1. Introduction
The Covid-19 pandemic posed a significant challenge to the immune system of the human population [
1]. The emergence of the novel SARS-CoV-2 virus in early 2020 unleashed a worldwide crisis faced by an entire vulnerable population without preexisting immunity tow this new infectious agent [
2]. Over the subsequent three years (2020-2022), a dynamic interplay occurred between the evolving protective immunity of the population and the viral agent. This interplay resulted in a progressive increase in the population's immunity against the virus, starting from nearly zero in early 2020 and reaching over 90% by the end of 2022 [
3,
4].
During the first year of the pandemic, the population's immune protection against the SARS-CoV-2 virus relied exclusively on natural infection. However, from the early months of 2021, mass vaccination campaigns using vaccines developed in record time in 2020 played a pivotal role in rapidly augmenting the protective immunity against the virus [
5].
The relationship between vaccination and natural immunization and the methodological aspects of vaccination, such as the number of vaccine doses and their administration intervals, have been the subject of many studies, considering their importance in delineating optimal vaccine strategies [
6,
7]. The contributions of infection and vaccine-induced immunization varied across different countries and populations, contingent upon vaccine availability, the intensity of vaccination campaigns, and the extent of population exposure to the virus [
8,
9]. Therefore, studying these indicators in different countries and populations is particularly important.
Since the onset of 2020, our research has been focused on studying the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 in the Albanian population, and we have carefully monitored the population's seropositivity progression throughout the three years of the pandemic [
10,
11]. Here we report analyses of the humoral immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 Spike-1 and anti-Nucleoprotein antigens in July-August 2021 and 2022.
Albania is a middle-income country in Eastern Europe, with comparatively low SARS-CoV-2 vaccination coverage and a relatively high true pandemic toll [
12]. Our primary objective in this study is to investigate the interaction between vaccination status (including the number of vaccine doses) and natural immunization in generating a seropositivity rate and antibody levels. We apply these antibody parameters as indicators of immunity in the general population and observe them in different exposure categories. These findings can contribute to developing strategies necessary to sustain a durable protective immunity against COVID-19 within the Albanian population, which can also be applied in middle-income societies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection Procedures
This study uses a repeated cross-sectional design. Two independent samples from the Albanian general population, comprising all age groups, were studied in July-August of 2021 and 2022 to assess seroprevalence in the Albanian general population. Participants were randomly selected from digital population registries associated with four primary healthcare centers (H.C.s) in Tirana and one in Berat City, collectively providing healthcare services to approximately 281,600 residents.
Healthcare professionals of these H.C.s were directed to select roughly 100 non-related individuals from each of the five age ranges (0-15 years, 16-30 years, 31-45 years, 46-60 years, and ≥61 years) in a randomized way. Individuals were invited to partake in the study via phone calls and were asked to visit the H.C.s to provide a blood sample and complete an interview once they consented to participation and laboratory testing.
Information concerning participant demographics, health status, symptoms, and data about COVID-19 infection in the past and vaccination history were gathered using a standardized questionnaire. For participants younger than 18 years, parents provided the necessary information. Blood samples were then sent to the Laboratory of Immunology of the University Hospital Center of Tirana for serological analysis.
To ensure sufficient numbers of participants in younger age categories, children aged 0-15 visiting the hospital for non-infectious diseases were also recruited. The 16-30 age category was bolstered with randomly selected high school and university students from a separate sample.
2.2. Serological Assessment of IgG Class Anti-Spike (S1) and Anti-Nucleoprotein (N) SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies
The dependent variable in this study is the immune response measured by anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody parameters. Each blood sample underwent serological testing via an ELISA method, utilizing two commercially available diagnostic kits (IgG Anti-S1-SARS-CoV-2 and IgG Anti-NCP-SARS-CoV-2 ELISA, Euroimmun, Luebeck, Germany) for the identification of SARS-CoV-2 anti-S1 and anti-N IgG antibodies, respectively. According to the manufacturer, these kits demonstrate a sensitivity and specificity of 94.4% and 99.6% for IgG anti-S1-SARS-CoV-2 and 94.6% and 99.8% for IgG anti-N-SARS-CoV-2. Results from both kits were evaluated quantitatively by calculating the optical density ratio of the sample compared to a calibrator (Index Ratio or I.R.), following the manufacturer's guidelines. A serum sample was considered seropositive if the I.R. was greater than 1.1 for either antibody type. Primary endpoints included seropositivity rates (applying the 1.1 I.R. cutoff) and I.R. levels of IgG anti-S1-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in serum samples.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Independent variables related to immunity, such as history of past COVID-19 infection and vaccination status, along with demographic data, were used to establish key categories. Differences in antibody levels (measured as proportions and medians) across each category were examined using the chi-square test for categorical variables and the Student's t-test for continuous variables. When the variable distribution was not normal, the Mann-Whitney test was employed. The significance level for all statistical analyses was set at 0.05. Analyses were stratified by age categories. All data were analyzed using MedCalc® Statistical Software version 20.210 (MedCalc Software Ltd, Ostend, Belgium;
https://www.medcalc.org; 2022).
