Submitted:
04 August 2023
Posted:
08 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents, materials and instruments
2.2. PADs preparation and analysis
2.3. Chemometric data treatment: Partial Least Square regression (PLS)
3. Results
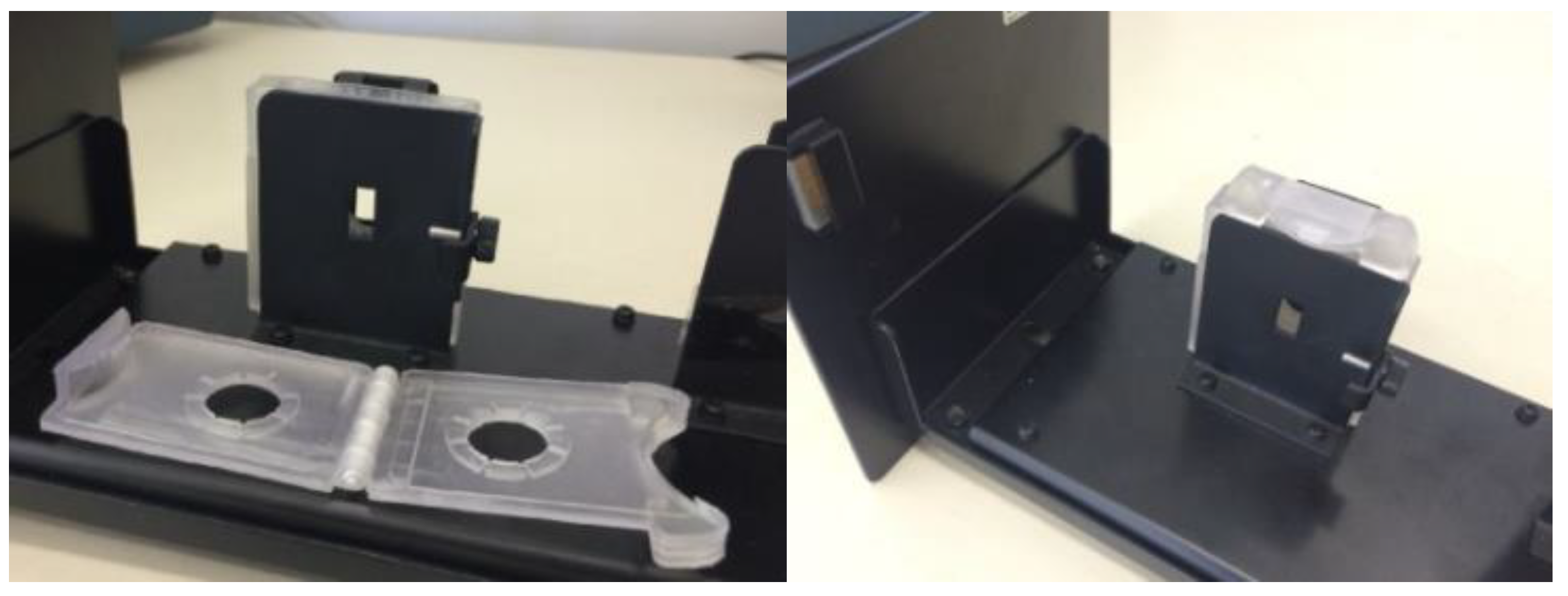
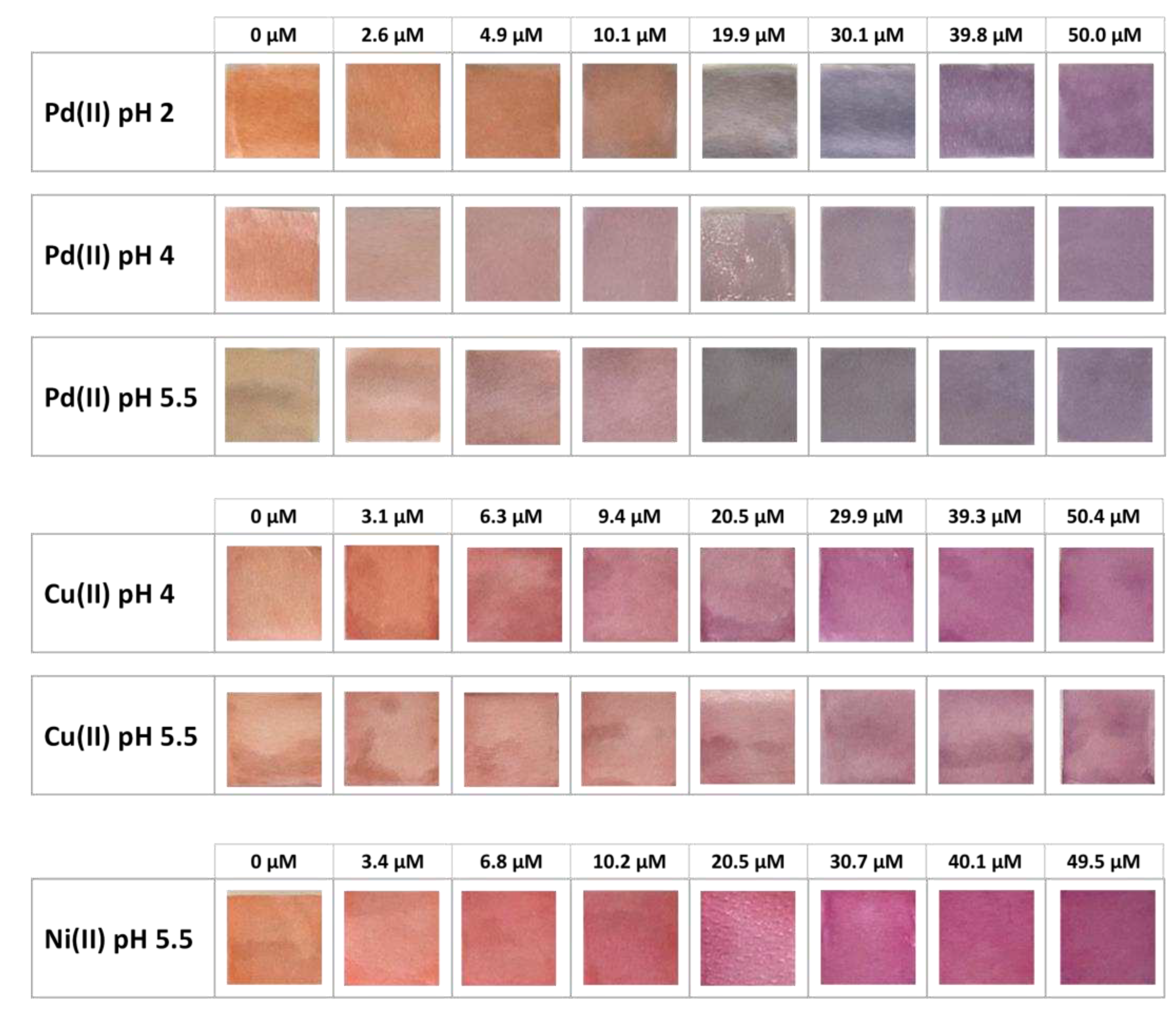
3.1. PADs preparation and analysis
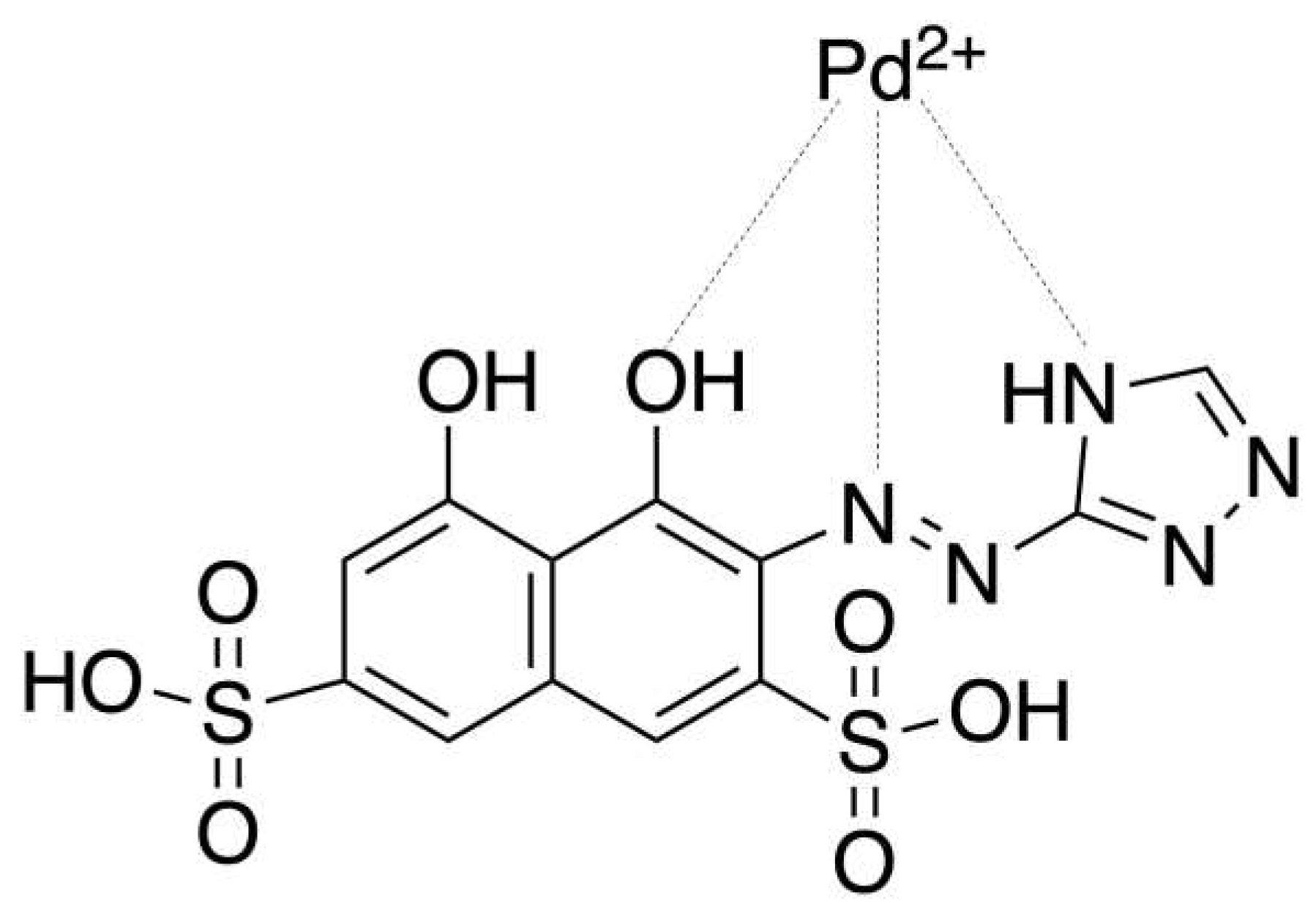
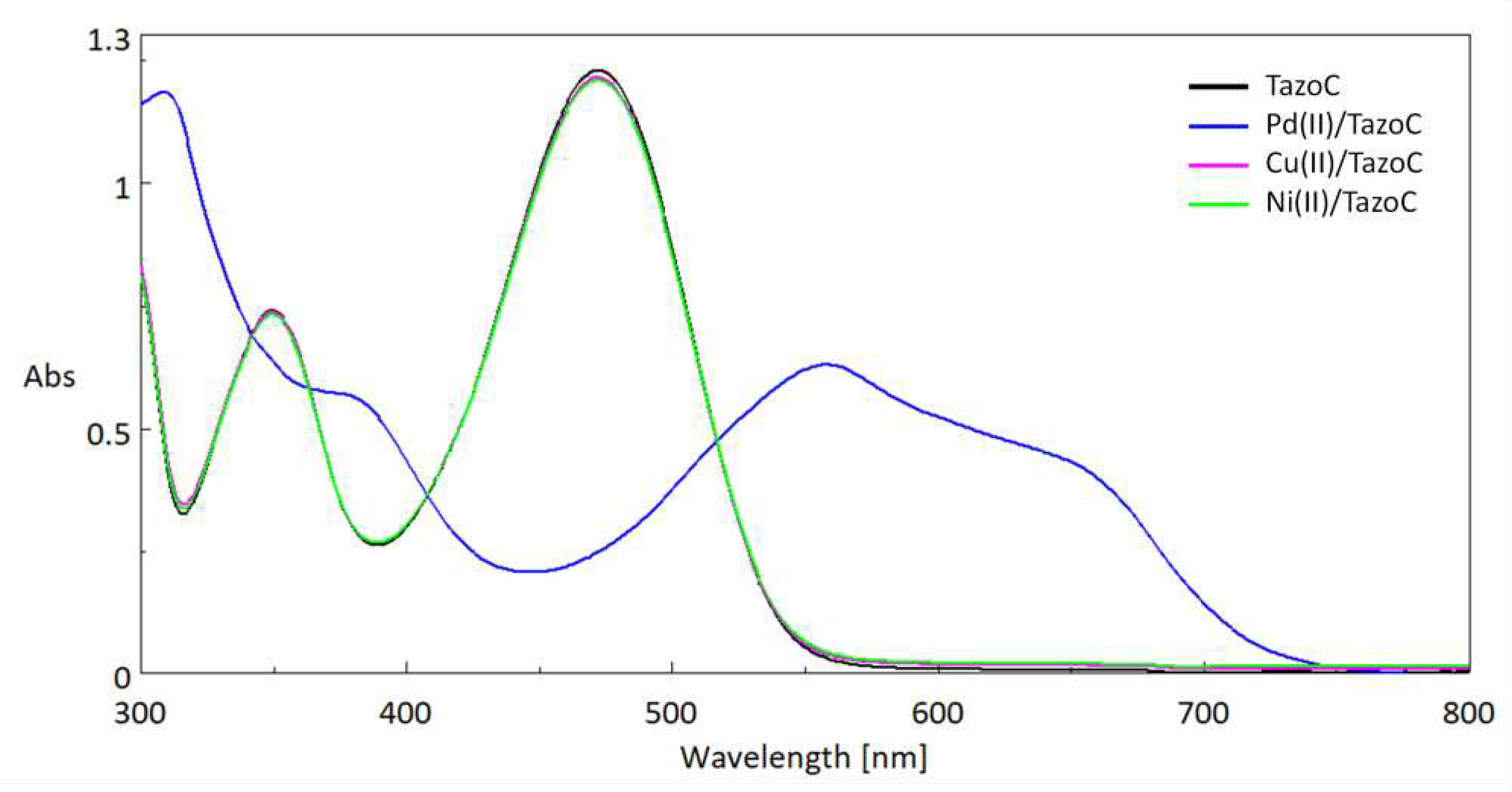
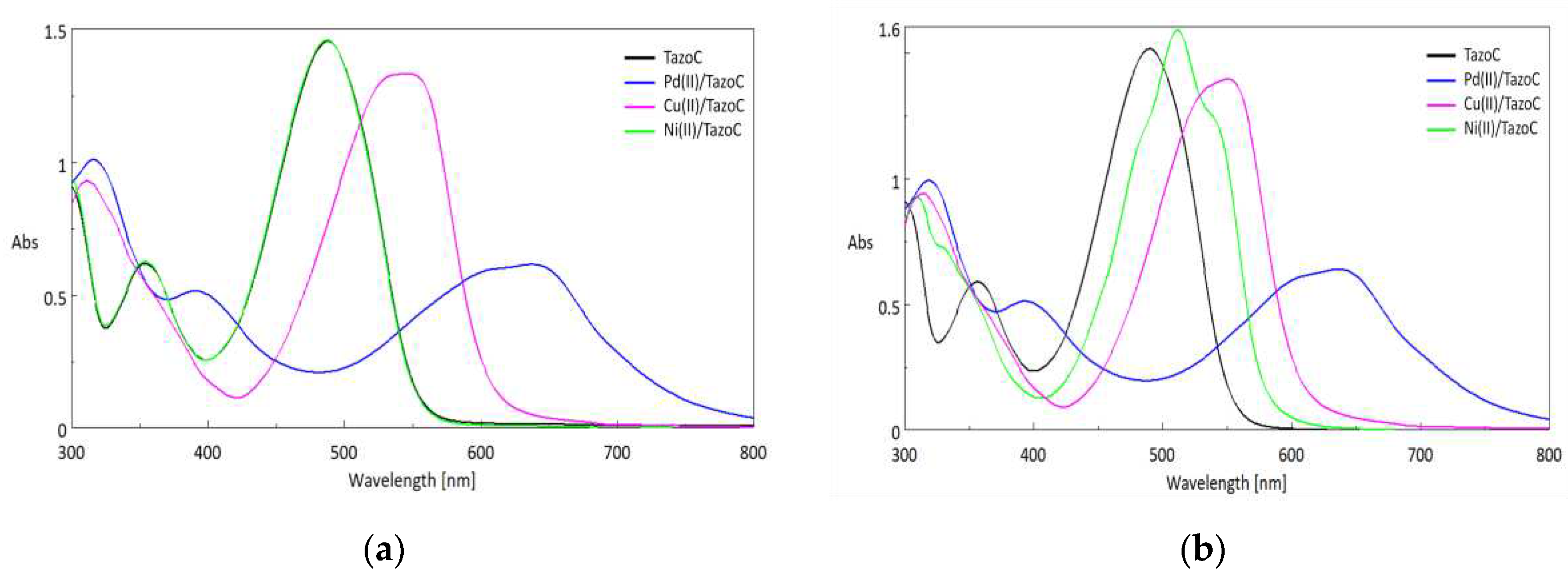
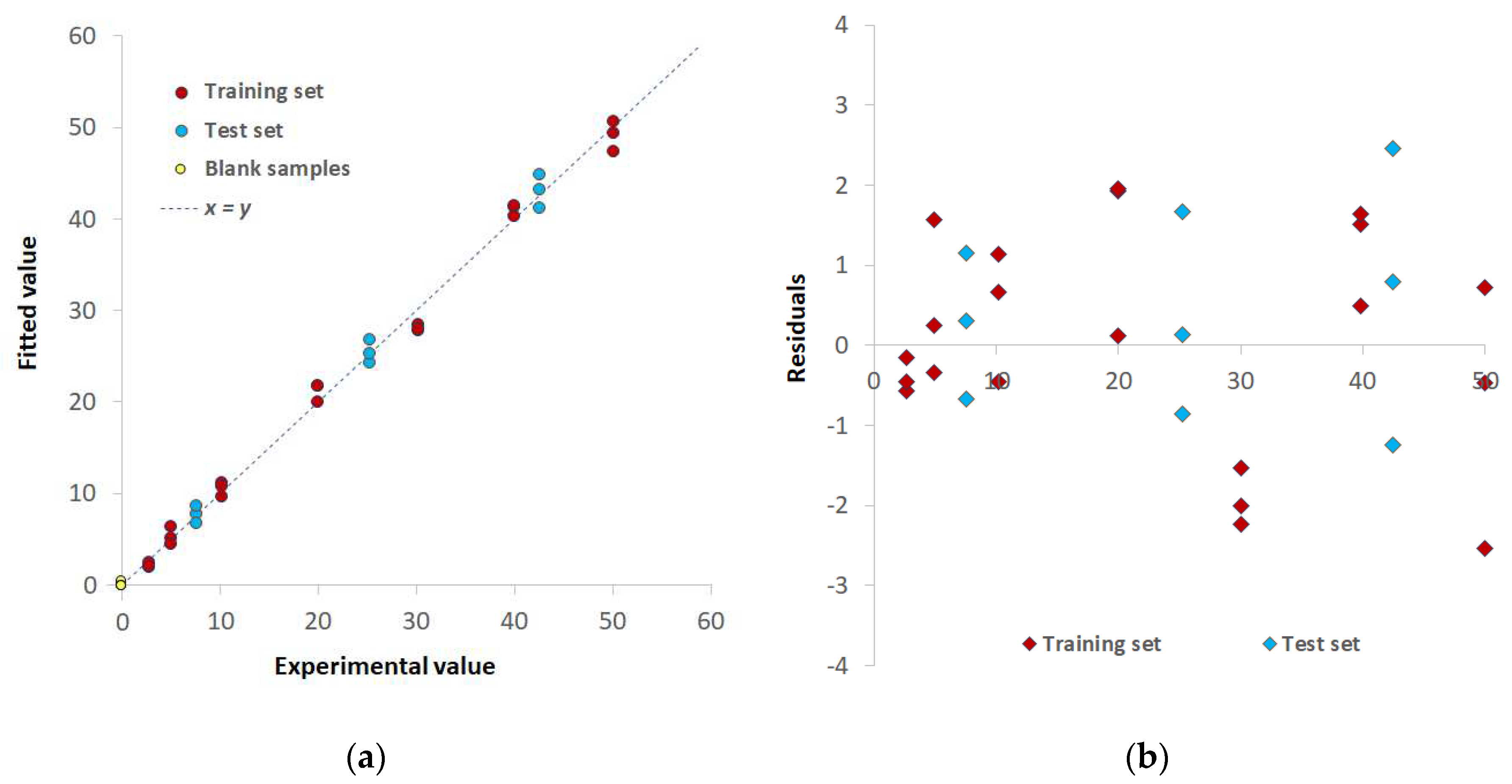
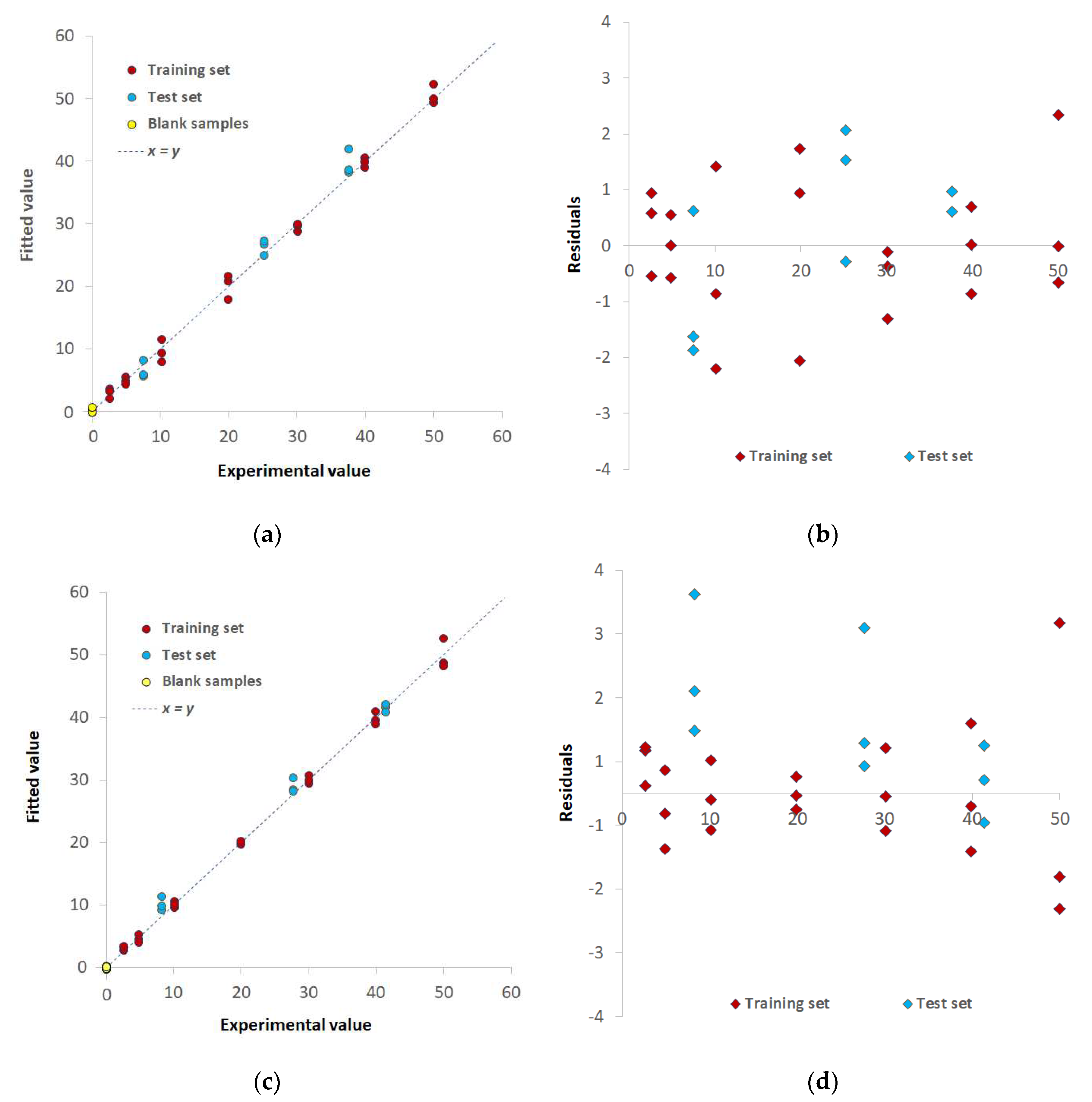
3.2. Chemometric-assisted Pd(II) determination by TazoC-PADs
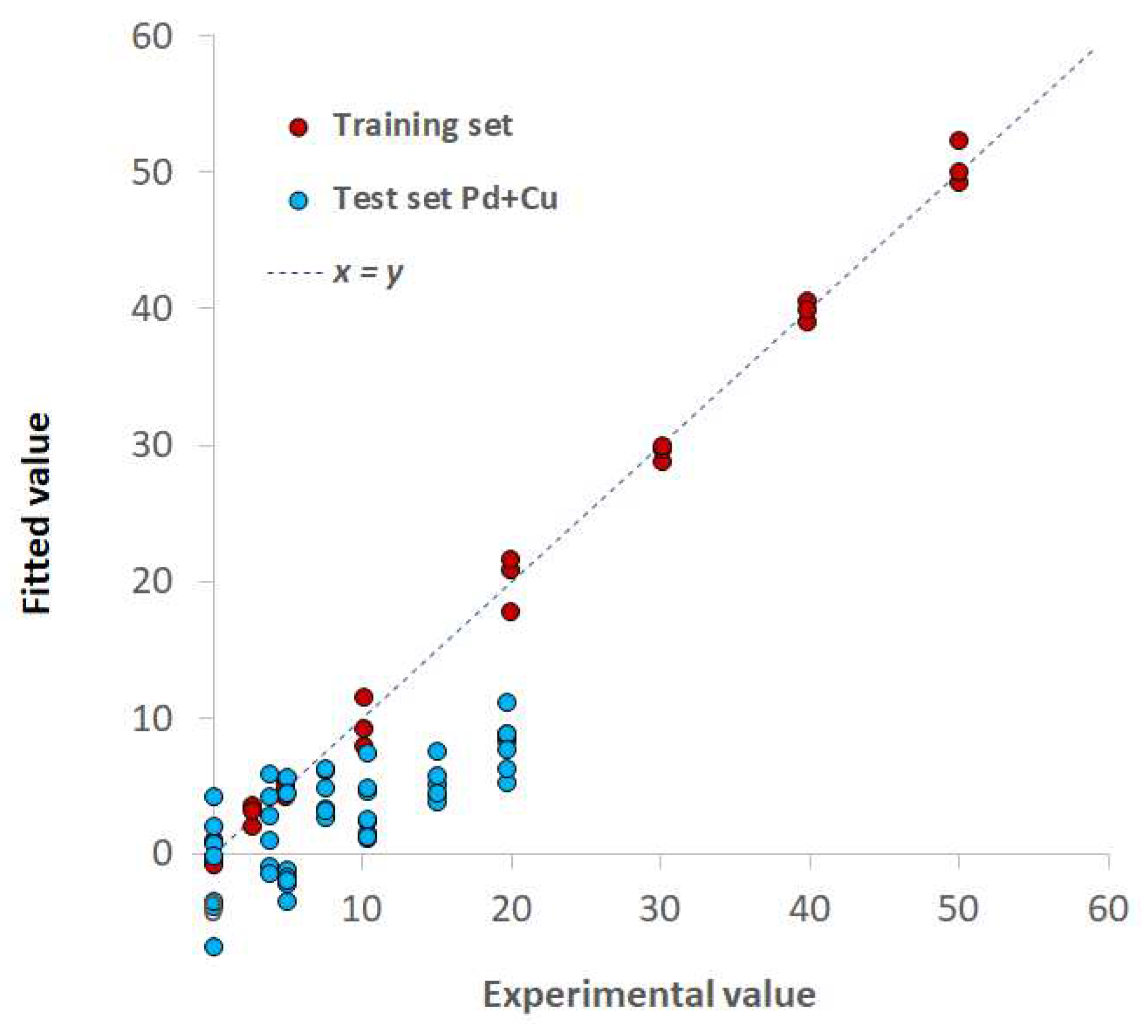
3.3. TazoC-PADs applications: interference tests and spiked tap waters analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leśniewska, B.A.; Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B.; Bocca, B.; Caimi, S.; Caroli, S.; Hulanicki, A. Platinum, palladium and rhodium content in road dust, tunnel dust and common grass in Białystok area (Poland): a pilot study. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 321, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietze, L.F.; Ila, H.; Bell, H.P. Enantioselective Palladium-Catalyzed Transformations. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 3453–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.-F.; Neumann, H.; Beller, M. Palladium-catalyzed carbonylative coupling reactions between Ar–X and carbon nucleophiles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4986–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sore, H.F.; Galloway, W.R.J.D.; Spring, D.R. Palladium-catalysed cross-coupling of organosilicon reagents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 41, 1845–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrzńska, K. Viewpoint Monitoring of platinum in the environment. J. Environ. Monit. 2000, 2, 99N–103N. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zischka, M.; Schramel, P.; Muntau, H.; Rehnert, A.; Gomez, M.G.; Stojanik, B.; Wannemaker, G.; Dams, R.; Quevauviller, P.; A Maier, E. A new certified reference material for the quality control of palladium, platinum and rhodium in road dust, BCR-723. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 851–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ek, K.H.; Morrison, G.M.; Rauch, S. Environmental routes for platinum group elements to biological materials—a review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2004, 334-335, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, S.; Morrison, G.M. Environmental Relevance of the Platinum-Group Elements. Elements 2008, 4, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, M.; Palacios, M.; Gómez, M.; Morrison, G.; Rauch, S.; McLeod, C.; Ma, R.; Caroli, S.; Alimonti, A.; Petrucci, F.; et al. Environmental risk of particulate and soluble platinum group elements released from gasoline and diesel engine catalytic converters. Sci. Total. Environ. 