1. Introduction
The development of urbanization has led to the emergence of different functional divisions of the urban system, such as residential, educational, commercial, industrial, and recreational areas[
1,
2,
3]. With the progress of urbanization and the continuous expansion of the city area, the existing types of urban functional zones have deviated from the earlier plans[
4]. Identifying urban functional areas and understanding the urban spatial structure and its changes are important for promoting rational planning of urban development, effective allocation of natural resources, and efficient management of ecosystems[
5]. Berry identified UFZs as the interconnection within areas through the distribution of activities and by flows of commodities between zones[
6]. Karlsson et al. identified the UFZs by measuring the economic activities and intra-regional transportation infrastructure that existed within the region, and the modes of transport of interconnection that existed between regions[
7].In 2007, the Ministry of Land and Resources issued the " Technical Regulations for the Evaluation of Urban Land Intensive Use Potential ( Trial ), " which defined urban functional areas as areas where land use function, use intensity, land use direction, and benchmark land price are generally consistent[
8]. Yuan et al. defined the UFZs as the areas developed to meet specific socioeconomic needs[
9]. Although previous studies have varied in their interpretations of urban functional areas, the researchers characterize UFZs by their zoning characteristics and activity characteristics. The zoning characteristics are used to define the zone boundaries, while the activity characteristics are used to identify the zone functions.
As mentioned above, different studies have defined UFZ differently. Among those studies, zoning plays a critical role in UFZ identification, which mainly focuses on how to partition the urban area into several spatial units where diverse socioeconomic activities (e.g. commercial, industrial, and educational activities) take place. The spatial segmentation methods mainly include grid-based segmentation, road network-based segmentation, and image-based segmentation[
10]. The grid-based segmentation method provides more granular results, as the segmented spatial units are generally smaller than those from other segmentation methods, with grid cell resolution ranging from 30m per pixel to 10 kilometers per pixel[
11,
12]. For example, Hou took the 800m × 800m grid in the central urban area of Zhengzhou as a fine-grained basic research unit, preprocessed and reclassified the POI data, and identified the urban functional area by calculating the proportion feature vector of each unit type[
13]. The road network-based segmentation method mainly includes defining segment boundaries from city-designated transportation zones or mapped road segments[
14,
15,
16]. Cheng analyzed the travel pattern of Beijing residents and the functional pattern of the city by using the land parcels obtained from road segmentation as the research unit and the one-month cab track data of Beijing[
17]. The commonly used image segmentation techniques based on remote sensing images are based on the spatial distribution characteristics of the image objects and the homogeneity of the functional types to generate urban functional area units. Zhou et al. proposed that the image was segmented into SOs (super object) by using single-scale division[
18]. Road as a regional boundary, is a carrier for urban residents to flow between functional areas and has a high degree of fit with the city. However, when using road network data for regional segmentation, there is no regulation on which level of the road should be selected as the standard of urban functional zone division[
19,
20,
21].To effectively express the hierarchical semantic information of urban functional zones, this paper will explore the significance of multi-scale functional zones division based on road network data.
In recent years. Many scholars have conducted relevant research on urban functional area attribute recognition, and the recognition algorithms used are mainly machine learning. Common machine learning algorithms include support vector machine (SVM), K nearest neighbor algorithm ( KNN ), Naive Bayes, and Random Forest (RF).SVM is a pattern recognition method based on statistical learning theory, the purpose of which is to find a hyperplane that makes it possible to correctly separate two types of data points as much as possible, and now many scholars have applied this algorithm in urban functional area recognition. Deng proposed a polygonal Voronoi diagram method to divide urban areas, generate fine spatial analysis units, and categorize the themes of spatial analysis units by SVM algorithm[
22]. Xu uses the seven designed features to characterize the rent/report mode and proposes a method for identifying the social function class of urban areas based on smooth support vector machine. The results show that this method can effectively identify different types of urban functional areas[
23]. The classical support vector machine algorithm only gives an algorithm for binary classification, while in the practical application of data mining, it is generally necessary to solve the multi-classification problem, but the support vector machine for the multi-classification problem solving effect is not satisfactory. K-nearest neighbor classification algorithm is a simple algorithm in data mining classification counting, which mainly relies on limited adjacent samples as the basis of classification. Liu uses DTW-based K-nearest neighbor classification algorithm to classify and identify urban functional areas and uses POI data to assist analysis to obtain the final functional layout of Chengdu[
24]. Yang proposed a new model based on the KNN algorithm to predict the urban AQI, quantifying the impact of wind factors on urban AQI and adding them to the KNN prediction results to obtain the final prediction results[
25]. The KNN algorithm is computationally intensive when the number of features is high and has low prediction accuracy for rare classes when the samples are unbalanced. Naive Bayes algorithm is a simple and effective classification algorithm, which is based on Bayes theorem and feature independence assumption. Xing extracts commodity text features from massive invoice data and realizes categorical coding recognition of invoices based on the Naive Bayes algorithm[
26]. Lefulebe uses PlaneScope images and Naive Bayesian algorithms to classify and detect changes in urban land use and land cover in Cape Town[
27]. However, Naive Bayes may cause the model to perform poorly when dealing with correlated features due to its feature independence assumptions, and in practice, features are not always completely independent of each other, and the performance of the algorithm may be degraded. Random forest algorithm is an integrated learning algorithm based on the decision tree algorithm, which is trained on the dataset by using multiple decision trees at the same time and obtains the final prediction through a voting mechanism or averaging. Grippa Identifies urban land use classifications at the block level using OpenStreetMap data and Random forest algorithms[
28]. Yao extracted the high-dimensional feature vector of POI through the World2 Vec model and trained the feature vector through the random forest algorithm to obtain the urban functional zone with high classification accuracy. Compared with the traditional K-means algorithm, the effectiveness of the random forest algorithm for urban functional zoning is verified[
29]. Random forest algorithms increase the diversity of classification trees by back-sampling and randomly changing the combination of predictor variables to improve the performance of single classification or regression trees. It has the advantages of low computational cost, high model performance, strong robustness, and low risk of over-fitting when processing data, and can better deal with the multi-classification problem of multi-source data functional areas. In the process of using the above machine learning algorithms, it is extremely important to establish training samples, and the quality of training samples is directly related to the training performance of the model. In previous studies, most of the studies produce training samples manually labeled, this method is time-consuming and laborious, and the accuracy of the training samples is not guaranteed. Therefore, in this study, a CA-RFM model that combines a clustering algorithm with random forest classification is used for data mining, and this method can produce training samples efficiently and accurately.
Based on the above analysis, this paper selects the multi-level road network segmentation method for spatial division, integrates dynamic taxi trajectory data with static POI data, and conducts experiments from the perspective of ' dynamic ' and ' static ', and adopts the interactive validation of the results of the CA-RFM model and the results of the quantitative identification of POIs, to carry out the identification of the urban functional zones on the scale of the multi-scale road network.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
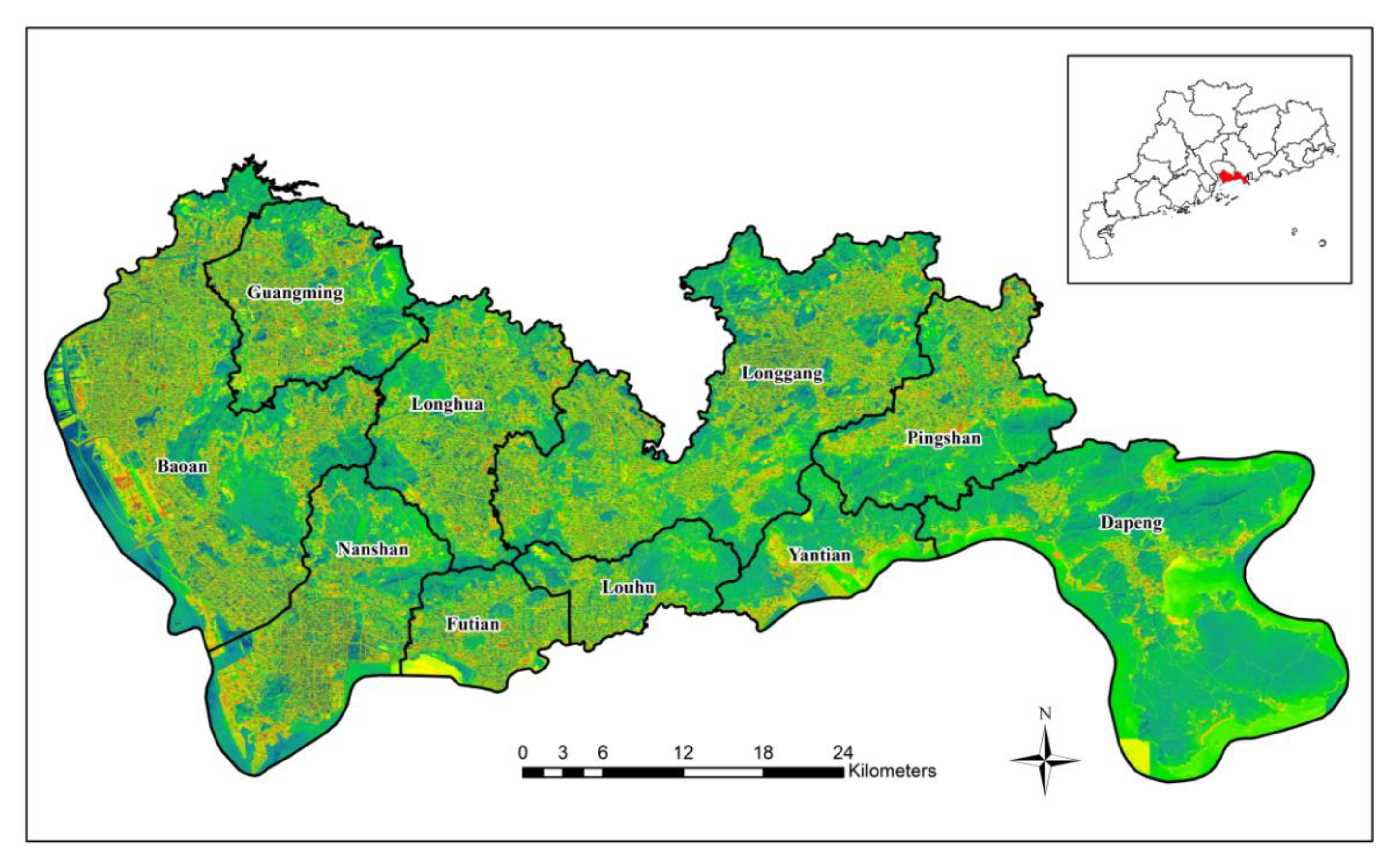
The study area is located in Shenzhen, China (
Figure 1), including Futian District, Luohu District, Nanshan District, Baoan District, Longgang District, and other nine administrative regions and a Dapeng New District, is China's special economic zone, national economic center city and international city. The total area of the study area is 1996.78 square kilometers, and the resident population is 10.7789 million. As one of the national economic centers and international cities, Shenzhen has complex and diverse urban landscapes with rich urban functional zoning. Shenzhen's urban spatial structure is very complex, and the distribution of urban functions is interlaced with each other, although the distribution of functional areas such as residential areas and commercial areas shows a certain regularity in general, the functions of many areas are not single, but mixed functional areas formed by the interaction of multiple functions.
