments. Foods 2023, 12, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, K.; Shui, S.S.; Yan, L.; Liu, C.; Zheng, L. Effect of Postharvest UV-B or UV-C Irradiation on Phenolic Compounds and Their Transcription of Phenolic Biosynthetic Genes of Table Grapes. Journal of Food Science and Technology 2018, 55, 3292–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, A.; Moldão-martins, M.; Costa, H.S.; Tânia, G.; Sanches-silva, A. Effect of UV-C Radiation on Bioactive Compounds of Pineapple ( Ananas Comosus L. Merr.) by-Products. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 2014, 95, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ambrocio, A.; Guerrero-Beltrán, J.A.; Aparicio-Fernández, X.; Ávila-Sosa, R.; Hernández-Carranza, P.; Cid-Pérez, S.; Ochoa-Velasco, C.E. Effect of Blue and Ultraviolet-C Light Irradiation on Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity of Habanero Pepper (Capsicum Chinense) during Refrigeration Storage. Postharvest Biology and Technology 2018, 135, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıkmış, S.; Barut Gök, S.; Levent, O.; Kombak, E. Moderate Temperature and UV-C Light Processing of Uruset Apple Juice: Optimization of Bioactive Components and Evaluation of the Impact on Volatile Profile, HMF and Color. Journal of Food Process Engineering 2021, 44, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alothman, M.; Bhat, R.; Karim, A.A. Effects of Radiation Processing on Phytochemicals and Antioxidants in Plant Produce. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2009, 20, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Győrfi, J.; Kovács, A.; Szabó, A. Increasing the Vitamin D Level of Oyster Mushrooms by UV Light. International Journal of Horticultural Science 2011, 17, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbinot Filho, C.A.; Borges, C.D. Efeitos Da Radiação UV-C Em Alface e Maçã Minimamente Processadas: Uma Revisão. Brazilian Journal of Food Technology 2020, 23, e2018321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grapiglia, J. Utilização de Tratamento Ultravioleta No Processamento Industrial de Água de Coco Associado a Diferentes Tratamentos Térmic., Universidade de Lisboa. Faculdade de Medicina Veternária. : Lisboa, 2021.
- Guerrero-Beltrán, J.A.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Inactivation of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Polyphenoloxidase in Mango Nectar Treated with UV Light. J Food Prot 2006, 69, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierscianowski, J.; Popović, V.; Biancaniello, M.; Bissonnette, S.; Zhu, Y.; Koutchma, T. Continuous-Flow UV-C Processing of Kale Juice for the Inactivation of E. Coli and Assessment of Quality Parameters. Food Research International 2021, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, F.; Pizarro-Oteíza, S.; Kasahara, I.; Labbé, M. Effect of Ultraviolet Light-Emitting Diode Processing on Fruit and Vegetable-Based Liquid Foods: A Review. Frontiers in Nutrition 2022, 9, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caminiti, I.M.; Palgan, I.; Muñoz, A.; Noci, F.; Whyte, P.; Morgan, D.J.; Cronin, D.A.; Lyng, J.G. The Effect of Ultraviolet Light on Microbial Inactivation and Quality Attributes of Apple Juice. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Carrillo, M.; Ferrario, M.; Guerrero, S. Effectiveness of UV-C Light Assisted by Mild Heat on Saccharomyces Cerevisiae KE 162 Inactivation in Carrot-Orange Juice Blend Studied by Flow Cytometry and Transmission Electron Microscopy. Food Microbiology 2018, 73, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, Z.; Unluturk, S. Processing of Clear and Turbid Grape Juice by a Continuous Flow UV System. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies 2016, 33, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beristaín-Bauza, S.; Martínez-Niño, A.; Ramírez-González, A.P.; Ávila-Sosa, R.; Ruíz-Espinosa, H.; Ruiz-López, I.I.; Ochoa-Velasco, C.E. Inhibition of Salmonella Typhimurium Growth in Coconut (Cocos Nucifera L.) Water by Hurdle Technology. Food Control 2018, 92, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Park, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, D.H. Synergistic Effect of Ohmic Heating and UV-C Irradiation for Inactivation of Escherichia Coli O157:H7, Salmonella Typhimurium and Listeria Monocytogenes in Buffered Peptone Water and Tomato Juice. Food Control 2019, 102, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandla, S.; Choudhary, R.; Watson, D.G.; Haddock, J. UV-C Treatment of Soymilk in Coiled Tube UV Reactors for Inactivation of Escherichia Coli W1485 and Bacillus Cereus Endospores. LWT 2012, 46, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgün, M.P.; Ünlütürk, S. Effects of Ultraviolet Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) on Microbial and Enzyme Inactivation of Apple Juice. International Journal of Food Microbiology 2017, 260, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyarkai Nambi, V.; Gupta, R.K.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, P.C. Degradation Kinetics of Bioactive Components, Antioxidant Activity, Colour and Textural Properties of Selected Vegetables during Blanching. Journal of Food Science and Technology 2016, 53, 3073–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamzalıoğlu, A.; Gökmen, V. Chapter 18 - Interaction between Bioactive Carbonyl Compounds and Asparagine and Impact on Acrylamide. In Acrylamide in Food; Gökmen, V., Ed.; Academic Press, 2016; pp. 355–376 ISBN 978-0-12-802832-2.
- Wood, J.D. Chapter 19 - Meat Composition and Nutritional Value. In Lawrie’s Meat Science (Ninth Edition); Toldrá, F., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing, 2023; pp. 665–685 ISBN 978-0-323-85408-5.
- Leyane, T.S.; Jere, S.W.; Houreld, N.N. Oxidative Stress in Ageing and Chronic Degenerative Pathologies: Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Counteracting Oxidative Stress and Chronic Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrales, M.; de Souza, P.M.; Stahl, M.R.; Fernández, A. Effects of the Decontamination of a Fresh Tiger Nuts’ Milk Beverage (Horchata) with Short Wave Ultraviolet Treatments (UV-C) on Quality Attributes. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 2012, 13, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, L.; Charles, F.; de Miranda, M.R.A.; Aarrouf, J. Understanding the Physiological Effects of UV-C Light and Exploiting Its Agronomic Potential before and after Harvest. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2016, 105, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abotaleb, M.; Liskova, A.; Kubatka, P.; Büsselberg, D. Therapeutic Potential of Plant Phenolic Acids in the Treatment of Cancer. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pala, Ç.U.; Toklucu, A.K. Effect of UV-C Light on Anthocyanin Content and Other Quality Parameters of Pomegranate Juice. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2011, 24, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro-Maza, J.; Guerrero-Beltran, J. Ultraviolet-C Light Effect on the Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Blackberry, Blueberry, and Raspberry Nectars. Journal of Food Research 2016, 5, p11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teja, C.K.; shankar, S.; moni, S.; Prabhakar, B.; Srini, P. ; Rao, vasa Effect of UV– C Light Treatment on Physicochemical and Bioactive Compounds in Apple and Pineapple Juices. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences 2017, 6, 2321–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhirasegaram, V.; Razali, Z.; George, D.S.; Somasundram, C. Comparison of UV-C Treatment and Thermal Pasteurization on Quality of Chokanan Mango (Mangifera Indica L.) Juice. Food and Bioproducts Processing 2015, 94, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, E.P.; Perin, E.C.; Schott, I.B.; Düsman, E.; da Silva Rodrigues, R.; Lucchetta, L.; Manfroi, V.; Rombaldi, C.V. Phenolic Compounds Are Dependent on Cultivation Conditions in Face of UV-C Radiation in ‘Concord’ Grape Juices (Vitis Labrusca). Lwt 2022, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Barrio, R.; Vidal-Guevara, M.L.