2002, 296, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savignan, L.; Faucher, S.; Chéry, P.; Lespes, G. Platinum group elements contamination in soils: Review of the current state. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Bencs, L.; Van Grieken, R. Platinum group elements in the environment and their health risk. Sci. Total. Environ. 2004, 318, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, M.-J.; Jafarian, I.; Farahani, S.; Khodadadi, R.; Tagavi, S.H.; Naserzadeh, P.; Mohammadi-Bardbori, A.; Arghavanifard, N. New mechanistic approach of inorganic palladium toxicity: impairment in mitochondrial electron transfer. Metallomics 2016, 8, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelone, M.; Nardi, E.; Pinto, V.; Cremisini, C. Analytical Methods to Determine Palladium in Environmental Matrices: A Review. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Taghizadeh, M.; Behbahani, M.; Asgharinezhad, A.A.; Salarian, M.; Dehghani, A.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Amini, M.M. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic metal-organic framework (MOF) as a novel sorbent, and its optimization by experimental design methodology for determination of palladium in environmental samples. Talanta 2012, 99, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, M.; Palacios, M. Control of interferences in the determination of Pt, Pd and Rh in airborne particulate matter by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 404, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgeva, M.; Pihlar, B. Determination of palladium by adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1997, 357, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, C. Voltammetric Peak Area as Instrumental Datum. A Possibility to Improve the Determination at Ultratrace Level Concentration of Platinum Group Metals (PGMs) and Lead. Application to Particulate Matter. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrowski, A.; Gawlicki, M.; Kapturski, P.; Mirceski, V.; Spasovski, F.; Zarębski, J. The Silver Amalgam Film Electrode in Adsorptive Stripping Voltammetric Determination of Palladium(II) as Its Dimethyldioxime Complex. Electroanalysis 2008, 21, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, M.; Thirumalraj, B.; Chen, S.-M.; Al-Hemaid, F.M.; Ali, M.A.; Elshikh, M.S. Development of electrochemical sensor for the determination of palladium ions (Pd2+) using flexible screen printed un-modified carbon electrode. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 485, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, P.; Xiong, C.; Zhang, K.; Cao, Q. Electrochemical sensor based on in situ polymerized ion-imprinted membranes at graphene modified electrode for palladium determination. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 771, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fan, J.; Peng, X. Colourimetric and fluorescent probes for the optical detection of palladium ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7943–7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, R.; Liu, J.