2.4. Ethics Statement
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Albanian Academy of Sciences (Project number 33-07-05-2020), and all participants provided informed written consent before enrollment in the study.
3. Results
In July-August 2021, 1716 individuals were included in the study, with an age range of 4-97 years and a median age of 52 years (95% CI 51-52 years). In July-August 2022, another cohort of 1899 individuals was enrolled using the same methodology, with a median age of 48 (95% CI 47-50 years) and an age range of 1 to 87 years. Demographic characteristics and information on SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccine-induced immunization are summarized in
Table 1.
3.1. Anti-S1 and anti-N Immune Response among Unvaccinated Individuals in 2021 and 2022
In August 2021, 56.5% of the individuals included in the study were unvaccinated, while in August 2022, 31.2% reported no prior vaccination. The rates of past COVID-19 infection were similar among the unvaccinated individuals in both years, with 54.1% and 51.4% in 2021 and 2022, respectively. However, as expected, the average interval time since the previous COVID-19 infection was 36.1% higher in 2022 compared to 2021 (p<0.0001) (
Table 1).
In 2022, the rate of anti-S1 seropositivity among unvaccinated individuals was 18.7% higher than in 2021 (p<0.0001), and the I.R. level of these antibodies was 2.28 times higher (
Table 2). Similarly, the rates of anti-N seropositivity and antibody levels in 2022 were 14.5% (p<0.0001) and 70% higher, respectively, compared to 2021 (
Table 3).
3.2. Vaccination Data in All Individuals Receiving at Least One Vaccine Dose in 2021 and 2022
In August 2022, there was a 27.3% increase in the number of individuals who had received at least one vaccine dose compared to the same period in 2021 (
Table 1). In terms of the type of vaccines received, in 2021, 43.9% of them had received the CoronaVac vaccine, 39.9% BioNTech/Pfizer (Comirnaty), 18.0% AstraZeneca (Vaxzevria), and 2.1% Sputnik V. One year later 64.8% of individuals had been vaccinated with BioNTech/Pfizer, 19.6% with CoronaVac, 13.8% with AstraZeneca and 0.9% with Sputnik V. Among those vaccinated in 2022, the time interval since the previous COVID-19 infection was approximately twice as long compared to 2021 (
Table 1).
3.3. Anti-S1 and anti-N Immune Response among Individuals Who Had Received Only One Vaccine Dose
In August 2021, 7.9% of the individuals included in the study had received only one first dose of the vaccine, on average, 36 days earlier (
Table 1). One year later, in August 2022, only 3.6% of the cohort reported receiving only one vaccine dose, on average, 330 days earlier. The 2022 group had 14.2% more past COVID-19 infections than those who received only one vaccine dose in 2021, but the difference was not statistically significant (p=0.095). This group had 18.6% significantly higher anti-S1 seropositivity (p=0.0007) (
Table 2). Moreover, this group's average level of anti-S1 antibodies was 53.0% higher (p<0.0001). Similarly, the anti-N seropositivity was 24.4% higher (p<0.0001), and the level of these antibodies was 2.3 times higher compared to 2021 (
Table 3).
3.4. Anti-S1 and anti-N Immune Responses among Individuals Who Had Received Two and Three Vaccine Doses
In 2022, the percentage of individuals who had received two vaccine doses was 12.4% higher compared to 2021 (p<0.0001). The average time interval from receiving the second dose was 299 days in 2022 compared to 46 days in 2021, and the same time interval since the previous COVID-19 infection was 90% higher in 2022. Also, the rate of individuals reporting symptomatic COVID-19 infection was 18.8% higher (p<0.0001) (
Table 1).
The anti-S1 seropositivity rate in the two doses vaccine group of the 2022 cohort was moderately higher than in 2021 (95.2% versus 91.7%, p=0.0015), as well as the mean antibody level (7.1 versus 6.3, p<0.0001) (
Table 2). Also, the anti-N seropositivity and antibody levels were consistently increasing in 2022 compared to 2021; on average, they were respectively 28.6% and 3.7 times higher (p<0.0001) (
Table 3).
In August 2022, 19.1% of the individuals in this cohort had received a third vaccine dose, 169 days earlier on average. The rate of previous COVID-19 infection was similar to those who had received the second dose (p=0.384) (
Table 1). Also, the seropositivity of anti-N antibodies showed no significant changes (p=0.218) (
Table 3).
