Submitted:
28 July 2023
Posted:
31 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Dynamic reactive device configuration index system based on Multiple-two-element notation
2.1. Multiple-two-element notation criterion
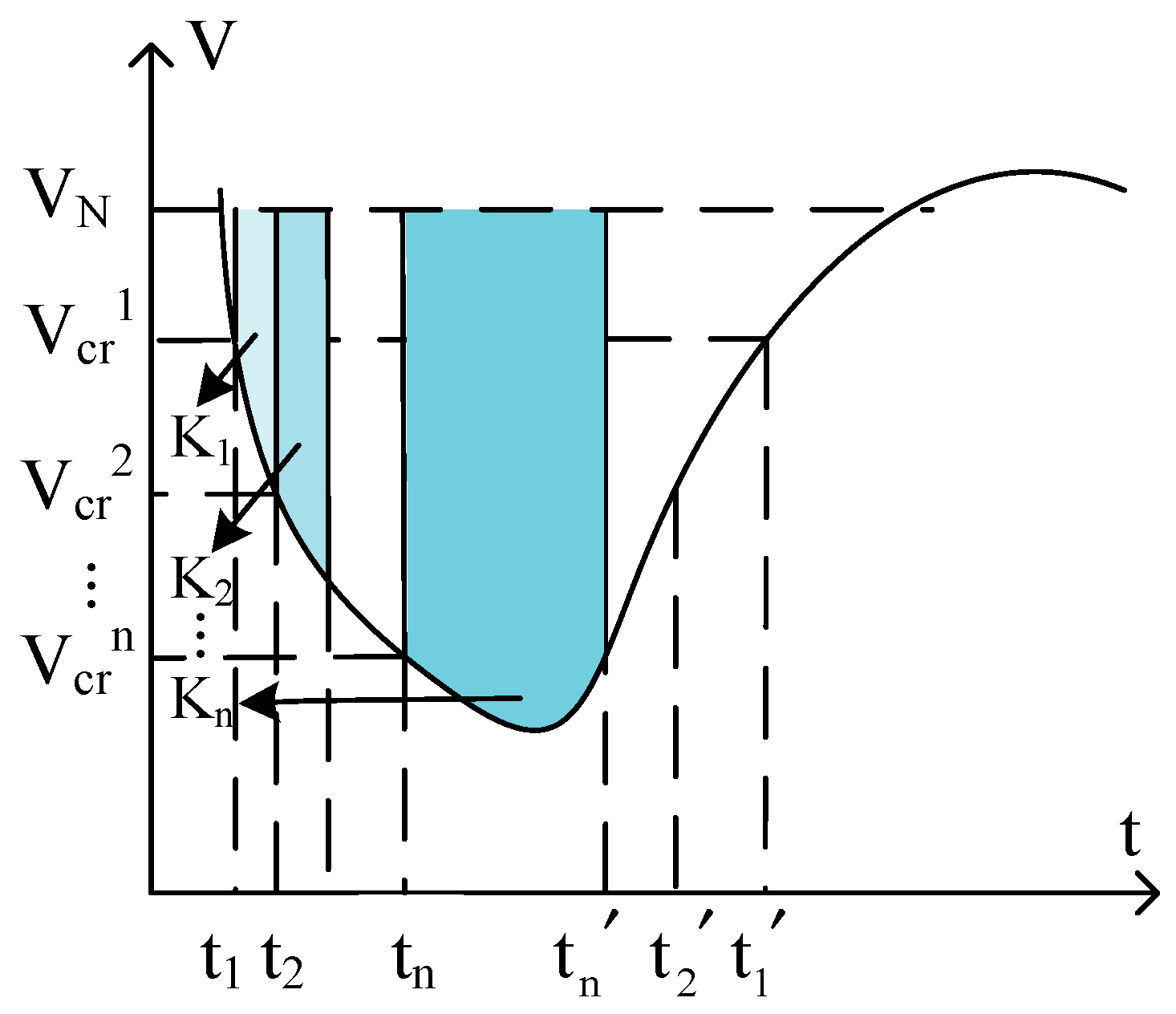
2.2. Indicator of safety margin for integrated transient voltage dips of the system
2.3. Set of worst failures
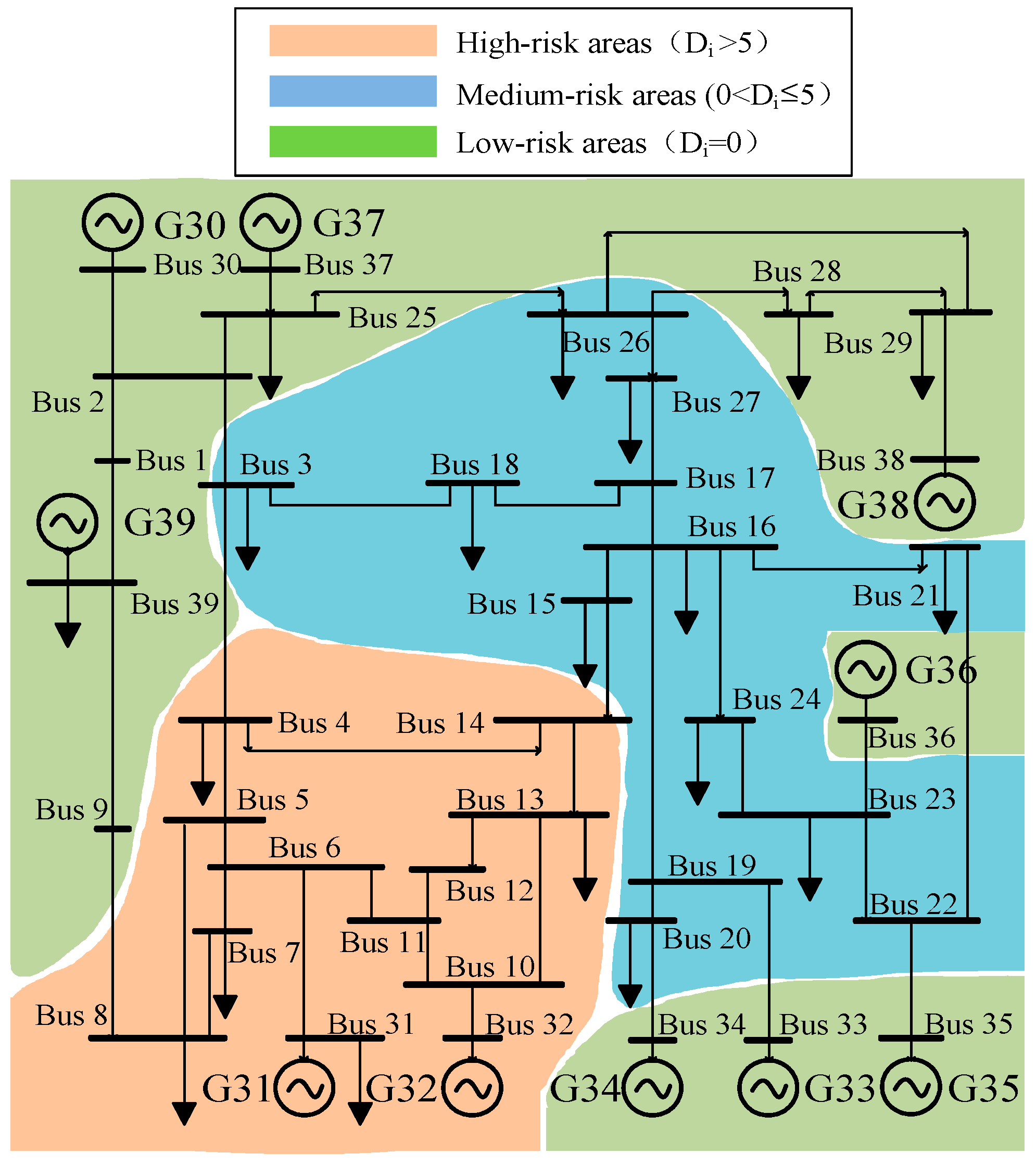
2.4. Regional classification of the risk of transient voltage destabilization
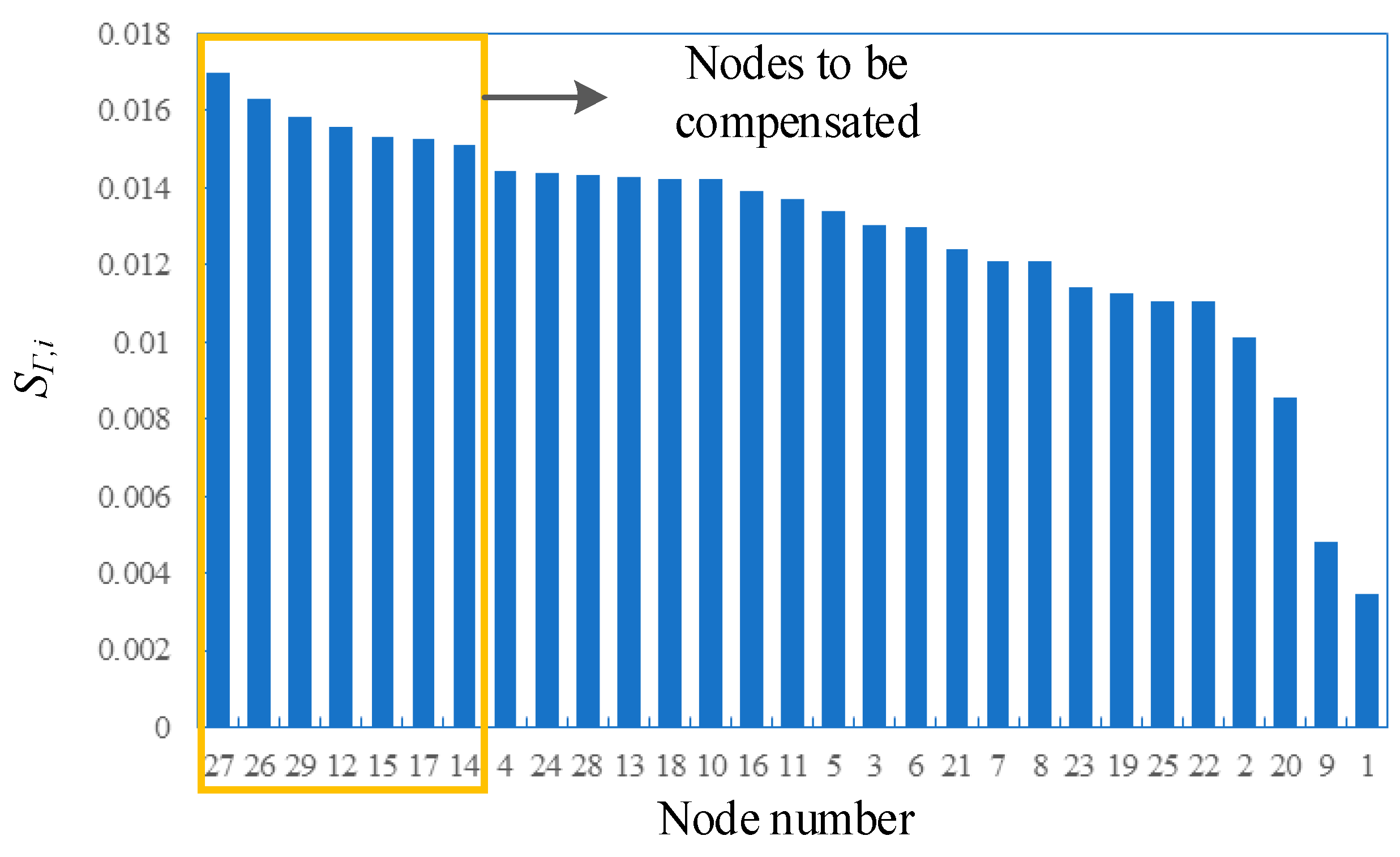
2.5. Sensitivity index
2.6. Dynamic reactive power compensation configuration index system
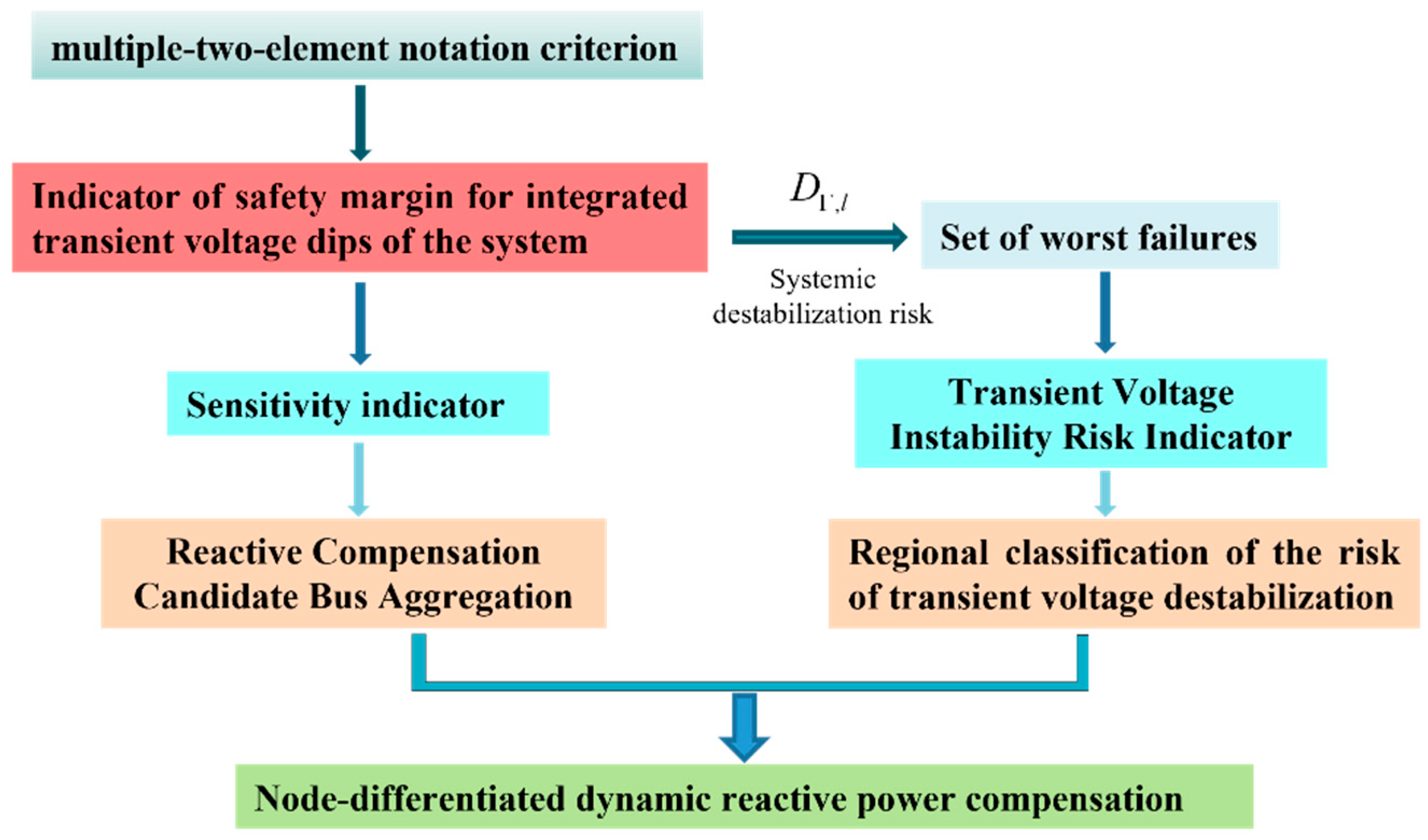
3. Node-differentiated dynamic reactive power compensation models
3.1. Device selection
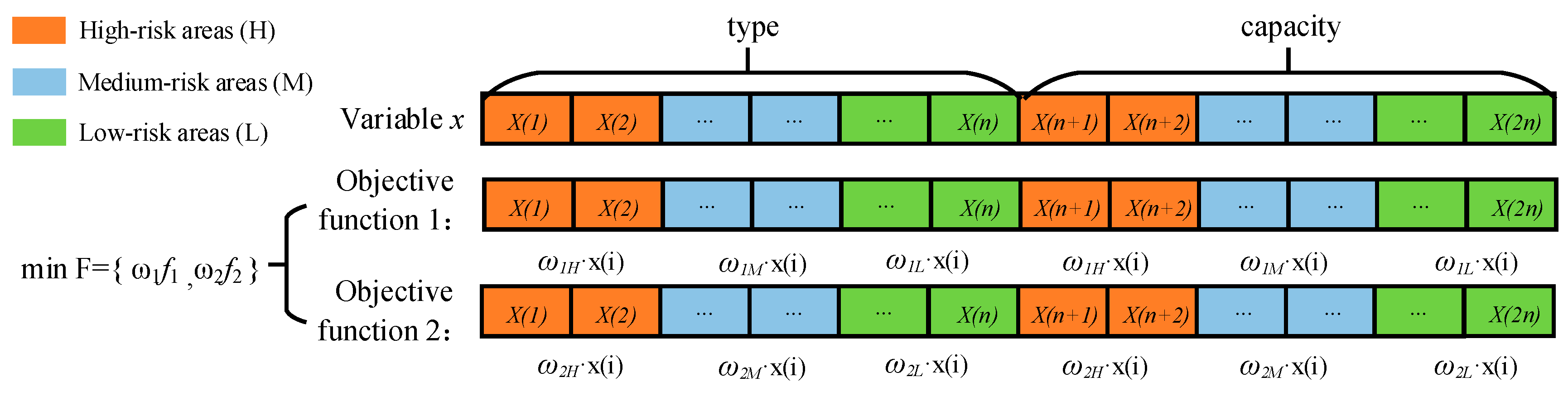
3.2. Configuration model
