1. Introduction
Andrographis paniculata (Burm. F.) Wall. ex. Nees is the first herbal medicine formally recognized for COVID-19 in Thailand [
1,
2,
3]. However, the clinical, efficacy, and safety results of various Herba Andrographidis preparations are contradictory [
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]. This study aimed to assess the clinical efficacy and safety of Kan Jang®, the fixed combination of
Andrographis paniculata (Burm. F.) Wall. ex. Nees and
Eleutherococcus senticosus (Rupr. & Maxim.) Maxim extracts in 140 patients with mild and moderate COVID-19 inflammatory symptoms in the last three days who were not requiring Intensive Care Unit (ICU) admission per protocol. It should be emphasized that the Kan Jang and Andrographis are two entirely different active substances of two different chemical compositions, with two other unique pharmacological and toxicological profiles /“biological signatures” (
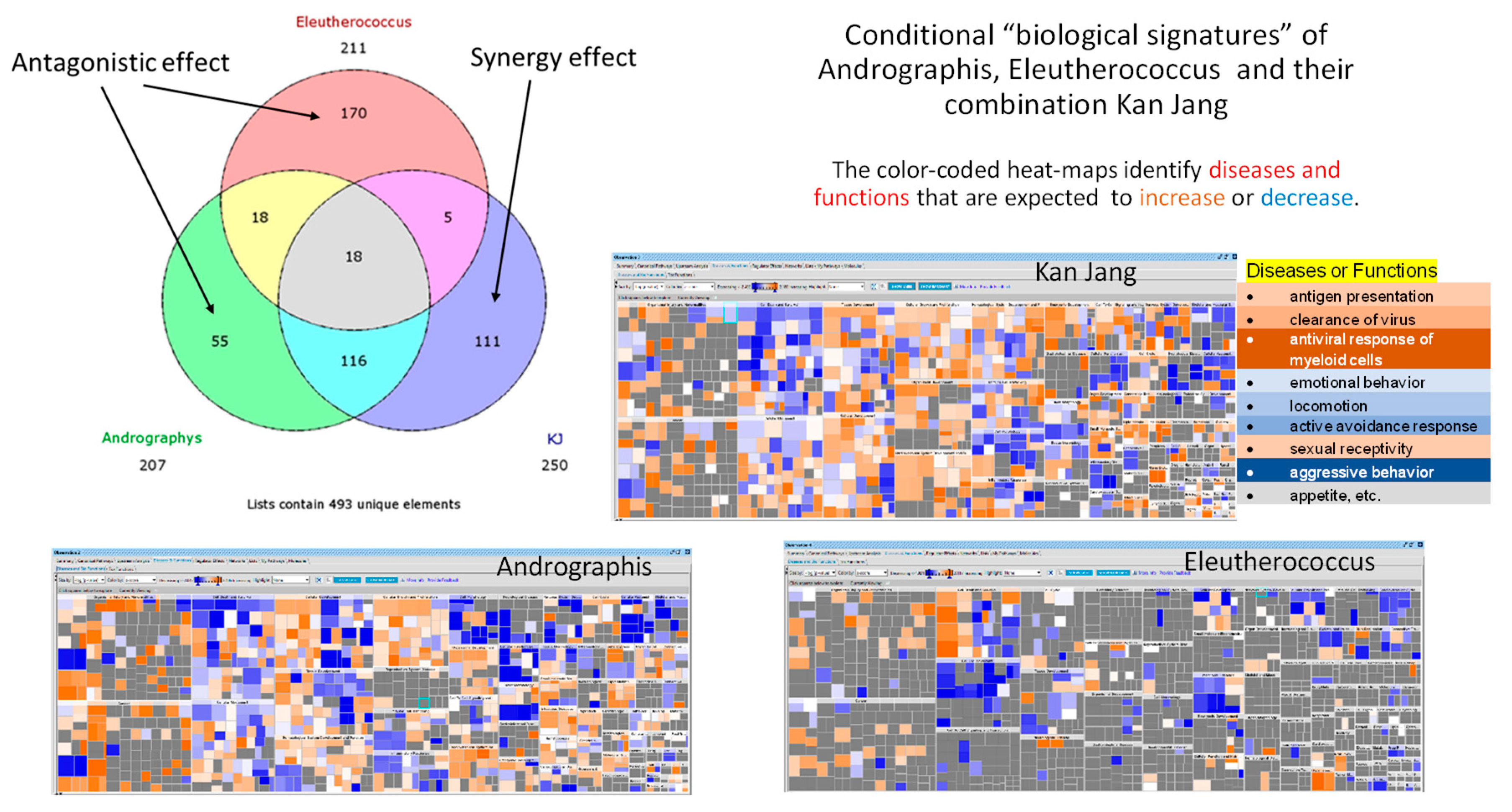
Figure 1), which are different from their ingredients and purified compounds, e.g., andrographolide, eleutheroside E, etc. [
12]. The study aimed to provide clinical validation of the effects of numerous preclinical studies of network pharmacology of Andrographis paniculata and Eleutherococcus senticosus and their possible synergy or antagonism [
12,
13].
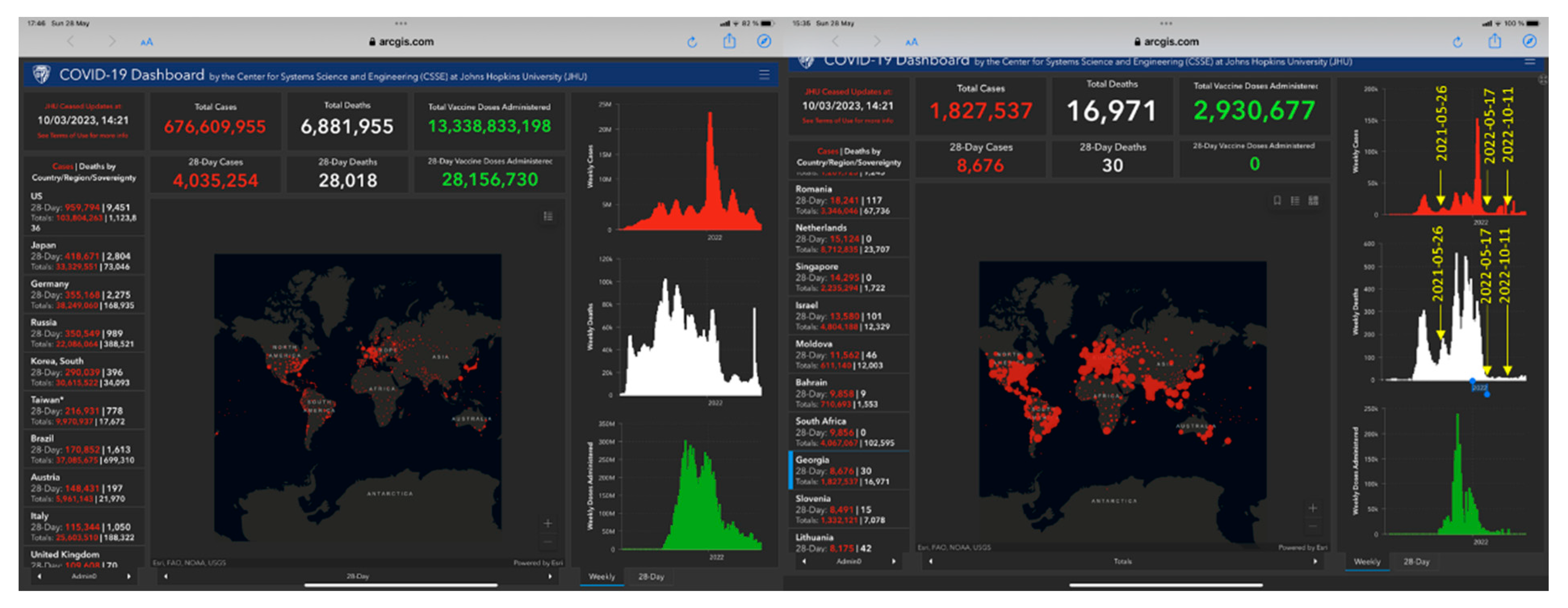
Recently we published the results of an interim analysis of this clinical trial in 86 patients recruited in Georgia during three waves of the SARS-Cov-2,
Figure 2 [
14]. The latest wave was evolving several SARS-Cov-2 variants characterized by a remarkable speed, lesser severe and intense, less comorbidity, and lower death rate, but a younger population, newer symptoms like gastrointestinal, more cases with breathlessness, and much higher positivity rate as compared to the 1st wave [
15]. The further recruiting of patients in the ongoing study was conducted from 2022-05-06 due to the spread of the last wave of the SARS-Cov-2 variants pandemic in Georgia,
Figure 2.
The study provides the results of the analysis in the overall sample size of 140 patients per protocol (PPP) and the intention to treat (ITT), including an additional subset of 54 patients admitted during the last wave epidemic, who were affected mainly by known and unknown mutants/variants of SARS-CoV-2.
2. Results
2.1. Patients
2.1.1. Demographic and Baseline Characteristics
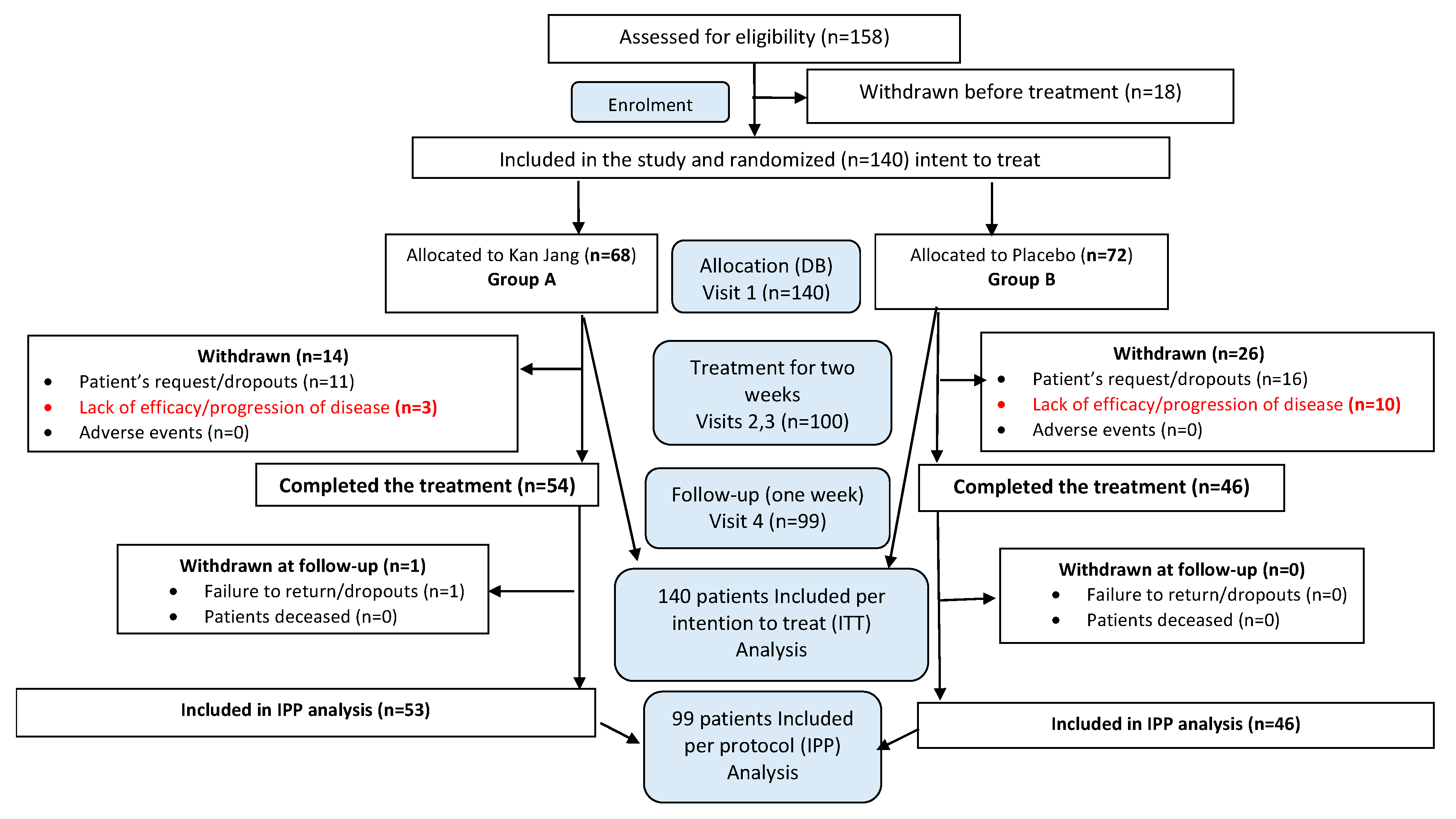
One hundred fifty-eight patients with confirmed diagnoses based on a positive SARS-CoV-2 test, experiencing mild to moderate COVID-19 symptoms were assessed for eligibility with at least 3 to 8 symptoms (fatigue, headache, nasal discharge, loss of smell, taste, cough, muscle pain, and body temperature from 37 to 38
oC) for the last three days before admitting the hospital. The study included one hundred forty patients and randomly assigned to two treatment groups, Kan Jang® (A) and Placebo (B),
Figure 3.
