Submitted:
01 August 2023
Posted:
07 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Objective
2.2. Data sources
2.3. Keywords used in articles selection process
2.4. Article selection, inclusion, and exclusion criteria
2.5. Limitations
2.6. Study design
2.7. Review period
3. Results
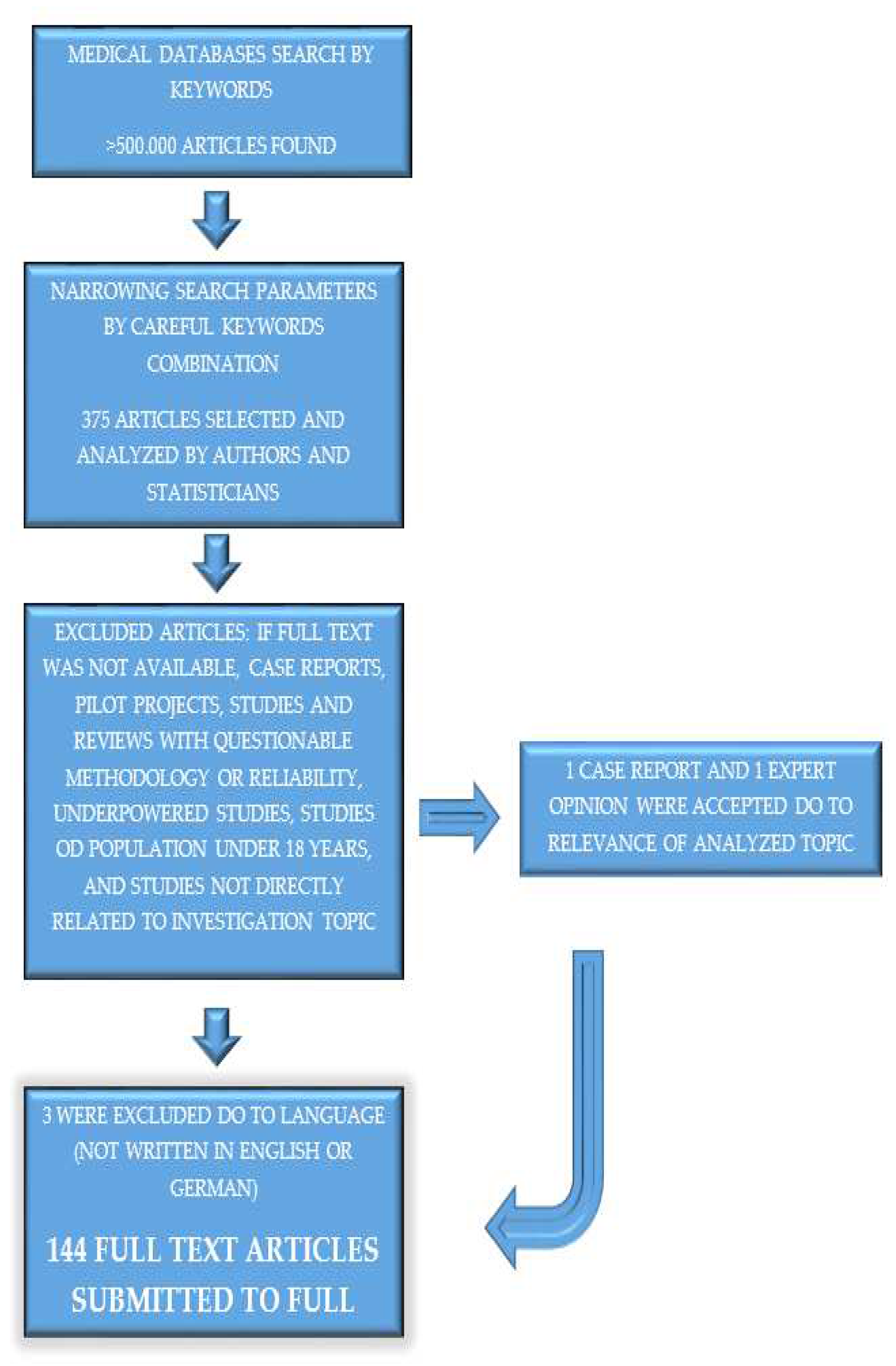
3.1. Article selection process
3.2. Statistics
4. Discussion
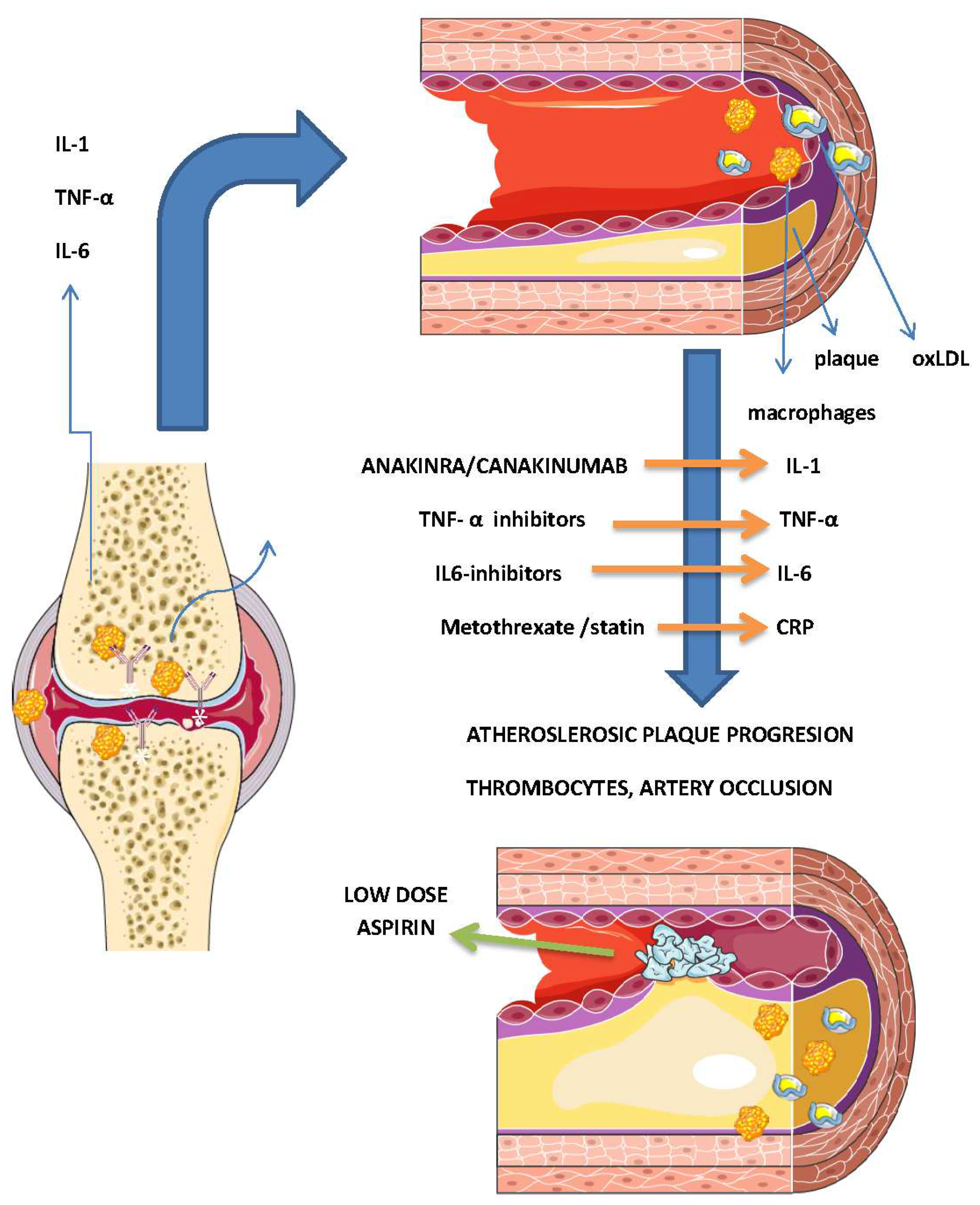
4.1. Chronic inflammation
4.2. Influence of medicaments
4.2.1. NSAIDs
4.2.2. Glucocorticoids
4.2.3. Classical DMARDs
4.2.4. Biologic agents
4.2.5. Small molecule inhibitors of Janus kinase
4.2.6. Statins
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitchell, D.M.; Spitz, P.W.; Young, D.Y.; Bloch, D.A.; McShane, D.J.; Fries, J.F. Survival, prognosis, and causes of death in rheumatoid-arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 1986, 29, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.L.; Coulton, B.L.; Symmons, D.P.M. Long-term outcome of threating rheumatoid arthritis – results after 20 years. Lancet, 1987, 1, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnett, F.C.; Edworthy, S.M.; Bloch, D.A.; McShane, D.J.; Fries, J.F.; Cooper, N.S.; Healey, L.A.; Kaplan, S.R.; Liang, M.H.; Luthra, H.S.; Medsger, T.A.; Mitchell, D.M.; Neustadt, D.H.; Pinals, R.S.; Schaller, J.G.; Sharp, J.T.; Wilder, R.L. The American-rheumatism-association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 1988, 31, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O.; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; Combe, B.; Costenbader, K.H.; Dougados, M.; Emery, P.; Ferraccioli, G.; Hazes, J.M.W.; Hobbs, K.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Kavanaugh, A.; Kay, J.; Kvien, T.K.; Laing, T.; Mease, P.; Menard, H.A.; Moreland, L.W.; Naden, R.L.; Pincus, T.; Smolen, J.S.; Stanislawska-Biernat, E.; Symmons, D.; Tak, P.P.; Upchurch, K.S.; Vencovsky, J.; Wolfe, F.; Hawker, G. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2010, 69, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.M.; Weinblatt, M.E. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet, 2001, 358, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symmons, D.P. M. Epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis: determinants of onset, persistence and outcome. Best Practice & Research in Clinical Rheumatology. 2002, 16, 707–722. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, R.; Hirano, F.; Kihara, M.; Yokoyama, W.; Yamazaki, H.; Harada, S.; Nanki, T.; Koike, R.; Miyasaka, N.; Harigai, M. High prevalence of cardiovascular comorbidities in patients with rheumatoid arthritis from a population-based cross-sectional study of a Japanese health insurance database. Modern Rheumatology. 2016, 26, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koivuniemi, R.; Paimela, L.; Leirisalo-Repo, M. Causes of death in patients with rheumatoid arthritis from 1971 to 1991 with special reference to autopsy. Clinical Rheumatology. 2009, 28, 1443–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maradit-Kremers, H.; Nicola, P.J.; Crowson, C.S.; Ballman, K.V.; Gabriel, S.E. Cardiovascular Death in Rheumatoid Arthritis A Population-Based Study. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2005, 52, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokka, T.; Abelson, B.; Pincus, T. Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis: 2008 update. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. 2009, 26, S35–S61. [Google Scholar]
- Meune, C.; Touze, E.; Trinquart, L.; Allanore, Y. High risk of clinical cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis: Levels of associations of myocardial infarction and stroke through a systematic review and meta-analysis. Archives of Cardiovascular Diseases. 2010, 103, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meune, C.; Touze, E.; Trinquart, L.; Allanore, Y. Trends in cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis over 50 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Rheumatology. 2009, 48, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avina-Zubieta, J.A.; Choi, H.K.; Sadatsafavi, M.; Etminan, M.; Esdaile, J.M.; Lacaille, D. Risk of Cardiovascular Mortality in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Arthritis and Rheumatism-Arthritis Care and Research. 2008, 59, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, P.W. A.; Anderson, R.; Ker, J.A.; Ally, M.T.M. Rheumatoid arthritis and risk of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular Journal of Africa. 2018, 29, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, S.; Lyall, D.M.; Mackay, D.F.; Porter, D.; McInnes, I.B.; Sattar, N.; Pell, J.P. Characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis and its association with major comorbid conditions: cross-sectional study of 502 649 UK Biobank participants. Rmd Open. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doornum, S.; McColl, G.; Wicks, I.P. Accelerated atherosclerosis - An extraarticular feature of rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2002, 46, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, L.; Visseren, J.; and others. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: Developed by the Task Force for cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice with representatives of the European Society of Cardiology and 12 medical societies With the special contribution of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology (EAPC). European Heart Journal 2021, 42, 3227–3337. [Google Scholar]
