1. Introduction
A large number of natural fibers with attractive properties for diverse composite applications are available [
1,
2]. They are being used widely due to their structural properties and good mechanical characteristics in addition to other benefits [
3,
4,
5,
6]. Despite these advantages, natural fiber and their composites possess some challenges. Lack of constancy and variation of their properties as well as their sensitivity to external environmental such as humidity and moisture are among vital challenges [
4,
5,
7,
8,
9,
10]. The moisture sensitivity of bio-composite majorly emanates from characteristics of both the fiber and the matrix.
First, natural fibers take the lion share of characteristics of bio-composite exposed to diverse environment because they are hydrophilic and they carry and transfer load. Since fibers are the principal load carrying component in fiber reinforced composites, their mechanical properties are vital [
11,
12,
13,
14]. Without specific conditioning or drying, their moisture content usually ranges from 5-13% [
1,
15]. This characteristic of natural fiber plays a critical role, since the strongly polarized fibers are inherently hygroscopic. They exhibit poor resistance to moisture, thus leading to high water absorption, and poor mechanical properties and dimensional stability [
16]. In such a condition, the fibers makes polymer impregnation more difficult, causing weak adhesion on the polymer matrix-fiber interface, which leads to internal tensions, porosity and premature failure of the system when they are used in composite [
4,
10]. Second, biodegradable plastics have relatively poor barrier properties extra care is required when natural fibers are combined with biodegradable thermoplastics [
17,
18,
19]
Multiple studies have indicated dependence of mechanical properties of both the fiber and the composites on moisture [
15,
16,
20]. When exposed to moisture, bio-composites display lower mechanical properties than synthetic fiber-reinforced composites as it badly affects the performance, physical and mechanical integrity [
5,
18,
21]. Consequently, swelling and shrinkage of the fibers surrounded by the matrix generate internal stresses at the interface and can eventually lead to the matrix creating significant degradation of the initial properties of the composite [
18]. For instance, a decreasing tendency of the tensile strength and young's modulus with increasing relative humidity for flax and nettle fibers is noticed; decrease of the Young modulus of flax fibers about 23% when relative humidity varies from 30-80% [
22].
The rate of water absorption of the bio-composite is another vital features for comparing materials [
23,
24]. Such as, untreated and acetylated Kenaf–PLA composites shows rapid water absorption on the first day, but the water uptake eventually reached a plateau state. Since the water absorption rate of PLA is less than 1%, the overall result can be interpreted as a result of water uptake of Kenaf or the interface [
6,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29]. Also, water absorption and in turn mechanical properties of PLA/Natural fiber composites depend on the fiber orientation, fiber volume fraction, the nature of the matrix and mainly on the adhesion between fiber and the matrix as well as amount of plasticizer [
4,
5,
25,
30,
31].
Thus, response of bio-composites to different environment depends on hydrophilic nature of both the fiber and matrix. Effect of fiber has been consistently reported throughout literatures to be vital in the overall moisture absorption of the composite. And, different fibers have different level of influence on the characteristics of the composites owing to their different properties. This study considers PLA-Enset composite and typifies hygroscopic characteristics and their resulting mechanical properties loss.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
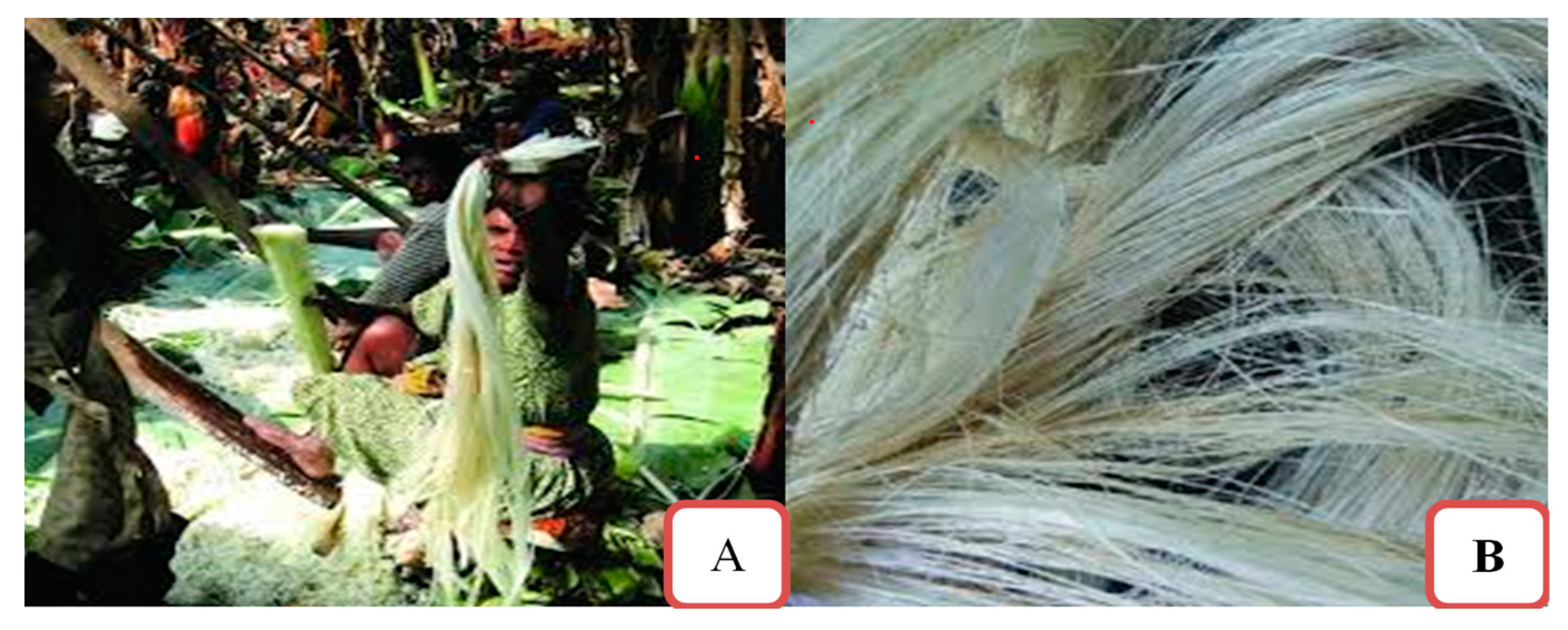
Enset fibers (
Figure 1B) were sourced from Ethiopian indigenous Enset plant (Ensete ventricosum) from Kokosa, Oromia, Ethiopia, found at 2627m altitude with min and max annual average temperature of 12 and 18
0C respectively [
32]. Manually extracted fibers from 3 different ages (1,2, & 3 years after the pulp is ready for first round extraction; approximately 5,6 & 7 years) of Enset plant using an in house developed technique [
1].