The groups did not show differences in baseline demographic, physical, and other critical clinical measurements, Table 1, except for lower physical activity scores in the Kan Jang group compared with placebo, higher muscle soreness score, loss of smell score, and upper respiratory symptoms score assessed by Wisconsin URS Survey.
Several blood parameters, specifically blood serum IL-6, D-dimer, C-reactive protein, neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils counts, were substantially high of normal ranges typical for acute viral inflammation. However, no significant difference between groups for these inflammatory markers was observed,
Table 1.
2.2. Efficacy
The therapeutic efficacy of Kan Jang® was assessed by comparing (i) -differences in the time to resolve inflammatory symptoms in Kan Jang® and placebo groups of patients and (ii)- differences in the relief severity of inflammatory symptoms from the baseline in Kan Jang® and placebo groups of patients. Treatment groups were compared for all efficacy outcome measures to assess primary and secondary endpoints.
2.2.1. Primary endpoints
The primary efficacy endpoints were: (i)- the rate of patients (%) with clinical deterioration, (ii) – the duration of hospitalization, (iii) – the time to virus clearance, and (iv) - the duration of the acute phase of disease assessed as the time from the start of study medicine to complete symptom resolution, (v) – fever resolution and relief the severity of fatigue, headache, sore throat, cough, rhinorrhea (nasal discharge/runny nose), myalgia (muscle pain), loss of smell and taste from baseline at two weeks, and (vi) - severity of Respiratory symptoms and quality of life by Wisconsin Upper Respiratory Symptom Survey Questionary Score.
2.2.1.1. The rate of patients with clinical deterioration and virus clearance.
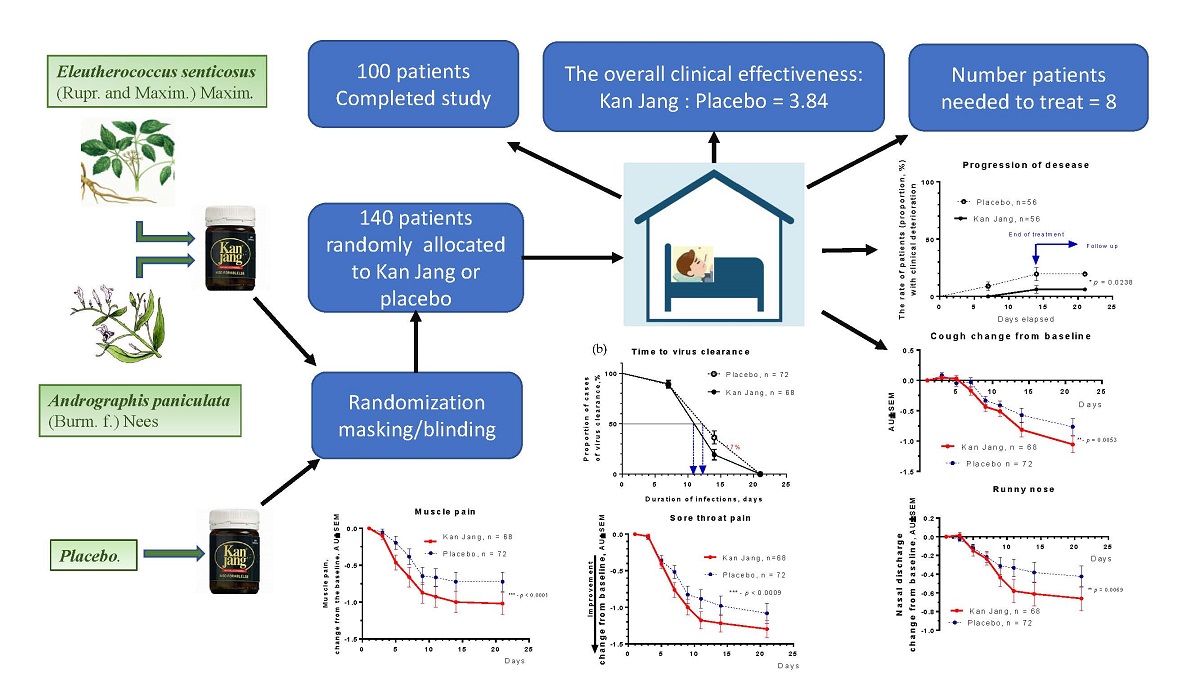
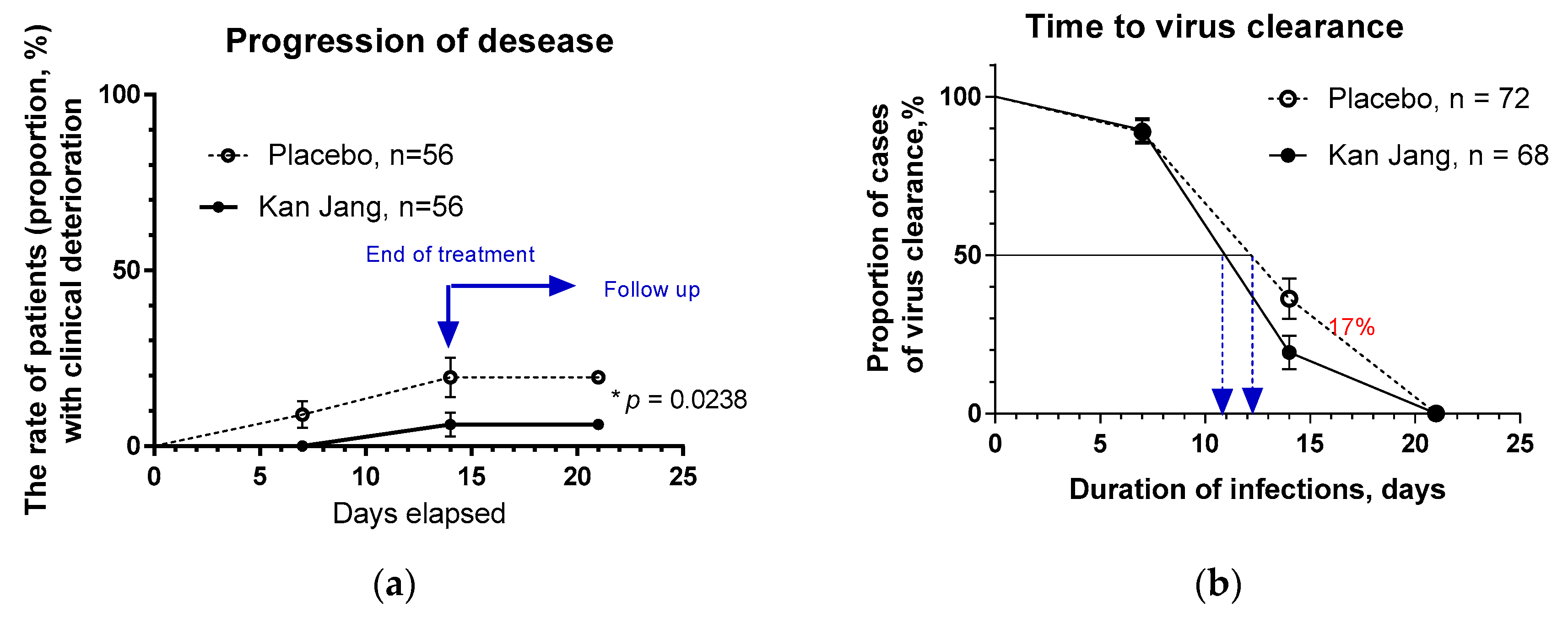
In Kan Jang®, Group A of 68 patients, 12 were dropouts, and three were withdrawn from the study due to lack of efficacy and disease progression; they continued the treatment with steroids and antibiotics,
Figure 4.
In Placebo Group B, of 72 patients, 16 were dropouts, and ten were withdrawn from the study due to lack of efficacy and disease progression; they continued the treatment with steroids and antibiotics,
Figure 4a.
The disease progression rate in the placebo group (56 patients) was 17.86%, while in the Kan Jang group (56 patients) was 5.36%;
p = 0.0176 (significant result) at 95% significance level (confidence 95%), power – 92.99%, IPP analysis;
Figure 4a.The statistical difference (St. Error 0.0477) in the rates of patients with clinical deterioration in the Kan Jang treatment (A) and placebo control (B) groups was significant,
p = 0.0236 in 140 patients included per intention to treat (ITT) analysis, observed power – 90.66%.
The overall clinical effectiveness, defined as the ratio of proportions of effective to ineffective cases in Kan Jang (94.54/5.36=17.65) to placebo control (82.14/17.86=4.6) group, was 3.84. Absolute risk reduction (ARR%) by Kan Jang treatment was 12.5%, while the relative risk reduction - 214.8%. The number of patients required to treat with Kan Jang to prevent one additional bad outcome (defined as the Number Needed to Treat, NNT = 1/ARR) was eight patients.
The percentage of patients with negative SARS-Cov-2 virus test was 17% lower in the Kan Jang group compared to placebo after 14 days (19.3%
vs 36.3%, difference - 17.0±8.5%,
p = 0.819) of the treatment,
Figure 4b. The rate of virus clearance was faster was 1.6 days shorter in the Kan Jang group (10.8 days) compared to the placebo (12.4 days), and the time to virus clearance in 50% of patients; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 1.686, 95% CI of ratio from 0.8698 to 3.269,
Figure 4b.
