1. Introduction
I Ching, also known as the Book of Changes, is a guide for the ancients to understand the world and grasp the natural laws of the universe. It is also the core of ancient Chinese wisdom and the general summary of the natural laws and social laws summarized by Chinese civilization in the long history. The 64 hexagrams of I Ching are composed of eight trigram hexagrams, which are used by ancient Chinese as a divination tool for good or bad luck in life.
After thousands of years of development, I Ching has been paid more and more attention by Chinese and Western scholars. It is not only the ideological source of Chinese culture, but also has an important impact on world religion, business, philosophy, medicine, and even physics, chemistry, mathematics and other disciplines. Leibniz believes that the idea of “Yin and Yang” of I Ching coincides with his own binary system. It is the “Chinese version” of binary thought. Jung, a western psychologist, believes that I Ching has synchronicity based on his understanding of it. Synchronicity is the opposite of causality. It regards the coincidence of events in space and time as not only accidental, but also related to the super psychological state of the observers [
1,
2].I Ching has also become an important discussion point of view in modern and contemporary science, such as DNA genetic codon, atomic structure and other disciplinary theories. So far, the discussion on I Ching is still popular. It can be seen that the exploration of the 64 hexagrams of I Ching may become a new research paradigm—the Chinese academic paradigm or the oriental civilization paradigm [
3].
In recent years, quantitative research on I Ching has gradually increased, especially the development of big data and artificial intelligence, which has further promoted the rapid progress of quantitative research on I Ching [
4,
5]. Ma Baoping used modern statistical methods to make a quantitative study of 4096 possible hexagrams, and reached the conclusion that the results of 64 hexagrams tended to normal distribution [
6].This in itself shows that there are certain rules implied in I Ching.Tang Yi used the Monte Carlo method to simulate the I Ching divination and calculate the change probability of 64 hexagrams [
7].However, there is no in-depth quantitative study on the relationship between main hexagram and the othor hexagrams, and on the hexagram change characteristics with a larger amount of data combined with visual charts. Some scholars have studied the changes of I Ching from different perspectives, trying to find some basic rules [
8].
From the perspective of cultural communication, the function of divination is not only the starting point for I Ching to go overseas, but also the core function to make it accepted in the western academic circles and folk. Big data technology coincides with divination of I Ching in thinking methods and technical performance. The principles of divination of I Ching provide a more macro philosophical perspective and profound enlightenment for understanding and developing big data [
9].The research on big data and artificial intelligence of I Ching has just started. In order to reveal the characteristics and laws of divination of I Ching, this paper uses computer technology to simulate the widely used coin divination method for big data analysis. Through statistics, induction, summary and reasoning, it focuses on solving the characteristics and laws of hexagram change and line (The lines in each hexagram of I Ching are called Yao.) change, and further brings scientific explanation to the change results and accuracy of 64 hexagram predictions.
This article declares as follows: (1) In Chinese,
the hexagrams of I Ching is called Gua. For ease of understanding, this article
chooses hexagram to represent Gua. (2) In Chinese, the line in the hexagram is
called Yao. For ease of understanding, this article chooses the line to
represent Yao.
2. Method and Principle
2.1. Coin toss Method in I Ching
The divination of I Ching is generally divided into three processes. The first is to use any divination method to obtain one of the 64 hexagrams as the original hexagram, and then refer to the original text of I Ching to read and understand the obtained hexagrams. The second is to wrong hexagrams, comprehensive hexagrams, mutual hexagrams, and changed hexagrams based on the original hexagram, further understanding the meaning of hexagrams from multiple perspectives [
10,
11].The third is to infer the development trend or divination result of things through the divination words of I Ching, combining the hexagram images and line(Yao) images, the hexagram words (divination words) and line(Yao) words, the relationship between line(Yao) positions, and the mechanism of the mutually reinforce and neutralize each other of Yin Yang and five elements.
