Submitted:
02 August 2023
Posted:
03 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature search and selection criteria
2.2. Data extraction
2.3. Statistical analyses
3. Results
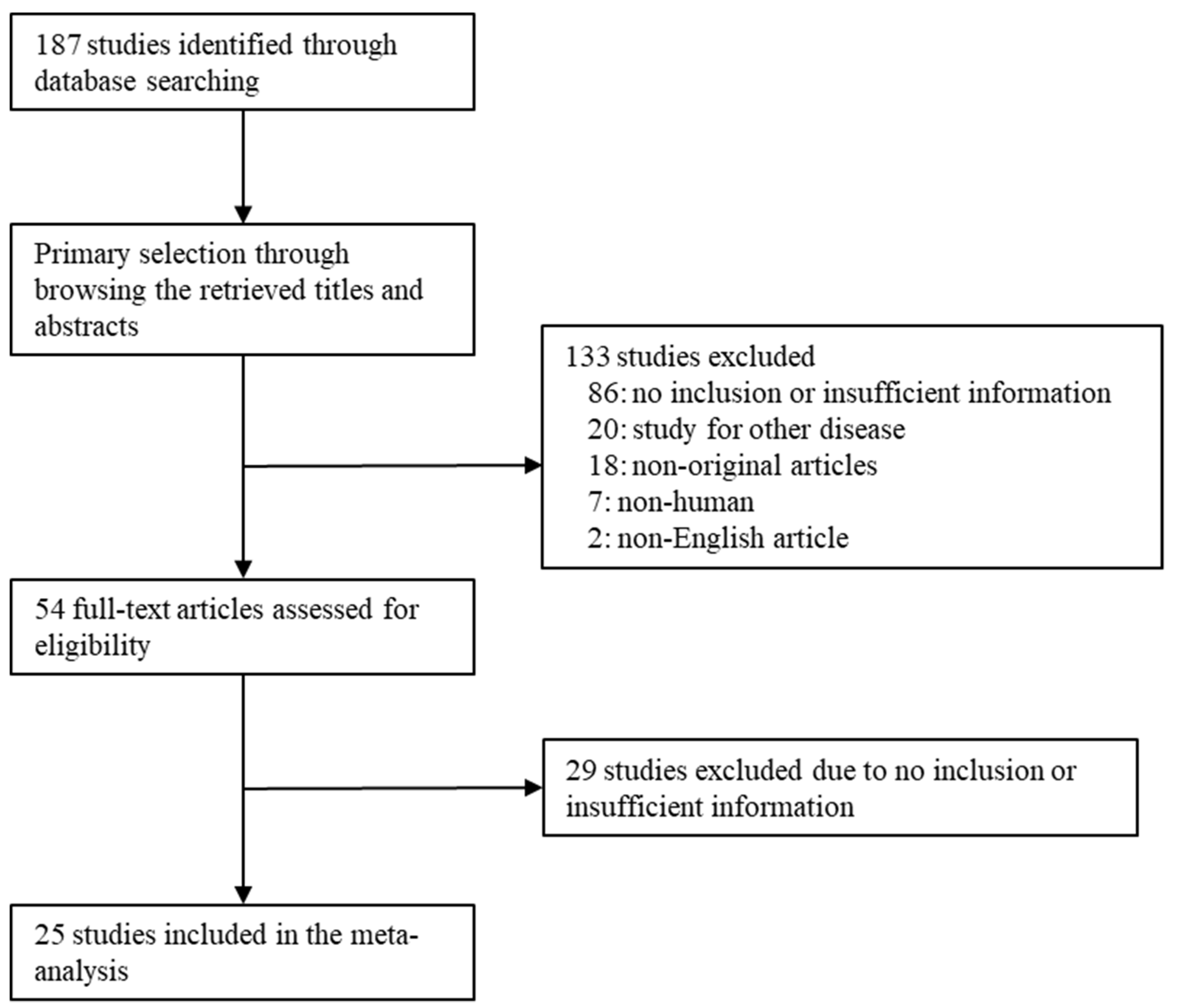
3.1. Selection and characteristics of studies
3.2. Immunohistochemical expression rates in urothelial carcinoma in situ
3.3. Diagnostic test accuracy review of immunohistochemical markers in urothelial carcinoma in situ
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casey, R.G.; Catto, J.W.F.; Cheng, L.; Cookson, M.S.; Herr, H.; Shariat, S.; Alfred Witjes, J.; Black, P.C. Diagnosis and management of urothelial carcinoma in situ of the lower urinary tract: A systematic review. Eur Urol 2015, 67, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Cheville, J.C.; Neumann, R.M.; Leibovich, B.C.; Egan, K.S.; Spotts, B.E.; Bostwick, D.G. Survival of patients with carcinoma in situ of the urinary bladder. Cancer 1999, 85, 2469–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaig, T.W.; Spiess, P.E.; Agarwal, N.; Bangs, R.; Boorjian, S.A.; Buyyounouski, M.K.; Chang, S.; Downs, T.M.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Friedlander, T.; et al. Bladder cancer, version 3.2020, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2020, 18, 329–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron, M.; Luthringer, D.J.; McKenney, J.K.; Hansel, D.E.; Westfall, D.E.; Parakh, R.; Mohanty, S.K.; Balzer, B.; Amin, M.B. Utility of a triple antibody cocktail intraurothelial neoplasm-3 (IUN-3-CK20/CD44s/p53) and a-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR) in the distinction of urothelial carcinoma in situ (CIS) and reactive urothelial atypia. Am J Surg Pathol 2013, 37, 1815–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Trpkov, K.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Grignon, D.; Members of the ISUP Immunohistochemistry in Diagnostic Urologic Pathology Group. Best practices recommendations in the application of immunohistochemistry in the bladder lesions: Report from the International Society of Urologic Pathology consensus conference. Am J Surg Pathol 2014, 38, e20–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallofré, C.; Castillo, M.; Morente, V.; Solé, M. Immunohistochemical expression of CK20, p53, and Ki-67 as objective markers of urothelial dysplasia. Mod Pathol 2003, 16, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenney, J.K.; Desai, S.; Cohen, C.; Amin, M.B. Discriminatory immunohistochemical staining of urothelial carcinoma in situ and non-neoplastic urothelium: An analysis of cytokeratin 20, p53, and CD44 antigens. Am J Surg Pathol 2001, 25, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, P.L.; Herrera, G.A. p53 protein and Ki-67 overexpression in urothelial dysplasia of bladder. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2002, 10, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alston, E.L.J.; Zynger, D.L. Does the addition of AMACR to CK20 help to diagnose challenging cases of urothelial carcinoma in situ? Diagn Pathol 2019, 14, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Stella, J.A., 3rd; Shah, A.B.; Gupta, N.S.; Williamson, S.R. CK20 and p53 Immunohistochemical Staining Patterns in Urinary Bladder Specimens With Equivocal Atypia. