1. Introduction
Chromium (Cr) is a frequent heavy metal contamination; it is influenced by both natural and human causes and is directly tied to the parent material that forms the soil, the kind of soil, the geological topography, the pH, the climate, and the type of land use[
1,
2]. There are several different valence forms of Cr in soil, while Cr(III) and Cr(VI) are the most prevalent and stable states in the environment[
3]. Cr(III) is a trace element that is less hazardous and necessary for human and animal metabolism[
4], but not essential for plants. Cr(VI) is almost several hundred times more toxic than Cr(III) and is more easily absorbed by plants due to its high mobility and bioavailability. Crop development will be hampered when Cr builds up in the soil in large quantities. Chromium ions can cause cell death in plants when they are absorbed in excessive quantities because the extra ions can bind to proteins in the cell protoplasm[
5]. Growing crops in chromium-contaminated areas could be dangerous because as a plant grows, absorbed chromium ions move to the surface and accumulate in the edible parts while consuming produce with excessive chromium levels can harm humans.
Fertilizer application as an agricultural activity is an essential part of agricultural production, while has a certain impact on heavy metals in the soil. It has become an agronomic measure with the potential for heavy metal remediation in recent years due to its simple operation, low cost, and easy promotion in large fields[
6,
7]. Fertilizers not only increase the nutrient elements in the soil to improve crop yield and quality, but also change the morphology of heavy metals in the soil, which in turn affects the uptake of heavy metals by plants, but different types of fertilizers have different remediation effects on heavy metals as a result of the different elements they contain[8-10]. Nitrogen fertilizer affects the activity of heavy metals mainly through inter-root acidification and alkalinization of nitrate and ammonium nitrogen[
11,
12], its transport affects the soil physicochemical environment, root surface iron film, and subcellular structure of various organs of the crop, therefore, it can mitigate the toxic effects of heavy metals on plants after nitrogen fertilizer application[
13,
14]; Fertilizers containing phosphorus have a solidifying effect on heavy metals in the soil by altering the soil environment, such as pH, CEC, and SOM, as well as influencing the uptake and transport of heavy metals by plants through the regulation of plant physiological metabolism[
15,
16]. Some organic fertilizers and restoration fertilizers can also be very good at repairing heavy metals. Tao et al. found that restoration fertilizers and zoysia can effectively reduce the content of cadmium in brown rice when applied alone or in combination, and the best effect was achieved with a reduction rate of 28.64% when applied in combination[
17]. However, it has also been shown that the long-term application of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers can, on the contrary, increase the biological effectiveness of heavy metals[
18]. The effects of different nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers on heavy metals have been studied differently, which may be related to different fertilizer application rates, crop types or soil environmental conditions, etc.
Soil conditioners have been widely used in recent years due to their effectiveness in the remediation of heavy metals in agricultural fields. For example, biochar can raise soil pH and increase the activity of soil urease and sucrase, thus reducing the effective state Cd content of soil[
19]. Under the condition of light Cd contamination in farmland, the addition of various passivation materials can reduce the effective state content of soil Cd and the content of Cd in rice to different degrees[
20]. Gao et al. found that the application of different soil conditioners could reduce the Cd content of rice and PX4 and SAX1 soil conditioners were the most effective in reducing the Cd content of rice when applied in season[
21]. It has also been found that the use of some soil conditioners may cause some damage to the nutrients, structure, and microbial community of the soil[
22,
23], add additional costs, and whether they can be used all year round, Therefore, it is necessary to study the effect of fertilization on heavy metals[
24].
The effect of fertilizers on heavy metals has been studied for a long time, but most of the studies mainly focus on the effect of organic fertilizers, trace elements, etc. on heavy metals or the effect of fertilizers on heavy metal cadmium, and less on the effect of different inorganic fertilizers on heavy metal chromium. In this paper, the effect of using different fertilizers on maize yield, remediation effect, and soil physicochemical properties under open field conditions in light to moderate chromium-contaminated soil with maize as the material, while selecting two soil conditioners with better remediation effect of heavy metals in previous experiments in our laboratory for comparison, and screening out fertilization measures suitable for local chromium contaminated soil through comprehensive effect.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Overview
The test location is situated in a village in Ming Guang, China, which has a warm-temperate continental monsoon climate with four distinct seasons, rain and heat, enough light, and a lengthy frost-free period. The average annual precipitation is 915 mm, and the average annual temperature is 15.2 °C, rice, maize and wheat are grown extensively. The experiment's crop is maize, which was previously planted as rice. The soil type is volcanic ash soil (also known as Guan Shan chicken dung soil), which has a medium soil fertility level. Before the test plot was divided, a background soil sample of one mixed soil sample from 0 to 20 cm was obtained using the five-point sampling method to determine the background values of each index in the test site. Soil pH was 5.23, SOM was 18.81 g·kg−1, total nitrogen(N) content was 1.31 g·kg−1, hydrolytic nitrogen(N) content was 154.82 mg·kg−1, available phosphorus(P) content was 10.57 mg·kg−1, available potassium(K) content was 164 mg·kg−1, total chromium heavy metal in the soil was 255.73 mg·kg−1, and total chromium heavy metal in the soil was 255.73 mg·kg−1, which is light to moderate pollution.
2.2. Experimental Design
The field trial was conducted in Ming Guang City in 2021, trial sites can be divided into the zone of additional conditioner application (Zone D) and the zone of different fertilizer types (Zone Y), with another control group (CK), a total of 8 treatments. Fertilizers used in zone D were the same as CK, and only nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers were changed in zone Y, all treatments were potassium chloride. Treatments-specific fertilizer and conditioner application and dosage are shown in
Table 1, fertilizer dosage is the discounted pure amount of each element, and conditioning agent dosage is the actual amount of each conditioner.
Each treatment plot was set up with three replications, and the plot experimental design was randomized in groups, with a total of 24 treatment plots with an area of 24 m2 (4 m*6 m), surrounded by a small trench of about 20 cm. Conditioner is applied one week before planting, turned into the soil after application, and mixed well, fertilizer is applied as base fertilizer one day after the balance of conditioner application. Maize was sown by hole sowing with 130 holes per plot. Urea was applied at a rate of 225 kg·hm−2 in all plots when the maize reached the trumpet stage. Irrigation water is irrigated with clean water sources to cut off the source of pollution, and the maize is sampled for harvest when it is ripe.
3.3. Experimental Materials
The test maize variety was Denghai 605, which was purchased at the local agricultural market; The test conditioner includes: Biochar and Conditioner PX5B, the biochar was purchased from Henan Woda Environmental Protection Material Co., Ltd, the conditioner PX5B was purchased from the Gefeng Environmental Protection Technology Co., Ltd(GFTEM). mainly composed of nanomaterials, clay minerals, and ferrous sulfate. Fertilizers for testing include: soil testing compound fertilizer (18-12-15), urea (N>46%), ammonium sulfite (N>24%), calcium magnesium phosphate (P2O5>12%), diammonium phosphate (N>18%, P2O5>46%) and potassium chloride (K2O>60%), Soil measuring formula compound fertilizer (18-12-15) was purchased and provided by local farmers, the rest of the fertilizers were purchased from the GFTEM.
4.4. Sample Collection and Determination
When samples were harvested, whole maize samples (including roots, straws, and grains) and soil samples were collected in batches from each plot. The plant samples were separated according to the roots, straws, and grains, and each ministry was first rinsed with tap water, then washed with deionized water, followed by killing in an oven at 105 ℃ for 30 min, drying at 40 ℃ to constant weight. The dried plant samples were crushed, sieved, and put in dry self-sealing bags for the determination of Cr content. The extraction method of Cr from plants: weigh 0.3~0.5 g of plant sample in a Teflon ablation tube, add 4 ml of HNO3, 2 ml of H2O2, 2 ml of deionized water, and leave it for 2 h. Put it into microwave ablation apparatus for ablation, after completion of ablation, placed it on a thermostatic hot plate at 160°C to drive the acid until nearly dry, then transferred to a 25 ml volumetric flask to fix the volume, finally inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy was used for the determination. The soil was dried naturally to remove debris, ground, and individually passed through 2 mm (10 mesh) and 0.149 mm (100 mesh) nylon mesh sieves, for analytical determination. The physical and chemical properties of the soil were determined by referring to the "Soil and Agrochemical Chemistry Analysis". The effective state of Cr in the soil was extracted by DTPA leaching agent and determined by atomic absorption spectrophotometer after extraction.
