Submitted:
04 August 2023
Posted:
07 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
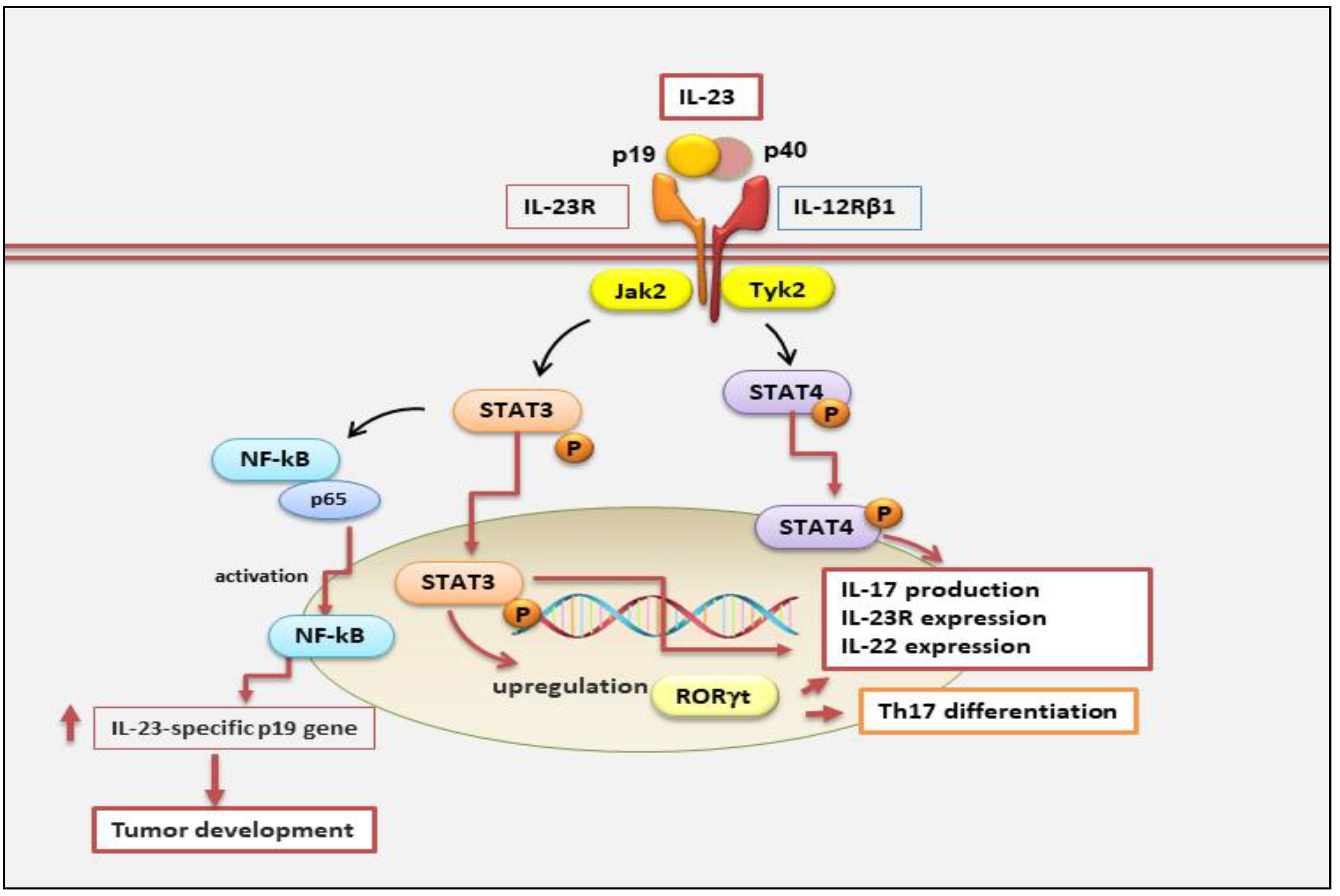
2. Structure of IL-23 and Its Receptor
3. Regulation of IL-23 Signaling
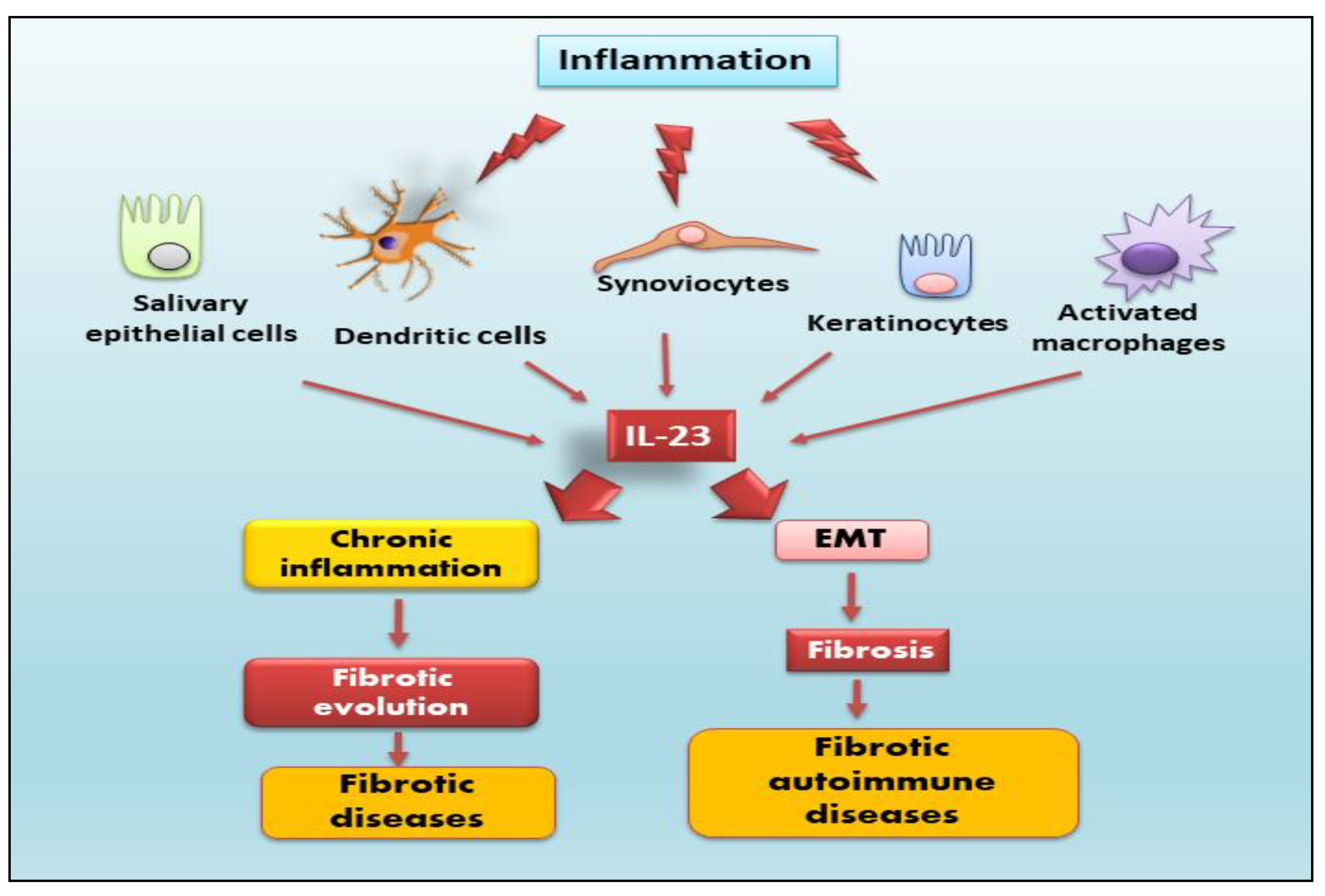
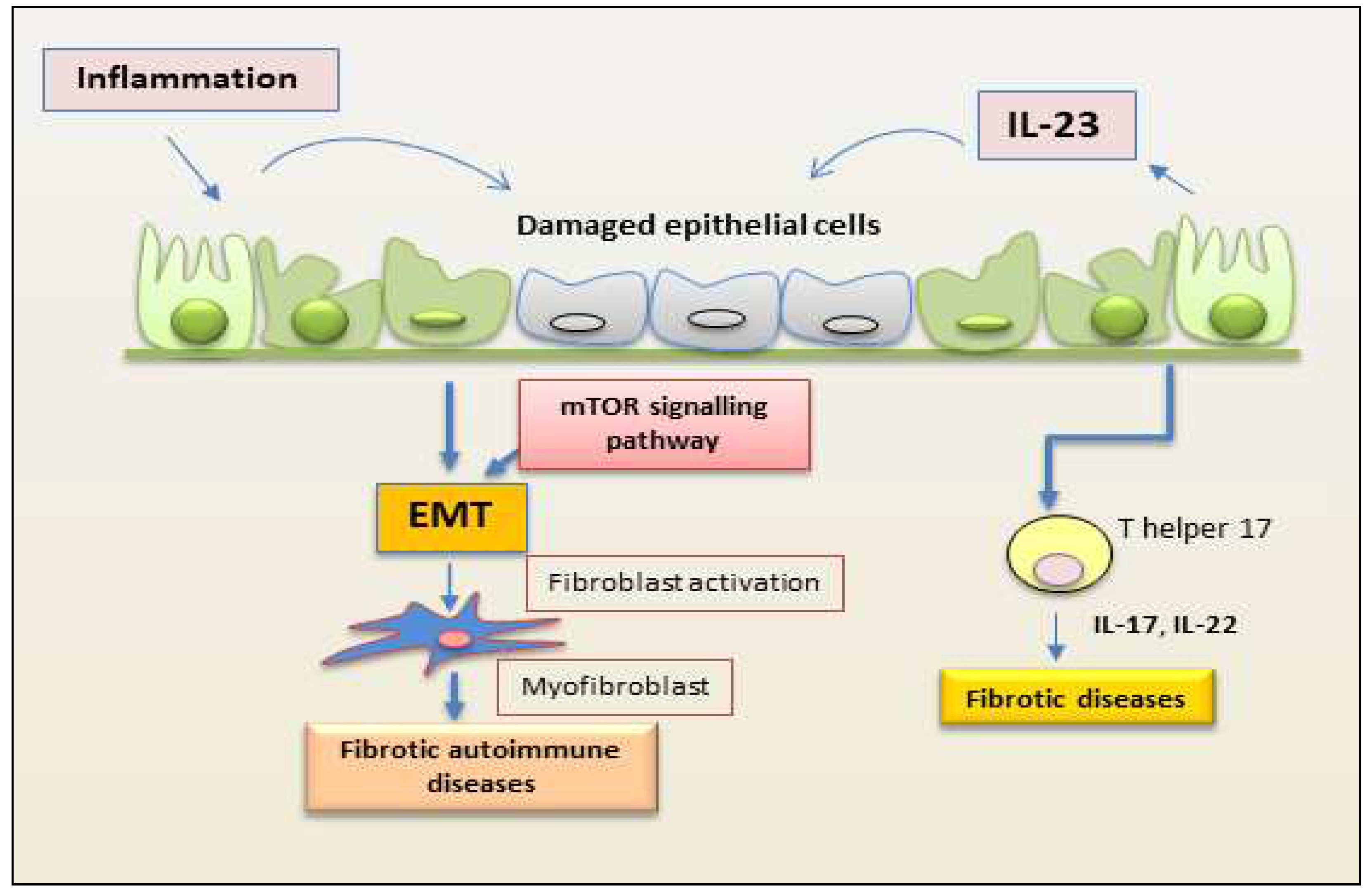
4. Role of IL-23 in the Fibrotic Process
4.1. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
4.2. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
4.3. Liver Fibrosis
5. Novel role of IL-23 in Autoimmune Fibrotic Diseases
5.1. Rheumatoid Arthritis
5.2. Crohn's Disease
5.3. Autoimmune Myocarditis
5.4. Sjӧgren’s Syndrome
5.5. Systemic Sclerosis
5.6. Multiple Sclerosis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pisetsky, D.S. Pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 2023, 19, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisto, M.; Ribatti, D.; Lisi, S. Organ Fibrosis and Autoimmunity: The Role of Inflammation in TGFβ-Dependent EMT. Biomolecules. 2021, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisto, M.; Lisi, S. Immune and Non-Immune Inflammatory Cells Involved in Autoimmune Fibrosis: New Discoveries. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chu, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; George, J.; Young, H.A.; Liu, G. Cytokines: From Clinical Significance to Quantification. Adv. Sci 2021, 8, e2004433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Kanneganti, T.D. The 'cytokine storm': Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic prospects. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 681–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvallet, E.; Semerano, L.; Assier, E.; Falgarone, G.; Boissier, M.C. Interleukin-23: A key cytokine in inflammatory diseases. Ann. Med. 2011, 43, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffen, S.L.; Jain, R.; Garg, A.V.; Cua, D.J. The IL-23-IL-17 immune axis: From mechanisms to therapeutic testing. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppmann, B.; Lesley, R.; Blom, B.; Timans, J.C.; Xu, Y.; Hunte, B.; Vega, F.; Yu, N.; Wang, J.; Singh, K.; et al. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity. 2000, 13, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxford, A.L.; Mair, F.; Becher, B. IL-23: One cytokine in control of autoimmunity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 2263–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.K.; Shi, X.; Han, M.M.; Zhang, X.M.; Wu, N.N.; Sheng, X.Y.; Wang, J.N. The regulatory mechanism and potential application of IL-23 in autoimmune diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 982238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.I.K.; Tye, G.J. Interleukin 23 and autoimmune diseases: Current and possible future