1. Introduction
Looking back over the past few decades, sepsis, one of the most studied acute and critical diseases has been defined as a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by systemic inflammation and dysregulation of the host's immune response to infection[
1]. To date, although progress has been made in the understanding and management of clinical sepsis, its morbidity and mortality remain high. Has been one of the leading causes of death in hospitals[
2]. Sepsis-induced injury, shock, and multiple organ dysfunction remain the leading causes of death in patients with sepsis and are necessary to understand the pathogenesis of COVID-19 virus sepsis[
3]. The lungs are particularly vulnerable to damage during sepsis, 50% of the time. The main risk factor for acute lung injury in patients is attributed to sepsis[
4]. From the molecular basis of pathogenicity and host response, the continuous exploration of the mechanism and pathogenic factors of sepsis-induced lung injury, and a large number of research results have guided new definitions and new treatment methods[
5,
6].
ALI and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) are common complications leading to acute lung failure, sepsis, and death worldwide, with high morbidity and mortality[
7]. Macrophages recruited and activated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and existing alveolar macrophages can release proinflammatory cytokines, induce neutrophil infiltration, further aggravate inflammation, endothelial barrier destruction, pulmonary microcirculation obstruction, and aggravate lung injury, leading to high mortality in patients with sepsis-induced lung injury[
8]. As an epidemic disease worldwide, it can lead to acute lung failure, pneumonia, interstitial edema, sepsis, and death[
9]. At present, there is no specific treatment process or accurate clinical diagnostic indicators for acute lung injury. It is very difficult to diagnose and treat acute lung injury in clinical practice, which greatly endangers the clinical treatment prognosis and life safety of patients.
This study attempted to use bioinformatics analysis to improve the clinical diagnostic criteria of sepsis patients with ALI. Since the lung is an organ at the highest risk for sepsis involvement, we used gene expression analysis to identify differential genes for ARDS/ALI in a cohort of patients with sepsis. We classified patients as sepsis or sepsis-induced ALI based on whether they had sepsis-induced lung injury, and compared gene expression profiles in each group to identify unique gene molecules that could distinguish the two groups. We use bioinformatics analysis, trying to distinguish based on the differences of gene expression of lung injury caused by sepsis patients and the study of pure sepsis patients search for genetic markers of lung injury caused by sepsis, expect to extract the lung injury induced by sepsis clinical markers, help in the clinical diagnosis of sepsis lung injury and further research in the future.
3. Discussion
The World Health Organization has identified sepsis as a global health priority, characterized by an overreaction to infection. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is the most common severe manifestation of multiple organ dysfunction syndromes, which is an important factor leading to the morbidity and mortality of sepsis[
4,
20]. Key loci play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of sepsis-associated acute lung injury (ALI) or ARDS[
11]. Biomarkers describe measurable indicators of a patient's clinical condition that can be measured accurately and reproducibly. For diagnosis, prognosis, early disease recognition, risk stratification, appropriate treatment (therapeutics), and judgment of trial-enriched biomarkers in patients with sepsis or suspected sepsis[
21]. Early diagnosis is the key to the prevention and control of the disease. Early identification of acute lung injury has always been a difficult point in treatment. More and more markers with high clinical value have been widely used. The development of new diagnostic markers has the role of early identification of diseases, evaluation of diseases, and guidance of clinical treatment, and has a positive impact on the prognosis of patients[
22].
In our study, six potential diagnostic biomarkers and targets for sepsis-induced ALI were screened from the database by bioinformatics analysis. With the development of modern medicine, the early detection and prevention of diseases have become the focus of people's attention. In the development of personalized medicine gene detection, if patients with these six genes can be identified early as disease prevention targets, it will greatly improve the prognosis of patients.
We used GSE10474 to analyze differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between patients with sepsis (sepsis + ALI) and patients without ALI. GSE10474 has been widely used in the analysis of disease markers[
23]. The R package "cluster profile" was used for the functional enrichment analysis of DEGs. Interacting Genes and proteins interaction networks were constructed in the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes and Proteins Interaction (PPI) and visualized by Cytoscape. Predictive analysis of microarray (PAM) was performed by R package "PAMR" to identify diagnostic biomarkers, and the diagnostic ability of diagnostic biomarkers was evaluated by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. In addition, the interaction between diagnostic biomarkers was analyzed by GeneMANIA. We also analyzed the functions of diagnostic biomarkers and predicted their corresponding drugs using Cytoscape plugin BiNGO and Web tool DGIdb. Finally, we analyzed the transcriptional regulation of these diagnostic biomarkers using miRNet, a web-based tool. Sepsis has 71 genes differentially expressed + ALI group, mainly involved in the immune-related biological processes and approaches. The STRING database showed that 31 DEGs had protein-protein interactions. In addition, PAM identified six diagnostic biomarkers from these 31 DEGs, including
HIST1H4H,
CDKN1A,
HMOX1,
NQO2,
RHOB, and
TREM1. ROC curve showed that the diagnostic biomarkers had the good diagnostic ability for sepsis and sepsis + ALI patients. GeneMANIA analysis revealed that many of them share common expressions or interact physically with each other. BiNGO analysis revealed the function of this diagnostic biomarker, which is mainly involved in immune-related biological processes. The DGIdb database showed that
CDKN1A had the largest number of targeted drugs. A total of 114 mins and 11 transcription factors that may be involved in regulating the expression of diagnostic genes were obtained. Finally, six potential diagnostic biomarkers and targets for septicemia-induced ALI were identified.
In our final screening
HIST1H4H,
CDKN1A,
HMOX1,
NQO2,
RHOB, and
TREM1. Previous studies have shown that
HIST1H4H is involved in the pathogenesis of liver tumors[
24].
CDKN1A has been studied more broadly, involving growth, development, and genetics[
25,
26].
HMOX1 is a molecule that has attracted extensive attention in cancer research[
27].
NQO2 has been extensively studied in biochemical and environmental contexts[
28].
RHOB is a gene that encodes human cancers[
29].
TREM1 has been studied extensively in atherosclerotic disease[
30]. These six molecules have been studied in other diseases or biological fields, which are also related to the pathophysiology of sepsis itself. Our study further suggested that among many biomarkers and molecules, these six biomarkers have a closer relationship with sepsis, which is worthy of further study. Previous studies will also help us to carry out subsequent molecular biology experiments, laying a certain foundation for further verification of the relationship between the six biomarkers and sepsis-induced lung injury[
31,
32,
33].
Accurate, early, disease diagnosis is helpful and important to the prognosis of patients. At present, in the articles on sepsis-induced organ damage, more studies focus on finding biomarkers in sepsis-related renal injury[
34,
35]. In contrast, the studies on sepsis-induced lung injury are more focused on pathogenesis, and the studies on biomarkers are relatively less updated and iterative[
36,
37]. Our research hopes to further continue and fill the gap in this area. At present, machine learning is also one of the research hotspots in disease diagnosis. Through deeper learning and interpretation of patient data, machine learning can better understand clinical patient characteristics, and thereby continuously improve treatment options[
38,
39]. Furthermore, personalized treatment plans can be further customized by in-depth analysis of individual patient data. Personalized treatment, for each patient's gene expression, is different, there will be different treatment focus[
40]. Combined with the development of artificial intelligence, it is believed that more accurate and forward-looking diagnostic indicators will emerge in near future. Early and complete diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis judgment processes for patients with sepsis lung injury will emerge, which will greatly improve the survival expectation and quality of life of patients. It can be seen that the functional analysis results of different genes are different, mainly in the two directions of immunity and infection, which are related to the basic pathophysiology of sepsis. Moreover, there were co-expression links between genes, suggesting that there may be unknown and common links between genes and known signaling pathways. For example, there is a link between CDKN1A and p53-p21-RB signaling[
41], etc., which awaits further exploration by our subsequent experiments.
Our study has some limitations. Due to the small size of the initial study population and validation cohort, the conclusions that may be drawn from this study are limited. The specific relevance of miRNAs and transcription factors to disease biology and development should be further verified in a larger number of subjects. Our results and findings need to be confirmed by subsequent studies and verified by more relevant experiments. In the following, we will further carry out follow-up studies on the selected biomarkers.
Conclusion
In this study, six potential diagnostic biomarkers and targets of sepsis-induced ALI were selected from the database through bioinformatics analysis, to have a positive impact and significance on the diagnosis and treatment of sepsis-induced lung injury.
Figure 1.
A. Vocano map of the expression of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in GSE44074. The abscissa shows the multiple of difference (ALIsepsis /Onlysepsis, logarithm). The ordinate represents -log10(Pvalue). Each dot in the figure represents a gene, with green and red dots representing significantly differentially expressed genes. The red dots indicate up-regulated gene expression (ALIsepsis relative to Onlysepsis), the green dots indicate down-regulated gene expression (ALIsepsis relative to Onlysepsis), and the gray dots indicate that there is no significant difference between these genes. B. Heat map of the expression of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in GSE44074. Each small square represents each gene, and its color indicates the expression level of the gene. The higher the expression level, the darker the color will be (red is high expression, blue is low expression). The first row represents the sample grouping, blue-green represents the ALIsepsis sample, and red represents the Onlysepsis sample. Each row represents the expression level of each gene in different samples, and each column represents the expression level of all differentially expressed genes in each tissue. The dendrogram on the left shows the results of the clustering analysis of different genes from different samples.
Figure 1.
A. Vocano map of the expression of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in GSE44074. The abscissa shows the multiple of difference (ALIsepsis /Onlysepsis, logarithm). The ordinate represents -log10(Pvalue). Each dot in the figure represents a gene, with green and red dots representing significantly differentially expressed genes. The red dots indicate up-regulated gene expression (ALIsepsis relative to Onlysepsis), the green dots indicate down-regulated gene expression (ALIsepsis relative to Onlysepsis), and the gray dots indicate that there is no significant difference between these genes. B. Heat map of the expression of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in GSE44074. Each small square represents each gene, and its color indicates the expression level of the gene. The higher the expression level, the darker the color will be (red is high expression, blue is low expression). The first row represents the sample grouping, blue-green represents the ALIsepsis sample, and red represents the Onlysepsis sample. Each row represents the expression level of each gene in different samples, and each column represents the expression level of all differentially expressed genes in each tissue. The dendrogram on the left shows the results of the clustering analysis of different genes from different samples.