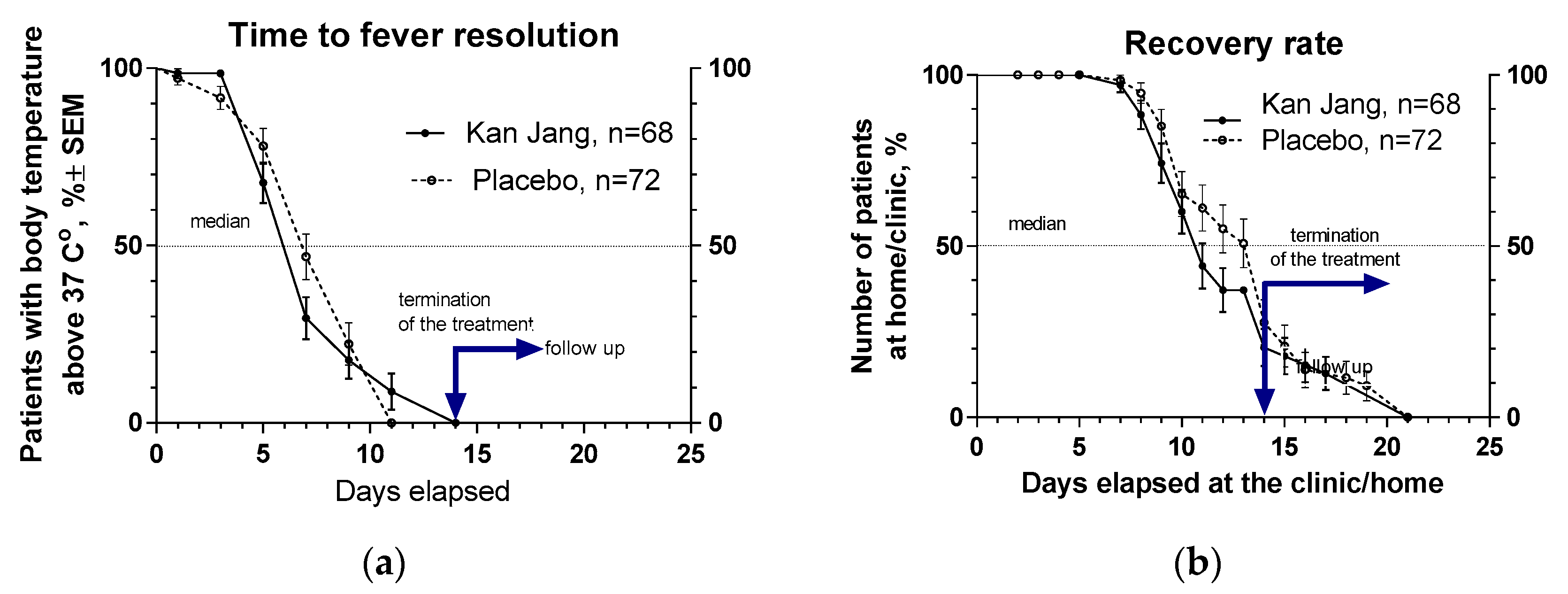
2.2.1.2. Recovery time and time to fever resolution.
The proportion of patients with high body temperature (from >370 C to < 380 C) was 17.3% lower in the Kan Jang group (29.5%), compared with to placebo group (46.8%), after one week of treatment; however, this difference was statistically insignificant,
Figure 5a. Duration of increased body temperature (from >370 C to < 380 C) was also shorter in the Kan Jang group vs. to placebo group; median recovery in Kan Jang® was six days, while in placebo – 7 days; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 1.336, 95% CI of ratio from 0.808 to 2.309,
Figure 5a.
The median (50%) number of patients who elapsed at the clinic was three days shorter in Kan Jang treatment (11 days) compared to placebo (14 days); the ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 0.7857, 95% CI of ratio from 0.530 to 1.164, hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 1.232, 95% CI of ratio from 0.778 to 1.951,
Figure 5b.
2.2.1.3. The severity and time to resolution of inflammatory symptoms
The occurrence of various inflammatory symptoms was quite different at the baseline of the cohort of COVID-19 patients recruited in this study (
Table 1); the most common symptoms were fatigue (in 100% of patients), headache (in 91% of patients), sore throat (in 62% of patients), cough (in 55% of patients), muscle pain (51%) and while rhinorrhea (27%) and loss of smell (16%) and taste (4%) were observed in minority of patients.
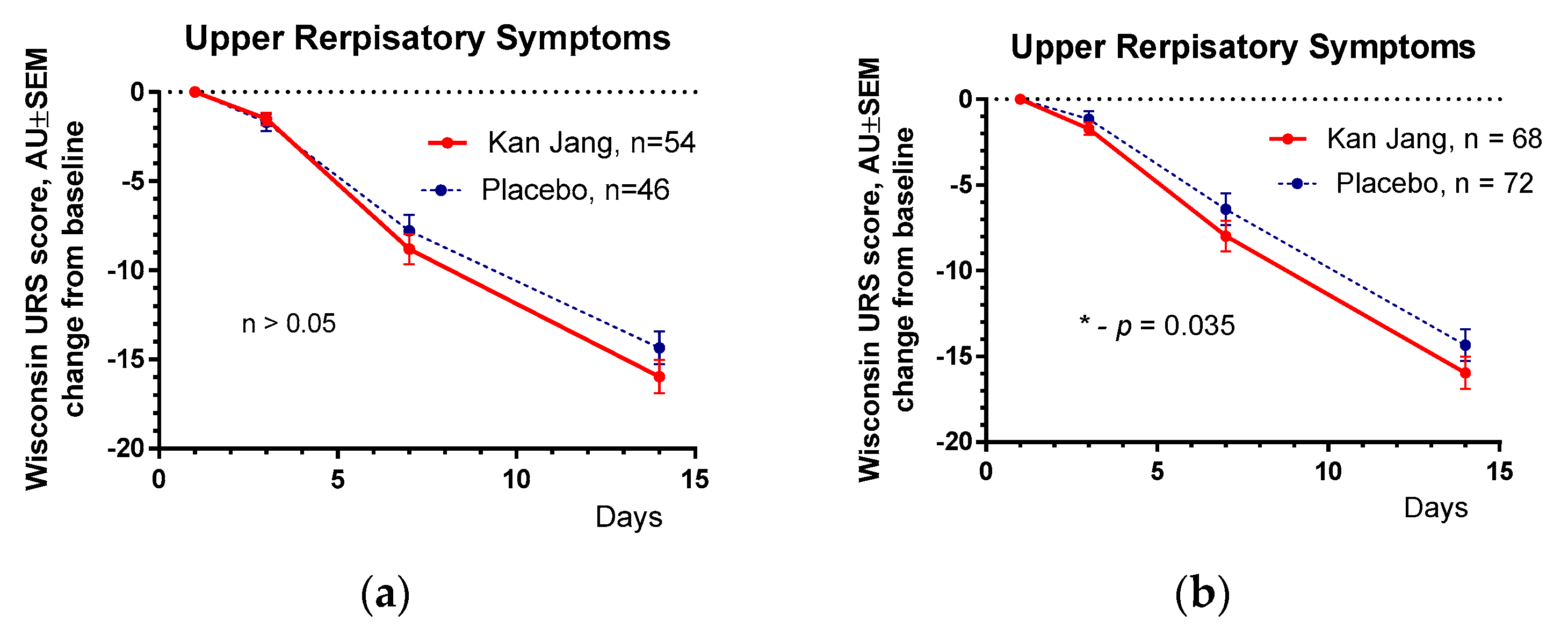
The results of the assessment of upper respiratory symptoms by the Wisconsin URTI survey (including runny and plugged nose, sneezing, sore throat, cough, hoarseness, head and congestion, and feeling tired) show a beneficial effect of Kan Jang compared with placebo,
Figure 6.
The severity of all inflammatory symptoms gradually decreased from the baseline to the end of therapy (Day 14) and the follow-up period (21 days) in both groups of patients,
Figure 6,
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9 and
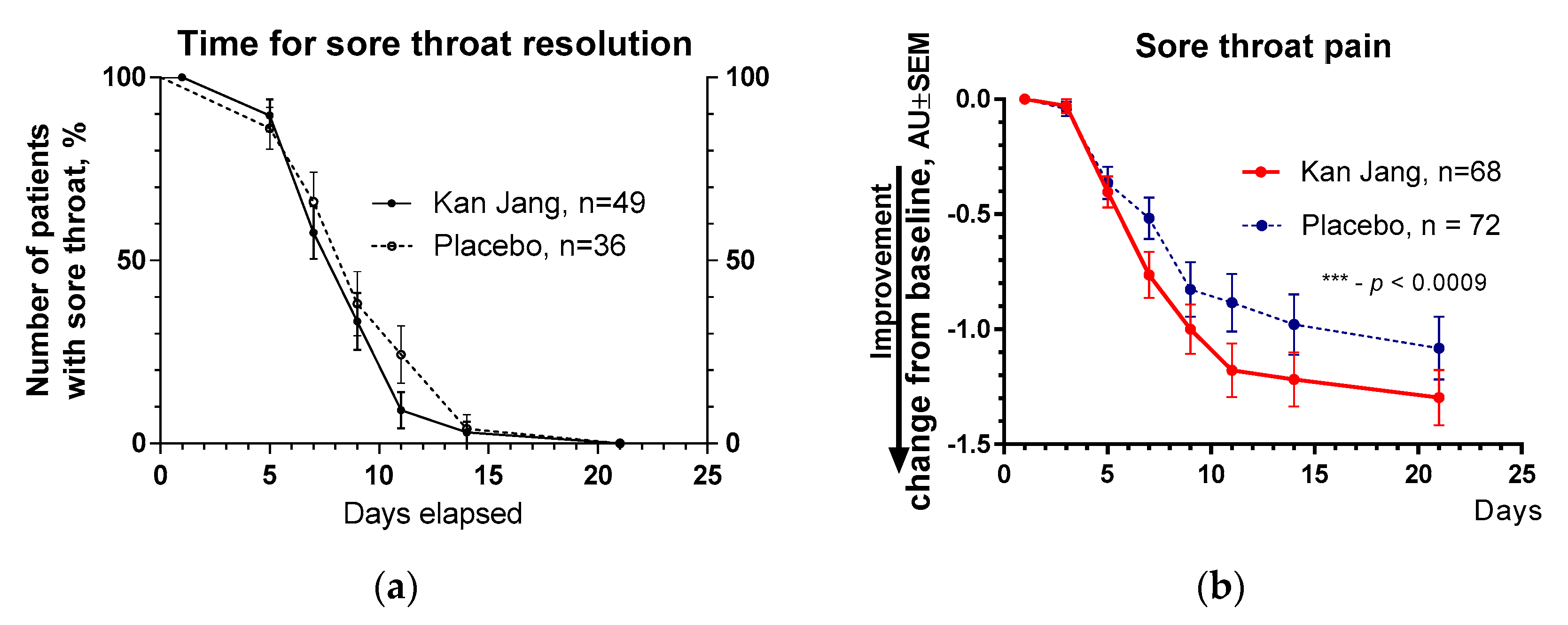
Figure 10. However, the improvement of relief of inflammatory symptoms of patients in the Kan Jang group was significantly better compared to placebo effects over time of treatment and the follow-up period in the Kan Jan group, including relief of sore throat (
Figure 7), rhinorrhea (nasal discharge/runny nose,
Figure 8), myalgia (muscle pain,
Figure 9), and cough (
Figure 10).
The rates of resolution of cough over time were similar in Kan Jang and the placebo groups,
Figure 10a; however, the relief of severity of the cough of patients taking Kan Jang over the time from baseline was significantly effective compared to placebo,
Figure 10b. The Kan Jang® relieved the severity of cough compared with placebo, as it was evident in ITT analysis in 140 randomized patients (
p = 0.053), in PPA analysis in 100 patients who completed the study (
p = 0.018), a subset of 54 patients during last wave of COVID-19 epidemic in Georgia (
p = 0.0049, ITT analysis), and a subset of 42 patients completed study during last wave of COVID-19 epidemic in Georgia (p = 0.0047, PPA analysis).