2.2. Data and Processing
As a kind of public transportation in the city, taxis attract passengers with their convenience and readily available. To make the research results reflect the travel situation of residents on working days and rest days, this paper selects the whole week trajectory data from 2015-12-07 (Monday) to 2015-12-13 (Sunday)for analysis, with a total of 419258185 records. Each record contains vehicle number, recording time, latitude and longitude, speed, direction, and vehicle status, and the data format is shown in
Table 1 below.
In the original taxi trajectory data, the OD points of each trajectory are extracted according to the unique identifier of the taxi and the trajectory time sequence. The OD data is extracted according to the taxi ID, passenger status, and timestamp. The passenger status is 1, indicating that the passenger is loaded, and 0 indicates that there is no passenger, then the point in a continuous trajectory where the passenger status changes from 0 to 1 is the starting point and the point where the passenger status changes from 1 to 0 is the destination point. The records are grouped by ID and arranged in ascending order of time, and the record whose passenger status becomes 1 is extracted as the starting point data, and the record whose passenger status becomes 0 is the destination point data, and the O and D points of each trajectory are obtained. The above process was repeated for all records within the date, and 3.86 million OD data were extracted from the 419 million GPS records.
The POI data is derived from the Gaode Map Open Platform, which records the types of activities of urban residents in a certain location. In this paper, we collected the 2018 point-of-interest data within Shenzhen, and the original POI data had a wide range of hierarchical classifications, with the major categories covering a variety of sub-categories, and there were problems of repetition and crossover in different classifications, Therefore, it is necessary to reclassify the POI data. According to the “ urban land use classification and Planning and construction land use standards ”, considering the types and attributes of urban functional areas, this study reclassified POI into public management public service facilities land, commercial service facilities land, residential land, industrial land, green space, and square land. The total number of cleaned POI data is 450591 records, and the classification table is shown in
Table 2.
The road network data is obtained from the official website of Open Street Map. The irregular grid composed of road network data is the basic unit representing the socio-economic functions of urban management and planning. Different levels of road networks divide the whole city into different regions. The road grades selected in this study include expressways, trunk roads, main roads, secondary roads, ordinary branches, residential roads, service roads, etc. To ensure data quality, operations such as removing overhanging points in roads, extending independent road lines to connect with adjacent roads, and finally removing unnecessary internal roads by hand are performed on the road network data.
2.3. Method
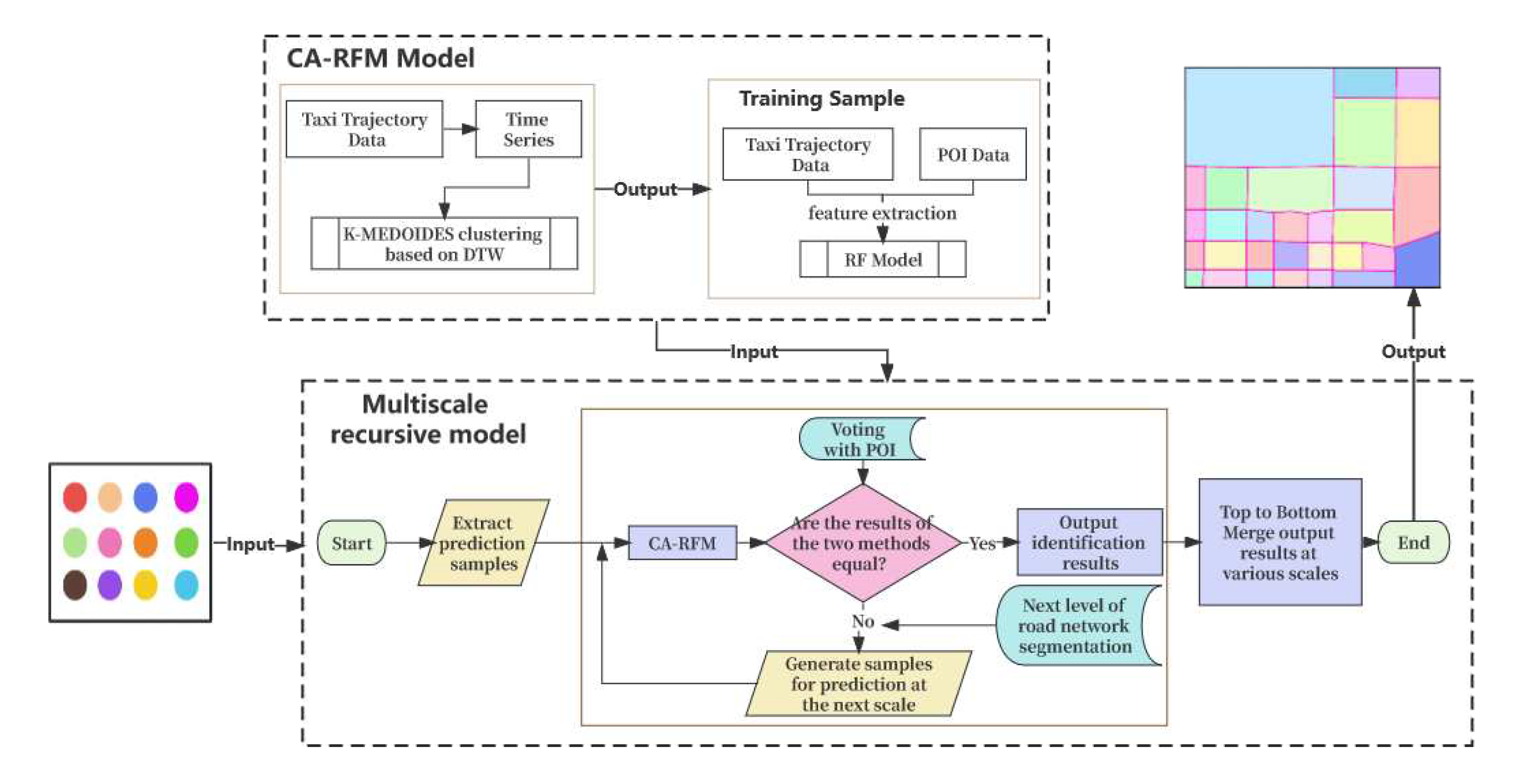
In this study, the trajectory data is transformed into a time feature sequence, and the information is mined to achieve the purpose of identifying functional areas. The workflow of urban main functional area identification is shown in
Figure 2, including the following three steps. Firstly, the K-MEDOIDS clustering algorithm based on DTW is used to cluster the time feature sequence, and the preliminary results of block clustering in the study area are obtained. Secondly, an ensemble method (CA-RFM model) combining clustering algorithm with random forest model is proposed. This method uses clustering algorithm to extract significant feature regions as input, effectively integrates time point features and POIs point features, and uses random forest model to automatically identify UFZ. Finally, up-bottom functional zoning identification: combining the semantic features of the city represented by POI, the functional zoning categories of multi-scale block units are finely identified level by level.