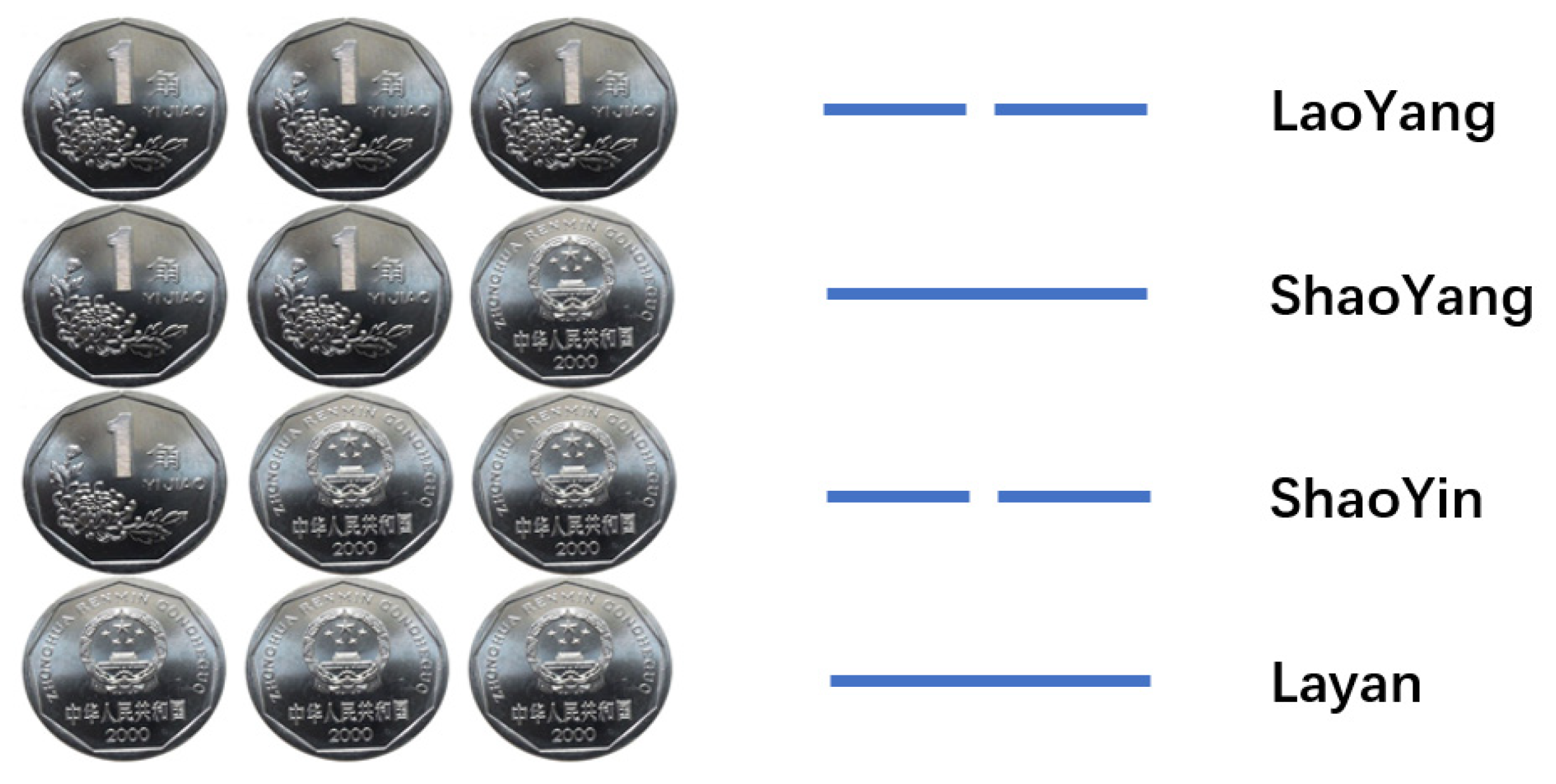
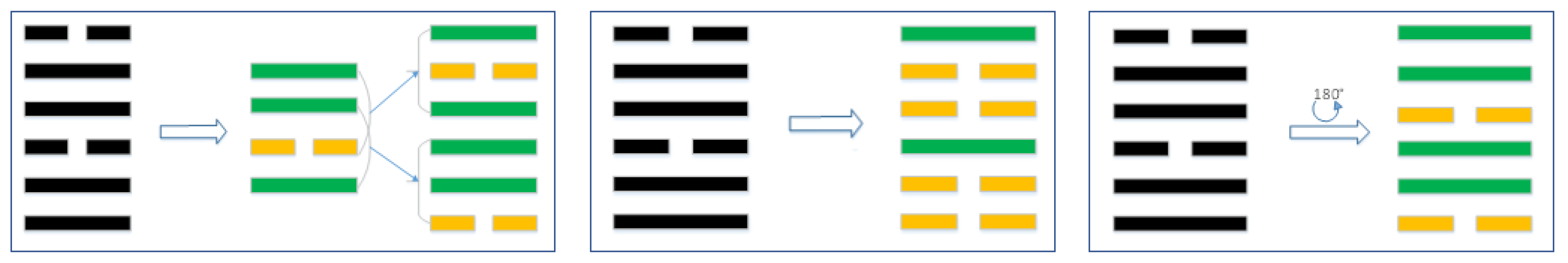
Coin toss method originated in the Yin and Shang period of China, and is still popular and widely used by many people. The process of coin toss method divination is as follows: the diviner takes out three coins (It is not possible to distinguish between ancient coins and current popular coins), and stipulates that the side marked with characters is the positive side, and the other side is the negative side. Put the coin between the two hands, shake it repeatedly and then throw it on the table to record the number of the front and the back. There must be four combinations of positive and negative: two positive and one negative (Shaoyang), two negative and one positive (Shaoyin), three positive (Laoyang, marked as dynamic line) and three negative (Laoyin, marked as dynamic line). The combination is shown in
Figure 1.There will be only one of four combinations for each roll.Repeat the operation 6 times to form 6 lines. One throw is a line, and six throw is a hexagram. From the first roll to the sixth roll, the start, second, third, fourth, fifth and upper lines are recorded respectively. The obtained hexagram is called the original hexagram.