-H.; Liu, B.-T. A review of recent developments in fluorescent sensors for the selective detection of palladium ions. Co-ord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 376, 196–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesuz, R.; Nurchi, V.M.; Lachowicz, J.I.; Alberti, G. Unusual PLS application for Pd(ii) sensing in extremely acidic solutions. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 7901–7907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, R.M.; Shahat, A.; Atta, A.H.; Farag-Allah, M.M. Development of a novel and potential chemical sensor for colorimetric detection of Pd(II) or Cu(II) in E-wastes. Microchem. J. 2021, 172, 106951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, M.; Kong, N.; Liu, J. Lab-on-paper micro-and nano-analytical devices: Fabrication, modification, detection and emerging applications. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1521–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, T.; McMahon, C.; Henry, C.S. Advances in Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 13, 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnaghi, L.R.; Alberti, G.; Pazzi, B.M.; Zanoni, C.; Biesuz, R. A green-PAD array combined with chemometrics for pH measurements. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 19460–19467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, Y.; Fu, J.-Z.; Wu, W.-B. Fabrication of paper-based microfluidic analysis devices: a review. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 78109–78127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sruthi, P.S.; Balasubramanian, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Kapoor, A.; Ponnuchamy, M.; Jacob, M.M.; Prabhakar, S. Eco-friendly pH detecting paper-based analytical device: Towards process intensification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1182, 338953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentele, M.M.; Cunningham, J.; Koehler, K.; Volckens, J.; Henry, C.S. Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Device for Particulate Metals. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4474–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.M.Z.; Brennan, J.D. β-Galactosidase-Based Colorimetric Paper Sensor for Determination of Heavy Metals. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8772–8778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariza-Avidad, M.; Salinas-Castillo, A.; Cuéllar, M.P.; Agudo-Acemel, M.; Pegalajar, M.C.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F. Printed Disposable Colorimetric Array for Metal Ion Discrimination. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8634–8641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morbioli, G.G.; Mazzu-Nascimento, T.; Stockton, A.M.; Carrilho, E. Technical aspects and challenges of colorimetric detection with microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs) - A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 970, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Carvelo, A.M.; Salloum-Llergo, K.D.; Cuadros-Rodríguez, L.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F.; Ramos, F. A perfect tandem: chemometric methods and microfluidic colorimetric twin sensors on paper. Beyond the traditional analytical approach. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzi, B.M.; Pistoia, D.; Alberti, G. RGB-Detector: A Smart, Low-Cost Device for Reading RGB Indexes of Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedpour, V.; Postma, G.J.; Heuvel, E.v.D.; Jansen, J.J.; Suzuki, K.; Citterio, D. Chemometrics-assisted microfluidic paper-based analytical device for the determination of uric acid by silver nanoparticle plasmon resonance. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 2305–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati-Rad, M.; Irandoust, M.; Mohammadi, S. Multivariate analysis of digital images of a paper sensor by partial least squares for determination of nitrite. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2016, 158, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataide, V.N.; Filho, L.A.P.; Guinati, B.G.S.; Moreira, N.S.; Gonçalves, J.D.; Ribeiro, C.M.G.; Grasseschi, D.; Coltro, W.K.T.; Salles, M.O.; Paixão, T.R.L.C. Combining chemometrics and paper-based analytical devices for sensing: An overview. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, M.; Riolo, C.; Soldi, T.; Cervo, G. Spectrophotometric study of the equilibria between lanathanum (III) and three azodyes. Ann. Chim. 1979, 69, 649–661. [Google Scholar]
- Pesavento, M.; Riolo, C.; Biesuz, R. Spectrophotometric Determination of Palladium(ll) with Four Water-soluble Heterocyclic Azo Dyes. Analyst 1985, 110, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, M.; Profumo, A. ChemInform Abstract: Evaluation of the Activity Coefficients of Some Sulfonated Azo Dyes and of Their Complexes with Metal Ions. ChemInform 1992, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, M.; Profumo, A.; Sastre, A.M. Chromatographic behaviour of trace metal ions on a strong base anion exchange resin functionalized by azo ligands. Talanta 1994, 41, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geladi, P.; Kowalski, B.R. Partial least-squares regression: a tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 1986, 185, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Sjöström, M.; Eriksson, L. PLS-regression: a basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 58(2), 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenlein, M.; Kaplan, A.M. A Beginner's Guide to Partial Least Squares Analysis. Understand. Stat. 2004, 3(4), 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaninejad-Darzi, S.K.; Torkamanzadeh, M. Simultaneous UV-Vis spectrophotometric quantification of ternary basic dye mixtures by partial least squares and artificial neural networks. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnaghi, L.R.; Alberti, G.; Pazzi, B.M.; Zanoni, C.; Biesuz, R. A green-PAD array combined with chemometrics for pH measurements. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 19460–19467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnaghi, L.R.; Capone, F.; Zanoni, C.; Alberti, G.; Quadrelli, P.; Biesuz, R. Colorimetric Sensor Array for Monitoring, Modelling and Comparing Spoilage Processes of Different Meat and Fish Foods. Foods 2020, 9, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, G.; Re, S.; Tivelli, A.M.C.; Biesuz, R. Smart sensory materials for divalent cations: a dithizone immobilized membrane for optical analysis. Anal. 2016, 141, 6140–6148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leardi, R.; Melzi, C.; Polotti, G. CAT (Chemometric Agile Tool). Available online: http://www.gruppochemiometria.it/index.php/software/19-download-the-rbased-chemometric-software (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- Younas, M.; Maryam, A.; Khan, M.; Nawaz, A.A.; Jaffery, S.H.I.; Anwar, M.N.; Ali, L. Parametric analysis of wax printing technique for fabricating microfluidic paper-based analytic devices (µPAD) for milk adulteration analysis. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2019, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Shi, W.; Qin, J.; Lin, B. Fabrication and Characterization of Paper-Based Microfluidics Prepared in Nitrocellulose Membrane By Wax Printing. Anal. Chem. 2009, 82, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungchai, W.; Chailapakul, O.; Henry, C.S. A low-cost, simple, and rapid fabrication method for paper-based microfluidics using wax screen-printing. Anal. 2010, 136, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, R.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Savitha, R.; Renganathan, T.; Pushpavanam, S. Fabrication of laser printed microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (LP-µPADs) for point-of-care applications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Kotera, K.; Suzuki, K.; Citterio, D. Inkjet-printed paper fluidic immuno-chemical sensing device. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398(2), 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klasner, S.A.; Price, A.K.; Hoeman, K.W.; Wilson, R.S.; Bell, K.J.; Culbertson, C.T. Paper-based microfluidic devices for analysis of clinically relevant analytes present in urine and saliva. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1821–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, J.; Nguyen, T.; Shen, W. Paper-Based Microfluidic Devices by Plasma Treatment. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9131–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Lu, H.; Wang, H.; Qin, Z. Highly selective and reversible chemosensor for Pd2+ detected by fluorescence, colorimetry, and test paper. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7(2), 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Chang, G.; Ren, X. Facile synthesis of new coumarin-based colorimetric and fluorescent chemosensors: Highly efficient and selective detection of Pd2+ in aqueous solutions. Sensors Actuators B: Chem. 2017, 240, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wei, T.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Qiang, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, X. Highly sensitive and selective ESIPT-based fluorescent probes for detection of Pd2+ with large Stocks shifts. Dye. Pigment. 2017, 140, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Chen, W.; Li, H.; Dai, Y.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Lu, H. A dual-functional colorimetric and “on-off” fluorescent probe based on purine derivative for detecting Pd2+ and Cu2+: Application as test strips. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 116, 107915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Gao, Q.; Liu, D.; Li, C.; Liu, S.; Xia, K.; Han, B.; Zhou, C. A single molecular sensor for selective and differential colorimetric/ratiometric detection of Cu2+ and Pd2+ in 100% aqueous solution. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 237, 118365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadros-Rodrı́guez, L.; Gámiz-Gracia, L.; Almansa-López, E.; Laso-Sánchez, J. Calibration in chemical measurement processes: I. A metrological approach. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2001, 20, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadros-Rodrı́guez, L.; Gámiz-Gracia, L.; Almansa-López, E.M.; Bosque-Sendra, J.M. Calibration in chemical measurement processes. II. A methodological approach. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2001, 20, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, L.K.; Searle, B.C.; Yang, H.-Y.; Hoofnagle, A.N.; Noble, W.S.; MacCoss, M.J. Matrix-Matched Calibration Curves for Assessing Analytical Figures of Merit in Quantitative Proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Methods Committee of the American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Environment Federation. 3030 preliminary treatment of samples In: Standard Methods For the Examination of Water and Wastewater. Lipps WC, Baxter TE, Braun-Howland E, editors. Washington DC: APHA Press. [CrossRef]
- Huber, L. Validation and Qualification in Analytical Laboratories, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.G.; Herrador, M.A.; Asuero, A.G. Intra-laboratory assessment of method accuracy (trueness and precision) by using validation standards. Talanta 2010, 82, 1995–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melber, Christine, Keller, Detlef, Mangelsdorf, Inge & International Programme on Chemical Safety. (2002). Palladium. World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/42401. (accessed on 3 July 2023).
