1. Introduction
In cold temperate regions of the Globe, during the Winter, deicing substances are often used on the roads to improve drivability and road safety, reducing accidents by up to 87% [
1,
2,
3]. Most commonly, inorganic salts (NaCl, CaCl
2, MgCl
2, KCl) are the main tool for ice melting in those regions [
3,
4]. Their usage can be traced back to the United States, by the end of the 1930s, and were adopted by other countries in the following decades [
3,
5]. As urbanized regions have grown, motor vehicles have become more common as a transportation option, leading to an exponential increase in salt usage for road safety improvement [
5]. The United States and Canada disperse as much as 24.5 million and 8 million tons, respectively, of road salt (mostly NaCl) [
6,
7,
8,
9]. While this positively impacts human road safety during winter, salt usage has been proven to have negative consequences, such as corrosion of automobiles, and road infrastructure degradation [
9,
10,
11].
A plethora of studies have shown that road-applied salt for ice melting is one major anthropogenic source of increased chloride (Cl
-) concentration in soil and water bodies, causing their salinization, more notably in high urbanized regions, which can reach chloride concentrations as high as 1344 mg/L [
2,
4,
5,
12]. The road salt enters the freshwater ecosystems by highway runoff resulting in high chloride concentrations [
4,
13]. The high chloride concentration impairs the freshwater aquatic biota by reducing food availability and a decrease in biodiversity [
2,
14,
15,
16,
17].
Many municipalities have installed real-time water quality monitoring stations to accurately assess the environmental impacts of winter road maintenance and reduce road salt application in salt-vulnerable areas. The large quantity of data collected at high frequency using a network of real-time monitoring stations is most efficiently analyzed by advanced deep learning models to provide accurate water quality forecasts. However, data-driven models, especially machine learning (ML) approaches, have been favoured by scientists due to their simpler implementation, faster processing time, and the inherent capacity to identify complex relationships in the data when compared to physical-based forecasting models [
18,
19,
20,
21]. In the work in [
22], experimental results for Water quality index (WQI) estimation for the Bhavani River, India, showed that the applied ANN configuration outperformed their benchmarking models, providing superior accuracy and error values. A similar result was found in another work [
23], where again ANN was employed for WQI forecasting in Warta River, Poland. Their best-assessed ANN configuration used five hidden neurons in a multilayer perceptron (MLP) structure, returning a value for root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.64, proving itself as an essential tool for surface water quality determination.
Future chloride concentrations also can benefit from the data-driven paradigm. In [
24], the authors propose a data-driven approach to determine future chloride levels in Florida, USA, for groundwater supply. Their approach showed robust performance when forecasting chloride, reaching RMSE and coefficient of determination (R
2) of 28 mg/L and 0.90, respectively. Another data-driven model was implemented by the authors in [
19]. Their proposed methodology, real-time chloride forecasting in Grand River, Canada, used an ensemble learning model combining multilayer perceptron MLP and stepwise cluster analysis (SCA). The proposed MLP-SCA achieved good results regarding RMSE, 11.58 mg/L, and R
2, 0.90. A regression tree-based ML model was suggested by Poor and Ullman [
25] for the determination of future levels of nitrate and chloride in the Willamette River, USA. Their analysis increased the R
2 values for chloride by 33% when compared to the multiple linear regression model, achieving a final value of 0.75. Their results proved that tree models could handle the complex nonlinearity within the assessed data.
In front of this, the data-driven approach shows great potential when applied to the hydrology/environment research area. However, the authors believe there is a deficiency in understanding the application of the deep learning paradigm for predicting chloride levels. Addressing this problem, the present work proposes to use a cutting-edge approach combining graph theory and DL to assess future chloride concentrations from spatiotemporal data for the Credit River, located in Ontario, Canada. This work expects to contribute to the field by:
Building a state-of-the-art model for chloride concentration, allowing more accurate and precise results
Analysis of the contribution of different time lags for the forecasted chloride concentration
Analysis of the importance of different input variables
The remainder of this work is divided as follows: in
Section 2, the methodology used is presented, followed by
Section 3, where the achieved results are shown. In
Section 4, there is a discussion of the results, and
Section 5 closes the work with a conclusion.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Credit River Characteristics and Dataset
The Credit River is in Southern Ontario, Canada, just west of Toronto. Its source is located in Orangeville, starting its way until reaching Lake Ontario in a 90 km trajectory [
26,
27]. The Credit River has a total drainage area of 93,000 ha, and its land is split into 35% for agriculture, 27% for urban, and the remaining 38% is of natural habitats, retaining an estimated population of 1 million people [
28,
29,
30]. The river is of significant conservation importance due to its rich aquatic biodiversity and its role as a vital water source for the local population [
26,
31]. A map showcasing the location of the Credit River watershed and its tributaries is presented in
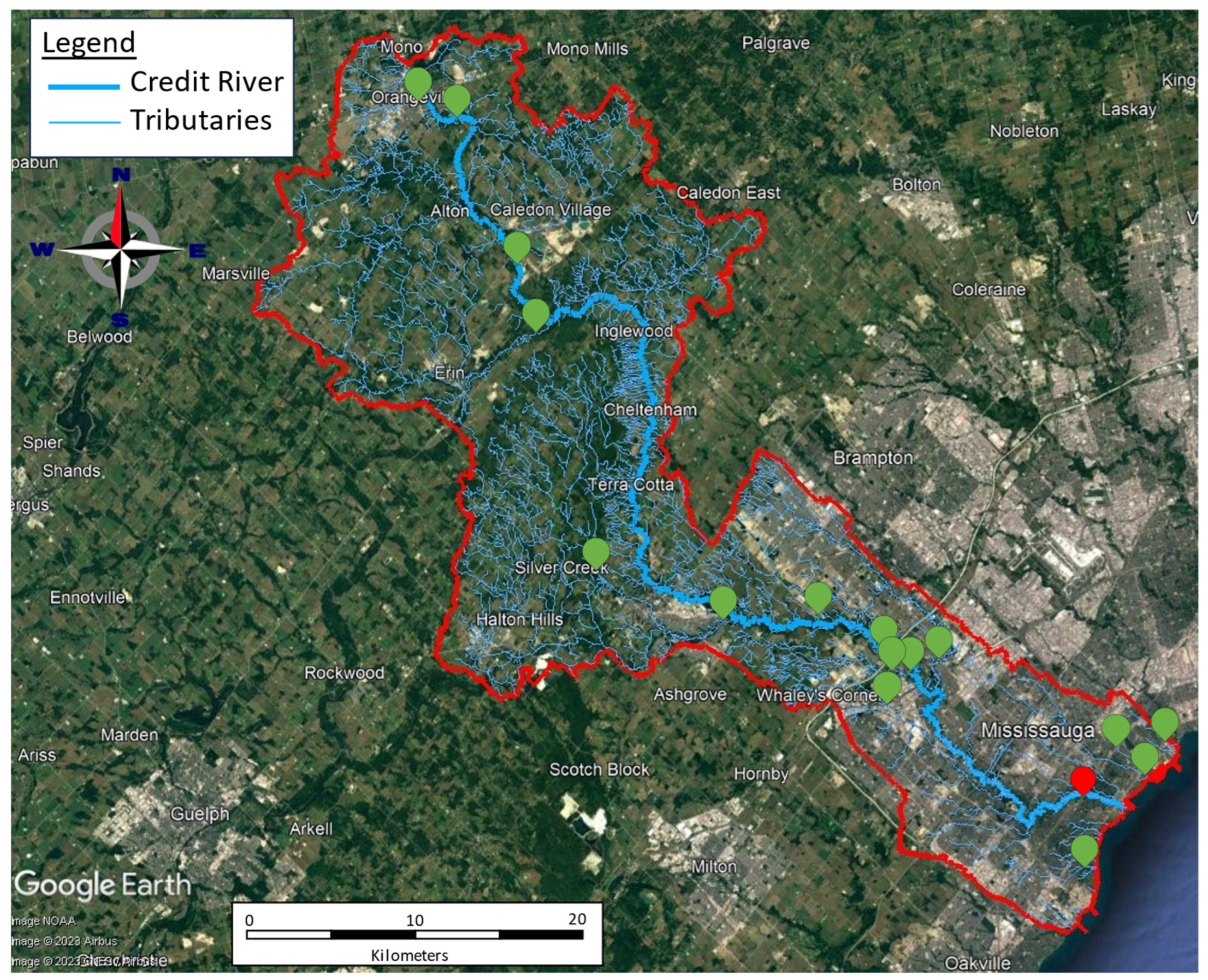
Figure 1, where the red mark represents the reference station, i.e., where the chloride concentration is being forecasted, while the green marks show the location of the neighbouring stations providing spatiotemporal data.
However, the highly urbanized Credit River watershed environment adds elevated pollutant concentrations to the river, risking human and animal lives. The present work proposes using a graph-based model called GNN-SAGE to estimate future pollutant concentration, namely chloride, in the Credit River. The used dataset contains historical data for the Credit River from 2016 to 2020. The stations distributed along the river’s course measure values for the water's physical-chemical characteristics and weather attributes.