2.2. Rules of Hexagram Changes
Dynamic lines(Dongyao): In the process of forming the hexagram, the lines of Laoyang or Laoyin appeared in the six flips of three coins, which are called dynamic lines.
Changing hexagrams(Biangua): This hexagram is the initial one, which reflects the initial information or current situation of things. In the process of forming the hexagram, if the Laoyang or Laoyin appears, the line in which it is located will become the opposite line, that is, the Laoyang will become the yin line, and the Laoyin will become the yang line.A new hexagram is formed according to the moving hexagram, which is called changing hexagram.The line corresponding to the action line of the hexagram is called the change line.A feedback relationship is formed between the dynamic line and the changing line. Therefore, the appearance of the dynamic line plays an important role in the interpretation of the hexagram, and can also reflect the mutual connection and transformation between things. According to the divination thought of I Ching that anode generates Yin and cathode generates Yang, Laoyang will become Shaoyin after the change of lines, and Laoyin will become Shaoyang after the change of lines. There are many ways to change hexagrams. Each hexagram can have many possibilities according to the number of changed lines and the position of lines. There are 4096 scenarios according to permutation and combination. The change of fortune represents the final result of the development and change of current things.
Change of line(Bianyao): when a dynamic line appears in the process of forming the hexagram, the corresponding line in the change of line is called a change of line.
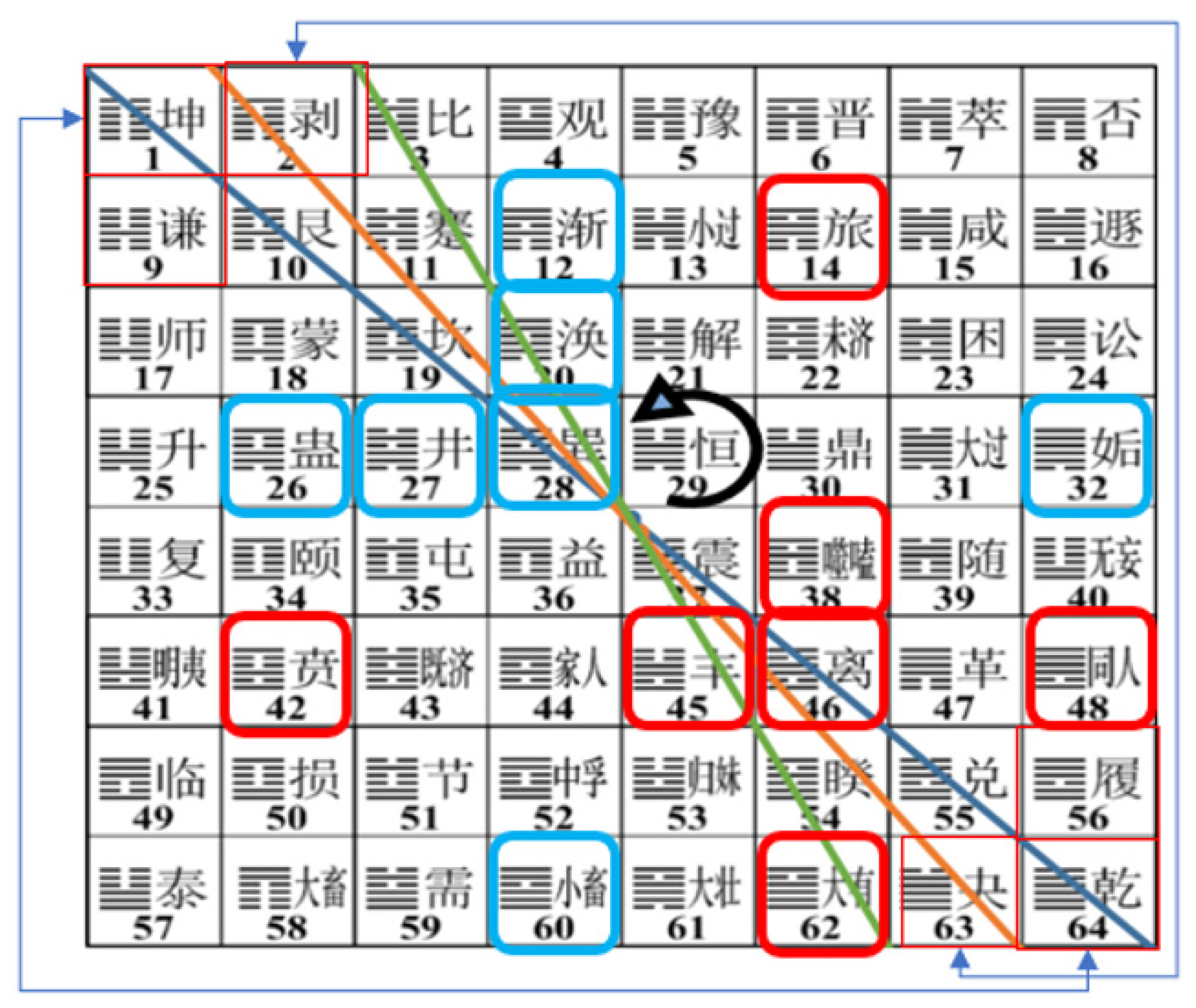
According to original hexagram, three other hexagrams can be deduced, namely mutual hexagram, wrong hexagram and comprehensive hexagram. This is also the source of the word “intricate” in Chinese idioms.
Mutual hexagram(Hugua): It is composed of the remaining four lines after removing the upper and lower. The specific combination method is: among the remaining four lines, the upper three lines and the lower three lines form a new hexagram, that is, the mutual hexagram of the hexagram. As shown in
Figure 2. Mutual hexagram is used to judge the intermediate process after an event occurs but before the result appears, reflecting the internal interaction of this divination over time.
Wrong hexagram (Cuogua): The new hexagram is called wrong hexagram after all the yin and Yang lines in this hexagram are inverted lines, that is, the yin and Yang properties of each line in the wrong hexagram are opposite to the original hexagram.
Figure 3.The wrong hexagram mainly looks at the development of things from the opposite perspective.It reflects the dialectical unity thought of I Ching.
