Submitted:
28 July 2023
Posted:
01 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental study
2.1.1. Cell culture
2.1.2. Irradiation
2.1.3. Immunocytochemistry
2.1.4. Statistical Analysis
2.2. Evaluating the percent contribution of HR to DSB repair
3. Results
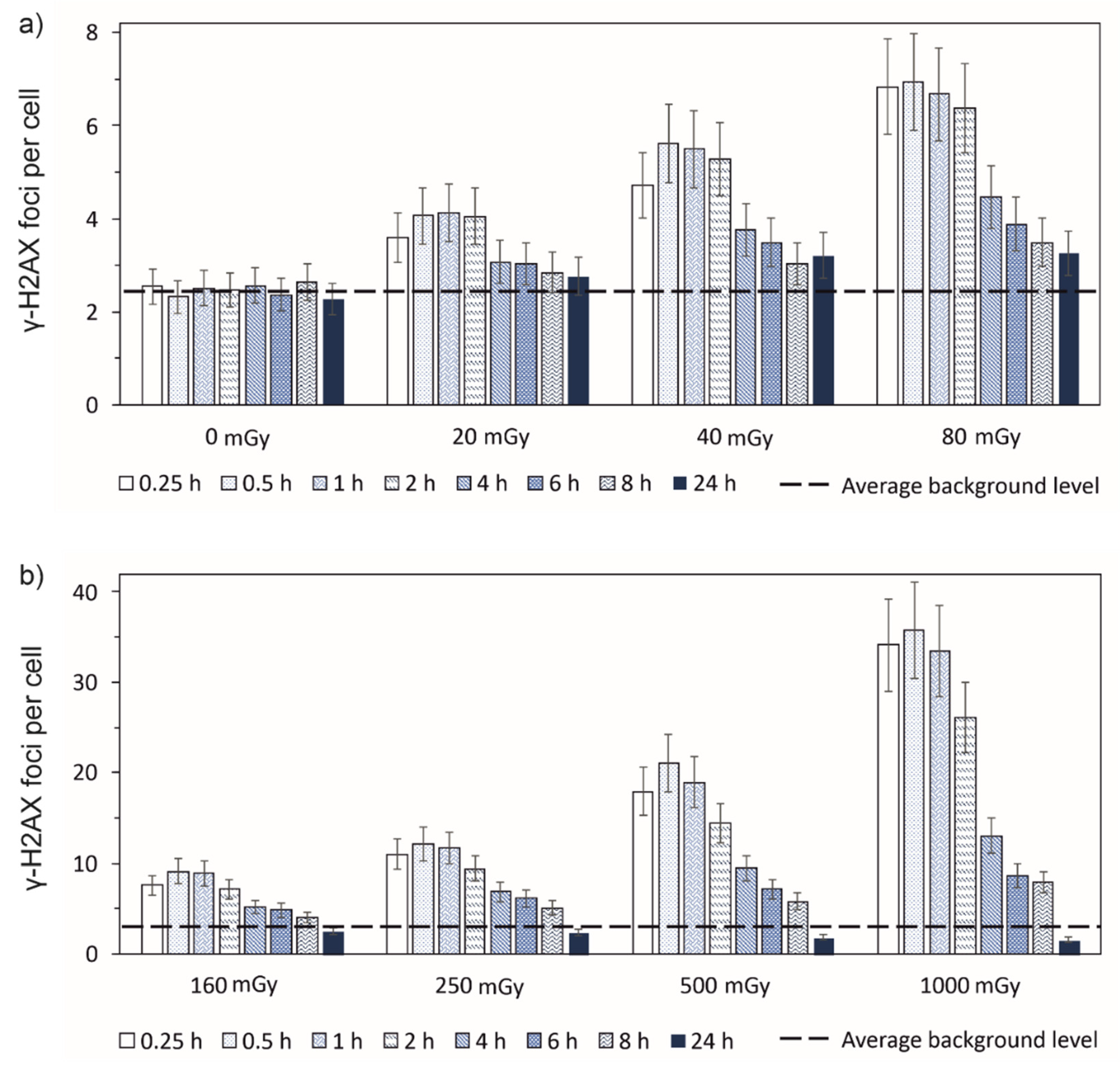
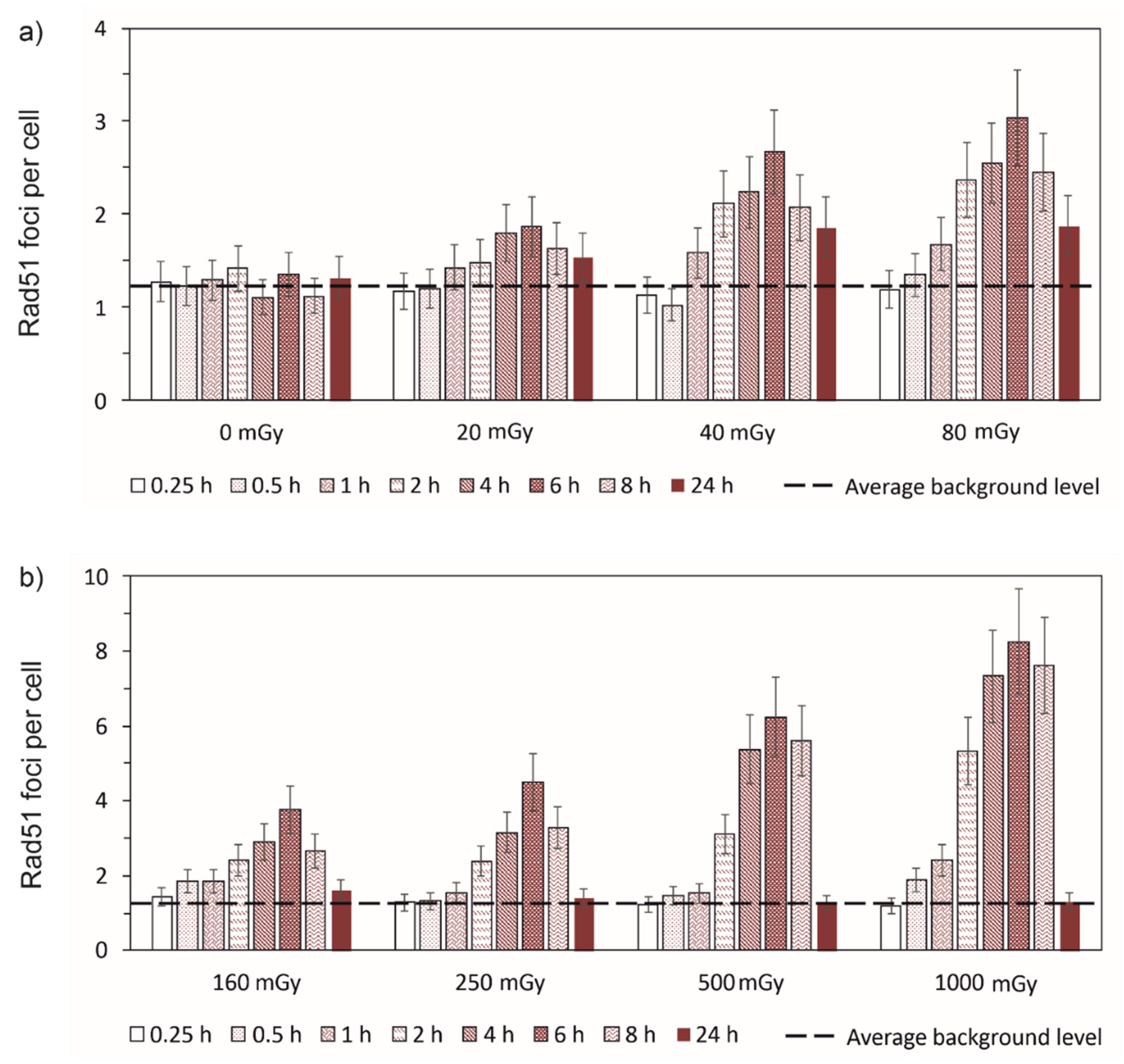
3.1. Experimental results
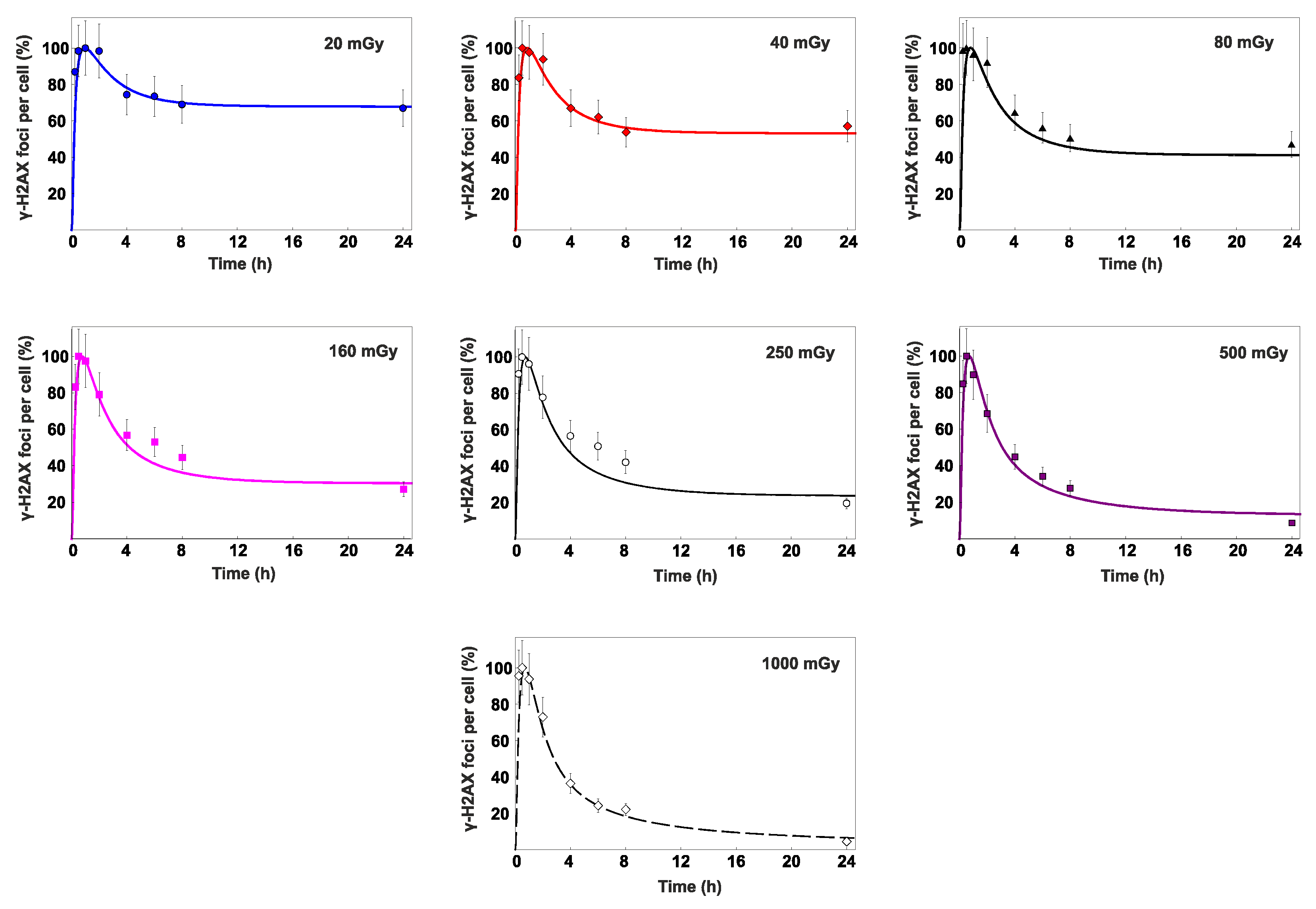
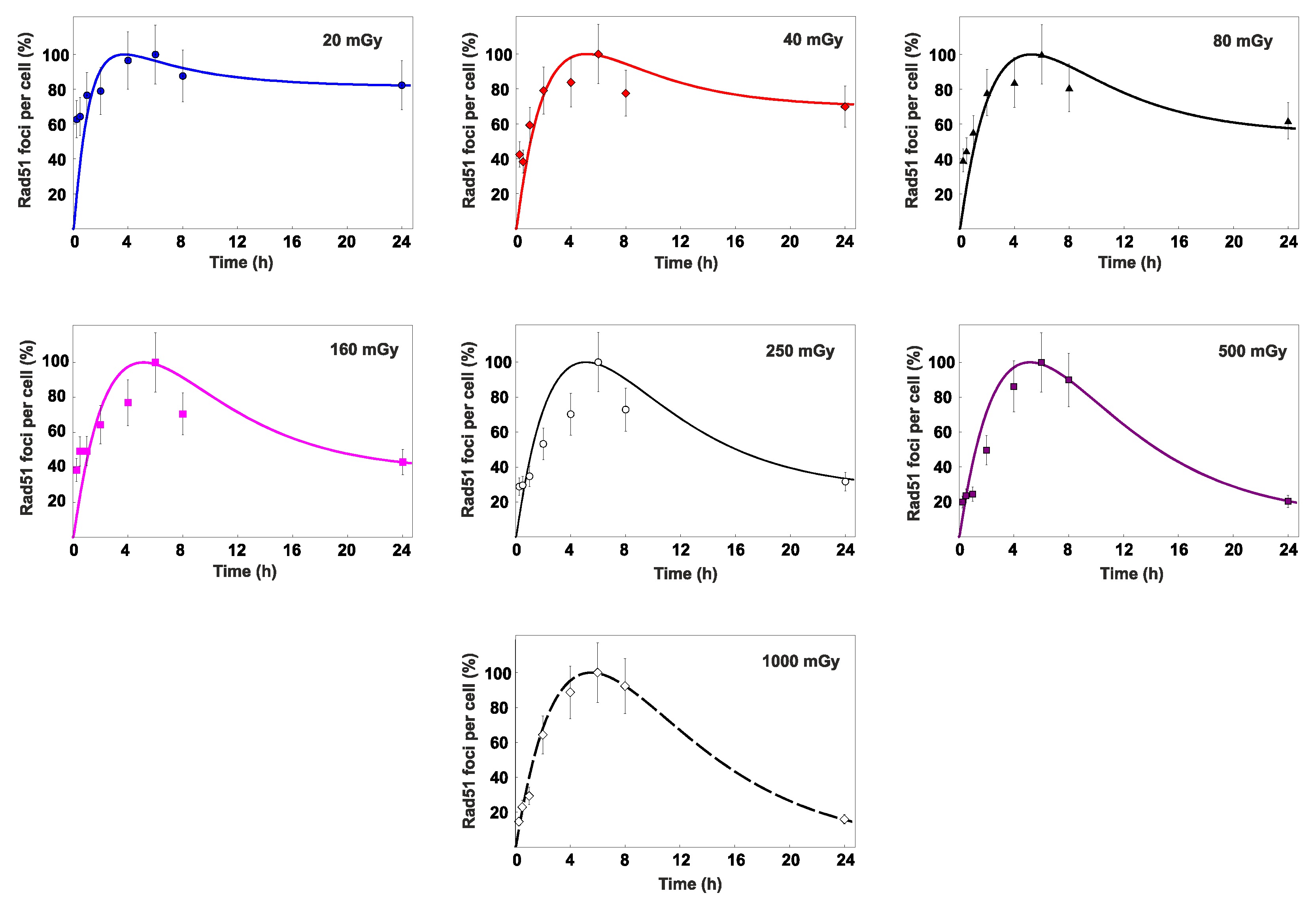
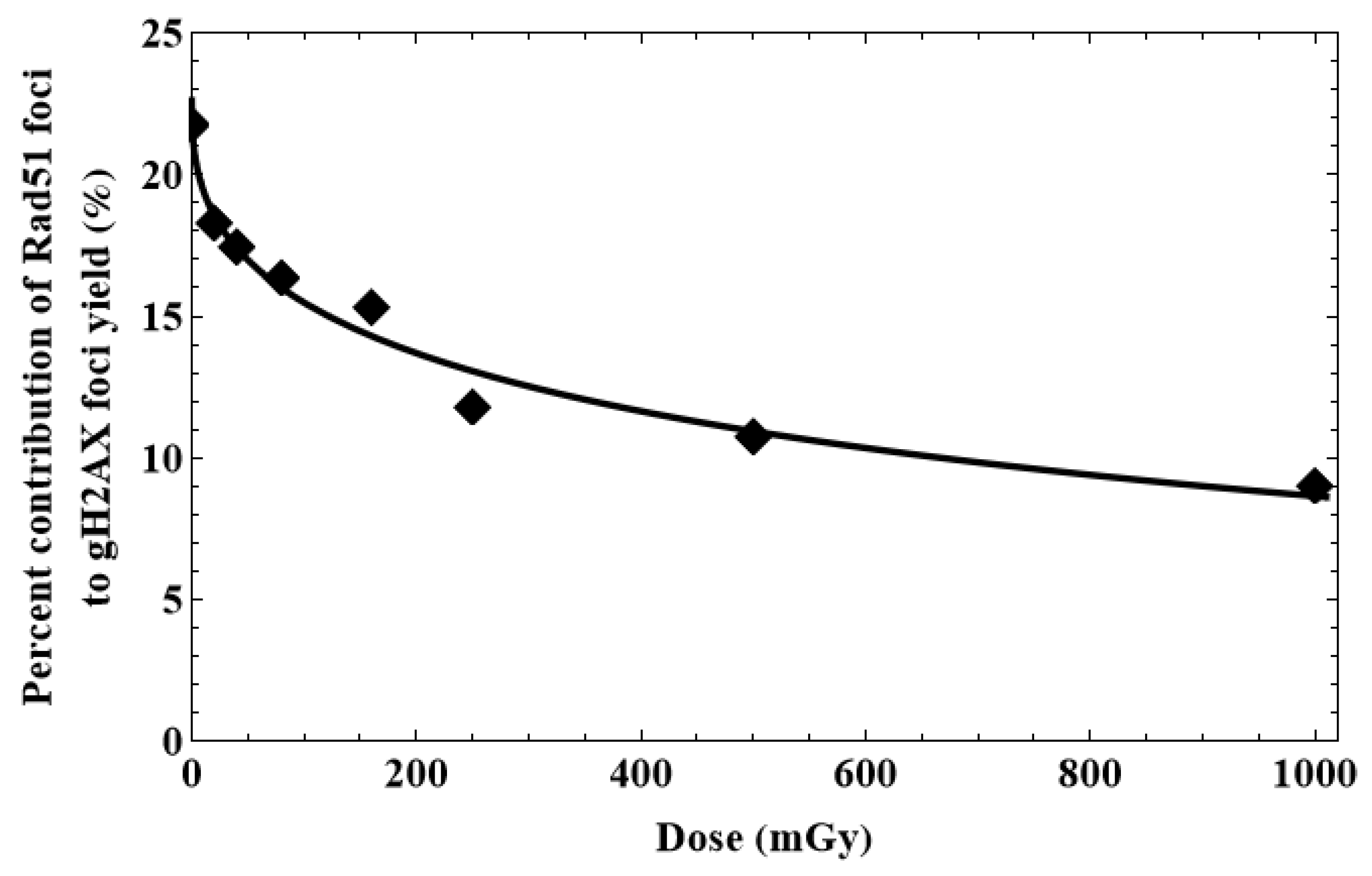
3.2. Percent contribution of HR to DSB repair
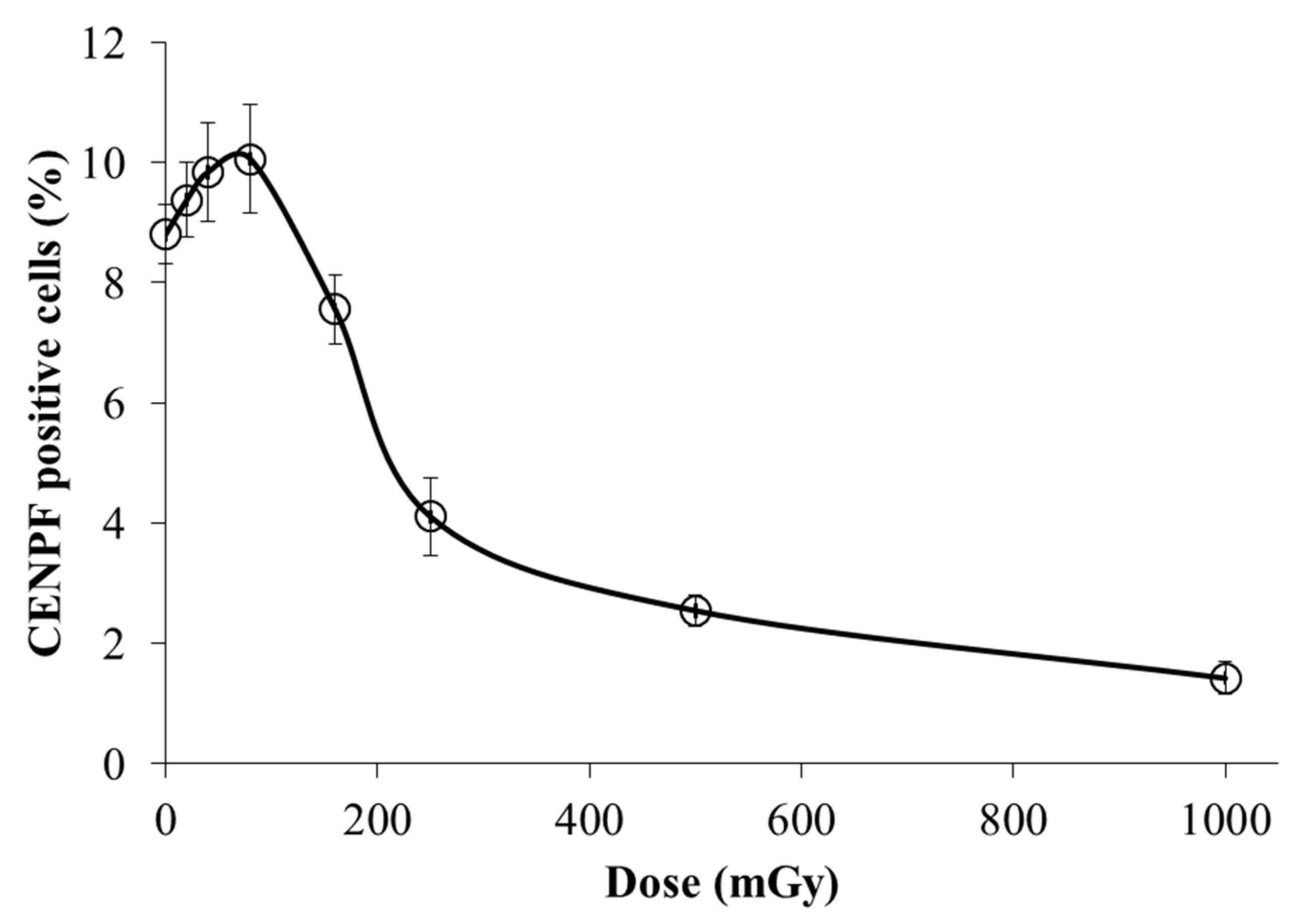
3.3. Dose-dependent changes in the S/G2-phase сell fractions
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Details the DSB repair model
Equations of the DSB model
Kinetic parameters of DSB repair model
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 27.5 | P–5 | 8.82 × 10–5 h–1 |
| b | 2.43×10–3 | P6 | 1.87×105 M–1 h–1 |
| K1 | 11.05 M–1 h–1 | P–6 | 1.55×10–3 h–1 |
| K–1 | 6.6×10–4 h–1 | P7 | 21.36 h–1 |
| K2 | M–1 h–1 | P8 | 1.20×104 M–1 h–1 |
| K–2 | 5.26×10–1 h–1 | P–8 | 2.49×10–4 h–1 |
| K3 | 1.86 M–1 h–1 | P9 | h–1 |
| K4 | M–1 h–1 | P10 | 7.20×10–3 h–1 |
| K–4 | 3.86×10–4 h–1 | P11 | 6.06×10–4 h–1 |
| K5 | 15.24 M–1 h–1 | P12 | 2.76×10–1 h–1 |
| K–5 | 8.28 h–1 | Q1 | 7.80×103 M–1 h–1 |
| K6 | 18.06 M–1 h–1 | Q–1 | 1.71×10–4 h–1 |
| K–6 | 1.33 h–1 | Q2 | 3.00×104 M–1 h–1 |
| K7 | 2.73×105 M–1 h–1 | Q3 | 6.00×103 M–1 h–1 |