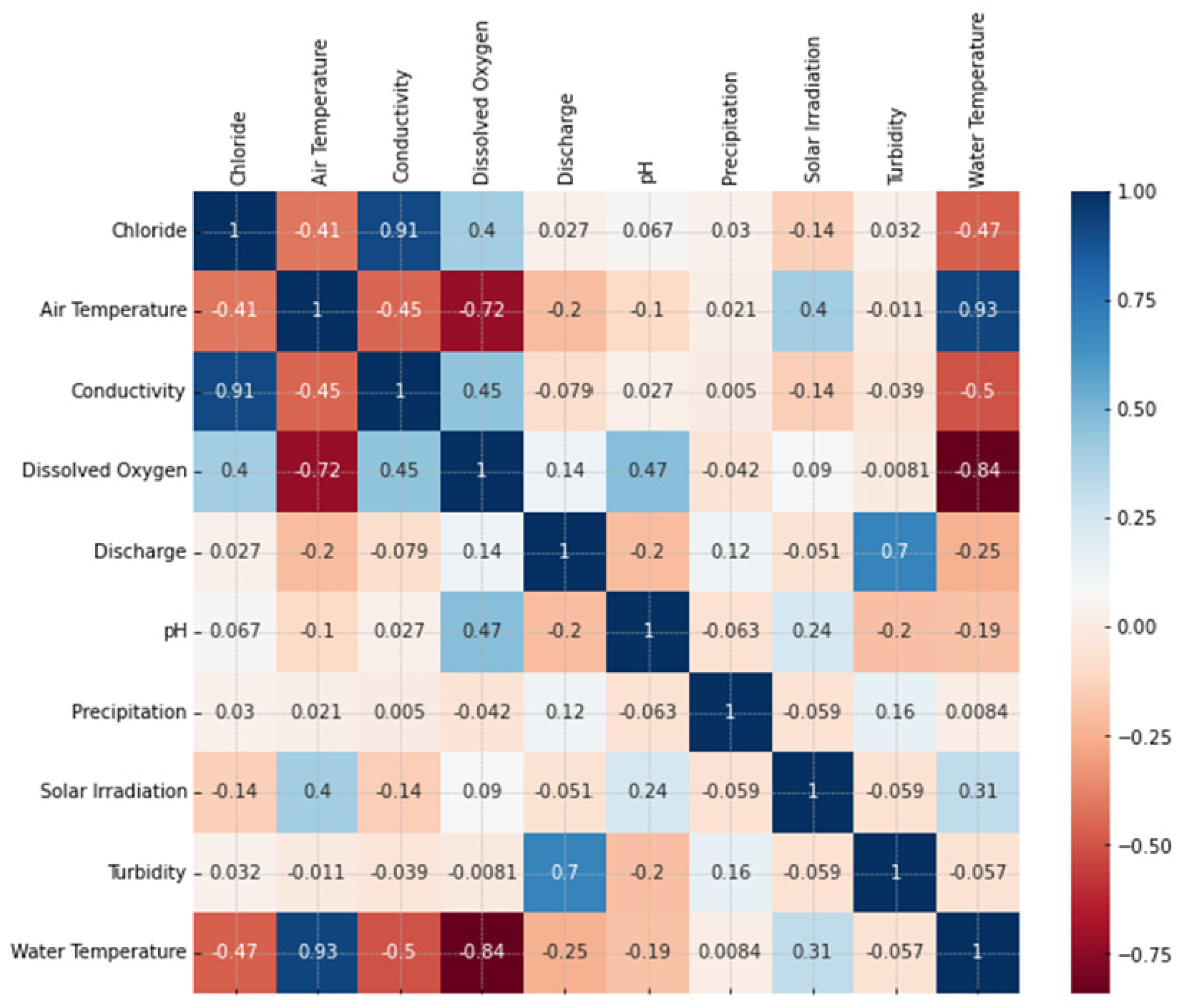
Figure 2 shows the correlation between each attribute in matrix form.
Figure 2 depicts the correlation matrix, with darker blue colors indicating highly correlated attributes and darker red showing a high negative correlation. The Figure 2.1 shows a strong positive correlation between chloride levels and water conductivity. Against common sense, this may indicate a collinear relationship between these two attributes, meaning that the conductivity information may be already provided to the model by the chloride data, which can hamper the model’s performance by increasing its variance [
32,
33]. Air and water temperatures have a moderately negative correlation with chloride, while dissolved oxygen has a moderately positive correlation. Although the remaining attributes have a weak correlation, these variables may add important information to the model due to the movement of salt dissolved in the river, helping its modeling and consequently, future chloride concentrations, as suggested by the SHAP analysis present in this work.
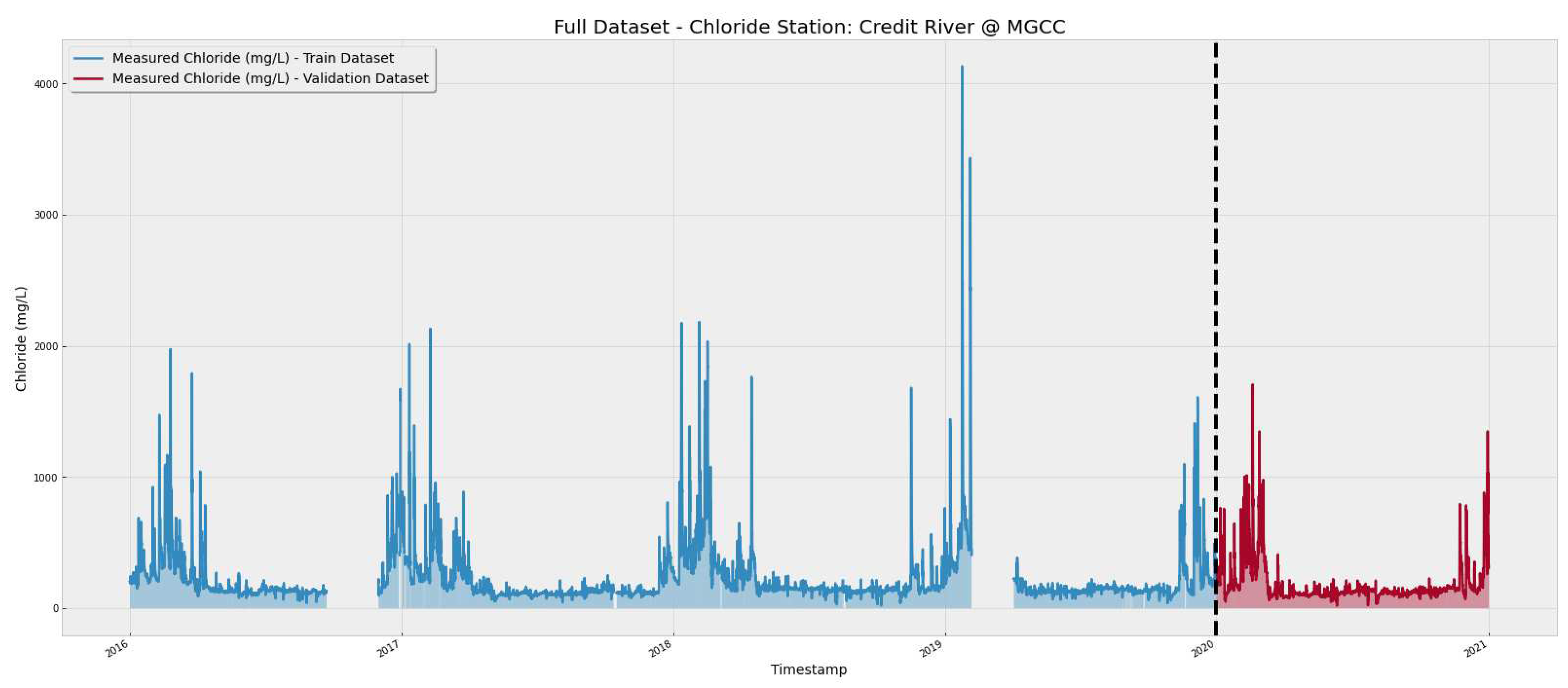
The dataset was split into training and validation. The training stage was performed using data containing the years from 2016 to 2019, and the validation stage was conducted using the year 2020, as shown in
Figure 3. In the figure, the blank spaces represent a gap in the historical data which were not used in the training phase.
2.2. Benchmarking Model
The performances of the Deep Neural Network based transformer (DNN-Transformer) and the Graph Neural Network Sample and Aggregate (GNN-SAGE) paradigms were evaluated using the benchmarking persistence model. Persistence is a simple forecasting model used as a minimal benchmarking tool. It states that the following attribute measurement is the same as the latest [
34,
35]. This approach can reach good results for short forecasting horizons. Still, its performance deteriorates for further future horizons as the model cannot track the influence of the dynamics of external factors impacting future values [
36,
37].
2.3. DNN-Transformer
In the original Transformer structure [
38], the encoder embeds data to a context vector using positional encoding and stacks a multi-head attention mechanism, determining how the provided input attends to each other. The encoder output is then fed to the decoder, which generates the most probable forthcoming word for NLP applications [
38]. Transformer-based models proved to have superior or competitive performance over recurrent neural networks when applied to different areas, such as speech recognition [
39], computer vision [
40,
41], and time-series forecasting [
42].