Comprehensive hexagram (Zonggua): The hexagram obtained by rotating the six lines of this hexagram 180 degrees is called comprehensive hexagram.It is like a pinhole image, or simply called “mirror divination” or “inverted divination”. Comprehensive divination is to think about the things to be measured from the perspective of outside and inside. As shown in
Figure 4.
The comprehensive hexagrams are relative. All 64 hexagrams are relative except 8.These eight divinatory symbols are Qian, Kun, Kan, Li, Daguo, Xiaoguo, Yi, Zhongfu. Among them, the first four hexagrams belong to cosmic phenomena, and the last four hexagrams belong to personnel phenomena. Both the cosmic phenomenon and the personnel phenomenon have their invariable nature, so there is no comprehensive divination.
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of basic characteristics of hexagram change.
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of basic characteristics of hexagram change.
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution characteristics of hexagram change by coin divination method 135 °.
Figure 5.
Spatial distribution characteristics of hexagram change by coin divination method 135 °.
2.3. Calculation of Assembly Combination of Hexagrams and Lines (Yao)
The coin toss method is different from other methods of divination. Each line has only one dynamic line. Since the three coins are randomly arranged for six times, there may be seven situations for each hexagram, that is, there is no change of dynamic line, dynamic line from one line to six lines. Every time these line changes occur, there will be various change situations, mutual hexagram, wrong hexagram and comprehensive hexagram. The statistics of these changes can reveal the characteristics and laws of the changed hexagrams and lines(Yao). This article adopts the method of taking up the change of six lines mentioned in Zhu Xi’s “Enlightenment of I Ching”, that is, the change of one line is accounted for by the words of the changed line in this hexagram; When the two lines are changed, the words of the two lines of the hexagram are used, and the upper line is the main line; If the three lines change, they will take up the words of the original hexagram and the changed hexagram; When the four lines change, the words of the two lines of the changed hexagram are used, and the lower line is the main line; If the five lines change, the unchanging lines in the changed hexagram are used for divination; If the six lines change, Qian and Kun use their Yongyao for divination, and the rest of the hexagrams use their hexagram words for divination; If the six lines are unchanged, divination is carried out according to the original hexagram words [
12].