- Standard Methods Committee of the American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Environment Federation. 3500-pd palladium In: Standard Methods For the Examination of Water and Wastewater. Lipps WC, Baxter TE, Braun-Howland E, editors. Washington DC: APHA Press. [CrossRef]

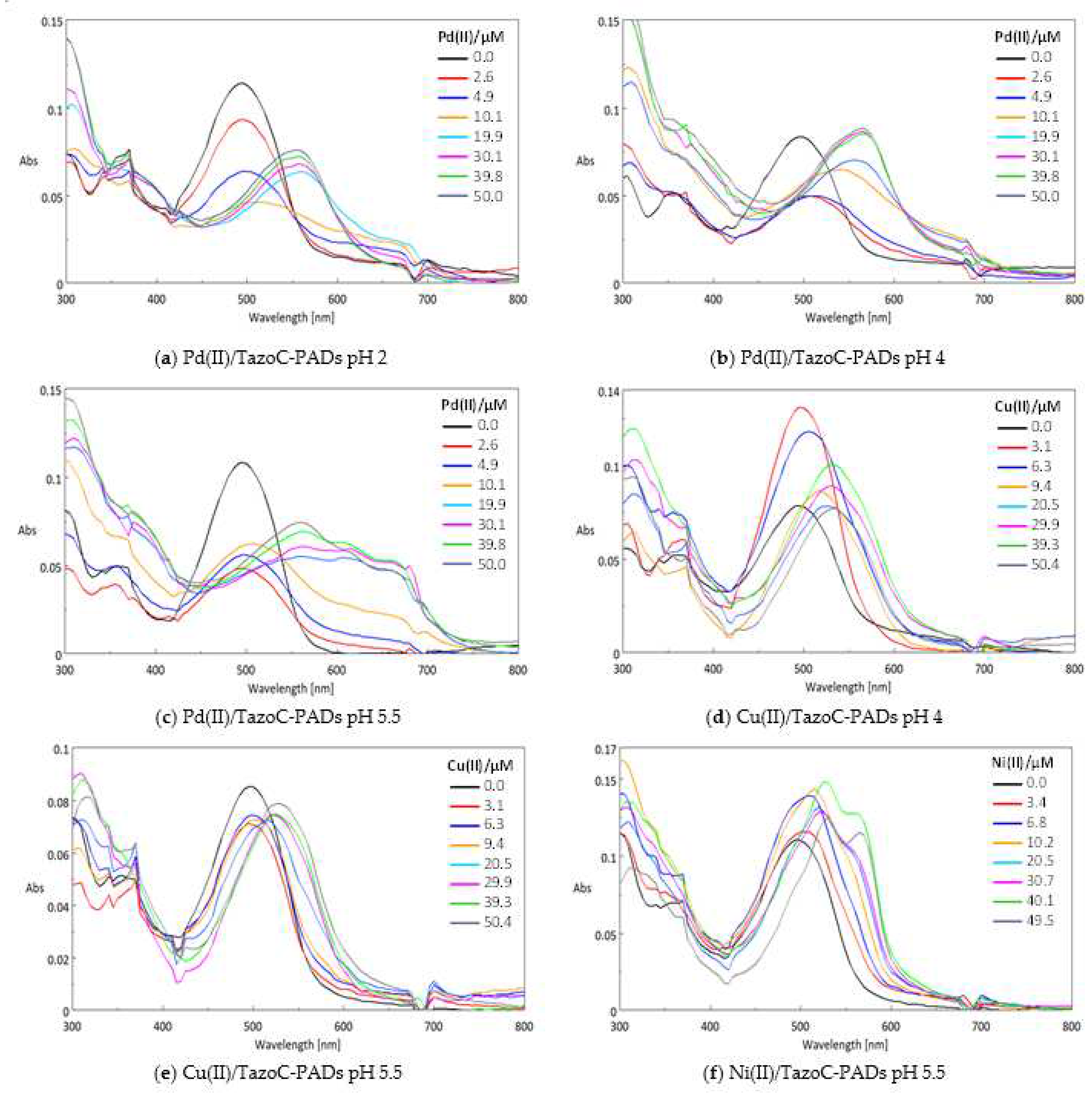
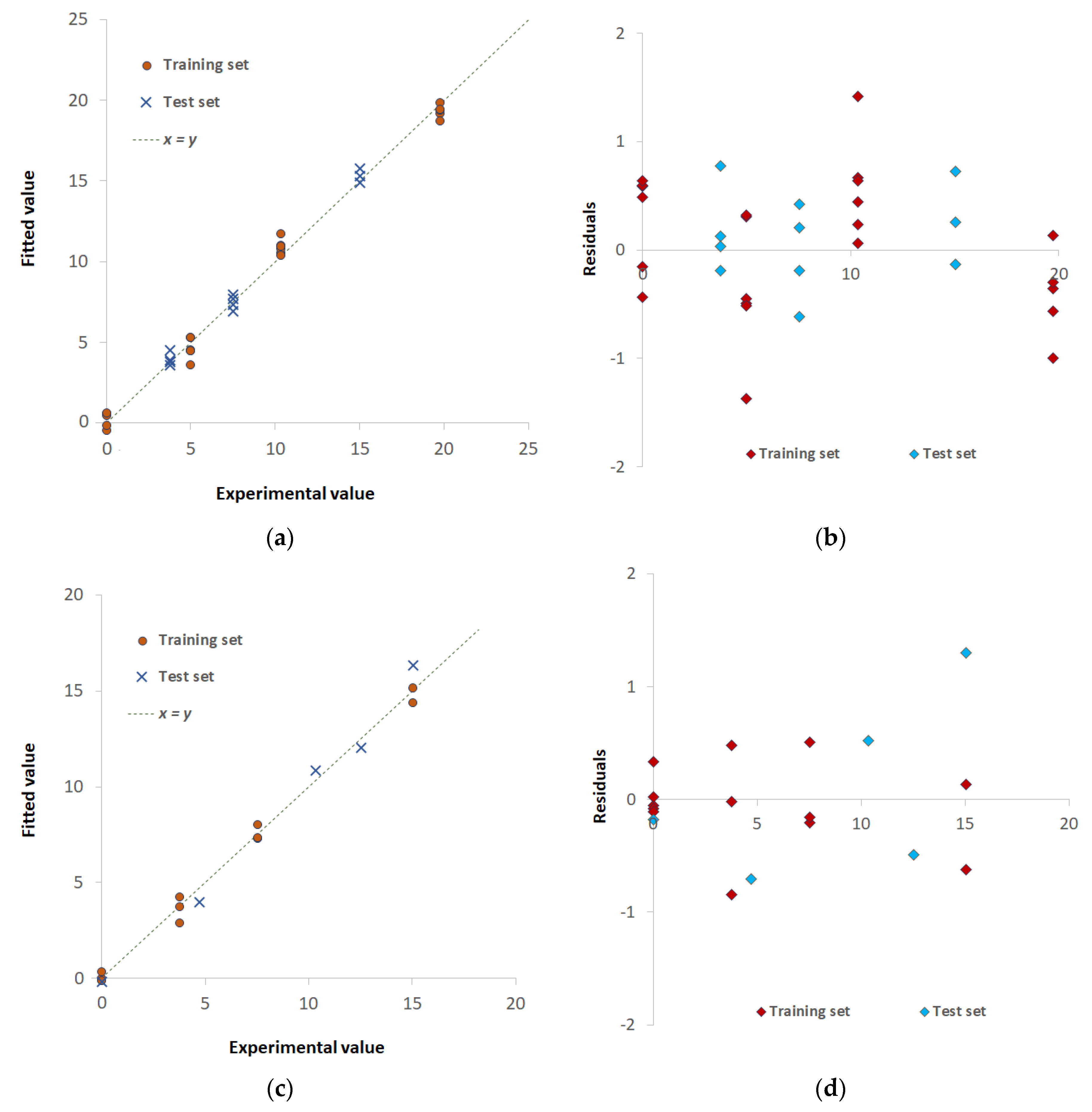
| Pd(II)/TazoC-PADs pH 2 |
Pd(II)/TazoC-PADs pH 4 | Pd(II)/TazoC-PADs pH 5.5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | LVs | 5 | 8 | 8 |
| %Exp.Var. CV | 98.61 | 96.92 | 98.02 | |
| RMSECV (μM) | 2.05 | 3.08 | 2.45 | |
| r2 model | 0.994 | 0.996 | 0.997 | |
| Test set | RMSEP (μM) | 1.86 | 1.92 | 1.55 |
| r2 prediction | 0.994 | 0.991 | 0.995 | |
| Blank samples | LOD (μM) | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| LOQ (μM) | 2.3 | 2.4 | 2.0 |
| Sensor | LOQ (μM) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Rhodamine B-based test papers | 2.5 | [58] |
| Coumarin-based test papers | 10 | [59] |