3.5. The Dynamics of anti-S1 Seropositivity and Antibody Levels among Groups of Individuals with Different Vaccination Statuses in 2021 and 2022
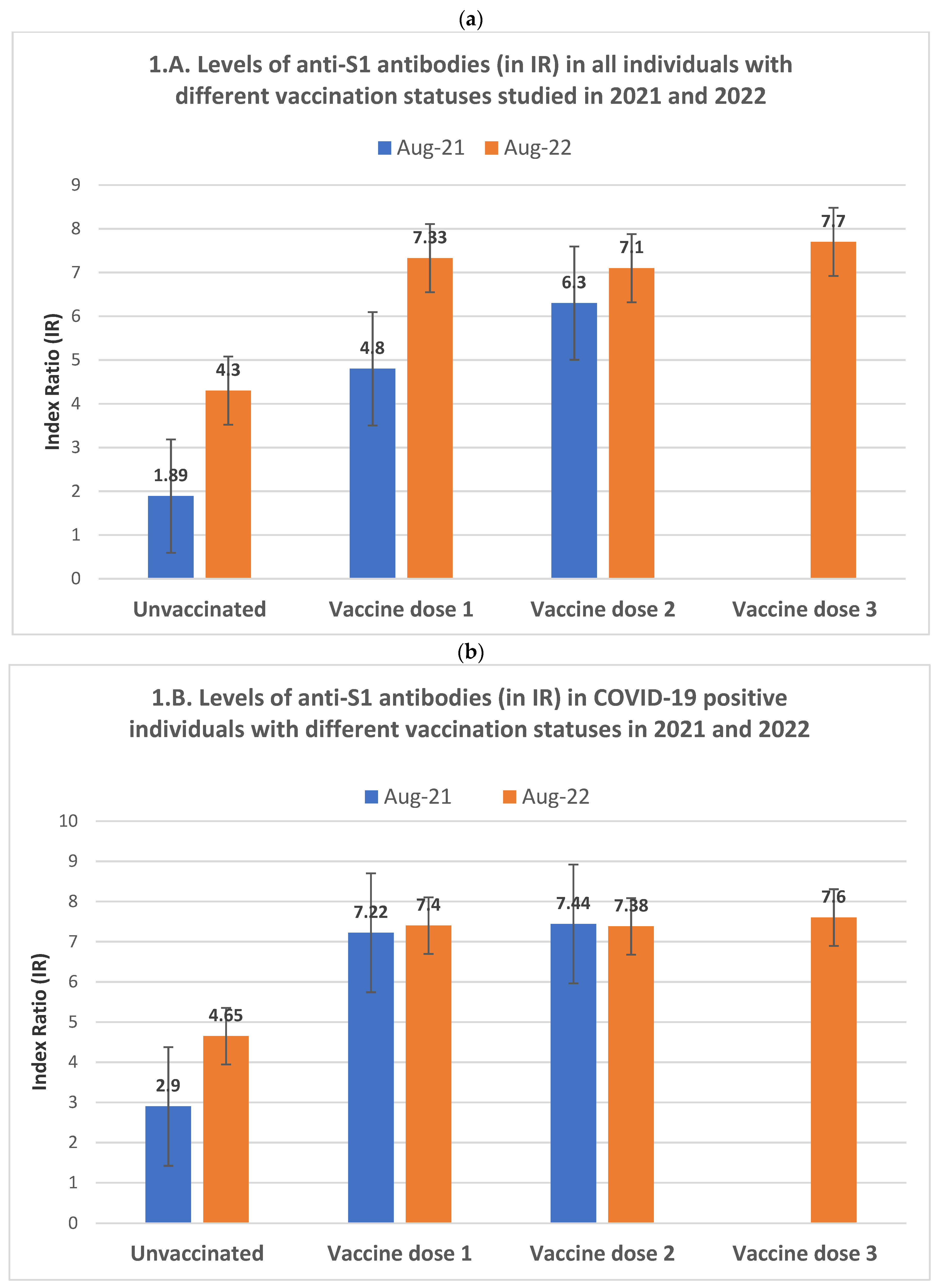
While both anti-S1 seropositivity rates and antibody levels in 2022 were higher than those of 2021 across all the vaccination status categories, there are differences between immunity profiles in 2021 and 2022. In the 2021 cohort, anti-S1 seropositivity and the average antibody levels increased almost uniformly from the unvaccinated group to those with one vaccine dose, reaching the highest values in double-vaccinated participants (
Table 2). This dynamic pattern of seropositivity and antibody levels differed in the 2022 cohort, where the maximum average values were already reached in individuals who received only one vaccine dose. Their antibody levels did not differ significantly from those with two vaccine doses in the same year (
Figure 1A).
Among the individuals in the 2022 cohort who received three vaccine doses, the anti-S1 antibody increase was statistically significant compared to those with two vaccine doses (p=0.002 and p<0.0001 for seropositivity and antibody levels, respectively) but not significant compared to those who received only one vaccine dose, probably due to the limited number of individuals in the latter group (
Table 2).
3.6. Influence of Previous COVID-19 Infection in the Relationship between Vaccination and Immune Response
The reported symptomatic COVID-19 infection rate was 57.5% in the 2022 cohort compared to 49.1% in 2021 (p<0.0001).