In order to calculate this change, we (1) use a random number generator to generate open interval random numbers within the specified range. The random number generator in the process of three coins starting generates only positive and negative coins, while ensuring that the generation of each random number is random and equal; (2) The number of random numbers will start from 104 Increase to 108; (3) Record the number of occurrences of the Laoyang, the Laoyin, the Shaoyang and the Shaoyin of each line, the number of occurrences of all the six lines from the unchanged line, and the occurrence of the transformation of each hexagram into other hexagrams (changing hexagrams, mutual hexagrams, wrong hexagrams and comprehensive hexagrams). (4) Map based on the probability distribution of each hexagram being transformed into other hexagrams to visualize the spatial characteristics of the hexagram transformation using a 64 matrix.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Basic Characteristics of Line(Yao) Change: Small Change is Normal
There are three scenarios of changes in Ching, namely No change, Simple change, and Difficult change.
No change: In the big data calculation, 17% of the hexagrams have no moving lines, which means that the invariable things in the universe account for less than 1/5 of all the changeable situations. One of our important tasks as humans is to continuously explore these unchanging laws. Although we know that there are laws in physics, chemistry, biology, medicine and many other fields in the laws of the universe, these laws are basically regional or local. The fundamental laws that constrain the universe, solar system, earth and all humanity have not yet been revealed.
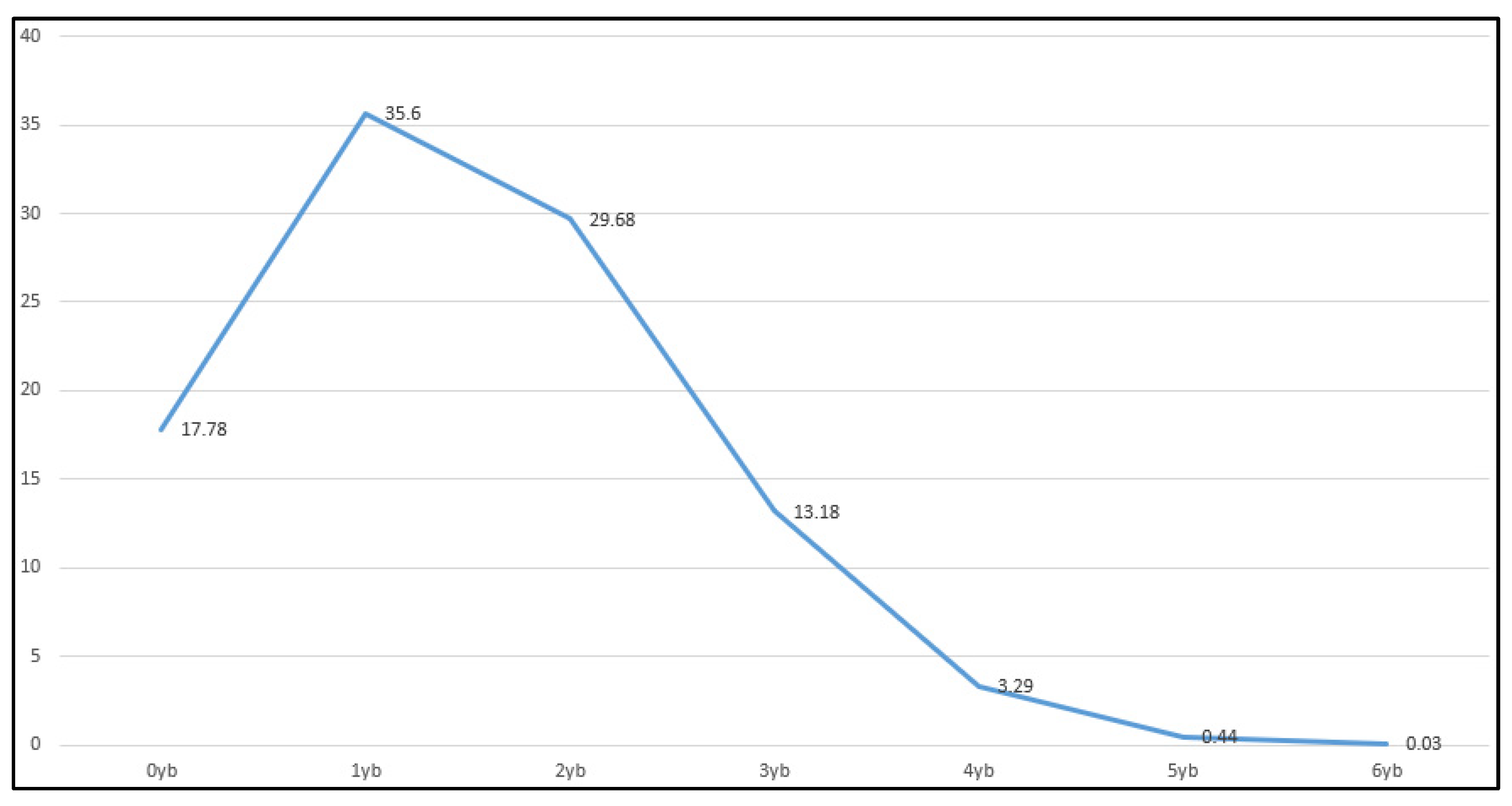
Simple change: Simplicity means simplifying the complicated truth. One Yin and one Yang are called Dao. Yin and Yang are the Dao, and the Dao is also simple, so called “the Dao is simple”. Simplicity is like a simple formula in mathematical science. Although the objective world is very complex, laws can be expressed through simple symbols. Simplicity also expresses the laws of the universe through simple Yin and Yang and several symbols. From the statistical analysis of big data, it can be found that simple changes have absolute advantages. The probabilities from one dynamic line to three dynamic lines are 35.60%, 29.68% and 13.18% respectively, and the total is close to 80%. This result shows that the normal state of everything in the world is in simple change.
Difficult change: Change means that things in the world will change. “Dao begets one.One begets Two.Two begets Three. Three lives and all things of creation “ comes from Laozi《Dao De Ching》. 《Dao De Ching》is Lao Tzu’s theory of cosmogenesis. In Eastern culture, more than three means more. The four dynamic lines and above of a hexagram are more changes and more changes are difficult change. The total probability from four to six dynamic lines is about 3%. This result shows that the proportion of sudden changes of events is very low, and the overview of extreme events is very low, but the result of mutation will lead to qualitative changes. So qualitative changes are difficult change too.