- Panoulas, V.F.; Metsios, G.S.; Pace, A.V.; et al. Hypertension in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008, 4, 1286–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innala, L.; Sjöberg, C.; Möller, B.; Ljung, L.; Smedby, T.; Södergren, A.; et al. Co-morbidity in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis - inflammation matters. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erba, G.; Grosso, G.; Valena, C.A.; Riva, M.; Allevi, E.; Betelli, M.; et al. Cardiovascular risk factor profile in Italian cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Results of a three years follow-up. J Hypertens. 2015, 33 Suppl 1, e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherghe, A.M.; Dougados, M.; Combe, B.; Landewé, R.; Mihai, C.; Berenbaum, F.; et al. Cardiovascular and selected comorbidities in early arthritis and early spondyloarthritis, a comparative study: results from the ESPOIR and DESIR cohorts. RMD Open. 2015, 1, e000128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, J.F.; Gourraud, P.A.; Cantagrel, A.; Davignon, J.L.; Constantin, A. Traditional cardiovascular risk factors in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Joint Bone Spine. 2011, 78, 179–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heliovaara, M.; Aho, K.; Aromaa, A.; Knekt, P.; Reunanen, A. SMOKING AND RISK OF RHEUMATOID-ARTHRITIS. Journal of Rheumatology. 1993, 20, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castellanos-De La Hoz, J.; Amaya-Amaya, J.; Molano-Gonzalez, N.; Gutierrez-Infante, F.; Anaya, J.M.; Rojas-Villarraga, A. The influence of cigarette smoking on disease activity and joint erosions in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2013, 72, 387–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klareskog, L.; Stolt, P.; Lundberg, K.; Kallberg, H.; Bengtsson, C.; Grunewald, J.; i sur. A new model for an etiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2006, 54, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsing, P.M. J.; van Gestel, A.M.; Swinkels, H.L.; Kiemeney, L.; van Riel, P. The relationship between disease activity, joint destruction, and functional capacity over the course of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2001, 44, 2009–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepoli, M.F.; Hoes, A.W.; Agewall, S.; Albus, C.; Brotons, C.; Catapano, A.L.; i sur. Task Force 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts). European Journal of Preventive Cardiology. 2016, 23, NP1–NP96. [Google Scholar]
- Baghdadi, L.R.; Woodman, R.J.; Shanahan, E.M.; Mangoni, A.A. The impact of traditional cardiovascular risk factors on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015, 10, e0117952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Li, H.; Li, X. Diabetes mellitus risk factors in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. 2015, 33, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Guin, A.; Sinhamahapatra, P.; Misra, S.; Mazumder, S.R.C.; Chatterjee, S.; Ghosh, A. Incidence and effect of insulin resistance on progression of atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis patients of long disease duration. Biomedical Journal, 2019, 42, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougados, M.; Soubrier, M.; Antunez, A.; Balsa, A.; Buch, M.H.; Casado, G.; et al. Prevalence of comorbidities in rheumatoid arthritis and evaluation of their monitoring: results of an international, cross-sectional study (COMORA). Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2020, 73, 62–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou, A.; Metsios, G.S.; Koutedakis, Y.; Nevill, A.M.; Douglas, K.M.; A. i sur. Redefining overweight and obesity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2007, 66, 1316–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, L.L.; Lanna, C.C.D.; Rocha, M.P.; et al. Recognition and control of hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology International 2018, 38, 1437–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beinsberger, J.; Heemskerk, J.W.M.; Cosemans, J. Chronic arthritis and cardiovascular disease: Altered blood parameters give rise to a prothrombotic propensity. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2014, 44, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, B.; Madej, M.; Luczak, A.; Malecki, R.; Wiland, P. Disease Activity, Oxidized-LDL Fraction and Anti-Oxidized LDL Antibodies Influence Cardiovascular Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine. 2016, 25, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, J.T.; Wasko, M.C.M.; Chung, C.P.; Szklo, M.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Kao, A.; i sur. Exploring the Lipid Paradox Theory in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Associations of Low Circulating Low-Density Lipoprotein Concentration With Subclinical Coronary Atherosclerosis. Arthritis & Rheumatology. 2011, 71, 1426–1436. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, C.M.; Young, S.P. Lipid and Metabolic Changes in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Current Rheumatology Reports. 2015, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, P.K.; Silver, J.; Winchester, R.J. The shared epitope hypothesis – an approach to understanding the molecular-genetics of susceptibility of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 1987, 30, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B. and Schett, G. MECHANISMS OF DISEASE: The Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. New England Journal of Medicine. 2011, 365, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Lau, J.; Wang, S.H.; Taneja, V.; Matteson, E.L.; Vassallo, R. Mechanisms of lung disease development in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Reviews Rheumatology. 