Among unvaccinated individuals, despite the rates of reported past COVID-19 infections being very similar in the 2021 and 2022 cohorts (
Table 1), there was a significant increase in both anti-S1 and anti-N antibodies in 2022 compared to 2021. This increase was considerably more pronounced among COVID-19 (-) individuals than among COVID-19 (+) (
Table 2).
In August 2021, the increase in anti-S1 seropositivity and antibody levels among vaccinated COVID-19 (-) individuals was proportional to the number of vaccine doses, similar to the dynamic observed in the general 2021 cohort (
Table 2). However, this dynamic differed in the same year's COVID-19 (+) group, where we observed that both anti-S1 seropositivity and antibody levels, likely in the 2022 cohort, had already reached their maximum average level in individuals with only one dose of the vaccine (
Figure 1B). No significant difference existed between them and those who received two vaccine doses (
Table 2).
COVID-19 (+) individuals of the 2022 cohort who had received the two doses of the vaccine presented a higher anti-S1 response than the same year COVID-19 (-) individuals with two vaccine doses (p=0.01 and p=0.002, respectively, for seropositivity and antibody level). Similarly, among the COVID-19 (-) individuals of the 2022 cohort who received a third vaccine dose, the anti-S1 antibody response was significantly higher than in those who received two vaccine doses (p=0.01 and p<0.0001 for seropositivity and level of antibodies, respectively). However, for COVID-19 (+) individuals, the corresponding values presented a relatively small statistical significance for the seropositivity rate (p=0.034) and were nonsignificant for the antibody levels (p=0.177). Similarly, no differences were observed between COVID-19 (+) and COVID-19 (-) groups that received the third vaccine dose (
Table 2).
3.7. Relationships of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies with Vaccination Status and Age of Individuals 60 and under (≤ 60 yrs) or 61 and over (≥ 61 yrs).
In August 2021, the anti-S1 seropositivity rate and antibody levels were 11.7% and 77.8% higher among ≥61 yrs unvaccinated individuals than those ≤ 60 yrs (p=0.0006 and p<0.0001, respectively,
Table 2). This difference was not observed in the 2022 cohort. The anti-N seropositivity and antibody levels were also significantly higher in the unvaccinated ≥ 61 age group than those ≤ 60 in both studied years (
Table 3). In August 2022, the average level of anti-S1 antibodies in the ≥61 age group who had received two vaccine doses was 46.8% higher than in the same age group in 2021 (p<0.0001), whereas the seropositivity rate was similar. These differences in the level of anti-S1 antibodies were not observed in the ≤60 age group, where both seropositivity and antibody levels were very similar in 2022 compared to 2021. In the 2022 cohort, the ≤60 group reached their average maximum anti-S1 antibody level with a single vaccine dose, while in the same cohort, the ≥61 group reached its highest level only after two and three vaccine doses (
Table 2). In August 2022, in the ≤60 age group who received a third vaccine dose, the increase in anti-S1 seroprevalence compared to the two-dose vaccine group was not statistically significant (p=0.084). However, the mean antibody level exceeded the significance threshold (p=0.002). Conversely, in the ≥61 age group, the seroprevalence rate increase between the second and the third doses was highly statistically significant (p=0.00011). Still, the increase in the level of antibodies did not reach the significance threshold in this group (p=0.105).