The density of the fibers was determined using a Pycnometer, Beckman model 930, in which helium gas at a pressure of 0.5bar was used as the displacement medium. During material preparation prior to the density measurement, the fibers were cut to different sizes based on the need mentioned on method part below.
Poly Lactic Acid (PLA 4043D, Nature works) in the pellet form, with a density of 1.24g/cm3 and melt flow rate of 65g/10 min is used for this study. The data sheet shows that the tensile strength, tensile elongation and tensile modulus are 60MPa, 6% and 3.6GPa respectively. The flexural strength and modulus from datasheet is 83Mpa and 3.8Gpa respectively.
Plasticizer: - is used to enhance the process-ability and improve the brittle nature of pure PLA is Proviplast 2624. Different percentages (2, 4, 6, 8 and 10%) of plasticizer were added to the virgin PLA compound based on its effect on ease during compounding, and evaluate their resulting effects on mechanical properties to select the optimum percentage of in the Enset-PLA compound.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Density Estimation and Fiber Preparation
Density of the fiber is measure at different level and condition based on the reason it is required for. A fiber from milled powder to 10mm as well as 100mm, and vacuum dried for 6hr and 24hr at 600C is used. Weight of these fibers is measured using sensitive balance with accuracy of 10-5gr. And, density of the fiber has been measured using Gas Pychnometery. Following density measurement single fiber characterization and fiber hygroscopic nature typifying has been done. Afterwards, manually chopped fibers to the desired lengths of approximately 5mm and 10mm has been prepared and dried for 6hr in vacuum drier at 600C before compounding using injection molding.
2.2.2. Compounding and Actual Fiber Ratio Substantiation
Compounding has been done for different fiber-matrix-plasticizer combinations based on design of experiment. The factors considered are fiber ration (10, 15, 20, & 25%), plasticizer ration (2, 4, 6, 8 & 10), fiber plant age (1, 2 & 3) and fiber size (5mm, 10mm). Number of experiment has been reduced conducting preliminary test to see the effects of the factors. Process of compounding has been done with extruder speed of 160rpm, melt temperature of 190C and die temperature 175C.
Then, the actual fiber concentration was cross-checked by dissolving the compound in Chloroform since PLA dissolves fully in chloroform. 140ml of Chloroform is used for a compound that weighs less than 10gr and dissolved. Full dissolving of the compound took 48hours. Since Chloroform is volatile, the drying of the fiber remain on the filtering paper was fast; the weigh is measure in 1hr and 48hr to see if there is residual chloroform. After separation is carried out, net weight of the filtered fiber is calculated against compound weight and comparison was made between the actual and measured fiber concentration for authenticity.
Table 1.
Comparison of Actual and machine set fiber ration in the compound.
Table 1.
Comparison of Actual and machine set fiber ration in the compound.
| Machine Set Ratio (%) |
Sample
Weight (gr) |
Filter
Paper (gr) |
Weight After Filtration (gr) |
Net Fiber Weight (gr) |
Net
Actual (gr) |
Difference
(%) |
| 15 |
0,373 |
0,455 |
0,501 |
0,046 |
12 |
17,7 |
| 20 |
0,321 |
0,457 |
0,512 |
0,055 |
17 |
14,3 |
| 25 |
0,355 |
0,445 |
0,521 |
0,076 |
21 |
14,4 |
2.2.3. Specimen Production and Testing
Specimens are produced using the injection molding process. Before processing, each compound was dried in pressurized air dryer (Moretto) for 8hr at 600C. The drying temperature is kept 600C to avoid sticking of the compound pellets with higher plasticizer ratio. The injection molding was performed with at 1900C Injection temperature, 1400bar pressure and cycle time of 61sec. Next, the standard tensile bars (dog bone) with known dimension and weight were dried and are submerged into distilled water. Increases in weights are measured daily to check moisture uptake and the absorption trend. Saturation point where there were no more uptakes was identified and 10 more days of submerging and testing are considered to enhance certainty. After typifying hygroscopic behavior, tensile and three point bending (3pb) strength of the material have been tested to investigate the moisture effect on strength considering a span length of 80mm and 0.01mm/sec rate for 3pb test. The result is compared with the strength before uptake to identify associated property losses.