2.2.2. Secondary endpoints
Secondary endpoints comprised the measures of (i) -Immune response marker IL-6 concentration in the serum, (ii) – blood hypercoagulation marker Dimer-D, (iii) - inflammatory marker C-reactive protein, (iv) - physical activity, (v) – physical performance, and (vi) - cognitive performance/
2.2.2.1. Blood serum markers of immune response and inflammation
At the beginning of the study, the baseline level of all selected markers of immune response and inflammation, IL-6, c-reactive protein, and D-dimer, were extensively higher than typical blood values,
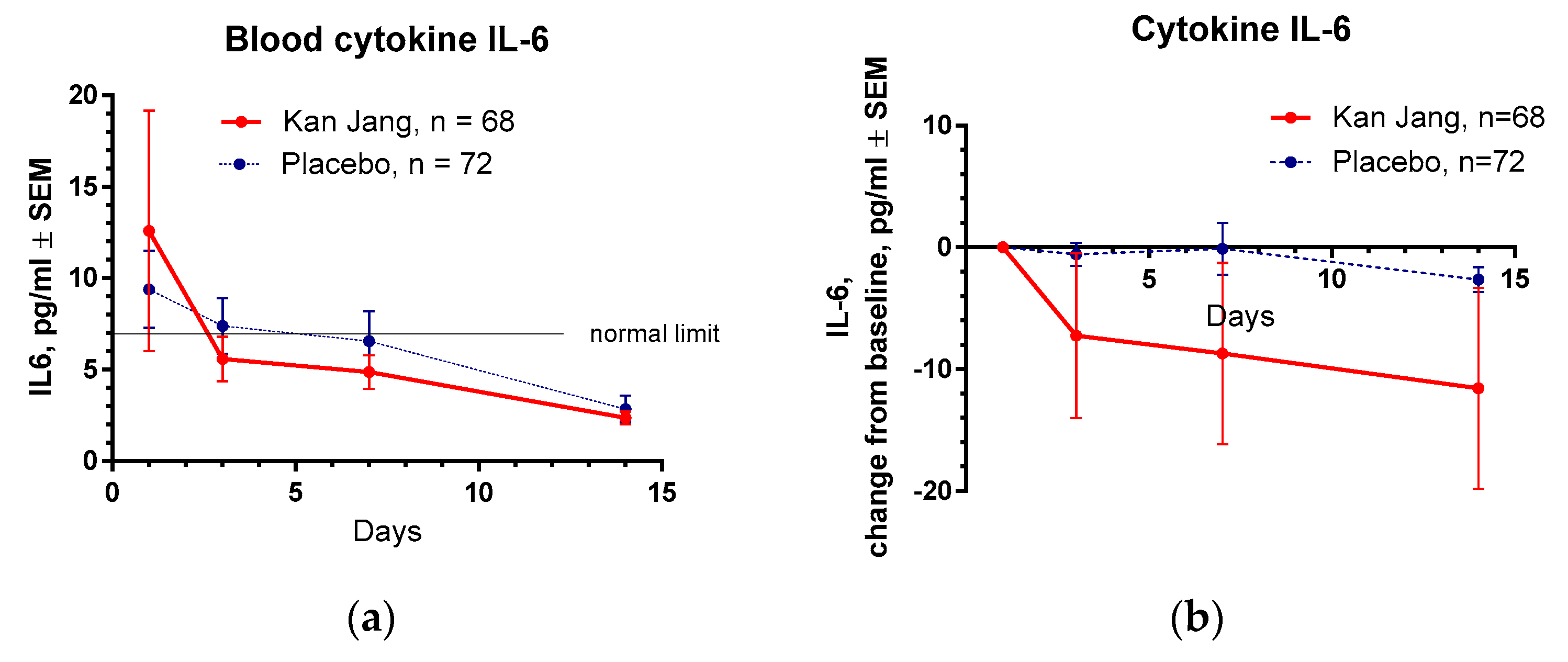
Table 1. In 3 days of the treatment with Kan Jang, the level of IL-6 reached the standard limit of 7 pg/ml, while in the placebo group, 14 days after randomization,
Figure 11 a.
Between-groups comparison of the changes in the level of cytokine IL-6 in the blood did not show significant interaction between treatment-time (p = 0.1619), despite the Kan Jang® treatment showing a noteworthy decrease in cytokine IL-6 in the blood (-11.575 pg/ml on the day 14
th) compared to the placebo (-2.246 pg/ml on the day 14
th),
Figure 11b, ITT analysis.
The level of C-reactive protein and D-dimer was also normalized in the blood of all patients at the end of treatment; however, the Kan Jang® treatment had no significant difference in effects on C-reactive protein and D-dimer compared to placebo, p>0.05, Figures in Supplement 2.
2.2.2.2. Physical activity, physical and cognitive performance
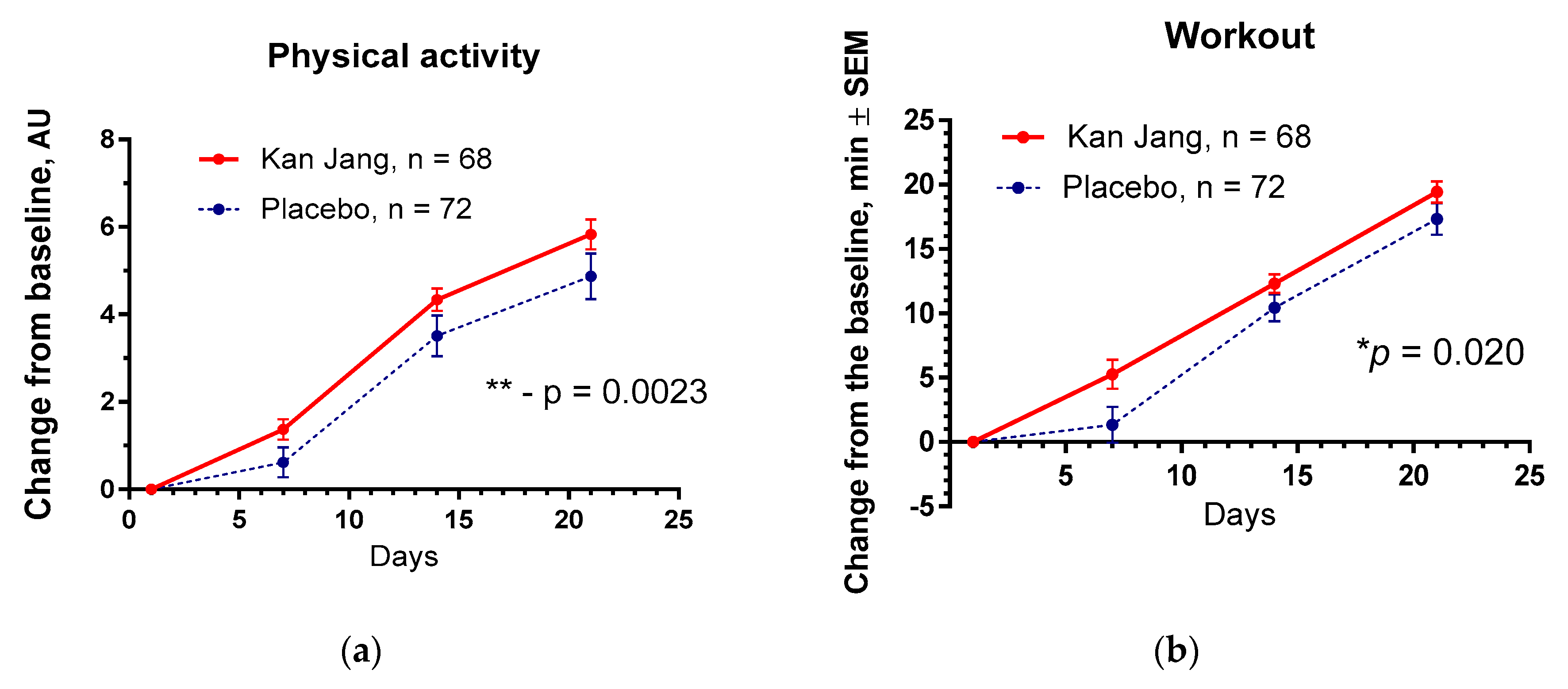
The Kan Jang® treatment significantly increased physical activity (p = 0.0023) and workout time (in min, p = 0.020) in patients compared to the placebo,
Figure 12.
No significant differences between the effects of Kan Jang® and placebo were observed on cognitive performance, quality of life, and other secondary outcomes.
2.3. Safety
No adverse events were recorded in the study. Regardless of causality, adverse events were monitored for all patients from the first dose and through the one-week follow-up period.
3. Discussion
Several antiviral drugs (Paxlovid™ [
17], Remdesivir, Bebtelovimab[
18], Molnupiravir [
19], Andrographis [
1,
2,
3]) and immune modulators (Olumiant, an Interleukin-6 receptor blocker [
20]) were approved by Drug regulatory Authorities against COVID-19 for treating non-hospitalized or hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Recently a systematic review and meta-analysis of 50 clinical trials (involving 11,624 patients) of Chinese herbal medicine in COVID-19 concluded that they are effective and safe in combination with conventional "Western" drugs, but the certainty of the evidence ranged from moderate to very low [
19]. Similar conclusions were made in other systematic reviews and meta-analyses of Chinese herbal medicine in COVID-19 [
21,
22,
23,
24,
25].
In this clinical trial, the efficacy of Kan Jang in patients with mild and moderate symptoms of COVID-19 was studied. In the first subset of 86 patients, Kan Jang was found to effectively relieve sore throat, muscle pain, and runny nose in patients with mild and moderate symptoms of COVID-19 [
14]. Further increase of the sample size to 140 patients resulted in improved efficacy of Kan Jang in ameliorating cough, sore throat/pain, runny nose, and muscle soreness and reducing the Wisconsin Upper Respiratory Symptoms score compared to placebo. Kan Jang® decreased blood inflammatory marker IL-6 over the recovery time in the subgroup of 86 patients with mild and moderate symptoms; however, the effect was statistically insignificant in the sample size of 140 patients, which was enriched with the 54 patients infected with less pathogenic variant during the last wave of COVID-19,
Figure 2.
Kan Jang® increased physical activity and workout; however, it did not affect cognitive functions (attention and memory), Quality of life Score, time to normalization of body temperature, inflammatory markers D-dimer, and c reactive protein compared with the placebo group.
Notably, the rate of patients with clinical deterioration and disease progression was significantly lower in the Kan Jang group than in the placebo group. The disease progression rate in the placebo group was about 2.5-fold higher than in the Kan Jang Group,
Figure 2. Absolute risk reduction (ARR) by Kan Jang treatment is 14%, and the relative risk reduction (RRR) of 243.9%. The number of patients required to treat (NNT) with Kan Jang to prevent one additional bad outcome was found to be eight patients. As a rule, the higher ARR and lower NNT are, the more effective the intervention is. For comparison, Paxlovid™ effectively reduced the risk of progression (ARR of 6.2%) to severe COVID-19 in symptomatic adults at high risk for progression to severe COVID-19, and the number Needed to Treat (NNT) was 17 patients [
17]. Paxlovid™, which, unlike Kan Jang, induces dysgeusia, diarrhea, hypertension, and myalgia [
17]. The safety of Kan Jang is an essential advantage compared to the safety of other anti-Covid-19 drugs [
17,
26,
27]. The treatment with Kan Jang® was well tolerated, and no adverse events were recorded in this study. That is consistent with the results of previous clinical studies where only four adverse events were recorded in one [
28] of six studies [
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33] with patients in the Kan Jang group. In that study, the only common adverse reaction was mild pruritus observed in 4 patients in the Kan Jang® group and six in the placebo group [
14], and no severe adverse reactions were observed.
Kan Jang has an excellent safety profile [
28,
34], presumably due to the contribution adaptogenic and antitoxic activity of Eleutherococcus [
35]. Cytoprotective (neuroprotective, hepatoprotective, cardioprotective), stress-protective, antioxidant, antitoxic, and immunomodulating activity of Eleutherococcus preparations was demonstrated in many experimental models on isolated cells and (in vitro and ex vivo) animals [
36,
37,
38,
39]. This evidence of the safety of the Kan Jang combination shows that the pharmacological activity and toxicity of multi-component drugs are different from their ingredients, and the effects observed on purified compounds cannot be just extrapolated to their combinations with other substances and
vice versa due to their multiple synergistic and antagonistic interactions in the organism [
12,
37,
38,
39],
Figure 1. In other words, the results obtained in this study are product specific. They cannot be applied to mono herbal drugs, e.g., Andrographis extract, which in turn is the mixture of 39 compounds such as andrographolides, flavonoids, etc., and deregulates quite a different number of genes than expected from a simple calculation of many constituents of the plant extracts [
12].
