Submitted:
26 July 2023
Posted:
27 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Questions
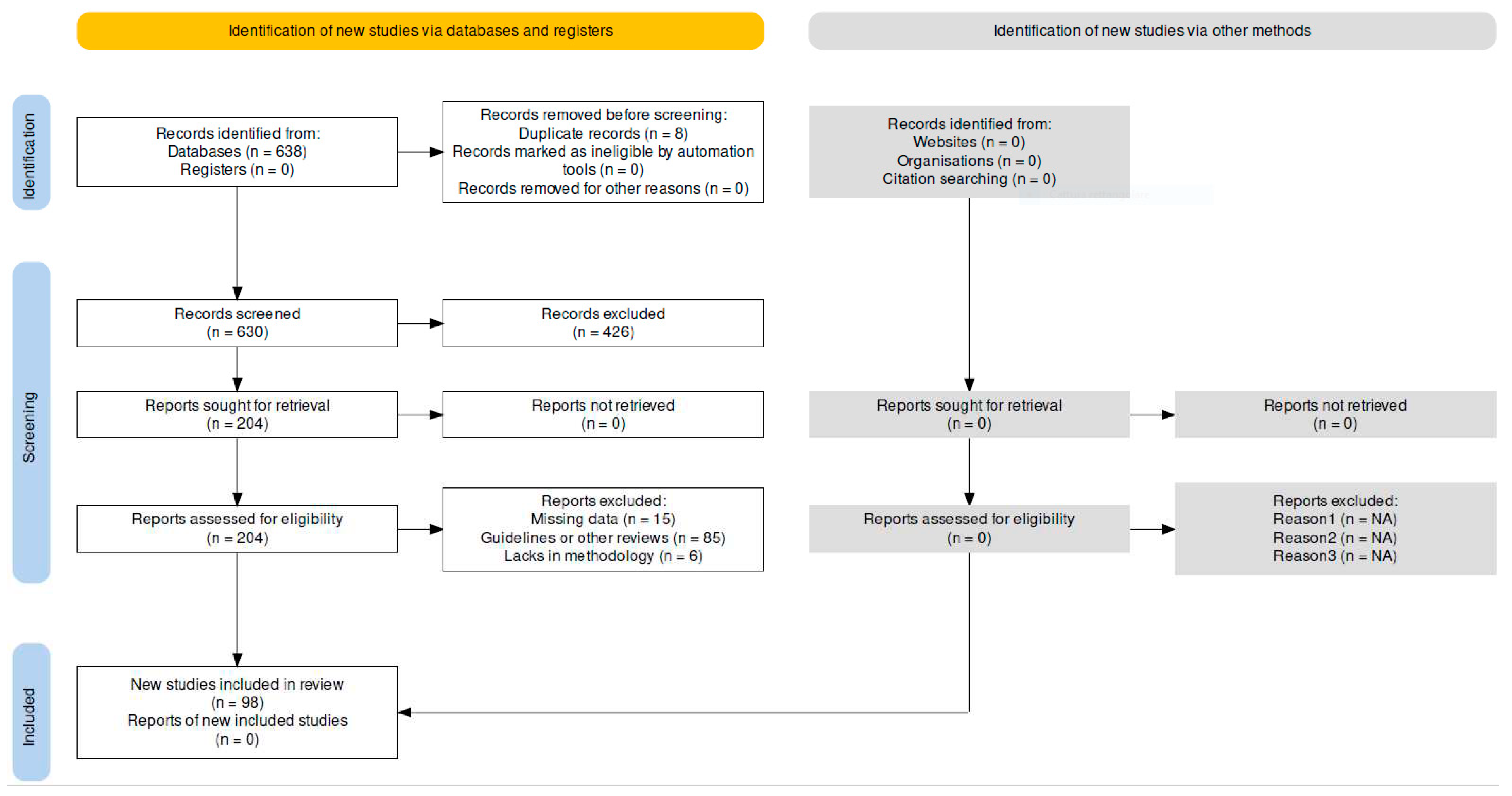
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Strategy and Literature Search
3. Results
| Substance | Reference | Specie |
Level of Evidence |
Dose & Duration |
Main Conclusions |
Clinical field of significance |
| Green tea | (47) | Human | RCT | 50 or 100 or 200 mg, single dose | Highest dose significantly increases excretion of cancerogen acrylamide | Antioxidant activity |
| (48) | Human | Non-RCT | 300 mg/day for 14 days | Slight decrease in plasma leukocyte count, significant increase in antioxidant status | ||
| (49) | Human | RCT | 1 cup single dose or 2 cups/day for 7 days | Increase in heme oxygenase-1 activity, decrease in lymphocytic DNA damage | ||
| (50) | Human | Non-RCT | 254 mg, single dose | Plasma PCOOH levels decreased with an inverse correlation to the increase in plasma EGCG levels | ||
| (51) | Human | RCT | 4 cups/day or 2 capsules/day for 8 weeks | Decrease in SAA levels | ||
| (52) | Human | RCT | 4 cups/day for 16 weeks | Decrease in urinary 8-OHdG levels in heavy smokers with mutations of glutathione-S-transferase | ||
| (53) | Human | RCT | 800 mg/day for 6 weeks | Beneficial period x treatment interaction in terms of body weight control in overweight subjects | Metabolism & cardiovascular health | |
| (54) | Human | RCT | 4 cups/day or 2 capsules/day for 8 weeks | Significant decrease in body weight and BMI | ||
| (55) | Human | RCT | 456 mg/day for 8 weeks | Mild changes in insulin level | ||
| (56) | Human | RCT | 630 mg/day for 14 weeks | Reduction in cholesterol levels | ||
| (57) | Human | RCT | 400 mg/day or 800 mg/day for 8 weeks | Reduction in LDL cholesterol and glucose-related markers | ||
| (58) | Human | RCT | 100 mg/day for 4 weeks | Improvements in insulin resistance | ||
| (59) | Human | RCT | 1450 mg, single dose | Reduction in some circulating catecholamines | ||
| (60) | Human | RCT | 1500 mg/day for 16 weeks | Within-group reduction in waist circumference, HOMA-IR index, insulin level; increase in ghrelin level | ||
| (61) | Human | RCT | 456 mg/day for 8 weeks | Reduction in HbA1c levels, borderline significant reduction in blood diastolic pressure | ||
| (62) | Human | RCT | 350 mg/day for 7 days | Reduction in insulin levels | ||
| (63) | Human | RCT | 800 mg/day for 8 weeks | Reduction in blood diastolic pressure | ||
| (64) | Human | RCT | 540 mg/day for 24 weeks | Improvements in skeletal muscle mass in sarcopenic subjects | Physical performance | |
| (65) | Human | RCT | 250 mg/day for 4 weeks | No negative effects on endurance-training adaptation | ||
| (66) | Human | RCT | 570 mg/day for 8 weeks | Improvements in aerobic capacity during training | ||
| (67) | Human | RCT | 1500 mg/day for 10 weeks | Improvements in metabolic and antioxidant status during physical exercise | ||
| (68) | Human | RCT | 900 mg/day for 52 weeks | Reduction in incidence of relapsing metachronous colorectal adenomas | Anti-cancer activity | |
| (69) | Human | Case-control | >2 cups/day for >20 years | Significant decrease in incidence of de novo myelodysplastic syndromes | ||
| (70) | Human | RCT | 600 mg/day for 24 weeks | No effect in preventing PCa incidence | ||
| (71) | Human | RCT | 600 mg/day for up to 20 weeks | No effect in preventing PCa incidence | ||
| (72) | Human | Non-RCT | 6000 mg/day for a median of 4 weeks | No anti-neoplastic activity in PCa patients | ||
| (73) | Human | RCT | 600 mg/day for 52 weeks | No effect in preventing PCa incidence in HGPIN patients | ||
| (74) | Human | RCT | 400 mg/day for 52 weeks | No effect in preventing PCa incidence in HGPIN and ASAP patients | ||
| (75) | Human | RCT | 843 mg/day for 52 weeks | Reduction of mammographic density in women aged 50-55 | ||
| (78) | Human | RCT | 800 mg/day for 16 weeks | Absence of recurrence in 1/3 of treated women with ovarian cancer | ||
| (79) | Human | RCT | 800 mg/day for 16 weeks | No protective effect on CIN | ||
| (76) | Human | RCT | 200 mg/day for up to 12 weeks | Lower recurrence of CIN | ||
| (80) | Human | RCT | N/A | Higher clinical response in uVIN | ||
| Sylmarin | (9) | Human | RCT | 160 mg 4 tablets/day for 10 weeks | The dietary supplement utilized in this study was shown to delay PSA progression after potentially curative treatment in a significant fashion | Anti-cancer activity |
| (10) | Human | RCT | 570 mg/day for 24 weeks | The combination of this study significantly reduced two markers of lipid metabolism known to be associated with PCa progression | ||
| (11) | Human | RCT | 570 mg daily for 24 weeks | Improvement of IPSS score, urodynamic parameters: maximal rate of urine flow (Qmax), average flow (Qave), V and RV, total PSA value | Antioxidant | |
| Sulforaphane | (29) | Human | RCT | Two tablets containing 10 mg sulforaphane each, three times/day for 24 weeks | Median log PSA slopes were consistently lower in sulforaphane-treated men | Anti-cancer activity |
| (30) | Human | RCT | Two 100-μmol/day taken 12 h apart. Mean intervention period was 4.4 wk | The supplement was associated with significant interactions in gene expression among some genes that are related to PCa development | ||