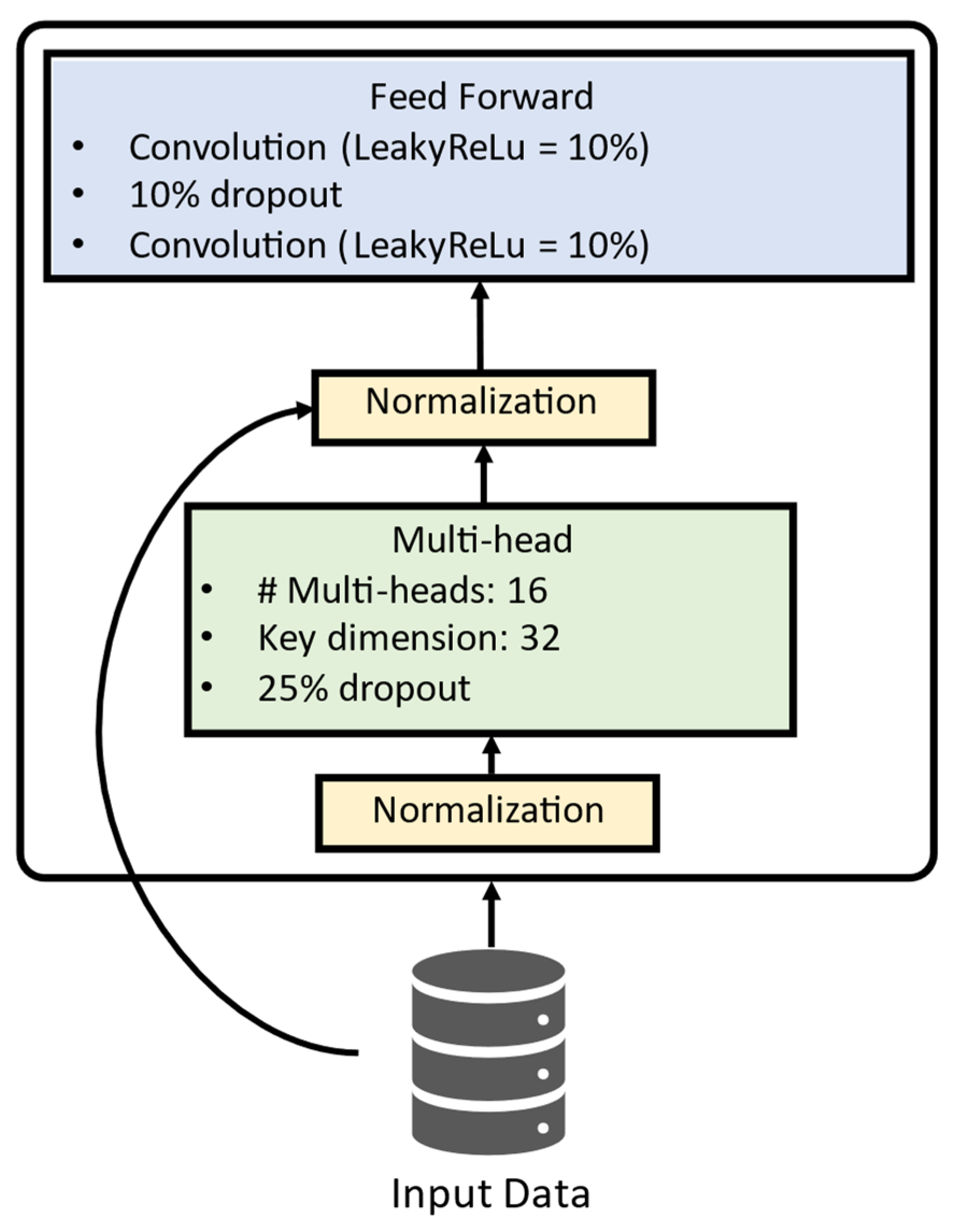
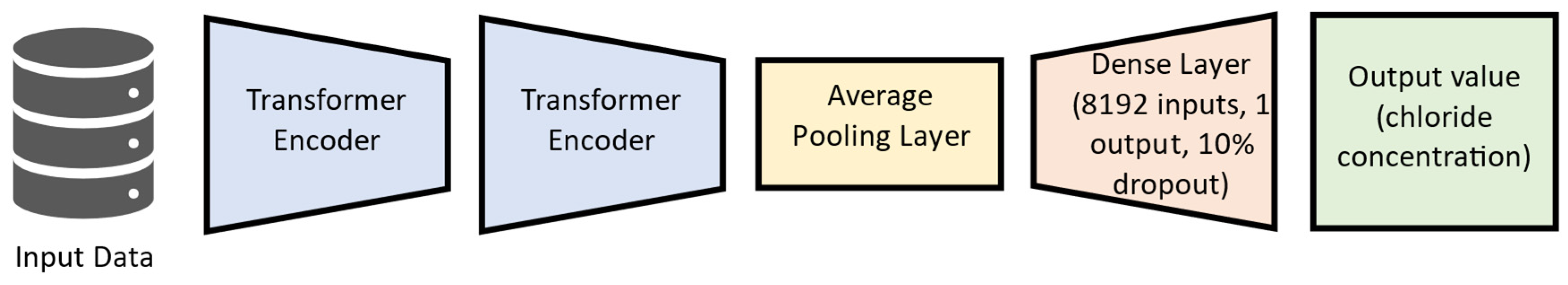
The present study adapted the transformer structure to the proposed regression problem of forecasting chloride concentration. The applied architecture for the transformer encoder and the DNN-Transformer architecture are presented in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5, respectively.
Figure 4 shows that the used transformer uses just the encoder structure for the present study. There, the input data is normalized before being fed to the multi-head structure, composed of 16 multi-head, each one with a key dimension equal to 32. After that, the processed data is again normalized with residual information from the original input dataset, then passed to the feed-forward structure, composed of convolutional layers activated by Leaky ReLu [
43], using a 10% dropout. The DNN-Transformer structure, depicted in
Figure 5, is composed of two encoders, followed by an average pooling layer. A dense layer with 8192 neurons follows the model, which finally outputs the predicted chloride concentration.
2.4. GNN-SAGE
The GNN-SAGE was first proposed [
44] as a general inductive framework for handling large graph structures. In this approach, nodes are equally sampled around an area of interest during the sampling phase. Afterward, the spatiotemporal information retrieved from these nodes is aggregated by an aggregate operator [
45]. This generates an embedding vector representing the node of interest, also being able to generalize unknown data disregarding the graph’s topology and structure [
44,
46,
47]. The GNN-SAGE model’s structure enables it to capture complex spatiotemporal patterns between a node and its neighbors, enhancing its forecasting performance compared to traditional ML and DL methods. This results in cutting-edge outcomes when applied to various time-series problems [
36,
37]. The GNN-SAGE structure used in this study is presented in
Figure 6.
In
Figure 6, the spatiotemporal data is fed to the first SAGE convolutional layer using 10% Leaky ReLu as the activation layer and 10% of dropout rate. The convolution process is repeated four times, identifying and extracting relevant structure patterns in the data. After that, the processed data is passed to a sequence of two dense layers using 10% Leaky ReLu, where the forecasted chloride concentration is finally output by the model.
2.5. SHAP Analysis
The Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) is a way to provide insight into how ML models work [
48]. The SHAP analysis, based on game theory, calculates the contribution of each input parameter used by the model for forecasting. This is done by evaluating the model for each situation where one of the independent variables is not used. This way, SHAP can identify relationships among the input data, identifying their influence, importance, and correlation over the model’s output [
36,
37,
46,
48]. The determination of the influence of each variable provides deeper insight into how the model provides its results, being a viable option to explain the analyzed ML paradigm locally. The employment of SHAP analysis by different knowledge areas, such as pharmaceutical [
49], engineering [
50], and social sciences [
51], places it as a valuable tool for researchers.
3. Results
3.1. Size of Time Window Effect
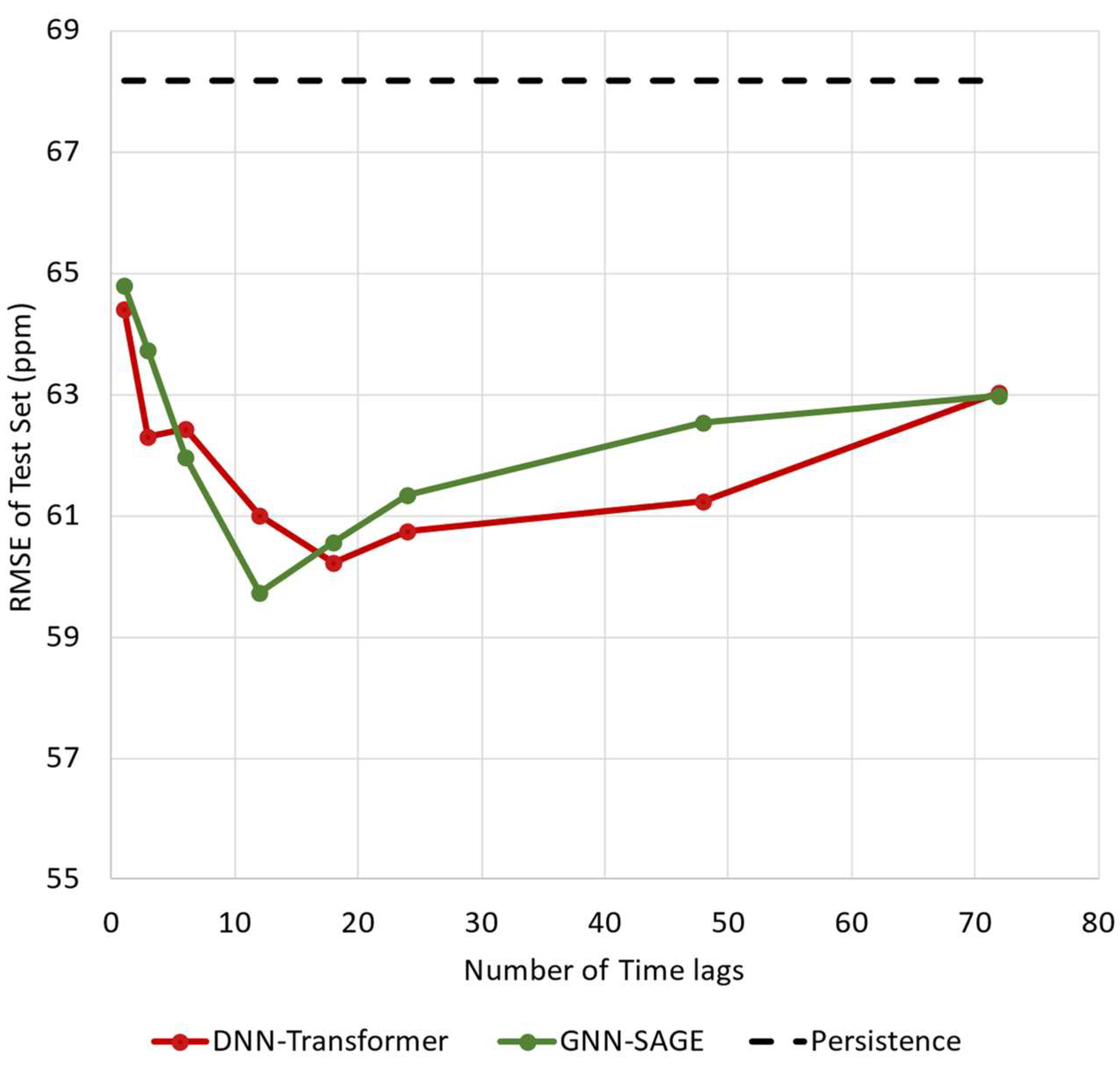
Figure 7 presents the results for the effect of different time window sizes, i.e., the number of time lags applied as inputs on both GNN-SAGE and DNN-Transformer models. To that end, it was set up that only chloride information would be used in this analysis.