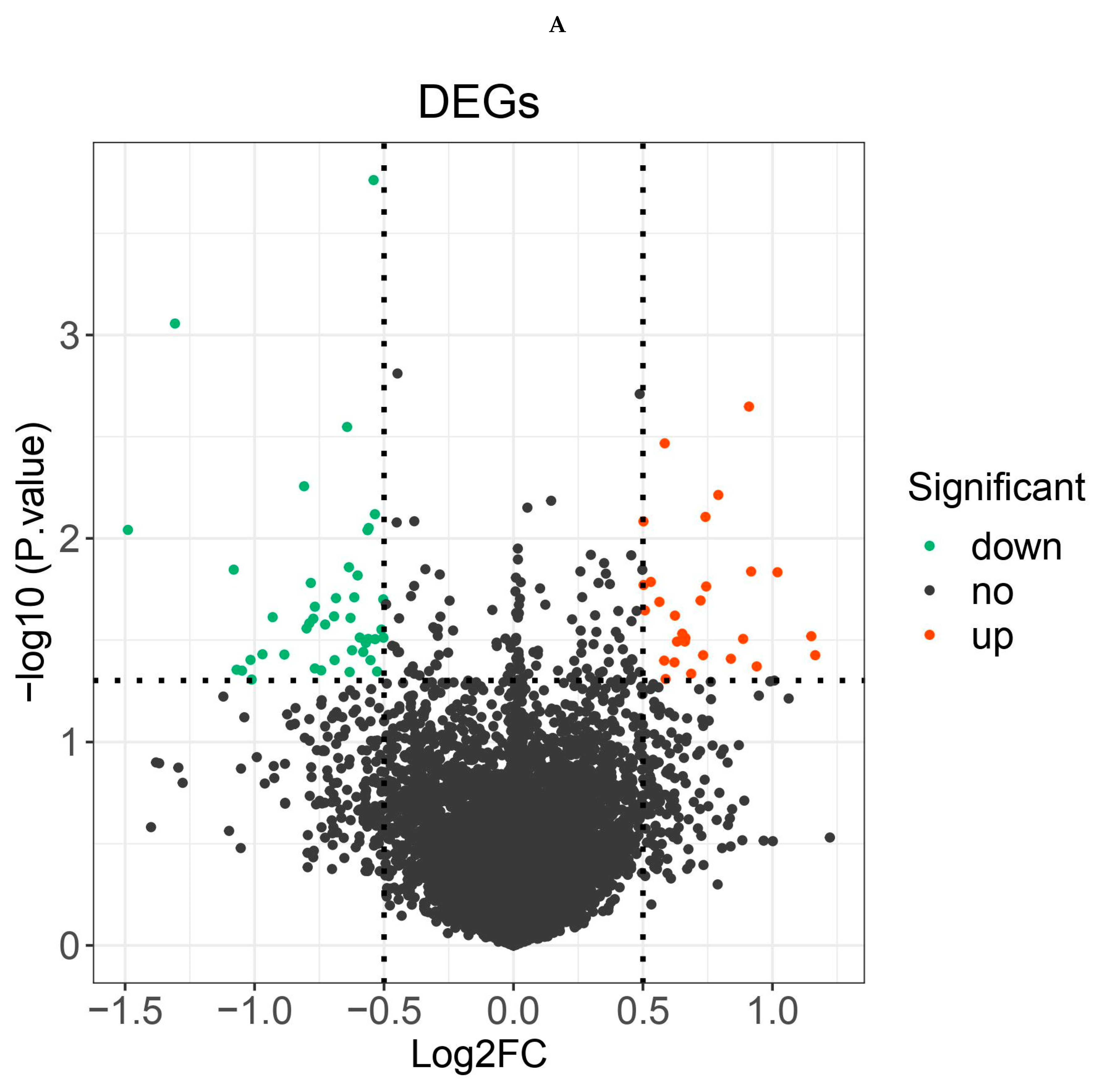
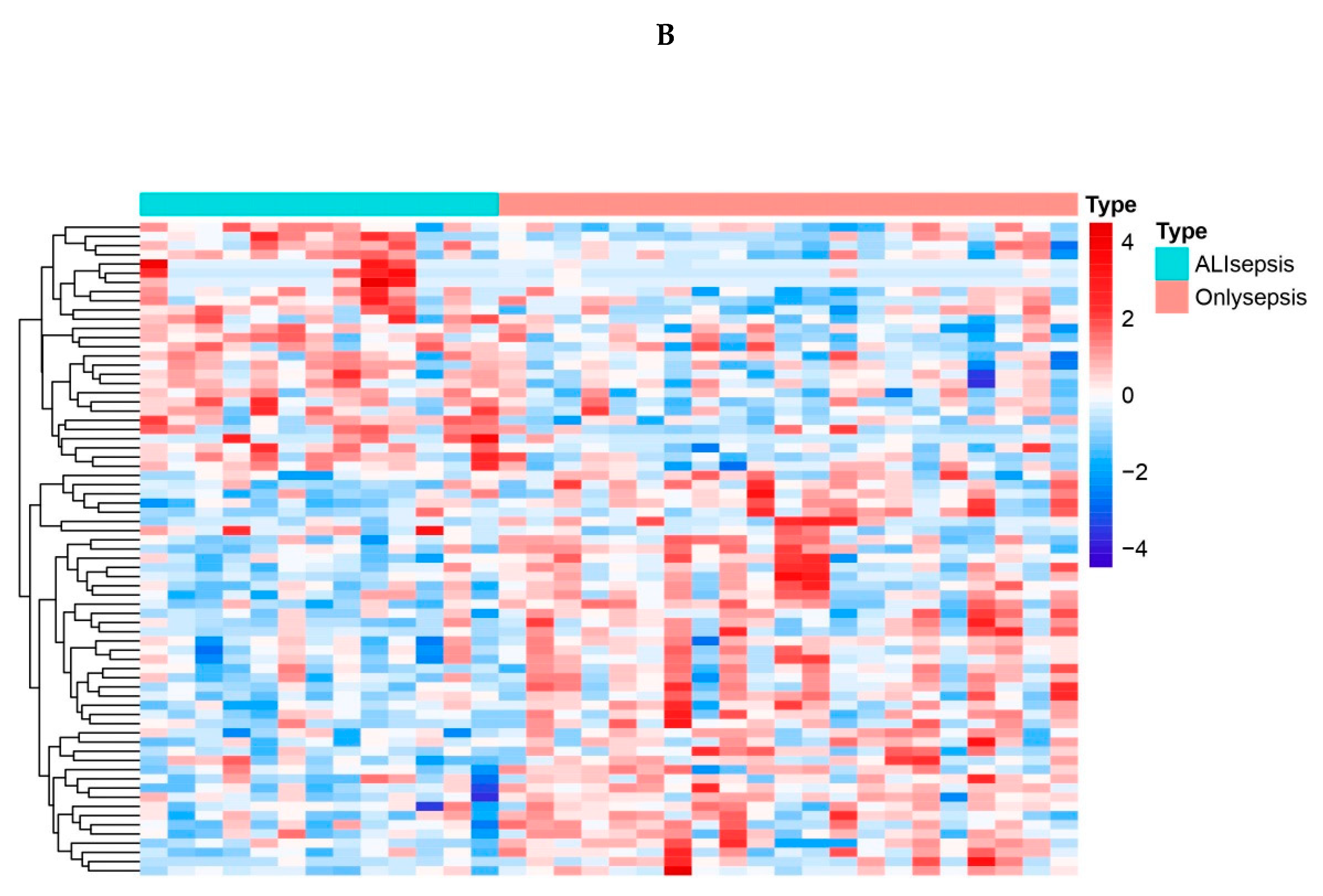
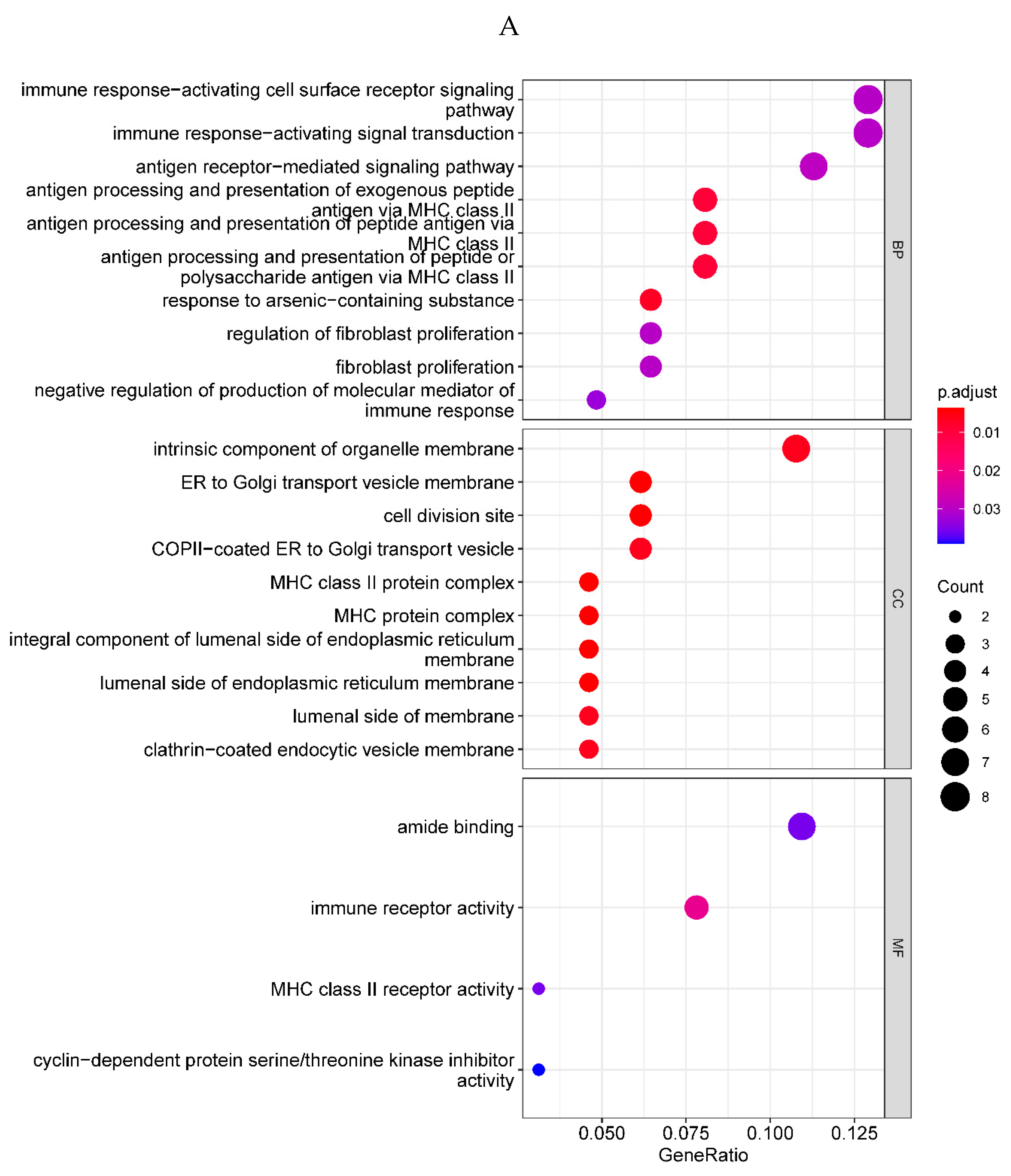
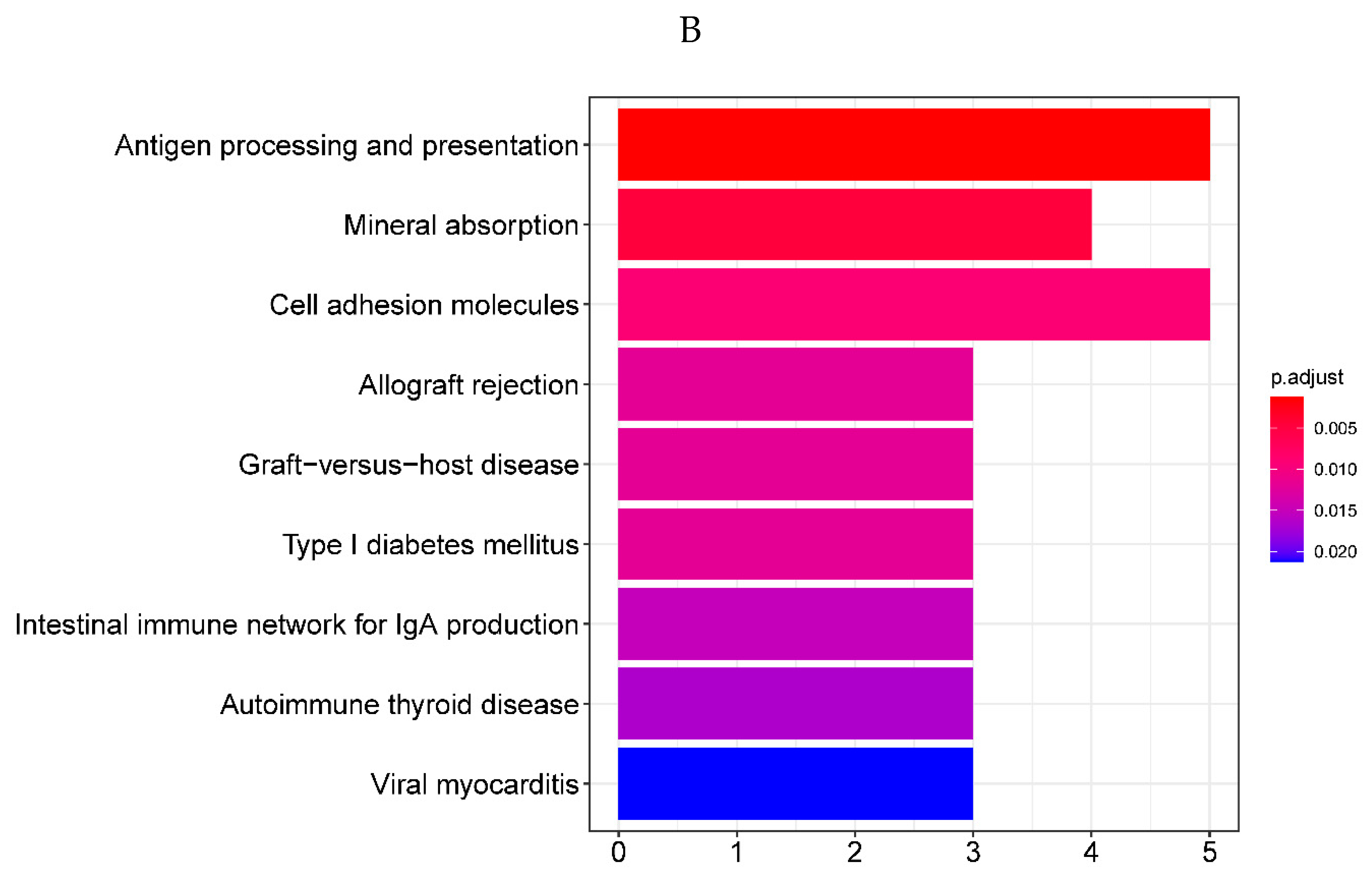
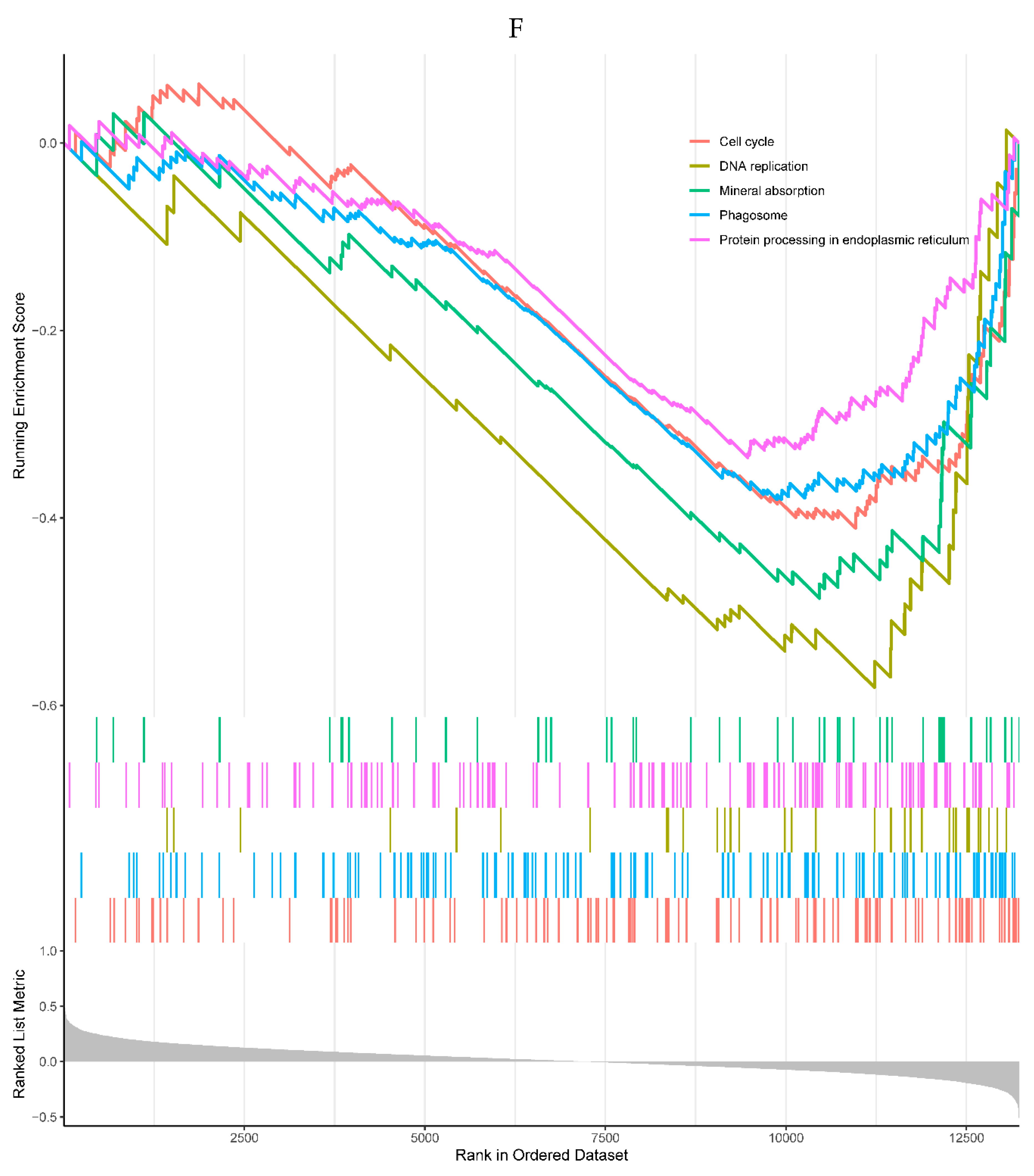
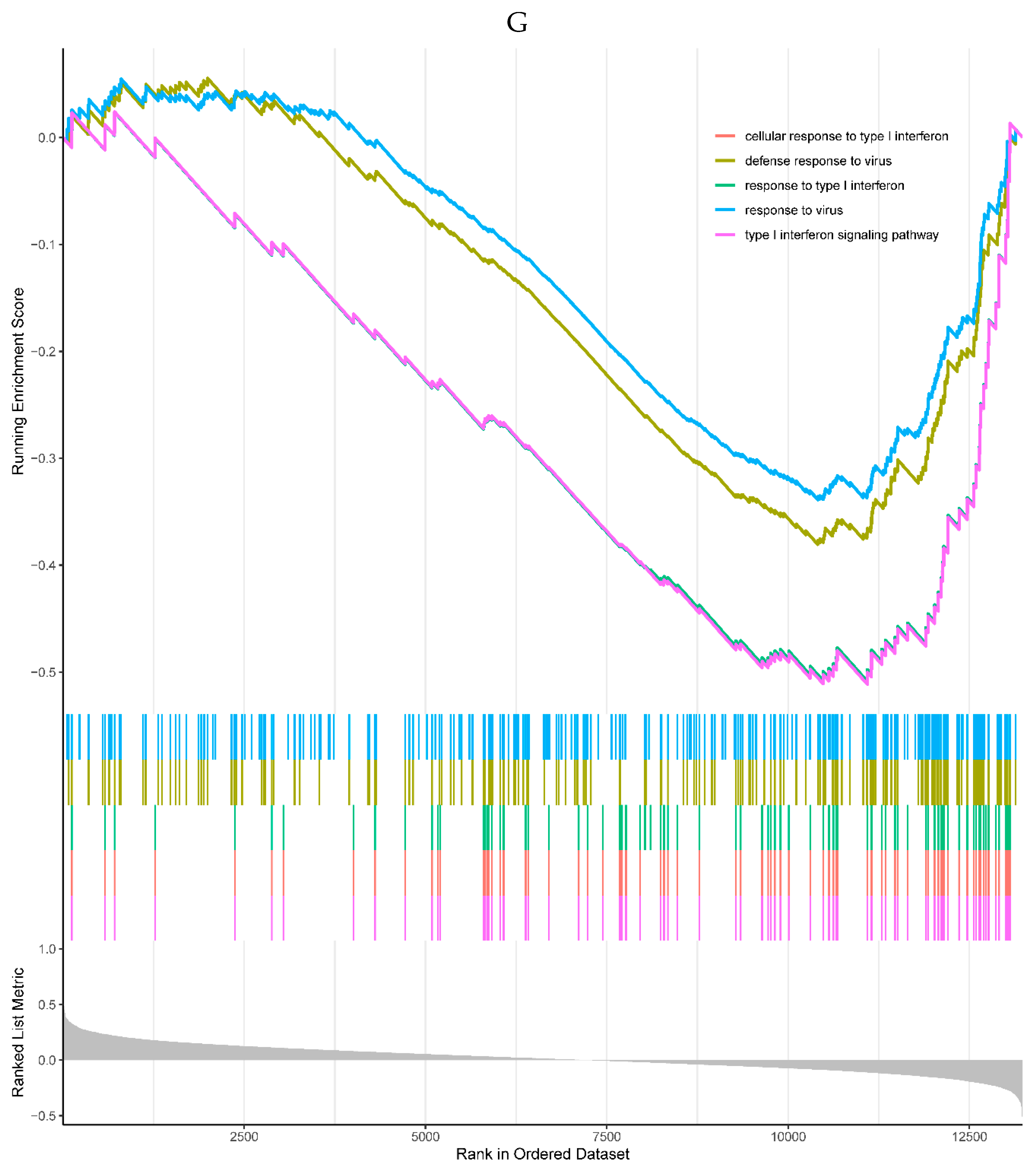
Figure 2.
A. Bubble plot of the top 10 GO terms in each field. A total of 91 GO terms were enriched for differentially expressed genes. The top 10 significantly enriched GO terms of various types showed that they were mainly enriched in immune regulatory biological processes such as immune activation and antigen response, as well as MHC protein complex and organelle membrane related cell components. B. Bar plot of the 9 KEGG pathways. Nine KEGG pathways were enriched, mainly for antigen processing and mineral absorption, etc.