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Espín, J.C. Preparation of a Resveratrol-Enriched Grape Juice Based on Ultraviolet C-Treated Berries. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 2009, 10, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoutsis, K.; Vuong, Q.V.; Pristijono, P.; Golding, J.B.; Bowyer, M.C.; Scarlett, C.J.; Stathopoulos, C.E. Enhancing the Total Phenolic Content and Antioxidants of Lemon Pomace Aqueous Extracts by Applying Uv-c Irradiation to the Dried Powder. Foods 2016, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pala, Ç.U.; Toklucu, A.K. Microbial, Physicochemical and Sensory Properties of UV-C Processed Orange Juice and Its Microbial Stability during Refrigerated Storage. LWT - Food Science and Technology 2013, 50, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmaz, H.; Söylemezoğlu, G. Effects of Vinification Techniques Combined with UV-C Irradiation on Phenolic Contents of Red Wines: Vinification Techniques and Phenolics…. Journal of Food Science 2017, 82, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.; Ameran, S.B.; Voon, H.C.; Karim, A.A.; Tze, L.M. Quality Attributes of Starfruit (Averrhoa Carambola L.) Juice Treated with Ultraviolet Radiation. Food Chemistry 2011, 127, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takikawa, A.Y. Cinética de Degradação Térmica de Antocianinas e Seu Impacto Na Cor e Na Capacidade Antioxidante in Vitro Em FrutasVermelhas., Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná. Campus de Mourão.: Campo Mourão, 2014.
- Esua, O.J.; Chin, N.L.; Yusof, Y.A.; Sukor, R. Combination of Ultrasound and Ultraviolet-C Irradiation on Kinetics of Color, Firmness, Weight Loss, and Total Phenolic Content Changes in Tomatoes during Storage. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 2019, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayán, E.; Condón, S.; Álvarez, I. Biological Aspects in Food Preservation by Ultraviolet Light: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol 2014, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esua, O.J.; Chin, N.L.; Yusof, Y.A.; Sukor, R. A Review on Individual and Combination Technologies of UV-C Radiation and Ultrasound in Postharvest Handling of Fruits and Vegetables. Processes 2020, 8, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayán, E.; Condón, S.; Álvarez, I. Continuous-Flow UV Liquid Food Pasteurization: Engineering Aspects. Food Bioprocess Technol 2014, 7, 2813–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio-Gutiérrez, O.; López-Malo, A.; Ramírez-Corona, N.; Palou, E. Enhancement of UVC-Light Treatment of Tangerine and Grapefruit Juices through Ultrasonic Atomization. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies 2017, 39, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouma, M.; Álvarez, I.; Condón, S.; Gayán, E. Pasteurization of Carrot Juice by Combining UV-C and Mild Heat: Impact on Shelf-Life and Quality Compared to Conventional Thermal Treatment. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies 2020, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagal, G.A.; Gabriel, A.A. Individual and Combined Mild Heat and UV-C Processes for Orange Juice against Escherichia Coli O157:H7. LWT 2020, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouma, M.; Condon, S.; Mañas, P.; Álvarez, I.; Gayán, E. The Use of UV Light for Food Preservation: An Overview. In High Intensity Pulsed Light in Processing and Preservation of Foods; 2016; pp. 1–40.
- Ochoa-Velasco, C.E.; Beristain-Bauza, S.C.; Hernández-Carranza, P.; Ruiz-López, I.I. A Reactor Engineering Approach to Describe Bacterial Inactivation during Continuous UV-C Light Processing. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 2021, 74, 102853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, N.; Urgu, M.; Saatli, T.E.; Koca, N.; Urgu, M.; Saatli, T.E. Ultraviolet Light Applications in Dairy Processing; IntechOpen, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78923-313-1.