Figure 7 shows the RMSE for different numbers of time lags for the proposed DNN-Transformer and GNN-SAGE models. The increase in the time window size proved to be beneficial for the graph-based model up to 12 hours. Beyond that threshold, the results started to deteriorate. For the DNN-Transformer, incorporating past information enhanced the model’s outcome for up to 18 hours, where more time lag values started to harm the model’s performance.
The GNN-SAGE and DNN-Transformer models outperformed persistence, with improvements of 12.4% and 11.7%. For the graph-based approach, the best result was obtained using 12 hours of past data reaching an RMSE value of 59.73 ppm, while DNN-Transformer needed 18 hours to provide its best outcomes for an RMSE of 60.24 ppm. Compared to the DNN-Transformer, the proposed GNN-SAGE improved its forecasting by 0.8% for that situation.
3.2. Chloride Concentration for 6-h Ahead Forecasting Horizon
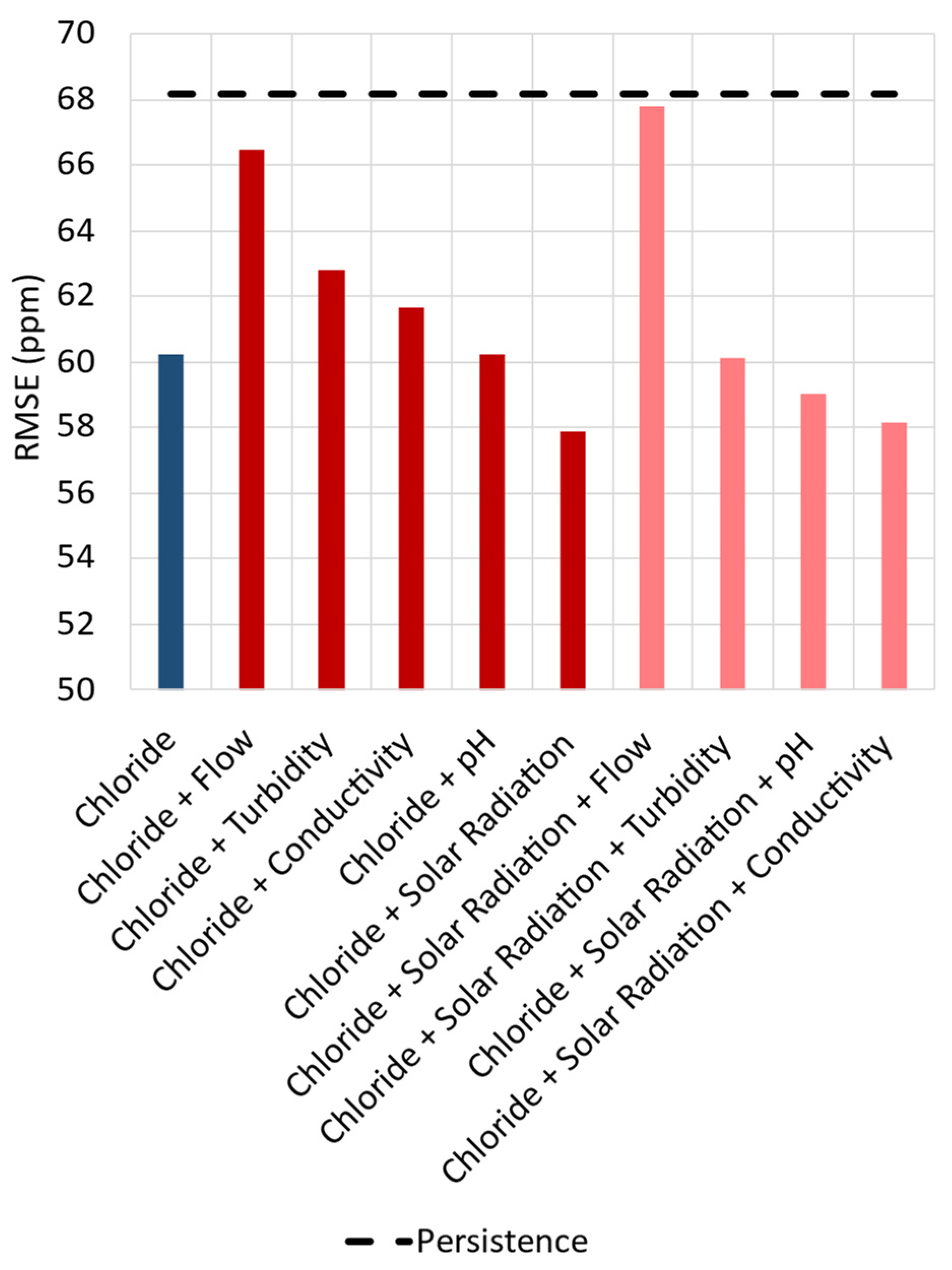
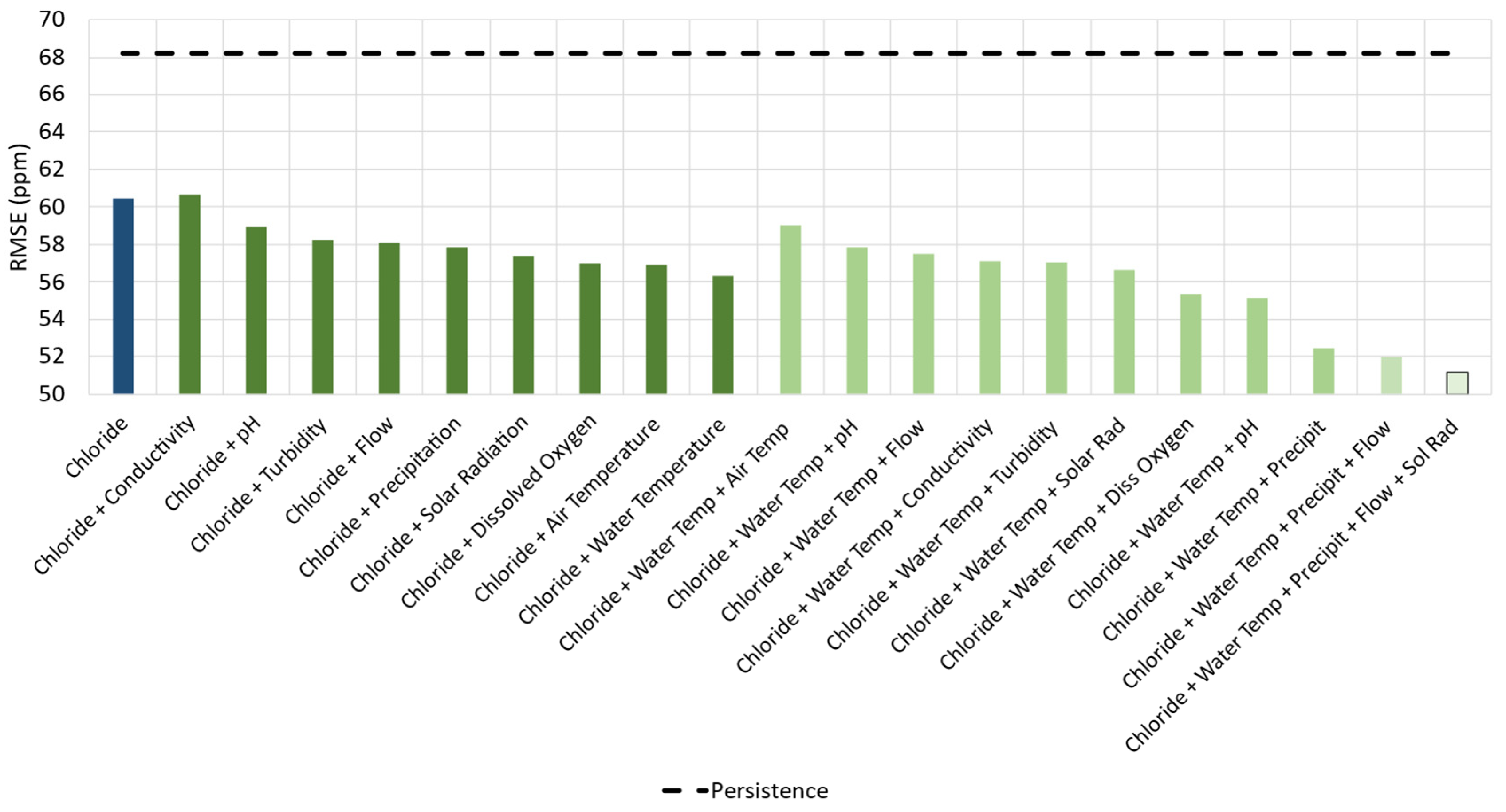
The impact of the input variables used on chloride forecasting was evaluated through a step-by-step analysis for a 6-h ahead forecast horizon. At first, the model used only past chloride concentrations as input to forecast future chloride concentrations. After each test, more input variables were introduced to the model. If the inclusion of a variable improved the model’s performance, it was kept as an input; otherwise, it was discarded. This procedure was repeated until all the input variables described in
Figure 2 were assessed, resulting in only selecting those variables that returned the best forecasting values in terms of RMSE. The results for this test are shown in
Figure 8, where the lighter the colour, the better the error achieved by the model.