Figure 2.
A. Bubble plot of the top 10 GO terms in each field. A total of 91 GO terms were enriched for differentially expressed genes. The top 10 significantly enriched GO terms of various types showed that they were mainly enriched in immune regulatory biological processes such as immune activation and antigen response, as well as MHC protein complex and organelle membrane related cell components. B. Bar plot of the 9 KEGG pathways. Nine KEGG pathways were enriched, mainly for antigen processing and mineral absorption, etc.
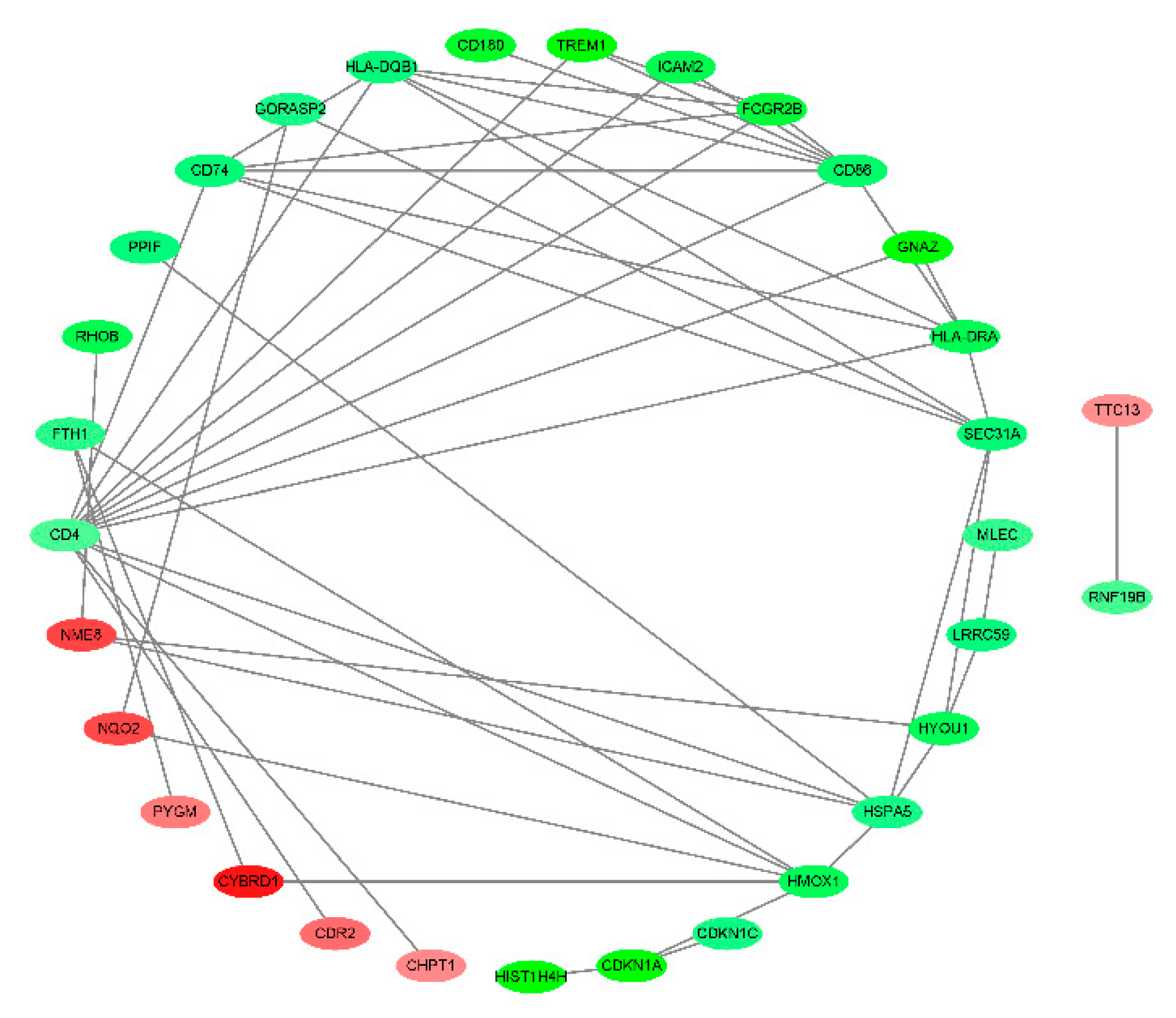
Figure 3.