2019, 15, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londei, M.; Savill, C.M.; Verhoef, A.; Brennan, F.; Leech, Z.A.; Duance, V.; Maini, R.N.; Feldmann, M. Persistence of collagen type-II-specific T-cell clones in the synovial-membrane of a patient with rheumatoid-arthritis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1987, 86, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glant, T.T.; Radacs, M.; Nagyeri, G.; Olasz, K.; Laszlo, A.; Boldizsar, F.; Hegyi, A.; Finnegan, A.; Mikecz, K. Proteoglycan-Induced Arthritis and Recombinant Human Proteoglycan Aggrecan G1 Domain-Induced Arthritis in BALB/c Mice Resembling Two Subtypes of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2011, 63, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijden, G.F. M.; Rijnders, A.W.M.; Bos, E.; deRoo, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; C. J., vanStaveren; Miltenburg, A.M.M.; Meijerink, J.H.; Elewaut, D.; F., deKeyser; Veys, E.; Boots, A.M.H.; C. Human cartilage glycoprotein-39 as a candidate autoantigen in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2011, 40, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; Yamamoto, K. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Reviews Disease Primers. 2018, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmester, G.R.; Feist, E.; Doerner, T. Emerging cell and cytokine targets in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Reviews Rheumatology. 2014, 10, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, F.; Bonaventura, A.; Liberale, L.; Paolino, S.; Torre, F.; Dallegri, F.; Montecucco, F.; Cutolo, M. Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Promoters and Opponents. Clinical Reviews in Allergy and Immunology. 2020, 58, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mewar, D.; Coote, A.; Moore, D.J.; Marinou, I.; Keyworth, J.; Dickson, M.C.; Montgomery, D.S.; Binks, M.H.; Wilson, A.G. Independent associations of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factor with radiographic severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research and Therapy. 2006, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolove, J.; Bromberg, R.; Deane, K.D.; Lahey, L.J.; Derber, L.A.; Chandra, P.E.; Edison, J.D.; Gilliland, W.R.; Tibshirani, R.J.; Norris, J.M.; Holers, V.M.; Robinson, W.H. Autoantibody Epitope Spreading in the Pre-Clinical Phase Predicts Progression to Rheumatoid Arthritis. Plos One. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Longo, F.J.; Oliver-Minarro, D.; de la Torre, I.; de Rabago, E.G.D.; Sanchez-Ramon, S.; Rodriguez-Mahou, M.; Paravisini, A.; Monteagudo, I.; Gonzalez, C.M.; Garcia-Castro, M.; Casas, M.D.; Carreno, L. Association Between Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibodies and Ischemic Heart Disease in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism-Arthritis Care & Research. 2009, 61, 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Sokolove, J.; Brennan, M.J.; Sharpe, O.; Lahey, L.J.; Kao, A.H.; Krishnan, E.; Edmundowicz, D.; Lepus, C.M.; Wasko, M.C.; Robinson, W.H. Citrullination Within the Atherosclerotic Plaque: A Potential Target for the Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2013, 65, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldino-Pardilla, L.; Zartoshti, A.; Ozbek, A.B.; Giles, J.T.; Weinberg, R.; Kinkhabwala, M.; Bokhari, S.; Bathon, J.M. Arterial Inflammation Detected With F-18-Fluorodeoxyglucose-Positron Emission Tomography in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatology. 2018, 70, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMizio, D.J.; Geraldino-Pardilla, L.B. Autoimmunity and Inflammation Link to Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology and Therapy. 2020, 7, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.P.; Kremers, H.M.; Crowson, C.S.; Snyder, M.R.; Therneau, T.M.; Roger, V.L.; Gabriel, S.E. Autoantibodies and the Risk of Cardiovascular Events. Journal of Rheumatology. 2009, 36, 2462–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, J.H.; van Nies, J.A.B.; Chipping, J.; Marshall, T.; Mil, A.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Verstappen, S.M.M. Rheumatoid factor and anti-citrullinated protein antibody positivity, but not level, are associated with increased mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from two large independent cohorts. Arthritis Research and Therapy. 2014, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, S.S.; Crowson, C.S.; Maradit-Kremers, H.; Themeau, T.M.; Roger, V.L.; Matteson, E.L.; Gabriel, S.E. Longterm Outcomes and Treatment After Myocardial Infarction in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology. 2013, 40, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackey, R.H.; Kuller, L.H.; Deane, K.D.; Walitt, B.T.; Chang, Y.F.; Holers, V.M.; Robinson, W.H.; Tracy, R.P.; Hlatky, M.A.; Eaton, C.B.; Liu, S.M.; Freiberg, M.S.; Talabi, M.B.; Schelbert, E.B.; Moreland, L.W. Rheumatoid Arthritis, Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Positivity, and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in the Women’s Health Initiative. Arthritis and Rheumatology. 2015, 67, 2311–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innala, L.; Moller, B.; Ljung, L.; Magnusson, S.; Smedby, T.; Sodergren, A.; Ohman, M.L.; Rantapaa-Dahlqvist, S.; Wallberg-Jonsson, S. Cardiovascular events in early RA are a result of inflammatory burden and traditional risk factors: a five year prospective study. Arthritis Research and Therapy. 2010, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik, A.; Ostanek, L.; Brzosko, I.; Brzosko, M.; Masiuk, M.; Machalinski, B.; Gawronska-Szklarz, B. The expansion of CD4+CD28- T cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003, 5(4), R210–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winchester, R.; Giles, J.T.; Nativ, S.; Downer, K.; Zhang, H.Z.; Bag-Ozbek, A.; Zartoshti, A.; Bokhari, S.; Bathon, J.M. Association of Elevations of Specific T cell and Monocyte Subpopulations in Rheumatoid Arthritis With Subclinical Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis. Arthritis and Rheumatology. 2016, 68, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Goek, O.; Zhang, X.Y.; Kopecky, S.L.; Frye, R.L.