Submitted:
02 August 2023
Posted:
04 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Radiomics
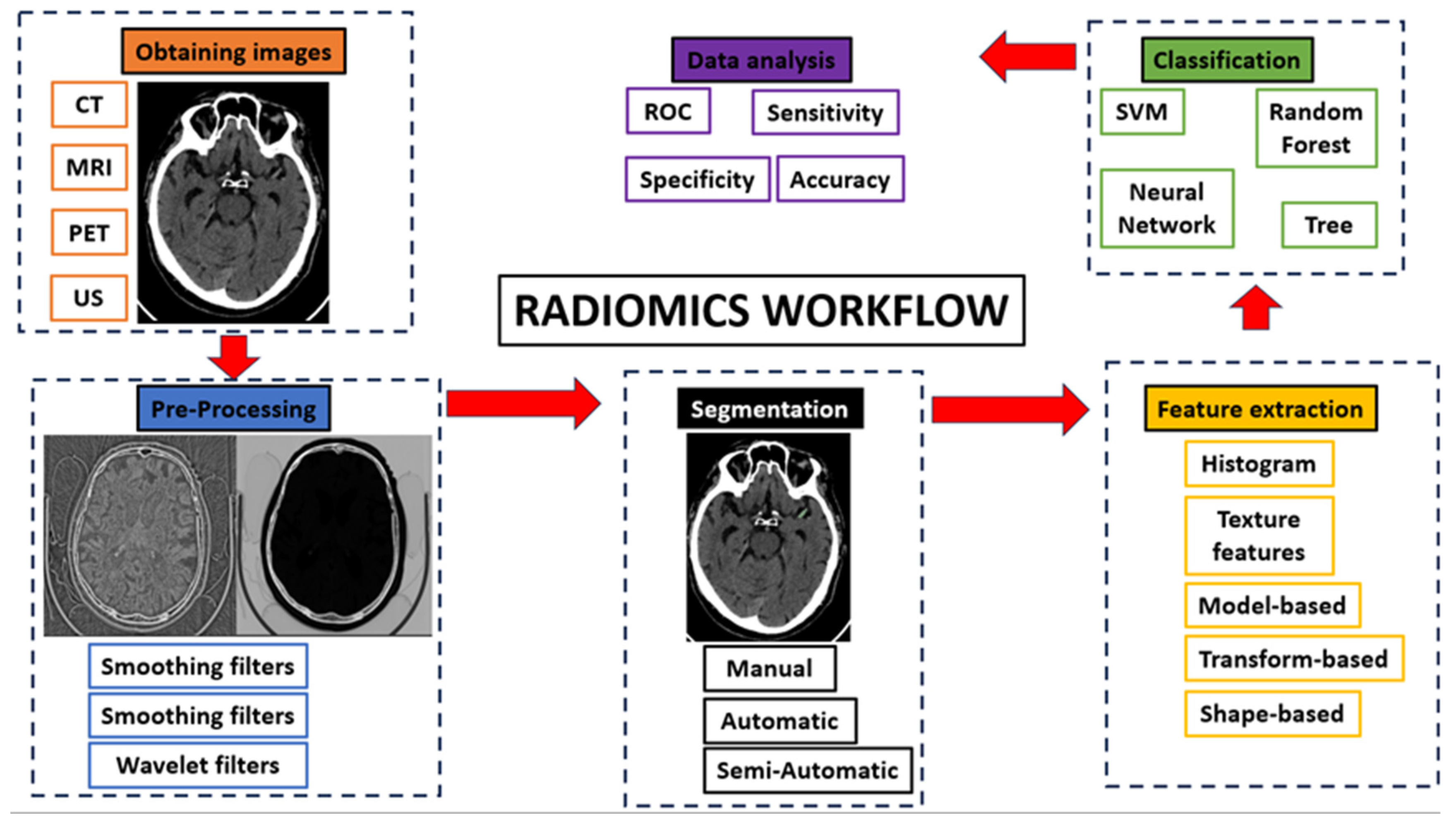
2.1. Radiomics Workflow
- Obtaining images: Radiomics can be applied to all types of medical imaging. There are published articles on the performance of radiomics in ultrasound, Non-Contrast Enhancement-CT (NCECT), Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA), MRI and PET. In this step, there can be a great deal of heterogeneity when using images acquired in different hospitals or even on different machines within the same hospital. Therefore, the acquired images are subjected to a standardization process in which we try to correct this source of heterogeneity [8].
- Pre-processing: The quality of the images can be improved by using the pre-processing tools. In this step, some image filters are used to reduce noise. The aim is to increase the predictive power of the classifiers [14].
- Segmentation: In this step, the region of interest is selected in the radiological image. The segmentation of this region can be done in three ways: manual, semi-automatic and automatic. Manual segmentation is the gold standard and the most commonly used method in the studies reviewed in this article. The main advantage of this model is the intervention of an expert radiologist in its performance. The main disadvantage of this model is the time required to manually segment the entire region of interest [15]. Automatic segmentation is based on automatic detection of the region of interest without human intervention. Finally, semi-automatic segmentation is performed under the supervision of an expert radiologist who can edit an initial automatic pre-segmentation. The advantage of this method is the speed of the segmentation and the fact that the human component remains [16]. With today's increasingly sophisticated segmentation software, semi-automatic 3D segmentation of an area of interest can be performed quickly and comfortably for the radiologist.