PPI analysis on the 71 DEGs. Fill the node color according to the logFC value. Green indicates a negative logFC value, red indicates a positive logFC value, darker green indicates a smaller logFC, and darker red indicates a larger logFC value.
Figure 3.
PPI analysis on the 71 DEGs. Fill the node color according to the logFC value. Green indicates a negative logFC value, red indicates a positive logFC value, darker green indicates a smaller logFC, and darker red indicates a larger logFC value.
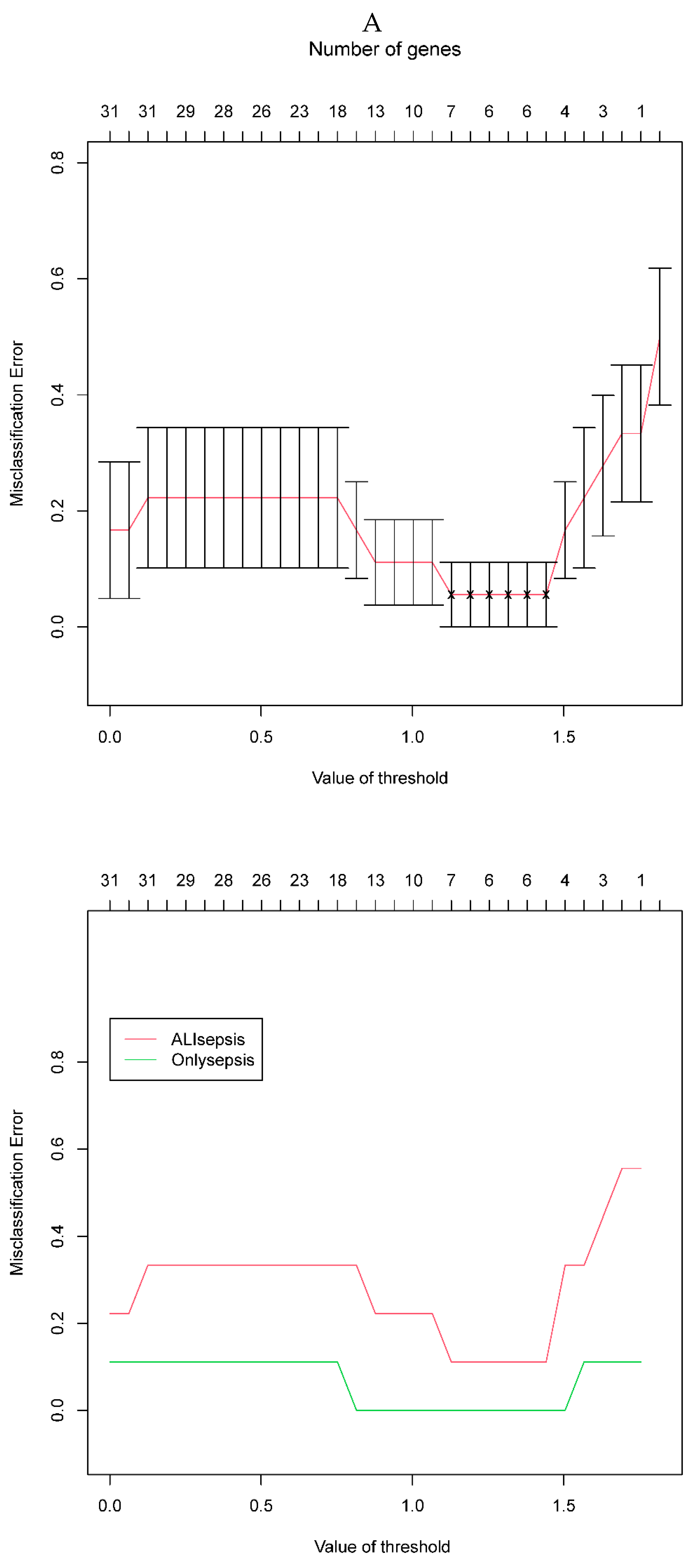
Figure 4.
A. Misclassification error of the cross-validation. B. Shrunk differences of the prognostic genes. The horizontal line (which looks like a dot because of its small value ) represents the score value, the vertical line is the value of 0. The score value less than 0 is on the left side of the vertical line while the value greater than 0 is on the right side of the vertical line, the larger the absolute value of the score value the longer the horizontal line. To get the most reliable genes with the lowest error rate. At this time, the threshold was 1.4, and six genes were screened, which were defined as diagnostic genes, namely HIST1H4H (H4C8), CDKN1A, HMOX1, NQO2,RHOB and TREM1.
Figure 4.
A. Misclassification error of the cross-validation. B. Shrunk differences of the prognostic genes. The horizontal line (which looks like a dot because of its small value ) represents the score value, the vertical line is the value of 0. The score value less than 0 is on the left side of the vertical line while the value greater than 0 is on the right side of the vertical line, the larger the absolute value of the score value the longer the horizontal line. To get the most reliable genes with the lowest error rate. At this time, the threshold was 1.4, and six genes were screened, which were defined as diagnostic genes, namely HIST1H4H (H4C8), CDKN1A, HMOX1, NQO2,RHOB and TREM1.
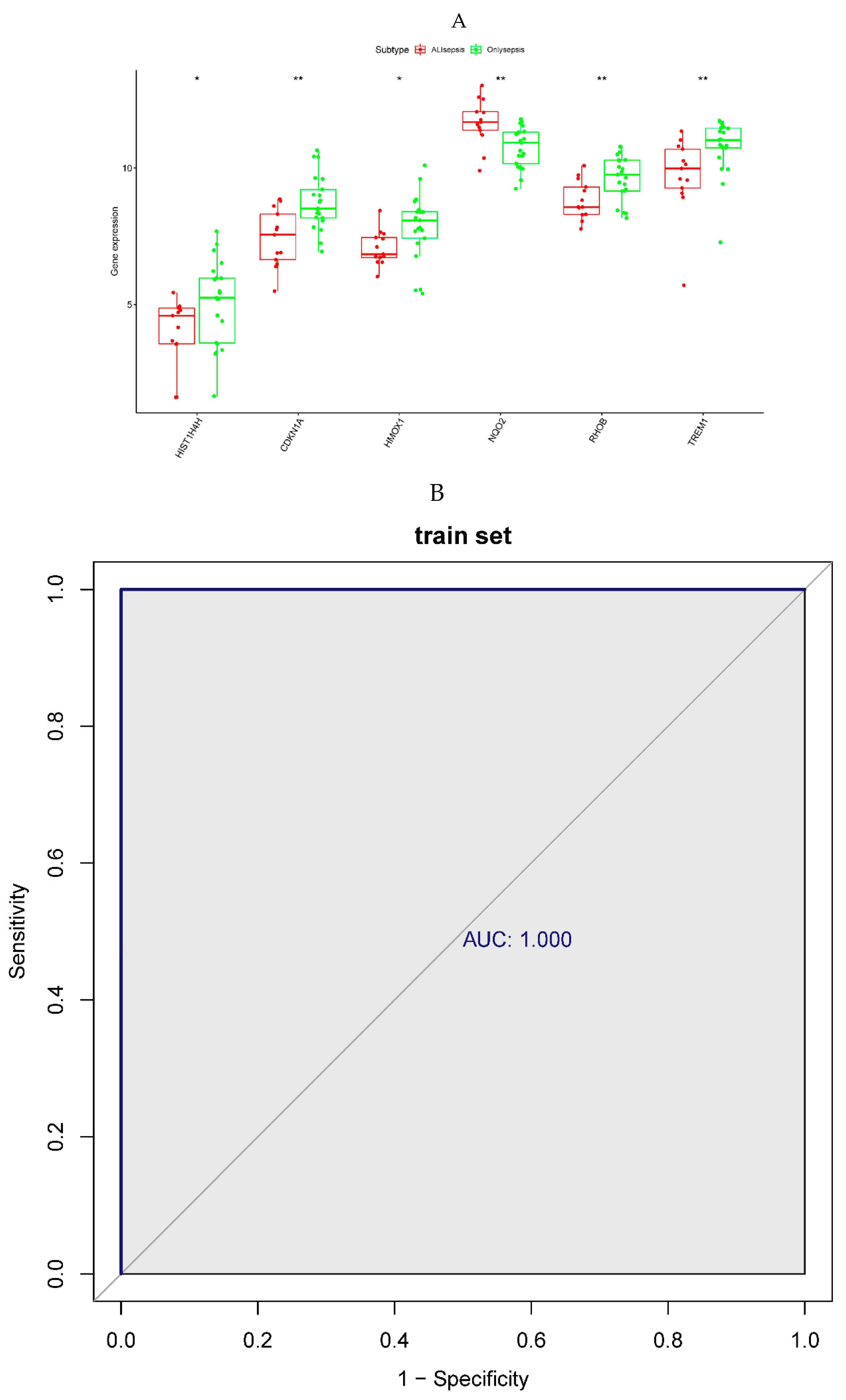
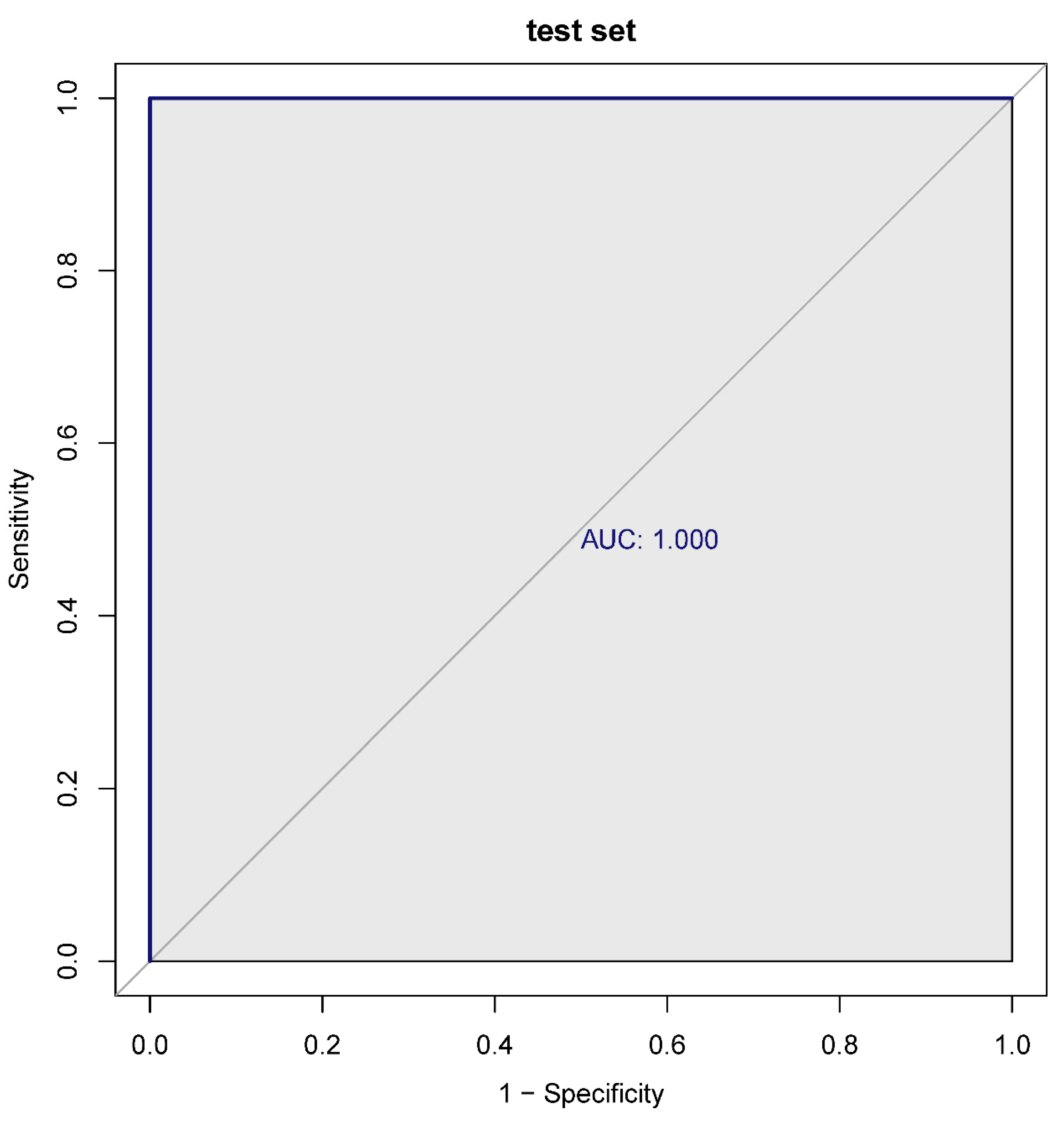
Figure 5.