therapies. Inflamm Res. 2020, 69, 463–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, E.; Vecellio, M.; Rogge, L. Editorial: Role of the IL-23/IL-17 Pathway in Chronic Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases: Mechanisms and Targeted Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 770275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senoo, S.; Taniguchi, A.; Itano, J.; Oda, N.; Morichika, D.; Fujii, U.; Guo, L.; Sunami, R.; Kanehiro, A.; Tokioka, F.; et al. Essential role of IL-23 in the development of acute exacerbation of pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2021, 321, L925–L940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Chen, S.; Qian, H.; Huang, W. Interleukin-23: As a drug target for autoimmune inflammatory diseases. Immunology. 2012, 135, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubler, U.; Chua, A.O.; Schoenhaut, D.S.; Dwyer, C.M.; McComas, W.; Motyka,R. ; Nabavi, N.; Wolitzky, A.G.; Quinn, P.M.; Familletti, P.C. Coexpression of two distinct genes is required to generate secreted bioactive cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4143–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimozato, O.; Ugai, S.; Chiyo, M.; Takenobu, H.; Nagakawa, H.; Wada, A.; Kawamura, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Tagawa, M. The secreted form of the p40 subunit of interleukin (IL)-12 inhibits IL-23 functions and abrogates IL-23-mediated antitumour effects. Immunology. 2006, 117, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, B.S.; Kastelein, R.A.; Cua, D.J. Understanding the IL-23/IL-17 immune pathway. Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brentano, F.; Ospelt, C.; Stanczyk, J.; Gay, R.E.; Gay, S.; Kyburz, D. Abundant expression of the interleukin (IL)23 subunit p19, but low levels of bioactive IL23 in the rheumatoid synovium: Differential expression and Toll-like receptor-(TLR) dependent regulation of the IL23 subunits, p19 and p40, in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusconi, M.; Musy, I.; Valente, D.; Maggi, E.; Priori, R.; Pecorella, I.; Mastromanno, L.; Di Cristofano, C.; Greco, A.; Armeli, F.; et al. Immunohistochemical detection of IL-17 and IL-23 improves the identification of patients with a possible diagnosis of Sjogren's syndrome. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Nan, L.; Wu, K.; Zhai, J. Research progress on the role and therapeutic significance of IL-23/Th17 in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. J. Liaoning Med. Coll. 2016, 37, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Pahan, K.; Jana, M. Induction of lymphotoxin-alpha by interleukin-12 p40 homodimer, the so-called biologically inactive molecule, but not IL-12 p70. Immunology 2009, 127, 312–325. [Google Scholar]