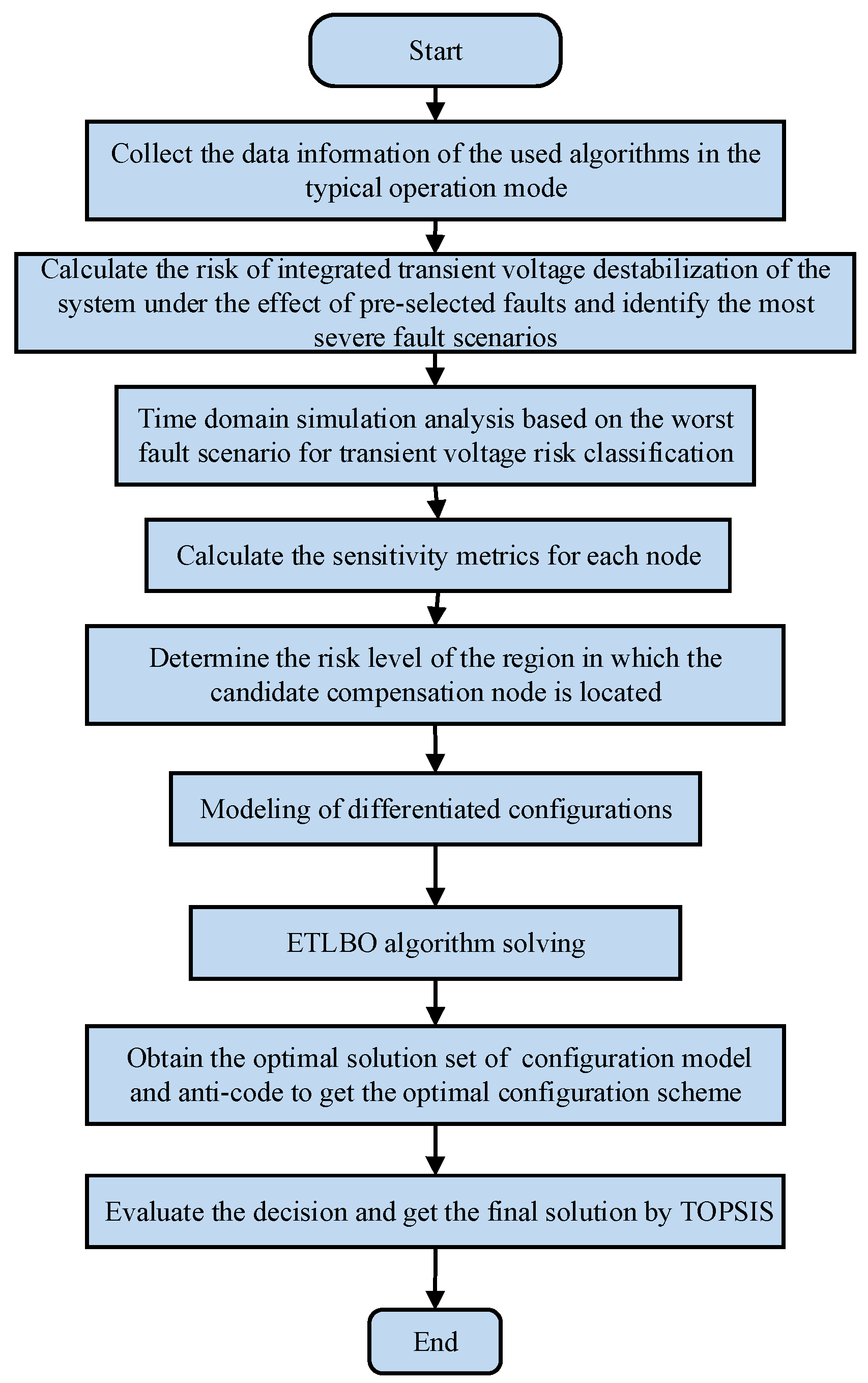
4. Solving Algorithm and Process
4.1. ETLBO optimization algorithm
4.2. TOPSIS Evaluation Method
4.3. Solution Steps
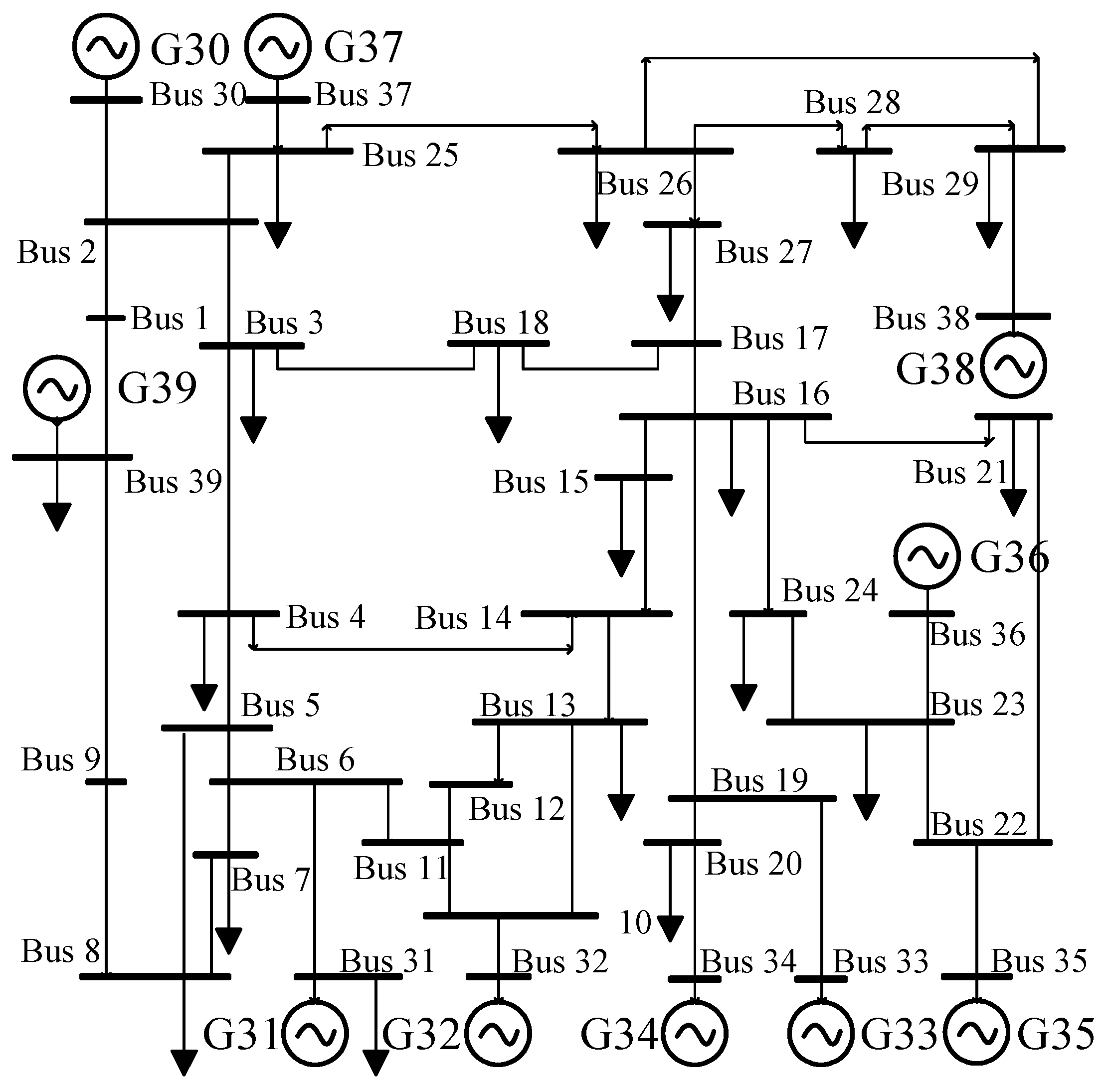
5. Example analysis
5.1. Candidate compensation nodes
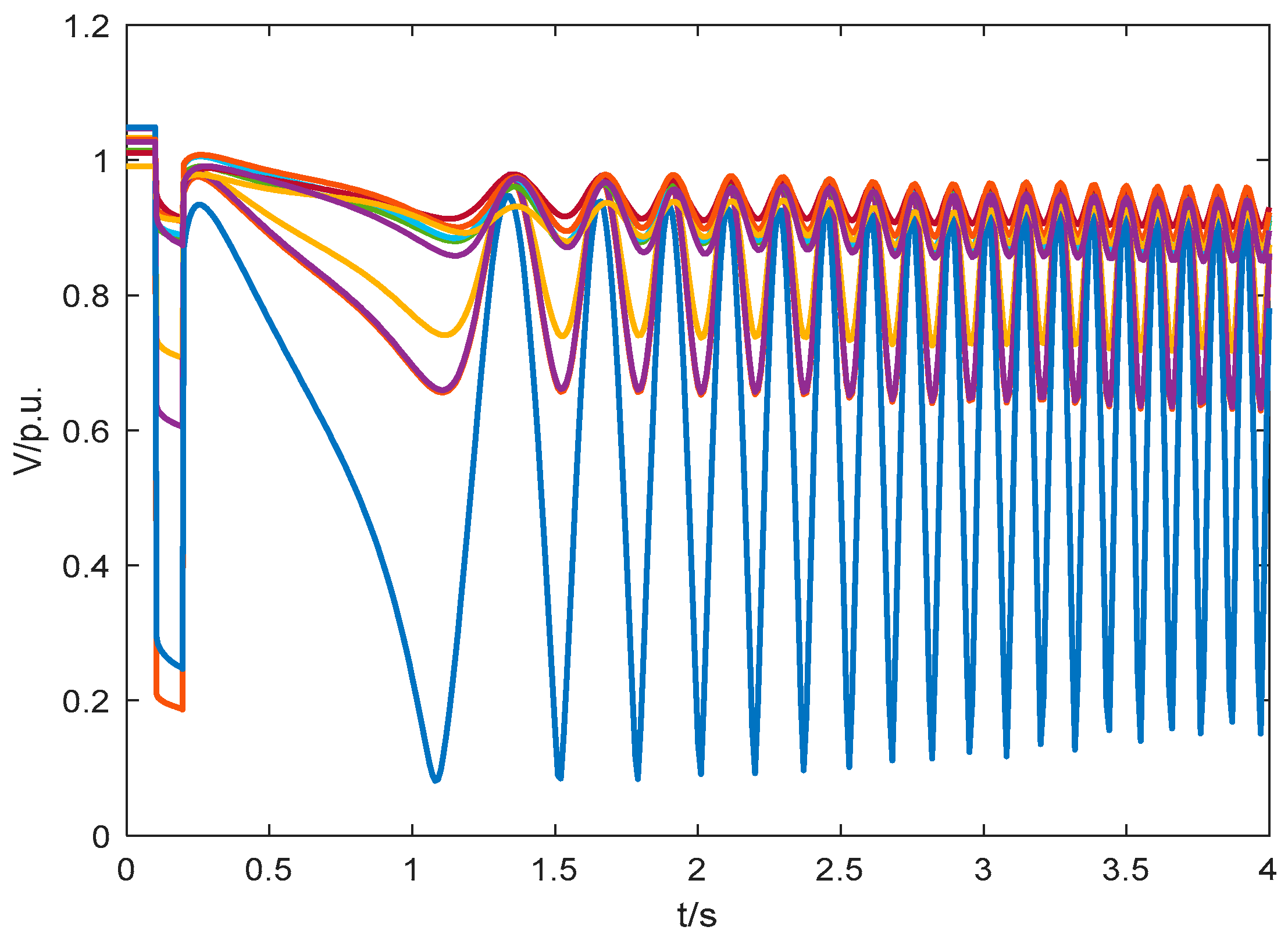
5.2. System transient voltage instability risk partitioning
| Nodal | Di | Number of instabilities | Nodal | Di | Number of instabilities | Nodal | Di | Number of instabilities |
| 1 | 0.0000 | 0 | 14 | 16.7118 | 6 | 27 | 1.7394 | 1 |
| 2 | 0.0000 | 0 | 15 | 4.2450 | 3 | 28 | 0.0000 | 1 |
| 3 | 0.5803 | 1 | 16 | 2.5523 | 1 | 29 | 0.0000 | 1 |
| 4 | 11.7646 | 6 | 17 | 2.3568 | 1 | 30 | 0.0000 | 0 |
| 5 | 10.3804 | 6 | 18 | 2.0995 | 1 | 31 | 7.3380 | 5 |
| 6 | 10.6489 | 6 | 19 | 1.5516 | 1 | 32 | 7.4773 | 5 |
| 7 | 9.9658 | 5 | 20 | 1.4768 | 1 | 33 | 0.0000 | 0 |