A. Expression level of the prognostic genes in the sepsis and sepsis + ALI groups. The abscissa represents the diagnostic gene, the ordinate represents the expression level of the gene, the red represents the ALIsepsis sample, the green represents the Onlysepsis sample, and the "*" represents P<0.05, "**" denotes P<0.01, "***" means P<0.001, "ns" means no difference. B. ROC curves of the training and testing set. As can be seen from the figure, the AUC values of the diagnostic genes in both the training and test sets were 1, indicating that the diagnostic genes can accurately distinguish ALIsepsis and Onlysepsis samples.
Figure 5.
A. Expression level of the prognostic genes in the sepsis and sepsis + ALI groups. The abscissa represents the diagnostic gene, the ordinate represents the expression level of the gene, the red represents the ALIsepsis sample, the green represents the Onlysepsis sample, and the "*" represents P<0.05, "**" denotes P<0.01, "***" means P<0.001, "ns" means no difference. B. ROC curves of the training and testing set. As can be seen from the figure, the AUC values of the diagnostic genes in both the training and test sets were 1, indicating that the diagnostic genes can accurately distinguish ALIsepsis and Onlysepsis samples.
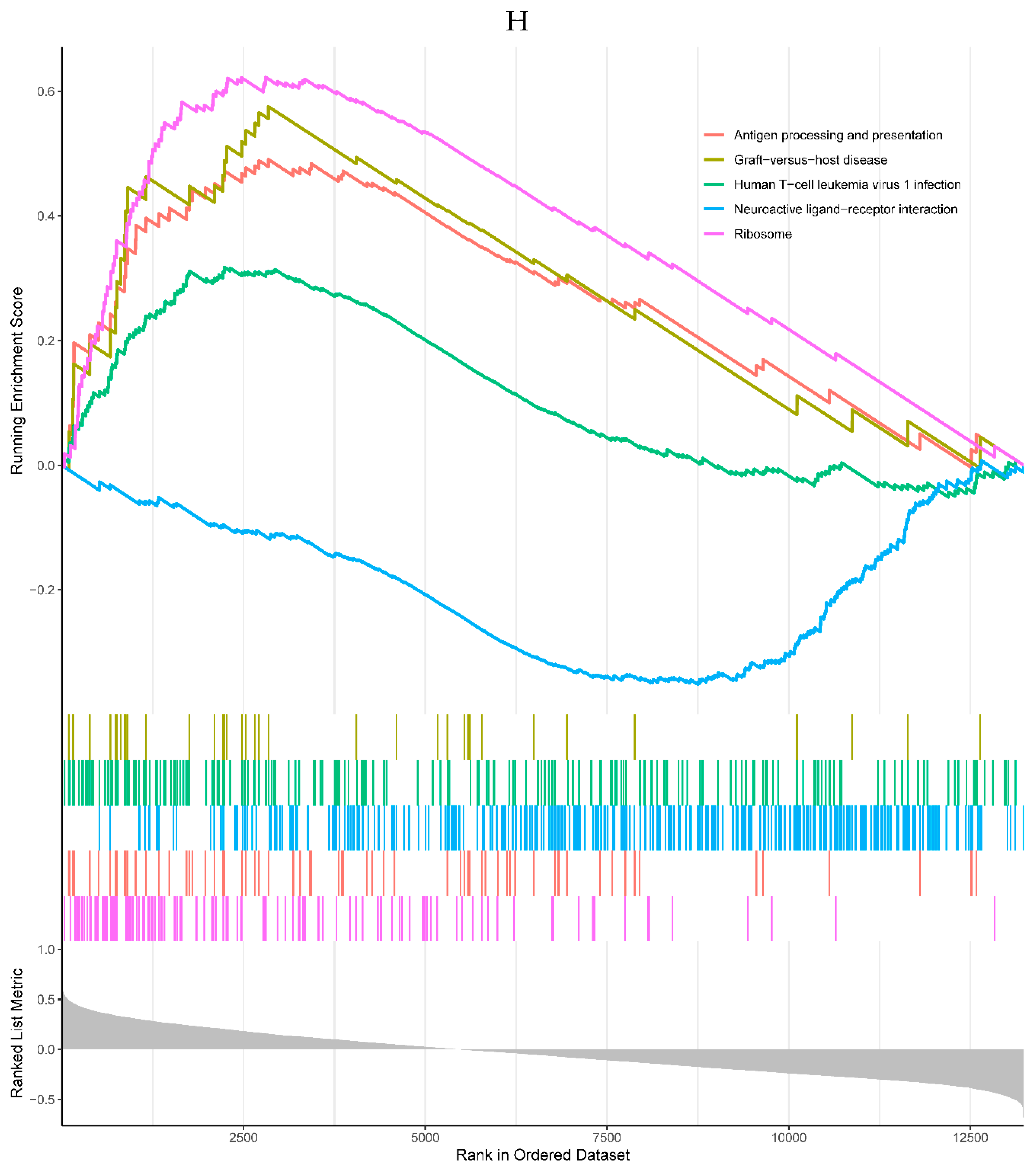
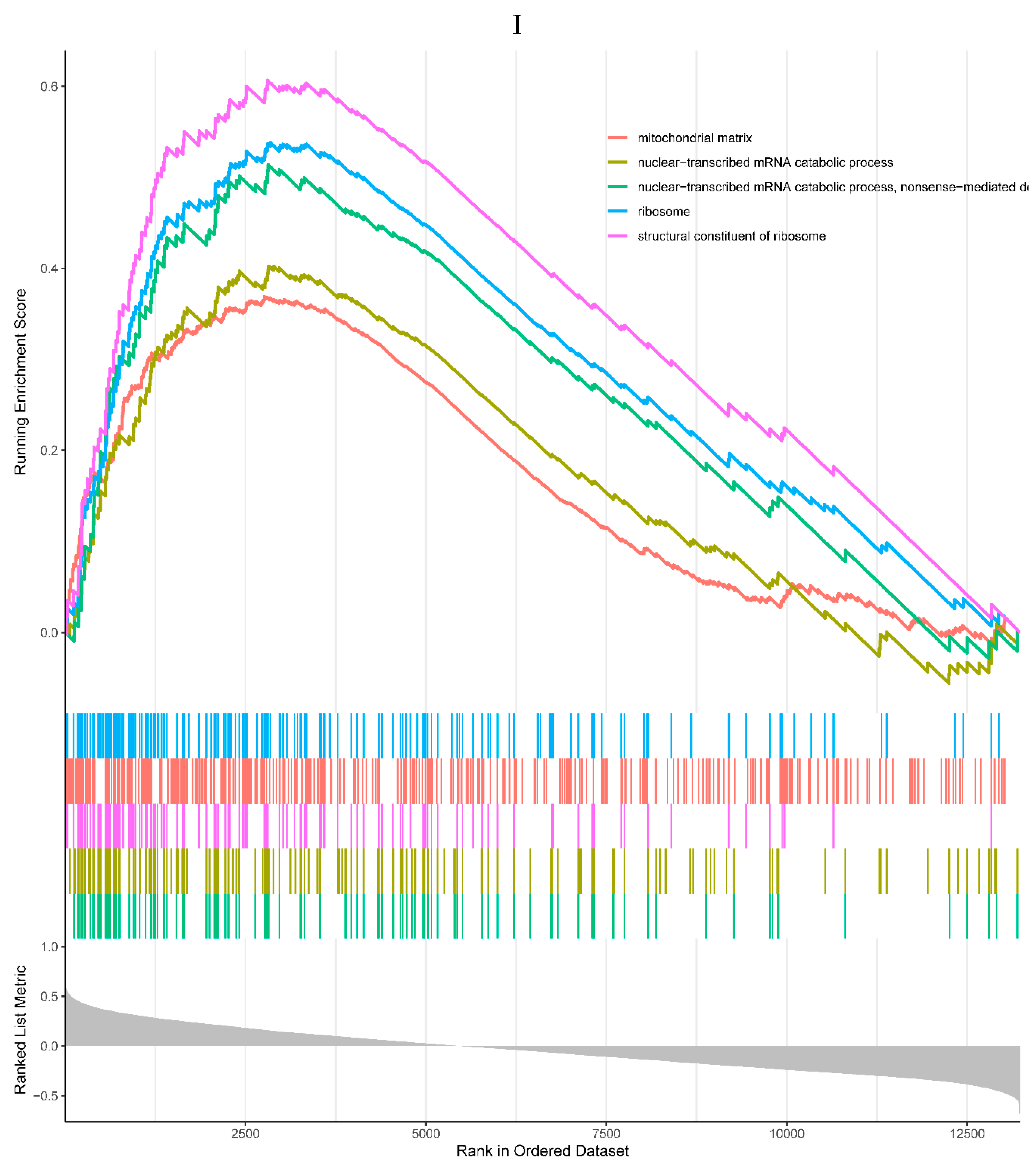
Figure 6.