| K–7 | 3.20 h–1 | Q–3 | 6.06×10–4 h–1 |
| K8 | 5.52×10–1 h–1 | Q4 | 1.66×10–6 h–1 |
| K9 | 1.66×10–1 h–1 | Q5 | 8.40×104 M–1 h–1 |
| K10 | 1.93×10–7/Nir M | Q–5 | 4.75×10–4 h–1 |
| K11 | 7.50×10–2 h–1 | Q6 | 11.58 h–1 |
| K12 | 11.10 h–1 | R1 | 2.39×103 M–1 h–1 |
| P1 | 1.75×103 M–1 h–1 | R–1 | 12.63 h–1 |
| P–1 | 1.33×10–4 h–1 | R2 | 4.07×104 M–1 h–1 |
| P2 | 7.21 h–1 | R3 | 9.82 h–1 |
| P3 | 1.37×104 M–1 h–1 | R4 | 1.47×105 M–1 h–1 |
| P–3 | 2.34 h–1 | R4 | 12.30 h–1 |
| P4 | 5.52×10–2 h–1 | R–4 | 2.72 h–1 |
| P5 | 1.20×105 M–1 h–1 | R5 | 1.65×10–1 h–1 |
| Nirrep |
References
- Jeggo, P.A.; Löbrich, M. DNA double-strand breaks: their cellular and clinical impact? Oncogene 2007, 26, 7717–7719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushmanov, A.; Vorobyeva, N.; Molodtsova, D.; Osipov, A.N. Utilization of DNA double-strand breaks for biodosimetry of ionizing radiation exposure. Environmental Advances 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerson, S.M.; Romney, C.; Schuck, P.L.; Stewart, J.A. To Join or Not to Join: Decision Points Along the Pathway to Double-Strand Break Repair vs. Chromosome End Protection. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 708763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Her, J.; Bunting, S. How cells ensure correct repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2018, 293, 