3.8. Particularities of Anti-N Seropositivity Rates and Antibody Levels Versus Vaccination Statuses by Year
The dynamics of anti-N antibodies over time differed from that of anti-S1 antibodies. In 2021, anti-N seropositivity rates and mean antibody levels were lower in individuals who received two doses of the vaccine than those who were not vaccinated (p<0.0001 and p<0.0001, respectively). However, in 2022, these levels remained unchanged among the groups of individuals with different vaccine doses (
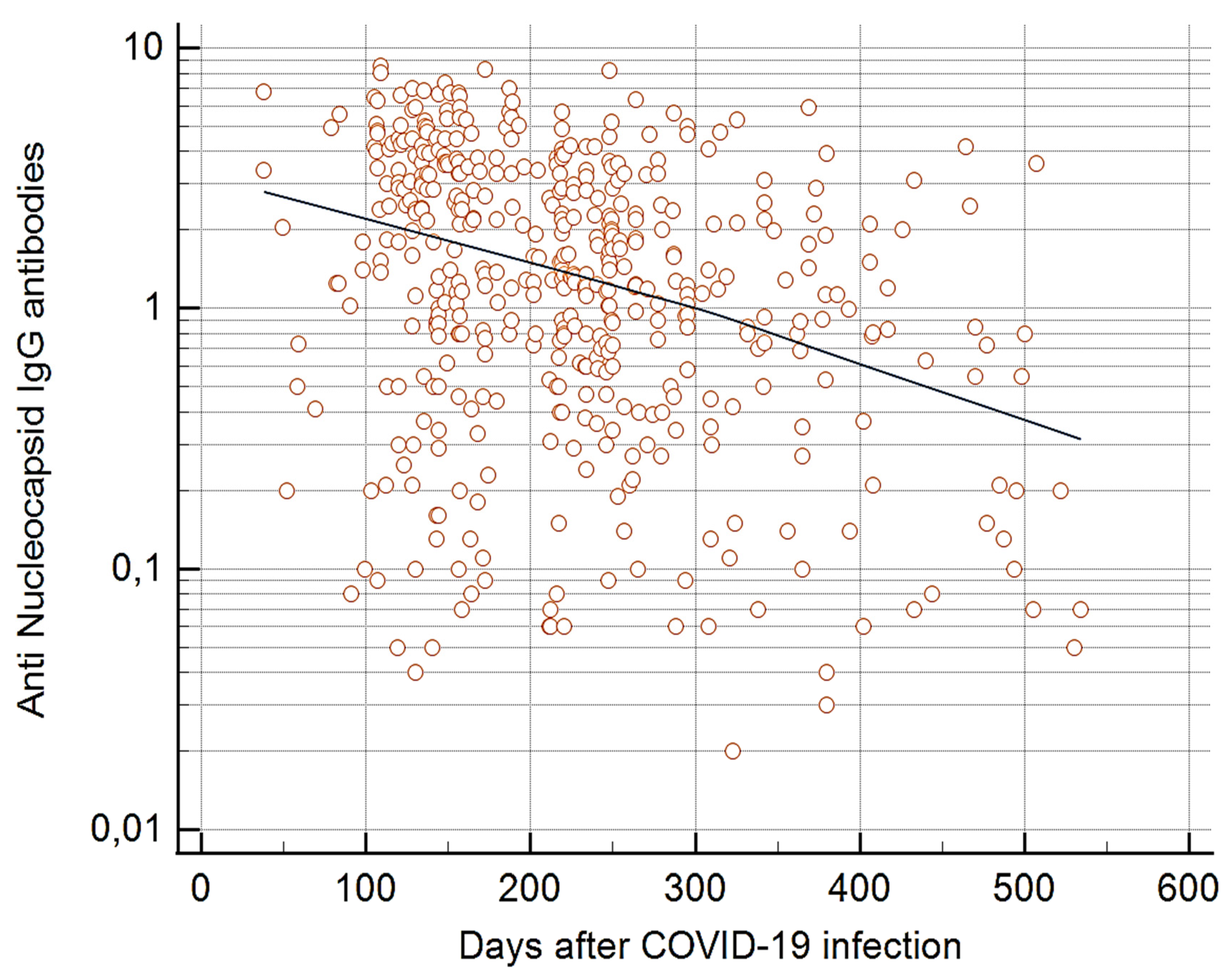
Table 3). In analyses of the level of anti-N antibodies and the time interval since COVID-19 infection, a significant inverse relationship was seen in 2021 (p<0.0001) (
Figure 2) but not in 2022. In contrast, no such association was seen in either year between the level of anti-S1 antibodies and the time interval since the previous COVID-19 infection.
4. Discussion
In this paper, we present the results of our study on the anti-S1 and anti-N humoral immune response in different individuals in the Albanian population with varying vaccination status. The study was conducted in two independent cohorts from the general population, with a one-year interval between July-August 2021 and July-August 2022.
Through August 2021, the Albanian population experienced three COVID-19 waves; the first two were with the original Wuhan virus variants, and the third with the alpha variant. In September 2021, the delta variant caused a fourth wave, followed by two consecutive waves from the beginning of 2022 until August 2022, caused by Omicron variants, which have largely passed at the time of this writing.
The rate of past symptomatic infection was 51.4% in the unvaccinated group of the 2022 cohort. Moreover, asymptomatic infections have been found in 42.3 % of the older than 20 Albanian population [
11]. Despite these findings, in the unvaccinated individuals of July-August 2022, the median anti-S1 seropositivity was 80.1%, while in all vaccinated individuals, comprising approximately 70% of the sample population, the seropositivity ranged from 95% to 99%. These data demonstrate that vaccination was crucial in reaching the population's collective immunity threshold [
13,
14], and it appears to have contributed significantly to controlling COVID-19 transmission in Albania, as no epidemic waves have been observed in Albania since September 2022 [
15].
Among the unvaccinated individuals in both the 2021 and 2022 cohorts, the rates of past symptomatic COVID-19 infections were similar. However, from 2021 to 2022, a more significant increase in seropositivity and antibody levels was observed in the COVID-19-negative unvaccinated individuals than in COVID-19-positive unvaccinated individuals. This finding seems to be attributed to the accumulation of non-reported asymptomatic (or quasi-symptomatic) COVID-19 infections during the last year of the pandemic [
16].
The higher anti-S1 and anti-N seropositivity among the ≥61 old unvaccinated individuals in 2021 compared to the ≤60 age group suggests that older Albanian individuals had high exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus during the early stages of the pandemic. This finding contrasts with a U.S. study reporting that persons aged ≥65 years were better protected from COVID-19 infection than younger people [
17]
. However, by August 2022 in Albania, exposure to the virus had leveled off among the two age groups.