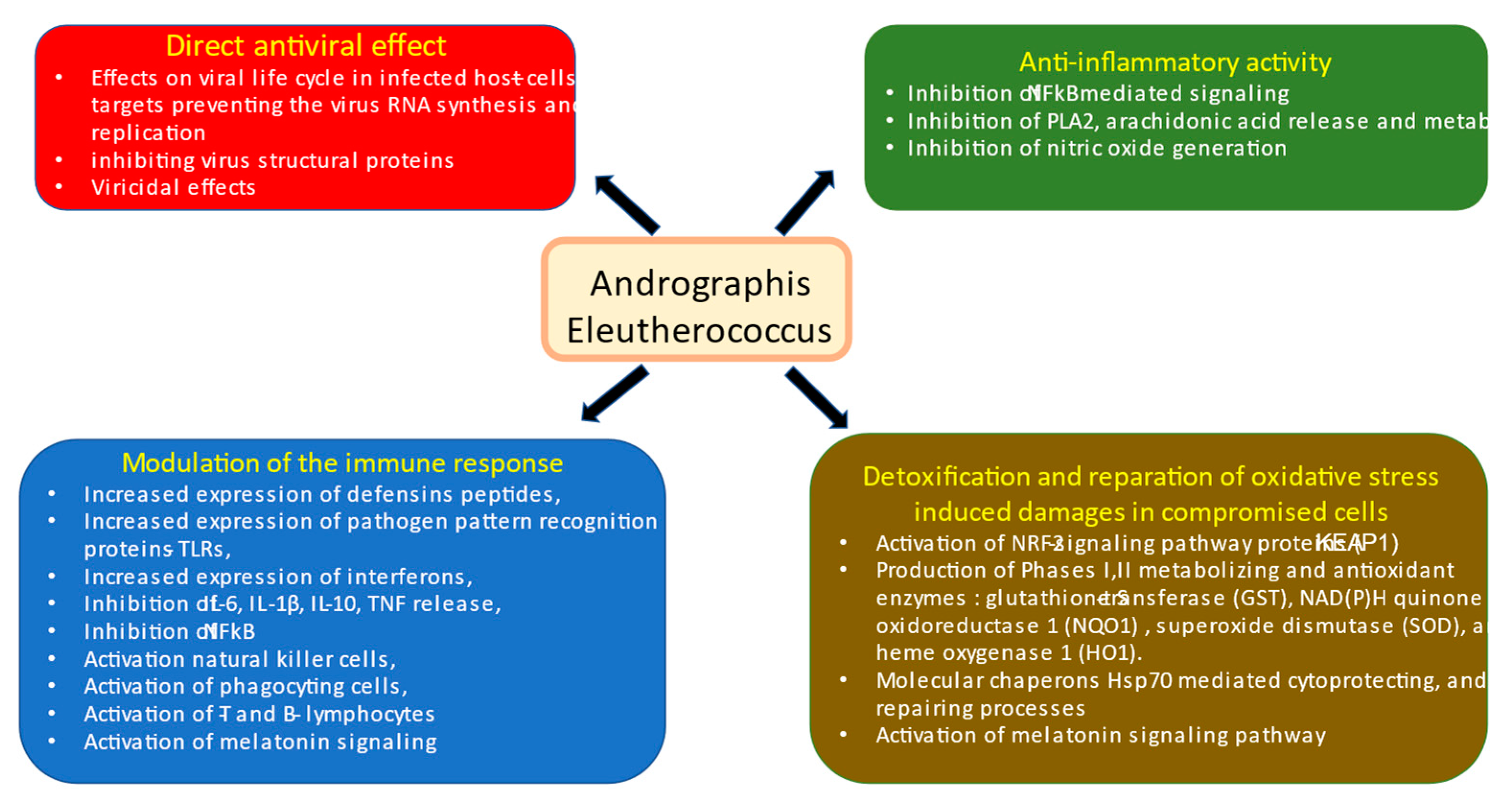
In this context, an essential difference in the mode and mechanisms of action of Kan-Jang and Andrographis compared with other drugs is its multitarget effects both directly on virus-receptor binding, viral membrane fusion into the host cell, viral replication, transcription, translocation, assembly, and release to infect other host cells [
13,
40], as well as indirect antiviral activity due to multiple effects on innate and adaptive immune systems, inflammatory response, and essentially on recovery oxidative stress-induced damages in compromised cells [
13],
Figure 13.
The results of this study are consistent with the previous publications [
14,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33] where Kan Jang effectively relief sore throat, runny nose, cough, and muscle pain of patients with various upper respiratory tract viral infections, including a variety of variants of SARS-Cov-2 virus resulting in quite different mild and moderate symptoms, virulence, and potential morbidity.
The limitations of our study were the short duration of symptoms of COVID-19 before treatment (for three days) and the lack of concomitant chronic diseases, which can increase the risk of progression of the disease and intensive care therapy for patients. Further studies are required in patients at high risk for progression of pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and septic shock.
4. Materials and Methods
This prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, quadruple-blind, two-parallel-group (
Figure 1 and Supplement 1), phase II interventional study was conducted at the Tbilisi State Medical University, Tbilisi, Georgia, with the approval of the Biomedical Research Ethics Committee of Tbilisi State Medical University and National Council on Bioethics (Registration Nr 3-2021/87, date of final protocol approval March 25, 2021, March 2021). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04847518.
https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04847518 (accessed on June 6, 2022).
Recruitment for the study was initiated on May 26, 2021, the 86th patient was recruited on March 30, 2022, and the study was completed on October 30, 2022.
The methods of the study were described in according to CONSORT recommendations [
41] in a recent publication in detail [
14] including study design, recruitment, and screening of patients, schedule of examinations, study population, patients inclusion and exclusion criteria, participant withdrawal, the intervention and comparator, doses and treatment regimens, methods of randomization and blinding, generation of sequence, allocation concealment, implementation, blinding of participants and personnel, completeness of outcome data, evaluation of compliance, statistical analysis, and sample size considerations [
14].
Overall, 158 patients were assessed for eligibility, and 140 patients with Mild COVID symptoms [
14] for the last three days, were randomized and included in the intention to treat analysis of the study (Supplement 1, Full Analysis Dataset). In total, 100 patients (71,4% of randomized) completed their respective treatment cycles according to protocol, while 40 patients (38,6% of randomized ) discontinued therapy after receiving at least one dose of study preparations due to the patient's request. Nighty-nine patients, who completed the treatment, were evaluated for treatment efficacy for two weeks (visits 2 and 3) of treatment and one week after completing the treatment (the follow-up visit 4) and comprised. The distribution between the study groups and the disposition of patients is shown in the flow chart in
Figure 1. The schedule of procedures and examinations is shown in
Table 3. 5. Conclusions
This study provides new evidence on the clinical efficacy and safety of adaptogens, specifically Kan Jang®, in the acute phase of mild COVID-19. Kan Jang® reduces the risk of disease progression, the duration of illness, virus clearance, and days of hospitalization, and accelerates recovery of patients, relief of sore throat, muscle pain, runny nose, and normalization of body temperature. Kan Jang® significantly relieves the severity of inflammatory URTI symptoms, including sore throat, cough, runny nose, and muscle pain, and increases patients' physical performance (workout) compared to placebo.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P.; methodology, A.P.; software, A.H., A.P., and N.M.; formal analysis, A.P.; investigation, L.R., E.P.; resources, L.R.; data curation, E.P., NM, and A.H.; writing—original draft preparation, A.P.; writing—review and editing, A.P., E.P.; supervision, R.S., and A.H.; project administration, R.S., and L.R.; funding acquisition, R.S., and L.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Swedish Herbal Institute AB in Vallberga, Sweden; Grant Nr 2021-1, dated February 20, 2021.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted at the Tbilisi State Medical University, Tbilisi, Georgia, with the approval of the Biomedical Research Ethics Committee of Tbilisi State Medical University and the National Council on Bioethics (Registration Nr 3-2021/87, date of final protocol approval March 25, 2021, March 2021). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04847518.
https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04847518 (accessed on June 6, 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
All participants provided written informed consent to join the study before inclusion.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article and supplementary materials.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the Swedish Herbal Institute for the supply of investigational products.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. A.P. is self-employed at the research and development company Phytomed AB and has no shares or financial interest in any pharmaceutical company. The funders had no role in the study's design, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Yuvejwattana, S. Thailand Clears Use of Herbal Medicine for Covid-19 Treatment. Bloomberg. December 30, 2020, 7:02 AM GMT+1. Available online: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2020-12-30/thailand-clears-use-of-herbal-medicine-for-covid-19-treatment.
- Yearsley, C. Thailand Approves Asian Herb Andrographis to Treat COVID-19. HerbalGram. 2021, 129, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Karbwang, J.; Na-Bangchang, K. Repurposed drugs for COVID-19 treatment. J. Thai. Trad. Alt. Med. 2021, 19, 285–302. [Google Scholar]
- Wanaratna, K.; Leethong, P.; Inchai, N.; Chueawiang, W.; Sriraksa, P.; Tabmee, A.; Sirinavin, S. Efficacy and safety of Andrographis paniculata extract in patients with mild COVID-19: A randomized controlled trial. medRxiv. 2021. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Efficacy-and-safety-of-Andrographis-paniculata-in-A-Wanaratna-Leethong/1f40a6181de4e0f15ab296673794210e82236455.
- Rattanaraksa, D.; Khempetch, R.; Poolwiwatchaikool, U.; Nimitvilai, S.; Loatrakul, O.; Srimanee, P. The efficacy and safety of Andrographis paniculata extract for the treatment of COVID-19 patients with mild symptoms, Nakhonpathom hospital. Reg. Med. J. 2021, 40, 269–281. [Google Scholar]
- Tanwettiyanont, J.; Piriyachananusorn, N.; Sangsoi, L.; Boonsong, B.; Sunpapoa, C.; Tanamatayarat, P.; Kanchanasurakit, S.; Na-Ek, N. The efficacy of Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Wall. ex Nees crude extract in hospitalized mild COVID-19 patients: a retrospective cohort study. medRxiv. 2022.
- Shanker, K.; Rangnekar, H.; Wele, A.; Soni, P.; Gaikwad, P.; Pal, A.; Bawankule, D.U.; Chanda, D. A randomized controlled pilot study of add-on therapy of CIM-MEG19 (standardized Andrographis paniculata formulation) in mild to moderate COVID-19. Phytomedicine Plus 2023, 3, 100398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lv, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, L.; Xu, Q.; Zou, X.; Ding, Y.; Tian, J.; Fan, J.; Fan, H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of Xiyanping injection in the treatment of COVID-19: A multicenter, prospective, open-label and randomized controlled trial. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 4401–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewdech, A.; Nawalerspanya, S.; Assawasuwannakit, S.; Chamroonkul, N.; Jandee, S.; Sripongpun, P. The use of Andrographis paniculata and its effects on liver biochemistry of patients with gastrointestinal problems in Thailand during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwettiyanont, J.; Piriyachananusorn, N.; Sangsoi, L.; Boonsong, B.; Sunpapoa, C.; Tanamatayarat, P.; Na-Ek, N.; Kanchanasurakit, S. Use of Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Wall. ex Nees and risk of pneumonia in hospitalised patients with mild coronavirus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 947373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intharuksa, A.; Arunotayanun, W.; Yooin, W.; Sirisa-Ard, P. A Comprehensive Review of Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees and Its Constituents as Potential Lead Compounds for COVID-19 Drug Discovery. Molecules 2022, 27, 4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panossian, A.; Seo, E.-J.; Wikman, G.; Efferth, T. Synergy assessment of fixed combinations of Herba Andrographidis and Radix Eleutherococci extracts by transcriptome-wide microarray profiling. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panossian, A.; Brendler, T. The Role of Adaptogens in Prophylaxis and Treatment of Viral Respiratory Infections. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratiani, L.; Pachkoria, E.; Mamageishvili, N.; Shengelia, R.; Hovhannisyan, A.; Panossian, A. Efficacy of Kan Jang® in Patients with Mild COVID-19: Interim Analysis of a Randomized, Quadruple-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.K.; Iyengar, K.P.; Vaishya, R. Differences between First wave and Second wave of COVID-19 in India. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2021, 15, 1047–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (2019- nCoV) infection is suspected: interim guidance. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/clinical-management-of-novel-cov.pdf.
- Lamb, Y.N. Nirmatrelvir Plus Ritonavir: First Approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antiviral Drugs That Are Approved, Authorized, or Under Evaluation for the Treatment of COVID-19. Last Updated: April 29, 2022. In: COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health. Accessed on April 29, 2022. https://files.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/guidelines/covid19treatmentguidelines.pdf; pp.140-221. Available online: https://files.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/guidelines/section/section_36.pdf.