2.3.1. Methods of Time Series Generation
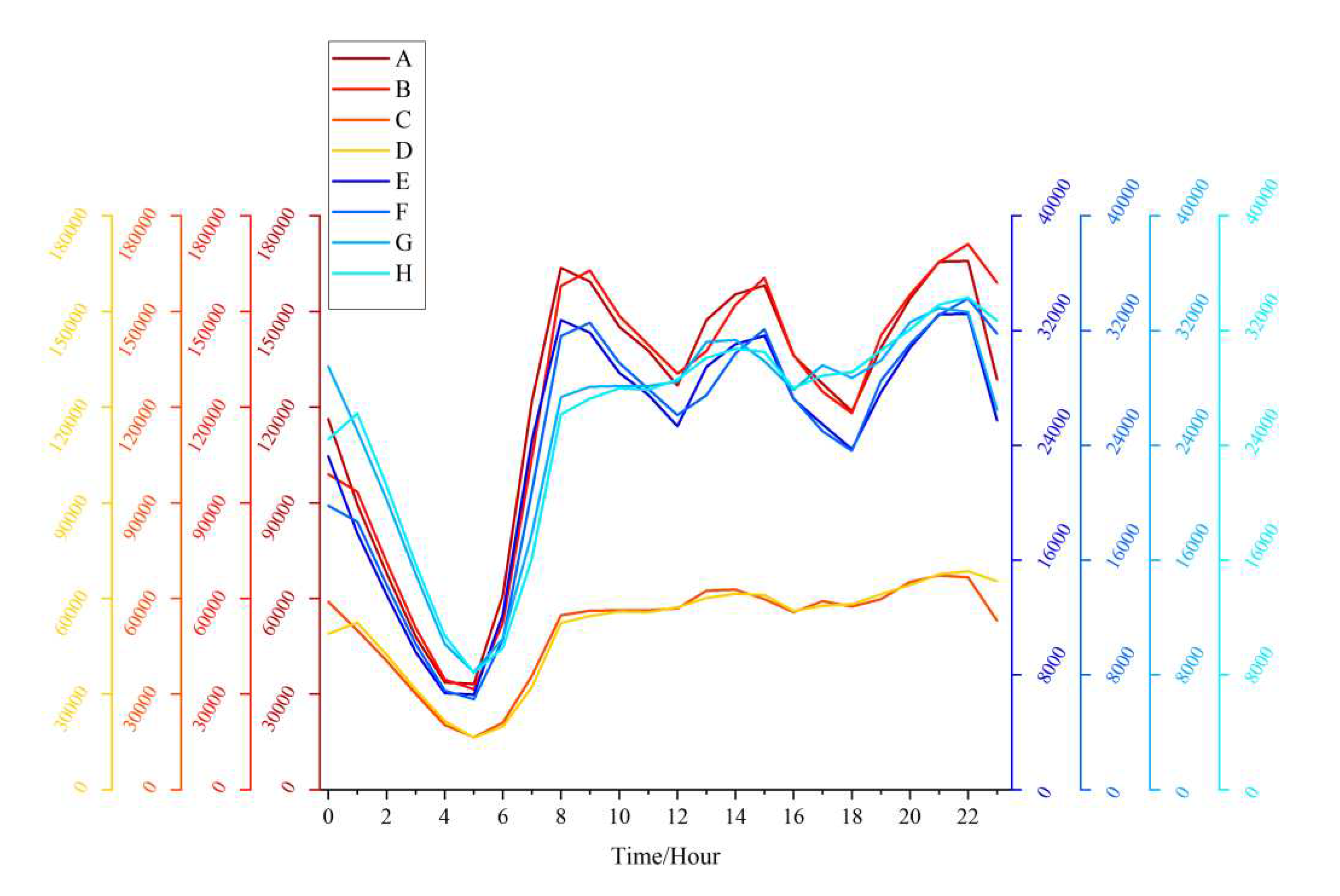
To understand the trips patterns of residents as a whole, the total number of passengers per hour on working days and rest days in TAZ was counted respectively, On this basis, the average number of hours per hour on working days and rest days is counted.
Figure 3 shows that there are large differences in the travel patterns of residents on workdays and weekends, so workdays and weekends should be treated separately. The daily data of the pickup and the drop-off point on the workdays and weekends intersect with the TAZ data. Then, the pick-up and drop-off numbers within each hour and each TAZ were counted. Finally, the average passenger numbers over 24 hours a day on workdays and weekends were calculated. We obtained 4 sets of data in TAZs.
In summary, the time series of each ultimately generated research unit as follows:
where represents the average outflow of workdays,
represents the average inflow of workdays,
represents the average outflow of weekends,
represents the average inflow of weekends.
2.3.2. Dynamic Time Warping
Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) algorithm finds the best correspondence between two observation sequences by regularizing the time dimension with certain constraints, which can explore the similarity and difference of time series with maximum flexibility, and it is the most commonly used quantitative method to measure the similarity of time series.
Given time series
and
,construct an n × m matrix grid,where the matrix element (i , j) is the distance between
and
,the DTW algorithm needs to ensure the minimum difference when aligning P and Q. Build path
, among them
, it is necessary to satisfy three conditions: boundary conditions, continuity conditions, and monotone conditions. The boundary condition is that the starting point of the path is the lower left corner element ( 1,1 ) of the matrix, and the endpoint is the upper right corner element (n, m); The continuity condition means that, except for the start and end points, each element on the path must have two points around it that are adjacent to each other; The monotonicity condition requires that the next element on the path must lie to the right of or above the previous element, while not spanning two elements. Among all the paths that satisfy the above three constraints, the one with the smallest
is selected as the output result, that is, the path with the smallest distance between P and Q is measured :
where
is the minimum cumulative distance of the current matrix element MAR(i , j) with
.
2.3.3. K-MEDOIDS clustering algorithm
For a large amount of data without labels, semi-supervised learning usually adopts manual methods to mark a small number of data labels with typical characteristics as training samples to train most of the remaining data without labels[
30].In this paper, training samples are generated by combining unsupervised learning with manual labeling, which greatly improves the accuracy of the experiment.
The DTW algorithm can be used to obtain the plot distance matrix, that is, the similarity matrix of the time series of taxi traffic volume of the block unit, based on which the clustering analysis can distinguish the differences between different plot types. In the phase of generating training samples, the clustering method used in this study is the K-median algorithm (K-MEDOIDS). K-MEDOIDS clustering is the preferred method in large-scale data clustering analysis, and K-MEDOIDS is less affected by outliers, which makes it more suitable for this study[
31].
To evaluate the reliability of the results of different clustering numbers, this study introduced Silhouette to evaluate the clustering quality of each cluster. In the context of the K-MEDOIDS algorithm, assuming that in an existing clustering result, where a(i) represents the mean value of the DTW distance between sample point i and other sample points in the same cluster and b(i) represent the mean value of the minimum DTW distance between sample point i and other clusters, then there are :
If s(i) is close to 1, it means that the sample point i matches well with the existing clustering results. If s(i) is close to -1, it means that the sample point i should belong to its neighbor clusters. The higher the mean value of s(i) of all points means the better the clustering results
2.3.4. CA-RFM Model
Random Forest (RF) is essentially a collection of many decision trees, and multiple trees are integrated through an integrated learning concept based on traditional decision tree algorithms, which ultimately results in a final prediction based on multiple tree voting. The randomness of RF is reflected in the fact that the training samples of each decision tree are randomly selected, and the splitting attributes of each node in the tree are also randomly selected. Therefore, the accuracy of random forest classification results greatly depends on the accuracy of training samples. The clustering algorithm obtains the preliminary division result of the functional area by directly clustering the time series data, and some areas have an inaccurate division. To make the classification results more credible, this study takes the regions with significant features of each category in the clustering results as the training sample regions of the random forest model and combines the clustering algorithm and the random forest model to construct the CA-RFM model. This combination of supervised and unsupervised learning to select samples increases the accuracy of the training samples to some extent and improves the precision of the experiment.
Given that several studies have confirmed that different urban functional areas have different time statistical features and POIs point features, but these two types of characteristics are seldom fully integrated and used for functional area classification, this study used the CA-RFM model to fuse these two types of characteristics, and the model was used to classify the functional areas.
Taxi OD data reflect the mobile information of passengers in different regions. Different functional areas provide different social functions, and the number of taxi pick-ups and drop-offs will change with time. Extracting 48-dimensional time statistical features of taxi pick-up and drop-off point data for one week in each basic analysis unit are extracted for functional area identification of each unit. Considering the differences in the travel of residents on workdays and weekends, the total number of taxis getting on and off per hour for 24 hours per day on workdays and weekends were counted separately in each of the basic units of analysis to generate a 96-dimensional data feature. The calculation method of the average statistics of the getting on and off points of each basic analysis unit is as follows:
The calculation method of the 24-hour average statistics of the getting on point of each basic analysis unit on workdays is shown in formula (3):
where
is the statistics of getting on points,
is the 24-dimensional vector of the number of getting on points on the kth working day;
is the mean form of the daily getting on point statistic
is a one-week taxi trajectory experimental dataset;
is the total number of workdays in a week.
The calculation method of the 24-hour average statistics of getting on points of each basic analysis unit on weekends is as above, and the number of days on the workdays can be replaced by the number of days on weekends.