3. Results
Moisture content of fiber extracted from different ages of the plant and different size have been measured using Karlfisher and Mettler Toledo moisture analyzer, after exposing them to room temperature. The measured moisture content of the fiber was 6.342- 6.62% (Karlfisher) while 5.5-8.2% (Mettler Toledo). In this regard, the fiber extracted from matured (3 years after the first pulp extraction) age plant absorbs slightly less (5.5% to 6.4% & 6.3 to 6.4% as per Mettler Toledo and Karlfisher respectively) moisture compared with the one extracted from younger plant. Conversely, the fiber with shorter length exhibits slightly higher moisture absorption compared with the longer one. This is resulted from the cutting of lumen in to different parts, exposing relatively larger surfaces area and porosities to absorb more moisture. This test gives first preliminary insight of the better moisture resistance matured age plant fiber.
3.1. Moisture Absorption and Release Characteristics
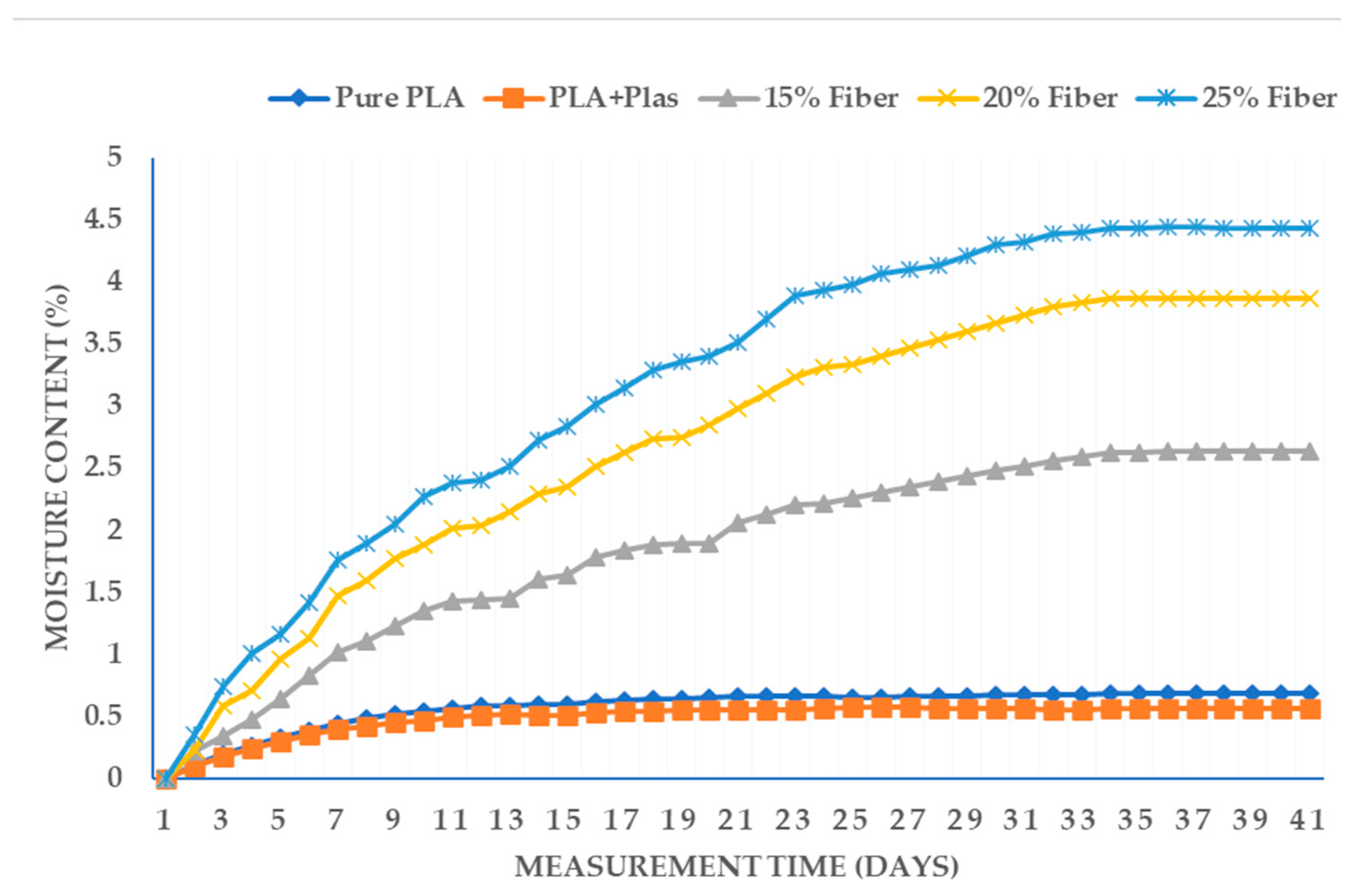
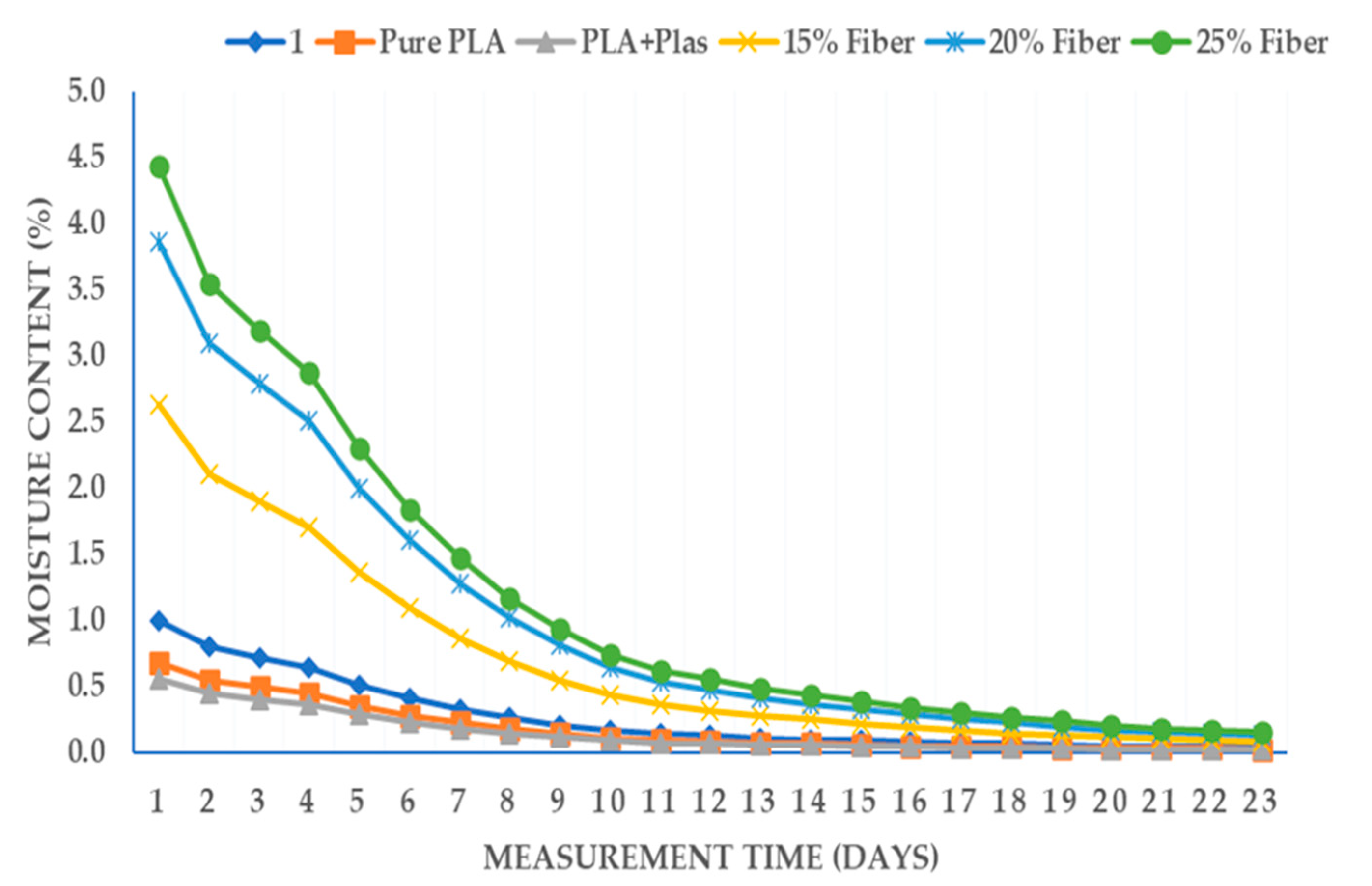
Moisture absorption and release characteristics of Enset-PLA composite for different scenario have been studied for 40 and 18 consecutive days respectively. The absorption and release trends are plotted on
Figure 2 and
Figure 3 below. The graphs show that moisture absorption arrives at saturation point or plateau in 26 days. In this scenario, the highest water absorption noticed is 4.7%, and is found for highest fiber concentration of 25% and lowest plasticizer percentage 6.3%.
This higher absorption is mainly caused by the hydrophilic nature of the fiber in the composite and this is in agreement with other related previous findings though rate of uptake differs based on fiber type [
4,
5,
22]. Correspondingly, the lowest water absorption (1.3%) in case of composites is found for the lowest fiber ratio of 15% and the highest plasticizer ratio scenario 6.25%. The moisture absorption decrease with increasing plasticizer ratio, here, is in agreement with other findings [
27,
34,
35,
36].
Similarly, moisture release trend and residual moisture at room temperature has been assessed after characterizing absorption. The release becomes nearly stable after 13th days at room temperature. The scenario with highest moisture release rate happens for highest absorbing case, 25% fiber, which is in agreement with other findings [
34,
36].
Figure 3 below shows the moisture release trend at room temperature with residual moisture comparing it against the dried specimen before submerging in to water.