Among the vaccinated individuals of the 2022 cohort, seropositivity and the levels of anti-S1 antibodies were comparable between individuals who received one and those who received both vaccine doses, which is not found in the 2021 cohort. This finding seems to result from the increased rate of individuals with past COVID-19 infections among the vaccinated in August 2022, compared to the previous year.
The presence of hybrid immunity, combining natural infection and vaccination, likely contributed also to the robust immune response observed in the COVID-19-positive individuals with only one vaccine dose in 2021 who had the same seropositivity rates and antibody levels as the same group of the 2022 cohort. The effect of hybrid immunity in generating a strong immune response has been shown in many studies [
18,
19,
20]. However, we have not encountered any other report demonstrating this effect in two different cohorts of the general population studied at a one-year interval between 2021 and 2022.
The impact of past COVID-19 infection on the amount of the immune response is clearly shown in the ≥61 age group who had received two vaccine doses. Although in the 2022 cohort, the anti-S1 seropositivity rate in this age group was not different from that of 2021, the level of anti-S1 antibodies was significantly higher compared to 2021. This finding has to be attributed to the higher rate of past COVID-19 infections in this age group, also confirmed by the seropositivity in anti-N antibodies, which was twice as high in this age group in 2022 compared to 2021.
In the ≤60 age group of 2022, the increase in seropositivity from the second to the third vaccine dose was insignificant, while the level of antibodies showed a significant increase. Conversely, in the ≥61age group who received a third vaccine dose, a significant increase was observed in seropositivity but not in the level of antibodies. Further, the ≤60 group of the 2022 cohort who received only a single vaccine dose showed comparable anti-S1 seroprevalence and antibody levels as those of the same age group receiving two or three vaccine doses. In the same year, individuals ≥61 reached this levels only after two vaccine doses. These findings confirm that individuals ≥61 have a more limited ability to generate a high humoral immune response [
21,
22].
Interestingly, the time elapsed from the previous COVID-19 infection or last vaccine dose did not play a significant role in the amplitude of the humoral immune response. The immune response remained robust despite the longer intervals between infection and vaccination in 2022 compared to 2021.
This finding
supports other studies reporting
that protection from only vaccination can
decrease over time, but vaccination after infection can maintain significantly higher antibody titer levels for a prolonged period [
23,
24].
The presence of anti-N antibodies indicates a natural SARS-CoV-2 infection [
16]. However, in the 2021 and 2022 cohorts, anti-N antibodies demonstrated lower sensitivity than anti-S1 antibodies. This finding is clearly shown among the unvaccinated individuals, in whom the anti-N seropositivity rates were in the 2021 and 2022 cohorts, respectively 17.0% and 21.2% lower than the corresponding anti-S1 seropositivity rates. The levels of anti-N antibodies also decreased over time, which is reported by other authors [
25].
It is important to acknowledge the limitations of our study, which is not a full longitudinal design or a controlled cohort. Due to the low number of vaccinations among individuals under 16, we could not study the antibody response according to vaccine doses in this age group. Our study focused on measuring the humoral immune response through anti-S1 and anti-N antibodies, not virus-neutralizing ones. Furthermore, we did not collect data on post-vaccination COVID-19 infections.
To our knowledge, no other reports, particularly in Eastern Europe, have demonstrated the role of hybrid immunity in generating anti-S1 and anti-N immune responses in relation to vaccination status and vaccine doses within the general population studied prospectively during the course of the pandemic.
In conclusion, our population-based seroepidemiological data confirm previous memory B-cell-based studies, reporting that in individuals with prior COVID-19 infection, one vaccine dose can be sufficient to generate a high-level immune response comparable to those receiving two doses [
26]. However, to achieve optimal protective levels of anti-S1 antibodies in individuals over 60 and those with immune deficiencies, a second and perhaps a third booster dose are necessary at intervals longer than the usual four weeks after the first dose to obtain a sufficiently protective level of immunity. Our findings may contribute to a better understanding of the dynamics of humoral immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 and improve vaccination strategies for COVID-19 control in the Albanian population. The specific patterns of immunity shown here should be evaluated in other countries if adequate population-based age-specific data are available.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.S., A.Y., F.C. and M.J.P. ; Methodology, G.S., A.Y., F.C., I.S.Q., M.K.P., E.S., E.L. and J.D.P; Software, G.S., F.C., and A,Y,; Validation, G.S., F.C., A,Y. and M.K.P.; Formal analysis, G.S., A.Y., F.C., I.S.Q., M.K.P., E.S., E.L., J.D.P and M.J.P; Investigation, G.S., A.Y., F.C., I.S.Q., M.K.P., E.S., E.L and J.D.P; Resources, G.S., A.Y., F.C., I.S.Q., M.K.P., E.S., E.L. and J.D.P; Data curation, G.S., A.Y., F.C., I.S.Q., M.K.P., E.S. E.L. and J.D.P; Writing—original draft preparation, G.S., A.Y., F.C., I.S.Q., M.K.P., E.S. and M.J.P.; Writing—review and editing, G.S., A.Y., F.C., M.K.P. and M.J.P.; Visualization, G.S., A.Y., F.C., I.S.Q., M.K.P., E.S. E.L. and M.J.P.; Supervision, G.S., A.Y., F.C., I.S.Q., M.K.P. and M.J.P; Project administration, G.S. and A.Y; Funding acquisition, G.S. and A.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding information
The study was funded by the Academy of Sciences of Albania and the Francophone University Agency (A.U.F.).