- Feature extraction and classification: There is a wealth of numerical data that can be extracted from medical images, known as radiomic features. There are several classes of radiomic features: Histogram features (grey level mean, maximum, minimum, variance and percentiles), texture features (absolute gradient, grey level co-occurrence matrix -GLCM-, grey level run length matrix -GLRLM-, grey level size zone matrix -GLSZM-, grey level distance zone matrix -GLDZM-, Neighborhood Grey Level Difference Matrix -NGTDM-, Neighborhood Grey Level Dependence Matrix -NGLDM-), model-based features, transform-based features (Fourier, Garbor, Wavelet) and shape-based features (geometric properties of ROIs) [14]. These numerical data are classified by automatic classifiers. These classifiers are capable of recognizing different groups of patterns depending on the objective we set for them. In this way, the classifiers learn the data patterns with a training cohort. Then, with a test cohort, these classifiers are able to classify the data we provide into the pattern that most closely resembles it. In addition to numerical data, automatic classifiers can be used to input clinical data to search for a combined model.
- Data analysis
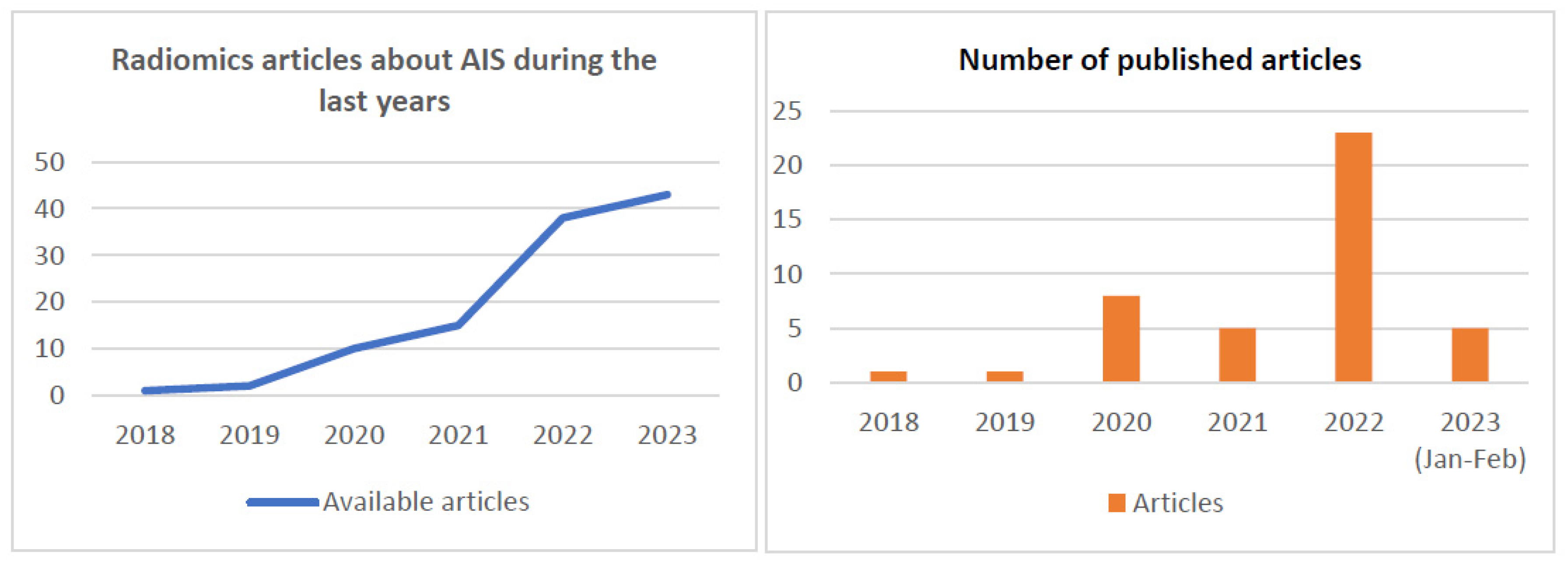
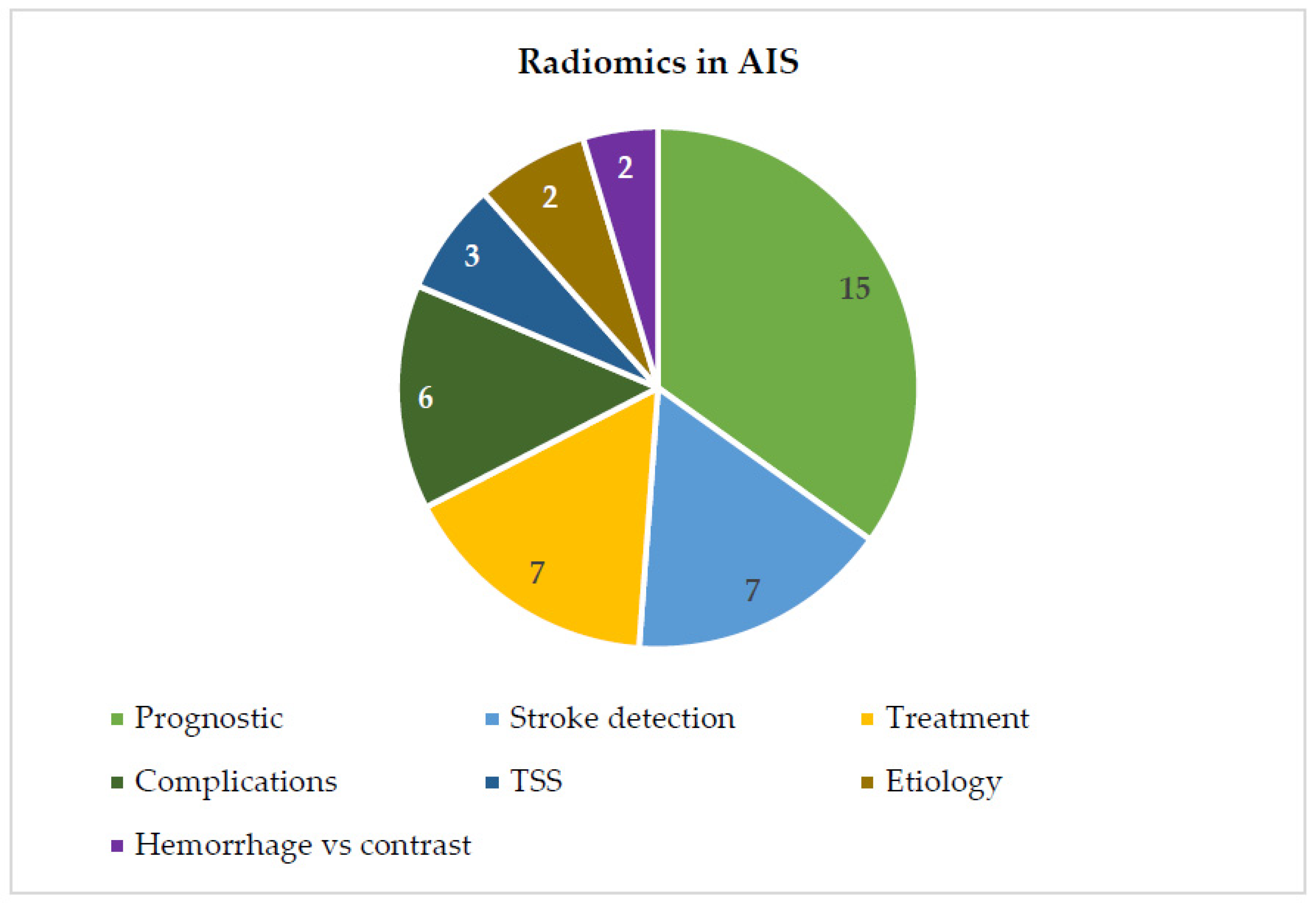
2.2. Radiomics in AIS
2.3. Prognostic Prediction
2.4. Detection of Ischemic Stroke
2.5. Treatment Predictions
2.6. Prediction of Complications after AIS
2.7. Etiology Prediction
2.8. Time Since Stroke Prediction
2.9. Differentiation Hemorrhage from Iodinated Contrast Extravasation after Thrombectomy
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Phipps MS, Cronin CA. Management of acute ischemic stroke. BMJ. 2020 Feb 13;368:l6983. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. (dec. 9, 2020). Global Health Estimates. Available from: https://www.who.