| (31) | Human | RCT | A weekly 300 mL portion of soup made from a standard broccoli or from an experimental broccoli genotypes with enhanced concentrations of glucoraphanin | Changes in gene expression and associated oncogenic pathways were attenuated in men on the glucoraphanin-rich broccoli soup in a dose-dependent manner. | ||
| Lycopene | (36) | Human | Non-RCT | 10 mg/day | A significant and maintained effect on PSA velocity over 1 year was demostrated | Anti-cancer activity |
| (38) | Human | RCT | 4 mg twice a day for 52 weeks | Lycopene delay or prevent HGPIN from developing into occult prostate cancer | ||
| (40) | Human | RCT | 30 mg/day for 3 weeks | Three weeks supplementation lowers PSA in patients with non-metastatic prostate cancer | ||
| Escine | (115) | Human | RCT | 10 days | Reduction in pain, decrease in the dilatation of the urinary tract, effective expulsion of the stone | Urolithiasis |
| (118) | Human | RCT | 60 mg/day for 2 months | Improvement in sperm density and in sperm motility | Male Infertility | |
| (121) | Human | RCT | 160 and 500 mg/day for 5 weeks | Decrease of pain, improvements regard to prostatic and urinary symptoms | CP/CPPS | |
| Reduced Glutathione | (102) | Human | RCT | N/A | Reduced glutathione reacts with lipid peroxides protecting germinal epithelium from ROS damage | Male Infertility |
| (106) | Human | Non-RCT | N/A | GSH can reactivate antioxidant enzymes stimulating increase in sperm count and decrease in morphological and motility changes | ||
| Tryptophan | (83) | Human | RCT | 200 mg/day for 7 days | Improvement of depressive mood in severe depression patients | Mood and cognition |
| (84) | RCT | 2000 or 4000 mg, single dose | Benefits on emotional function | |||
| (85) | Non-RCT | 25 mg/kg of body weight for 12 weeks | Mental state improvement on elderly subjects with mood disorders | |||
| (86) | RCT | 200 mg or 400 mg/day for 12 weeks | Improvements in social interaction | |||
| (87) | RCT | 800 mg, single dose | Promotion of charitable behaviour | |||
| (88) | RCT | 1000 mg for 19 days | Benefits on emotional and social function | |||
| (89) | Case-control | N/A | Higher intake of tryprophan is linked to reduced emotion-related impulsivity | |||
| (90) | RCT | 100 mg, single dose | Influence on attention-switching tasks | |||
| (91) | RCT | N/A | Reduction of chronic pain in fibromyalgia syndrome | Chronic pain | ||
| (92) | RCT | 280 mg/day for 16 weeks | Improvement in environmental enteropathy | Gastrointestinal health | ||
| (93) | RCT | N/A | Improvement in gastrointestinal symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome | |||
| (94) | Non-RCT | N/A | Decrease in fatigue perception during aerobic exercise | Physical performance |
4. Discussion
4.1. Silymarin
4.2. Sulforaphane
4.3. Lycopene
4.4. Green Tea
4.5. Tryptophan
4.6. Glutathione
4.7. Escin
4.8. Limitations of the study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, F.; Du, M.; Blumberg, J.B.; Chui, K.K.H.; Ruan, M.; Rogers, G.; Shan, Z.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, F.F. Association Among Dietary Supplement Use, Nutrient Intake, and Mortality Among U.S. Adults: A Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierzejska, R.E. Dietary Supplements-For Whom? The Current State of Knowledge about the Health Effects of Selected Supplement Use. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronis, M.J.J.; Pedersen, K.B.; Watt, J. ADVERSE EFFECTS OF NUTRACEUTICALS AND DIETARY SUPPLEMENTS. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 58, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazak, R.; Walterova, D.; Kren, V. Silybin and Silymarin - New and Emerging Applications in Medicine. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 315–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, X.; Agarwal, R. Silibinin Decreases Prostate-Specific Antigen with Cell Growth Inhibition via G1 Arrest, Leading to Differentiation of Prostate Carcinoma Cells: Implications for Prostate Cancer Intervention. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1999, 96, 7490–7495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Deep, G.; Blouin, M.J.; Pollak, M.N.; Agarwal, R. Silibinin Suppresses in Vivo Growth of Human Prostate Carcinoma PC-3 Tumor Xenograft. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 2567–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raina, K.; Blouin, M.-J.; Singh, R.P.; Majeed, N.; Deep, G.; Varghese, L.; Glodé, L.M.; Greenberg, N.M.; Hwang, D.; Cohen, P.; et al. Dietary Feeding of Silibinin Inhibits Prostate Tumor Growth and Progression in Transgenic Adenocarcinoma of the Mouse Prostate Model. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11083–11091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschoyle, R.D.; Greaves, P.; Patel, K.; Marsden, D.A.; Brown, K.; Steward, W.P.; Gescher, A.J. Evaluation of the Cancer Chemopreventive Efficacy of Silibinin in Genetic Mouse Models of Prostate and Intestinal Carcinogenesis: Relationship with Silibinin Levels. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, F.H.; Roobol, M.J.; Boevé, E.R.; De Mutsert, R.; Zuijdgeest-Van Leeuwen, S.D.; Kersten, I.; Wildhagen, M.F.; Van Helvoort, A. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study in Men with Prostate Cancer and Rising PSA: Effectiveness of a Dietary Supplement. Eur. Urol. 2005, 48, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidlar, A.; Vostalova, J.; Ulrichova, J.; Student, V.; Krajicek, M.; Vrbkova, J.; Simanek, V. The Safety and Efficacy of a Silymarin and Selenium Combination in Men after Radical Prostatectomy - a Six Month Placebo-Controlled Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky. Olomouc. Czech. Repub. 2010, 154, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vostalova, J.; Vidlar, A.; Ulrichova, J.; Vrbkova, J.; Simanek, V.; Student, V. Use of Selenium-Silymarin Mix Reduces Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms and Prostate Specific Antigen in Men. Phytomedicine 2013, 21, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, B.P.; Dennehy, C.; Ramirez, G.; Sapp, J.; Lawrence, V.A. Milk Thistle for the Treatment of Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Med. 2002, 113, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.-Y.; Kang, N.-I.; Lee, H.-K.; Jang, K.Y.; Park, J.-W.; Park, B.-H. Sulforaphane Protects Kidneys against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury through Induction of the Nrf2-Dependent Phase 2 Enzyme. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 2214–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Jia, Z.; Strobl, J.S.; Ehrich, M.; Misra, H.P.; Li, Y. Potent Induction of Total Cellular and Mitochondrial Antioxidants and Phase 2 Enzymes by Cruciferous Sulforaphane in Rat Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells: Cytoprotection against Oxidative and Electrophilic Stress. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2008, 8, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lii, C.-K.; Liu, K.-L.; Cheng, Y.-P.; Lin, A.-H.; Chen, H.-W.; Tsai, C.-W. Sulforaphane and Alpha-Lipoic Acid Upregulate the Expression of the Pi Class of Glutathione S-Transferase through c-Jun and Nrf2 Activation. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soane, L.; Li Dai, W.; Fiskum, G.; Bambrick, L.L. Sulforaphane Protects Immature Hippocampal Neurons against Death Caused by Exposure to Hemin or to Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Qian, Q.; Adaikalakoteswari, A.; Rabbani, N.; Babaei-Jadidi, R.; Thornalley, P.J. Activation of NF-E2-Related Factor-2 Reverses Biochemical Dysfunction of Endothelial Cells Induced by Hyperglycemia Linked to Vascular Disease. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2809–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, C.S.; Gao, S.; Lee, G.-H.; Kim, D.S.; Park, B.-H.; Chae, S.W.; Chae, H.-J.; Kim, S.H. Sulforaphane Protects Ischemic Injury of Hearts through Antioxidant Pathway and Mitochondrial K(ATP) Channels. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 61, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Kobori, N.; Aronowski, J.; Dash, P.K. Sulforaphane Reduces Infarct Volume Following Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Rodents. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 393, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.-H.; Park, M.; Suh, J.-H.; Choi, H.-S. Protective Effects of an Extract of Young Radish (Raphanus Sativus L) Cultivated with Sulfur (Sulfur-Radish Extract) and of Sulforaphane on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.-Y.; Kim, E.-K.; Moon, W.-S.; Park, J.-W.; Kim, H.-J.; So, H.-S.; Park, R.; Kwon, K.-B.; Park, B.-H. Sulforaphane Protects against Cytokine- and Streptozotocin-Induced Beta-Cell Damage by Suppressing the NF-KappaB Pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 235, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Rutz, J.; Maxeiner, S.; Grein, T.; Thomas, A.; Juengel, E.; Chun, F.K.H.; Cinatl, J.; Haferkamp, A.; Tsaur, I.; et al. Plant-Derived Sulforaphane Suppresses Growth and Proliferation of Drug-Sensitive and Drug-Resistant Bladder Cancer Cell Lines In Vitro. Cancers (Basel). 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, G.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Kim, W.J.; Park, K.Y.; Choi, Y.H. Sulforaphane Induces Apoptosis in T24 Human Urinary Bladder Cancer Cells through a Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Mitochondrial Pathway: The Involvement of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Kang, T.W.; Jung, Y. Do; Zhang, C.; Lian, S. Sulforaphane Inhibits Nonmuscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Cells Proliferation through Suppression of HIF-1α-Mediated Glycolysis in Hypoxia. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7844–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Han, M.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Moon, S.K.; Kim, W.J.; Hwang, H.J.; Park, K.Y.; Choi, Y.H. Sulforaphane Induces Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Mitotic Arrest and Subsequent Apoptosis in Human Bladder Cancer 5637 Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 64, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, N.; Kim, H.; Chandra, P.K.; Talwar, S.; Sharma, P.