10502–10511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Merkher, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, N.; Leonov, S.; Chen, Y. Recent advances in therapeutic strategies for triple-negative breast cancer. Journal of Hematology & Oncology 2022, 15, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallmyr, A.; Tomkinson, A. Repair of DNA double-strand breaks by mammalian alternative end-joining pathways. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2018, 293, 10536–10546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitor, A.C.; Huertas, P.; Legube, G.; de Almeida, S.F. Studying DNA Double-Strand Break Repair: An Ever-Growing Toolbox. Front Mol Biosci 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, T.; Allen, R.; Wyllie, A. Defying death after DNA damage. Nature 2000, 407, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinner, A.; Wu, W.; Staudt, C.; Iliakis, G. -H2AX in recognition and signaling of DNA double-strand breaks in the context of chromatin. Nucleic Acids Research 2008, 36, 5678–5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raavi, V.; Perumal, V.; F. D. Paul, S. Potential application of γ-H2AX as a biodosimetry tool for radiation triage. Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research 2021, 787, 108350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothkamm, K.; Barnard, S.; Moquet, J.; Ellender, M.; Rana, Z.; Burdak-Rothkamm, S. DNA damage foci: Meaning and significance. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis 2015, 56, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osipov, A.; Chigasova, A.; Yashkina, E.; Ignatov, M.; Fedotov, Y.; Molodtsova, D.; Vorobyeva, N.; Osipov, A.N. Residual Foci of DNA Damage Response Proteins in Relation to Cellular Senescence and Autophagy in X-Ray Irradiated Fibroblasts. Cells 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkova, A.; Ozerov, I.V.; Pustovalova, M.; Grekhova, A.; Eremin, P.; Vorobyeva, N.; Eremin, I.; Pulin, A.; Zorin, V.; Kopnin, P.; et al. γH2AX, 53BP1 and Rad51 protein foci changes in mesenchymal stem cells during prolonged X-ray irradiation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 64317–64329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, O.; Cucinotta, F. Dynamical modeling approach to risk assessment for radiogenic leukemia among astronauts engaged in interplanetary space missions. Life Sciences in Space Research 2018, 16, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talemi, S.; Kollarovic, G.; Lapytsko, A.; Schaber, J. Development of a robust DNA damage model including persistent telomere-associated damage with application to secondary cancer risk assessment. Scientific Reports 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R. Two-lesion kinetic model of double-strand break rejoining and cell killing. Radiation Research 2001, 156, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, R.; Hahnfeld, P.; Brenner, D. The link between low-LET dose-response relations and the underlying kinetics of damage production/repair/misrepair. International Journal of Radiation Biology 1997, 72, 351–374. [Google Scholar]