- Gómez-López, V.M.; Koutchma, T.; Linden, K. Chapter 8 - Ultraviolet and Pulsed Light Processing of Fluid Foods. In Novel Thermal and Non-Thermal Technologies for Fluid Foods; Cullen, P.J., Tiwari, B.K., Valdramidis, V.P., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, 2012; ISBN 978-0-12-381470-8. [Google Scholar]
- Popović, V.; Koutchma, T. Characterizing the Performance of a Continuous-Flow UV-LED System for Treatment of Juices and Beverages Using Multiple Wavelengths. Food Eng Rev 2021, 13, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junqua, R.; Vinsonneau, E.; Ghidossi, R. Microbial Stabilization of Grape Musts and Wines Using Coiled UV-C Reactor. OENO One 2020, 54, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, B.; Fiege, J.; Cvetkova, S.; Gräf, V.; Scharfenberger-Schmeer, M.; Durner, D.; Stahl, M. Comparison and Prediction of UV-C Inactivation Kinetics of S. Cerevisiae in Model Wine Systems Dependent on Flow Type and Absorbance. LWT 2022, 169, 114062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengel, Y.; Cimbala, J.; Joshi, J. FLUID MECHANICS LAMINAR AND TURBULENT FLOWS. 2022.
- Hirt, B.; Hansjosten, E.; Hensel, A.; Gräf, V.; Stahl, M. Improvement of an Annular Thin Film UV-C Reactor by Fluid Guiding Elements. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 2022, 77, 102988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csapó, J.; Prokisch, J.; Albert, Cs.; Sipos, P. Effect of UV Light on Food Quality and Safety. Acta Universitatis Sapientiae, Alimentaria 2019, 12, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossitto, P.V.; Cullor, J.S.; Crook, J.; Parko, J.; Sechi, P.; Cenci-Goga, B.T. Effects of UV Irradiation in a Continuous Turbulent Flow UV Reactor on Microbiological and Sensory Characteristics of Cow’s Milk. Journal of Food Protection 2012, 75, 2197–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutchma, T.; Parisi, B.; Unluturk, S.K. Evaluation of Uv Dose in Flow-Through Reactors for Fresh Apple Juice and Cider. Chemical Engineering Communications 2006, 193, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutchma, T.; Keller, S.; Chirtel, S.; Parisi, B. Ultraviolet Disinfection of Juice Products in Laminar and Turbulent Flow Reactors. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 2004, 5, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendyala, B.; Patras, A.; Sudhir Gopisetty, V.V.; Sasges, M. UV-C Inactivation of Microorganisms in a Highly Opaque Model Fluid Using a Pilot Scale Ultra-Thin Film Annular Reactor: Validation of Delivered Dose. Journal of Food Engineering 2021, 294, 110403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, A. Suspension Taylor-Couette Flow: Investigation of Particle Loading Effects on Transitions between Flow Regimes, 2019.
- Var, I.; Uzunlu, S. A Glance at Food Processing Applications; BoD – Books on Demand, 2022; ISBN 978-1-83969-767-8.
- Elçiçek, H.; Güzel, B. TC-UV Reactor Evaluated as an Alternative Option for Treatment of Ballast Water. J ETA Maritime Sci 2020, 8, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Forney, L.J.; Koutchma, T.; Giorges, A.T.; Pierson, J.A. Optimum UV Disinfection between Concentric Cylinders. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 3444–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowska, M.; Koutchma, T.; Kostrzynska, M.; Tang, J.; Defelice, C. Evaluation of Mixing Flow Conditions to Inactivate Escherichia Coli in Opaque Liquids Using Pilot-Scale Taylor–Couette UV Unit. Journal of Food Engineering 2014, 120, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, R.; Pratap-Singh, A. Characterization of Continuous-Flow Pulsed UV Light Reactors for Processing of Liquid Foods in Annular Tube and Coiled Tube Configurations Using Actinometry and Computational Fluid Dynamics. Journal of Food Engineering 2021, 304, 110590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Stahl, M.R.; Graef, V.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Huch, M. UV-C Treatment of Juices to Inactivate Microorganisms Using Dean Vortex Technology. Journal of Food Engineering 2011, 107, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Briviba, K.; Gräf, V.; Greiner, R.; Herrmann, C.; Kuballa, T.; Stahl, M.R. UV-C Treatment Using a Dean Vortex Technology — Impact on Apple Juice Enzymes and Toxicological Potential. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 2013, 20, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barut Gök, S. UV-C Treatment of Apple and Grape Juices by Modified UV-C Reactor Based on Dean Vortex Technology: Microbial, Physicochemical and Sensorial Parameters Evaluation. Food Bioprocess Technol 2021, 14, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gök, S.B. EFFECT OF UV-C TREATMENT ON MICROBIAL POPULATION AND BIOACTIVE COMPOUNDS OF ORANGE JUICE USING MODIFIED REACTOR BASED ON DEAN VORTEX FLOW. The Journal of Food 2021, 46, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopisetty, V.V.S.; Patras, A.; Pendyala, B.; Kilonzo-Nthenge, A.; Ravi, R.; Pokharel, B.; Zhang, L.; Si, H.; Sasges, M. UV-C Irradiation as an Alternative Treatment Technique: Study of Its Effect on Microbial Inactivation, Cytotoxicity, and Sensory Properties in Cranberry-Flavored Water. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 2019, 52, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finjan, R.A.R.A. Characterization of a Novel Taylor-Couette Ultraviolet Reactor for Non-Thermal Pasteurization of Milk, University of Guelph, 2011.