The calculation method of the 24-hour average statistics of the getting off point of each basic analysis unit on workdays is as shown in formula (4) :
where
is the statistics of getting off points,
is the 24-dimensional vector of the number of getting off points on the kth working day;
is the mean form of the daily getting off point statistic;
is a one-week taxi trajectory experimental dataset;
is the total number of weekends in a week.
Considering each functional area's different areas, the density of each face OD point is calculated as a feature to make up for the OD point flow information lost by normalization processing. In summary, the time statistical characteristics of each research unit are finally generated as 97 dimensions, that is :
where
is the average outflow characteristics of the workdays,
is the average inflow characteristics of the workdays,
is the average outflow characteristics of the weekends,
is the average inflow characteristics of the weekends, and
is the point density characteristics, a total of 97 dimensions.
The number of POIs points reflects the absolute value difference of different types of interest points in the functional area, which can be used to assist in judging the actual functional attributes of the functional area. However, the absolute value of POIs may also cover the actual dominant attribute information in the region, so the point density and enrichment index of POIs are introduced as auxiliary discriminant information. Twelve representative types of POI are selected from the general category of POI, which are catering service, scenic spot, company and enterprise, shopping service, finance and insurance, science and education and cultural service, housing, life service, sports and leisure service, medical and health service, government agencies and social organizations, and accommodation service. For each plot divided, the point density and enrichment index of each type of POI point in the plot are calculated [
32].
The density of POIs points is expressed as:
where
is the density of type i POI in the functional area of type j;
is the number of type i POIs in the class j functional area;
is the total area of the class j functional area.
The POIs enrichment index is expressed as:
where
is the enrichment index of the class i POI in the class j functional area;
is the number of type I POIs in the class j functional area;
is the total number of POIs in the class j functional area;
is the total number of type i POIs; N is the total number of all POIs in the entire study area. The higher the F indicates the higher the enrichment index of type i POI in the class j functional area.
In summary, the final 24-dimensional features of POIs points for each research unit were generated, i.e:
where
is the density feature of 12 types of POI, and
is the enrichment index feature of 12 types of POI.
2.3.5. Quantitative identification of POI
POI contains a large amount of semantic information about urban functions and is a way to quantitatively identify functional areas. Considering the large difference in the amount of POI data between different categories and the differences in the geographic entities they represent and the public awareness, this study introduces the two indicators of Frequency Density (FD) and Category Ratio (CR) to determine the functional attributes, and the calculation formulas are as follows [
33].
where i represents the i-th of the five POI types;
is the number of the i-th type of POI in the block unit;
is the total number of i-th type of POI;
is the frequency density of i-th type of POI in the block unit to the total number of POIs of that type.
is the ratio of the frequency density of i-th type of POI to the frequency density of all types of POI in the block unit.
The FD and CR of each type of POI within each functional area unit are calculated according to the formula. Referring to the research of Chi Jiao et al., and through multiple adjustment tests, the CR value of 30 % is determined as the standard to judge the nature of the functional area of the unit [
34]. That is, when the proportion of a certain type of POI type is greater than 30%, the unit is judged to be a single functional area; when the proportion of all POI types in the unit does not exceed 30%, the area is determined to be a mixed functional area, and the mixed type depends on the two most dominant POI types in the unit; three and more than three mixed cases are not considered in this study.
2.3.5. Multi-scale recursive recognition method based on cross-validation
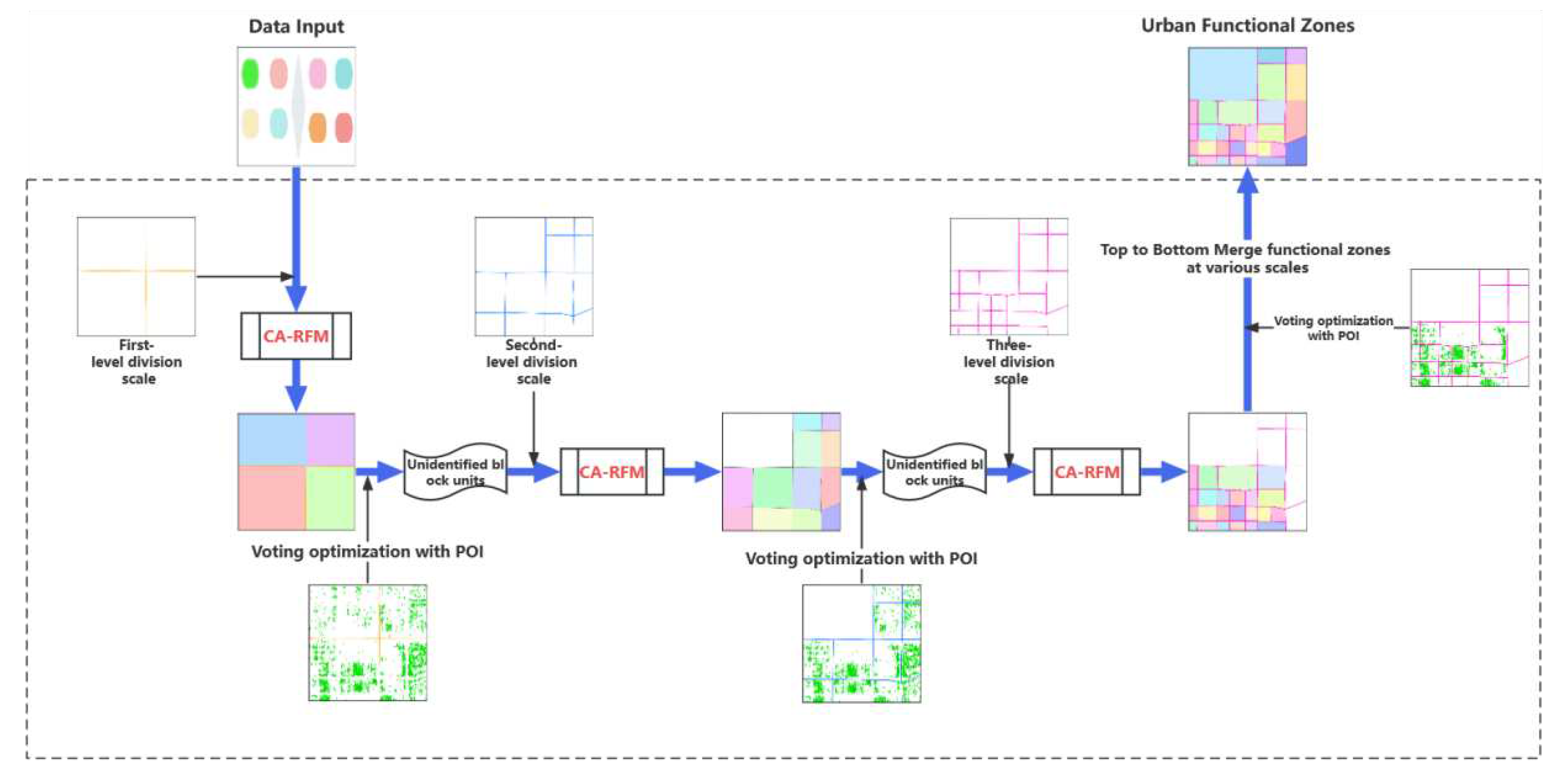
The auxiliary data used in the delineation of urban functional zones varies, while the block unit formed by the road network is closer to the boundary of urban functional zones, easy to obtain, and is the most widely used data in the delineation of functional zones. The road network-based method can better estimate the actual distribution of urban roads, and the use of multilevel urban road networks divided into functional district block units can better meet the scientific management of urban planning departments and assist decision-making. For this reason, this study proposes a multi-level research unit division method based on road grade, i.e., using highways, trunk roads, and main roads as the first-level unit demarcation line, adding ordinary street roads based on the first-level demarcation line as the second-level demarcation line, and adding service roads based on the second-level demarcation line as the third-level demarcation scale, to obtain the third-level scale research unit.
Based on multi-level road network division, a multi-scale recursive identification method based on cross-validation is proposed by combining the results of CA-RFM model extraction and POI quantitative identification, as shown in
Figure 4. The CA-RFM model is used to determine the urban functional area category of the block unit at each scale. In this process, the POI-based voting was used to verify the identification based on the CA-RFM model. and the results of the validation determined which blocks would be divided into sub-blocks at the next scale. Whether the block unit is divided into the next scale depends on the consistency of the extraction results of the two methods, to realize the top-down hierarchical division from large-scale road network to small-scale road network.
This study formulates the principles that the method needs to follow. Firstly, after calculating the CR values of all POI types in each block unit, the attribute similarity between the quantitative identification of POI based on CR judgment and the identification based on the CA-RFM model is calculated to determine whether the urban functional area is divided and the attributes of the block unit.
(1) For the unit with a CR value greater than 30 % of POI type, if the functional attributes determined by CR are consistent with the functional identification results of the CA-RFM model, the functional area attributes of the block unit are determined and the block unit is no longer divided. If the functional attributes determined by CR are inconsistent with the identification results of the CA-RFM model, the block unit is further divided until the functional attributes of the two methods are consistent.