- Vasu Saini, Luis Guada, Dileep R. Yavagal. Global Epidemiology of Stroke and Access to Acute Ischemic Stroke Interventions. Neurology. 2021 Nov 16;97(20 Supplement 2):S6. [CrossRef]
- Broderick JP, Palesch YY, Demchuk AM, Yeatts SD, Khatri P, Hill MD, Jauch EC, Jovin TG, Yan B, Silver FL, von Kummer R, Molina CA, Demaerschalk BM, Budzik R, Clark WM, Zaidat OO, Malisch TW, Goyal M, Schonewille WJ, Mazighi M, Engelter ST, Anderson C, Spilker J, Carrozzella J, Ryckborst KJ, Janis LS, Martin RH, Foster LD, Tomsick TA; Interventional Management of Stroke (IMS) III Investigators. Endovascular therapy after intravenous t-PA versus t-PA alone for stroke. N Engl J Med. 2013 Mar 7;368(10):893-903. Epub 2013 Feb 7. Erratum in: N Engl J Med. 2013 Mar 28;368(13):1265. PMID: 23390923; PMCID: PMC3651875. [CrossRef]
- Kidwell CS, Jahan R, Gornbein J, Alger JR, Nenov V, Ajani Z, Feng L, Meyer BC, Olson S, Schwamm LH, Yoo AJ, Marshall RS, Meyers PM, Yavagal DR, Wintermark M, Guzy J, Starkman S, Saver JL; MR RESCUE Investigators. A trial of imaging selection and endovascular treatment for ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2013 Mar 7;368(10):914-23. Epub 2013 Feb 8. PMID: 23394476; PMCID: PMC3690785. [CrossRef]
- Fargen, Kyle M. MD, MPH; Singla, Amit MD; Mocco, J MD, MS. The New England Journal of Medicine Stroke Trials: What Do They Really Mean?. Neurosurgery 62():p 137-140, August 2015. |. [CrossRef]
- Wintermark M, Bogousslavsky J. Imaging of acute ischemic brain injury: the return of computed tomography. Curr Opin Neurol. 2003 Feb;16(1):59-63. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, Carvalho S, van Stiphout RG, Granton P, Zegers CM, Gillies R, Boellard R, Dekker A, Aerts HJ. Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur J Cancer. 2012 Mar;48(4):441-6. Epub 2012 Jan 16. PMID: 22257792; PMCID: PMC4533986. [CrossRef]
- Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology [Internet]. [cited 2023 Feb 28]. Available from: https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/radiol.2015151169 [PubMed].