| 2-(2′-hydroxyphenyl)benzothiazole-based test papers | 4.7 | [60] |
| PTAID-based test papers1 | 100 | [61] |
| SAS-IMIs-based test silica plates2 | 10 | [62] |
| TazoC-based test papers3 | 2-2.4 | This work |
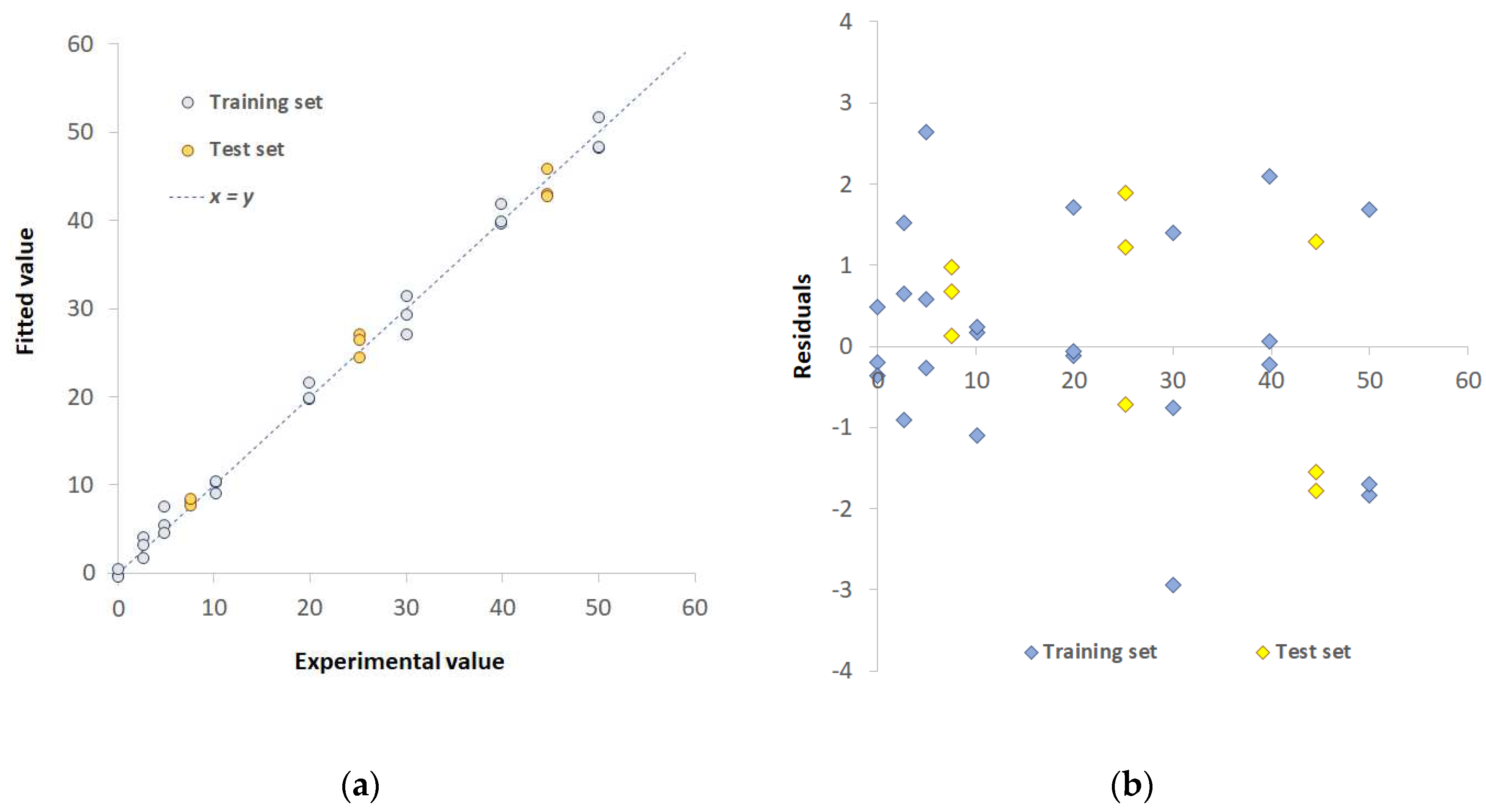
| Pd(II)+Cu(II)/TazoC-PADs pH 4 |
Pd(II)+Cu(II)+Ni(II)/TazoC-PADs pH 5.5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | LVs | 8 | 7 |
| %Exp.Var. CV | 93.07 | 74.2 | |
| RMSECV (μM) | 1.92 | 2.33 | |
| r2 model | 0.992 | 0.995 | |
| Test set | RMSEP (μM) | 1.41 | 0.86 |
| r2 prediction | 0.993 | 0.990 |
| Pd(II)/TazoC-PADs TW | ||
|---|---|---|
| Training set | LVs | 5 |
| %Exp.Var. CV | 98.73 | |
| RMSECV (μM) | 1.96 | |
| r2 model | 0.995 | |
| Test set | RMSEP (μM) | 2.06 |
| r2 prediction | 0.992 |
| Pd(II) added (μM) |
Pd(II) foundICP-OES (µM) |
Pd(II) foundTazoC-PADs (µM) |
Rc% | E% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.5 | 7.4(3) | 8.1(5) | 108 | 8 |
| 25.2 | 25.0(4) | 26(1) | 103 | 3 |
| 44.6 | 45.2(7) | 44(2) | 98 | -2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