From the analysis of the above results, it can be found that 80% of the event probability is in a simple change, the extreme mutation probability accounts for a very small proportion, and the constant proportion is about 17%.This may be the basic characteristic law of the world reflected by the changes of the six lines.According to the three-point reasoning of I Ching, event changes can be divided into three states: unchanged, general changes and extreme changes. This change is a partial normal curve. See
Figure 3.
In addition, in terms of the proportion of each line, one line accounts for the largest proportion (more than 1/3) among many lines, which shows that in the analysis of changes in things, it is of great reference value to choose a starting method with only dynamic line.
3.2. Basic Characteristics of Line(Yao) Change: Balance of Yin and Yang
Using the method of three coins to start divination, we can get the probability of the occurrence of the four images (Laoyang, Laoyin, Shaoyang, Shaoyin) in I Ching, namely 12.51%, 12.50%, 37.49%, and 37.51%.The occurrence probability of Yin and Yang lines is equal, both 50%. The occurrence probability of Laoyang is equal to that of Laoyin, and the occurrence probability of Shaoyang is equal to that of Shaoyin. The result of the three coins’ divination method is that the ratio of Laoyang to Laoyin is 1:1, which just confirms the conclusion of ancient scholar Xiang Zongsan that the ratio of Laoyang to Laoyin is close to 1:1 according to “Zuo Zhuan” and “Guo Yu” [
6].
3.3. Basic Characteristics of Hexagram Change: Small Probability Certainty and Large Probability Uncertainty
One billion random hexagram divinations were made, and the maximum and minimum conversion probabilities of 64 hexagrams were calculated. Three obvious results can be obtained: (1) The minimum probability corresponds to the hexagrams at both ends of the diagonal of the 64*64 hexagram matrix, and they are each other’s minimum conversion probability hexagrams. For example, the lowest change probability of the kun is the Qian; The minimum change probability of the Bo is the Guai. See Figure 6. (2) The hexagram with the maximum change probability of each hexagram must have two hexagrams of its nearest neighbor in the 64 hexagram matrix. For example, the maximum conversion probability of the Kun includes the Fengdi Bo and the Difeng Qian, while the maximum conversion probability of the Qian includes the Zetian Guai and the Tianze Lv. (3) Other hexagrams with high probability of changing hexagrams are generally in 1, 2, or 3 positions at the center of the hexagram. For example, the maximum probability of changing the hexagram of Li Weihuo is not only Leihuo Feng and Huofeng Shike, but also Tianhuo Tongren and Huotian Dayou that are separated by one, and Huoshan Lv and Sahnhuo Bi that are separated by three. This images show that in the process of the change of 64 hexagrams, there are usually multiple hexagrams that may occur in one hexagram, which also shows that the change of things has obvious uncertainty.