(2) For all units with CR values of POI types less than 30 %, if the functional attributes determined by CR are consistent with the functional identification results of the CA-RFM model, the results are retained and the unit will not be divided. If the functional attributes determined by CR are inconsistent with the functional identification results of the CA-RFM model, the block unit is further divided until the functional attributes of the two methods are consistent.
(3) For the unit that does not contain POI (CR is a null value), it is called a null value unit. The recognition result of the CA-RFM model will be the terminal functional area category of the block unit and will not be divided. For the unit that does not contain trajectory data or the number of time statistical features of 0 exceeds 80 % of the total number of features, the functional attributes determined by the CR value are the terminal functional area category of the unit and will not be divided. For the block unit with inconsistent attribute results obtained by the two methods in the third level division, the functional attribute determined by the CR value is the final functional area category of the unit; for the unit that contains neither POI data nor trajectory data, they are referred to as no-value unit and are not used as discriminatory regions.
3. Results
3.1. Training sample generation of CA-RFM model
For the training of the CA-RFM model, training samples with labels are essential. To obtain the training samples, the K-medoids algorithm was utilized to cluster the preprocessed time series data, the reliability of the number of clusters is evaluated by the silhouette coefficient. The change in the silhouette value with the number of clusters K is shown in
Figure 5a–c. The larger the silhouette value is, the better the clustering effect will be. From the graph, it can be seen that there are inflection points at each level when the number of clusters is 7,6 and 6, respectively. Considering the change of Silhouette with K and the size of the data volume, the number of clusters at each level of the road network is finally determined to be 7,6, and 6.
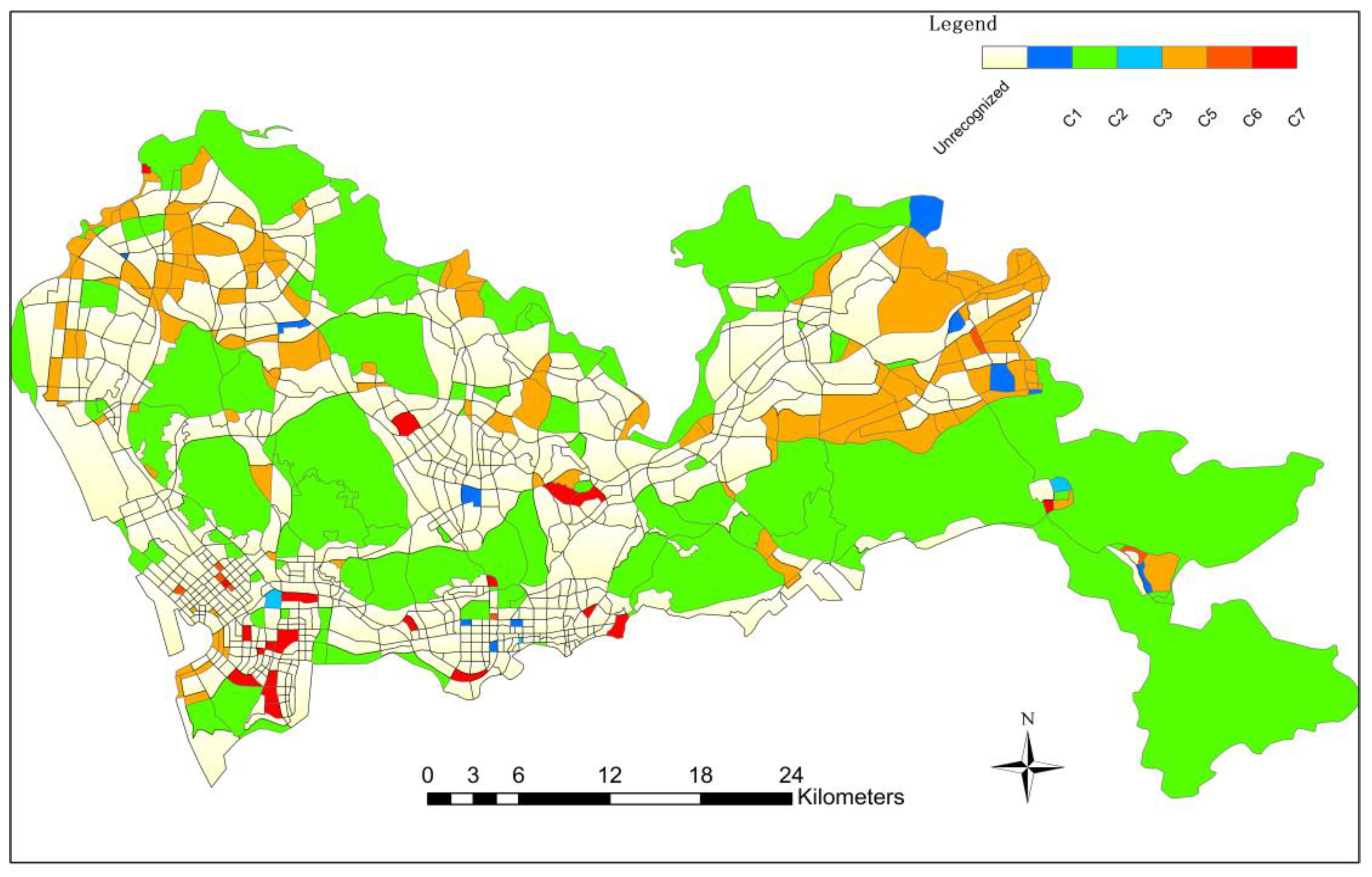
According to the overall planning of Shenzhen City, the POI enrichment index of each type in each block unit and the category of urban functional areas marked by high-definition remote sensing images, this study selects a certain amount of significant feature areas from
Figure 6a–c as the input of the CA-RFM model, and generates training samples for training the model. The sample size of industrial and commercial mixed area(C1), green scenic spot(C2), life and recreation mixed area(C3), mature commercial area(C4), industrial/public service mixed area(C5), public and commercial mixed area(C6) and urban residential area(C7) are all 75.