Ethical considerations
The study was approved by decision Nr. 33, May 7, 2020, of the Academy of Sciences of Albania Ethics Committee. Study participants provided written informed consent.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the essential contribution of Bruna Shiroka, Blerta Berberi, Bujar Mema, Ilirjan Gjyzari, Dritan Ulqinaku, Spartak Caka, Adelina Selimaj, Antea Garo and the technical support of the company SwissMed Ltd.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chowdhury MA, Hossain N, Kashem MA, Shahid MA, Alam A. Immune response in COVID-19: A review. J Infect Public Health. 2020 Nov;13(11):1619-1629. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atzrodt CL, Maknojia I, McCarthy RDP, Oldfield TM, Po J, Ta K.T.L., Stepp HE, Clements TP. A Guide to COVID-19: a global pandemic caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. FEBS J. 2020 Sep;287(17):3633-3650. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balloux F, Tan C, Swadling L, Richard D, Jenner C, Maini M, van Dorp L. The past, current and future epidemiological dynamic of SARS-CoV-2. Oxf Open Immunol. 2022 Jun 20;3(1):iqac003. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaassen F, Chitwood MH, Cohen T, Pitzer VE, Russi M, Swartwood NA, Salomon JA, Menzies NA. Changes in population immunity against infection and severe disease from SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants in the United States between December 2021 and November 2022. Clin Infect Dis. 2023 Apr 19:ciad210. 20 December. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey RA, Rassen JA, Kabelac CA, Turenne W, Leonard S, Klesh R, Meyer WA 3rd, Kaufman HW, Anderson S, Cohen O, Petkov VI, Cronin KA, Van Dyke AL, Lowy DR, Sharpless NE, Penberthy LT. Association of SARS-CoV-2 Seropositive Antibody Test With Risk of Future Infection. JAMA Intern Med. 2021 May 1;181(5):672-679. 1 May. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashte S, Gulbake A, El-Amin Iii SF, Gupta A. COVID-19 vaccines: rapid development, implications, challenges and future prospects. Hum Cell. 2021 May;34(3):711-733. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feikin DR, Higdon MM, Abu-Raddad LJ, Andrews N, Araos R, Goldberg Y, Groome MJ, Huppert A, O'Brien KL, Smith PG, Wilder-Smith A, Zeger S, Deloria Knoll M, Patel MK. Duration of effectiveness of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease: results of a systematic review and meta-regression. Lancet. 2022 Mar 5;399(10328):924-944. Erratum in: Lancet. 2022 Apr 4;: Erratum in: Lancet. 2023 Feb 25;401(10377):644. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shioda K, Chen Y, Collins MH, Lopman BA. Population-Level Relative Effectiveness of the COVID-19 Vaccines and the Contribution of Naturally Acquired Immunity. J Infect Dis. 2023 March 28;227(6):773-779. 28 March. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaassen F, Chitwood MH, Cohen T, Pitzer VE, Russi M, Swartwood NA, Salomon JA, Menzies NA. Population immunity to pre-Omicron and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variants in U.S. states and counties through December 1, 2021. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2022 Mar 1:2021.12.23.21268272. Update in: Clin Infect Dis. 2022 June 20. 1 December. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulcebe G, Ylli A, Cenko F, Kurti-Prifti M. Rapid increase of SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence during the 2020 pandemic year in the population of the city of Tirana, Albania.medRxiv 2021.02.18.21251776. [CrossRef]
- Cenko F, Ylli A, Prifti M, Shyti E, Lazri E, Perry MJ, Sulcebe G. Estimating the seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies: Understanding population-level immunity in Albania at the end of the Alpha variant wave. J Glob Health. 2022 July 25;12:03054. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ylli A, Burazeri G, Wu YY, Sentell T. COVID-19 excess deaths in Eastern European countries associated with weaker regulation implementation and lower vaccination coverage. East Mediterr Health J. 2022 October 30;28(10):776-780. 30 October. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson D, Flasche S, Jit M, Kucharski AJ; CMMID COVID-19 Working Group; Centre for Mathematical Modelling of Infectious Disease (CMMID) COVID-19 Working Group. The potential for vaccination-induced herd immunity against the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 variant. Euro Surveill. 2021 May;26(20):2100428. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- langovan D, Hussain SMS, Virudhunagar Muthuprakash S, Devi Periadurai N, Viswanath Nalankilli A, Volvoikar H, Ramani P, Sivasubramaniam J, Mohanram K, Surapaneni KM. Impact of COVID-19 Vaccination on Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 among the Health Care Workers in a Tertiary Care Centre, South India. Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Nov 19;10(11):1967. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COVID-19 Data Repository by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University. National Agency for Information Society. Available online: https://coronavirus.al/statistika/.