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Sikka, S.C.; Mondal, D. Multimodal Actions of the Phytochemical Sulforaphane Suppress Both AR and AR-V7 in 22Rv1 Cells: Advocating a Potent Pharmaceutical Combination against Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2774–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutz, J.; Thaler, S.; Maxeiner, S.; Chun, F.K.H.; Blaheta, R.A. Sulforaphane Reduces Prostate Cancer Cell Growth and Proliferation In Vitro by Modulating the Cdk-Cyclin Axis and Expression of the CD44 Variants 4, 5, and 7. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juengel, E.; Maxeiner, S.; Rutz, J.; Justin, S.; Roos, F.; Khoder, W.; Tsaur, I.; Nelson, K.; Bechstein, W.O.; Haferkamp, A.; et al. Sulforaphane Inhibits Proliferation and Invasive Activity of Everolimus-Resistant Kidney Cancer Cells in Vitro. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 85208–85219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipolla, B.G.; Mandron, E.; Lefort, J.M.; Coadou, Y.; Della Negra, E.; Corbel, L.; Le Scodan, R.; Azzouzi, A.R.; Mottet, N. Effect of Sulforaphane in Men with Biochemical Recurrence after Radical Prostatectomy. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila). 2015, 8, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Garzotto, M.; Davis, E.W. 2nd; Mori, M.; Stoller, W.A.; Farris, P.E.; Wong, C.P.; Beaver, L.M.; Thomas, G. V; Williams, D.E.; et al. Sulforaphane Bioavailability and Chemopreventive Activity in Men Presenting for Biopsy of the Prostate Gland: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutr. Cancer 2020, 72, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traka, M.H.; Melchini, A.; Coode-Bate, J.; Al Kadhi, O.; Saha, S.; Defernez, M.; Troncoso-Rey, P.; Kibblewhite, H.; O’Neill, C.M.; Bernuzzi, F.; et al. Transcriptional Changes in Prostate of Men on Active Surveillance after a 12-Mo Glucoraphanin-Rich Broccoli Intervention-Results from the Effect of Sulforaphane on Prostate CAncer PrEvention (ESCAPE) Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhamre, S.; Sahoo, D.; Tibshirani, R.; Dill, D.L.; Brooks, J.D. Temporal Changes in Gene Expression Induced by Sulforaphane in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Prostate 2009, 69, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przybylska, S.; Tokarczyk, G. Lycopene in the Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Y.; Xu, F.; Xu, S.; Shang, X. Oral Lycopene Administration Attenuates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress by Regulating Plasma Lipids in Rats with Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Epididymitis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 6517–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limpens, J.; Schröder, F.H.; De Ridder, C.M.A.; Bolder, C.A.; Wildhagen, M.F.; Obermüller-Jevic, U.C.; Krämer, K.; Van Weerden, W.M. Combined Lycopene and Vitamin E Treatment Suppresses the Growth of PC-346C Human Prostate Cancer Cells in Nude Mice. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, N.J.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, G.; Pramanik, R.; Barber, J.A.; Martin, F.L.; Morris, J.D.H.; Muir, G.H. Lycopene Inhibits DNA Synthesis in Primary Prostate Epithelial Cells in Vitro and Its Administration Is Associated with a Reduced Prostate-Specific Antigen Velocity in a Phase II Clinical Study. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2006, 9, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konijeti, R.; Henning, S.; Moro, A.; Sheikh, A.; Elashoff, D.; Shapiro, A.; Ku, M.; Said, J.W.; Heber, D.; Cohen, P.; et al. Chemoprevention of Prostate Cancer with Lycopene in the TRAMP Model. Prostate 2010, 70, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, N.K.; Saxena, S.; Singh, U.P.; Goyal, N.K.; Arora, R.P. Lycopene as a Chemopreventive Agent in the Treatment of High-Grade Prostate Intraepithelial Neoplasia. Urol. Oncol. 2005, 23, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Poppel, H.; Tombal, B. Chemoprevention of Prostate Cancer with Nutrients and Supplements. Cancer Manag. Res. 2011, 3, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paur, I.; Lilleby, W.; Bøhn, S.K.; Hulander, E.; Klein, W.; Vlatkovic, L.; Axcrona, K.; Bolstad, N.; Bjøro, T.; Laake, P.; et al. Tomato-Based Randomized Controlled Trial in Prostate Cancer Patients: Effect on PSA. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.N.; Liu, Y. Bin; Li, B.H. Lycopene Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effect to Inhibit Prostate Cancer Progression. Asian J. Androl. 2018, 21, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minutoli, L.; Altavilla, D.; Marini, H.; Rinaldi, M.; Irrera, N.; Pizzino, G.; Bitto, A.; Arena, S.; Cimino, S.; Squadrito, F.; et al. Inhibitors of Apoptosis Proteins in Experimental Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Effects of Serenoa Repens, Selenium and Lycopene. J. Biomed. Sci. 2014, 21, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Morais Junior, A.C.; Schincaglia, R.M.; Passarelli, M.; Pimentel, G.D.; Mota, J.F. Acute Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Supplementation Alters Postprandial Lipids after a Fast-Food Meal in Healthy Young Women: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Jia, W.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, A.; Zhu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, P.; Jiao, J.; et al. Metabolomics Strategy Comprehensively Unveils the Effect of Catechins Intervention on the Biomarkers of Exposure to Acrylamide and Biomarkers of Cardiometabolic Risk. Environ. Int. 2022, 169, 107517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, G.M.; Gana, K.; Rahman, K. Dietary Supplementation with Green Tea Extract Promotes Enhanced Human Leukocyte Activity. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2015, 12, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.K.; Choi, S.; Siu, P.M.; Benzie, I.F.F. Effects of Single Dose and Regular Intake of Green Tea (Camellia Sinensis) on DNA Damage, DNA Repair, and Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression in a Randomized Controlled Human Supplementation Study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1379–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Ninomiya, M.; Okubo, T.; Aoi, N.; Juneja, L.R.; Kim, M.; Yamanaka, K.; Miyazawa, T. Tea Catechin Supplementation Increases Antioxidant Capacity and Prevents Phospholipid Hydroperoxidation in Plasma of Humans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 3967–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Du, M.; Sanchez, K.; Leyva, M.J.; Betts, N.M.; Blevins, S.; Wu, M.; Aston, C.E.; Lyons, T.J. Green Tea Minimally Affects Biomarkers of Inflammation in Obese Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrition 2011, 27, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, I.A.; Harris, R.B.; Chow, H.-H.S.; Dean, M.; Brown, S.; Ali, I.U. Effect of a 4-Month Tea Intervention on Oxidative DNA Damage among Heavy Smokers: Role of Glutathione S-Transferase Genotypes. Cancer Epidemiol. biomarkers Prev. a Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. cosponsored by Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2004, 13, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.L.; Lane, J.; Holyoak, C.; Nicol, B.; Mayes, A.E.; Dadd, T. Health Effects of Green Tea Catechins in Overweight and Obese Men: A Randomised Controlled Cross-over Trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 1880–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Sanchez, K.; Leyva, M.J.; Wu, M.; Betts, N.M.; Aston, C.E.; Lyons, T.J. Green Tea Supplementation Affects Body Weight, Lipids, and Lipid Peroxidation in Obese Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2010, 29, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukino, Y.; Shimbo, M.; Aoki, N.; Okubo, T.; Iso, H. Randomized Controlled Trial for an Effect of Green Tea Consumption on Insulin Resistance and Inflammation Markers. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo). 2005, 51, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, R.; Kotani, K.; Ayabe, M.; Tsuzaki, K.; Shimada, J.; Sakane, N.; Takase, H.; Ichikawa, H.; Yonei, Y.; Ishii, K. Minor Effects of Green Tea Catechin Supplementation on Cardiovascular Risk Markers in Active Older People: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2013, 13, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.H.; Spicer, D.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Tseng, C.-C.; Yang, C.S.; Pike, M.C. Effect of 2-Month Controlled Green Tea Intervention on Lipoprotein Cholesterol, Glucose, and Hormone Levels in Healthy Postmenopausal Women. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila). 2012, 5, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dower, J.I.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Gijsbers, L.; Zock, P.L.; Kromhout, D.; Hollman, P.C.H. Effects of the Pure Flavonoids Epicatechin and Quercetin on Vascular Function and Cardiometabolic Health: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churm, R.; Williams, L.M.; Dunseath, G.; Prior, S.L.; Bracken, R.M. The Polyphenol Epigallocatechin Gallate Lowers Circulating Catecholamine Concentrations and Alters Lipid Metabolism during Graded Exercise in Man: A Randomized Cross-over Study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-H.; Liao, Y.-L.; Lin, S.-C.; Tsai, T.-H.; Huang, C.-J.; Chou, P. Does Supplementation with Green Tea Extract Improve Insulin Resistance in Obese Type 2 Diabetics? A Randomized, Double-Blind, and Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Altern. Med. Rev. 2011, 16, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Fukino, Y.; Ikeda, A.; Maruyama, K.; Aoki, N.; Okubo, T.; Iso, H. Randomized Controlled Trial for an Effect of Green Tea-Extract Powder Supplementation on Glucose Abnormalities. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.J.; McGlory, C.; MacInnis, M.J.; Allison, M.K.; Phillips, S.M.; Gibala, M.J. Green Tea Extract Does Not Affect Exogenous Glucose Appearance but Reduces Insulinemia with Glucose Ingestion in Exercise Recovery. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 121, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.L.; Lane, J.; Coverly, J.; Stocks, J.; Jackson, S.; Stephen, A.; Bluck, L.; Coward, A.; Hendrickx, H. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with the Green Tea Polyphenol Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate on Insulin Resistance and Associated Metabolic Risk Factors: Randomized Controlled Trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, Y.; Mori, H. Essential Amino Acid and Tea Catechin Supplementation after Resistance Exercise Improves Skeletal Muscle Mass in Older Adults with Sarcopenia: An Open-Label, Pilot, Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2023, 42, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.