- Milly, P. j.; Toledo, R. t.; Chen, J.; Kazem, B. Hydrodynamic Cavitation to Improve Bulk Fluid to Surface Mass Transfer in a Nonimmersed Ultraviolet System for Minimal Processing of Opaque and Transparent Fluid Foods. Journal of Food Science 2007, 72, M407–M413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food & Beverage. Nuvonic - formerly Aquionics, Hanovia, Berson, Orca.
- Choudhary, R.; Bandla, S. Ultraviolet Pasteurization for Food Industry. International Journal of Food Science and Nutrition Engineering 2012, 2, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Gonzalez, O.; Buckow, R.; Koutchma, T.; Balasubramaniam, V.M. Energy Requirements for Alternative Food Processing Technologies—Principles, Assumptions, and Evaluation of Efficiency. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety 2015, 14, 536–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, A.; Danekar, R.; Prasad, E. UV Disinfection Equipment Market Size, Share & Industry Analysis - 2027 Available online:. Available online: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/UV-disinfection-equipment-market (accessed on 8 April 2023).
- Koutchma, T. UV Light for Processing Foods. Ozone: Science & Engineering 2008, 30, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, T.R.; Silva, E.O.; Rodrigues, S.; Fernandes, F.A.N. Drying of Mangoes Applying Pulsed UV Light as Pre-Treatment. In Proceedings of the 21st International Drying Symposium; July 4 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, F.I.G.; Vieira, M.C.; Silva, C.L.M. Inactivation Kinetics of Peroxidase in Zucchini (Cucurbita Pepo L.) by Heat and UV-C Radiation. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 2012, 13, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavilla, M.; Gayán, E. Chapter 7 - Consumer Acceptance and Marketing of Foods Processed Through Emerging Technologies. In Innovative Technologies for Food Preservation; Barba, F.J., Sant’Ana, A.S., Orlien, V., Koubaa, M., Eds.; Academic Press, 2018; pp. 233–253 ISBN 978-0-12-811031-7.
- Monteiro, M.L.G.; Deliza, R.; Mársico, E.T.; de Alcantara, M.; de Castro, I.P.L.; Conte-Junior, C.A. What Do Consumers Think About Foods Processed by Ultraviolet Radiation and Ultrasound? Foods 2022, 11, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, M.M.; Pimentel, T.C.; Freitas, M.Q.; da Cunha, D.T.; Silva, R.; Guimarães, J.T.; Scudino, H.; Esmerino, E.A.; Duarte, M.C.K.H.; Cruz, A.G. Consumer Innovativeness and Perception about Innovative Processing Technologies: A Case Study with Sliced Prato Cheese Processed by Ultraviolet Radiation. International Journal of Dairy Technology 2021, 74, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA ECFR. 21 CFR Part 179 - Irradiation in the Production, Processing and Handling of Food Available online:. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-21/chapter-I/subchapter-B/part-179 (accessed on 9 May 2023).