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018, 142, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgari, M.; Nabi Maybodi, M.; Abolhasani, M. Differential diagnosis of urothelial carcinoma in situ from non-neoplastic urothelia: Analysis of CK20, CD44, P53 and Ki67. Med J Islam Repub Iran 2016, 30, 400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barth, I.; Schneider, U.; Grimm, T.; Karl, A.; Horst, D.; Gaisa, N.T.; Knüchel, R.; Garczyk, S. Progression of urothelial carcinoma in situ of the urinary bladder: A switch from luminal to basal phenotype and related therapeutic implications. Virchows Arch 2018, 472, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, D.; Hamdy, F.C.; Rehman, I.; Patterson, J.; Cross, S.S.; Feeley, K.M.; Stephenson, Y.; Meuth, M.; Catto, J.W. Evidence for the early onset of aberrant promoter methylation in urothelial carcinoma. J Pathol 2006, 209, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgecombe, A.; Nguyen, B.N.; Djordjevic, B.; Belanger, E.C.; Mai, K.T. Utility of cytokeratin 5/6, cytokeratin 20, and p16 in the diagnosis of reactive urothelial atypia and noninvasive component of urothelial neoplasia. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2012, 20, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garczyk, S.; Bischoff, F.; Schneider, U.; Golz, R.; von Rundstedt, F.C.; Knüchel, R.; Degener, S. Intratumoral heterogeneity of surrogate molecular subtypes in urothelial carcinoma in situ of the urinary bladder: Implications for prognostic stratification of high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Virchows Arch 2021, 479, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacek, J.; Brisuda, A.; Babjuk, M.; Zamecnik, J. Expression of cancer stem cells markers in urinary bladder urothelial carcinoma and its precursor lesions. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 2021, 165, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ick, K.; Schultz, M.; Stout, P.; Fan, K. Significance of p53 overexpression in urinary bladder transitional cell carcinoma in situ before and after bacillus Calmette-Guérin treatment. Urology 1997, 49, 541–546; discussion 546–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Wu, C.; Eslami, Z.; Tanguay, S.; Aprikian, A.; Kassouf, W.; Brimo, F. The role of immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis of flat urothelial lesions: A study using CK20, CK5/6, P53, Cd138, and Her2/Neu. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 18, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunju, L.P.; Lee, C.T.; Montie, J.; Shah, R.B. Utility of cytokeratin 20 and Ki-67 as markers of urothelial dysplasia. Pathol Int 2005, 55, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, K.A.; Murati Amador, B.; Parimi, V.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; Choi, W.; Hahn, N.M.; Kates, M.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; McConkey, D.; Hoque, M.O.; et al. Urothelial Carcinoma In Situ of the Bladder: Correlation of CK20 Expression With Adaptive Immune Resistance, Response to BCG Therapy, and Clinical Outcome. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2021, 29, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Jimenez, R.E.; Montironi, R.; Patriarca, C.; Blanca, A.; Menendez, C.L.; Algaba, F.; Cheng, L. Flat urothelial carcinoma in situ of the bladder with glandular differentiation. Hum Pathol 2011, 42, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, D.J.; Amin, M.B.; Smith, S.C. CK20 versus AMACR and p53 immunostains in evaluation of Urothelial Carcinoma in Situ and Reactive Atypia. Diagn Pathol 2020, 15, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, J.K.; Przybycin, C.G.; McKenney, J.K.; Magi-Galluzzi, C. Immunohistochemical staining patterns of Ki-67 and p53 in florid reactive urothelial atypia and urothelial carcinoma in situ demonstrate significant overlap. Hum Pathol 2020, 98, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, E.; Pinheiro, N.F.; Heney, N.M.; Kaufman, D.S.; Shipley, W.U.; Gurski, C.; Spicer, B.; Paner, G.P.; Gown, A.M.; Amin, M.B. Immunohistochemistry as an adjunct in the differential diagnosis of radiation-induced atypia versus urothelial carcinoma in situ of the bladder: A study of 45 cases. Hum Pathol 2013, 44, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, E.; Kakehi, Y.; Okuno, H.; Habuchi, T.; Okada, Y.; Yoshida, O. Strong correlation of basement membrane degradation with p53 inactivation and/or MDM2 overexpression in superficial urothelial carcinomas. J Urol 1997, 158, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangoi, A.R.; Falzarano, S.M.; Nicolas, M.; McKenney, J.K. Carcinoma In Situ With Plasmacytoid Features: A Clinicopathologic Study of 23 Cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2019, 43, 1638–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Yanai, H.; Morito, T.; Oda, W.; Shin-no, Y.; Yamadori, I.; Tshushima, T.; Yoshino, T. Association between the expression pattern of p16, pRb and p53 and the response to intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy in patients with urothelial carcinoma in situ of the urinary bladder. Pathol Int 2011, 61, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz-Dräger, B.J.; van Roeyen, C.R.; Grimm, M.O.; Gerharz, C.D.; Decken, K.; Schulz, W.A.; Bültel, H.; Makri, D.; Ebert, T.; Ackermann, R. P53 accumulation in precursor lesions and early stages of bladder cancer. World J Urol 1994, 12, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, S.F.; Kim, J.H.; Ayala, G.E.; Kho, K.; Wheeler, T.M.; Lerner, S.P. Cyclooxygenase-2 is highly expressed in carcinoma in situ and T1 transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. J Urol 2003, 169, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Tokuhara, Y.; Hosokawa, S.; Ohsaki, H.; Morinishi, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Teramoto, N.; Hirakawa, E. Overexpression of the PPAR-γ protein in primary Ta/T1 non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma. Mol Clin Oncol 2022, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, J.; Abraira, V.; Muriel, A.; Khan, K.; Coomarasamy, A. Meta-DiSc: A software for meta-analysis of test accuracy data. BMC Med Res Methodol 2006, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, L.E.; Shapiro, D.; Littenberg, B. Combining independent studies of a diagnostic test into a summary ROC curve: Data-analytic approaches and some additional considerations. Stat Med 1993, 12, 1293–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straccia, P.; Fiorentino, V.; Martini, M.; Pierconti, F. A systematic review and meta-analysis of CK20, CD44, Ki67 and p53 as im-munohistochemical markers in bladder carcinoma in situ. Actas Urol Esp (Engl Ed) 2022, 46, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| First Author | Location | Organ | No of patients | Interpreted markers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIS | RA/Non-neoplatic/ Normal urothelium |