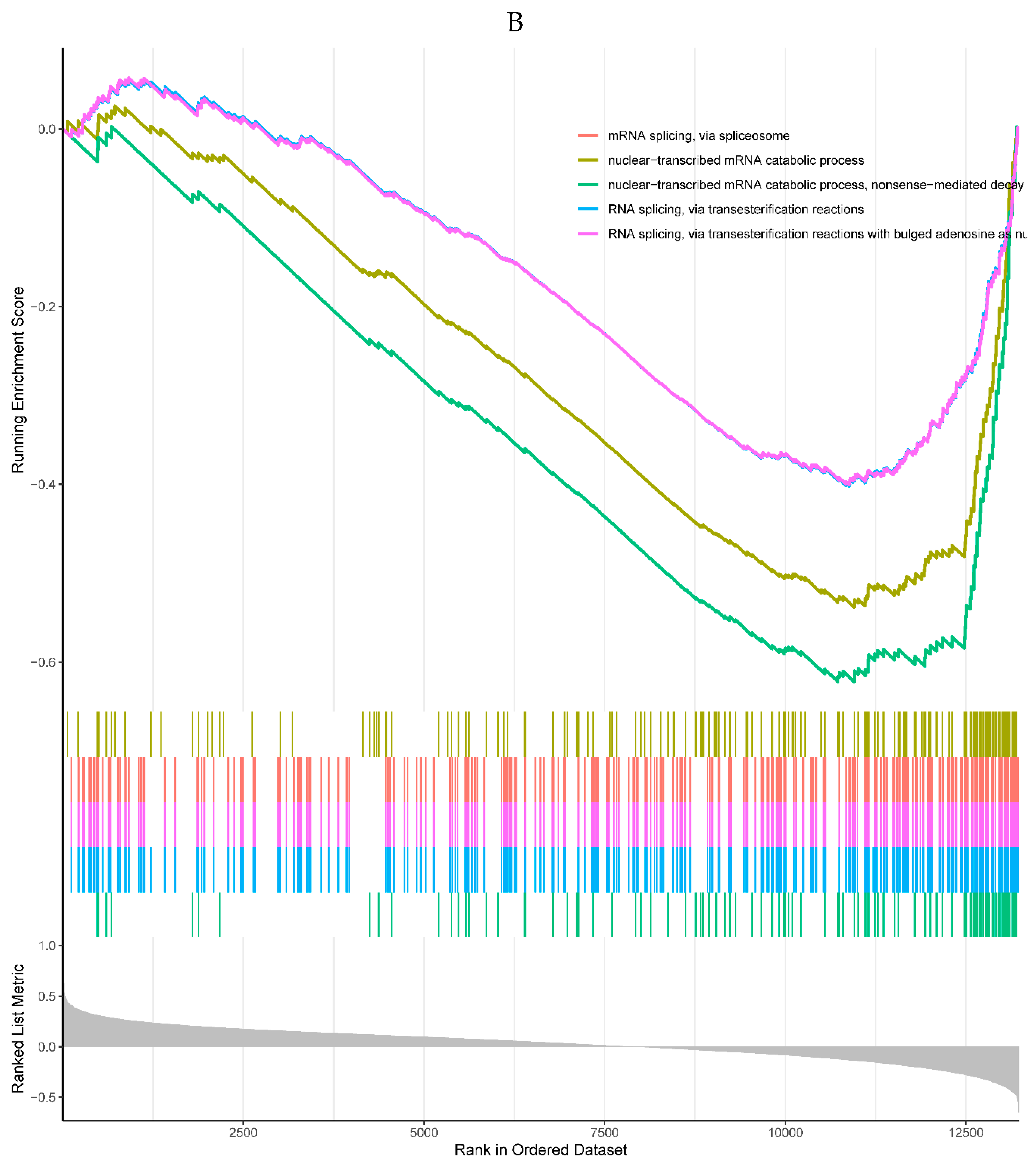
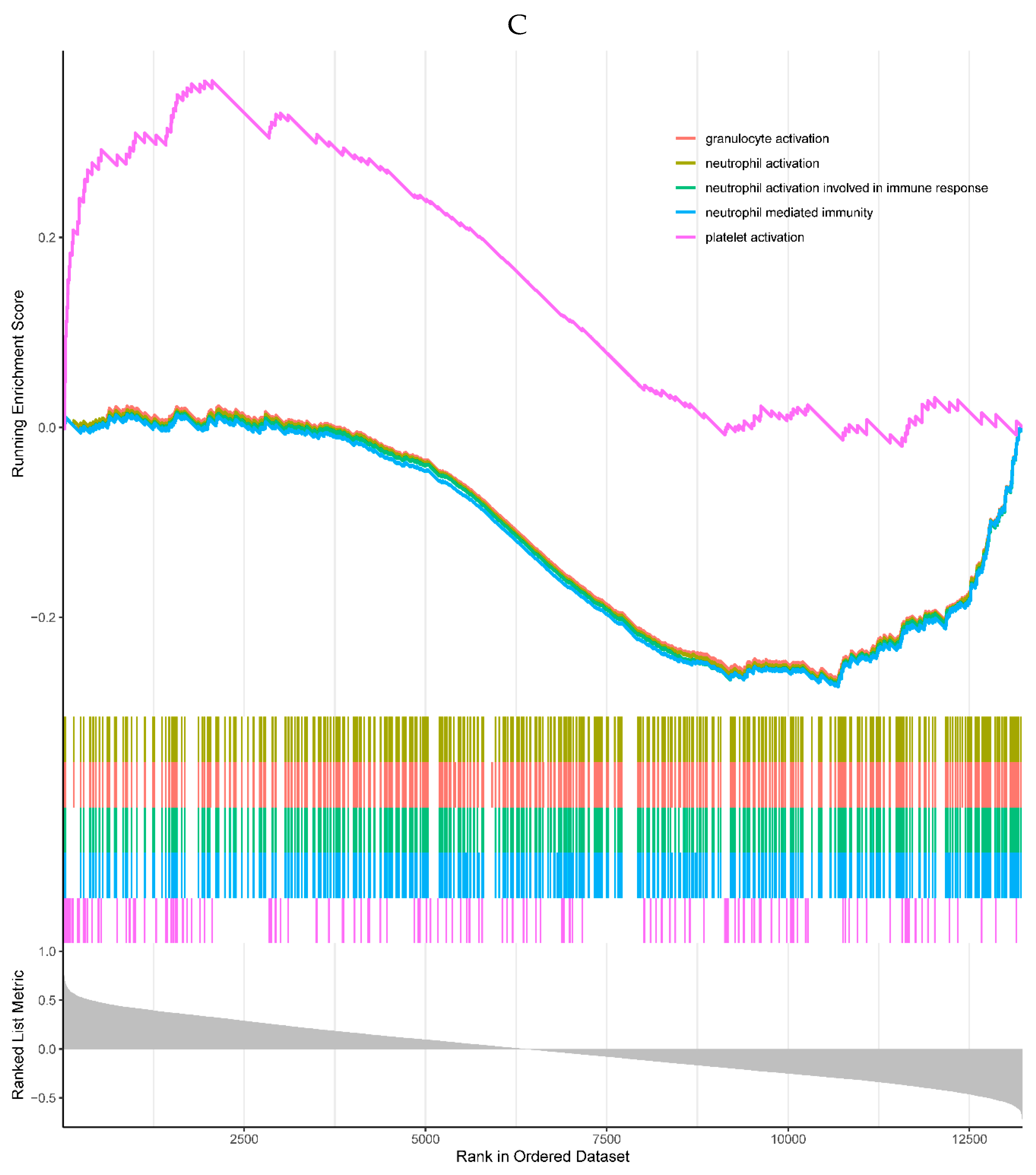
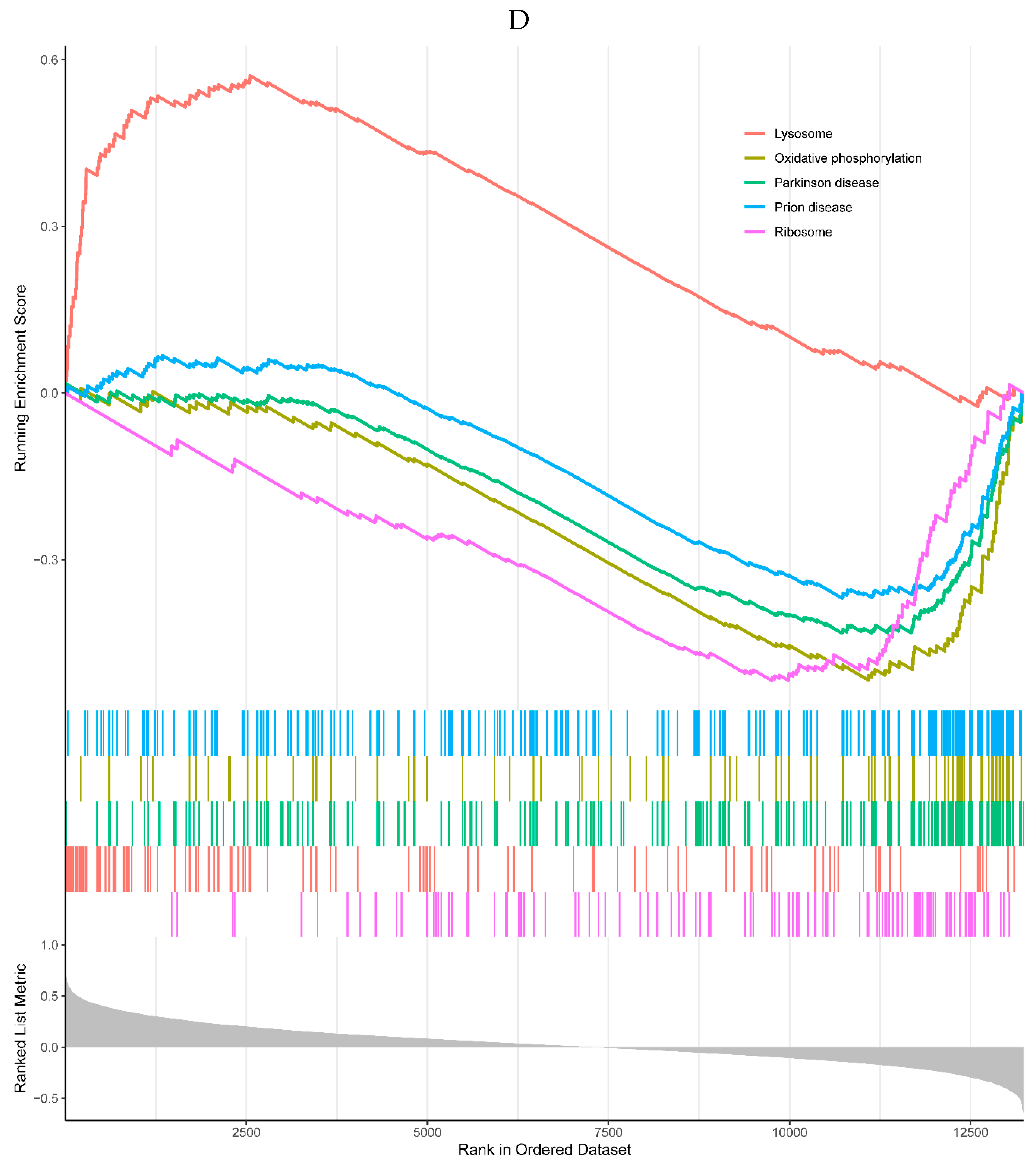
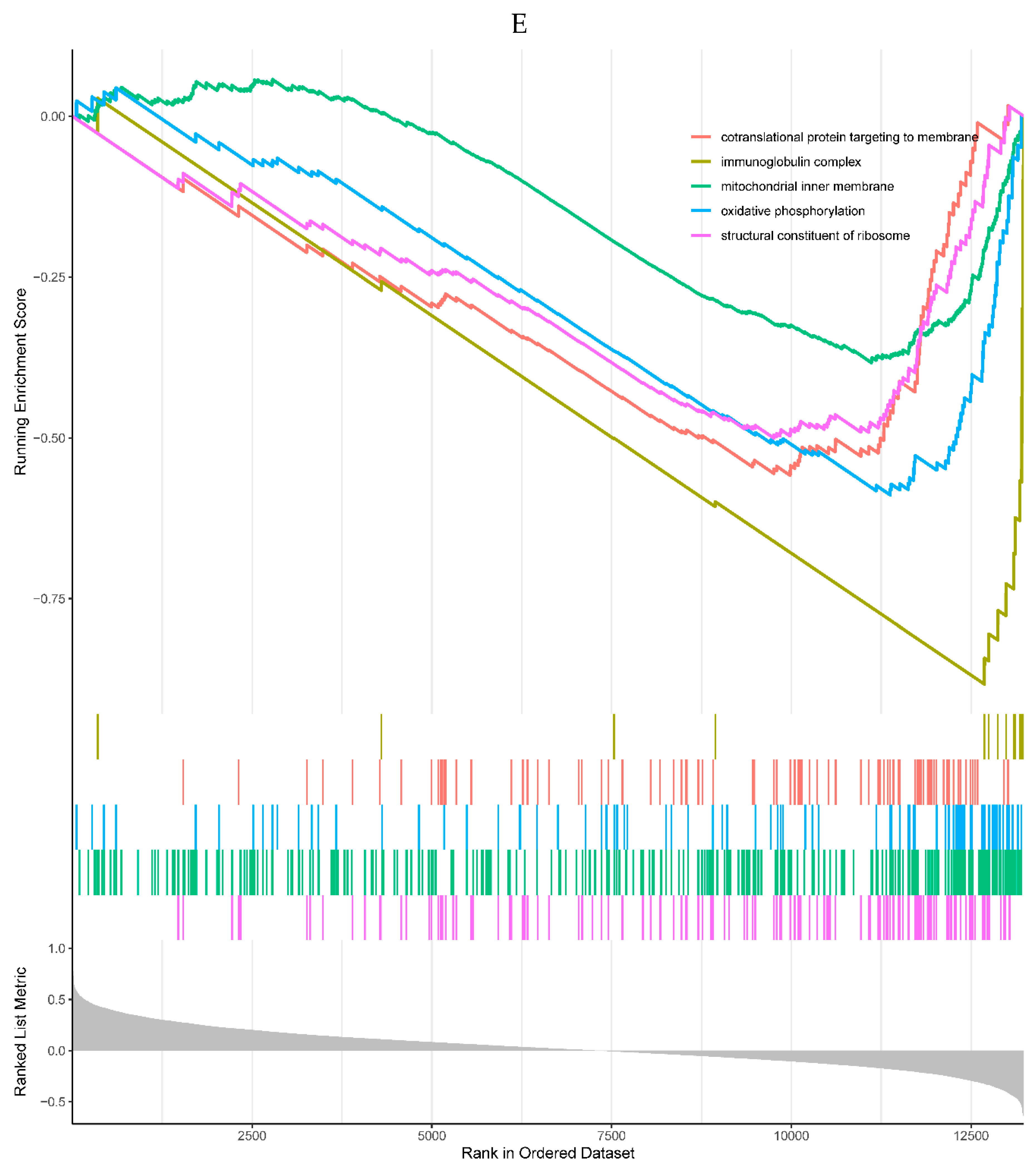
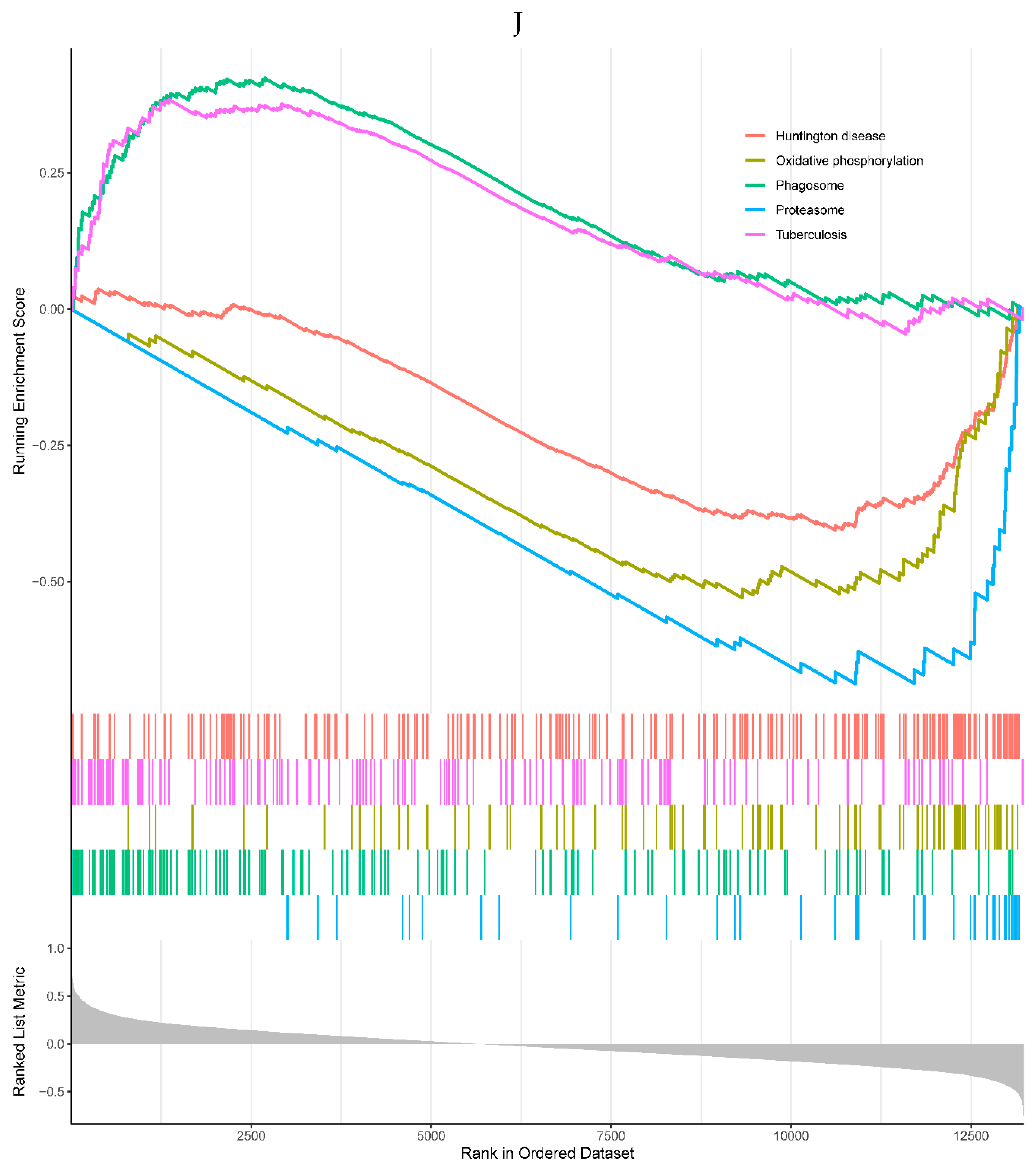
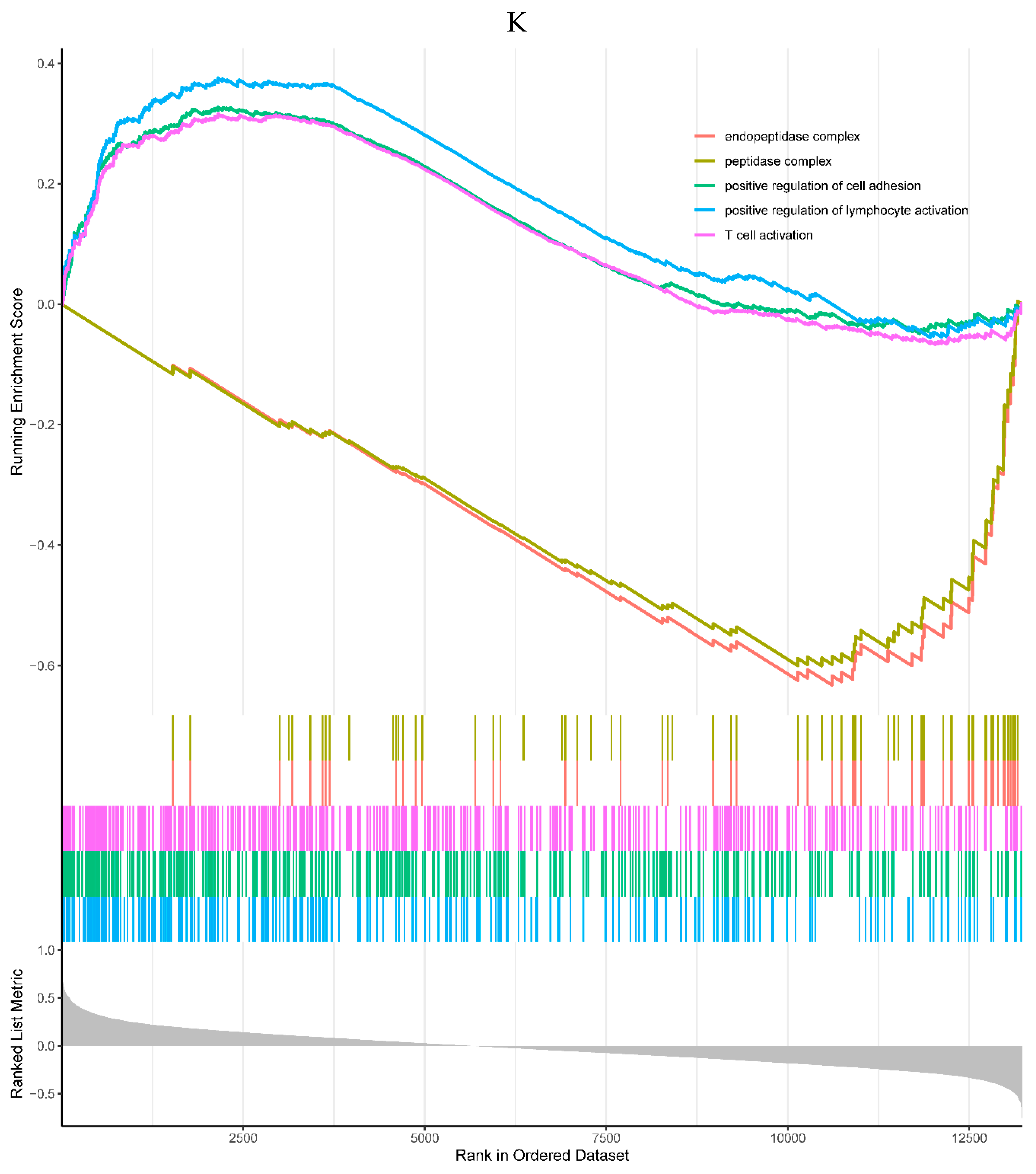
A, B. HIST1H4 related KEGG pathways and GO processes. . C. CDKN1A related GO processes. The KEGG pathway was not enriched. D, E. HMOX1 related KEGG pathways and GO processes. F, G. NQO2 related KEGG pathways and GO processes. . H, I. RHOB related KEGG pathways and GO processes. J, K. TREM1 related KEGG pathways and GO processes.
Figure 6.
A, B. HIST1H4 related KEGG pathways and GO processes. . C. CDKN1A related GO processes. The KEGG pathway was not enriched. D, E. HMOX1 related KEGG pathways and GO processes. F, G. NQO2 related KEGG pathways and GO processes. . H, I. RHOB related KEGG pathways and GO processes. J, K. TREM1 related KEGG pathways and GO processes.
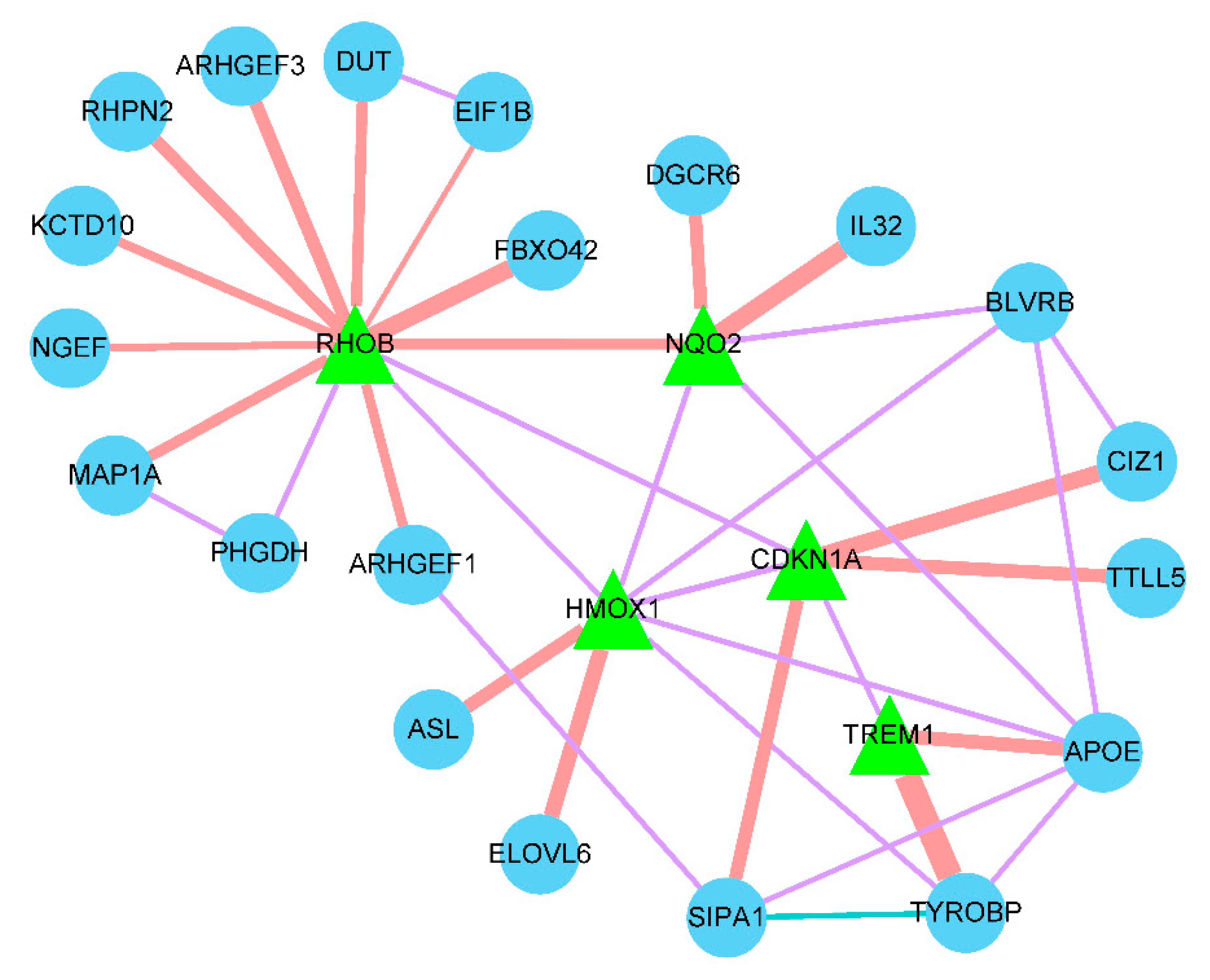
Figure 7.
Interaction of the prognostic genes. The green triangle represents the diagnostic gene, the blue dot represents the other genes related to the diagnostic gene, the orange line represents the physical interaction relationship, the purple line represents the co-expression relationship, the green line represents the co-localization relationship, and the line thickness represents the relationship weight, the larger the weight, the thicker the line.
Figure 7.
Interaction of the prognostic genes. The green triangle represents the diagnostic gene, the blue dot represents the other genes related to the diagnostic gene, the orange line represents the physical interaction relationship, the purple line represents the co-expression relationship, the green line represents the co-localization relationship, and the line thickness represents the relationship weight, the larger the weight, the thicker the line.
Figure 8.
Hierarchy of the biological functions. Sort by 'Corr p-val' from smallest to largest. The top 10 significantly enriched biological processes were intracellular signaling pathway, anti-apoptotic regulation, intracellular signal transduction, GTP-mediated signal transduction, intracellular signal induction of apoptosis, mast cell activation involved in the negative regulation of immune response, mast cell and leukocyte degranulation negative regulation of immune response.
Figure 8.