- Awartani F, Qutob NM, Asia MR. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies among Vaccinated and Non-Vaccinated Adults in the West Bank: Results of a Repeated Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Aug 17;10(8):1332. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones JM, Manrique IM, Stone MS, Grebe E, Saa P, Germanio CD, Spencer BR, Notari E, Bravo M, Lanteri MC, Green V, Briggs-Hagen M, Coughlin MM, Stramer SL, Opsomer J, Busch MP. Estimates of SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence and Incidence of Primary SARS-CoV-2 Infections Among Blood Donors, by COVID-19 Vaccination Status - United States, April 2021-September 2022. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 June 2;72(22):601-605. 20 April. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang Z, Muecksch F, Schaefer-Babajew D, Finkin S, Viant C, Gaebler C, Hoffmann HH, Barnes CO, Cipolla M, Ramos V, Oliveira TY, Cho A, Schmidt F, Da Silva J, Bednarski E, Aguado L, Yee J, Daga M, Turroja M, Millard KG, Jankovic M, Gazumyan A, Zhao Z, Rice CM, Bieniasz PD, Caskey M, Hatziioannou T, Nussenzweig MC. Naturally enhanced neutralizing breadth against SARS-CoV-2 one year after infection. Nature. 2021 Jul;595(7867):426-431. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg Y, Mandel M, Bar-On YM, Bodenheimer O, Freedman LS, Ash N, Alroy-Preis S, Huppert A, Milo R. Protection and Waning of Natural and Hybrid Immunity to SARS-CoV-2. N Engl J Med. 2022 Jun 9;386(23):2201-2212. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobrovitz N, Ware H, Ma X, Li Z, Hosseini R, Cao C, Selemon A, Whelan M, Premji Z, Issa H, Cheng B, Abu Raddad LJ, Buckeridge DL, Van Kerkhove MD, Piechotta V, Higdon MM, Wilder-Smith A, Bergeri I, Feikin DR, Arora RK, Patel MK, Subissi L. Protective effectiveness of previous SARS-CoV-2 infection and hybrid immunity against the omicron variant and severe disease: a systematic review and meta-regression. Lancet Infect Dis. 2023 May;23(5):556-567. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj V, Gadi N, Spihlman AP, Wu SC, Choi CH, Moulton VR. Aging, Immunity, and COVID-19: How Age Influences the Host Immune Response to Coronavirus Infections? Front Physiol. 2021 Jan 12;11:571416. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer M, Constancias F, Worth C, Meyer A, Muller M, Boussuge A, Kaltenbach G, Schmitt E, Chayer S, Velay A, Vogel T, Fafi-Kremer S, Karcher P. Humoral immune response after COVID-19 infection or BNT162b2 vaccine among older adults: evolution over time and protective thresholds. Geroscience. 2022 Jun;44(3):1229-1240. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelman B, van der Straten K, Lavell AHA, Schinkel M, Slim MA, Poniman M, Burger JA, Oomen M, Tejjani K, Vlaar APJ, Wiersinga WJ, Smulders YM, van Vught LA, Sanders RW, van Gils MJ, Bomers MK, Sikkens JJ; Amsterdam UMC COVID-19 S3/HCW study group. Time since SARS-CoV-2 infection and humoral immune response following BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination. EBioMedicine. 2021 Oct;72:103589. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumley S.F., Wei J., O'Donnell D., Stoesser N.E., Matthews P.C., Howarth A., Hatch S.B., Marsden B.D., Cox S., James T., et al. The Duration, Dynamics, and Determinants of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Antibody Responses in Individual Healthcare Workers. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021;73:e699–e709. [CrossRef]
- Van Elslande, J., Oyaert M., Lorent N., Vande Weygaerde Y., Van Pottelbergh G., Godderis L., Van Ranst M., André E., Padalko E., Lagrou K., et al. Lower Persistence of Anti-Nucleocapsid Compared to Anti-Spike Antibodies up to One Year after SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022;103:115659. [CrossRef]
- Goel RR, Apostolidis SA, Painter MM, Mathew D, Pattekar A, Kuthuru O, Gouma S, Hicks P, Meng W, Rosenfeld AM, Dysinger S, Lundgreen KA, Kuri-Cervantes L, Adamski S, Hicks A, Korte S, Oldridge DA, Baxter AE, Giles JR, Weirick ME, McAllister CM, Dougherty J, Long S, D'Andrea K, Hamilton JT, Betts MR, Luning Prak ET, Bates P, Hensley SE, Greenplate AR, Wherry EJ. Distinct antibody and memory B cell responses in SARS-CoV-2 naïve and recovered individuals following mRNA vaccination. Sci Immunol. 2021 Apr 15;6(58):eabi6950. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).