In
Figure 8, the best result was combining chloride and solar radiation resulting in an RMSE of 57.86 ppm. Adding more than two variables showed no improvement over the transformer performance, indicating that the model could not extract the spatiotemporal information from the additional inputs. Solar radiation, on the other hand, appears capable of providing temporal information in terms of seasonality, both yearly and daily, improving the model's forecasting capacity. The results for forecasting chloride concentrations 6-h ahead are presented in
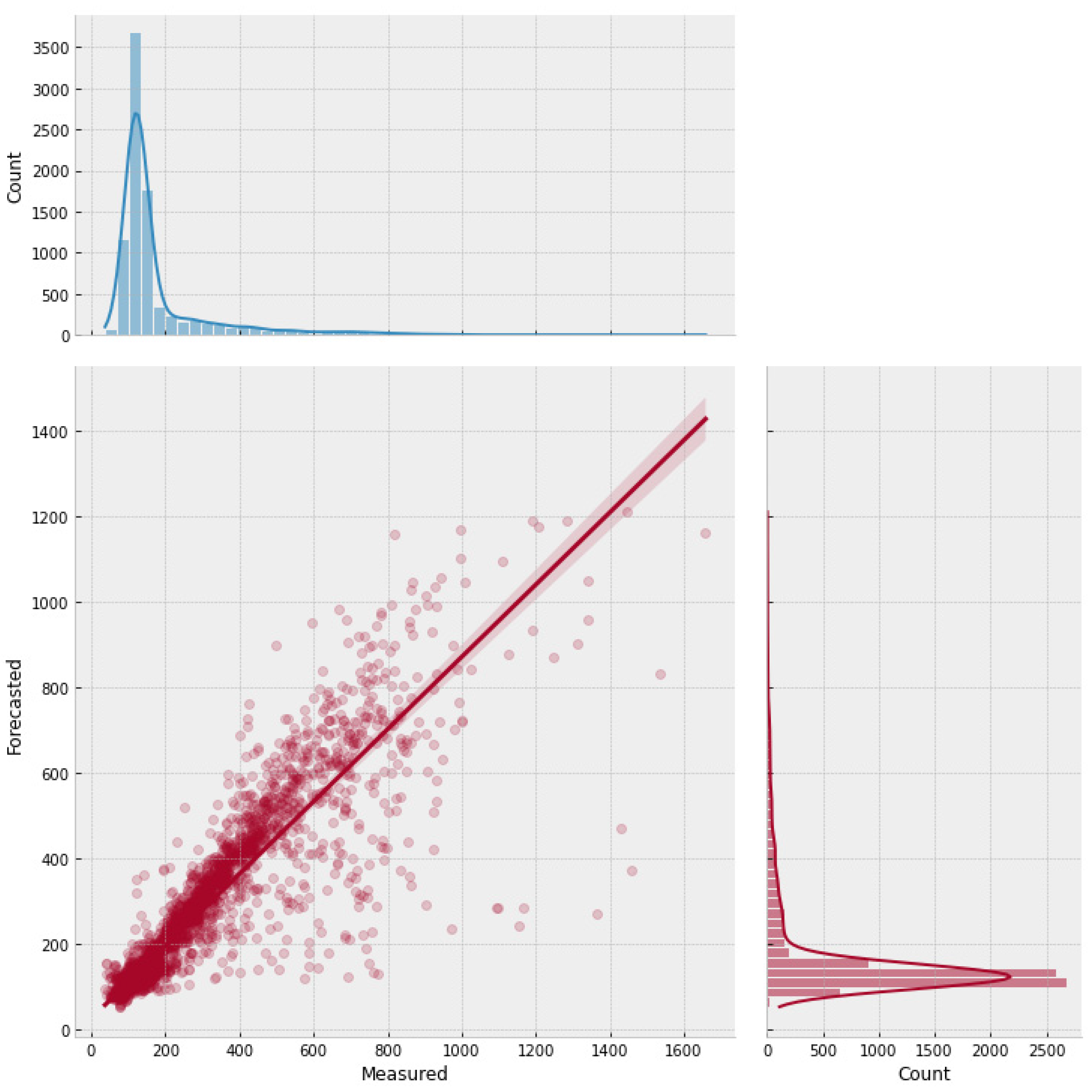
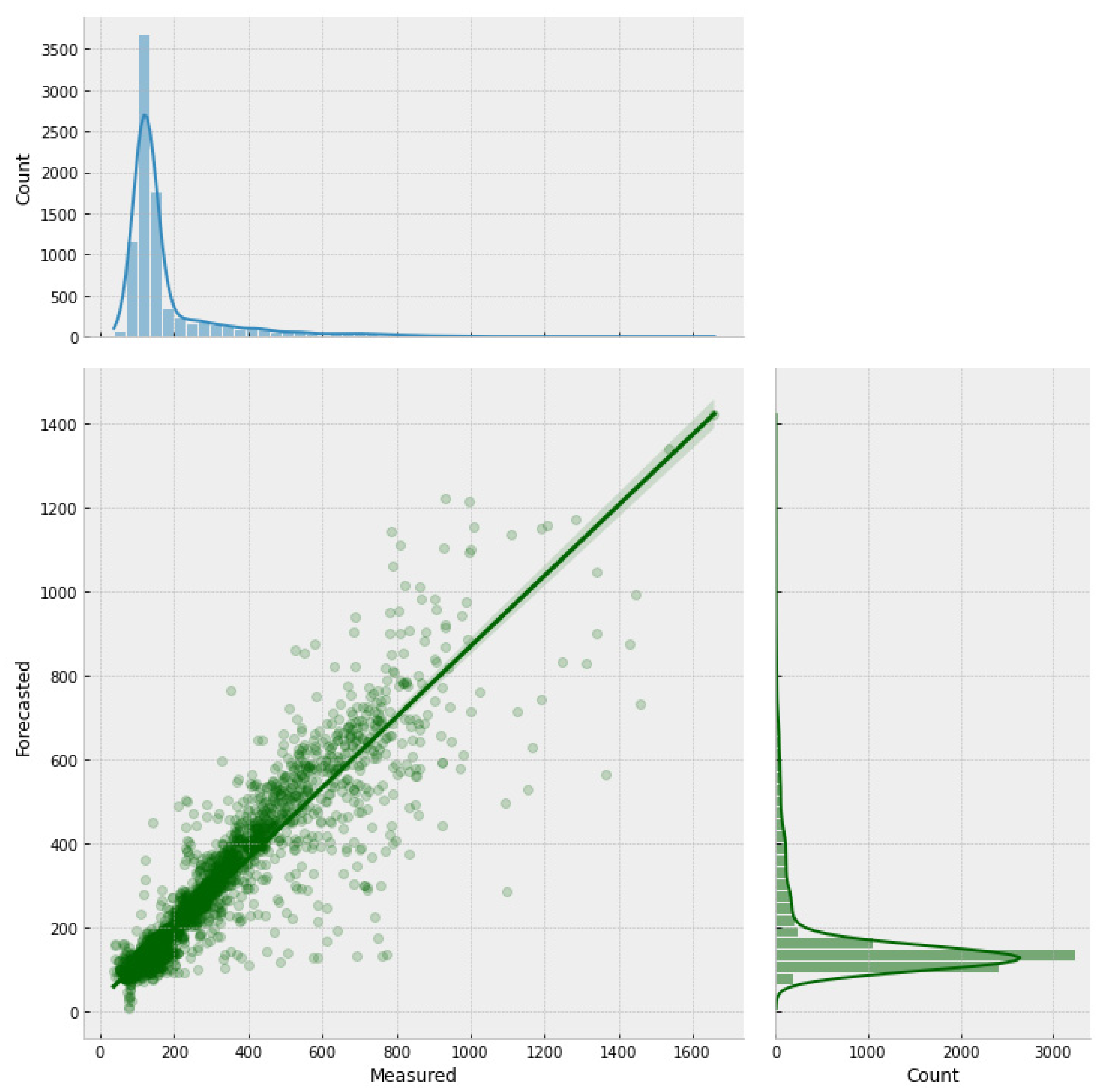
Figure 9.
Figure 9 presents the scatter plot for the transformer model and the marginal distributions for the actual and forecasted concentration values. The graph shows good agreement between the measured and actual chloride values, as it is possible to notice the clustered points around the regression line, which reached a coefficient of determination of 82%, and by both marginal distributions having similar distributions. The DNN-Transformer model reached error values for RMSE of 57.86 ppm and an MBE of -1.97 ppm, suggesting a slight underestimation of the forecasted values.
The results regarding the variable testing for the proposed GNN-SAGE model are presented in
Figure 10.
As shown in
Figure 10, the model’s forecasting ability improved with the inclusion of additional variables. For this case, the best solution was reached using chloride, water temperature, precipitation, flow, and solar radiation, resulting in an RMSE of 51.16 ppm.
The worse DNN-Transformer model’s performance can be explained because it could not identify and extract the spatiotemporal information underlying the dataset. This ultimately prevented the model generalization of the problem, returning inferior results than the GNN-SAGE. The proposed model, however, could extract and identify the spatiotemporal relationship between input and output variables, improving its generalization and, consequently, its forecasting due to its better understanding of the graph-structured data [
52], as verified in previous studies [
35,
36,
37].
Figure 11 shows the scatter plot for the GNN-SAGE model.
Figure 11 demonstrates that the forecasted and actual data are in good agreement once more. Compared to the deep learning transformer approach, the proposed SAGE model could cluster the points even closer to the regression line, having a more similar marginal distribution for its data and an improved coefficient of determination of 88%. The graph-based paradigm had RMSE and MBE errors of 51.16 ppm and -0.64 ppm, respectively. Compared to the RMSE errors of persistence and DNN-Transformer, the GNN-SAGE model increased forecasting by 25% and 12%, respectively. These findings show that the GNN-SAGE model can produce more accurate and precise results than the benchmarking models. The superior results for the graph model can be visualized in
Figure 12 and
Figure 13.