Hierarchy of the biological functions. Sort by 'Corr p-val' from smallest to largest. The top 10 significantly enriched biological processes were intracellular signaling pathway, anti-apoptotic regulation, intracellular signal transduction, GTP-mediated signal transduction, intracellular signal induction of apoptosis, mast cell activation involved in the negative regulation of immune response, mast cell and leukocyte degranulation negative regulation of immune response.
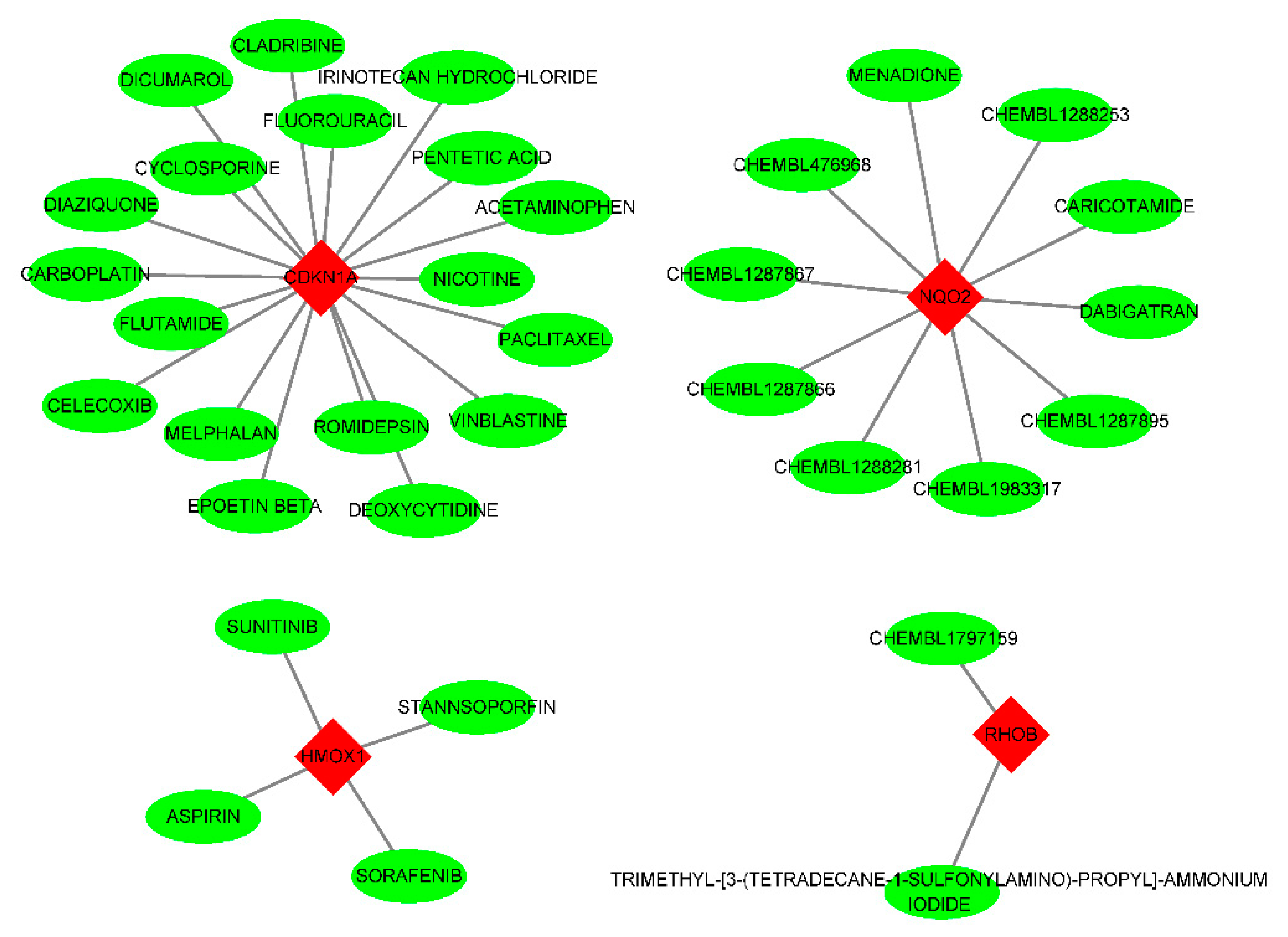
Figure 9.
Drug-gene interactions. Through our online website
https://dgidb.genome.wustl.edu/ gene diagnosis, predicting the corresponding drug molecules, in its HIST1H4H TREM1 did not predict to related drugs.
Figure 9.
Drug-gene interactions. Through our online website
https://dgidb.genome.wustl.edu/ gene diagnosis, predicting the corresponding drug molecules, in its HIST1H4H TREM1 did not predict to related drugs.
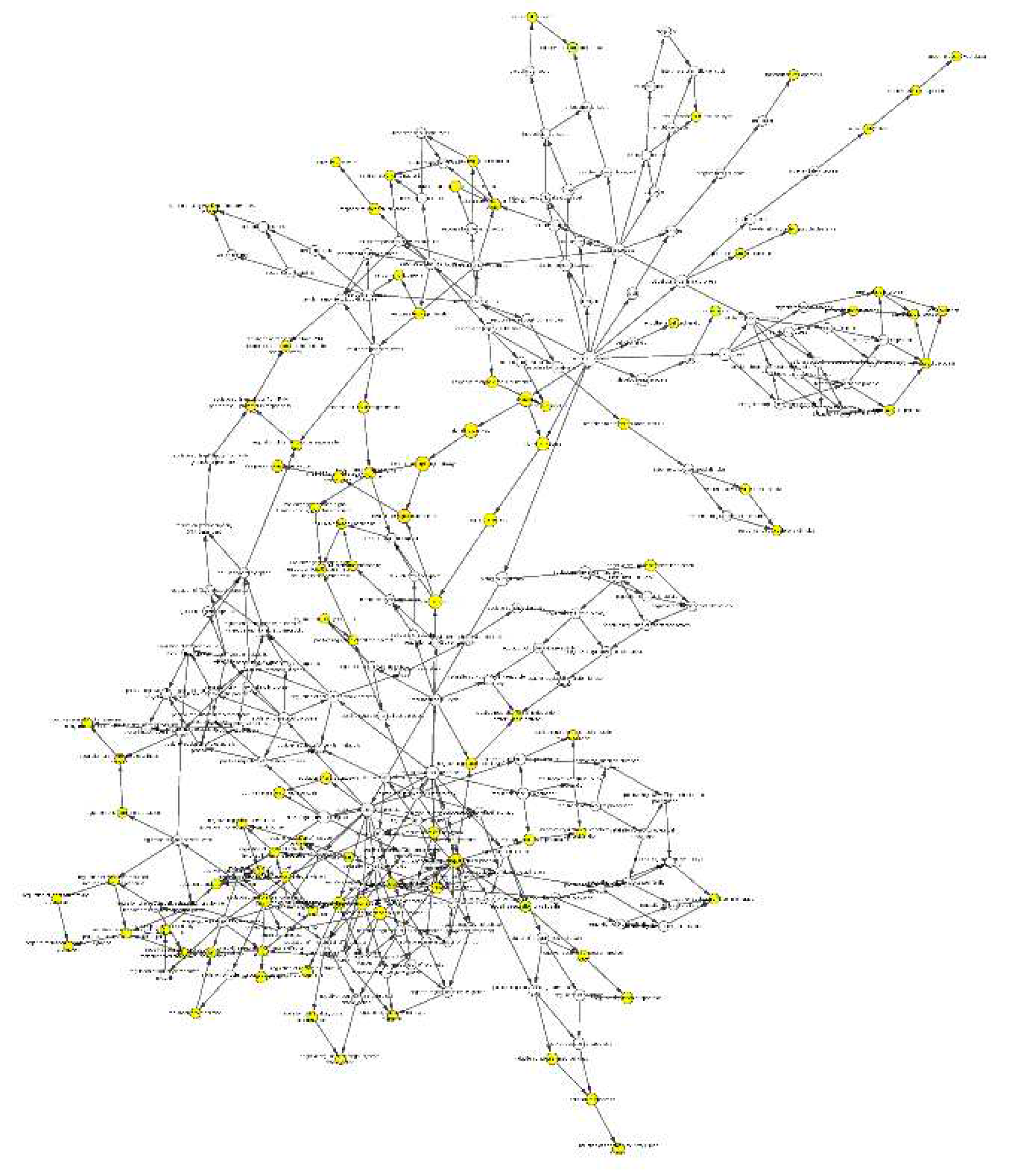
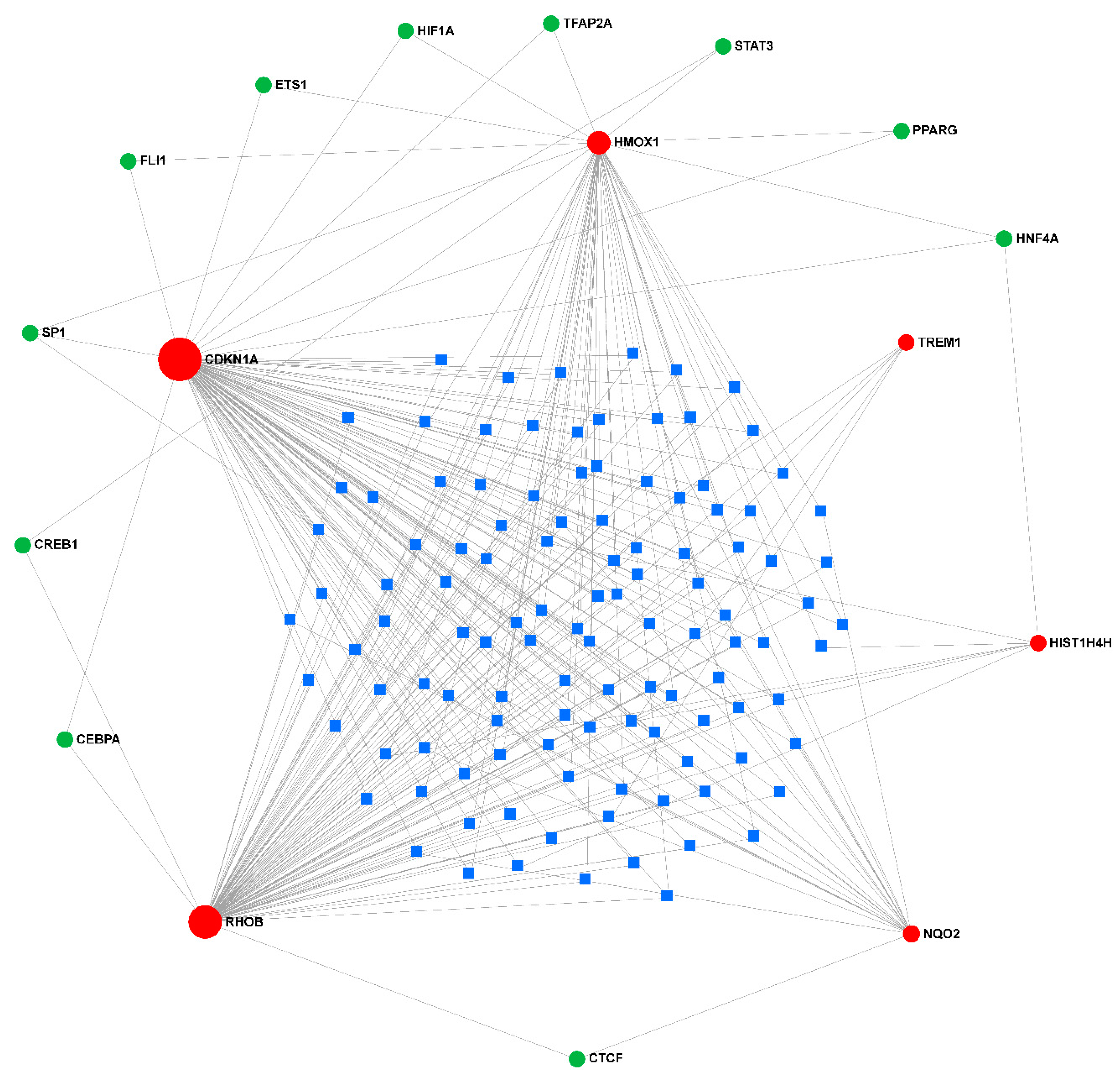
Figure 10.
Gene-TF-miRNA network. Red dots represent diagnostic genes, green dots represent TFs, blue squares represent mirnas, and the size of the dots indicates connectivity.
Figure 10.
Gene-TF-miRNA network. Red dots represent diagnostic genes, green dots represent TFs, blue squares represent mirnas, and the size of the dots indicates connectivity.