5.5. Statistical Data Analysis
The experimental data were calculated using Microsoft Excel 2016, with Origin 2018 applied for the graphs. Statistical analysis and ANOVA between different treatments were calculated using IBM SPSS Statistics 22.0 software, and the differences mentioned in the text were significant all referring to P<0.05. the aboveground bioconcentration factor (BCF), primary translocation factor (PTF), and secondary translocation factor (STF) in the upper part of the maize ground were used to characterize the uptake and translocation capacity of maize for Cr, respectively.
Relevant indicators were calculated according to the following formula:.
3. Results
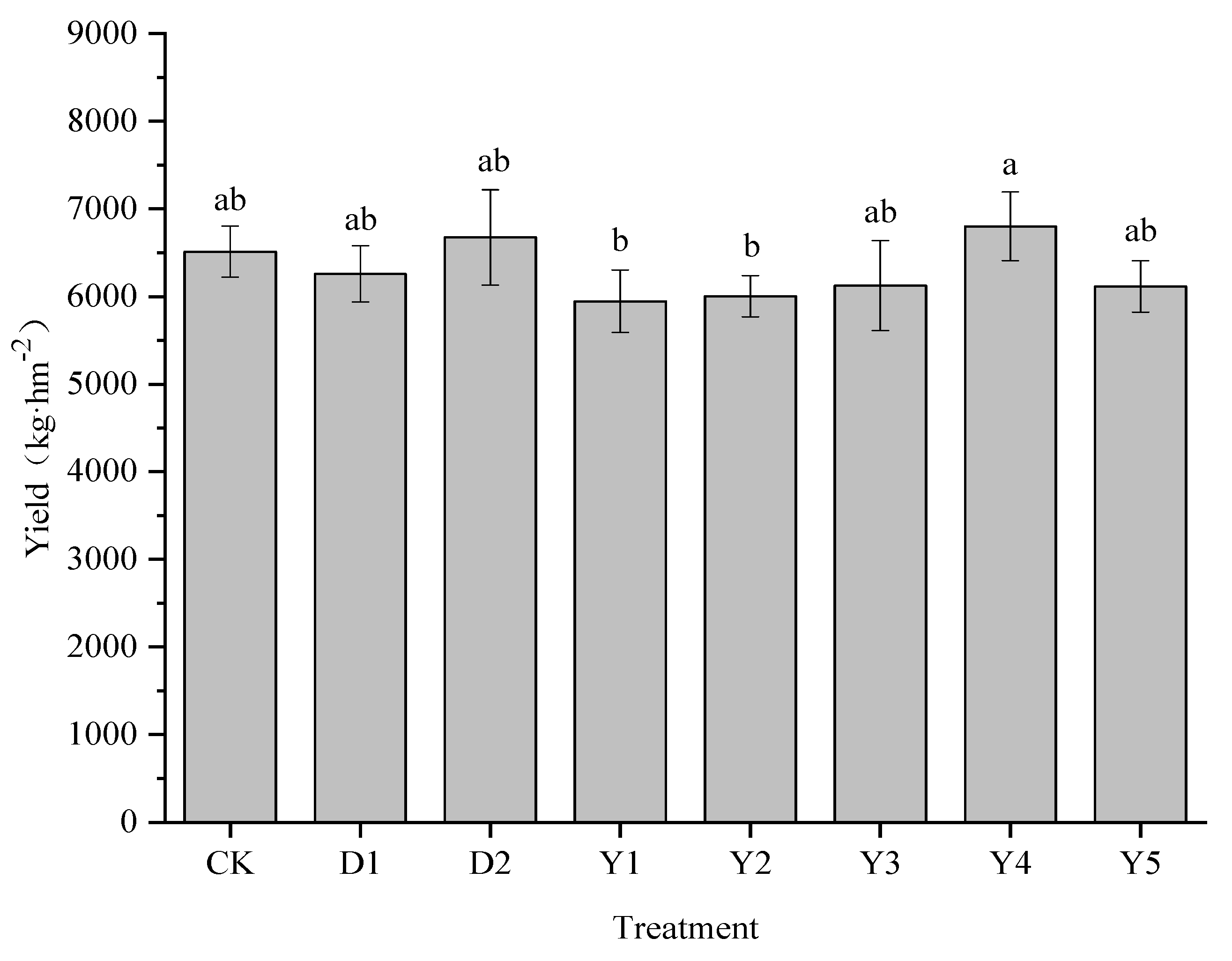
3.1. Effect of Fertilizers and Conditioners on maize yield
Figure 1 illustrates how several treatments affected the yield of maize, which ranged from 5945.40 to 6800.40 kg·hm
−2. Compared to CK (6511.50 kg·hm
−2), maize yield was enhanced to 6733.35 kg·hm
−2 under D2 treatment, with an increase of 2.5%. whereas the D1 treatment had a decrease in maize yield but no significant difference.
Under several other fertilization conditions (Y1-Y5), the highest maize yield of 6800.40 kg·hm−2 was achieved under Y4 treatment, it was the treatment with the best effect on maize yield improvement, compared to both CK and D2 treatments, raising by 4.44% and 1.90%, respectively. While the maize yields under the Y1, Y2, Y3, and Y5 treatments varied from 5945.33 to 6124.44 kg·hm−2, all of them were lower than the CK, D1, and D2 treatments, but none of them differed significantly from each other either.
3.2. Differences in Cr content of various parts of maize by fertilizers and conditioners
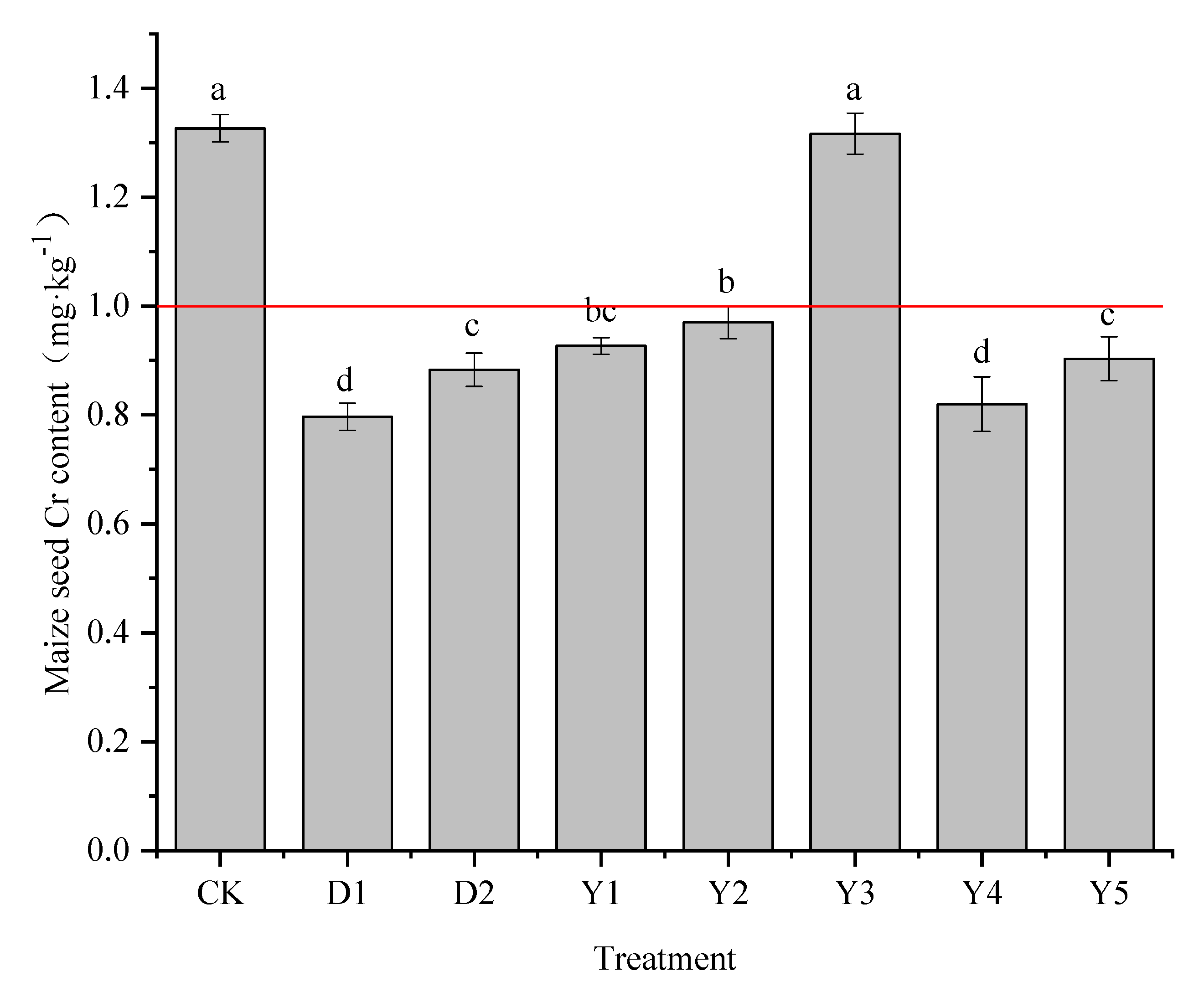
3.2.1. Cr content in maize grains
The main concern for the safe use of agricultural products mainly lies in the edible parts, and the Cr content of maize grains under different treatments is shown in
Figure 2. The Cr content of maize grains in the CK treatment was 1.33 mg·kg
−1, which exceeded the national food safety standards of China, therefore consumption of maize grown in this area could lead to a threat to human health. With the addition of the two conditioners, the Cr content in maize grains was 0.80 mg·kg
−1 and 0.88 mg·kg
−1, with a reduction rate of 39.95% and 33.42%, respectively, and the Cr content in maize grains was reduced to within the national food safety standards of China.