| 8 | 9.5830 | 5 | 21 | 2.1258 | 1 | 34 | 0.0000 | 0 |
| 9 | 0.0000 | 0 | 22 | 1.6480 | 1 | 35 | 0.0000 | 0 |
| 10 | 11.2007 | 6 | 23 | 1.7070 | 1 | 36 | 0.0000 | 0 |
| 11 | 11.5400 | 6 | 24 | 2.6959 | 1 | 37 | 0.0000 | 0 |
| 12 | 11.2962 | 6 | 25 | 0.0000 | 0 | 38 | 0.0000 | 0 |
| 13 | 10.8595 | 6 | 26 | 0.3354 | 2 | 39 | 0.0000 | 0 |
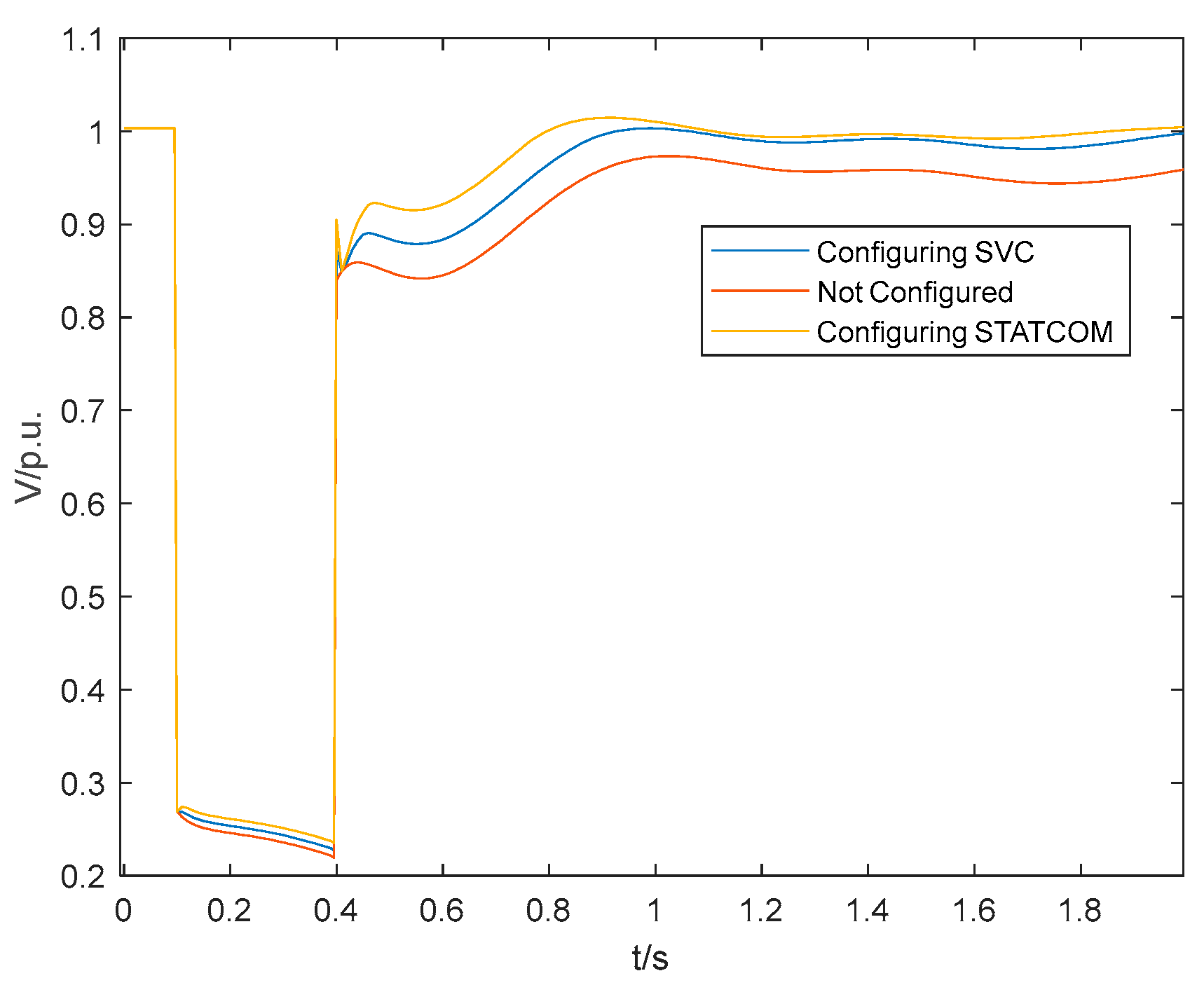
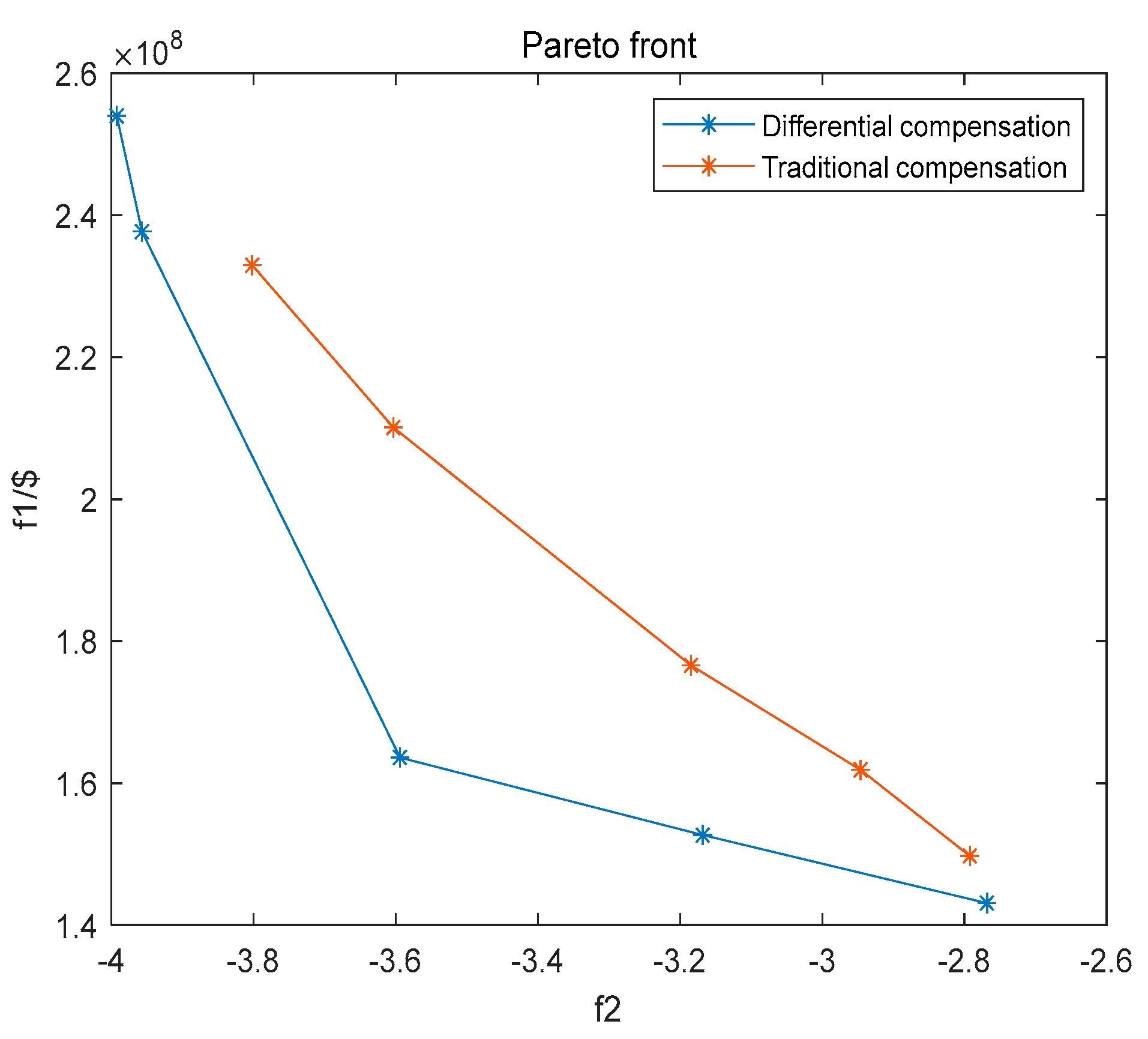
5.3. Configuration results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sami, M.; Gheorghe, S.; Toma, L. Transient stability improvement and voltage regulation in power system hosting Renewables by SVC. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Energy Technologies (ICECET); 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Opana, S.; Charles, J.K.; Nabaala, A. STATCOM Application for Grid Dynamic Voltage Regulation: A Kenyan Case Study. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE PES/IAS PowerAfrica 2020; pp. 1–5.
- Zhang, J. Research on Dynamic Reactive Power Compensation Configuration of High Proportion New Energy Grid. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th Asia Conference on Power and Electrical Engineering (ACPEE) 2020; pp. 2002–2006.
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jian, W.; Tang, F. Optimal Configuration Method of Dynamic Reactive Power Compensation Device Considering Reducing Commutation Failure Risk of Multi-infeed DC System. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 4th Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2) 2020; pp. 3233–3237.
- Cui, J. Research on transient voltage characterization and control of AC and DC power grids. Master's Thesis (M.A.), North China Electric Power University, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- National Energy Administration. Technical specification for power system safety and stability calculation; China Electric Power Press: Beijing, China, 2013; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- China Southern Power Grid Co. Guidelines for calculation and analysis of safety and stability of the Southern Power Grid; Guangzhou, China, 2009; p. 8.
- Overbye, T.J.; Klump, R.P. Effective Calculation of Power System Low-Voltage Solutions. IEEE Trans 1996, 11, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Wildenhues, S.; Rueda, J.L.; Erlich, I. Optimal allocation and sizing of dynamic var sources using heuristic optimization. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2015, 30, 2538–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; He, H. A practical site selection method for dynamic reactive power compensation in multi-infeed DC power grid. Power System Technology 2014, 38, 1753–1757. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, A.; Zhou, J.; Liu, R. Research on practical transient voltage stability margin index using multiple binary table criterion. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering 2018, 38, 4117–4125+4317. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Research on reactive power compensation measures to improve the safety and stability level of 750kV sending end power grid in Northwest New Ganqing. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering 2015, 35, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Sun, S. Quantitative assessment method of transient voltage in distribution network containing high penetration wind power. China Electric Power 2022, 55, 152–162. [Google Scholar]
- Eltamaly, A.M.; El-Sayed, A.-H.M.; Mohamed, Y.S.; Elghaffar, A.N.A. A Modified Techniques of Transmission System by Static Var Compensation (SVC) for Voltage Control. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th International Conference on Modeling Simulation and Applied Optimization (ICMSAO) 2019; pp. 1–5.
- Yarlagadda, V.; Garikapati, A.K.; Gadupudi, L.; Kapoor, R.; Veeresham, K. Comparative Analysis of STATCOM and SVC on Power System Dynamic Response and Stability Margins with time and frequency responses using Modelling. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Smart Technologies and Systems for Next Generation Computing (ICSTSN) 2022; pp. 1–8.