- Porto-Álvarez, J.; Barnes, G.T.; Villanueva, A.; García-Figueiras, R; Baleato-González, S.; Huelga Zapico, E; Souto-Bayarri, M. Digital Medical X-ray Imaging, CAD in Lung Cancer and Radiomics in Colorectal Cancer: Past, Present and Future. Appl. Sici. 2023, 13, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G. , Manjila, S., Sakla, N. et al. Radiomics and radiogenomics in gliomas: a contemporary update. Br J Cancer 125, 641–657 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos AK, Gaitanis A, Gkiozos I, Athanasiadis EI, Chatziioannou SN, Syrigos KN, Thanos D, Chatziioannou AN, Papanikolaou N. Radiomics/Radiogenomics in Lung Cancer: Basic Principles and Initial Clinical Results. Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 25;14(7):1657. PMID: 35406429; PMCID: PMC8997041. [CrossRef]
- Porto-Álvarez, J.; Cernadas, E.; Aldaz Martínez, R.; Fernández-Delgado, M.; Huelga Zapico, E.; González-Castro, V.; Baleato-González, S.; García-Figueiras, R.; Antúnez-López, J.R.; Souto-Bayarri, M. CT-Based Radiomics to Predict KRAS Mutation in CRC Patients Using a Machine Learning Algorithm: A Retrospective Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demircioğlu, A. The effect of preprocessing filters on predictive performance in radiomics. Eur Radiol Exp. 2022 Dec;6(1):40. Epub 2022 Sep 1. PMID: 36045274; PMCID: PMC9433552. [CrossRef]
- van Timmeren JE, Cester D, Tanadini-Lang S, Alkadhi H, Baessler B. Radiomics in medical imaging-"how-to" guide and critical reflection. Insights Imaging. 2020 Aug 12;11(1):91. PMID: 32785796; PMCID: PMC7423816. [CrossRef]
- Parmar C, Rios Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, Jermoumi M, Carvalho S, Mak RH, Mitra S, Shankar BU, Kikinis R, Haibe-Kains B, Lambin P, Aerts HJ. Robust Radiomics feature quantification using semiautomatic volumetric segmentation. PLoS One. 2014 Jul 15;9(7):e102107. PMID: 25025374; PMCID: PMC4098900. [CrossRef]
- Mayerhoefer ME, Materka A, Langs G, Häggström I, Szczypiński P, Gibbs P, Cook G. Introduction to Radiomics. J Nucl Med. 2020 Apr;61(4):488-495. Epub 2020 Feb 14. PMID: 32060219; PMCID: PMC9374044. [CrossRef]
- Avery EW, Behland J, Mak A, Haider SP, Zeevi T, Sanelli PC, Filippi CG, Malhotra A, Matouk CC, Griessenauer CJ, Zand R, Hendrix P, Abedi V, Falcone GJ, Petersen N, Sansing LH, Sheth KN, Payabvash S. CT angiographic radiomics signature for risk stratification in anterior large vessel occlusion stroke. Neuroimage Clin. 2022;34:103034. Epub 2022 May 7. PMID: 35550243; PMCID: PMC9108990. 7 May. [CrossRef]
- Cui H, Wang X, Bian Y, Song S, Feng DD. Ischemic stroke clinical outcome prediction based on image signature selection from multimodality data. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018 Jul;2018:722-725. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang H, Sun Y, Ge Y, Wu PY, Lin J, Zhao J, Song B. A Clinical-Radiomics Nomogram for Functional Outcome Predictions in Ischemic Stroke. Neurol Ther. 2021 Dec;10(2):819-832. Epup 2021 Jun 25. PMID: 34170502; PMCID: PMC8571444. [CrossRef]
- Gerbasi, A.; Konduri, P.; Tolhuisen, M.; Cavalcante, F.; Rinkel, L.; Kappelhof, M.; Wolff, L.; Coutinho, J.M.; Emmer, B.J.; Costalat, V.; et al. Prognostic Value of Combined Radiomic Features from Follow-Up DWI and T2-FLAIR in Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo Y, Yang Y, Cao F, Liu Y, Li W, Yang C, Feng M, Luo Y, Cheng L, Li Q, Zeng X, Miao X, Li L, Qiu W, Kang Y. Radiomics features of DSC-PWI in time dimension may provide a new chance to identify ischemic stroke. Front Neurol. 2022 Nov 4;13:889090. PMID: 36408497; PMCID: PMC9672479. [CrossRef]
- Guo Y, Yang Y, Wang M, Luo Y, Guo J, Cao F, Lu J, Zeng X, Miao X, Zaman A, Kang Y. The Combination of Whole-Brain Features and Local-Lesion Features in DSC-PWI May Improve Ischemic Stroke Outcome Prediction. Life (Basel). 2022 Nov 11;12(11):1847. PMID: 36430982; PMCID: PMC9694195. [CrossRef]
- Jiang L, Miao Z, Chen H, Geng W, Yong W, Chen YC, Zhang H, Duan S, Yin X, Zhang Z. Radiomics Analysis of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Long-Term Unfavorable Outcomes Risk for Acute Stroke. Stroke. 2023 Feb;54(2):488-498. Epub 2022 Dec 6. PMID: 36472198. [CrossRef]
- Li L, Li M, Chen Z, Lu F, Zhao M, Zhang H, Tong D. Prognostic value of radiomics-based hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign for patients with acute ischemic stroke after thrombectomy strategy. Front Neurol. 2023 Jan 13;13:1037204. PMID: 36712442; PMCID: PMC9880054. [CrossRef]
- Ramos LA, van Os H, Hilbert A, Olabarriaga SD, van der Lugt A, Roos YBWEM, van Zwam WH, van Walderveen MAA, Ernst M, Zwinderman AH, Strijkers GJ, Majoie CBLM, Wermer MJH, Marquering HA. Combination of Radiological and Clinical Baseline Data for Outcome Prediction of Patients With an Acute Ischemic Stroke. Front Neurol. 2022 Apr 1;13:809343. PMID: 35432171; PMCID: PMC9010547. [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Liu Y, Hong Z, Wang Y, Lu X. Combining machine learning with radiomics features in predicting outcomes after mechanical thrombectomy in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022 Oct;225:107093. Epub 2022 Aug 28. PMID: 36055039. [CrossRef]