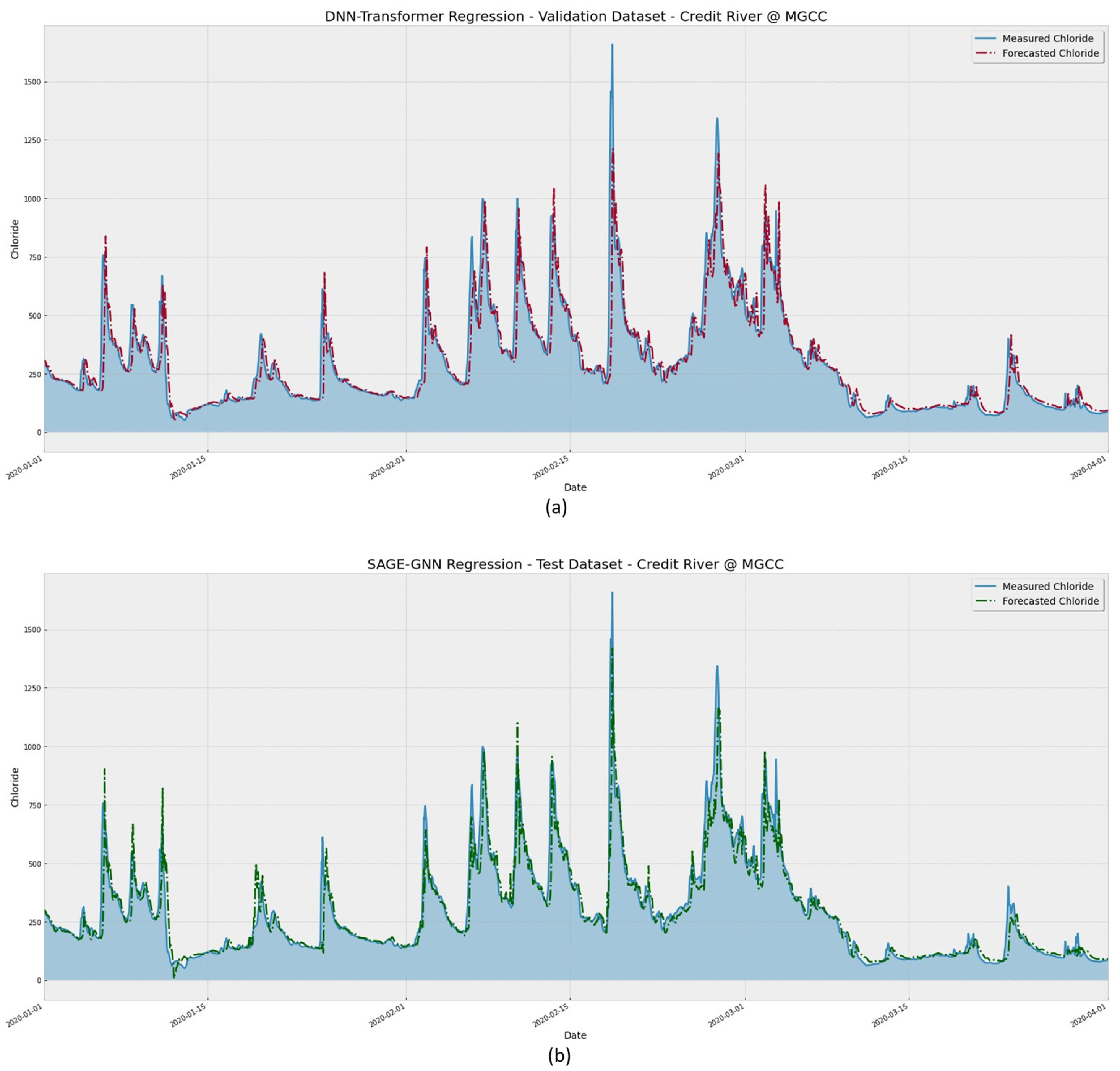
The continuous line in
Figure 12 represents the observed chloride values, while the dashed line represents the predicted values. It is possible to visualize that both DNN-Transformer and the proposed SAGE models can adequately identify the peaks during the assessed period. However, the GNN-SAGE provides more accurate results: analyzing the period between 15 February 2020 and 1 March 2020, GNN-SAGE closely followed the concentration peak, providing results near to the actual observed chloride concentration values, surpassing the transformer’s performance for the same period.
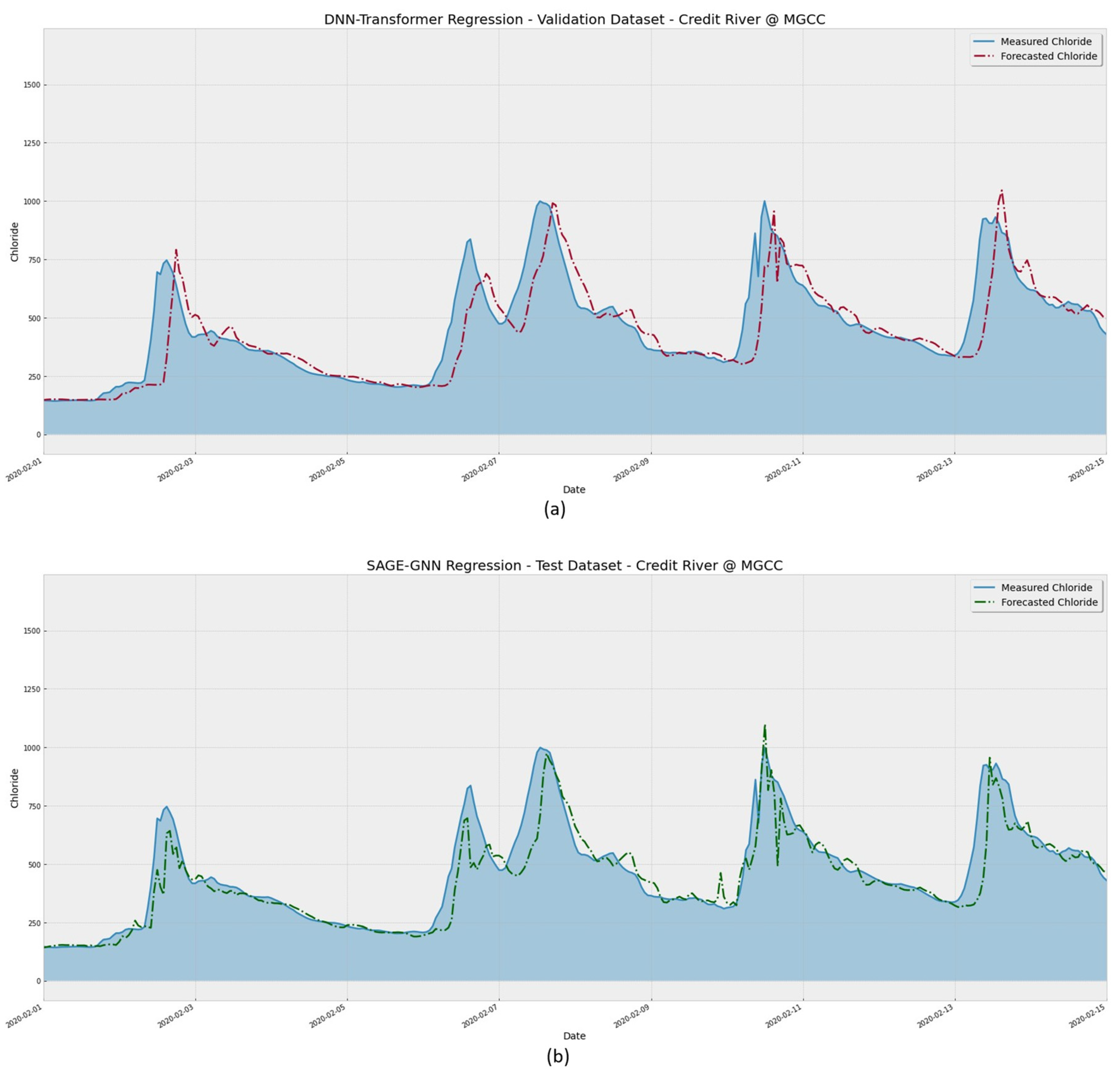
Figure 13 presents a closer look at the assessed period.
Figure 13 shows model performance forecasting the chloride concentration at a range narrower than in
Figure 12. It is easier to verify that the SAGE model was better at identifying the concentration peaks, as seen for the dates 11 and 13 of February 2020. The proposed model reduced the lag between actual and forecasted values. This lag is known in the literature and can be attributed to the need for more spatiotemporal data for extended time windows as the leading forecasting time increases [
53,
54,
55]. However, the proposed model reduced this gap when applied to different time-series forecasting problems, providing more accurate and reliable predictions in longer-horizon forecasts [
36,
37].
3.3. SHAP analysis results
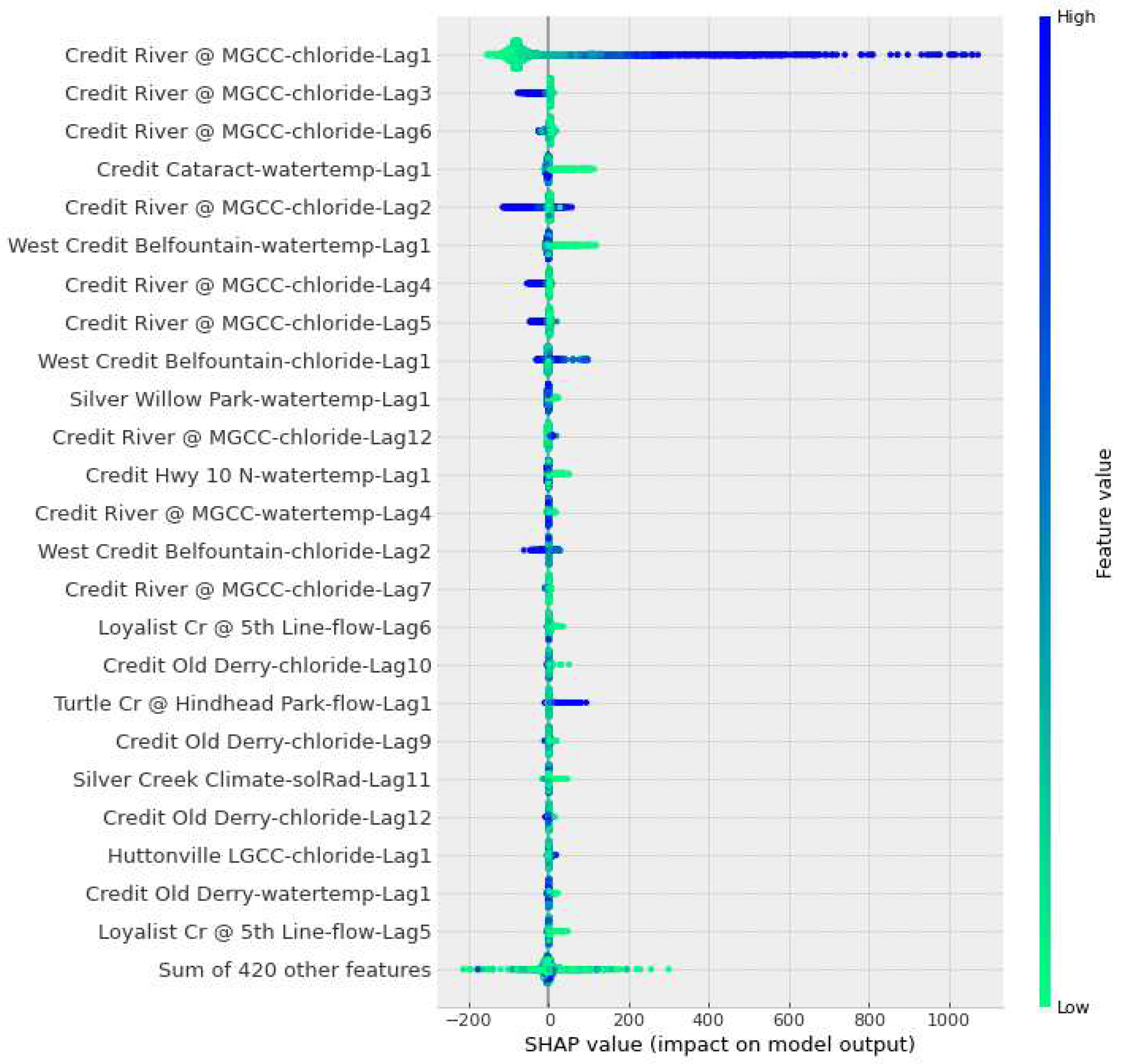
The results of the SHAP analysis are presented in
Figure 14. The results are organized in descending order, where the closer to the top, the more important the attribute is for the forecasted value. The rightmost bar in the figure represents the correlation between the variable and the output value. A higher correlation indicates a higher feature value. Furthermore, negative SHAP values indicate that the attribute had a negative influence over the forecasting, and vice versa.