Under several other fertilization conditions (Y1-Y5), the Cr content of maize grains ranged from 0.82 to 1.32 mg·kg−1, which was reduced compared to CK, with the rate of reduction ranging from 0.75% to 38.19%. The Cr content of Y1, Y2, Y4, and Y5 treatments ranged from 0.82 to 0.97 mg·kg−1, all of which reduced the Cr content in maize grains to less than 1.0 mg·kg−1. The maize grains had the lowest Cr concentration of all of them in Y4, the best treatment, with a decrease rate of 38.19% in comparison to CK. When compared to D1 and D2 treatments, the reducing effect of the Y4 treatment was superior to D2, and no significant difference from D1. Y1 and Y5 treatments were also effective in reducing the Cr content of maize grains, with reduction rates of 30.15% and 31.91%, respectively, and the reduction effects were similar to those of the D2 treatment. The reduction rate of Y2 treatment was only 26.89%. However, the Y3 treatment had little effect on reducing the grains Cr content of maize, and the grains Cr content was 1.32 mg·kg−1, which was only 0.01 mg·kg−1 compared to CK, the reduction effect was not significant and exceeded the limit value standard of China.
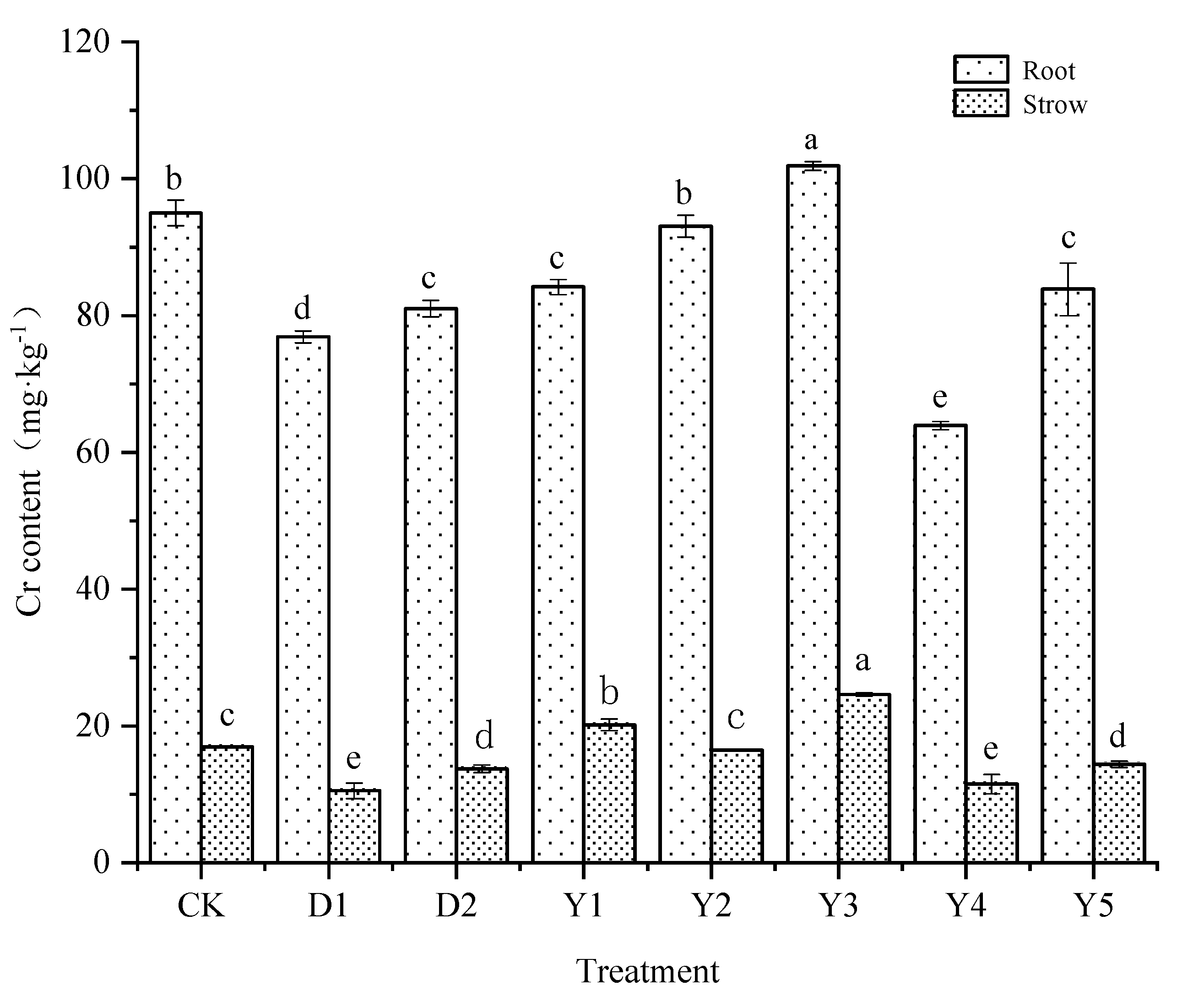
3.2.2. Cr content in maize roots and straws
After the uptake of heavy metal Cr by maize, the distribution of Cr in various plant tissues eventually affects the content in the maize grains.
Figure 3 shows the Cr content in maize roots and straws under different treatments, combined with
Figure 2, which shows that the different treatments will have some effect on the Cr content in various parts of maize. The Cr content of maize roots, straws, and grains under CK treatment was 94.99, 16.93, and 1.33 mg·kg
−1, respectively, which showed a rapidly decreasing pattern of roots > straws > grains Cr content in each tissue, the Cr content in roots reached more than five times of the Cr content of straws, and even tens of times of the Cr content in grains. The Cr levels of the roots under D1 and D2 treatments were 76.89 mg kg-1 and 83.85 mg kg-1, respectively, while the Cr contents of the straws were 10.51 mg kg-1 and 13.73 mg kg-1. The Cr contents of roots and straws were significantly lower under the D1 and D2 treatments compared to the CK treatments, just like the effect they were on grains. The decrease of Cr concentration in all components of maize was improved by both conditioners, and the D1 treatment had a better reduction impact than the D2 treatment.