||||
| Alston 2019 [9] | USA | UB | 42 | 30 | CK20, AMACR |
| Arias-Stella 2018 [10] | USA | UB | 69 | CK20 | |
| Aron 2013 [4] | Canada | UB | 43 | 35 | CK20, CD44, AMACR |
| Asgari 2016 [11] | Iran | UB | 20 | 40 | CK20, CD44, p53 |
| Barth 2018 [12] | Germany | UB | 156 | CK20 | |
| Dhawan 2006 [13] | UK | UB | 65 | 56 | CK20, p53 |
| Edgecombe A [14] | Canada | UB | 20 | 10 | CK20 |
| Garczyk 2021 [15] | Germany | UB | 99 | CK20 | |
| Hacek 2021 [16] | Czech Republic | UB | 32 | CD44 | |
| Ick 1997 [17] | USA | UB | 12 | p53 | |
| Jung 2014 [18] | Canada | UB | 41 | 52 | CK20, p53 |
| Kunju 2005 [19] | USA | UB | 50 | 50 | CK20 |
| Lombardo 2021 [20] | USA | UB | 43 | CK20, p53 | |
| Lopez-Beltran 2010 [21] | Spain | UB | 39 | CK20, p53 | |
| Mallofré 2003 [6] | USA | UB/UT | 50 | 50 | CK20, p53 |
| McKenney 2001 [7] | UB | 21 | 25 | CK20, CD44, p53 | |
| Neal 2020 [22] | USA | UB | 15 | 15 | CK20, AMACR, p53 |
| Nguyen 2020 [23] | USA | UB | 40 | 40 | CK20, CD44, p53 |
| Oliva 2013 [24] | USA | UB | 17 | 28 | CK20, CD44, p53 |
| Ozdemir 1997 [25] | Japan | UB/UT | 18 | p53 | |
| Sangoi 2019 [26] | USA | UB | 25 | CK20, CD44, p53 | |
| Sato 2011 [27] | Japan | UB | 27 | p53 | |
| Schmitz-Dräger 1994 [28] | Germany | UB | 24 | p53 | |
| Shariat 2003 [19] | USA | UB | 39 | p53 | |
| Tanaka 2022 [30] | Japan | UB | 19 | p53 | |
| Number of subsets |
Fixed effect [95% CI] |
Heterogeneity test [p-value] |
Random effect [95% CI] |
Egger’s Test [p-value] |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK20 | 19 | 0.722 [0.686, 0.755] | < 0.001 | 0.803 [0.726, 0.862] | 0.002 |
| CD44 | 7 | 0.364 [0.265, 0.476] | < 0.001 | 0.142 [0.033, 0.449] | 0.037 |
| AMACR | 3 | 0.824 [0.720, 0.895] | 0.726 | 0.824 [0.720, 0.895] | 0.339 |
| p53 | 18 | 0.585 [0.537, 0.631] | < 0.001 | 0.600 [0.510, 0.683] | 0.143 |
| Number of subsets |
Fixed effect [95% CI] |
Heterogeneity test [p-value] |
Random effect [95% CI] |
Egger’s Test [p-value] |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK20 | 16 | 28.848 [17.968, 46.318] | 0.001 | 71.313 [30.176, 168.530] | < 0.001 |
| CD44 | 7 | 0.017 [0.007, 0.043] | 0.370 | 0.016 [0.006, 0.043] | 0.110 |
| AMACR | 3 | 142.931 [31.109, 656.697] | 0.968 | 142.931 [31.109, 656.697] | 0.116 |
| p53 | 11 | 8.955 [5.413, 14.814] | 0.011 | 16.774 [6.713, 41.916] | 0.008 |
| Included studies |
Sensitivity (%) [95% CI] |
Specificity (%) [95% CI] |
Diagnostic OR [95% CI] |
AUC on SROC |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK20 | 16 | 0.937 [0.910, 0.957] | 0.773 [0.735, 0.809] | 77.22 [30.17, 172.85] | 0.942 |
| CD44 * | 7 | 0.865 [0.803, 0.913] | 0.767 [0.698, 0.827] | 61.11 [23.08, 161.81] | 0.940 |
| AMACR | 3 | 0.984 [0.915, 1.000] | 0.829 [0.725, 0.906] | 142.93 [31.11, 656.70] | 0.770 |
| p53 | 11 | 0.843 [0.794, 0.884] | 0.657 [0.607, 0.705] | 17.17 [6.72, 43.87] | 0.711 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