Figure 14 also shows that the top three most influential variables for the model’s forecasting is the chloride concentration from the reference station. Moreover, the SHAP results show that neighbouring stations contribute to the model’s output. These stations provided important information regarding water temperature, which is the fourth most influential attribute, solar radiation, which may provide seasonality information, and flow. This states the importance of spatiotemporal information coming from the surroundings of the reference station in improving the model’s forecasting [
35,
36,
37,
56].
4. Discussion
The proposed GNN-SAGE model implemented in this research proved to be a reliable tool for the estimation of future chloride concentrations for the Credit River. Based on graph theory and deep learning, its structure can satisfactorily identify and extract complex spatiotemporal dependencies in the data from the neighbouring stations. Its superior performance for time series applications is well documented in the literature, where this approach returns state-of-the-art results for its forecasting [
36,
37]. The same behaviour was observed in the present work, where the GNN-SAGE paradigm outperformed both persistence and DNN-Transformer models, achieving RMSE and R
2 values of 52.16 ppb and 0.88, a substantial improvement over the other assessed models.
The GNN-SAGE approach also reduced the lag between forecasted and actual measured chloride concentrations, a common phenomenon in time series forecasting as larger forecasting windows require more data [
53,
54,
55]. The narrowing of this prediction gap is fundamental for providing more accurate and precise future chloride concentrations, allowing better decision-making and policy development by the stakeholders and environmental agencies.
The conducted SHAP analysis provided an insightful examination of the GNN-SAGE model. Its results showed that the forecasting of Cl- depends on local and neighbouring concentration ion levels. The SHAP analysis also depicts water temperature and solar radiation as other essential variables in chloride forecasting, showcasing the seasonal behaviour of chloride.
We compared the results of chloride forecasting found in the literature with those obtained using GNN-SAGE. However, it is important to note that directly comparing different predictive models can be challenging. Each study has its own methodology and unique characteristics, making it difficult to draw direct comparisons between the models. Also, since WQI forecasting using machine learning is much more explored than direct chloride prediction, not as many works are available for comparison using this approach. The literature found results are presented in
Table 1.
In work [
19], chloride concentration was estimated for a 1-hour forecasting horizon for the Grand River, Ontario, Canada. The authors proposed an ML model combining multiple-layer perceptron with stepwise cluster analysis for this task. Their approach is based on ensemble learning, which has been proven to boost time-series forecasting results [
20]. When comparing the GNN-SAGE model to their results, it is evident that the graph-based approach delivers better error values for a longer horizon, at 52.16 ppb, but with a slightly lower R
2 value of 0.88. This indicates that GNN-SAGE can provide more accurate results than traditional approaches such as SCA-MLP. Another ML learning model is proposed in work [
25], where the authors employed the regression tree paradigm to future chloride estimation in the Willamette River watershed in the USA. This work is an improvement over the author’s previous study [
57], where they first proposed chloride forecasting using multiple regression analysis. Comparing both studies, the tree-based model outperformed the former approach, increasing R
2 from 0.64 to 0.85. The proposed GNN-SAGE architecture surpasses the results found in both studies, providing a superior coefficient of determination of 0.88, meaning an improvement of 3.5% over the regression tree forecasting. In work [
24] a data-driven approach was used to evaluate future chloride concentrations in Deltona, Florida. Unlike the other mentioned studies, the authors proposed estimating Cl
- concentration for groundwater supply. The used model resulted in an RMSE of 28.00 mg/L and R
2 of 0.90. Similarly to the results found in [
19], GNN-SAGE once again can reduce the RMSE error for the chloride estimation, with a slightly reduced coefficient of determination. Again, this suggests the superior performance of the GNN-SAGE over this data-driven approach for chloride forecasting.
5. Conclusions
In this work, our developed GNN-SAGE model was employed to forecast chloride concentrations. Our GNN-SAGE model was trained with historical data from 2016 to 2020 collected from stations distributed along the Credit River course. The model was subsequently tested using different data inputs. The best configuration for the proposed graph model was reached using as input variables past data of chloride, water temperature, precipitation, flow, and solar radiation, together with a time lag of 12 hours.
To assess the proposed model, DNN-Transformer and the benchmarking persistence models were also evaluated for chloride forecasting. When compared to the other two models for a 6-hour forecasting horizon, the GNN-SAGE model outperformed both in terms of RMSE and R2 evaluation metrics, achieving values of 52.16 ppb and 0.88, respectively. The SHAP analysis was also developed in this study, generated better insight into the model’s forecasting. The SHAP results provided an understanding of how spatiotemporal data from neighbouring stations majorly affect the GNN-SAGE results. The SHAP analysis captured seasonality playing an important part in chloride estimation, since flow, water temperature, and solar radiation are also relevant attributes.
A comparison of the GNN-SAGE model with results from the literature revealed that it delivers state-of-the-art performance for estimating chloride levels, achieving superior RMSE values and comparable R2 values. This comparison deems the proposed GNN-SAGE as a reliable tool for chloride forecasting, providing accurate and precise estimations of Cl- up to 6 hours in advance.
The accurate predictions provided by the GNN-SAGE model show potential for real-time water quality management, aiding in developing regulatory guidelines for adaptive road salt management plans to better protect the vulnerable aquatic freshwater ecosystems in urban streams.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.V.G.T. and B.G.; methodology, P.A.C.R., J.V.G.T., and B.G.; software, P.A.C.R.; validation, P.A.C.R., J.V.G.T., and B.G.; formal analysis, P.A.C.R.; investigation, P.A.C.R., J.V.G.T., and B.G.; resources, J.V.G.T. and B.G.; data curation, J.V.G.T. and B.G.; writing—original draft preparation, V.O.S., and P.A.C.R.; writing—review and editing, V.O.S., P.A.C.R., J.V.G.T., and B.G.; visualization, V.O.S. and P.A.C.R.; supervision, J.V.G.T. and B.G.; project administration, J.V.G.T. and B.G.; funding acquisition, B.G. and J.V.G.T. All authors read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) Alliance, grant No. 401643, in association with Lakes Environmental Software Inc., and by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico—Brasil (CNPq), grant no. 303585/2022-6.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Beck, H.E.; Zimmermann, N.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Wood, E.F. Present and Future Köppen-Geiger Climate Classification Maps at 1-Km Resolution. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180214. [CrossRef]
- Arnott, S.E.; Celis-Salgado, M.P.; Valleau, R.E.; DeSellas, A.M.; Paterson, A.M.; Yan, N.D.; Smol, J.P.; Rusak, J.A. Road Salt Impacts Freshwater Zooplankton at Concentrations below Current Water Quality Guidelines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9398–9407. [CrossRef]
- Hintz, W.D.; Fay, L.; Relyea, R.A. Road Salts, Human Safety, and the Rising Salinity of Our Fresh Waters. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2022, 20, 22–30. [CrossRef]
- Oswald, C.J.; Giberson, G.; Nicholls, E.; Wellen, C.; Oni, S. Spatial Distribution and Extent of Urban Land Cover Control Watershed-Scale Chloride Retention. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 278–288. [CrossRef]
- Valleau, R.E.; Paterson, A.M.; Smol, J.P. Effects of Road-Salt Application on Cladocera Assemblages in Shallow Precambrian Shield Lakes in South-Central Ontario, Canada. Freshw. Sci. 2020, 39, 824–836. [CrossRef]
- Government of Canada, P.S. and P.C. Five-Year Review of Progress : Code of Practice for the Environmental Management of Road Salts : En14-54/2012E-PDF - Government of Canada Publications - Canada.Ca Available online: https://publications.gc.ca/site/eng/9.695258/publication.html (accessed on 24 July 2023).