- Quan G, Ban R, Ren JL, Liu Y, Wang W, Dai S, Yuan T. FLAIR and ADC Image-Based Radiomics Features as Predictive Biomarkers of Unfavorable Outcome in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke. Front Neurosci. 2021 Sep 16;15:730879. PMID: 34602971; PMCID: PMC8483716. [CrossRef]
- Tang TY, Jiao Y, Cui Y, Zhao DL, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Meng XP, Yin XD, Yang YJ, Teng GJ, Ju SH. Penumbra-based radiomics signature as prognostic biomarkers for thrombolysis of acute ischemic stroke patients: a multicenter cohort study. J Neurol. 2020 May;267(5):1454-1463. Epub 2020 Feb 1. PMID: 32008072. [CrossRef]
- Tolhuisen ML, Hoving JW, Koopman MS, Kappelhof M, van Voorst H, Bruggeman AE, Demchuck AM, Dippel DWJ, Emmer BJ, Bracard S, Guillemin F, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Mitchell PJ, van Zwam WH, Hill MD, Roos YBWEM, Jovin TG, Berkhemer OA, Campbell BCV, Saver J, White P, Muir KW, Goyal M, Marquering HA, Majoie CB, Caan MWA; MR CLEAN-NO IV and HERMES investigators. Outcome Prediction Based on Automatically Extracted Infarct Core Image Features in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Jul 23;12(8):1786. PMID: 35892499; PMCID: PMC9331690. [CrossRef]
- Yu H, Wang Z, Sun Y, Bo W, Duan K, Song C, Hu Y, Zhou J, Mu Z, Wu N. Prognosis of ischemic stroke predicted by machine learning based on multi-modal MRI radiomics. Front Psychiatry. 2023 Jan 9;13:1105496. PMID: 36699499; PMCID: PMC9868394. [CrossRef]
- Zhou Y, Wu D, Yan S, Xie Y, Zhang S, Lv W, Qin Y, Liu Y, Liu C, Lu J, Li J, Zhu H, Liu WV, Liu H, Zhang G, Zhu W. Feasibility of a Clinical-Radiomics Model to Predict the Outcomes of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Korean J Radiol. 2022 Aug,23(8):811-820. [CrossRef]
- Guan Y, Wang P, Wang Q, Li P, Zeng J, Qin P, Meng Y. Separability of Acute Cerebral Infarction Lesions in CT Based Radiomics: Toward Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Diagnosis. Biomed Res Int. 2020 Nov 15;2020:8864756. PMID: 33274231; PMCID: PMC7683107. [CrossRef]
- Guo Y, Yang Y, Cao F, Wang M, Luo Y, Guo J, Liu Y, Zeng X, Miu X, Zaman A, Lu J, Kang Y. A Focus on the Role of DSC-PWI Dynamic Radiomics Features in Diagnosis and Outcome Prediction of Ischemic Stroke. J Clin Med. 2022 Sep 13;11(18):5364. PMID: 36143010; PMCID: PMC9504165. [CrossRef]
- Zhang H, Chen H, Zhang C, Cao A, Lu Q, Wu H, Zhang J, Geng D. A radiomics feature-based machine learning models to detect brainstem infarction (RMEBI) may enable early diagnosis in non-contrast enhancement CT. Eur Radiol. 2023 Feb;33(2):1004-1014. Epub 2022 Sep 28. PMID: 36169689. [CrossRef]
- Zhang R, Zhu L, Zhu Z, Ge Y, Zhang Z, Wang T. Apparent diffusion coefficient map based radiomics model in identifying the ischemic penumbra in acute ischemic stroke. Ann Palliat Med. 2020 Sep;9(5):2684-2692. Epub 2020 Jul 24. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su JH, Meng LW, Dong D, Zhuo WY, Wang JM, Liu LB, Qin Y, Tian Y, Tian J, Li ZH. Noninvasive model for predicting future ischemic strokes in patients with silent lacunar infarction using radiomics. BMC Med Imaging. 2020 Jul 8;20(1):77. PMID: 32641095; PMCID: PMC7346609. [CrossRef]
- Tang M, Gao J, Ma N, Yan X, Zhang X, Hu J, Zhuo Z, Shi X, Li L, Lei X, Zhang X. Radiomics Nomogram for Predicting Stroke Recurrence in Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis. Front Neurosci. 2022 Apr 12;16:851353. PMID: 35495035; PMCID: PMC9039339. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Sun Y, Zhu J, Zhuang Y, Song B. Diffusion-weighted imaging-based radiomics for predicting 1-year ischemic stroke recurrence. Front Neurol. 2022 Oct 28;13:1012896. PMID: 36388230; PMCID: PMC9649925. [CrossRef]
- Hofmeister J, Bernava G, Rosi A, Vargas MI, Carrera E, Montet X, Burgermeister S, Poletti PA, Platon A, Lovblad KO, Machi P. Clot-Based Radiomics Predict a Mechanical Thrombectomy Strategy for Successful Recanalization in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke. 2020 Aug;51(8):2488-2494. Epub 2020 Jul 20. PMID: 32684141; PMCID: PMC7382538. [CrossRef]
- Sarioglu O, Sarioglu FC, Capar AE, Sokmez DF, Mete BD, Belet U. Clot-based radiomics features predict first pass effect in acute ischemic stroke. Interv Neuroradiol. 2022 Apr;28(2):160-168. Epub 2021 . PMID: 34000866; PMCID: PMC9131494. 18 May. [CrossRef]
- Patel TR, Santo BA, Baig AA, Waqas M, Monterio A, Levy EI, Siddiqui AH, Tutino VM. Histologically interpretable clot radiomic features predict treatment outcomes of mechanical thrombectomy for ischemic stroke. Neuroradiology. 2023 Apr;65(4):737-749. Epub 2023 Jan 4. PMID: 36600077. [CrossRef]