- Lea, D.E. Actions of Radiations on Living Cells; University Press: Cambridge, 1946. [Google Scholar]
- Osipov, A.N.; Pustovalova, M.; Grekhova, A.; Eremin, P.; Vorobyova, N.; Pulin, A.; Zhavoronkov, A.; Roumiantsev, S.; Klokov, D.Y.; Eremin, I. Low doses of X-rays induce prolonged and ATM-independent persistence of γH2AX foci in human gingival mesenchymal stem cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27275–27287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pustovalova, M.; Astrelina, Т.A.; Grekhova, A.; Vorobyeva, N.; Tsvetkova, A.; Blokhina, T.; Nikitina, V.; Suchkova, Y.; Usupzhanova, D.; Brunchukov, V.; et al. Residual γH2AX foci induced by low dose x-ray radiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells do not cause accelerated senescence in the progeny of irradiated cells. Aging 2017, 9, 2397–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakl, L.; Marková, E.; Koláriková, L.; Belyaev, I. Biodosimetry of Low Dose Ionizing Radiation Using DNA Repair Foci in Human Lymphocytes. Genes 2020, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belov, O.; Krasavin, E.; Lyashko, M.; Batmunkh, M.; Sweilam, N. A quantitative model of the major pathways for radiation-induced DNA