- Chognard, G.; Bellemare, L.; Pelletier, A.N.; Dominguez-Punaro, M.C.; Beauchamp, C.; Guyon, M.J.; Charron, G.; Morin, N.; Sivanesan, D.; Kuchroo, V.; et al. The dichotomous pattern of IL-12r and IL-23R expression elucidates the role of IL-12 and IL-23 in inflammation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 89092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, M.M.; Way, S.S. Interleukin-17 in host defence against bacterial, mycobacterial and fungal pathogens. Immunology. 2009, 126, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korta, A.; Kula, J.; Gomułka, K. The Role of IL-23 in the Pathogenesis and Therapy of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamero, A.C.; Castillo-González, R.; Pastor-Fernández, G.; Mariblanca, I.R.; Pino, J.; Cibrian, D.; Navarro, M.N. IL-23 signaling regulation of pro-inflammatory T-cell migration uncovered by phosphoproteomics. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000646. [Google Scholar]
- Venken, K.; Jacques, P.; Mortier, C.; Labadia, M.E.; Decruy, T.; Coudenys, J.; Hoyt, K.; Wayne, A.L.; Hughes, R.; Turner, M.; et al. RORγt inhibition selectively targets IL-17 producing iNKT and γδ-T cells enriched in Spondyloarthritis patients. Nat Commun. 2019, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noack, M.; Miossec, P. Synoviocytes and skin fibroblasts show opposite effects on IL-23 production and IL-23 receptor expression during cell interactions with immune cells. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.; Nadiv, O.; Luknar-Gabor, N.; Agar, G.; Beer, Y.; Katz, Y. Synergism between tumor necrosis factor α and interleukin-17 to induce IL-23 p19 expression in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 1854–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, M.; Ziegler, H.K. Paradoxical anti-inflammatory actions of TNF-alpha: Inhibition of IL-12 and IL-23 via TNF receptor 1 in macrophages and dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 5024–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.H.G. IL-17 and IL-17-producing cells in protection versus pathology. Nat Rev Immunol 2023, 23, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Ghilardi, N.; Xie, M.H.; de Sauvage, F.J.; Gurney, A.L. Interleukin-23 promotes a distinct CD4 T cell activation state characterized by the production of interleukin-17. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 1910–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boniface, K.; Blom, B.; Liu, Y.J.; de Waal Malefyt, R. From interleukin-23 to T-helper 17 cells: Human T-helper cell differentiation revisited. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 226, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddur, M.S.; Miossec, P.; Kaveri, S.V.; Bayry, J. Th17 cells: Biology, pathogenesis of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, and therapeutic strategies. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinocca, C.; Rizzo, C.; Fasano, S.; Grasso, G.; La Barbera, L.; Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G. Role of the IL-23/IL-17 Pathway in Rheumatic Diseases: An Overview. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 637829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunte, K.; Beikler, T. Th17 Cells and the IL-23/IL-17 Axis in the Pathogenesis of Periodontitis and Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukazaki, H.; Kaito, T. The Role of the IL-23/IL-17 Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Spondyloarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salleeh, F.; Petro, T.M. TLR3 and TLR7 are involved in expression of IL-23 subunits while TLR3 but not TLR7 is involved in expression of IFN-beta by Theiler's virus-infected RAW264.7 cells. Microbes Infect. 2007, 9, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, U.; Ballinger, M.N.; Zeng, X.; Newstead, M.J.; Cornicelli, M.D.; Standiford, T.J. Cooperative interactions between TLR4 and TLR9 regulate interleukin 23 and 17 production in a murine model of gram negative bacterial pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Smyth, M.J.; Teng, M.W.L. Interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-23 and Their Conflicting Roles in Cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018, 10, a028530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortylewski, M.; Xin, H.; Kujawski, M.; Lee, H.; Liu, Y.; Harris, T.; Drake, C.; Pardoll, D.; Yu, H. Regulation of the IL-23 and IL-12 balance by Stat3 signaling in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2009, 15, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.M.; Subleski, J.J.; Wigginton, J.M.; Wiltrout, R.H. Immunotherapy of cancer by IL-12-based cytokine combinations. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2007, 7, 1705–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, E.M.; Tsarovsky, N.W.; Sondel, P.M.; Rakhmilevich, A.L. Interleukin-12 as an in situ cancer vaccine component: A review. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2022, 71, 2057–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langrish, C.L.; Chen, Y.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Mattson, J.; Basham, B.; Sedgwick, J.D.; Mc Clanahan, T.; Kastelein, R.A.; Cua, D.J. IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldhoen, M.; Hocking, R.J.; Atkins, C.J.; Locksley, R.M.; Stockinger, B. TGF beta in the context of an inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity. 2006, 24, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.O.; Panopoulos, A.D.; Nurieva, R.; Chang, S.H.; Wang, D.; Watowich, S.S.; Dong, C. STAT3 regulates cytokine-mediated generation of inflammatory helper T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 9358–9363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Ivanov, I.I.; Spolski, R.; Min, R.; Shenderov, K.; Egawa, T.; Levy, D.E.; Leonard, W.J.; Littman, D.R. IL-6 programs T(H)-17 cell differentiation by promoting sequential engagement of the IL-21 and IL-23 pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morena, D.; Fernández, J.; Campos, C.; Castillo, M.; López, G.; Benavent, M.; Izquierdo, J.L. Clinical Profile of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Real Life. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, U.; Miyahara, N.; Taniguchi, A.; Waseda, K.; Morichika, D.; Kurimoto, E.; Koga, H.; Kataoka, M.; Gelfand, E.W.; Cua, D.J.; et al. IL-23 is essential for the development of elastase-induced pulmonary inflammation and emphysema. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 55, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, R.; Chikuma, S.; Shichita, T.; Morita, R.; Sekiya, T.; Ouyang, W.; Ueda, T.; Seki, H.; Morisaki, H.; Yoshimura, A. Innate-like function of memory Th17 cells for enhancing endotoxin-induced acute lung inflammation through IL-22. Int. Immunol. 2016, 28, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasse, P.; Riteau, N.; Vacher, R.; Michel, M.L.; Fautrel, A.; di Padova, F.; Fick, L.; Charron, S.; Lagente, V.; Eberl, G.; et al. IL-1 and IL-23 mediate early IL-17A production in pulmonary inflammation leading to late fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jia, S.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L. Serum cytokine levels and other associated factors as possible immunotherapeutic targets and prognostic indicators for lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1064616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.; Kellerman, R. Gastrointestinal Conditions: Inflammatory Bowel Disease. FP Essent. 2022, 516, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Lago, I.; Blackwell, J.; Mateos, B.; Marigorta, U.M. .; Barreiro-de Acosta, M.; Pollok, R. Recent Advances and Potential Multi-Omics Approaches in the Early Phases of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.; Weiss, C.R.; Wang, S.; Qing, G.; Yang, X.; Warrington, R.J.; Bernstein, C.N.; Peng, Z. Reversing Ongoing Chronic Intestinal Inflammation and Fibrosis by Sustained Block of IL-12 and IL-23 Using a Vaccine in Mice. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmalski, M.; Frankowski, R.; Ziółkowska, S.; Różycka-Kosmalska, M.; Pietras, T. What's New in the Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banini, B.A.; Sanyal, A.J. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Natural History, Diagnosis, and Current Treatment Options. Clin. Med. Insights Ther. 2016, 8, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Sánchez, N.; Valencia-Rodríguez, A.; Coronel-Castillo, C.; Vera-Barajas, A.; Contreras-Carmona, J.; Ponciano-Rodríguez, G.; Zamora-Valdés, D. The cellular pathways of liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, M.; Schilling, A.K.; Meertens, J.; Hering, I.; Weiss, J.; Jurowich, C.; Kudlich, T.; Hermanns, H.M.; Bantel, H.; Beyersdorf, N.; et al. Progression from Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver to Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Is Marked by a Higher Frequency of Th17 Cells in the Liver and an Increased Th17/Resting Regulatory T Cell Ratio in Peripheral Blood and in the Liver. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albhaisi, S.; Noureddin, M. Current and Potential Therapies Targeting Inflammation in NASH. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 767314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Wang, K.; Aoyama, T.; Grivennikov, S.I.; Paik, Y.; Scholten, D.; Cong, M.; Iwaisako, K.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; et al. Interleukin-17 signaling in inflammatory, Kupffer cells, and hepatic stellate cells exacerbates liver fibrosis in mice. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia, J.E.; Sorenson, C.; Flanagan, S.; Nunez, V.; Jones C; et al. IL-23 signaling is not an important driver of liver inflammation and fibrosis in murine non-alcoholic steatohepatitis models. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laria, A.; Lurati, A.M.; Zizzo, G.; Zaccara, E.; Mazzocchi, D.; Re, K.A.; Marrazza, M.; Faggioli, P.; Mazzone, A. Interstitial Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Practical Review. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 837133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Lau, J.; Roden, A.C.; Matteson, E.L.; Sun, J.; Luo, F.; Tschumperlin, D.J.; Vassallo, R. IL-23 amplifies the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of mechanically conditioned alveolar epithelial cells in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease through mTOR/S6 signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2021, 321, L1006–L1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Cao, A.; Yao, S.; Evans-Marin, H.L.; Liu, H.; Wu, W.; Carlsen, E.D.; Dann, S.M.; Soong, L.; Sun, J.; et al. mTOR Mediates IL-23 Induction of Neutrophil IL-17 and IL-22 Production. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 4390–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, R.; Alam, M.M.; Zhao, X.F.; Liao, Y.; Shen, J.; Morgan, S.; Huang, T.; Lee, H.; Lee, E.; Huang, Y.; et al. Induction of autophagy in Cx3cr1+ mononuclear cells limits IL-23/IL-22 axis-mediated intestinal fibrosis. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, B.; Jin, T.; Ocansey, D.K.W.; Jiang, J.; Mao, F. Intestinal Fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and the Prospects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 835005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vdovenko, D.; Wijnen, W.J.; Zarak Crnkovic, M.; Blyszczuk, P.; Bachmann, M.; Costantino, S.; Paneni, F.; Camici, G.G.; Luescher, T.F.; Eriksson, U. IL-23 promotes T-cell mediated cardiac inflammation but protects the heart from fibrosis. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, ehaa946.3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Diny, N.L.; Ong, S.; Barin, J.G.; Hou, X.; Rose, N.R.; Talor, M.V.; Čiháková, D. Pathogenic IL-23 signaling is required to initiate GM-CSF-driven autoimmune myocarditis in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkett, P.R.; Meyer, G.; Kuchroo, V.K. ; Pouring fuel on the fire: Th17 cells, the environment, and autoimmunity. J. Clin. Invest. 2015, 125, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.Q.; Hu, M.H.; Li, Y.; Stewart, C.; Peck, A.B. Salivary gland tissue expression of interleukin-23 and interleukin-17 in sjogren's syndrome: Findings in humans and mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, N.; Li, T.; Wang, H. Blockade of Th17 response by IL-38 in primary sjogren's syndrome. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 127, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccia, F.; Guggino, G.; Rizzo, A.; Ferrante, A.; Raimondo, S.; Giardina, A.; Dieli, F. , Campisi, G.; Alessandro, R., Triolo, G. Potential involvement of IL-22 and IL-22-producing cells in the inflamed salivary glands of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Q.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Chen, W.; Fan, X.; Zhang, D. Pathogenesis and treatment of Sjogren's syndrome: Review and update. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1127417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soypaçacı, Z.; Gümüş, Z.Z.; Çakaloğlu, F.; Özmen, M.; Solmaz, D.; Gücenmez, S.; Gercik, Ö.; Akar,S. Role of the mTOR pathway in minor salivary gland changes in Sjogren's syndrome and systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, S.K.; Cho, M.L.; Her, Y.M.; Oh, H.J.; Park, M.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Woo, Y.J.; Ju, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Kim, H.Y.; et al. TLR2 ligation induces the production of IL-23/IL-17 via IL-6, STAT3 and NF-kB pathway in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truchetet, M.E.; Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. Current Concepts on the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 262–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, F.A.; Allawh, T.; Jimenez, S.A. Pharmacological treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: An updated review and current approach to patient care. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2023, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komura, K.; Fujimoto, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Ogawa, F.; Hara, T.; Muroi, E.; Takehara, K.; Sato, S. Increased serum interleukin 23 in patients with systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, C.S.; Farooqi, N.; O'Brien, K.; Gran, B. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) as a model for multiple sclerosis (MS). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1079–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastelein, R.A.; Hunter, C.A.; Cua, D.J. Discovery and biology of IL-23 and IL-27: Related but functionally distinct regulators of inflammation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurasawa, K.; Hirose, K.; Sano, H.; Endo, H.; Shinkai, H.; Nawata, Y.; Takabayashi, K.; Iwamoto, I. Increased interleukin-17 production in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 2000, 43, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammad, G.A.; Eltanawy, R.M.; Fawzy, R.M.; et al. Serum interleukin 23 and its associations with interstitial lung disease and clinical manifestations of scleroderma. Egypt. J. Bronchol. 2018, 12, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.; Gupta, G.D.; Mehan, S. Cellular and Molecular Evidence of Multiple Sclerosis Diagnosis and Treatment Challenges. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Behi, M.; Dubucquoi, S.; Lefranc, D.; Zéphir, H.; De Seze, J.; Vermersch, P.; Prin, L. New insights into cell responses involved in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. Immunol Lett. 2005, 96, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Langrish, C.L.; McKenzie, B.; Joyce-Shaikh, B.; Stumhofer, J.S.; McClanahan, T.; Blumenschein, W.; Churakovsa, T.; Low, J.; Presta, L.; et al. . Anti-IL-23 therapy inhibits multiple inflammatory pathways and ameliorates autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cua, D.J.; Sherlock, J.; Chen, Y.; Murphy, C.A.; Joyce, B.; Seymour, B.; Lucian, L.; To, W.; Kwan, S.; Churakova, T.; et al. . Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature. 2003, 421, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahern, P.P.; Schiering, C.; Buonocore, S.; McGeachy, M.J.; Cua, D.J.; Maloy, K.J.; Powrie, F. Interleukin-23 drives intestinal inflammation through direct activity on T cells. Immunity 2010, 33, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