- Zhang H, Polson J, Nael K, Salamon N, Yoo B, Speier W, Arnold C. A Machine Learning Approach to Predict Acute Ischemic Stroke Trhombectomy Reperfusion using Discriminative MR Image Features. IEEE EMBS Int Conf Biomed Health Inform. 2021 Jul; 2021:10.1109/bhi50953.2021.9508597. Epub 2021 Aug 10. PMID: 358132219; PMCID: PMC9261292. [CrossRef]
- Xiong X, Wang J, Ke J, Hong R, Jiang S, Ye J, Hu C. Radiomics-based intracranial thrombus features on preoperative noncontrast CT predicts successful recanalization of mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Feb 1;13(2):682-694. Epub 2023 Jan 2. PMID: 36819277; PMCID: PMC9929391. [CrossRef]
- van Voorst H, Bruggeman AAE, Yang W, Andriessen J, Welberg E, Dutra BG, Konduri PR, Arrarte Terreros N, Hoving JW, Tolhuisen ML, Kappelhof M, Brouwer J, Boodt N, van Kranendonk KR, Koopman MS, Hund HM, Krietemeijer M, van Zwam WH, van Beusekom HMM, van der Lugt A, Emmer BJ, Marquering HA, Roos YBWEM, Caan MWA, Majoie CBLM; MR CLEAN Registry investigators. Thrombus radiomics in patients with anterior circulation acute ischemic stroke undergoing endovascular treatment. J Neurointerv Surg. 2022 Jul 26:neurintsurg-2022-019085. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35882552. [CrossRef]
- Qiu W, Kuang H, Nair J, Assis Z, Najm M, McDougall C, McDougall B, Chung K, Wilson AT, Goyal M, Hill MD, Demchuk AM, Menon BK. Radiomics-Based Intracranial Thrombus Features on CT and CTA Predict Recanalization with Intravenous Alteplase in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019 Jan;40(1):39-44. Epub 2018 Dec 20. PMID: 30573458; PMCID: PMC7048606. [CrossRef]
- Fu B, Qi S, Tao L, Xu H, Kang Y, Yao Y, Yang B, Duan Y, Chen H. Image Patch-Based Net Water Uptake and Radiomics Models Predict Malignant Cerebral Edema After Ischemic Stroke. Front Neurol. 2020 Dec 23;11:609747. PMID: 33424759; PMCID: PMC7786250. [CrossRef]
- Jiang L, Zhang C, Wang S, Ai Z, Shen T, Zhang H, Duan S, Yin X, Chen YC. MRI Radiomics Features From Infarction and Cerebrospinal Fluid for Prediction of Cerebral Edema After Acute Ischemic Stroke. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Mar 3;14:782036. PMID: 35309889; PMCID: PMC8929352. [CrossRef]
- Wen X, Li Y, He X, Xu Y, Shu Z, Hu X, Chen J, Jiang H, Gong X. Prediction of Malignant Acute Middle Cerebral Artery Infarction via Computed Tomography Radiomics. Front Neurosci. 2020 Jul 7;14:708. PMID: 32733197; PMCID: PMC7358521. [CrossRef]
- Meng Y, Wang H, Wu C, Liu X, Qu L, Shi Y. Prediction Model of Hemorrhage Transformation in Patient with Acute Ischemic Stroke Based on Multiparametric MRI Radiomics and Machine Learning. Brain Sci. 2022 Jun 29;12(7):858. PMID: 35884664; PMCID: PMC9313447. [CrossRef]
- Xie G, Li T, Ren Y, Wang D, Tang W, Li J, Li K. Radiomics-based infarct features on CT predict hemorrhagic transformation in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Front Neurosci. 2022 Sep 21;16:1002717. PMID: 36213752; PMCID: PMC9533555. [CrossRef]
- Liu J, Tao W, Wang Z, Chen X, Wu B, Liu M. Radiomics-based prediction of hemorrhage expansion among patients with thrombolysis/thrombectomy related-hemorrhagic transformation using machine learning. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2021 Nov 24;14:17562864211060029. PMID: 35173809; PMCID: PMC8842178. [CrossRef]
- Chen Y, He Y, Jiang Z, Xie Y, Nie S. Ischemic stroke subtyping method combining convolutional neural network and radiomics. J Xray Sci Technol. 2023;31(2):223-235. P: PMID: 36591693; PMCID, 3659. [CrossRef]
- Jiang J, Wei J, Zhu Y, Wei L, Wei X, Tian H, Zhang L, Wang T, Cheng Y, Zhao Q, Sun Z, Du H, Huang Y, Liu H, Li Y. Clot-based radiomics model for cardioembolic stroke prediction with CT imaging before recanalization: a multicenter study. Eur Radiol. 2023 Feb;33(2):970-980. Epub 2022 Sep 6. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng Y, Wan S, Wu W, Chen F, Jiang J, Cai D, Bao Z, Li Y, Zhang L. Computed Tomography Angiography-Based Thrombus Radiomics for Predicting the Time Since Stroke Onset. Acad Radiol. 2023 Jan 23:S1076-6332(22)00690-0. Epub ahead of print. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao X, Mao L, Lv S, Ren Z, Li W, Ren K. CT radiomics features as a diagnostic tool for classifying basal ganglia infarction onset time. J Neurol Sci. 2020 May 15;412:116730. Epub 2020 Feb 10. 15 May. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen X, Shu Z, Li Y, Hu X, Gong X. Developing a model for estimating infarction onset time based on computed tomography radiomics in patients with acute middle cerebral artery occlusion. BMC Med Imaging. 2021 Oct 11;21(1):147. PMID: 34635087; PMCID: PMC8507216. [CrossRef]