3.2. Effect of Plasticizer Ratio on Moisture Absorption
Effects of plasticizer on the moisture uptake have been noticed to be significant. Considering different scenario, increase in plasticizer ratio enhances moisture resistance; an increase in the plasticizer from 4% to 6.25% results in 0.5% less moisture uptake for 25% fiber ration of the composite which equals about 11% of the overall moisture absorption. The trend remain similar other fiber ratios considered. The results are in agreement with other findings stating presence of plasticizer reduces moisture absorption [
34,
36]. It should be noted that literature reports some variation in the total decrease of moisture uptake with respect to fiber and plasticizer content. The reason behind can be properties of fibers involved, the processing and testing condition.
3.3. Effects of Moisture on Mechanical Properties
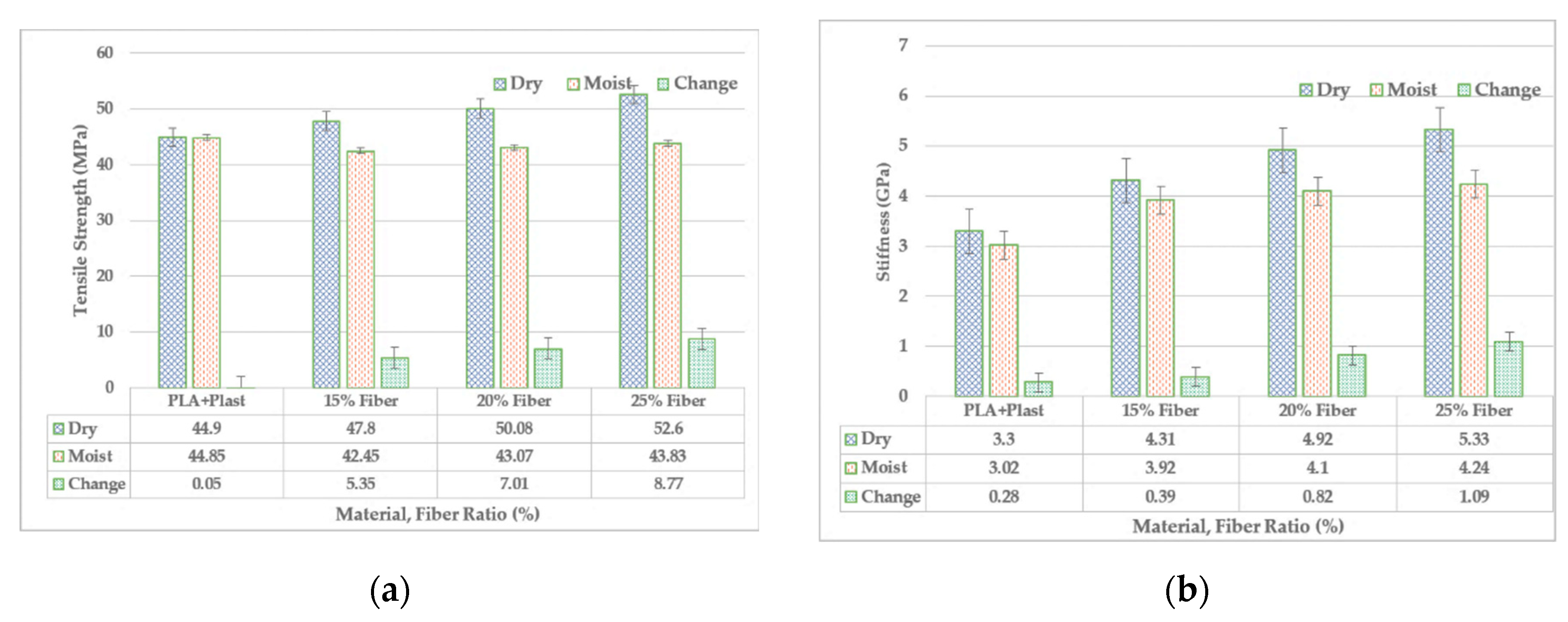
Effects off moisture have been assessed. Figures 6 and 7 present the effect of moisture on mechanical properties of Enset-PLA composite with comparison before and after the submersion in water. After moisture absorption, tensile strength and stiffness of the material declines. The highest deterioration occurs for high fiber concentration and lowest plasticizer ratio. Maximum property loss happens for 25% fiber with 6.25% plasticizer; the tensile strength and stiffness decreases by 16.7% and 20% respectively. The level of deterioration of mechanical properties of Enset-PLA composite is slightly better than some other PLA based bio-composite exposed to the nearly similar environment [
37,
38]. For instance, injection molded PLA/Cordenka composite exhibit smaller tensile strength when compared with Enset/PLA composite but with similar trend. The difference emanates from type and properties of fibers, and processing condition.
Figure 4.
Effects of moisture on mechanical properties (a) on Tensile Strength and (b) on Modulus.
Figure 4.
Effects of moisture on mechanical properties (a) on Tensile Strength and (b) on Modulus.