3.2. Multi-scale recursive urban functional area identification results
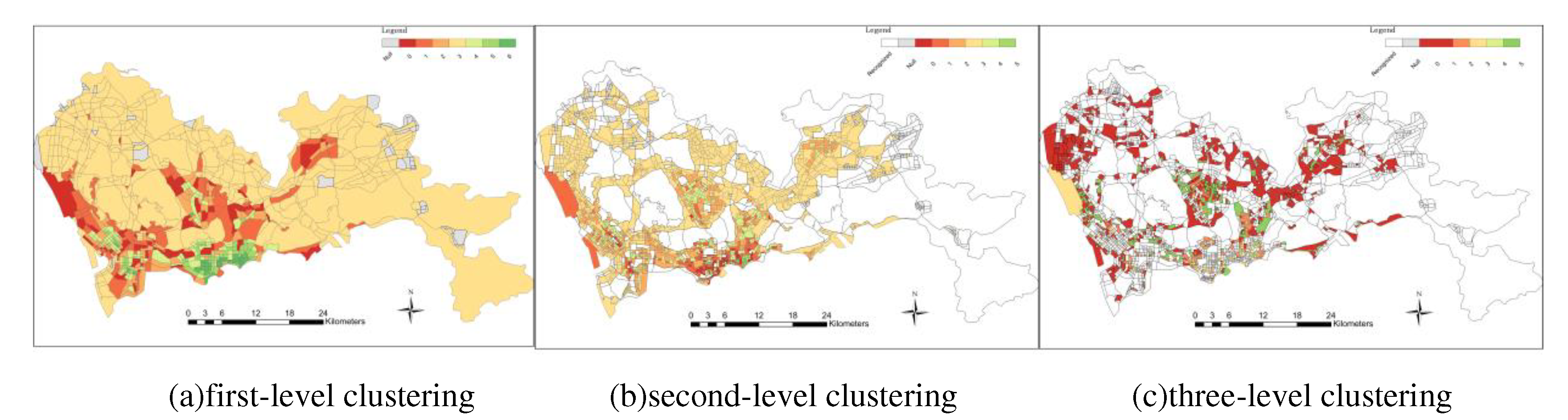
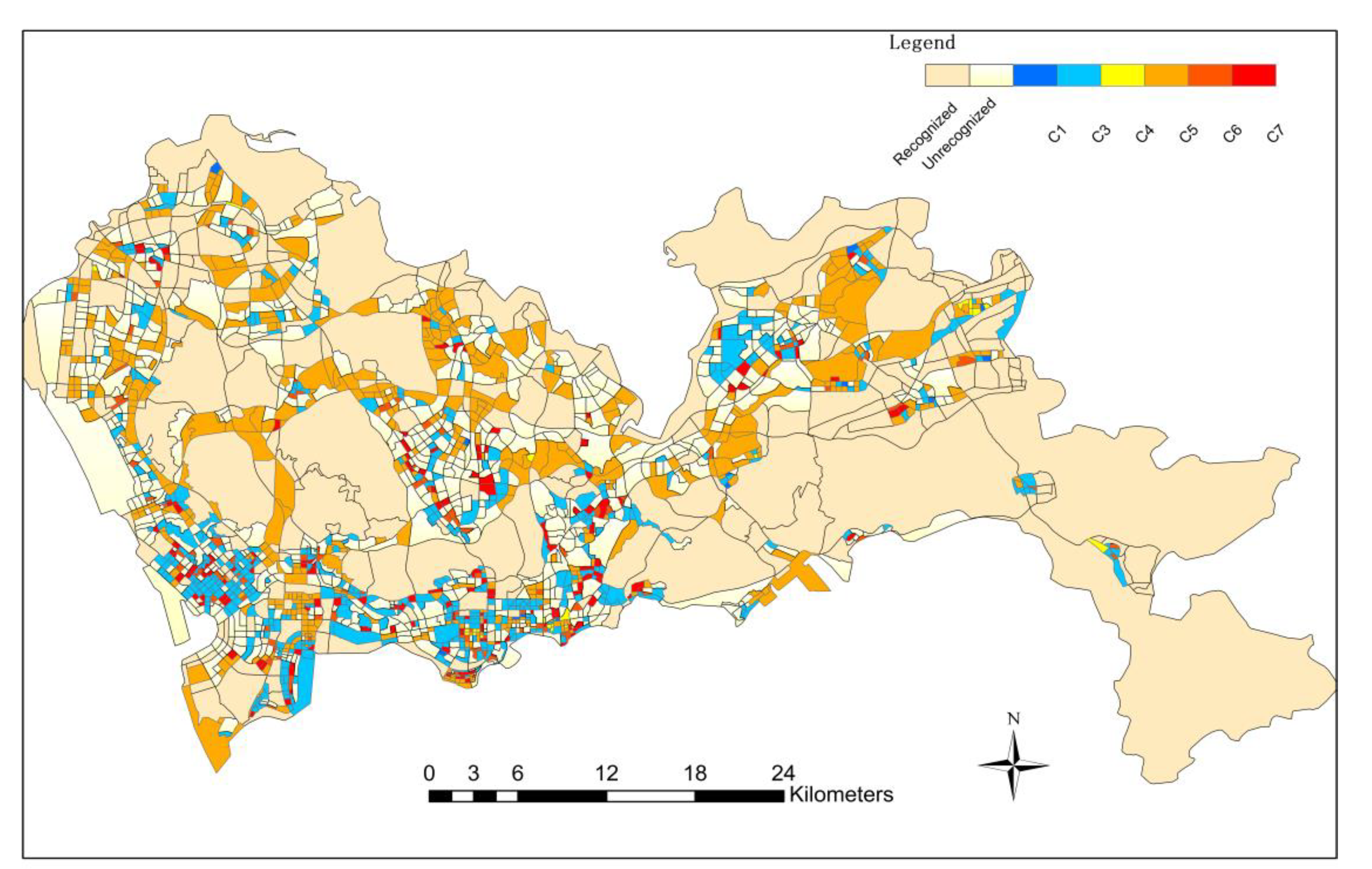
Figure 7 shows the identification results of functional areas with highways, trunk roads, and main roads as the first-level division scale. The road grade used in the first-level division scale is mainly responsible for the long-distance and fast transportation services of the city. It can be used as a landmark road of a city, and its zoning scale is relatively large. The study area was divided into 919 first-level block units, of which only 270 units were successfully identified by the multi-scale model, and the remaining 649 units did not reach the threshold of similarity calculation. The results show that the functional attributes of these 649 units are highly heterogeneous, and there are multiple categories of functional areas within the block units. These first-level block units need to be subdivided on the next scale.
Taking ordinary streets as the dividing boundary, a total of 2071 secondary block units are divided. The similarity algorithm is used to calculate the recognition results of the CA-RFM model. A total of 1308 secondary block units are successfully identified, and the remaining 763 secondary block units need to be divided at the next scale (
Figure 8). In the secondary division, the number of identified functional areas has soared, especially in the mixed area of life and recreation and the mixed area of industry / public service. This also shows that in urban planning and design, many factories, public service areas, and residential areas are designed with ordinary streets as the boundary. In addition, ordinary streets are used to connect most areas of the city. Residential areas, industrial areas, and public service areas are generally located near convenient streets.
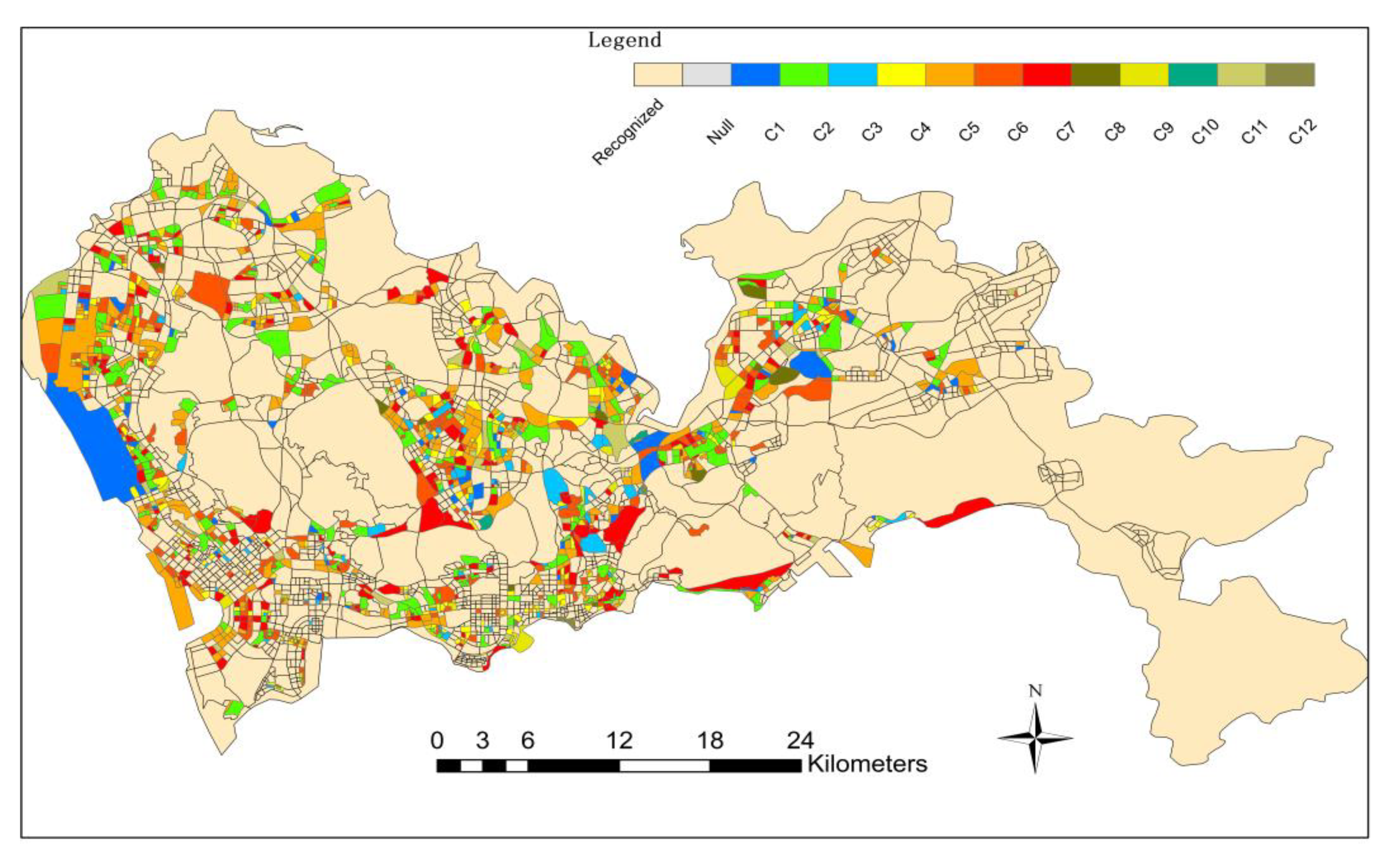
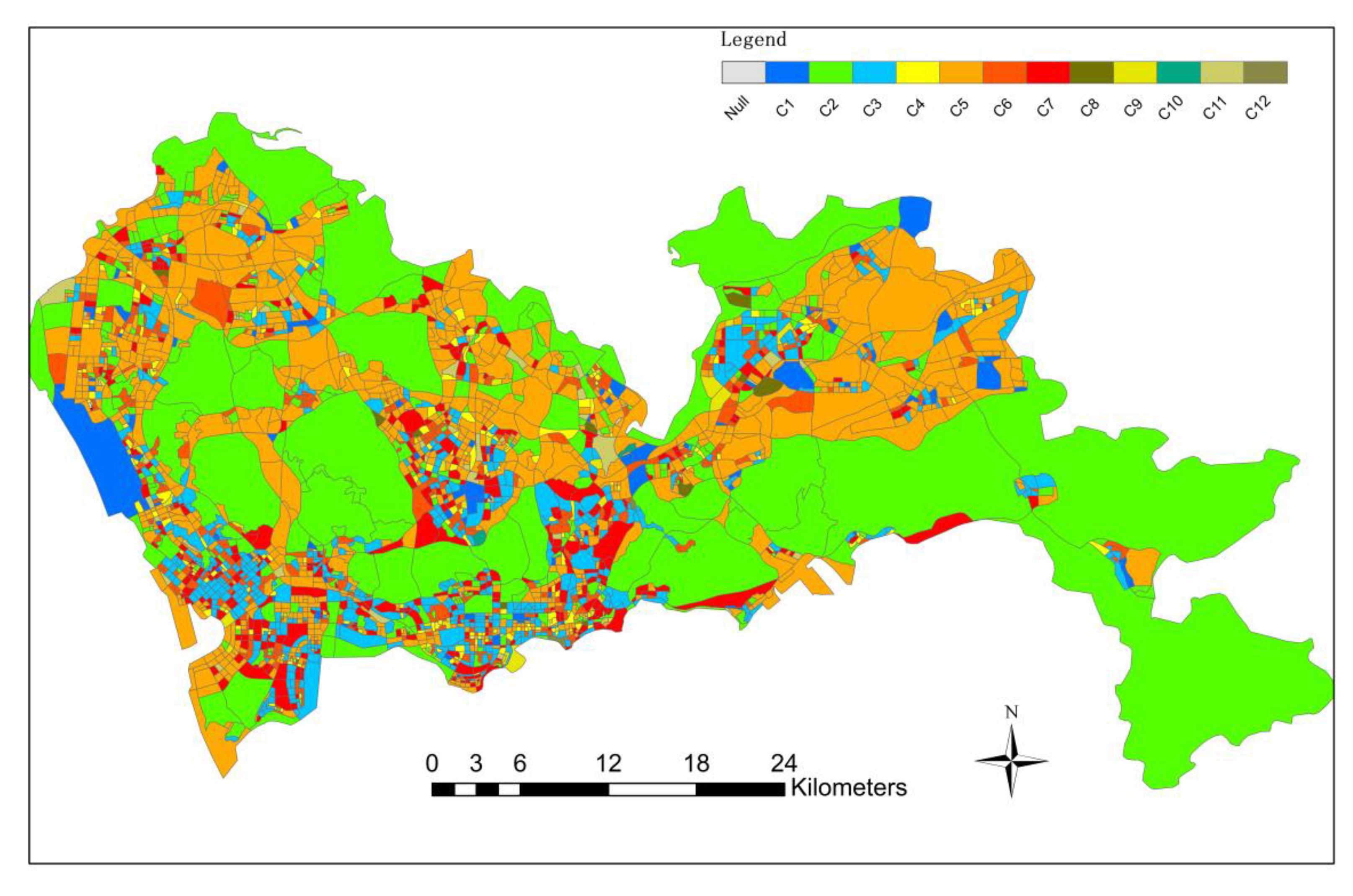
Figure 9 shows the results of the final level of block unit identification using service roads, with a total of 1,510 tertiary block units identified, and some smaller-scale mixed public and commercial areas and urban residential areas identified in large numbers. At the same time, functional areas mainly based on industrial mixed functions(industrial-green mixed areas, industrial-residential mixed areas)and functional areas mainly based on public-service mixed functions(public-green mixed areas, public-residential mixed areas)are also identified. In the last block unit, 12 types were identified, namely: C1-industrial and commercial mixed, C2-green scenic spot, C3-life and recreation mixed area, C4-mature commercial area, C5-industrial / public service mixed area, C6-public commercial mixed area, C7-urban residential area, C8-industrial and