- Zhang YQ, Liu AF, Man FY, Zhang YY, Li C, Liu YE, Zhou J, Zhang YD, Lv J, Jiang WJ. MRI radiomic features-based machine learning approach to classify ischemic stroke onset time. J Neurol. 2022 Jan;269(1):350-360. Epub 2021 Jul 4. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen X, Li Y, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Yang J, Pang P, Wang Y, Cheng J, Chen H, Guo Y. CT-based radiomics for differentiating intracranial contrast extravasation from intraparenchymal haemorrhage after mechanical thrombectomy. Eur Radiol. 2022 Jul;32(7):4771-4779. Epub 2022 Feb 3. PMID: 35113213; PMCID: PMC9213289. [CrossRef]
- Ma Y, Wang J, Zhang H, Li H, Wang F, Lv P, Ye J. A CT-based radiomics nomogram for classification of intraparenchymal hyperdense areas in patients with acute ischemic stroke following mechanical thrombectomy treatment. Front Neurosci. 2023 Jan 10;16:1061745. PMID: 36703995; PMCID: PMC9871784. [CrossRef]
- Yip SS, Aerts HJ. Applications and limitations of radiomics. Phys Med Biol. 2016 Jul 7;61(13):R150-66. Epub 2016 Jun 8. PMID: 27269645; PMCID: PMC4927328. [CrossRef]
- Cardenas CE, Yang J, Anderson BM, Court LE, Brock KB. Advances in Auto-Segmentation. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2019 Jul;29(3):185-197. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambin, P. , Leijenaar, R., Deist, T. et al. Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14, 749–762 (2017). [CrossRef]
| Author | Year | Type | N | Target | Territory | RF | Technique | Results | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avery et al. [18] | 2022 | R | 829 | Prognostic prediction | ALVO | 1116 | CTA | AUC between 0.81-0.82 | RF could help in patients with limited clinical information |
| Cui H et al. [19] | 2018 | R | 70 | Prognostic prediction | NA | 251 | MRI | AUC of 0.821-0983 | The classification model improves when RF were included. |
| Wang et al. [20] | 2021 | R | 598 | Prognostic prediction | Infarct | 402 | MRI | AUC of 0.80 | Combined nomogram based on MRI has a good performance in prognosis prediction |
| Gerbasi A et al. [21] | 2022 | R | 164 | Prognostic prediction | ALVO | 107 | MRI | AUC of 0.85 | Combined model can help in the long-term functional outcome prediction |
| Guo Y et al. [22] | 2022 | R | 56 | Prognostic prediction | NA | 65800 | MRI | AUC of 0.908 and 0.884 Acc of 0.821 and 0.864 | RF can help to predict functional outcomes in ischemic stroke patients |
| Guo Y et al. [23] | 2022 | R | 78 | Prognostic prediction | WB | 1674 | MRI | AUC of 0.971 | RF can predict functional recover y after three months |
| Jiang L et al. [24] | 2022 | R | 1716 | Prognostic prediction | NA | NA | MRI | AUC of 0.862 | A combined model can predict outcomes of AIS patients |
| Li et al. [25] | 2023 | R | 102 | Prognostic prediction | MCA | 1389 | MRI | AUC of 0.88 and 0.79 | Combined model can predict poor prognosis in AIS patients |
| Ramos et al. [26] | 2022 | R | 3279 | Prognostic prediction | WB | 1260 | CTA | AUC of 0.61 | Combined model obtained better results than clinical model |
| Li et al. [27] | 2022 | R | 260 | Prognostic prediction | Infarct | 1936 | MRI | AUC of 0.945 and 0.920 | MRI-based radiomics has high predictive efficiency for prognostic prediction of AIS patients after thrombectomy |
| Quan et al. [28] | 2021 | R | 190 | Prognostic prediction | Hyperintensities | 753 | MRI | AUC of 0.926-0.864 | MRI-based radiomics can predict unfavorable outcome (mRS>=2) |
| Tang et al. [29] | 2020 | R | 168 | Prognostic prediction | Penumbra | 456 | CT/MRI | AUC of 0.886 | Radiomics nomogram adds more value to the current clinical decision-making process |
| Tolhuisen et al. [30] | 2022 | R | 206 | Prognostic prediction | Infarct | 100 | MRI | AUC of 0.88-0.81 | MRI-based radiomics can provide important information to functional outcome prediction in AIS patients |
| Yu et al. [31] | 2022 | R | 148 | Prognostic prediction | Infarct | 4744 | MRI | AUC of 0.902 Acc of 0.831 Sens of 0.739 Spec of 0.902 |
Radiomics model based on MRI imaging can predict clinical outcomes in AIS patients |
| Zhou et al. [32] | 2022 | R | 522 | Prognostic prediction | Ischemic | 1310 | MRI | AUC of 0.868-0.890 | Combined model outperformed individual clinical or radiomics models in predicting AIS outcomes |
| Guan Y et al. [33] | 2020 | R | 56 | Identification of IS | NA | 1301 | CT/MNR | Best Acc of 0.7748 | There are RF correlated with acute cerebral infarction |
| Guo Y et al. [34] | 2022 | R | 88 | Identification of IS | WB | 1674 | MRI | AUC of 0.925 (IS), 0.853 (NIHSS), 0.828 (outcome prediction) | RF is a potential clinical tool which could help in the diagnosis and outcome prediction before treatment. |
| Zhang et al. [35] | 2023 | R | 355 | Identification of IS | Brainstem | 1781 | CT | AUC of 0.99 and 0.91 | CT-based radiomics can detect early brainstem infarction |
| Zhang R et al. [36] | 2020 | R | 241 | Identification of ischemic penumbra | DWI hypodensities | 896 | MRI | AUC of 0.92 and 0.90 Sens of 0.93 and 0.88 Spec of 0.75 and 0.74 Acc of 0.82 and 0.80 |