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration Code of Federal Regulations. Title 21, Volume 3, 21CFR179. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?fr=179.41 (accessed on 14 May 2023).
- COMMISSION IMPLEMENTING REGULATION (EU) 2017/ 2470 - of 20 December 2017 - Establishing the Union List of Novel Foods in Accordance with Regulation (EU) 2015/ 2283 of the European Parliament and of the Council on Novel Foods.
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) Safety of UV-Treated Milk as a Novel Food Pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 258/97. EFSA Journal 2016, 14, 4370. [CrossRef]
- Food Safety Advances in UV-C Light Technology Improve Safety and Quality Attributes of Juices, Beverages, and Milk Products Available online:. Available online: https://www.food-safety.com/articles/6125-advances-in-uv-c-light-technology-improve-safety-and-quality-attributes-of-juices-beverages-and-milk-products#References (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- FOOD SAFETY AUTHORITY OF IRELAND Appraisal of New and Emerging Food Processing Technologies and Their Potential Risks to Food Safety Available online:. Available online: www.fsai.ie (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Mulrooney, K. Appraisal of New and Emerging Food Processing Technologies and Their Potential Risks to Food Safety.
- Novel Food Regulation in Israel - From Directive to Regulation - Novel Food Regulation - Gsap Available online:. Available online: https://www.gsap.co.il/novel-food-regulation-in-israel-from-directive-to-regulation/ (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Health Canada Ultraviolet Light Treatment of Apple Juice/Cider Using the CiderSure 3500 Available online:. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/food-nutrition/genetically-modified-foods-other-novel-foods/approved-products/novel-food-information-ultraviolet-light-treatment-apple-juice-cider-using-cidersure-3500.html (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- FSSAI Approves Use of SurePure’s Photopurification Technology Available online:. Available online: https://nuffoodsspectrum.in/2013/08/23/fssai-approves-use-of-surepures-photopurification-technology.html (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Yan, R.; Yun, J.; Gurtler, J.; Fan, X. Radiochromic Film Dosimetry for UV-C Treatments of Apple Fruit. Postharvest Biology and Technology 2017, 127, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedler, E.; F. Chavez, D.; Alfiya, Y.; Gilboa, Y.; Gross, A. Impact of Suspended Solids and Organic Matter on Chlorine and UV Disinfection Efficiency of Greywater. Water 2021, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauceda-Gálvez, J.N.; Martinez-Garcia, M.; Hernández-Herrero, M.M.; Gervilla, R.; Roig-Sagués, A.X. Short Wave Ultraviolet Light (UV-C) Effectiveness in the Inactivation of Bacterial Spores Inoculated in Turbid Suspensions and in Cloudy Apple Juice. Beverages 2021, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Huang, R.; Chen, H. Application of Ultraviolet C Technology for Surface Decontamination of Fresh Produce. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2017, 70, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihen, C.; Mani-López, E.; Franco-Vega, A.; Jiménez-Munguía, M.T.; López-Malo, A.; Ramírez-Corona, N. Performance of UV-LED and UV-C Treatments for the Inactivation of Escherichia Coli ATCC 25922 in Food Model Solutions: Influence of Optical and Physical Sample Characteristics. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 2023, 85, 103314–103314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roselló-Soto, E.; Poojary, M.M.; Barba, F.J.; Koubaa, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Mañes, J.; Moltó, J.C. Thermal and Non-Thermal Preservation Techniques of Tiger Nuts’ Beverage “Horchata de Chufa”. Implications for Food Safety, Nutritional and Quality Properties. Food Research International 2018, 105, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, M.L.G.; Mutz, Y. da S.; Francisco, K. de A.; Rosário, D.K.A. do; Conte-Junior, C.A. Combined UV-C Technologies to Improve Safety and Quality of Fish and Meat Products: A Systematic Review. Foods 2023, 12, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassar, J.R.; Mills, E.W.; Campbell, J.A.; Demirci, A. Pulsed Ultraviolet Light Treatment of Chicken Parts. Meat and Muscle Biology 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).