Under several other fertilization conditions (Y1-Y5), The Cr content in maize roots and straws under Y2, Y4 and Y5 treatments ranged from 63.92 to 93.06 mg·kg−1 and 11.52 to 16.47 mg·kg−1, respectively, which all reduced the Cr content in maize roots and straws compared to CK. Among them, Y4 treatment had the best effect in reducing Cr content in maize roots and straws, with the reduction rate of 32.71% and 31.96%, respectively, which the reduction effect for roots was better than D1 and D2 treatments, but the reduction effect for straws was slightly worse than D1 treatment but equally better than D2 treatment. Second, the Y5 treatment could produce the same reduction impact as the D2 treatment, with reductions of 14.69% and 15.03% on roots and straws, respectively. Although the Y2 treatment reduced the Cr content in maize roots and straws, the effect was not significant. While Y3 could not reduce the Cr content of maize roots and straws compared to CK and D1, D2 treatments.
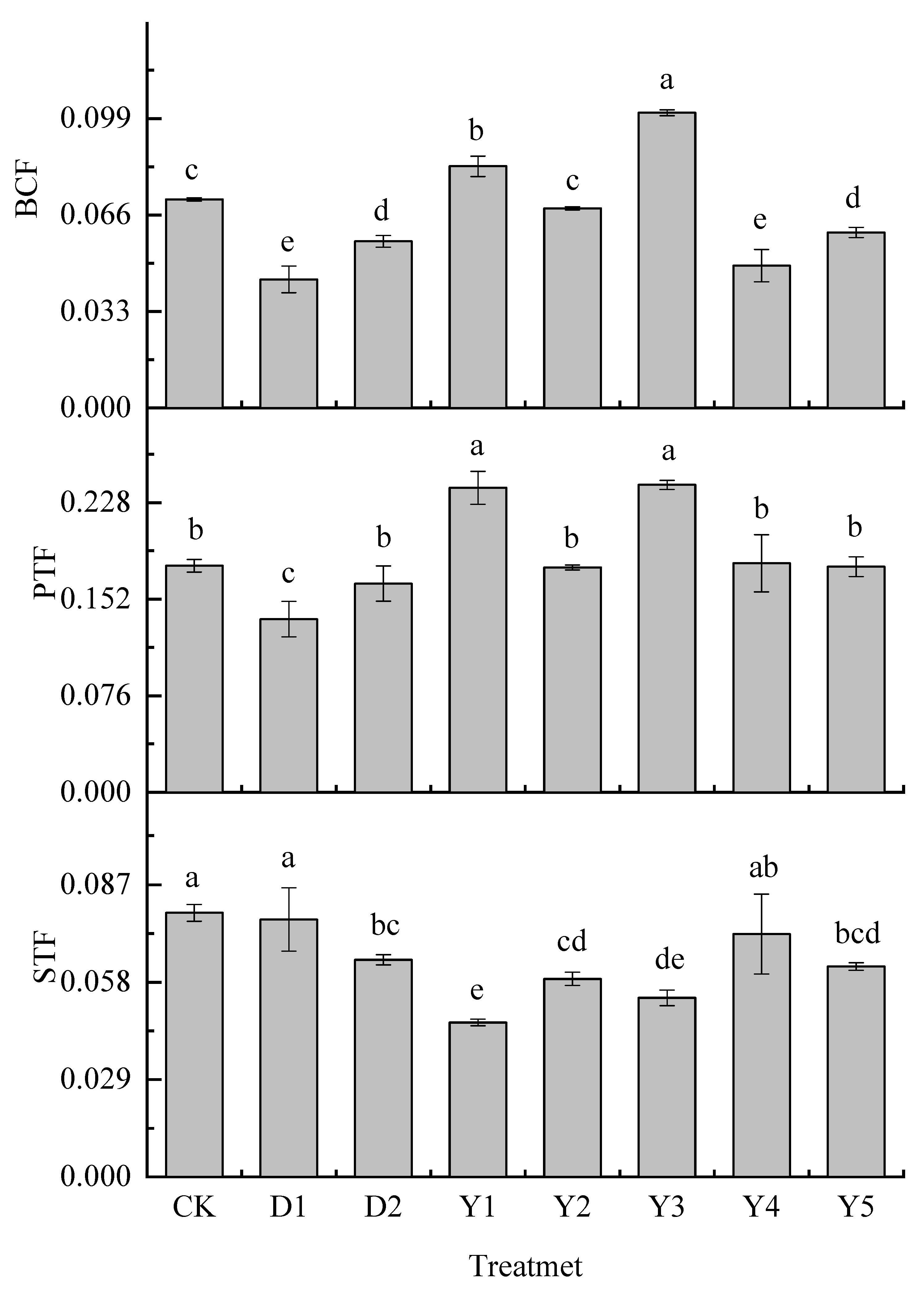
3.3. Effect of fertilizers and conditioners on bioconcentration and translocation factor of maize
Crops’ own enrichment and transport capacity of heavy metals are important factors influencing the content of heavy metals in various parts of the plant. The bioconcentration factor reflects the magnitude of the plant's ability to absorb heavy metals from the soil, and the translocation factor reflects the magnitude of the crop's ability to transport heavy metals between sites after uptake.
Figure 2 shows the bioconcentration and translocation factor of Cr in maize under different treatments. The enrichment capacity of Cr in the upper portion of the maize ground is less, as shown in
Figure 2 and
Figure 3, and it is primarily concentrated in the roots after being absorbed by the maize. After Cr entered the maize roots, it started to transport to the above ground, the PTF of maize to Cr was significantly stronger than the STF. Both D1 and D2 treatments reduced BCF, PTF, and STF, and D1 treatment was more effective in reducing BCF and PTF than D2 treatment, with a reduced rate of 38.31% and 23.55%, respectively, but D2 was more effective in reducing STF than D1 treatment, with a reduced rate of 17.80%.
Y2, Y4 and Y5 treatments were equally effective in reducing BCF and STF in maize compared to CK. The reduction of BCF under these three treatments reached 4.21%, 31.77%, and 15.88%, respectively, with Y4 treatment showing the best reduction effect, even better than D1 and D2 treatments. The reduction of STF reached 25.00%, 8.06%, and 20.34%, respectively, and the reduction effect of Y2 and Y5 were better than D1 and D2 treatments, Y4 treatment was better than D1 treatment but not as good as D2 treatment.Y1 and Y3 treatments also reduced STF of maize, with the reduction rate reaching 41.53% and 32.21%, respectively, and the reduction effect was also better than D1 and D2 treatments, being the two treatments with the best effect in reducing STF of maize but it led to an increase in BCF and PTF.
Overall it appeared that the Y2 treatment reduced both BCF, PTF, and STF of maize the same as D1 and D2 treatments, but it was less effective in reducing BCF and STF than D1 and D2 treatments, while the other fertilization treatments only partially reduced BCF, PTF or STF of maize.
Figure 4.
Enrichment and Translocation Factor of Cr in Maize. Note: D1 is formulated fertilizer + biochar; D2 is formulated fertilizer + Conditioner PX5B; Y1 is urea – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y2 is urea - diammonium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y3 is urea – calcium magnesium phosphate, diammonium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y4 is ammonium sulfite – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y5 is ammonium sulfite, urea – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride.
Figure 4.
Enrichment and Translocation Factor of Cr in Maize. Note: D1 is formulated fertilizer + biochar; D2 is formulated fertilizer + Conditioner PX5B; Y1 is urea – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y2 is urea - diammonium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y3 is urea – calcium magnesium phosphate, diammonium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y4 is ammonium sulfite – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y5 is ammonium sulfite, urea – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride.