MRI-based radiomics can identify ischemic penumbra in AIS patients |
| Su et al. [37] | 2020 | R | 148 | Stroke prediction | Lacunar lesions | 1209 | CT | C-Index of 0.7864-0.7140 | CT-based radiomics can provide information for the prediction of future ischemic strokes in patients with silent lacunar infarction |
| Tang et al. [38] | 2022 | R | 156 | Stroke recurrence | Plaque | 402 | MRI | AUC of 0.899-0.803 | MRI-based radiomics provide important information for predict stroke recurrence in SICAS patients |
| Wang et al. [39] | 2022 | R | 1003 | Stroke recurrence | Infarct | 513 | MRI | AUC of 0.847 | MRI-based radiomics could help to predict 1-year AIS recurrence |
| Hofmeister et al. [40] | 2020 | R | 156 | Predict MTB strategy | Clot | 9 | CT | AUC of 0.88 | Clot-based RF can help with the MTB strategy |
| Sarioglu et al. [41] | 2022 | R | 52 | Predict fist pass effect | Clot | 12 | CT | Acc of 0.83 | Clot-based RF can estimate successfully recanalization |
| Patel et al. [42] | 2023 | R | 293 | Predict first pass effect | Clot | 227 | CT/CTA | AUC of 0.832-0.787 Acc of 0.760-0.787 |
Clot-based radiomics are potential candidate markers for first pass effect prediction |
| Zhang et al. [43] | 2021 | R | 141 | TICI scale prediction | Infarct | 321 | MRI | AUC of 0.7442 | MRI-based radiomics can provide important information about the patient response to thrombectomy |
| Xiong et al. [44] | 2023 | R | 256 | TICI scale prediction | Clot | 1130 | CT | AUC of 0.860-0.849 | CT-based radiomics can predict the successfully recanalization in AIS patients after stent retrieve therapy |
| Van Voorst et al. [45] | 2022 | R | 699 | Recanalization | Clot | - | CT | - | Clot-based radiomics are independently associated with reperfusion, but the results of the clinical and radiomics model was similar |
| Qui et al. [46] | 2019 | R | 67 | Recanalization after ateplase | Clot | 326 | CT/CTA | AUC of 0.85 | Clot-based radiomics are more predictive of recanalization with ateplase than other classical clot features |
| Fu B et al. [47] | 2020 | R | 116 | Predict malignant cerebral edema | MCA | 13 | NECT | AUC of 0.96 | Radiomics could help to predict MCE using NECT |
| Jiang et al. [48] | 2022 | R | 389 | Predict malignant cerebral edema | Stroke and CSF | 1316 | MRI | AUC 0.83-0.86 Acc 0.85-0.81 |
MRI radiomic features can provide information for predicting cerebral edema in AIS patients |
| Wen et al. [49] | 2020 | R | 126 | Predict mMCAi | MCA territory | 396 | CT/CTA | AUC of 0.917-0.913 | CT-based radiomics can be a tool to predicting the risk of mMCAi |
| Meng et al. [50] | 2022 | R | 71 | Predict hemorrhage transformation | Infarct | 5400 | MRI | AUC of 0.911 Acc of 0.894 |
Combined model based on MRI radiomic features can predict the hemorrhage transformation in AIS patients |
| Xie et al. [51] | 2022 | R | 118 | Predict hemorrhage transformation | Infarct | 851 | CT | AUC of 0.845-0.750 | CT-based radiomics could help to prediction of hemorrhage transformation in AIS patients |
| Liu et al. [52] | 2021 | R | 104 | Predict hemorrhage expansion | Hemorrhage | 1691 | CT | AUC of 0.91-0.87 Sens of 0.83-0.60 Spec 0.89-0.85 |
CT-based radiomics can predict hemorrhage expansion |
| Chen Y et al. [53] | 2022 | R | 82 | Etiology prediction | NA | 116 | CTA | AUC of 0.9018 Acc of 0.8929 |
Radiomics could effectively predict the subtype of ischemic stroke |
| Jiang J et al. [54] | 2023 | R | 403 | Etiology prediction | Clot | NA | CT | AUC of 0.838 | Clot-based RF can identify the CE strokes. |
| Cheng Y et al. [55] | 2022 | R | 221 | Time since stroke | Clot | 944 | CTA | AUC of 0.803 AUC of 0.813-0.803 |
Radiomics can estimate the TSS in patients with AIS. |
| Yao et al. [56] | 2020 | R | 316 | Time since stroke | Infarct | 295 | CT | AUC of 0.982-0.974 Sens of 0.929-0.951 Spec of 0.959-0.961 |
Radiomics is useful in the determination of TSS in basal ganglia infarction |
| Wen et al. [57] | 2021 | R | 123 | Time since stroke | ASPECTS | 396 | CT/CTA | AUC of 0.808-0.833 | CT-based radiomics can discriminate the TSS in patients with MCAO in the M1 segment. |
| Zhang et al. [58] | 2022 | R | 84 | Time since stroke | - | 4312 | MRI | AUC of 0.754 Acc of 0.788 |
MRI based radiomics could aid in decision-making for thrombolysis in patients with unknown stroke onset |
| Chen X et al. [59] | 2022 | R | 101 | Differentiate IPH vs contrast | NA | 1316 | NECT | AUC of 0.848 and 0.826; Acc of 0.776, S of 0.767, Spec of 0.789 | RF can differentiate IPH from contrast extravasation after MT. |
| Ma Y et al. [60] | 2022 | R | 100 | Hemorrhage vs Iodinated contrast extravasation | Hyperdense area | 1316 | CT | AUC of 0.972 and 0.926 in training and validation cohorts | Combined nomogram based on CT-radiomic features can differentiate between hemorrhage and iodine contrast extravasation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