double-strand break repair. Journal of Theoretical Biology 2015, 366, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucinotta, F.A.; Pluth, J.M.; Anderson, J.A.; Harper, J.V.; O'Neill, P. Biochemical kinetics model of DSB repair and induction of gamma-H2AX foci by non-homologous end joining. Radiat Res 2008, 169, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleei, R.; Weinfeld, M.; Nikjoo, H. Single strand annealing mathematical model for double strand break repair. journal of Molecular Engineering and Systems Biology 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleei, R.; Nikjoo, H. Biochemical DSB-repair model for mammalian cells in G1 and early S phases of the cell cycle. Mutation Research-Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis 2013, 756, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decottignies, A. Alternative end-joining mechanisms: a historical perspective. Front Genet 2013, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decottignies, A. Microhomology-mediated end joining in fission yeast is repressed by Pku70 and relies on genes involved in homologous recombination. Genetics 2007, 176, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salles, D.; Mencalha, A.; Ireno, I.; Wiesmuller, L.; Abdelhay, E. BCR-ABL stimulates mutagenic homologous DNA double-strand break repair via the DNA-end-processing factor CtIP. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.; Harper, J.; Cucinotta, F.; O'Neill, P. Participation of DNA-PKcs in DSB Repair after Exposure to High- and Low-LET Radiation. Radiation Research 2010, 174, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.; Stanley, F.; Goodarzi, A. The repair of environmentally relevant DNA double strand breaks caused by high linear energy transfer irradiation - No simple task. DNA Repair 2014, 17, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennardo, N.; Cheng, A.; Huang, N.; Stark, J. Alternative-NHEJ Is a Mechanistically Distinct Pathway of Mammalian Chromosome Break Repair. Plos Genetics 2008, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelot, C.; Magdalou, I.; Lopez, B.S. Replication stress in Mammalian cells and its consequences for mitosis. Genes (Basel) 2015, 6, 267–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.P.; Mirkin, E.V. So similar yet so different: The two ends of a double strand break. Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis 2018, 809, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, I.M.; Chen, J. Histone H2AX is phosphorylated in an ATR-dependent manner in response to replicational stress. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 47759–47762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firsanov, D.V.; Solovjeva Lv Fau - Svetlova, M.P.; Svetlova, M.P. H2AX phosphorylation at the sites of DNA double-strand breaks in cultivated mammalian cells and tissues.