- Molnupiravir_COVID19-MSD - Art 5(3) - Conditions for Use (europa.eu). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/referral/lagevrio-also-known-molnupiravir-mk-4482-covid-19-article-53-procedure-conditions-use-conditions_en.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2022).
- World Health Organization. Therapeutics and COVID-19. Therapeutic Management of Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19. Last Updated: February 24 2022. Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/management/clinicalmanagement/hospitalized-adults--therapeutic-management/ (accessed on 7 August 2022).
- Tong, L.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, S.; Yang, Y.; Luo, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, F. Combination of Chinese herbal medicine and conventional western medicine for coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1175827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Hu, H.; Qiang, X.; Lin, S.; Pang, B.; Cao, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, W.; et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine for COVID-19: A Network Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2022, 50, 883–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-T.; Ji, C.-H.; Dai, R.-C.; Hei, P.-J.; Liang, J.; Wu, X.-Q.; Li, Q.-S.; Yang, J.-C.; Mao, W.; Guo, Q. Traditional Chinese medicine treatment for COVID-19: An overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. J. Integr. Med. 2022, 20, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Xu, N.; Zhou, Y.; Song, J.; Liu, J.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, R. Contribution of traditional Chinese medicine combined with conventional western medicine treatment for the novel coronavirus disease ( COVID -19), current evidence with systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytotherapy Res. 2021, 35, 5992–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.-B.; Fang, M.; Liang, C.-H.; Lan, H.-D.; Shen, C.; Yan, L.-J.; Hu, X.-Y.; Han, M.; Robinson, N.; Liu, J.-P. Therapeutic effects and safety of oral Chinese patent medicine for COVID-19: A rapid systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2021, 60, 102744–102744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izcovich, A.; Siemieniuk, R.A.; Bartoszko, J.J.; Ge, L.; Zeraatkar, D.; Kum, E.; Qasim, A.; Khamis, A.M.; Rochwerg, B.; Agoritsas, T.; et al. Adverse effects of remdesivir, hydroxychloroquine and lopinavir/ritonavir when used for COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e048502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupte, V.; Hegde, R.; Sawant, S.; Kalathingal, K.; Jadhav, S.; Malabade, R.; Gogtay, J. Safety and clinical outcomes of remdesivir in hospitalised COVID-19 patients: a retrospective analysis of active surveillance database. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narimanyan, M.; Jamalyan, K.; Balyan, A.; Barth, A.; Palm, S.; Wikman, G.; Panossian, A. Early intervention with Kan Jang® to treat upper-respiratory tract infections: A randomized, quadruple-blind study. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2021, 11, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielian, E.; Shukarian, A.; Goukasova, G.; Chandanian, G.; Panossian, A.; Wikman, G.; Wagner, H. A double blind, placebo-controlled study of Andrographis paniculata fixed combination Kan Jang in the treatment of acute upper respiratory tract infections including sinusitis. Phytomedicine 2002, 9, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulichenko, L.L.; Kireyeva, L.; Malyshkina, E.N.; Wikman, G. A randomized, controlled study of Kan Jang® versus amantadine in the treatment of influenza in Volgograd. J. Herb. Pharmacother. 2003, 173, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchior, J.; Palm, S.; Wikman, G. Controlled clinical study of standardized Andrographis paniculata extract in common cold — a pilot trial. Phytomedicine 1997, 3, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchior, J.; Spasov, A.; Ostrovskij, O.; Bulanov, A.; Wikman, G. Double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot and Phase III study of activity of standardized Andrographis paniculata Herba Nees extract fixed combination (Kan jang®) in the treatment of uncomplicated upper-respiratory tract infection. Phytomedicine 2000, 7, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasov, A.A.; Ostrovskij, O.V.; Chernikov, M.V.; Wikman, G. Comparative controlled study of Andrographis paniculata fixedcombination, Kan Jang and an Echinacea preparation as adjuvant, in the treatment of uncomplicated respiratory disease in children. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panossian, A.; Wikman, G. Efficacy of Andrographis paniculata in upper respiratory tract (URT) infectious diseases and the mechanism of action. In Evidence and Rational Based Research on Chinese Drugs; Wagner, H., Ulrich Merzenich, G., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2012; pp. 137–180. [Google Scholar]
- Brekhman, I.I. On antitoxic action of Eleutherococcus. Mosc. Med. 1982, 37. [Google Scholar]
- HMPC—Committee on HerbalMedicinal Products. Assessment Report on Eleutherococcus senticosus (Rupr. etMaxim.) Maxim, Radix.EMA/HMPC/680615/2013. March 25 2014, pp. 1–51. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/herbal-report/final-assessment-report-eleutherococcus-senticosus-rupr-et-maxim-maxim-radix_en.pdf (accessed on 30May 2022).
- Seo, E.-J.; Klauck, S.M.; Efferth, T.; Panossian, A. Adaptogens in chemobrain (Part II): Effect of plant extracts on chemotherapy-induced cytotoxicity in neuroglia cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 58, 152743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.-J.; Klauck, S.M.; Efferth, T.; Panossian, A. Adaptogens in chemobrain (Part III): Antitoxic effects of plant extracts towards cancer chemotherapy-induced toxicity - transcriptome-wide microarray analysis of neuroglia cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 56, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panossian, A.; Seo, E.-J.; Klauck, S.M.; Efferth, T. Adaptogens in chemobrain (part IV): adaptogenic plants prevent the chemotherapeutics-induced imbalance of redox homeostasis by modulation of expression of genes encoding Nrf2-mediated signaling proteins and antioxidant, metabolizing, detoxifying enzymes in neuroglia cells. Longhua Chin. Med. 2020, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, X.Y.; Chan, J.S.W.; Tan, T.Y.C.; Teh, B.P.; Razak, M.R.M.A.; Mohamad, S.; Mohamed, A.F.S. Andrographis paniculata (Burm. F.) Wall. Ex Nees, Andrographolide, and Andrographolide Analogues as SARS-CoV-2 Antivirals? A Rapid Review. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2021, 16, 1934578X211016610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnier, J.J.; Boon, H.; Rochon, P.; Moher, D.; Barnes, J.; Bombardier, C.; CONSORT Group. Recommendations for reporting randomized controlled trials of herbal interventions: explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiology 2006, 59, 1134–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Venn diagrams showing the number of deregulated genes in neuroglia cells in response to Andrographis, Eleutherococcus, and their fixed combination Kan Jang (KJ). The diagram includes overlapping sections, and sections associated with synergistic interactions of Andrographis and Eleutherococcus in Kan Jang (111 unique genes) [
12]. Conditional "biological signatures” are shown in the form of the color-coded heatmaps which identified the diseases and biological functions associated with gene expression in response to Andrographis, Eleutherococcus, and Kan Jang.
Figure 1.
Venn diagrams showing the number of deregulated genes in neuroglia cells in response to Andrographis, Eleutherococcus, and their fixed combination Kan Jang (KJ). The diagram includes overlapping sections, and sections associated with synergistic interactions of Andrographis and Eleutherococcus in Kan Jang (111 unique genes) [
12]. Conditional "biological signatures” are shown in the form of the color-coded heatmaps which identified the diseases and biological functions associated with gene expression in response to Andrographis, Eleutherococcus, and Kan Jang.
Figure 2.
The figure shows six waves of the Covid-19 pandemic, including the number of infected patients recorded over time (in red color charts) in Georgia and worldwide. In white colors are shown the number of deaths and the number of vaccinations (in green colors). Eighty-six patients were studied during three waves characterized by the most severe period of a pandemic from 2021-05-26 to 2022-03-30, while the subset of 54 patients was studied on the last wave of less harmful SARS-Cov-2 variants infection from 2022-05-17 and 2022-10-30. All 140 patients were diagnosed as mild and moderate COVID-19 according to WHO classification [
16].
Figure 2.
The figure shows six waves of the Covid-19 pandemic, including the number of infected patients recorded over time (in red color charts) in Georgia and worldwide. In white colors are shown the number of deaths and the number of vaccinations (in green colors). Eighty-six patients were studied during three waves characterized by the most severe period of a pandemic from 2021-05-26 to 2022-03-30, while the subset of 54 patients was studied on the last wave of less harmful SARS-Cov-2 variants infection from 2022-05-17 and 2022-10-30. All 140 patients were diagnosed as mild and moderate COVID-19 according to WHO classification [
16].
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the trial. For details on the disposition of patients, see Supplement 1.
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the trial. For details on the disposition of patients, see Supplement 1.
Figure 4.
(a) -The rate of patients with clinical deterioration in the treatment and control groups; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 0,2906, 95% CI of ratio from 0.094 to 0.894. (b) – The virus clearance in the treatment and control groups: Kaplan–Meier curves show the percent of patients with SARS-Cov-2 virus over the time from randomization (Day 1) to the end of the treatment (Day 14) and the follow-up period for one week (Day 21) in the treatment and control groups; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 1.686, 95% CI of ratio from 0.8698 to 3.269.
Figure 4.
(a) -The rate of patients with clinical deterioration in the treatment and control groups; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 0,2906, 95% CI of ratio from 0.094 to 0.894. (b) – The virus clearance in the treatment and control groups: Kaplan–Meier curves show the percent of patients with SARS-Cov-2 virus over the time from randomization (Day 1) to the end of the treatment (Day 14) and the follow-up period for one week (Day 21) in the treatment and control groups; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 1.686, 95% CI of ratio from 0.8698 to 3.269.
Figure 5.
(a) - Duration of increased body temperature (from >370 C to < 380 C) in the treatment and control groups; median recovery: Kan Jang®, – 6 days, placebo – 7 days; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 1.336, 95% CI of ratio from 0.808 to 2.309. (b) - Duration of hospitalization in the treatment group and control group; Kaplan–Meier curves show the percent of patients hospitalized over the time from randomization (Day 1) to the end of the treatment (Day 14) and followed up for one week (Day 21) in the treatment and control groups.
Figure 5.
(a) - Duration of increased body temperature (from >370 C to < 380 C) in the treatment and control groups; median recovery: Kan Jang®, – 6 days, placebo – 7 days; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 1.336, 95% CI of ratio from 0.808 to 2.309. (b) - Duration of hospitalization in the treatment group and control group; Kaplan–Meier curves show the percent of patients hospitalized over the time from randomization (Day 1) to the end of the treatment (Day 14) and followed up for one week (Day 21) in the treatment and control groups.
Figure 6.
(a) – Between-groups comparison of the changes from the baseline of Wisconsin Upper Respiratory Symptom Survey Questionary Scores in patients of group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 21 shows the statistically significant positive effect of Kan Jang treatment vs. placebo both (a) - in 140 patients included per intention to treat (ITT) analysis (p = 0.035), and (b) - in 100 patients included in analysis per protocol (p > 0.05).
Figure 6.
(a) – Between-groups comparison of the changes from the baseline of Wisconsin Upper Respiratory Symptom Survey Questionary Scores in patients of group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 21 shows the statistically significant positive effect of Kan Jang treatment vs. placebo both (a) - in 140 patients included per intention to treat (ITT) analysis (p = 0.035), and (b) - in 100 patients included in analysis per protocol (p > 0.05).
Figure 7.
(a) – Time to relieve sore throat in the treatment and control groups: Kaplan–Meier curves show the percent of patients with a sore throat over the time from randomization (Day 1) to the end of the treatment (Day 14) and follow up for one week (Day 21); median recovery, Kan Jang®, – 7 days, placebo – 11 days; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = = 1.36, 95% CI of ratio from 0,7350 to 2,516. (b) – Relief of the sore throat; the changes in the severity of the symptom from the baseline of patients in group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 21. Between-group comparison of the changes in the severity of the symptom from the baseline over time shows significant interaction (p = 0.0009). The Kan Jang® treatment has a statistically significant effect on the relief of the sore throat compared to the placebo, ITT analysis.
Figure 7.