This results from effects triggered by moisture to bring swelling, de-bonding, bond breaking, and internal stress because of the fiber concentration and associated hydrophilic nature [
15,
16,
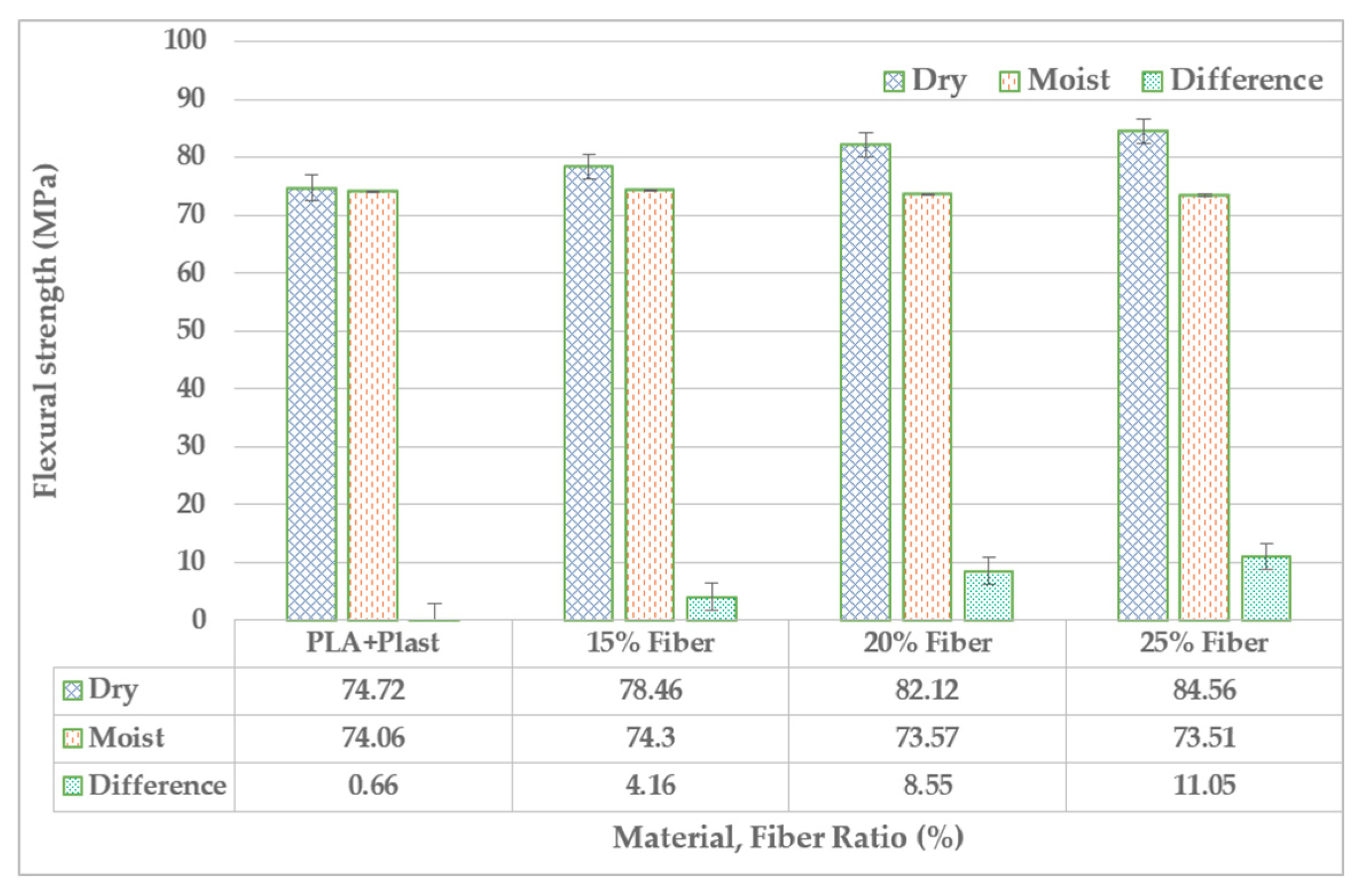
20]. Amount of property loss due to moisture uptake is comparable almost equal with property gain resulted from increasing fiber concentration before moisture uptake. This is evident from Figure 6; strength of all 15%, 20% and 25% fiber concentration has significant difference after absorption of moisture. But, the stiffness is differently affected; the increase in fiber concentration have significant enhancement on stiffness both before and after moisture uptake despite the difference in the percentage of increase. Hence, unlike tensile strength, increasing fiber ratio significantly enhances the stiffness in both condition of with and without moisture uptake. Strength of Enset-PLA composite after property losses has comparable strength with Cordenka-PLA (50.4, 50.7 and 57.9 for 10, 20 and 30% fiber ration) and Flax-PLA (42.7, 49.2 and 54.1 for 10, 20 and 30% of fiber ration respectively) composite. Likewise, bending strength is another property affected by moisture. Figure 6 below summarizes the effect of moisture on flexural strength of Enset-PLA composite.
Figure 5.
Effects of moisture on bending strength of Enset-PLA.
Figure 5.
Effects of moisture on bending strength of Enset-PLA.
The above graph shows that bending strength is highly affected by moisture absorption. The maximum and minimum flexural strength losses are 13.06% and 5.31% and they are for 25% and 15% fiber ratio composite respectively. Increasing fiber ratio for Enset-PLA composite exposed to moisture doesn’t increase the flexural strength. The property gain resulted from introducing more fiber compensated property loss due to its hydrophilicity of the composite. Yet, slight decrease in strength is noticed when fiber ratio increased under moisture exposition. This is resulted from effect of hydrophilic fiber in the composite and resulting interfacial bond weakening and swelling up of the specimen [
35,
37].
3.4. Statistical Analysis and Result Summary
Statistical analysis performed to find effect of individual factors on the moisture absorption jointly with the interaction effect of up 3 levels has been checked. To do this, significance level of factors, analysis of variance and desirability check have been conducted. The results can be summarized as follows.