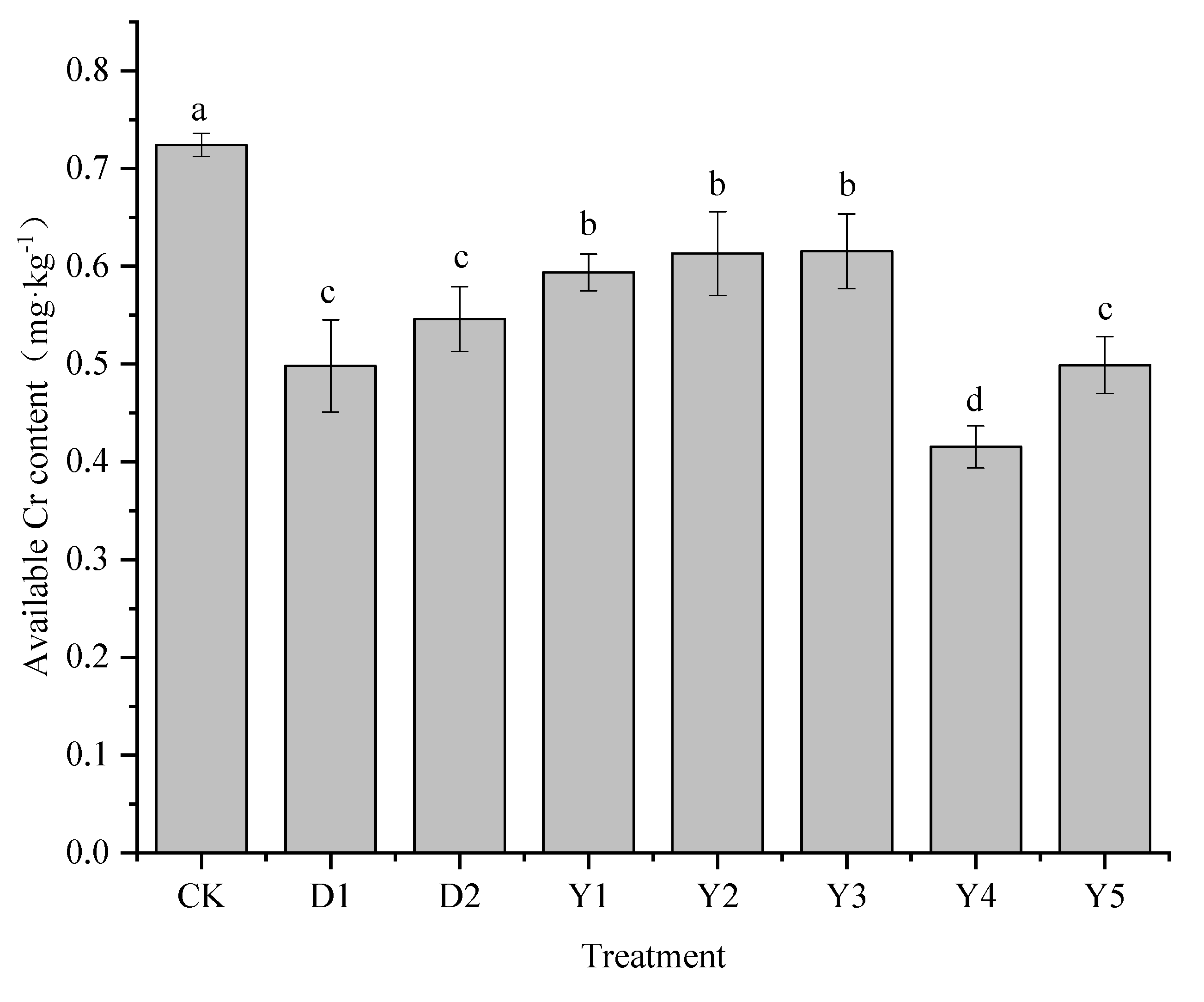
3.4. Effect of fertilizers and conditioners on available content of Cr
The available content of heavy metal is an important indicator of the bioavailability of heavy metals and its level can be used to determine whether different treatments can achieve certain remediation effects. The effects of different treatments on soil available content of Cr are shown in
Figure 5, and the available content of Cr in the soil under CK treatment reached more than 0.7, showing that this location has a high level of bioaccessibility of Cr in the soil. The available content of Cr in D1 and D2 treated soils was 0.50 mg·kg
−1 and 0.55 mg·kg
−1, respectively, which could significantly reduce the effective state of Cr compared with CK, and the reduction of 31.24% and 24.62%, respectively, which had a better effect on reducing the available content of Cr.
Under several other fertilization conditions (Y1-Y5), Y1 to Y5 treatments significantly reduced the effectiveness of soil Cr compared to Ck, with the content ranging from 0.42 to 0.59 mg·kg−1 and the reduction rate ranging from 15.05% to 42.66%. The reduction effect of Y1-Y5 treatments is: Y4>Y5>Y1>Y2>Y3, both Y4 and Y5 treatments achieved a better effect of reducing the available content of Cr, reduction rate can reach more than 30% in all cases. Compared to the conditioners, the Y4 treatment reduced the available content of Cr better than the D1 and D2 treatments, with 11.42% and 18.05% higher reduction rates than D1 and D2, respectively. The available content of Cr in the soil under Y5 treatment was 0.50 mg·kg−1, which was not as effective as Y4 but had a similar remediation effect as D1 treatment. While Y1, Y2 and Y3 treatments were not as effective as D1 and D2 treatments in reducing Cr in the soil available, with Y3 treatment being the least effective in reducing available content of Cr.
Figure 5.
Effects of fertilizers and conditioners on available Cr in soil. Note: D1 is formulated fertilizer + biochar; D2 is formulated fertilizer + Conditioner PX5B; Y1 is urea – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y2 is urea - diammonium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y3 is urea – calcium magnesium phosphate, diammonium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y4 is ammonium sulfite – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y5 is ammonium sulfite, urea – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride.
Figure 5.
Effects of fertilizers and conditioners on available Cr in soil. Note: D1 is formulated fertilizer + biochar; D2 is formulated fertilizer + Conditioner PX5B; Y1 is urea – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y2 is urea - diammonium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y3 is urea – calcium magnesium phosphate, diammonium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y4 is ammonium sulfite – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride; Y5 is ammonium sulfite, urea – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride.