green mixed area, C9-public residential mixed area, C10-public green mixed area, C11-industrial and residential mixed area, C12-green residential mixed area. Among them, the mixed area mainly composed of industrial and public service mainly includes some small office areas, small factories, and factories, etc., which are relatively small in area, so it is necessary to divide the functional zoning unit of the minimum scale road. It can be seen that the land use types in Shenzhen are mainly mixed with residential land, industrial land, and public land.
Finally, the classification results of the above three scales are combined to obtain the overall functional area identification results of the study area, as shown in
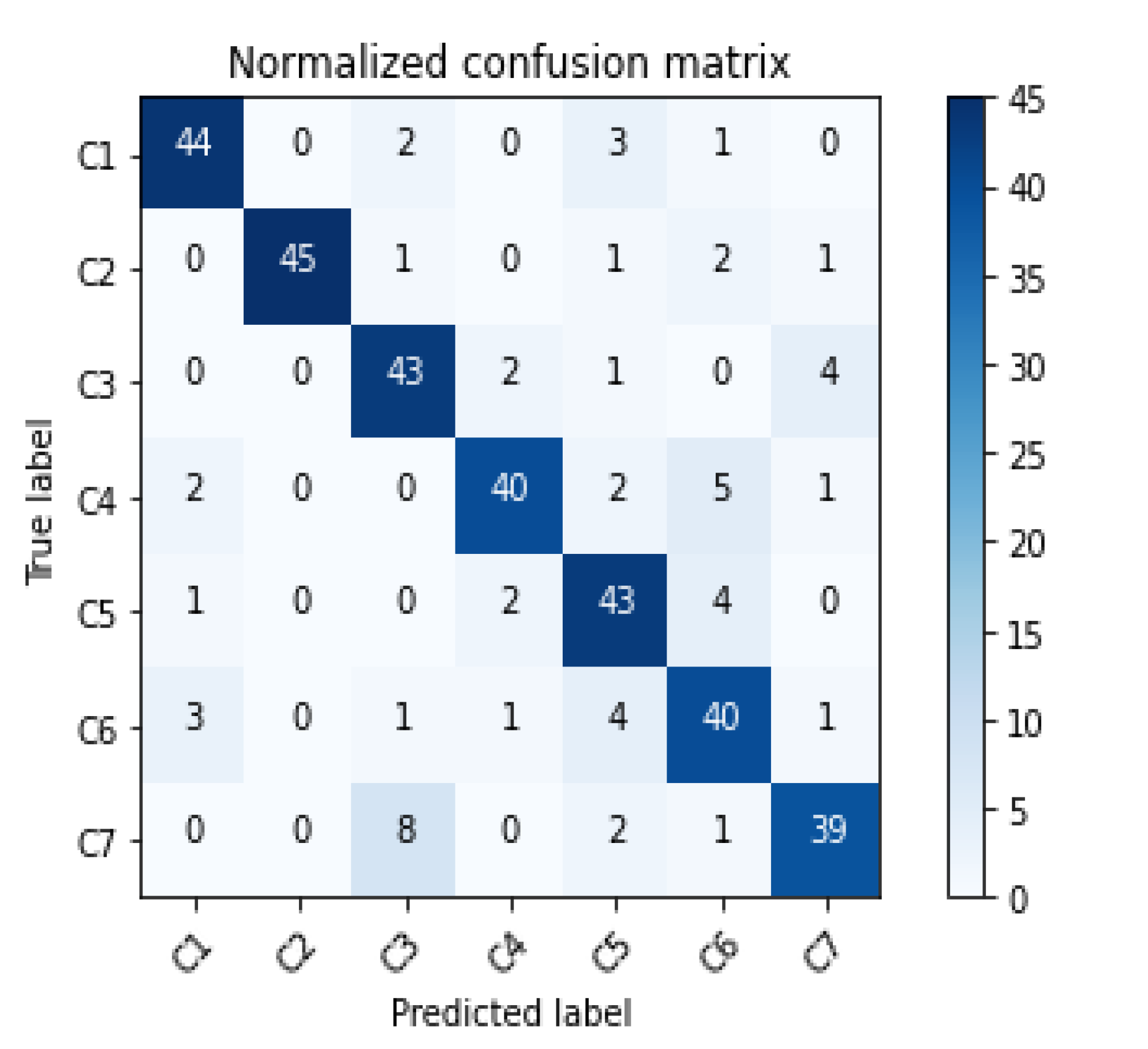
Figure 10. Based on the division from the large-scale road network to the small-scale road network, this method realizes the identification of multi-scale urban functional areas from top to bottom. The study area is divided into 3088 block units. For each type of functional area type, a certain amount of block units in the classification results are extracted. The results are tested with the overall planning of Shenzhen City and the ' Mapping of Basic Urban Land Use Types in China: Preliminary Results in 2018 '[
35]. The calculation results of the confusion matrix are as follows (
Figure 11), and the overall recognition accuracy is 0.874 %. The above experiments demonstrate that the multiscale recursive recognition method combines the two methods organically. On the one hand, it realizes the mutual test of the two recognition results and improves the extraction accuracy of the functional area. The accuracy of the recognition results of the CA-RFM model is tested by using the functional semantic information implied by POI. The CA-RFM solves the problem that there is no POI data in some units and POI may have inaccurate data. On the other hand, it reduces the unnecessary division of some blocks and improves the operation efficiency of the model.
4. Contrast experiment
To verify the performance of the multi-scale recursive identification method based on cross-validation in identifying urban functional areas, the functional area identification results of this paper's method (E) and the single-scale POI quantitative identification method (A), the multi-scale POI quantitative identification method (B), the single-scale CA-RFM model (C), and the multi-scale CA-RFM model (D) are compared, respectively. To keep the variables constant, the block units of each layer obtained in
Figure 10. are used as single-scale functional area constraint boundaries, and the three-level scales of this study are used as multi-scale functional area identification constraint boundaries.
Table 3. below shows the accuracy comparison of different examples.