-
Mineral Commodity Summaries; 2019;
- Prosser, R.S.; Rochfort, Q.; McInnis, R.; Exall, K.; Gillis, P.L. Assessing the Toxicity and Risk of Salt-Impacted Winter Road Runoff to the Early Life Stages of Freshwater Mussels in the Canadian Province of Ontario. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 589–597. [CrossRef]
- Szklarek, S.; Górecka, A.; Wojtal-Frankiewicz, A. The Effects of Road Salt on Freshwater Ecosystems and Solutions for Mitigating Chloride Pollution - A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150289. [CrossRef]
- Zítková, J.; Hegrová, J.; Anděl, P. Bioindication of Road Salting Impact on Norway Spruce (Picea Abies). Transp. Res. Part Transp. Environ. 2018, 59, 58–67. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Chu, C.; Qiao, N.; Wang, L.; Yang, F.; Sheng, Y.; Guan, B.; Niu, D.; Geng, J.; Chen, H. Performance Evaluation of Asphalt Mixture Exposed to Dynamic Water and Chlorine Salt Erosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 121–126. [CrossRef]
- Kane, D.D.; Manning, N.F.; Johnson, L.T. When It Snows It Pours: Increased Chloride Concentrations in the Cuyahoga River during the Last Half Century. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2022, 48, 1573–1586. [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.M.; Biastoch, R.G. Detecting Changes in the Benthic Invertebrate Community in Response to Increasing Chloride in Streams in Toronto, Canada. Freshw. Sci. 2016, 35, 353–363. [CrossRef]
- Giri, S. Water Quality Prospective in Twenty First Century: Status of Water Quality in Major River Basins, Contemporary Strategies and Impediments: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116332. [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, K.M.; Singh, K.; Binns, A.D.; Whiteley, H.R.; Gharabaghi, B. Effects of Urbanization on Stream Flow, Sediment, and Phosphorous Regime. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128283. [CrossRef]
- Dugan, H.A.; Skaff, N.K.; Doubek, J.P.; Bartlett, S.L.; Burke, S.M.; Krivak-Tetley, F.E.; Summers, J.C.; Hanson, P.C.; Weathers, K.C. Lakes at Risk of Chloride Contamination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6639–6650. [CrossRef]
- E, B.; Zhang, S.; Driscoll, C.T.; Wen, T. Human and Natural Impacts on the U.S. Freshwater Salinization and Alkalinization: A Machine Learning Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 889, 164138. [CrossRef]
- Costa Rocha, P.A.; Johnston, S.J.; Oliveira Santos, V.; Aliabadi, A.A.; Thé, J.V.G.; Gharabaghi, B. Deep Neural Network Modeling for CFD Simulations: Benchmarking the Fourier Neural Operator on the Lid-Driven Cavity Case. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3165. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Sekerinski, E.; Han, J.-C.; Zhou, Y. Real-Time Prediction of River Chloride Concentration Using Ensemble Learning. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118116. [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, T.C.; Rocha, P.A.C.; Carvalho, P.C.M.; Fernández-Ramírez, L.M. Ridge Regression Ensemble of Machine Learning Models Applied to Solar and Wind Forecasting in Brazil and Spain. Appl. Energy 2022, 314, 118936. [CrossRef]
- Marinho, F.P.; Rocha, P.A.C.; Neto, A.R.R.; Bezerra, F.D.V. Short-Term Solar Irradiance Forecasting Using CNN-1D, LSTM, and CNN-LSTM Deep Neural Networks: A Case Study With the Folsom (USA) Dataset. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2023, 145, 041002. [CrossRef]
- Nair, J.P.; Vijaya, M.S. River Water Quality Prediction and Index Classification Using Machine Learning. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2325, 012011. [CrossRef]
- Kulisz, M.; Kujawska, J. Application of Artificial Neural Network (ANN) for Water Quality Index (WQI) Prediction for the River Warta, Poland. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2130, 012028. [CrossRef]
- El-Jaat, M.; Hulley, M.; Tétreault, M. Evaluation of the Fast Orthogonal Search Method for Forecasting Chloride Levels in the Deltona Groundwater Supply (Florida, USA). Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1809–1820. [CrossRef]
- Poor, C.J.; Ullman, J.L. Using Regression Tree Analysis to Improve Predictions of Low-Flow Nitrate and Chloride in Willamette River Basin Watersheds. Environ. Manage. 2010, 46, 771–780. [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.; Mandrak, N.E. Historical Changes in the Fish Communities of the Credit River Watershed. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2019, 22, 316–328. [CrossRef]
- McGovarin, S.; Nishikawa, J.; Metcalfe, C.D. Vitellogenin Induction in Mucus from Brook Trout (Salvelinus Fontinalis). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 878–883. [CrossRef]
- Rosenfield, M.F.; Miedema Brown, L.; Anand, M. Increasing Cover of Natural Areas at Smaller Scales Can Improve the Provision of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services in Agroecological Mosaic Landscapes. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 303, 114248. [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Murison, L.; McBean, E. Characteristics of Nearshore Water Quality of Lake Ontario Coast under Credit Valley Conservation Jurisdiction, Ontario, Canada. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2022, 48, 326–335. [CrossRef]
- Socio-Demographic Profile of the Credit River Watershed Available online: https://cvc.ca/document/socio-demographic-profile-of-the-credit-river-watershed/ (accessed on 27 July 2023).
- Chu, C.; Minns, C.K.; Lester, N.P.; Mandrak, N.E. An Updated Assessment of Human Activities, the Environment, and Freshwater Fish Biodiversity in Canada. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 135–148. [CrossRef]
- Dawoud, I.; Abonazel, M.R. Robust Dawoud–Kibria Estimator for Handling Multicollinearity and Outliers in the Linear Regression Model. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2021, 91, 3678–3692. [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.Y.-L.; Leow, S.M.H.; Bea, K.T.; Cheng, W.K.; Phoong, S.W.; Hong, Z.-W.; Chen, Y.-L. Mitigating the Multicollinearity Problem and Its Machine Learning Approach: A Review. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1283. [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Kleissl, J.; Gueymard, C.A.; Pedro, H.T.C.; Coimbra, C.F.M. History and Trends in Solar Irradiance and PV Power Forecasting: A Preliminary Assessment and Review Using Text Mining. Sol. Energy 2018, 168, 60–101. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Santos, V.; Costa Rocha, P.A.; Scott, J.; Van Griensven Thé, J.; Gharabaghi, B. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Bidimensional Wind Speed Forecasting: Development and Thorough Assessment of LSTM and Ensemble Graph Neural Networks on the Dutch Database. Energy 2023, 278, 127852. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Santos, V.; Costa Rocha, P.A.; Scott, J.; Van Griensven Thé, J.; Gharabaghi, B. A New Graph-Based Deep Learning Model to Predict Flooding with Validation on a Case Study on the Humber River. Water 2023, 15, 1827. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Santos, V.; Costa Rocha, P.A.; Scott, J.; Van Griensven Thé, J.; Gharabaghi, B. Spatiotemporal Air Pollution Forecasting in Houston-TX: A Case Study for Ozone Using Deep Graph Neural Networks. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 308. [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need 2017.
- Dong, L.; Xu, S.; Xu, B. Speech-Transformer: A No-Recurrence Sequence-to-Sequence Model for Speech Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP); April 2018; pp. 5884–5888.
- Bi, J.; Zhu, Z.; Meng, Q. Transformer in Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Computer Science, Electronic Information Engineering and Intelligent Control Technology (CEI); September 2021; pp. 178–188.
- Parvaiz, A.; Khalid, M.A.; Zafar, R.; Ameer, H.; Ali, M.; Fraz, M.M. Vision Transformers in Medical Computer Vision—A Contemplative Retrospection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 122, 106126. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xiao, X.; Ding, Q.; Zhao, P.; Wei, Y.; Huang, J. Adversarial Sparse Transformer for Time Series Forecasting. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc., 2020; Vol. 33, pp. 17105–17115.
- Liew, S.S.; Khalil-Hani, M.; Bakhteri, R. Bounded Activation Functions for Enhanced Training Stability of Deep Neural Networks on Visual Pattern Recognition Problems. Neurocomputing 2016, 216, 718–734. [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, W.; Ying, Z.; Leskovec, J. Inductive Representation Learning on Large Graphs. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc., 2017; Vol. 30.
- Zhou, J.; Cui, G.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Sun, M. Graph Neural Networks: A Review of Methods and Applications. AI Open 2020, 1, 57–81. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Santos, V.; Costa Rocha, P.A.; Scott, J.; Van Griensven Thé, J.; Gharabaghi, B. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Bidimensional Wind Speed Forecasting: Development and Thorough Assessment of LSTM and Ensemble Graph Neural Networks on the Dutch Database. Energy 2023, 278, 127852. [CrossRef]
- Labonne, M. Hands-On Graph Neural Networks Using Python.
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc., 2017; Vol. 30.
- Akbar, S.; Ali, F.; Hayat, M.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, S.; Gul, S. Prediction of Antiviral Peptides Using Transform Evolutionary & SHAP Analysis Based Descriptors by Incorporation with Ensemble Learning Strategy. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2022, 230, 104682. [CrossRef]
- Abdulalim Alabdullah, A.; Iqbal, M.; Zahid, M.; Khan, K.; Nasir Amin, M.; Jalal, F.E. Prediction of Rapid Chloride Penetration Resistance of Metakaolin Based High Strength Concrete Using Light GBM and XGBoost Models by Incorporating SHAP Analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128296. [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Lam, J.C.K.; Li, V.O.K. What Dictates Income in New York City? SHAP Analysis of Income Estimation Based on Socio-Economic and Spatial Information Gaussian Processes (SSIG). Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 60. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tong, H.; Xu, J.; Maciejewski, R. Graph Convolutional Networks: A Comprehensive Review. Comput. Soc. Netw. 2019, 6, 11. [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, Z. Interpretable Spatio-Temporal Attention LSTM Model for Flood Forecasting. Neurocomputing 2020, 403, 348–359. [CrossRef]
- Dazzi, S.; Vacondio, R.; Mignosa, P. Flood Stage Forecasting Using Machine-Learning Methods: A Case Study on the Parma River (Italy). Water 2021, 13, 1612. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Long, M. Autoformer: Decomposition Transformers with Auto-Correlation for Long-Term Series Forecasting. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc., 2021; Vol. 34, pp. 22419–22430.
- Baïle, R.; Muzy, J.-F. Leveraging Data from Nearby Stations to Improve Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasts. Energy 2023, 263, 125644. [CrossRef]
- Poor, C.J.; McDonnell, J.J.; Bolte, J. Testing the Hydrological Landscape Unit Classification System and Other Terrain Analysis Measures for Predicting Low-Flow Nitrate and Chloride in Watersheds. Environ. Manage. 2008, 42, 877–893. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).