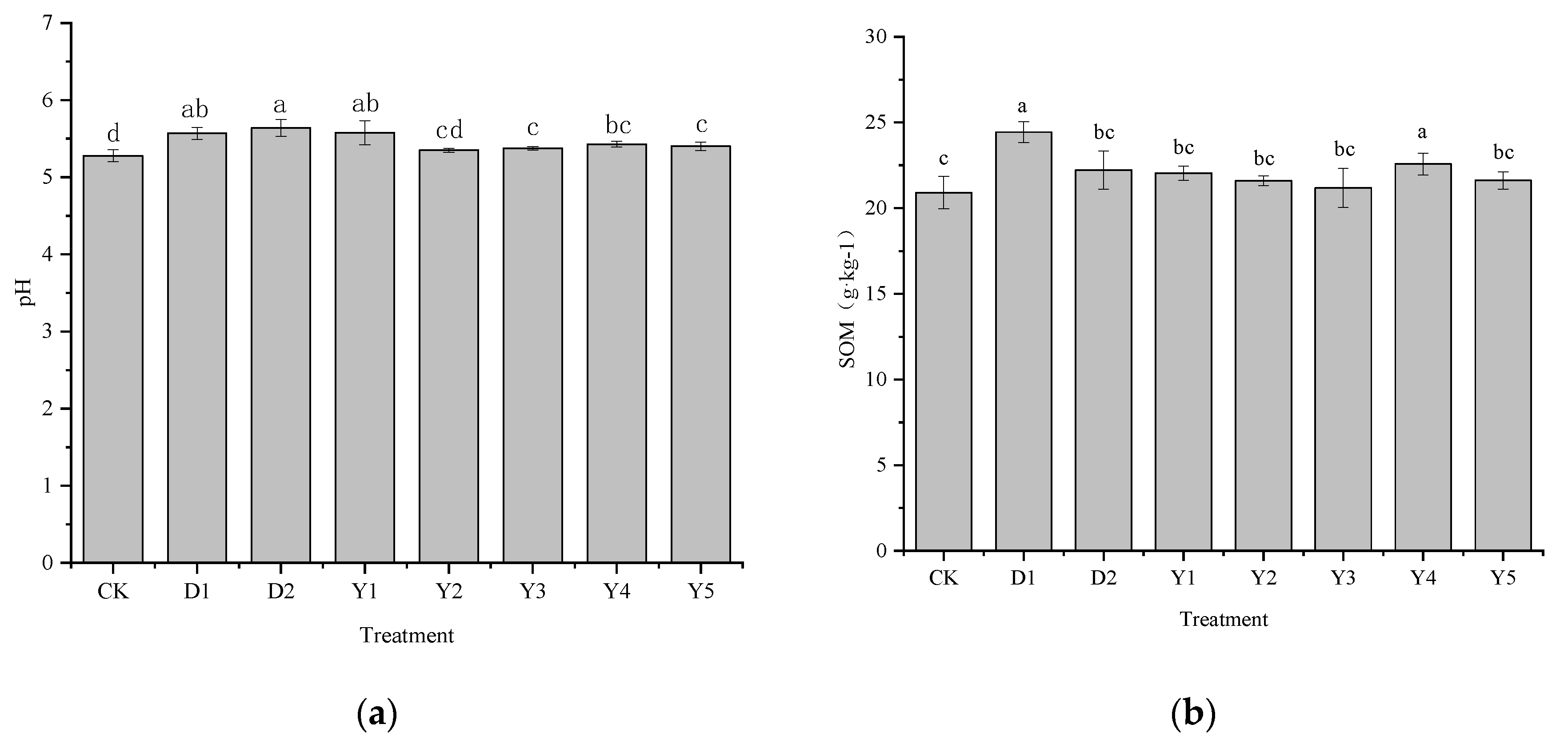
3.5. Effect of fertilizers and conditioners on pH and soil organic matter
The pH and soil organic matter (SOM) have a significant impact on how well plants absorb Cr. The most important factor influencing the effectiveness and morphological distribution of heavy metals is pH, the higher the pH, the less effective the heavy metals are and the less likely they are to be utilized by plants. SOM is also useful in reducing the effectiveness of heavy metals by increasing the content of SOM because it exhibits a large number of groups and also has certain adsorption properties. After maize maturity, soil pH (
Figure 6 A) and SOM (
Figure 6 B) under the CK treatment were 5.28 and 20.91 g·kg
−1, respectively. D1 and D2 treatments led to an increase in both pH and SOM. pH was raised by 0.29 and 0.36 units, with an increase of 5.49% and 6.82%, respectively, while SOM was 24.44 g·kg
−1 and 22.22 g·kg
−1, with an increase of 16.88% and 6.27%, respectively.
Under the amended fertilizer treatments (Y1-Y5), both soil pH and SOM content also increased, with increases ranging from 1.33% to 5.62% and 1.32% to 8.00% respectively. The best increase in soil pH was achieved by the Y1 treatment (5.58), an increase of 0.3 units compared to CK. However, the effect of changing fertilizer type on SOM was only significant for the Y4 treatment, where SOM reached 22.58 g·kg−1, an increase of 1.67 g·kg−1 compared to CK. In contrast, compared to the D1 and D2 treatments, all fertilizer treatments were less effective in increasing pH than the D2 treatment, while all treatments were less effective in increasing SOM than the D1 treatment. Y1 and D1 treatments were similar in their ability to increase pH to around 5.57. The effect of Y4 treatment on SOM enhancement was not as good as D1, but it was non-significant and better than D2 compared to D1.
3.6. Effect of fertilizers and conditioners on soil nutrient content
The impact of different fertilizers on soil nutrients is crucial in addition to limiting the uptake of Cr by maize, and changes in fertilizer can also result in changes in soil nutrients (
Table 2). Total N in the soil was 1.53 g·kg
−1 during the CK treatment, whereas hydrolytic N, available P, and available K were each 162.86, 12.02, and 253.33 mg·kg
−1, respectively. The soil total N and available P content of this plot in the maturity stage of maize were moderate, and available K was high, with good soil nutrients, according to the grading standard for the primary traits of arable land quality in Anhui Province. After the conditioners were added, the total N and available K levels under the D1 treatment were 1.43 mg·kg
−1 and 219.67 mg·kg
−1, respectively, which were lower than those under the CK treatment. However, the available P and hydrolytic N levels increased relative to the CK treatment, by 2.21 mg·kg
−1 and 23.02 mg·kg
−1, respectively. Except for available P, which was considerably lower by 8.57% compared to the CK treatment, none of the other nitrogen content measurements—total N, hydrolytic N, and available K—were significantly different under the D2 treatment from those under CK.
Under several other fertilization conditions (Y1-Y5), Y1, Y4 and Y5 treatments could increase the soil available P content with an increase ranging from 1.80% to 5.41%, but none of them were significant, while Y2 and Y3 treatments made the decrease of soil available P content. All fertilizer treatments resulted in a reduction in soil total N, hydrolytic N, and available K contents. The reduction in total N ranged from 12.00% to 18.00%, hydrolytic N from 11.60% to 17.96%, and available P from 9.08% to 36.71%. Total N was decreased by 12.0% to 18.0%, hydrolytic N by 11.60% to 17.96%, and available P by 9.08% to 36.71%.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of different fertilizers on Cr content, bioconcentration and translocation factor of various parts of maize
Different fertilizers can influence the growth of crops and the uptake of heavy metals by affecting the physiological activity of plants due to the presence of different elements. It was found that phosphorus fertilizer reduced Cr uptake and accumulation by rice roots and migration to the above ground, and also reduced Cr uptake by crops such as tomato [
25,
26]. Mahmut Tepecik et al. found lower Cr content in herbs by different fertilizer applications with added mono-ammonium phosphate treatment compared to NPK compound fertilizer (15:15:15) treatment[
27]. The effectiveness of different types of phosphate fertilizers on the remediation of different heavy metals also varies. Zhang et al. found that calcium magnesium phosphate can reduce the uptake of heavy metals Cd and Pb by vegetables[
28], and Dong et al. found that calcium magnesium phosphate can reduce the uptake of Cd and As by maize[
29]. Shen et al. found that diammonium phosphate had a significant blunting effect on soil heavy metal Cd and also reduced the content of As, Pb, Cd and Zn in rape roots, stems, husks, and rape grains[
30], but the effects of different types of phosphorus fertilizers on Cr uptake have rarely been reported. In this study, no significant effect of each treatment on maize yield was found, Cr content in maize grains was significantly reduced by replacing phosphate fertilizer with calcium magnesium phosphate or diammonium phosphate, and the reduction effect of calcium magnesium phosphate was better. Cr is mainly concentrated in the maize roots after being absorbed by maize, which is consistent with previous studies[
31,
32]. Although both calcium-magnesium phosphate and diammonium phosphate reduced the straw-to-grain translocation factor of Cr in maize, calcium-magnesium phosphate increased the aboveground bioconcentration factor and root-to-straw translocation factor of Cr in maize, resulting in increased Cr content in straws. This is different from previous studies that calcium magnesium phosphate promotes the synthesis of phytochelating peptides in the rice root system, inhibits the uptake of Cd by the root system and its transport to the aboveground, as well as increases the phosphorus content and amino acid content in rice thereby directly or indirectly reducing the accumulation of Cd in rice[
33,
34], which may be due to the different types of crops and the different elements of heavy metal. In contrast, diammonium phosphate had no significant effect on Cr transport in maize and aboveground bioconcentration factor as well as Cr content in roots and straws. The 1:1 combination of both calcium magnesium phosphate and diammonium phosphate not only failed to significantly reduce the Cr content of maize grains but also increased the Cr content of maize roots and straws, indicating that these two phosphate fertilizers may not be suitable for simultaneous application.