According to the combination of different scales and methods, five groups of comparative experiments were generated. From the perspective of ' scale ', based on the same method, the overall accuracy OA and Kappa of group B were higher than those of group A, at the same time, the multi-scale recognition results of group CD were also better than the single-scale recognition results. From the perspective of ' method ', the POI quantitative identification method is better than the CA-RFM model based on the same single scale in the two groups of AC, and the CA-RFM model is better than the POI quantitative identification based on the same multi-scale in the two groups of BD. On the whole, the multi-scale recognition results are better than the single-scale recognition results. In this case, the method of this study (group E) obtained the highest OA and Kappa coefficients: OA-0.874, Kappa-0.853. In contrast, the method proposed in this paper has the best recognition effect.
5. Conclusions
With the deepening of urbanization, the urban structure presents complex and regular characteristics, and the identification of urban functional areas is a challenging research field. In the era of big data, the emergence of massive data has added new data sources to the identification of urban functional areas. However, single data has inevitable defects in the identification of functional areas. Therefore, this paper uses a combination of multi-source data to improve the accuracy and reliability of functional area identification. Combined with taxi trajectory data, POI data, and multi-scale road network data, a multi-scale recursive identification method of urban functional areas based on POI frequency density analysis and the CA-RFM model is proposed. Experiments and comparisons show the feasibility and superiority of the method. The contribution of this study is mainly manifested in two aspects :
(1) The K-MEDOIDS clustering based on DTW is used to cluster the time series data, and the original output of the clustering is used as the input of the CA-RFM model. This auxiliary method is used to select the sample area, which improves accuracy and efficiency. The UFZ classification results also show the effectiveness of these sample area selections.
(2) Using multi-level road network to decompose block units step by step, combined with POI quantitative identification and CA-RFM model, a multi-scale recursive identification method of urban functional areas based on interactive verification is proposed, which realizes the fine extraction of functional areas from top to bottom, avoids the defects of the single road network, and the interactive verification of the two methods improves the overall classification accuracy. In addition, the identification results of the joint use of the CA-RFM model and CR can reduce the negative effects in some blocks when there is no POI data, no cab track data, and too little track data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.L. and G.C.; methodology, T.L. and G.C.; validation, T.L.; formal analysis, T.L.; investigation, T.L.; writing—original draft preparation, T.L.; writing—review and editing, G.C.; visualization, T.L.; supervision, G.C.; project administration, G.C. and J.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Universities of Henan Province (NSFRF180329), the MOE (Ministry of Education in China) Project of Humanities and Social Sciences (15YJCZH018), Science and Technology Project of Henan Province (162102210063).
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this study can be obtained from the first author by 15639116331@163.com with reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Assem, H. , Xu, L., Buda, T. S., & O'Sullivan, D. (2016, November). Spatio-temporal clustering approach for detecting functional regions in cities. In 2016 IEEE 28th international conference on tools with artificial intelligence (ICTAI) (pp. 370-377). IEEE.
- Chen, S., Tao, H., Li, X., & Zhuo, L. (2016). Discovering urban functional regions using latent semantic information: Spatiotemporal data mining of floating cars GPS data of Guangzhou. Acta Geographica Sinica, 71(3), 471-483.
- Long, Y., Shen, Z., Long, Y., & Shen, Z. (2015). Discovering functional zones using bus smart card data and points of interest in Beijing. Geospatial analysis to support urban planning in Beijing, 193-217.
- Antikainen, J. (2005). The concept of functional urban area. Findings of the ESPON project 1.1. 1Informationen zur Raumentwicklung, (7), 447-456.
- Salkin, P. E. (1999). The politics of land use reform in New York: challenges and opportunities. . John's L. Rev., 73, 1041.
- Berry, B. J. (1968, December). Interdependency of spatial structure and spatial behavior: A general field theory formulation. In Papers of the Regional Science Association (Vol. 21, pp. 205-227). Springer-Verlag.
- Karlsson, C. (2007). Clusters, functional regions and cluster policies. JIBS and CESIS Electronic Working Paper Series (84), 3.
- 国土资源部.城市土地集约利用潜力评价技术规程(试行)[S]. 2007.
- Yuan, N. J. , Zheng, Y., Xie, X., Wang, Y., Zheng, K., & Xiong, H. (2014). Discovering urban functional zones using latent activity trajectories. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 27(3), 712–725. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X., Wang, C., Li, Z., & Ning, H. (2021). A 100 m population grid in the CONUS by disaggregating census data with open-source Microsoft building footprints. Big Earth Data, 5(1), 112-133. [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y., Hou, D., & Xing, H. (2017). Rapid detection of land cover changes using crowdsourced geographic information: a case study of Beijing, China. Sustainability, 9(9), 1547. [CrossRef]
- Jongman, B., Wagemaker, J., Revilla Romero, B., & Coughlan de Perez, E. (2015). Early flood detection for rapid humanitarian response: harnessing near real-time satellite and Twitter signals. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 4(4), 2246-2266. [CrossRef]
- 侯华伟.(2020).基于多源数据的城市功能区识别方法研究(硕士学位论文,河南财经政法大学).https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD202002&filename=1020625764.nh.
- García-Palomares, J. C., Salas-Olmedo, M. H., Moya-Gomez, B., Condeco-Melhorado, A., & Gutierrez, J. (2018). City dynamics through Twitter: Relationships between land use and spatiotemporal demographics. Cities, 72, 310-319. [CrossRef]
- Hu, T. , Yang, J., Li, X., & Gong, P. (2016). Mapping urban land use by using landsat images and open social data. Remote sensing 8(2), 151. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X., & Long, Y. (2016). Automated identification and characterization of parcels with OpenStreetMap and points of interest. Environment and Planning B: Planning and Design, 43(2), 341-360. [CrossRef]
- 程静,刘家骏 & 高勇.(2016).基于时间序列聚类方法分析北京出租车出行量的时空特征. 地球信息科学学报(09),1227-1239.
- Zhou, W., Ming, D., Lv, X., Zhou, K., Bao, H., & Hong, Z. (2020). SO–CNN based urban functional zone fine division with VHR remote sensing image. Remote Sensing of Environment, 236, 111458. [CrossRef]
- Song, J., Lin, T., Li, X., & Prishchepov, A. V. (2018). Mapping urban functional zones by integrating very high spatial resolution remote sensing imagery and points of interest: A case study of Xiamen, China. Remote Sensing, 10(11), 1737. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y., & Karimi, K. (2016). Urban function connectivity: Characterisation of functional urban streets with social media check-in data. Cities, 55, 9-21. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y., & Karimi, K. (2016). Urban function connectivity: Characterisation of functional urban streets with social media check-in data. Cities, 55, 9-21.
- Deng, Y., & He, R. (2022). Refined Urban Functional Zone Mapping by Integrating Open-Source Data. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11(8), 421. [CrossRef]
- Xu, H., & Ying, J. (2019). Recognizing social function of urban regions by using data of public bicycle systems. Chinese Journal of Electroni. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X., Tian, Y., Zhang, X., & Wan, Z. (2020). Identification of urban functional regions in chengdu based on taxi trajectory time series data. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 9(3), 158. [CrossRef]
- 杨丰玉,王宝英,陈英,冯涛 & 陈涛苹.(2019).种考虑风力作用的KNN城市AQI预测算法. 计算机应用研究(06),1679-1682+1722. [CrossRef]
- 邢志壮.(2019).基于多源数据的政务信息系统的研究与应用(硕士学位论文,北京邮电大学).https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbname=CMFD201902&filename=1019112663.nh.
- Lefulebe, B. E., Van der Walt, A., & Xulu, S. (2022). Fine-scale classification of urban land use and land cover with planetscope imagery and machine learning strategies in the city of Cape Town, South Africa. Sustainability, 14(15), 9139. [CrossRef]
- Grippa, T., Georganos, S., Zarougui, S., Bognounou, P., Diboulo, E., Forget, Y., ... & Wolff, E. (2018). Mapping urban land use at street block level using openstreetmap, remote sensing data, and spatial metrics. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 7(7), 246. [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y., Li, X., Liu, X., Liu, P., Liang, Z., Zhang, J., & Mai, K. (2017). Sensing spatial distribution of urban land use by integrating points-of-interest and Google Word2Vec model. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 31(4), 825-848. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X. , & Goldberg, A. B. (2022). Introduction to semi-supervised learning. Springer Nature.
- Zhu, C., Cheng, G., & Wang, K. (2017). Big data analytics for program popularity prediction in broadcast TV industries. Ieee Access, 5, 24593-24601. [CrossRef]
- 姚尧,张亚涛,关庆锋,麦可 & 张金宝.(2019).使用时序出租车轨迹识别多层次城市功能结构. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版)(06),875-884. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y. , & Han, Y. (2019). Identification of urban functional areas based on POI data: A case study of the Guangzhou economic and technological development zone. Sustainability, 11(5), 1385. [CrossRef]
- 池娇,焦利民,董婷,谷岩岩 & 马雅兰.(2016).基于POI数据的城市功能区定量识别及其可视化. 测绘地理信息(02),68-73. [CrossRef]
- 宫鹏,陈斌,李雪草,刘涵,王杰,白玉琪... & 徐冰.(2020).2018年中国基本城市土地利用类型制图(EULUC-China)(英文). Science Bulletin(03),182-187.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).