The main effect of individual factors has been analyzed and the Fiber ratio and plasticizer ratio are found to be strongly significant in affecting the moisture absorption and release characteristics of Enset-PLA composite while fiber plant age and fiber length are less significant.
Moisture has significant effect in tensile and flexural strength loss to the extent it almost balances the property gain resulted from the increment of fiber ratio in the composite. However, the effect of moisture is lesser on tensile modulus though it has smaller effect.
The combined effect of plasticizer ratio; fiber ratio and residual moisture on tensile and bending strength is significant. This can also be noticed from
Figure 4a and
Figure 5 above. One of the reasons for the tensile strength and flexural strength to show insignificant increase with increasing fiber ration is related with the effect of the aforementioned factors. Increasing fiber ration gives significant increase in both tensile and flexural strength when tested before submerging into water and allowing the test specimen absorb moisture.
4. Conclusions
From the all the aforementioned result, the following conclusion can be drawn. Enset fiber is an attractive natural fiber that can be compounded with PLA to give competitive and slightly better mechanical properties compared with other selected natural fibers. It gives competitive tensile and flexural strength before and after exposition to moisture and loss of some mechanical properties. In the later regards, fiber ratio takes the lion share in hydrophilic nature of the Enset-PLA composite though there variation of rate of absorption based on fiber type and ratio. Though bending strength gets enhanced with increasing fiber ration without submerging it into moisture, it doesn’t get enhanced with increasing fiber ration after exposition to moisture. The amount of property gain from adding more fiber is compensated with the amount of property loss resulted from the hydrophilicity introduced be the same added fiber ration. On the other hand, No significant change in tensile strength is noticed for composite when increasing fiber ratio for moisture absorbing test specimen. Unlike tensile strength, increasing fiber ratio significantly enhances the stiffness in both condition of with and without moisture absorption. The individual effects of fiber ration and plasticizer concentration in the composite of Enset-PLA are more significant.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Mekelle University (Ethiopian Institute of Technology-Mekelle), KU Leuven and Addis Ababa Science and Technology University (AASTU) for privileging us with lab facilities for different tests we have conducted. Inline, we are thankful to all lab technicians in these institutions together with MSc and PhD students working in the laboratory we are using for their unreserved cooperation and help.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- A. Abdela, M. Versteyhe, and F. Taddese, “Characterization of Single Enset Fiber Tensile Properties Using Optimal Experimental Design and Digital Image Correlation Technique,” Int. J. Mech. Eng. Appl., vol. 8, no. 1, p. 8, 2020. [CrossRef]
- D. K. Rajak, D. D. Pagar, P. L. Menezes, and E. Linul, “Fiber-reinforced polymer composites: Manufacturing, properties, and applications,” Polymers (Basel)., vol. 11, no. 10, 2019. [CrossRef]
- K. Arun Kumar, S. M. Sudhanan, K. M. Kumar, and G. Ranjith Kumar, “A STUDY ON PROPERTIES OF NATURAL FIBRES -A Review,” Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol., vol. 10, pp. 2395–56, 2017. Available online: https://www.irjet.net/archives/V4/i10/IRJET-V4I10244.pdf.
- F. B. Ebanda and N. Boris, “review article a literature review on natural fibers, its properties and influence of water absorption on mechanical a literature review on natural fibers, its properties and influence of water absorption on mechanical properties of composites,” no. July, 2019.
- B. E. Fabien, N. Boris, and A. Ateba, “A literature review on natural fibers, its properties and influence of water absorption on mechanical properties of composites,” Int. J. Recent Adv. Multidiscip. Res., vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 4790–4797, 2019. Available online: www.ijramr.com.
- J. Kova, J. P. Mofokeng, A. S. Luyt, and T. Ta, “Comparison of injection moulded, natural fibre-reinforced composites with PP and PLA as matrices,” 2011. [CrossRef]
- J. S. Borrell et al., “Enset in Ethiopia: A poorly characterized but resilient starch staple,” Ann. Bot., vol. 123, no. 5, pp. 747–766, 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. S. Borrell et al., “Enset-based agricultural systems in Ethiopia: A systematic review of production trends, agronomy, processing and the wider food security applications of a neglected banana relative,” Plants, People, Planet, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 212–228, 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Haag and J. Müssig, “Scatter in tensile properties of flax fibre bundles: influence of determination and calculation of the cross-sectional area,” J. Mater. Sci., vol. 51, no. 17, pp. 7907–7917, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Y. Bao, “Hydrothermal aging behaviors of CMR / PLA biocomposites,” 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. F. M. Alkbir, S. M. Sapuan, A. A. Nuraini, and M. R. Ishak, “Fibre properties and crashworthiness parameters of natural fibre-reinforced composite structure: A literature review,” Compos. Struct., vol. 148, pp. 59–73, 2016. [CrossRef]
- R. B. Adusumalli, K. C. Venkateshan, C. Kunchi, and S. R. Vadlamani, “Tensile testing of single fibres,” Procedia Struct. Integr., vol. 14, no. November, pp. 150–157, 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. K. Ilankeeran, P. M. Mohite, and S. Kamle, “Axial Tensile Testing of Single Fibres,” Mod. Mech. Eng., vol. 02, no. 04, pp. 151–156, 2012. [CrossRef]
- J. Cline, V. Wu, and P. Moy, “Assessment of the Tensile Properties for Single Fibers,” 2018.