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. De novo expression of killer immunoglobulin-like receptors and signaling proteins regulates the cytotoxic function of CD4 T cells in acute coronary syndromes. Circulation Research. 2003, 93, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitriu, I.E.; Baruah, P.; Finlayson, C.J.; Loftus, I.M.; Antunes, R.F.; Lim, P.; Bunce, N.; Kaski, J.C. High Levels of Costimulatory Receptors OX40 and 4-1BB Characterize CD4 (+) CD28 (null) T Cells in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome. Circulation Research. 2010, 110, 857–U150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Mejias, R.; Castaneda, S.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, C.; Corrales, A.; Ferraz-Amaro, I.; Genre, F.; Remuzgo-Martinez, S.; Rodriguez-Rodriguez, L.; Blanco, R.; Llorca, J.; Martin, J.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A. Cardiovascular risk assessment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: The relevance of clinical, genetic and serological markers. Autoimmunity Reviews. 2016, 15, 1013–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liuzzo, G.; Biasucci, L.M.; Brugaletta, S.; Digianuario, G.; Pinnelli, M.; Giubilato, G.; Giubilato, S.; Colafrancesco, V.; Rebuzzi, A.G.; Crea, F. An unusual population of T-lymphocytes, (CD4+CD28null) T-cells, is associated with the recurrence of acute coronary events in patients with unstable angina. Circulation. 2005, 112, U586–U586. [Google Scholar]
- Libby, P. Inflammatory mechanisms: The molecular basis of inflammation and disease. Nutrition Reviews. 2007, 65, S140–S146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, D.I.; Holmes, M.V.; Kuchenbaecker, K.B.; Engmann, J.E.L.; Shah, T.; Sofat, R.; Guo, Y.R.; Chung, C.; Peasey, A.; Ster, R.P.; Mooijaart, S.P.; Ireland, H.A.; Leusink, M.; Langenberg, C.; Li, K.; Palmen, J.; Howard, P.; Cooper, J.A.; Drenos, F.; Hardy, J.; Nalls, M.A.; Li, Y.R.; Lowe, G.; Stewart, M.; Bielinski, S.J.; Peto, J.; Timpson, N.J.; Gallacher, J.; Dunlop, M.; Houlston, R.; Tomlinson, I.; Tzoulaki, I.; Luan, J.; Boer, J.M.A.; Forouhi, N.G.; Onland-Moret, N.C.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; Schnabel, R.B.; Hubacek, J.A.; Kubinova, R.; Baceviciene, M.; Tamosiunas, A.; Pajak, A.; Topor-Madry, R.; Malyutina, S.A.; Baldassarre, D.; Sennblad, B.; Tremoli, E.; de Faire, U.; Ferrucci, L.; Bandenelli, S.; Tanaka, T.; Meschia, J.F.; Singleton, A.; Navis, G.; Leach, I.M.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Ford, I.; Epstein, S.E.; Burnett, M.S.; Devaney, J.M.; Jukema, J.W.; Westendorp, R.G.J.; de Borst, G.J.; van der Graaf, Y.; de Jong, P.A.; der Zee, A.H.M.-V.; Klungel, O.H.; de Boer, A.; Doevendans, P.A.; Stephens, J.W.; Eaton, C.B.; Robinson, J.G.; Manson, J.E.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; Frayling, T.M.; Price, J.F.; Whincup, P.H.; Morris, R.W.; Lawlor, D.A.; Smith, G.D.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Redline, S.; Lange, L.A.; Kumari, M.; Wareham, N.J.; Verschuren, W.M.M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Whittaker, J.C.; Hamsten, A.; Dudbridge, F.; Delaney, J.A.C.; Wong, A.; Kuh, D.; Hardy, R.; Castillo, B.A.; Connolly, J.J.; van der Harst, P.; Brunner, E.J.; et al. The interleukin-6 receptor as a target for prevention of coronary heart disease: a mendelian randomisation analysis. Lancet. 2012, 379, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Kaptoge, S.; Seshasai, S.R.K.; Gao, P.; Freitag, D.F.; Butterworth, A.S.; Borglykke, A.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Gudnason, V.; Rumley, A.; Lowe, G.D.O.; Jorgensen, T.; Danesh, J. Inflammatory cytokines and risk of coronary heart disease: new prospective study and updated meta-analysis. European Heart Journal. 2014, 35, 578–U35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Oever, I.A. M.; Sattar, N.; Nurmohamed, M.T. Thromboembolic and cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: role of the haemostatic system. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2014, 73, 954–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, H.Y.; Migliarino, S.; Czesnikiewicz-Guzik, M.; Guzik, T.J. Hypertension: Focus on autoimmunity and oxidative stress. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2018, 125, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.J. L.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; van Eijk, I.C.; Verkleij, C.J.N.; Marx, P.F. Thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor and its relation with inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2009, 68, 1232–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habets, K.L. L.; Trouw, L.A.; Levarht, E.W.N.; Korporaal, S.J.A.; Habets, P.A.M.; de Groot, P.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Toes, R.E.M. Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies contribute to platelet activation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research & Therapy. 2015, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.W.; Chen, H.M.; Ju, H.X.; Sun, M.Z.; Jin, H. Platelet indices in patients with chronic inflammatory arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Platelets. 2020, 31, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agca, R.; Hopman, L.; Laan, K.J.C.; van Halm, V.P.; Peters, M.J.L.; Smulders, Y.M.; Dekker, J.M.; Nijpels, G.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Boers, M.; Lems, W.F.; Nurmohamed, M.T. Cardiovascular Event Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis Compared with Type 2 Diabetes: A 15-year Longitudinal Study. Journal of Rheumatology. 