-C.; Lin, J.-C.; Bernard, J.R.; Liao, Y.-H. Green Tea Extract Supplementation Does Not Hamper Endurance-Training Adaptation but Improves Antioxidant Capacity in Sedentary Men. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. = Physiol. Appl. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 40, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, N.; Soga, S.; Shimotoyodome, A. Daily Consumption of Tea Catechins Improves Aerobic Capacity in Healthy Male Adults: A Randomized Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Trial. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 2412–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, E.; Afzalpour, M.E.; Nayebifar, S. Combined High-Intensity Interval Training and Green Tea Supplementation Enhance Metabolic and Antioxidant Status in Response to Acute Exercise in Overweight Women. J. Physiol. Sci. 2020, 70, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, C.M.; Lee, D.H.; Seo, A.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.B.; Son, W.-C.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, S.J.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, N.; et al. Green Tea Extracts for the Prevention of Metachronous Colorectal Polyps among Patients Who Underwent Endoscopic Removal of Colorectal Adenomas: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, M.; Jin, J.; Holman, C.D.J. Tea Consumption Reduces the Risk of de Novo Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Leuk. Res. 2015, 39, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontero, P.; Marra, G.; Soria, F.; Oderda, M.; Zitella, A.; Baratta, F.; Chiorino, G.; Gregnanin, I.; Daniele, L.; Cattel, L.; et al. A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo Controlled Phase I-II Study on Clinical and Molecular Effects of Dietary Supplements in Men with Precancerous Prostatic Lesions. Chemoprevention or “Chemopromotion”? Prostate 2015, 75, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Garzotto, M.; Beer, T.M.; Thuillier, P.; Lieberman, S.; Mori, M.; Stoller, W.A.; Farris, P.E.; Shannon, J. Effects of ω-3 Fatty Acids and Catechins on Fatty Acid Synthase in the Prostate: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatoi, A.; Ellison, N.; Burch, P.A.; Sloan, J.A.; Dakhil, S.R.; Novotny, P.; Tan, W.; Fitch, T.R.; Rowland, K.M.; Young, C.Y.F.; et al. A Phase II Trial of Green Tea in the Treatment of Patients with Androgen Independent Metastatic Prostate Carcinoma. Cancer 2003, 97, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micali, S.; Territo, A.; Pirola, G.M.; Ferrari, N.; Sighinolfi, M.C.; Martorana, E.; Navarra, M.; Bianchi, G. Effect of Green Tea Catechins in Patients with High-Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia: Results of a Short-Term Double-Blind Placebo Controlled Phase II Clinical Trial. Arch. Ital. di Urol. Androl. organo Uff. [di] Soc. Ital. di Ecogr. Urol. e Nefrol. 2017, 89, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.B.; Pow-Sang, J.; Egan, K.M.; Spiess, P.E.; Dickinson, S.; Salup, R.; Helal, M.; McLarty, J.; Williams, C.R.; Schreiber, F.; et al. Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Green Tea Catechins for Prostate Cancer Prevention. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila). 2015, 8, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samavat, H.; Ursin, G.; Emory, T.H.; Lee, E.; Wang, R.; Torkelson, C.J.; Dostal, A.M.; Swenson, K.; Le, C.T.; Yang, C.S.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Green Tea Extract Supplementation and Mammographic Density in Postmenopausal Women at Increased Risk of Breast Cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila). 2017, 10, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, F.A.R.; Cornelison, T.; Nuño, T.; Greenspan, D.L.; Byron, J.W.; Hsu, C.-H.; Alberts, D.S.; Chow, H.-H.S. Results of a Phase II Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Polyphenon E in Women with Persistent High-Risk HPV Infection and Low-Grade Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 132, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parish, M.; Massoud, G.; Hazimeh, D.; Segars, J.; Islam, M.S. Green Tea in Reproductive Cancers: Could Treatment Be as Simple? Cancers (Basel). 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trudel, D.; Labbé, D.P.; Araya-Farias, M.; Doyen, A.; Bazinet, L.; Duchesne, T.; Plante, M.; Grégoire, J.; Renaud, M.-C.; Bachvarov, D.; et al. A Two-Stage, Single-Arm, Phase II Study of EGCG-Enriched Green Tea Drink as a Maintenance Therapy in Women with Advanced Stage Ovarian Cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 131, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, W.-S.; Yoo, J.; Huh, S.-W.; Kim, C.-K.; Lee, J.-M.; Namkoong, S.-E.; Bae, S.-M.; Lee, I.P. Protective Effects of Green Tea Extracts (Polyphenon E and EGCG) on Human Cervical Lesions. Eur. J. cancer Prev. Off. J. Eur. Cancer Prev. Organ. 2003, 12, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, J.; Slade, D.; Goddard, H.; Dawson, C.; Ganesan, R.; Velangi, S.; Sahu, B.; Kaur, B.; Hughes, A.; Luesley, D. Sinecatechins Ointment as a Potential Novel Treatment for Usual Type Vulval Intraepithelial Neoplasia: A Single-Centre Double-Blind Randomised Control Study. BJOG 2021, 128, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, E.; Chen, O.; Liska, D.J.; Blumberg, J.B. Dietary Supplements for Weight Management: A Narrative Review of Safety and Metabolic Health Benefits. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernstrom, J.D. Effects and Side Effects Associated with the Non-Nutritional Use of Tryptophan by Humans. J. Nutr. 2012, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujita, N.; Akamatsu, Y.; Nishida, M.M.; Hayashi, T.; Moritani, T. Effect of Tryptophan, Vitamin B6, and Nicotinamide-Containing Supplement Loading between Meals on Mood and Autonomic Nervous System Activity in Young Adults with Subclinical Depression: A Randomized, Double-Blind, and Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo). 2019, 65, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, E.L.; Vargas, K.; Hogan, E.; Holmes, A.; Rogers, P.J.; Wittwer, J.; Kloek, J.; Goralczyk, R.; Mohajeri, M.H. Effects of Acute Treatment with a Tryptophan-Rich Protein Hydrolysate on Plasma Amino Acids, Mood and Emotional Functioning in Older Women. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014, 231, 4595–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chojnacki, C.; Gąsiorowska, A.; Popławski, T.; Konrad, P.; Chojnacki, M.; Fila, M.; Blasiak, J. Beneficial Effect of Increased Tryptophan Intake on Its Metabolism and Mental State of the Elderly. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Yamashiro, D.; Ogawa, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Cho, D.; Iizuka, A.; Tsukamoto-Yasui, M.; Takada, M.; Isokawa, M.; Nagao, K.; et al. Intake of Seven Essential Amino Acids Improves Cognitive Function and Psychological and Social Function in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenbergen, L.; Sellaro, R.; Colzato, L.S. Tryptophan Promotes Charitable Donating. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajeri, M.H.; Wittwer, J.; Vargas, K.; Hogan, E.; Holmes, A.; Rogers, P.J.; Goralczyk, R.; Gibson, E.L. Chronic Treatment with a Tryptophan-Rich Protein Hydrolysate Improves Emotional Processing, Mental Energy Levels and Reaction Time in Middle-Aged Women. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 350–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javelle, F.; Li, D.; Zimmer, P.; Johnson, S.L. Dietary Intake of Tryptophan Tied Emotion-Related Impulsivity in Humans. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2021, 91, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, C.R.; Jonkman, L.M. Attention Switching after Dietary Brain 5-HT Challenge in High Impulsive Subjects. J. Psychopharmacol. 2007, 21, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, V.; Secchettin, E.; Castellani, C.; Martini, A.; Mazzocchi, E.; Picelli, A.; Polati, E.; Donadello, K.; Valenti, M.T.; Carbonare, L.D. Comparison between Acupuncture and Nutraceutical Treatment with Migratens® in Patients with Fibromyalgia Syndrome: A Prospective Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis-Auguste, J.; Besa, E.; Zyambo, K.; Munkombwe, D.; Banda, R.; Banda, T.; Watson, A.; Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Swann, J.; Kelly, P. Tryptophan, Glutamine, Leucine, and Micronutrient Supplementation Improves Environmental Enteropathy in Zambian Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 1240–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, G.; Saracino, I.M.; Pavoni, M.; Nipote, B.; Colucci, R.; Capone, P.; Sannino, A.; Forte, F.; Vergori, E.D.E.; Brancaccio, M.; et al. Efficacy of a New Nutraceutical Formulation: L-Tryptophan, Probiotics, Charcoal, Chamomile, Mint, and Licorice (COLONIR®) in the Improvement of Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Subjects with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Minerva Gastroenterol. 2023, 69, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javierre, C.; Segura, R.; Ventura, J.L.; Surez, A.; Rosés, J.M. L-Tryptophan Supplementation Can Decrease Fatigue Perception during an Aerobic Exercise with Supramaximal Intercalated Anaerobic Bouts in Young Healthy Men. Int. J. Neurosci. 2010, 120, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K. Biotransformation. Fundam. Toxicol. 2016, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Zhen, C.; Liu, J.; Yang, P.; Hu, L.; Shang, P. Unraveling the Potential Role of Glutathione in Multiple Forms of Cell Death in Cancer Therapy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, M.T.; Chen, H.H.W. Role of Glutathione in the Regulation of Cisplatin Resistance in Cancer Chemotherapy. Met. Based. Drugs 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shertzer, H.G.; Schneider, S.N.; Nebert, D.W.; Dalton, T.P. Glutamate Cysteine Ligase Catalysis: Dependence on ATP and Modifier Subunit for Regulation of Tissue Glutathione Levels. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 33766–33774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, A.I.; Parikh, R.A.; Appleman, L.J.; Hahm, E.R.; Singh, K.; Singh, S. V Broccoli-Derived Sulforaphane and Chemoprevention of Prostate Cancer: From Bench to Bedside. Curr. Pharmacol. reports 2015, 1, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, E.; Micheli, L.; Noto, D.; Fiaschi, A.I.; Menchiari, A.; Cerretani, D. Resistin in Human Seminal Plasma: Relationship with Lipid Peroxidation, CAT Activity, GSH/GSSG Ratio, and Semen Parameters. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisht, S.; Dada, R. Oxidative Stress: Major Executioner in Disease Pathology, Role in Sperm DNA Damage and Preventive Strategies. Front. Biosci. (Schol. Ed). 2017, 9, 420–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancilla, H.; Maldonado, R.; Cereceda, K.; Villarroel-Espíndola, F.; Oca, M.M. De; Angulo, C.; Castro, M.A.; Slebe, J.C.; Vera, J.C.; Lavandero, S.; et al. Glutathione Depletion Induces Spermatogonial Cell Autophagy. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 2283–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flaherty, C.; Scarlata, E. OXIDATIVE STRESS AND REPRODUCTIVE FUNCTION: The Protection of Mammalian Spermatozoa against Oxidative Stress. Reproduction 2022, 164, F67–F78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foresta, C.; Flohé, L.; Garolla, A.; Roveri, A.; Ursini, F.; Maiorino, M. Male Fertility Is Linked to the Selenoprotein Phospholipid Hydroperoxide Glutathione Peroxidase. Biol. Reprod. 2002, 67, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanin, A.M.; Ahmed, H.H.; Kaddah, A.N. A Global View of the Pathophysiology of Varicocele. Andrology 2018, 6, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallelli, L. Escin: A Review of Its Anti-Edematous, Antiinflammatory, and Venotonic Properties. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2019, 13, 3425–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnould, T.; Janssens, D.; Michiels, C. Effect of Aescine on Hypoxia-Induced Activation of Human Endothelial Cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 315, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montopoli, M.; Froldi, G.; Comelli, M.C.; Prosdocimi, M.; Caparrotta, L. Aescin Protection of Human Vascular Endothelial Cells Exposed to Cobalt Chloride Mimicked Hypoxia and Inflammatory Stimuli. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annoni, F.; Mauri, A.; Marincola, F.; Resele, L.F. Venotonic Activity of Escin on the Human Saphenous Vein. Arzneimittelforschung. 1979, 29, 672–675. [Google Scholar]
- Longiave, D.; Omini, C.; Nicosia, S.; Berti, F. The Mode of Action of Aescin on Isolated Veins: Relationship with PGF2 Alpha. Pharmacol. Res. Commun. 1978, 10, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallelli, L.; Cione, E.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L. Glucocorticoid-Like Activity of Escin: A New Mechanism for an Old Drug. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcoli Renali: Come Si Formano, Si Curano e Prevengono - ISSalute.
- Al-Azzawi, I.S. The Role of Aescin versus Prednisolone in the Management of Symptomatic Lower Ureteral Calculi: A Comparative Study. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2021, 71(Suppl 8, S77–S81. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yao, L.; Chu, L.; Du, H.; Fu, F. Protective Effects of Escin against Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulcer in Mice. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2014, 24, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.H.; Ma, M.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z.S.; Wan, C.F.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.F.; Wang, J.L.; et al. Effects of Aescin on Testicular Repairment in Rats with Experimentally Induced Varicocele. Andrologia 2014, 46, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yan, F.; Xia, X.; Xu, D.; Cui, X. Escin Improves Sperm Quality in Male Patients with Varicocele-Associated Infertility. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Kang, M.; Lee, Y.J.; Choi, W.S.; Chun, Y.S.; Kwak, C.; Kim, H.H. Cytotoxic Effects of Escin on Human Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells through the Induction of Apoptosis and G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest. Urology 2014, 84, 982–e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.L.; Chao, W.T.; Li, Y.H.; Ou, Y.C.; Wang, S.S.; Chiu, K.Y.; Yuan, S.Y. Escin Induces Apoptosis in Human Bladder Cancer Cells: An in Vitro and in Vivo Study. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 840, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, A.; Cai, T.; Luise, L. Di; D’alterio, C.; CAVA, G.L.A.; Cirigliano, L.; Giovanni, A. Di; Gallelli, L.; Capece, M. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Association with Bromelain and Escin for the Management of Patients Affected by Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome. Biomed. reports 2022, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agenzia Europea per i Medicinali. Rapporto Di Valutazione Su Aesculus Hipocastanum L., Seme; 2009. Disponibile Da: Http://Www.Ema. Europa.Eu/Documents/Herbal-Report/Assessment-Report-Aesculus-Hippo Castanum-l-Semen_en.Pdf. Accesso Effettuato Il 30 Ot.
- Siebert, U.; Brach, M.; Sroczynski, G.; Überla, K. Efficacy, Routine Effectiveness, and Safety of Horsechestnut Seed Extract in the Treatment of Chronic Venous Insufficiency. A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials and Large Observational Studies. Int. Angiol. 2002, 21, 305–315. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