- M. Z. Rong, M. Q. Zhang, Y. Liu, Z. W. Zhang, G. C. Yang, and H. M. Zeng, “Mechanical Properties of Sisal Reinforced Composites in Response to Water Absorption,” vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 407–426, 2002. [CrossRef]
- Salih, R. Zulkifli, and C. H. Azhari, “Tensile Properties and Microstructure of Alkali Treatment,” Fibers, vol. 8, no. 26, pp. 1–10, 2020.
- M. Yusefi and M. Khalid, “Evaluation of water absorption of polyvinyl alcohol- starch biocomposite reinforced with sugarcane bagasse nanofibre : Optimization using Two-Level Factorial Design Evaluation of water absorption of polyvinyl alcohol-starch biocomposite reinforced with su,”. [CrossRef]
- P. Zakikhani, R. Zahari, M. T. H. Sultan, and D. L. Majid, “Morphological, mechanical, and physical properties of four bamboo species,” BioResources, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 2479–2495, 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. R. M. Asyraf et al., “ur na f,” J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Grant, B. Regez, S. Kocak, J. D. Huber, and A. Mooers, “Results in Materials Anisotropic properties of 3-D printed Poly Lactic Acid ( PLA ) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene ( ABS ) plastics,” Results Mater., vol. 12, p. 100227, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Chaitanya and I. Singh, “Processing of PLA / sisal fiber biocomposites using direct- and extrusion-injection molding,” Mater. Manuf. Process., vol. 32, no. 5, pp. 468–474, 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. K. Mohapatra and S. Mohanty, “Properties and characterization of biodegradable poly ( lactic acid ) ( PLA )/ poly ( ethylene glycol ) ( PEG ) and PLA / PEG / organoclay : A study of crystallization kinetics, rheology, and compostability,” 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. E. Alves Fidelis, T. V. C. Pereira, O. D. F. M. Gomes, F. De Andrade Silva, and R. D. Toledo Filho, “The effect of fiber morphology on the tensile strength of natural fibers,” J. Mater. Res. Technol., vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 149–157, 2013. [CrossRef]
- H. Fernandes, M. De Queiroz, and M. Doina, “The effect of multiscale hybridization on the mechanical properties of natural fiber-reinforced composites,” no. May, 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. Gunti, R. P. A. V, and A. V. S. S. K. S. Gupta, “Mechanical and Degradation Properties of Natural Fiber-Reinforced PLA Composites : Jute, Sisal, and Elephant Grass,” 2018. [CrossRef]
- G. Rajesh, A. V. R. Prasad, and A. Gupta, “Mechanical and degradation properties of successive alkali treated completely biodegradable sisal fiber reinforced poly lactic acid composites,” 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Natterodt et al., Special Issue : Recent Advances in Applied Polymer Science Special Issue : Recent Advances in Applied Polymer Science, vol. 45520. 2018.
- K. C. Y. Lin, W. Guo, and S. W. T. Don, “Flammability and tensile properties of polylactide nanocomposites with short carbon fibers,” pp. 1605–1612, 2015. [CrossRef]
- D. Garlotta, “A Literature Review of Poly ( Lactic Acid ),” vol. 9, no. 2, 2002. [CrossRef]
- A. Gloria et al., “Technical features and criteria in designing fiber-reinforced composite materials: From the aerospace and aeronautical field to biomedical applications,” J. Appl. Biomater. Biomech., vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 151–163, 2011. [CrossRef]
- U. C. Paul, D. Fragouli, I. S. Bayer, A. Zych, and A. Athanassiou, “E ff ect of Green Plasticizer on the Performance of Microcrystalline Cellulose / Polylactic Acid Biocomposites,” 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. Tiki, Y. Mulatu, and E. Environment, “Indigenous knowledge on highland bamboo ( Yushania alpina ) management and utilization practices in Kokosa Woreda, South East Ethiopia,” no. July, 2018. [CrossRef]
- G. Blomme et al., “Assessing enset fibre yield and quality for a wide range of enset [Ensete ventricosum (Welw.) Cheesman] landraces in Ethiopia,” Fruits, vol. 73, no. 6, pp. 328–341, 2018. [CrossRef]
- K. Shinyama and S. Fujita, “The Effects of Plasticizer on the Mechanical and Electrical Characteristics of PLA,” pp. 1–4, 2008. [CrossRef]
- C. Science, H. Kim, and J. R. Dorgan, “Bio-composites of kenaf fibers in polylactide : Role of improved interfacial adhesion in the carding process,” no. 19, 2009. 20 February. [CrossRef]
- M. Gao and L. Lu, “Physical properties of plasticized PLA / HNTs bionanocomposites : effects of plasticizer type and content Physical properties of plasticized PLA / HNTs bionanocomposites : effects of plasticizer type and content,” 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. Anggono and H. Purwaningsih, “Biobased PLA / sugarcane bagasse fiber composites : Effect of fiber characteristics and interfacial adhesion on properties' cz o J a,” vol. 143, 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. Mandal, H. Bhunia, and P. K. Bajpai, “Thermal degradation kinetics of PP / PLA nanocomposite blends,” 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. K. Bajpai and I. Singh, “Development and characterization of PLA-based green composites : A review,” pp. 52–81, 2014. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).