(a) – Time to relieve sore throat in the treatment and control groups: Kaplan–Meier curves show the percent of patients with a sore throat over the time from randomization (Day 1) to the end of the treatment (Day 14) and follow up for one week (Day 21); median recovery, Kan Jang®, – 7 days, placebo – 11 days; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = = 1.36, 95% CI of ratio from 0,7350 to 2,516. (b) – Relief of the sore throat; the changes in the severity of the symptom from the baseline of patients in group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 21. Between-group comparison of the changes in the severity of the symptom from the baseline over time shows significant interaction (p = 0.0009). The Kan Jang® treatment has a statistically significant effect on the relief of the sore throat compared to the placebo, ITT analysis.
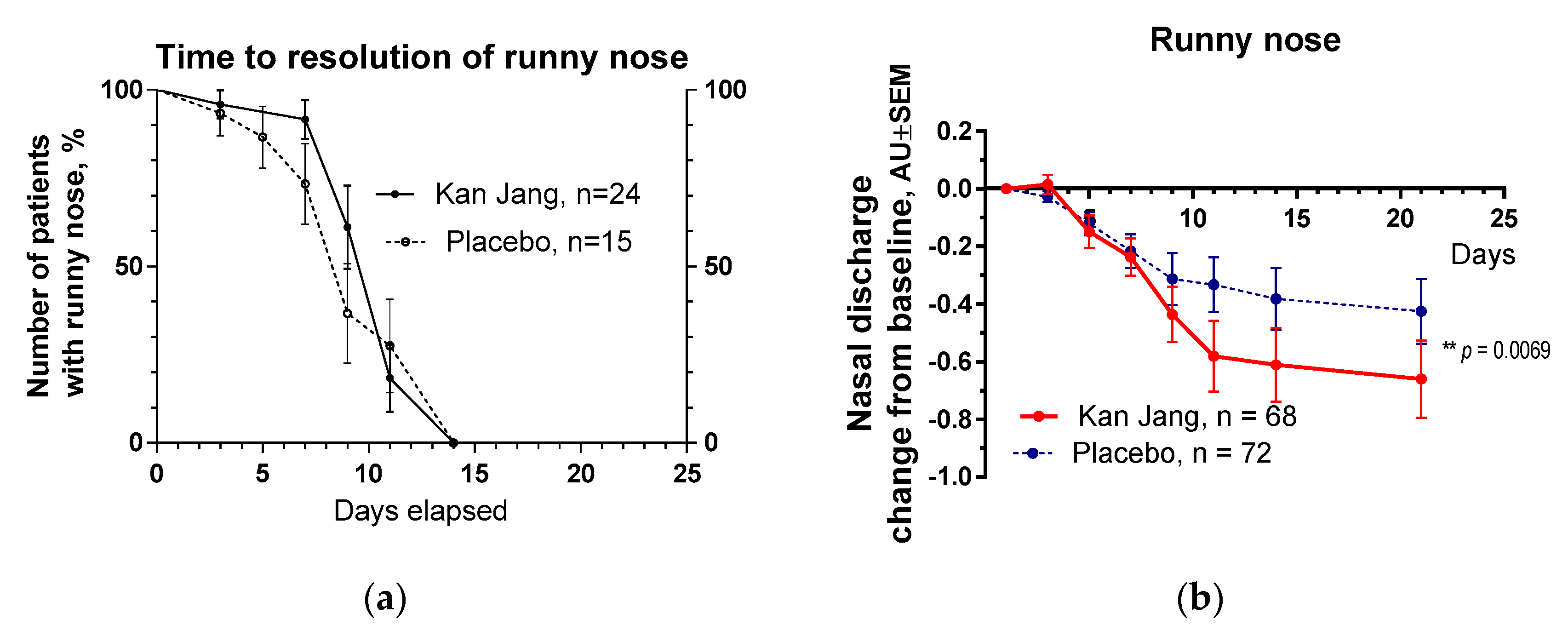
Figure 8.
(a) – Time to a resolution of runny nose in the treatment and control groups: Kaplan–Meier curves show the percent of patients with runny nose over the time from randomization (Day 1) to the end of the treatment (Day 14) and follow up for one week (Day 21) and in the treatment and control groups; median recovery: Kan Jang®, – 14 days, placebo – 14 days; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 0,672, 95% CI of ratio from 0,2321 to 1,944. (b) – Reduction of nasal discharge; the changes in the severity of the symptom from the baseline of patients in group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 21. Between-group comparison of the changes in the symptom severity from the baseline over time shows significant interaction (p = 0.0069). The Kan Jang® treatment has a statistically significant effect on the reduction of nasal discharge compared to the placebo ITT analysis.
Figure 8.
(a) – Time to a resolution of runny nose in the treatment and control groups: Kaplan–Meier curves show the percent of patients with runny nose over the time from randomization (Day 1) to the end of the treatment (Day 14) and follow up for one week (Day 21) and in the treatment and control groups; median recovery: Kan Jang®, – 14 days, placebo – 14 days; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 0,672, 95% CI of ratio from 0,2321 to 1,944. (b) – Reduction of nasal discharge; the changes in the severity of the symptom from the baseline of patients in group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 21. Between-group comparison of the changes in the symptom severity from the baseline over time shows significant interaction (p = 0.0069). The Kan Jang® treatment has a statistically significant effect on the reduction of nasal discharge compared to the placebo ITT analysis.
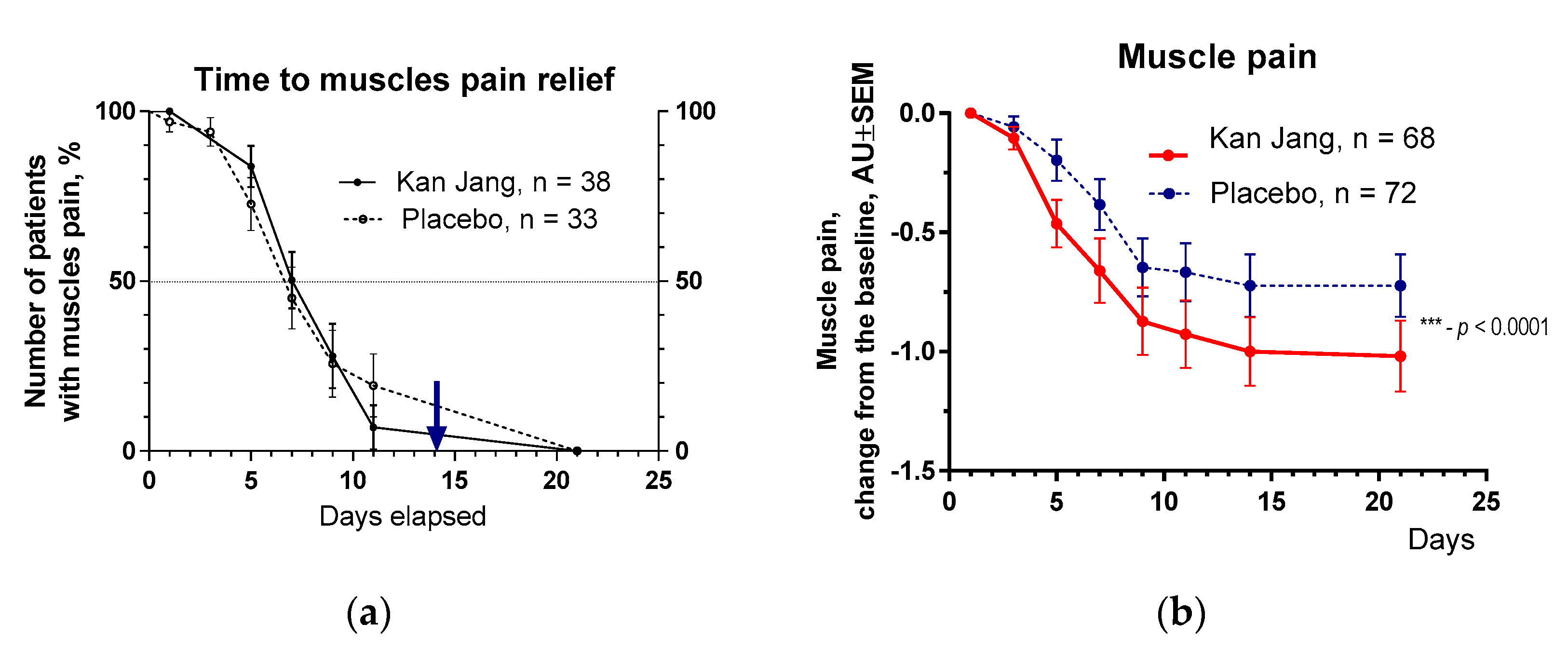
Figure 9.
(a) – Time to muscle pain relief in the treatment and control groups. Kaplan–Meier curves show the percent of patients with muscle pain over the time from randomization (Day 1) to the end of the treatment (Day 14) and follow-up for one week (Day 21); median recovery, Kan Jang®, – 9 days, placebo – 11 days; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 0,8965, 95% CI of ratio from 0,4434 to 1,812. (b) – Relief of the muscles pain; the changes in the severity of the symptom from the baseline of patients in group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 21 Between-groups comparison of the changes in the severity of the symptom from the baseline over time in 140 patients included per intention to treat (ITT) shows significant interaction (p < 0.0001). Statistical significance of the effects of Kan Jang® treatment vs. placebo on muscle pain relief is shown as: * - p < 0.05, ** - p < 0.001, *** - p < 0.0001.
Figure 9.
(a) – Time to muscle pain relief in the treatment and control groups. Kaplan–Meier curves show the percent of patients with muscle pain over the time from randomization (Day 1) to the end of the treatment (Day 14) and follow-up for one week (Day 21); median recovery, Kan Jang®, – 9 days, placebo – 11 days; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 0,8965, 95% CI of ratio from 0,4434 to 1,812. (b) – Relief of the muscles pain; the changes in the severity of the symptom from the baseline of patients in group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 21 Between-groups comparison of the changes in the severity of the symptom from the baseline over time in 140 patients included per intention to treat (ITT) shows significant interaction (p < 0.0001). Statistical significance of the effects of Kan Jang® treatment vs. placebo on muscle pain relief is shown as: * - p < 0.05, ** - p < 0.001, *** - p < 0.0001.
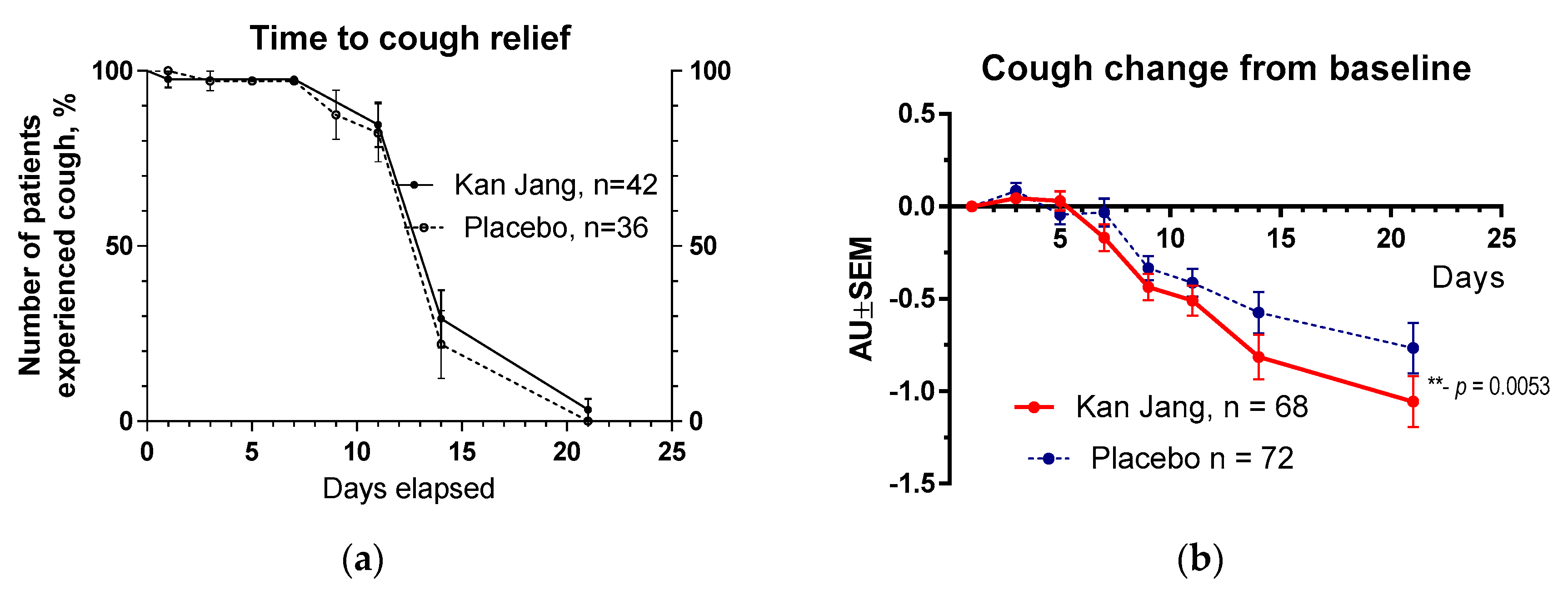
Figure 10.