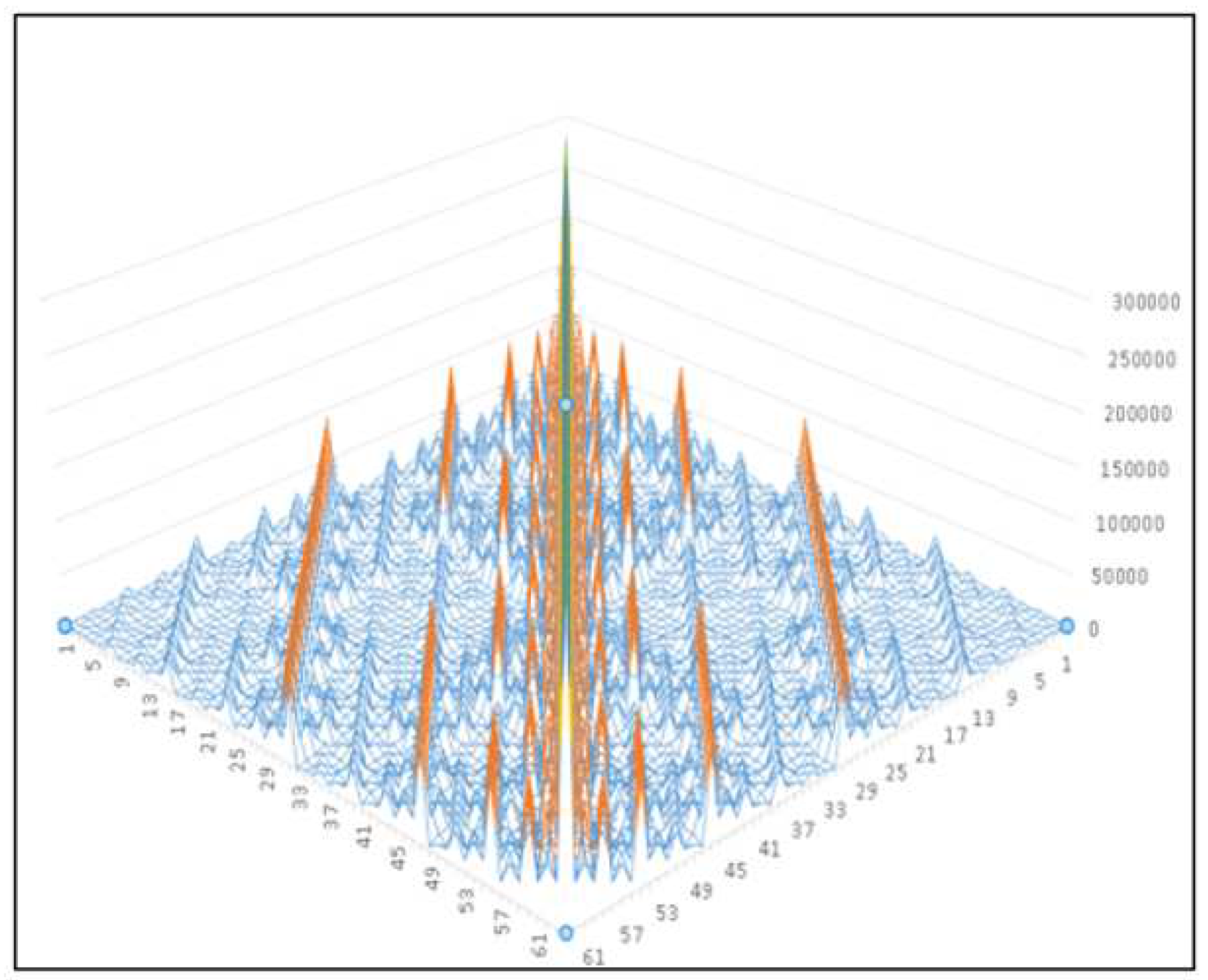
3.4. 64 Hexagram Topographic Map: Fractal Geometric Characteristics
Considering that once the hexagram is determined, no matter whether there is a dynamic line or not, the mutual hexagram, the wrong hexagram and the comprehensive hexagram are determined. Therefore, no further statistical analysis will be made. According to the statistics of the relationship between original hexagram and the changed hexagram, and drawing with the help of the representation of topographic map. It is found that the topographic map with the probability of change hexagram has the characteristics of axial symmetry and fractal geometry after 1 billion random hexagram divinations by coin toss method. The fractal geometric characteristics mainly show that the changes on both sides of the symmetry are presented based on the triangle background.See Figure 7.