- Mourad, A.; Youcef, Z. Wheeled Mobile Robot Path Planning and Path Tracking in a static environment using TLBO AND PID- TLBO control. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 21st international Ccnference on Sciences and Techniques of Automatic Control and Computer Engineering (STA) 2022; pp. 116–121.
- Valluru, H.V.; Khandavilli, S.; Sela, N.V.S.K.C.; Thota, P.R.; Muktevi, L.N.V. Modified TLBO Technique for Economic Dispatch Problem. In Proceedings of the 2018 Second International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS) 2018; pp. 1970–1973.
- Arif, Y.M.; Nugroho, S.M.S.; Hariadi, M. Selection of Tourism Destinations Priority using 6AsTD Framework and TOPSIS. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Seminar on Research of Information Technology and Intelligent Systems (ISRITI) 2019; pp. 346–351.
- Zhou, S.; Zhu, L.; Guo, X. Power system voltage stability and its control; China Electric Power Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, B. Analysis of commutation failure in multi-infeed HVDC system under different load models. Power System Protection and Control 2015, 43, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Failure Number | DΓ,l | Failure Number | DΓ,l | Failure Number | DΓ,l |
| 1 | 0.0909 | 17 | 0.9490 | 33 | 0.2714 |
| 2 | 0.0796 | 18 | 0.9148 | 34 | 1.7133 |
| 3 | 0.4212 | 19 | 0.7055 | 35 | 0.8796 |
| 4 | 0.4380 | 20 | 0.8705 | 36 | 0.3278 |
| 5 | 0.6902 | 21 | 0.9528 | 37 | 0.5423 |
| 6 | 0.4949 | 22 | 0.6184 | 38 | 0.6378 |
| 7 | 0.8572 | 23 | 0.6772 | 39 | 0.3311 |
| 8 | 0.8787 | 24 | 0.8356 | 40 | 0.2553 |
| 9 | 0.9739 | 25 | 0.6696 | 41 | 0.3781 |
| 10 | 0.8299 | 26 | 0.4717 | 42 | 0.2440 |
| 11 | 0.8614 | 27 | 0.5254 | 43 | 0.1699 |
| 12 | 0.9562 | 28 | 0.5051 | 44 | 0.2006 |
| 13 | 0.7955 | 29 | 0.3624 | 45 | 0.2976 |
| 14 | 0.3163 | 30 | 0.3121 | 46 | 0.3557 |
| 15 | 0.0928 | 31 | 0.3784 | ||
| 16 | 0.9501 | 32 | 0.2797 |
| Nodal | Γ | SΓ,i | Nodal | Γ | SΓ,i |
| 1 | -5.48855 | 0.003469 | 16 | -4.96675 | 0.013905 |
| 2 | -5.15575 | 0.010125 | 17 | -4.8989 | 0.015262 |
| 3 | -5.0114 | 0.013012 | 18 | -4.9498 | 0.014244 |
| 4 | -4.9407 | 0.014426 | 19 | -5.09815 | 0.011277 |
| 5 | -4.99185 | 0.013403 | 20 | -5.23305 | 0.008579 |
| 6 | -5.0139 | 0.012962 | 21 | -5.04085 | 0.012423 |
| 7 | -5.05725 | 0.012095 | 22 | -5.10995 | 0.011041 |
| 8 | -5.05815 | 0.012077 | 23 | -5.0916 | 0.011408 |
| 9 | -5.4201 | 0.004838 | 24 | -4.94405 | 0.014359 |
| 10 | -4.9501 | 0.014238 | 25 | -5.1098 | 0.011044 |
| 11 | -4.97635 | 0.013713 | 26 | -4.84815 | 0.016277 |
| 12 | -4.8839 | 0.015562 | 27 | -4.8134 | 0.016972 |
| 13 | -4.947 | 0.0143 | 28 | -4.9461 | 0.014318 |
| 14 | -4.9066 | 0.015108 | 29 | -4.8698 | 0.015844 |
| 15 | -4.89625 | 0.015315 |
| Device type | Operational life / a | Installation costs / $ | Reimbursement unit price / [$∙Mvar-1] |
| SVC | 10 | 1.3×107 | 3×104 |
| STATCOM | 10 | 2.6×107 | 9×104 |
| Compensation nodal |
Scheme 1 | Scheme 2 | Scheme 3 | Scheme 4 | Scheme 5 | |||||
| Capacity /Mvar |
Type | Capacity /Mvar |
Type | Capacity /Mvar |
Type | Capacity /Mvar |
Type | Capacity /Mvar |
Type | |
| Bus-12 | 463 | SVC | 372 | STATCOM | 438 | SVC | 306 | STATCOM | 433 | SVC |
| Bus-15 | 453 | STATCOM | 255 | SVC | 225 | SVC | 206 | SVC | 460 | STATCOM |
| Bus-17 | 478 | SVC | 456 | SVC | 114 | SVC | 300 | SVC | 418 | STATCOM |
| Bus-26 | 238 | STATCOM | 310 | SVC | 363 | SVC | 240 | SVC | 91 | SVC |
| Bus-27 | 406 | SVC | 402 | SVC | 395 | SVC | 397 | SVC | 454 | SVC |
| Bus-29 | 201 | STATCOM | 115 | SVC | 85 | SVC | 195 | SVC | 318 | STATCOM |
| Scheme | Cost /$ | Γ | Closeness value |
| 1 | 2.3769×108 | 3.9567 | 0.4179 |
| 2 | 1.6360×108 | 3.5939 | 0.7707 |
| 3 | 1.4310×108 | 2.7685 | 0.6202 |
| 4 | 1.5268×108 | 3.1681 | 0.6894 |
| 5 | 2.5398×108 | 3.9922 | 0.3798 |
| Method of compensation | Cost/$ | Γ | Total number of instabilities |
| Uncompensated | 0 | -5.6620 | 106 |
| Traditional compensation method | 2.1008×108 | 3.6032 | 78 |
| Differentiated compensation method | 1.6360×108 | 3.5939 | 79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