(a) – Time to resolution of cough in the treatment and control groups: Kaplan–Meier curves show the percent of patients with cough over the time from randomization (Day 1) to the end of the treatment (Day 14) and follow up for one week (Day 21) and in the treatment and control groups; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 0,7027, 95% CI of ratio from 0,2744 to 1,799. (b) – Relief of the cough; the changes in the severity of the symptom from the baseline of patients in group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 21. Between-group comparison of the changes in the symptom severity from the baseline over time shows significant interaction (p = 0,0053). The Kan Jang® treatment significantly relieved cough compared to the placebo, ** - p < 0.01; ITT analysis.
Figure 10.
(a) – Time to resolution of cough in the treatment and control groups: Kaplan–Meier curves show the percent of patients with cough over the time from randomization (Day 1) to the end of the treatment (Day 14) and follow up for one week (Day 21) and in the treatment and control groups; hazard ratio Kan Jang/placebo = 0,7027, 95% CI of ratio from 0,2744 to 1,799. (b) – Relief of the cough; the changes in the severity of the symptom from the baseline of patients in group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 21. Between-group comparison of the changes in the symptom severity from the baseline over time shows significant interaction (p = 0,0053). The Kan Jang® treatment significantly relieved cough compared to the placebo, ** - p < 0.01; ITT analysis.
Figure 11.
(a) – Concentration of IL-6 (mean ± S.D.) of the blood of patients in group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 14. (b) - The changes from the baseline of the levels (mean ± S.D.) of cytokine IL-6 in the blood of patients in group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 14. Between-groups comparison of the changes in the level of cytokine IL-6 in the blood from the baseline over time shows an insignificant difference (p = 0.1619) between groups A and B.
Figure 11.
(a) – Concentration of IL-6 (mean ± S.D.) of the blood of patients in group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 14. (b) - The changes from the baseline of the levels (mean ± S.D.) of cytokine IL-6 in the blood of patients in group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 14. Between-groups comparison of the changes in the level of cytokine IL-6 in the blood from the baseline over time shows an insignificant difference (p = 0.1619) between groups A and B.
Figure 12.
Between-group comparison of the changes from the baseline of (a) - the overall physical activity and (b) - physical performance/workout time (in min) of patients in group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 21 shows the statistically significant positive effect of Kan Jang treatment vs. placebo both in 140 patients included per intention to treat (ITT) analysis.
Figure 12.
Between-group comparison of the changes from the baseline of (a) - the overall physical activity and (b) - physical performance/workout time (in min) of patients in group A (Kan Jang) and group B (placebo) over the time from Day 1 to Day 21 shows the statistically significant positive effect of Kan Jang treatment vs. placebo both in 140 patients included per intention to treat (ITT) analysis.
Figure 13.
Schematic diagram of reported effects of Andrographis and Eleutherococcus elucidated in animal and cell culture models: (i) modulatory effects on immune response (blue block), (ii) anti-inflammatory activity (green bock), (iii) detoxification and repair of oxidative stress-induced damage in compromised cells (brown block), and (iv) direct antiviral effect via infraction with viral docking or replication (red block), modified from Panossian and Brendler [
13].
Figure 13.
Schematic diagram of reported effects of Andrographis and Eleutherococcus elucidated in animal and cell culture models: (i) modulatory effects on immune response (blue block), (ii) anti-inflammatory activity (green bock), (iii) detoxification and repair of oxidative stress-induced damage in compromised cells (brown block), and (iv) direct antiviral effect via infraction with viral docking or replication (red block), modified from Panossian and Brendler [
13].
Table 1.
Baseline demographic characteristics, outcome measures, and laboratory biochemical and hematological measurements.
Table 1.
Baseline demographic characteristics, outcome measures, and laboratory biochemical and hematological measurements.
| |
Unit |
|
Group A Kan Jang
ADAPT n=50 |
|
Group B
Placebo |
Signif. of difference |
| Parameters |
|
n |
mean |
S.D. |
n |
mean |
S.D. |
p-value |
| Age |
years |
68 |
50.35 |
17.82 |
72 |
45.74 |
16.82 |
0.143b
|
| Gender, Male/Female, % - 53/87=61% |
Male/Female |
68 |
28/40=70% |
72 |
25/47=53% |
0.785 |
|
| BMI |
kg/m2
|
68 |
24.58
|
3.274 |
72 |
24.52
|
3.376
|
0.908b
|
| Start of symptoms |
days |
68 |
<3 |
|
72 |
<3 |
|
|
| Viral load, SARS-Cov2 |
% |
68 |
100 |
72 |
100 |
|
| Body temperature |
o C |
68 |
37.86
|
0.58
|
72 |
37.7
|
0.59 |
0.148b
|
| Fatigue, 100% patients |
A.U. |
68 |
1.794 |
0.407 |
72 |
1.819 |
0.539 |
0.755b
|
| Headache, 91% of patients |
A.U. |
64 |
1.859 |
0.393 |
63 |
1.794 |
0.480 |
0.443b
|
| Sore throat, 62% of patients |
A.U. |
49 |
1.776 |
0.422 |
38 |
1.632 |
0.633 |
0.2573b
|
| Cough, 55% of patients |
A.U. |
41 |
1.902 |
0.490 |
36 |
1.833 |
0.378 |
0.606b
|
| Pain in muscles, 51% of patients |
A.U. |
39 |
1.872* |
0.656 |
32 |
1.469* |
0.671 |
0.013a |
| Runny nose, 27% of patients |
A.U. |
23 |
1.957 |
0.475 |
15 |
1.733 |
0.458 |
0.247b 0.247b
|
| Loss of smell, 16% of patients |
A.U. |
8 |
2.375* |
0.744 |
14 |
1.714* |
0.469 |
0.036b |
| Loss of taste, 4% of patients |
A.U. |
4 |
2.500 |
0.577 |
2 |
3.000 |
0 |
0.312b
|
| Physical activity |
A.U. |
68 |
12.75* |
2.984 |
72 |
13.85* |
3.005 |
0.019b |
| Physical activity (daily walk) |
min |
68 |
7.279* |
8.614 |
72 |
12.57* |
13.45 |
0.008b |
| Decreased attention (d2-test) |
%E (errors) |
68 68 |
28.34 |
21.47 |
72 |
26.00 |
26.83 |
0.189b
|
| URTI |
WI score |
68 |
17.59* |
6.497 |
72 |
14.69* |
5.832 |
0.006a |
| QOL |
WI score |
68 |
36.29 |
12.15 |
72 |
37.14 |
12.81 |
0,163b
|
| Blood serum IL-6 (normal level < 7 pg/mL) |
pg/mL |
68 |
12.60 |
54.29 |
72 |
9.39 |
17.86 |
0.970b
|
| D-dimer (normal range from 0.1 to 0.5 mg/L) |
mg/L |
68 |
0.812 |
1.528 |
72 |
4.431 |
32.94 |
0.672b
|
| C-reactive protein (normal level < 5 mg/L) |
mg/L |
68 |
12.74 |
13.82 |
72 |
16.86 |
23.30 |
0.989 |
| ALT (normal level < 35 U/L) |
U/L |
68 |
27.69 |
19.90 |
72 |
26.79 |
20.46 |
0.831 |
| AST (normal level < 32 U/L) |
U/L |
68 |
25.32 |
19.07 |
72 |
26.83 |
19.49 |
0.241 |
| Total WBC count (normal range: 3.6-11.0 x 109cells/L ) |
109/L |
68 |
5.872 |
1.863 |
72 |
5.271 |
1.936 |
0.064 |
|
| Erythrocytes, RBC (normal range: 3.8-5.8 x 1012cells/L) |
1012/L |
68 |
4.699 |
0.479 |
72 |
4.770 |
0.601 |
0.231 |
|
| Hemoglobin. Hb (normal range 13.5-17.0 g/dl) |
g/dl |
68 |
12.95 |
1.647 |
72 |
13.51 |
1.706 |
0.053 |
|
| Hematocrit, HCT (normal range: 40-50, L/L) |
L/L |
68 |
40.48 |
4.924 |
72 |
41.56 |
6.179 |
0.064 |
|
| Platelet Count (normal range 150-380 x 103 cells/μL) |
103 μL |
68 |
207.1 |
49.49 |
72 |
200.8 |
51.22 |
0.565 |
|
| Neutrophils count (normal range: 1.8-7.5 x 109cells/L ) |
109/L |
68 |
60.090* |
11.80 |
72 |
62.49* |
13.43 |
0.458 |
|
| Lymphocyte count (normal range: 1.0-4.0 x 109cells/L ) |
109/L |
68
|
28.72* |
11.47 |
72 |
27.54* |
12.33 |
0.560 |
|
| Monocyte count ((normal range: 0.1-1.0 x 109cells/L ) |
109/L |
68 |
9.194* |
15.47 |
72 |
6.457* |
3.572 |
0.132 |
|
| Eosinophil count ((normal range: 0.1-0.4 x 109cells/L ) |
109/L |
68 |
1.615* |
1.391 |
72 |
1.285* |
1.136 |
0.144 |
|
| Basophil Count ((normal range: 0.01-0.1 x 109cells/L ) |
109/L |
68 |
0.471* |
0.229 |
72 |
0.477* |
0.296 |
0.722 |
|
Table 3.
Schedule of examinations and procedures.
Table 3.
Schedule of examinations and procedures.
| |
Treatment |
Follow-up |
| |
Day 1
Screening |
Day 3 |
Day 5 |
Day 7 |
Day 9 |
Day 11 |
Day 14 |
Day
21 |
| Doctor's visits |
1 Baseline |
|
|
2 |
|
|
3 |
4 |
| Eligibility check/Information |
* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Informed consent |
* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Clinical examination |
* |
|
|
* |
|
|
* |
* |
| Enrollment and allocation to intervention |
* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Treatment (Kan Jang and placebo) |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
|
| Biomarker assessments |
| Body temperature (fever) |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
| COVID-19 PCR test |
* |
|
|
* |
|
|
* |
* |
| Blood serum cytokine IL-6 (pg/mL) |
* |
* |
|
* |
|
|
* |
|
| D-dimer (mg/L) |
* |
|
|
* |
|
|
* |
|
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) |
* |
|
|
* |
|
|
* |
|
| Blood cells count analysis |
* |
|
|
* |
|
|
* |
|
| ALT/AST |
* |
|
|
* |
|
|
|
|
| Clinician and observer reported outcomes assessments |
Cognitive performance (tests for
attention and memory): d2 test
Wisconsin URS Survey Score |
*
* |
* |
|
*
* |
|
|
*
* |
*
|
| Drug intake accountability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
* |
|
| Adverse events |
|
|
|
* |
|
|
* |
* |
| Patient-reported outcomes assessments |
| Mild COVID symptoms:
|
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
* |
| Workout, min |
* |
|
|
* |
|
|
* |
* |
| Physical activity (questionnaire) |
* |
|
|
* |
|
|
* |
* |
Paracetamol intake recording
Rescue medication intake recording |
*
* |
*
* |
*
* |
*
* |
*
* |
*
* |
*
* |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).