- Pustovalova, M.; Grekhova, A.; Astrelina, Т.; Nikitina, V.; Dobrovolskaya, E.; Suchkova, Y.; Kobzeva, I.; Usupzhanova, D.; Vorobyeva, N.; Samoylov, A.; et al. Accumulation of spontaneous γH2AX foci in long-term cultured mesenchymal stromal cells. Aging 2016, 8, 3498–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grekhova, A.K.; Pustovalova, M.V.; Eremin, P.S.; Ozerov, I.V.; Maksimova, O.A.; Gordeev, A.V.; Vorobyeva, N.Y.; Osipov, A.N. Evaluation of the Contribution of Homologous Recombination in DNA Double-Strand Break Repair in Human Fibroblasts after Exposure to Low and Intermediate Doses of X-ray Radiation. Biology Bulletin 2020, 46, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bee, L.; Fabris, S.; Cherubini, R.; Mognato, M.; Celotti, L. The efficiency of homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining systems in repairing double-strand breaks during cell cycle progression. PloS one 2013, 8, e69061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varis, A.; Salmela, A.L.; Kallio, M.J. Cenp-F (mitosin) is more than a mitotic marker. Chromosoma 2006, 115, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharmalingam, S.; Sreetharan, S.; Brooks, A.L.; Boreham, D.R. Re-evaluation of the linear no-threshold (LNT) model using new paradigms and modern molecular studies. Chem Biol Interact 2019, 301, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boreham, D.R.; Dolling, J.A.; Somers, C.; Quinn, J.; Mitchel, R.E.J. The adaptive response and protection against heritable mutations and fetal malformation. Dose-Response 2006, 4, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murley, J.S.; Baker, K.L.; Miller, R.C.; Darga, T.E.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Grdina, D.J. SOD2-mediated adaptive responses induced by low-dose ionizing radiation via TNF signaling and amifostine. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2011, 51, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojima, M.; Eto, H.; Ban, N.; Kai, M. Radiation-induced bystander effects induce radioadaptive response by low-dose radiation. Radiation Protection Dosimetry 2011, 146, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plews, M.; Simon, S.L.R.; Boreham, D.R.; Parchaliuk, D.; Wyatt, H.; Mantha, R.; Frost, K.; Lamoureux, L.; Stobart, M.; Czub, S.; et al. A radiation-induced adaptive response prolongs the survival of prion-infected mice. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2010, 49, 1417–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.; Lemon, J.A.; Boreham, D.R. Radiation-induced DNA damage and the relative biological effectiveness of 18F-FDG in wild-type mice. Mutagenesis 2014, 29, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeraraghavan, J.; Natarajan, M.; Herman, T.S.; Aravindan, N. Low-dose γ-radiation-induced oxidative stress response in mouse brain and gut: Regulation by NFκB-MnSOD cross-signaling. Mutation Research - Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis 2011, 718, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladenova, V.; Mladenov, E.; Stuschke, M.; Iliakis, G. DNA Damage Clustering after Ionizing Radiation and Consequences in the Processing of Chromatin Breaks. [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.A.; Meek, K. Choosing the right path: does DNA-PK help make the decision?
- Dos Santos, M.; Villagrasa, C.; Clairand, I.; Incerti, S. Influence of the DNA density on the number of clustered damages created by protons of different energies. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms 2013, 298, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydberg, B. Clusters of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation: Formation of short DNA fragments.2. Experimental detection. Radiation Research 1996, 145, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobrich, M.; Cooper, P.; Rydberg, B. Non-random distribution of DNA double-strand breaks induced by particle irradiation. International Journal of Radiation Biology 1996, 70, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoglund, E.; Blomquist, E.; Carlsson, J.; Stenerlow, B. DNA damage induced by radiation of different linear energy transfer: initial fragmentation. International Journal of Radiation Biology 2000, 76, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