The Cr content in maize grains, straws, and roots was further reduced by replacing all or part of the urea with ammonium sulfite. The PCS-AS@PVA-Fe
3O
4 composite made by some method with the participation of ammonium sulfite (AS) could reduce Cr(VI) to Cr(III) by SO
32-, which could effectively control the migration of Cr(VI) in soil and plant uptake, and also release ammonium salts to promote plant growth[
35,
36]. Meanwhile, the addition of ammonium sulfite was able to significantly reduce the Cr bioconcentration factor in the upper part of the maize ground but did not have a significant effect on the Cr translocation factor of maize, indicating that the main effect of ammonium sulfite may be to reduce the Cr(VI) in the soil, reduce the uptake of Cr by maize, and then reduce the Cr content in maize grains, while it had less effect on the Cr transport in maize, and the reduction effect increased with the increase of ammonium sulfite application.
4.2. Changes in effective state Cr content and pH and organic matter of soils
Soil pH and SOM are two important factors affecting the effectiveness of heavy metals in soil, and other nutrient conditions can also affect the effectiveness of heavy metals in various ways[
37,
38]. The amount of calcium magnesium phosphate and diammonium phosphate that was applied to the soil reduced the effective state of the heavy metals Cd and Pb, but after reaching a certain amount, the effective state of heavy metals did not decrease with the increase of applied amount, and the effect was better with calcium magnesium phosphate at small applied amounts[
39,
40], which is similar to the findings of this paper, and the reduction of effective state Cr was better with calcium magnesium phosphate. This may be caused by the different effects of calcium magnesium phosphate and diammonium phosphate on soil pH. According to studies, adding calcium magnesium phosphate raises soil pH while lowering Eh[
33,
41,
42], Zhou et al. found that diammonium phosphate significantly reduced soil pH and TCLP extracted state content of Cd by passivating Cd-contaminated soil with different phosphate fertilizers, and the TCLP extracted state content was significantly negatively correlated with soil fast-acting phosphorus content[
43], but Zhao et al. found that the soil pH was significantly increased in the early stage of diammonium phosphate application and began to decrease after 15 days[
44]. Calcium magnesium phosphate, diammonium phosphate, or calcium magnesium phosphate applied 1:1 with diammonium phosphate all increased soil pH and SOM, but the effect on SOM enhancement was not significant. Therefore, calcium magnesium phosphate and diammonium phosphate mainly affect the effective state of Cr by influencing soil pH, and calcium magnesium phosphate can raise soil pH better than diammonium phosphate, which is more effective in reducing the effective state of Cr.
Ammonium sulfite is often used in industry to treat certain wastes due to its strong oxidizing effect[45-47]. The reduction of soil effective state Cr after replacing all or part of urea with ammonium sulfite was superior to the treatment that changed only phosphorus fertilizer, which is a result of the reduction of Cr(VI) to Cr(III) under acidic conditions by utilizing the decreasing property of SO
32-, which converts Cr(VI) to a precipitate of hydroxide, thus making the leaching of Cr(VI) less toxic[
48,
49]. Simultaneous application of calcium magnesium phosphate together can increase soil pH, which increases not only reduces the effectiveness of Cr[
50], but the oxidation rate of ammonium sulfite increases with increasing pH at pH < 7[
46], these may be the reasons that lead to a better effect on the reduction of effective state Cr after changing both nitrogen and phosphate fertilizers compared to changing only phosphate fertilizers.
Changing both nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers reduced the content of Cr in maize grains and the effectiveness of Cr in soil, but there were some differences in the effects and mechanisms of action, and the effects of different combinations or dosages of fertilizers on the uptake of Cr in maize under chromium contaminated conditions could be further explored subsequently. The actual application process also requires comprehensive consideration according to the actual conditions of the soil and planting, to choose a more appropriate fertilization method.
5. Conclusions
The Cr content of maize in different tissues showed that roots>straws>grains. urea - calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride, urea - diammonium phosphate - potassium chloride, ammonium sulfite – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride, and ammonium sulfite, urea - calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride fertilizer with treatments can significantly reduce the Cr content in maize grains, ammonium sulfite – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride with the best effect, can achieve the same effect with the two conditioners.
The two conditioners reduced the enrichment of Cr in the upper part of the maize ground and the ability of each site to transport Cr. Both urea - calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride and urea - diammonium phosphate - potassium chloride reduced Cr translocation from stalk to maize grains, but urea – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride increased Cr on the aboveground bioconcentration factor and root-to-stalk translocation factor of maize. Ammonium sulfite – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride and ammonium sulfite, urea – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride treatments did not have significant effects on Cr transport among maize parts but were able to reduce Cr enrichment in the aboveground well.
All treatments increased soil pH and SOM and decreased the effectiveness of Cr in the soil. After changing the fertilizer, only the urea – calcium magnesium phosphate - potassium chloride treatment did not lead to a reduction in soil effective phosphorus, while the rest of the treatments led to varying degrees of reduction in soil total nitrogen, hydrolytic nitrogen, and fast-acting potassium.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.Y.; methodology, Y.M.; software, X.Z.; validation, J.Z. and Y.M.; formal analysis, C.C.; investigation, H.H.; resources, Y.M.; data curation, Y.G.; writing—original draft preparation, J.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.Z.; visualization, W.Y.; supervision, Y.W. and Y.M.; project administration, X.Z.; funding acquisition, Y.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Key Research and Development Program of Anhui Province (2022m07020004), Natural Resources Science and Technology Project of Anhui Province (2022-k-8), and Anhui Provincial Science and Technology Major Research Project of Engineering (17030701053).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request to the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jiang, X.C.; Xu, J.; Li, R.Y.; Jia, Y.F.; Yang, P.; Luo, J. Guangdong Province: Spatial distribution char-acteristics, source apportionment and influencing factors. Earth Science Frontiers 2023, 30, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, X.P.; Shi, X.L.; Sui, H.J.; Su, H.; Yang, H. Influential factors of spatial distribution of Cd and Cr in regional soils. Soils 2018, 50, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, A.; Bibi, I.; Niazi, N.K.; Ok, Y.S.; Murtaza, G.; Shahid, M.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Li, D.; Mahmood, T. Chromium(VI) sorption efficiency of acid-activated banana peel over organo-montmorillonite in aqueous solutions. International Journal of Phytoremediation 2017, 19, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.S. Essential trace elements in human health and disease. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 1985, 4, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fytili, D.; Zabaniotou, A. Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods - A review. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews 2008, 12, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Y; Wang, P.; Wu, X.C.; Li, Z.P.; Zhou, D.M. Effect of long-term fertilization experiment on concentration of micronutrients and heavy metals in soil and brown rice. Acta Pedologica Sinica 2009, 46, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Liao, X. Y.; Wang, L.Q.; Zhang, Y. Z. Evaluation on effect of strengthening agronomic measures in cadmium-contaminated paddy field. Journal of Agro-Environment Science 2018, 37, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.J.; Li, H.; Di, Z.Z.; Liu, L. Effects of different potassium levels on Cr absorbed and physiological characteristics of the maize seedlings. Journal of Agro-Environment Science 2009, 28, 2246–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.Y.; Kang, L.Y.; Yan, Z.J.; Qu, M.S.; Liu, Z.F.; Zhang, C.Z.; Chen, Q. Effects of biogas manure replacing chemical fertilizer on accumulation of nutrient and heavy metal in greenhouse vegetable soil. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering 2017, 33, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Duan, C.Q.; Zhu, Y.N.; Zhang, X.H.; Wang, C.X. Effect of chemical fertilizers on the fractionation of Cu, Cr and Ni in contaminated soil. Environmental Geology 2007, 52, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.G.; Liu, P.; Song, Z.G.; Zhang, Q. Progress in Fertilization on Behavior of Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soils. Journal of Agro-Environment Science 2006, 328–333. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.J.; Shen, W.S.; Lin, X.G. Chemical fertilizer reduction technology and its agronomic and ecological environment effects. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China 2022, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Jiang, B.B.; Pan, Y. Z.; Tan, M.; Zhang, M.Q.; Yang, Y.L.; Liu, S.L. Mitigation of different forms of exogenous nitrogen on Cd toxicity to solanum nigrum. Journal of Agro-Environment Science 2015, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.T.; Xiang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.S; Ao, H.J. Research progress on effects of nitrogen fertilizer management on cadmium uptake and transport in rice. Crop Research 2023, 37, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y. F.; Xing, H.; Wu, W.H.; Wen, X.J.; Gu, C.; Ye, K.; Gu, G.P. Control of heavy metal accumulations in soil-cabbage(Brassica chinensis L.)system of lead/zinc mine tailings using phosphorus fertilizer. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture & Life Sciences) 2017, 43, 787–796. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Z.; Wang, Q.Q.; Mi, Z.D.; Wan, Y.N.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.F. Effect of fertilizers containing phosphorus on the remediation of heavy metals contamination in soil-plant system. Phosphate & Compound Fertilizer 2020, 35, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.H.; Yuan, X.F.; Wu, X.D.; Wang, Y.; Lu, H.J.; Ye, W.L; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.H. Effects of repair fertilizer and milk vetch(Astragalus sinicus L.)on cadmium uptake and accumulation in rice. Journal of Agro-Environment Science 2023, 42, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Peng, W.F.; Chen, R.Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhong, Z.X.; Nong, Y.D.; Luo, J.Q.; Zhang, X.Y. Types of phosphorus fertilizers and their influences on cadmium and phosphorus interactions in soil-plant systems. Soils and Crops 2019, 8, 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ma, Y.H.; Li, J.X. Effect of Biochar Addition on Soil Available Cadmium and Enzyme Activities. Chinese Journal of Soil Science 2020, 51, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y; Yang, M.L.; Oudom-daove, P.; Yang, Q.B.; Li, D.; Ma, Y.H. Study on effects and aftereffects of passivation materials on remediation of Cd polluted farmland soil. The Administration and Technique of Environmental 2021, 33, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.L.; Daove, P.o.; Bao, G.L.; Li, D.; Ma, Y.H.; Li, J.X. Comparison of remediation effects of different soil conditioners on paddy fields with mild cadmium pollution. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China 2022, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.W.; Chen, X.B.; Liu, X.W.; Song, Q.M.; Li, Y.B.; Cai, X.D. Effects of organic and inorganic fertilizers on heavy metal immobilization in paddy Soil. Journal of Agro-Environment Science 2015, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.M.; Wang, X.J.; Dang, X.L. Research progress on remediation of heavy metal cadmium in farmland soil with amendments. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences 2020, 48, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jin, Q.; Tan, J. Effects of Water Stress and Nitrogen Levels on Grapes Heavy Metal Absorption. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences 2017, 30, 2031–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.P.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhu, Y.N.; Liu, J.; Huang, H.T. Effect of different fertilizers on Cr uptake and distribution in paddy plant. In Proceedings of the Symposium of the 2012 academic annual meeting of the Chinese Society of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, Guangzhou; 2012; pp. 154–161. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Salah, Y.; Oudadesse, H.; Lefeuvre, B.; Tounsi, S.; El Feki, H. Purified monoammonium phosphate fertilizer promotes the yield and reduces heavy metals accumulation in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.). International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 2022, 19, 1753–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepecik, M.; Esetlili, B.C.; Ozturk, B.; Anac, D. Effect of different fertilizers on peppermint - Essential and non-essential nutrients, essential oils and yield. Italian Journal of Agronomy 2022, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, M.K. Inactivation effect of mixed amendments on heavy metals in complex polluted vegetable soil. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi 2020, 32, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.Y.; Wang, K.; Deng, Q.; Ren, L.J.; Li, J.Q.; Zhang, C.Q.; Zhang, N.M.; Bao, L. Effect of calcium-magnesium-phosphate fertilizer on Cd and As absorption of maize in compound polluted farmland. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China 2022, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, Z.J.; Hou, W.Q.; Xu, D.C.; WU, J.F.; Ji, T.T. Effects of different immobilization materials on heavy metal migration in contaminated soil-rape. Journal of Agro-Environment Science 2020, 39, 2779–2788. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.Y.; Cheng, H.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Hao, Q.P.; Chang, J.L.; Huang, F.; Yan, M.; Zhang, G.S. Effects of wood vinegar of fungus chaff on physiological and biochemistry index and heavy metal enrichment and transfer of maize in Cu and Cr contaminated soil. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences 2019, 48, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.T.; Hu, H.H.; Ying, C.Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, F.H.; Jiang, H.Y.; Ma, Y.H. Study on Chromium Uptake and Transfer of Different Maize Varieties in Chromium-Polluted Farmland. Sustainability 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L. Mechanism of Phosphate Fertilizer Inhibiting Cadmium accumulation in rice. Doctor, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2021.
- Yuan, K. Effects of amino acids and calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer on cadmium accumulation in rice. Doctor, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2021.
- Ren, J.Y.; Zhang, G.L.; Wang, D.F.; Cai, D.Q.; Wu, Z.Y. Honeycomb-like magnetic cornstalk for Cr(VI) removal and ammonium release. Bioresource Technology 2019, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.Y. Removal of Cr(VI) from environment and food by high energy electron beam irradiation and composites. Master, Anhui University, 2020.
- Zhao, B.Z.; Maeda, M.; Zhang, J.B.; Zhu, A.N.; Ozaki, Y. Accumulation and chemical fractionation of heavy metals in andisols after a different, 6-year fertilization management. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2006, 13, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Ali, S.; Zhang, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Qiu, B.; Wu, F.; Zhang, G. The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environmental Pollution 2011, 159, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C. The influence of different additives on Lead-zinc slag contaminated soil in available heavy metal content. GuizhouChemical Industry 2010, 35, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C. Study on soil amendment inhibition heavy mentals absorption by Afalfa. Master, Guizhou University, 2010.
- Cai, X.; Long, X.X.; Zhong, Y.X.; Wu, Q.T. Inorganic-organic amendments for immobilization of metal contaminants in an acidic soil. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae 2015, 35, 3991–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Zhou, J.W.; Liu, H.Y.; Luo, Y.M.; Wu, L.H.; Xin, Z.J. Effects of amendments on the alleviation of aluminum toxicity and cadmium and zinc uptake by Sedum plumbizincicola in acid soils. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology 2020, 36, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Liang, C.H.; Du, L.Y.; Wei, Q. Evaluation on passivation effect of cadmium in soil under different phosphate fertilizers levels. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation 2014, 34, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Feng, W.Q.; Qing, Y.S.; Yu, H.; Liao, M.L.; Jia, K.L.T.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, C.Q.; Tu, S.H. Eeffects of application of nitrogen, phosphorus and potssium fertilizers on soil pH and cadmium availability. Acta Pedologica Sinica 2010, 47, 953–961. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, C.M.; Huang, J.; Li, W.B.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z.T.; Ren, K.M. Effects of ammonium sulfite on electrolytic manganese. Hydrometallurgy of China 2022, 41, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.W.; Zhou, Y.B; Li, J.P. Study on oxidation of ammonium sulfite. Guangzhou Chemical Industry 2009, 37, 132–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.Y.; Long, H.Y.; Su, H.F. Reduction of selenium in electrolytic manganese anodic solution using ammonium sulfite. Hydrometallurgy of China 2021, 40, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.L. The research of chromium contaminated soil solidification/stabilization. Master, Chongqing University, 2011.
- Cheng, Q.; Wang, C.; Doudrick, K.; Chan, C.K. Hexavalent chromium removal using metal oxide photocatalysts. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental 2015, 176, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Feng, J.; Zou, D.M.; Jiu, Y.D.; Wu, X.F.; Su, C.L.; Zhao, M. Effects of alkaline liquid fertilizer on bioavailability,accumula-tion and migration of heavy metals in Sauropus androgynus-soil. Journal of Southern Agriculture 2022, 53, 3336–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).