4. Conclusions
I Ching, which has been circulating for thousands of years in Chinese civilization, has become the common cultural heritage of the world. Exploring the “Dao” of this cultural heritage will be the common task of scholars all over the world. The development from theology to philosophy and then to science has promoted the continuous evolution of human society. However, in addition to bringing endless benefits to people, the scientific era also brings huge technological traps to people. How to use the ancient civilization thought to guide human society to enjoy the benefits and human progress brought by the new civilization, and avoid bringing more negative harm to mankind. So far, there is no good answer. This paper starts from the study of the divination of the ancient book “Book of Changes”, which has been the basic function of divination for thousands of years, and discusses the various characteristics or laws of changes that may exist in it.
With the help of big data and statistical analysis methods, this paper has obtained some enlightening results:
- (1)
Changes of things are mostly simple changes. The probability of 1 billion randomly generated hexagrams from one to three dynamic lines is close to 80%. This result shows that the normal state of everything in the world is in simple change.
- (2)
About 17% of the hexagrams have no dynamic lines, which means that the number of hexagrams without dynamic lines accounts for less than 1/5 of the total number of variable hexagrams.
- (3)
Small probability certainty and large probability uncertainty. According to the statistical law of changes in I Ching, the probability of the occurrence of the absolute changing hexagram is very small, with relative certainty. There are many kinds of probability of changing the hexagram in general change, and more uncertainties appear. Among these uncertainties, there is relative certainty. This is the large probability of changing hexagram, which must include the two closest hexagrams.
- (4)
After generating 1 billion hexagrams at random, the topographic map with the probability of changing hexagrams has axial symmetry and fractal geometric characteristics, and the fractal characteristics are mainly manifested in that the changes on both sides of the symmetry are presented based on the triangle background.
From the perspective of the maximum and minimum conversion probabilities and the geometric figure of changing hexagrams corresponding to this hexagram, the divination of I Ching itself is a random phenomenon, and the possibility of any one of them is 1/4096.If we add 450 hexagram words and lines words in I Ching, it can cover all stages of the whole operation process [
5]. In fact, it is also the use of the overall sample to infer the development and change of an individual’s social personnel events, which also reflects the full sample thinking of big data.Today, we still have a superficial grasp of the theory and methodology of I Ching, and we cannot really peel off the scientific elements of this divination. However, we believe that in the modern society where big data and artificial intelligence, especially GPT, are developing by leaps and bounds, people’s scientific understanding and scientific grasp of I Ching will increasingly become a reality, and even its scientific application value will radiate amazing brilliance for today’s society.
References
- Yang, Le. ”Synchrony” and Hyperpsychology. Journal of Lvliang Institute of Education, 2011,28 (03): 5–6.
- Storm L., A. . Parapsychological Investigation of the I Ching: The Relationship Between PSI, Intuition, and Time Perspective. The Journal of Parapsychology, 2006, 70(1): 121.
- Jia Lijun, Xu Yun, He Dahao. From the physical Big Data to the Metaphysical I Ching: on the Different Paths and the Same Destination of Scientific Research Paradigms. Science and Management, 2022,42 (04): 66–73.
- Lan Ping. ChatGPT on I Ching at Six Levels, International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Publications, 2023,5(9):173–183.
- Chen, C.L.P. , Zhang T., Chen L., Tam S.C.. I-Ching Divination Evolutionary Algorithm and its Convergence Analysis, IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017,47(01):2–13. [CrossRef]
- Ma Baoping. Distribution Rules for the Number of Hexagrams in I Ching, Journal of Lanzhou Commercial College,1994,(04):75–78+84.
- Tang, Yi. Monte Carlo Simulation of the 64 hexagrams in I Ching. Northern Essays, 2017,(05): 43–46.
- McKenna T K, McKenna D J. The invisible landscape: Mind, hallucinogens, and the I Ching. Harper San Francisco, 1993.
- Wu Hongbin. Research on Divination Value of I Ching. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Social Science Edition), 2018,26 (06): 88–93.
- Chen, C.L.P. , Zhang T., Chen L., et al. I-Ching Divination Evolutionary Algorithm and its Convergence Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016:1–12. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Qingyu. The Intricate Invariant Group and the Sequence Structure of San Gua. Philosophical Research, 2000,(12): 68–72+77.
- Zhu Xi, Zheng Yuanding. Enlightenment of I Ching. Hualing Publishing Press. 2015.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).