2020, 47, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cugno, M.; Marzano, A.V.; Asero, R.; Tedeschi, A. Activation of blood coagulation in chronic urticaria: pathophysiological and clinical implications. Intern Emerg Med. 2010, 5, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, E.; Ganeshalingam, K.; Semb, A.G.; Szekanecz, Z.; Nurmohamed, M. Cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: recent advances in the understanding of the pivotal role of inflammation, risk predictors and the impact of treatment. Rheumatology. 2014, 53, 2143–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, F.; Bonaventura, A.; Liberale, L.; Paolino, S.; Torre, F.; Dallegri, F.; Montecucco, F.; Cutolo, M. Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Promoters and Opponents. Clinical Reviews in Allergy and Immunology. 2020, 58, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E.; Crowson, C.S.; Kremers, H.M.; Roger, V.L.; Fitz-Gibbon, P.D.; Therneau, T.M.; Gabriel, S.E. Lipid paradox in rheumatoid arthritis: the impact of serum lipid measures and systemic inflammation on the risk of cardiovascular disease. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2011, 70, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Everett, B.M.; Thuren, T.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Chang, W.H.; Ballantyne, C.; Fonseca, F.; Nicolau, J.; Koenig, W.; Anker, S.D.; Kastelein, J.J.P.; Cornel, J.H.; Pais, P.; Pella, D.; Genest, J.; Cifkova, R.; Lorenzatti, A.; Forster, T.; Kobalava, Z.; Vida-Simiti, L.; Flather, M.; Shimokawa, H.; Ogawa, H.; Dellborg, M.; Rossi, P.R.F.; Troquay, R.P.T.; Libby, P.; Glynn, R.J.; Grp, C.T. Antiinflammatory Therapy with Canakinumab for Atherosclerotic Disease. New England Journal of Medicine. 2017, 377, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodson, N.J.; Brookhart, A.M.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Silman, A.J.; Solomon, D.H. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use does not appear to be associated with increased cardiovascular mortality in patients with inflammatory polyarthritis: results from a primary care based inception cohort of patients. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2009, 68, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, C.; Martin, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: A disease associated with accelerated atherogenesis. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2005, 35, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerola, A.M.; Kerola, T.; Kauppi, M.J.; Kautiainen, H.; Virta, L.J.; Puolakka, K.; Nieminen, T.V.M. Cardiovascular comorbidities antedating the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2013, 72, 1826–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Södergren, A.; Karp, K.; Boman, K.; Eriksson, C.; Lundström, E.; Smedby, T.; Söderlund, L.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Wållberg-Jonsson, S. Atherosclerosis in early rheumatoid arthritis: very early endothelial activation and rapid progression of intima media thickness. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010, 12(4), R158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gay, M.A.; González-Juanatey, C.; Miranda-Filloy, J.A.; García-Unzueta, M.T.; Llorca, J. Lack of association between flow-mediated endothelium-dependent vasodilatation and biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction in patients with severe rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2012, 32(12), 4071–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Minno, M.N.; Ambrosino, P.; Lupoli, R.; Di Minno, A.; Tasso, M.; Peluso, R.; Tremoli, E. Clinical assessment of endothelial function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis of literature studies. Eur J Intern Med. 2015, 26(10), 835–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosino, P.; Tasso, M.; Lupoli, R.; Di Minno, A.; Baldassarre, D.; Tremoli, E.; Di Minno, M.N. Non-invasive assessment of arterial stiffness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of literature studies. Ann Med. 2015, 47(6), 457–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, J.T.; Wasko, M.C.M.; Chung, C.P.; Szklo, M.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Kao, A.; Bokhari, S.; Zartoshti, A.; Stein, C.M.; Bathon, J.M. Exploring the Lipid Paradox Theory in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Associations of Low Circulating Low-Density Lipoprotein Concentration With Subclinical Coronary Atherosclerosis. Arthritis and Rheumatology. 2019, 71, 1426–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paccou, J.; Renard, C.; Liabeuf, S.; Kamel, S.; Fardellone, P.; Massy, Z.A.; Brazier, M.; Mentaverri, R. Coronary and Abdominal Aorta Calcification in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Relationships with Traditional Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Disease Characteristics, and Concomitant Treatments. Journal of Rheumatology. 2014, 41, 2137–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGettigan, P.; Henry, D. Cardiovascular risk and inhibition of cyclooxygenase - A systematic review of the observational studies of selective and nonselective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase. Jama-Journal of the American Medical Association. 2006, 296, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, P.M.; Baigent, C.; Godwin, J.; Halls, H.; Emberson, J.R.; Patrono, C. Do selective cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors and traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs increase the risk of atherothrombosis? Meta-analysis of randomised trials. Bmj-British Medical Journal. 2006, 332, 1302–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubille, C.; Richer, V.; Starnino, T.; McCourt, C.; McFarlane, A.; Fleming, P.; Siu, S.; Kraft, J.; Lynde, C.; Pope, J.; Gulliver, W.; Keeling, S.; Dutz, J.; Bessette, L.; Bissonnette, R.; Haraoui, B. The effects of tumour necrosis factor inhibitors, methotrexate, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids on cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2015, 74, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabassi, A.; Tedeschi, S.; Perlini, S.; Verzicco, I.; Volpi, R.; Gonzi, G.; Del Canale, S. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug effects on renal and cardiovascular function: from physiology to clinical practice. European Journal of Preventive Cardiology. 2020, 27, 850–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G. ; Capodanno, D.; Longo, G.; Capranzano, P.; Tamburino, C. Updates on NSAIDs in patients with and without coronary artery disease: pitfalls, interactions and cardiovascular outcomes. Expert Review of Cardiovascular Therapy. 2014, 12, 1185–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparyan, A.Y.; Ayvazyan, L.; Cocco, G.; Kitas, G.D. Adverse Cardiovascular Effects of Antirheumatic Drugs: Implications for Clinical Practice and Research. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2012, 18, 1543–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, C.C.; Sugano, K.; Wang, J.G.; Fujimoto, K.; Whittle, S.; Modi, G.K.; Chen, C.H.; Park, J.B.; Tam, L.S.; Vareesangthip, K.; Tsoi, K.K.F.; Chan, F.K.L. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) therapy in patients with hypertension, cardiovascular, renal or gastrointestinal comorbidities: joint APAGE/APLAR/APSDE/APSH/APSN/PoA recommendations. Gut. 2020, 69, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.Y.; Du, X.P. Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs and Hypertension. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics. 2014, 69, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, B.; Aldington, S.; Weatherall, M.; Shirtcliffe, P.; Beasley, R. Risk of cardiovascular events and celecoxib: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 2006, 99, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helin-Salmivaara, A.; Virtanen, A.; Vesalainen, R.; Gronroos, J.M.; Klaukka, T.; Idanpaan-Heikkila, J.E.; Huupponen, R. NSAID use and the risk of hospitalization for first myocardial infarction in the general population: a nationwide case-control study from Finland. European Heart Journal. 2006, 27, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeweiss, S.; Solomon, D.H.; Wang, P.S.; Rassen, J.; Brookhart, M.A. Simultaneous assessment of short-term gastrointestinal benefits and cardiovascular risks of selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors and nonselective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - An instrumental variable analysis. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2006, 54, 3390–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabule, J.; Adebajo, A. Comparative evaluation of cardiovascular outcomes in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis on recommended doses of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal Disease. 2014, 6, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rincon, I.; Battafarano, D.F.; Restrepo, J.F.; Erikson, J.M.; Escalante, A. Glucocorticoid Dose Thresholds Associated With All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatology. 2014, 66, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubrier, M.; Chamoux, N.B.; Tatar, Z.; Couderc, M.; Dubost, J.J.; Mathieu, S. Cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine, 2014, 81, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, V.; Rachapalli, S.; Choy, E.H. Safety of medium- to long-term glucocorticoid therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Rheumatology. 2009, 48, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruyssen-Witrand, A.; Fautrel, B.; Saraux, A.; Le Loet, X.; Pham, T. Cardiovascular risk induced by low-dose corticosteroids in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic literature review. Joint Bone Spine. 2011, 78, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agca, R.; Heslinga, S.C.; Rollefstad, S.; Heslinga, M.; McInnes, B.; Peters, M.J.L.; Kvien, T.K.; Dougados, M.; Radner, H.; Atzeni, F.; Primdahl, J.; Sodergren, A.; Jonsson, S.W.; van Rompay, J.; Zabalan, C.; Pedersen, T.R.; Jacobsson, L.; de Vlam, K.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Semb, A.G.; Kitas, G.D.; Smulders, Y.M.; Szekanecz, Z.; Sattar, N.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Nurmohamed, M.T. EULAR recommendations for cardiovascular disease risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of inflammatory joint disorders: 2015/2016 update. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2017, 76, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suissa, S.; Bernatsky, S.; Hudson, M. Antirheumatic drug use and the risk of acute myocardial infarction. Arthritis and Rheumatism-Arthritis Care and Research. 2006, 55, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rempenault, C.; Combe, B.; Barnetche, T.; Gaujoux-Viala, C.; Lukas, C.; Morel, J.; Hua, C. Metabolic and cardiovascular benefits of hydroxychloroquine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2018, 77, 98–103. J1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widdifield, J.; Abrahamowicz, M.; Paterson, J.M.; Huang, A.J.; Thorne, J.C.; Pope, J.E.; Kuriya, B.; Beauchamp, M.E.; Bernatsky, S. Associations Between Methotrexate Use and the Risk of Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Elderly-onset Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology. 2019, 46, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westlake, S.L.; Colebatch, A.N.; Baird, J.; Curzen, N.; Kiely, P.; Quinn, M.; Choy, E.; Ostor, A.J.K.; Edwards, C.J. Tumor necrosis factor antagonists and the risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review. Rheumatology. 2011, 50, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micha, R.; Imamura, F.; von Ballmoos, M.W.; Solomon, D.H.; Hernan, M.A.; Ridker, P.M.; Mozaffarian, D. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Methotrexate Use and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. American Journal of Cardiology. 2011, 108, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.J.; Wasko, M.C.M.; Antohe, J.L.; Sartorius, J.A.; Kirchner, H.L.; Dancea, S.; Bili, A. Hydroxychloroquine Use Associated With Improvement in Lipid Profiles in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Arthritis Care and Research. 2011, 63, 530–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Xu, X.H.; Lin, N.; Lu, H.D. Metabolic and cardiovascular benefits of hydroxychloroquine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2019, 78, E21–E21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles-Schoeman, C.; Wang, X.Y.; Lee, Y.Y.; Shahbazian, A.; Navarro-Millan, I.; Yang, S.; Chen, L.; Cofield, S.S.; Moreland, L.W.; O’Dell, J.; Bathon, J.M.; Paulus, H.; Bridges, S.L.; Curtis, J.R. Association of Triple Therapy With Improvement in Cholesterol Profiles Over Two-Year Followup in the Treatment of Early Aggressive Rheumatoid Arthritis Trial. Arthritis and Rheumatology. 2016, 68, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, D.H.; J. Avorn; Katz, J.N.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Setoguchi, S.; Levin, R.; Schneeweiss, S. Immunosuppressive medications and hospitalization for cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2006, 54, 3790–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewe, R.; Breedveld, F.C.; Buch, M.; Burmester, G.; Dougados, M.; Emery, P.; Gaujoux-Viala, C.; Gossec, L.; Nam, J.; Ramiro, S.; Winthrop, K.; de Wit, M.; Aletaha, D.; Betteridge, N.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Boers, M.; Buttgereit, F.; Combe, B.; Cutolo, M.; Damjanov, N.; Hazes, J.M.W.; Kouloumas, M.; Kvien, T.K.; Mariette, X.; Pavelka, K.; van Riel, P.; Rubbert-Roth, A.; Scholte-Voshaar, M.; Scott, D.L.; Sokka-Isler, T.; Wong, J.B.; van der Heijde, D. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2014, 73, 492–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, D.H.; Curtis, J.R.; Saag, K.G.; Lii, J.; Chen, L.; Harrold, L.R.; Herrinton, L.J.; Graham, D.J.; Kowal, M.K.; Kuriya, B.; Liu, L.; Griffin, M.R.; Lewis, J.D.; Rassen, J.A. Cardiovascular Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Comparing TNF-alpha Blockade with Nonbiologic DMARDs. American Journal of Medicine. 2013, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussirot, E. Effects of TNF alpha inhibitors on adiposity and other cardiovascular risk factors: implications for the cardiovascular prognosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opinion on Drug Safety. 2015, 14, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnabe, C.; Martin, B.J.; Ghali, W.A. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha Therapy and Cardiovascular Events in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care and Research. 2011, 63, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsson, L.T. H.; Turesson, C.; Gulfe, A.; Kapetanovic, M.C.; Petersson, I.F.; Saxne, T.; Geborek, P. Treatment with tumor necrosis factor blockers is associated with a lower incidence of first cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology. 2005, 32, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Ljung, L.; Rantapaa-Dahlqvist, S.; Jacobsson, L.T.H.; Askling, J.; Study, G.A. Response to biological treatment and subsequent risk of coronary events in rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2016, 75, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpouzas, G.A.; Ormseth, S.R.; Hernandez, E.; Budoff, M.J. Impact of Cumulative Inflammation, Cardiac Risk Factors, and Medication Exposure on Coronary Atherosclerosis Progression in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatology. 2020, 72, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Fumery, M.; Singh, A.G.; Singh, N.; Prokop, L.J.; Dulai, P.S.; Sandborn, W.J.; Curtis, J.R. Comparative Risk of Cardiovascular Events With Biologic and Synthetic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Care and Research. 2020, 72, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.S.; Packer, M.; Lo, K.H.; Fasanmade, A.A.; Willerson, J.T.; Investigators, A. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, trial of infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor-alpha, in patients with moderate-to-severe heart failure - Results of the Anti-TNF Therapy Against Congestive Heart Failure (ATTACH) trial. Circulation. 2003, 107, 3133–3140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leporini, C.; Russo, E.; D’Angelo, S.; Arturi, F.; Tripepi, G.; Peluso, R.; Grembiale, R.D.; Olivieri, I.; De Sarro, G.; Ursini, F. Insulin-Sensiting Effects of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Reviews on Recent Clinical Trials. 2018, 13, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castagne, B.; Viprey, M.; Martin, J.; Schott, A.M.; Cucherat, M.; Soubrier, M. Cardiovascular safety of tocilizumab: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Plos One. 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divonne, M.D.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Salliot, C. Safety of biologic DMARDs in RA patients in real life: A systematic literature review and meta-analyses of biologic registers. Joint Bone Spine. 2017, 84, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, T.T.; Tsoi, M.F.; Cheung, B.M.Y. Effect of TNF inhibitors on subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2015, 74, 685–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daien, C.I.; Duny, Y.; Barnetche, T.; Daures, J.P.; Combe, B.; Morel, J. Effect of TNF inhibitors on lipid profile in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2012, 71, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.W.; Hong, D.S.; Zhang, Y.; Sang, Y.L.; Yang, Z.H.; Zhang, X.G. Association Between Anti-TNF Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis and Hypertension A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Medicine. 2015, 94. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.K.; Kwak, S.G.; Choe, J.Y. Association between biologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs and incident hypertension in patients with rheumatoid arthritis Results from prospective nationwide KOBIO Registry. Medicine. 2020, 99, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, R.J.; Solomon, D.H.; Schneeweiss, S.; Danaei, G.; Liao, K.P.; Kim, S.C. Tumor Necrosis Factor- Inhibitor Use and the Risk of Incident Hypertension in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Epidemiology. 2016, 27, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.Z.; Kang, E.H.; Brill, G.; Desai, R.J.; Kim, S.C. Cardiovascular (CV) Risk after Initiation of Abatacept versus TNF Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with and without Baseline CV Disease. Journal of Rheumatology. 2018, 45, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiff, M.H.; Kremer, J.M.; Jahreis, A.; Vernon, E.; Isaacs, J.D.; van Vollenhoven, R.F. Integrated safety in tocilizumab clinical trials. Arthritis Research and Therapy. 2011, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, R.; Lin, Y.; John, G.S.; van der Heijde, D.; Qiu, C.F.; Gomez-Reino, J.J.; Maldonado-Cocco, J.A.; Stanislav, M.; Seriolo, B.; Burmester, G.R. Long-term safety with Sarilumab plus conventional synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs and Sarilumab monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis: An integrated analysis with 9000 patient-years of follow up. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2019, 78, 1130–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Ikonomidis, I.; Lekakis, J.P.; Nikolaou, M.; Paraskevaidis, I.; Andreadou, I.; Kaplanoglou, T.; Katsimbri, P.; Skarantavos, G.; Soucacos, P.N.; Kremastinos, D.T. Inhibition of interleukin-1 by anakinra improves vascular and left ventricular function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Circulation. 2008, 117, 2662–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Emery, P.; Bingham, C.O.; Keystone, E.C.; Fleischmann, R.M.; Furst, D.E.; Tyson, N.; Collinson, N.; Lehane, P.B. Long-term safety of rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis: 9.5-year follow-up of the global clinical trial programme with a focus on adverse events of interest in RA patients. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2013, 72, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, A.L.; Singh, J.A. Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Older Adults and Elderly Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: What Role Can Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs Play in Cardiovascular Risk Reduction? Drugs and Aging. 2019, 36, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Thompson, L.; Giles, J.T.; Bathon, J.M.; Salmon, J.E.; Beaulieu, A.D.; Codding, C.E.; Carlson, T.H.; Delles, C.; Lee, J.S.; Sattar, N. Effect of interleukin-6 receptor blockade on surrogates of vascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: MEASURE, a randomised, placebo-controlled study. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2015, 74, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Nakamura, H.; Toyoizumi, S.; Zwillich, S.H.; Tofacitinib, I. Study Phase II Study of Tofacitinib (CP-690,550) Combined With Methotrexate in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and an Inadequate Response to Methotrexate. Arthritis Care and Research. 2011, 63, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Burmester, G.R.; Rooney, T.P.; Witt, S.; Walls, C.D.; Issa, M.; Salinas, C.A.; Saifan, C.; Zhang, X.; Cardoso, A.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Takeuchi, T. Cardiovascular Safety During Treatment With Baricitinib in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatology. 2019, 71, 1042–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, A.; Salgado, E.; Maneiro, J.R.; Mera, A.; Carmona, L.; Gómez-Reino, J.J. Lipid profile changes in patients with chronic inflammatory arthritis treated with biologic agents and tofacitinib in randomized clinical trials: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, Jan;67(1), 117-27.
- Zhang, J.; Xie, F.; Yun, H.; Chen, L.; Muntner, P.; Levitan, E.B.; Safford, M.M.; Kent, S.T.; Osterman, M.T.; Lewis, J.D.; Saag, K.; Singh, J.A.; Curtis, J.R. Comparative effects of biologics on cardiovascular risk among older patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2016, 75, 1813–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E.; Karmacharya, P.; Garcia, A.D.; Davis, J.; Murad, M.H.; Crowson, C. What Is the Effect of Statins on the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis? Results of a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis and Rheumatology. 2019, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Soulaidopoulos, S.; Nikiphorou, E.; Dimitroulas, T.; Kitas, G.D. The Role of Statins in Disease Modification and Cardiovascular Risk in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Frontiers in Medicine. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danninger, K.; Hoppe, U.C.; Pieringer, H. Do statins reduce the cardiovascular risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis? International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases. 2014, 17, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, B.; Yin, Y.-F.; Zhao, L.-D.; Wang, L.; Zheng, W.-J.; Chen, H.; Wu, Q.-J.; Tang, F.-L.; Zhang, F.-C.; Shan, G.; Zhang, X. Effect of 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl-Coenzyme A Reductase Inhibitor on Disease Activity in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis A Meta-Analysis. Medicine. 2015, 94. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




