Submitted:
26 July 2023
Posted:
28 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
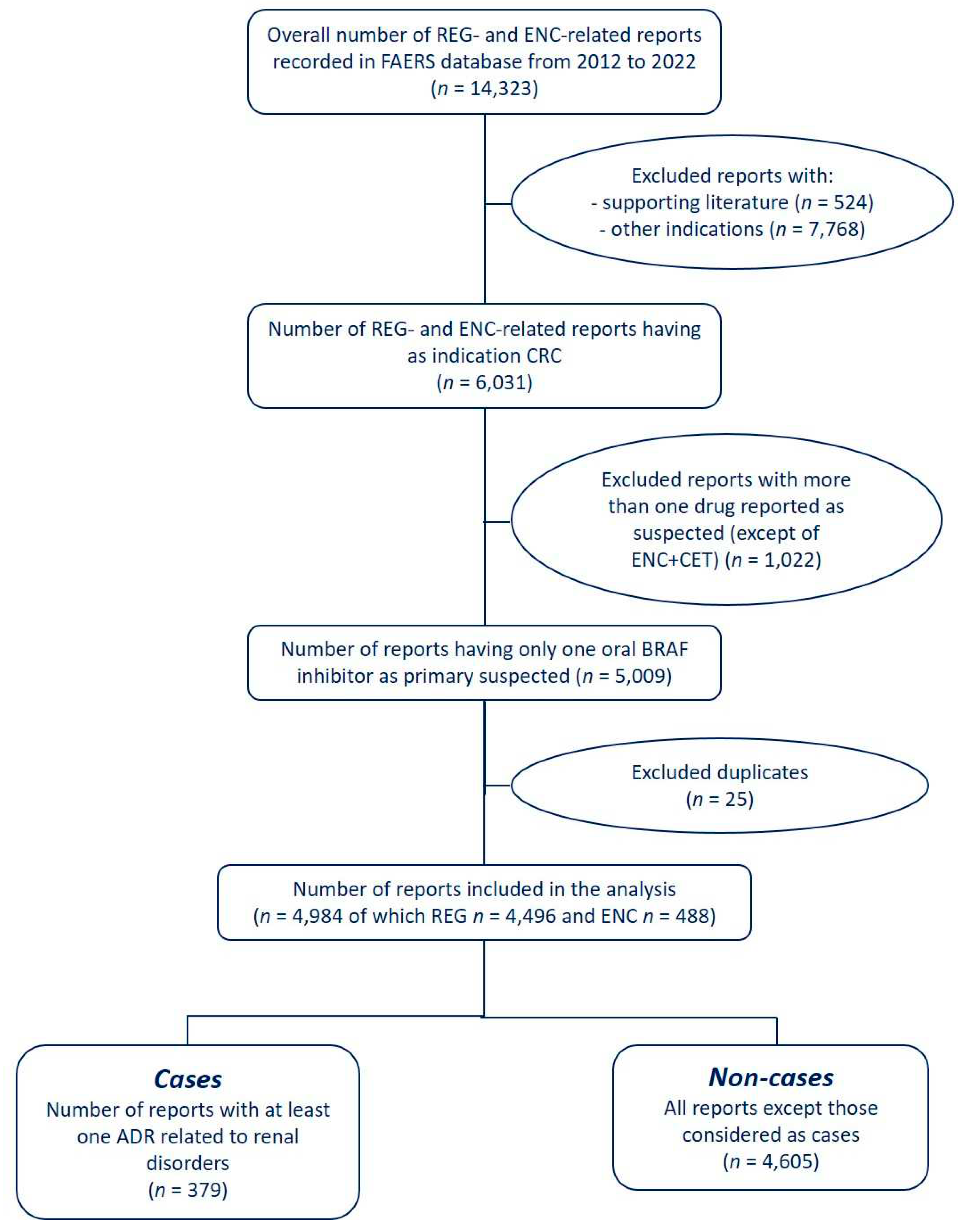
2.1. Data Source and Case Definition
2.2. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
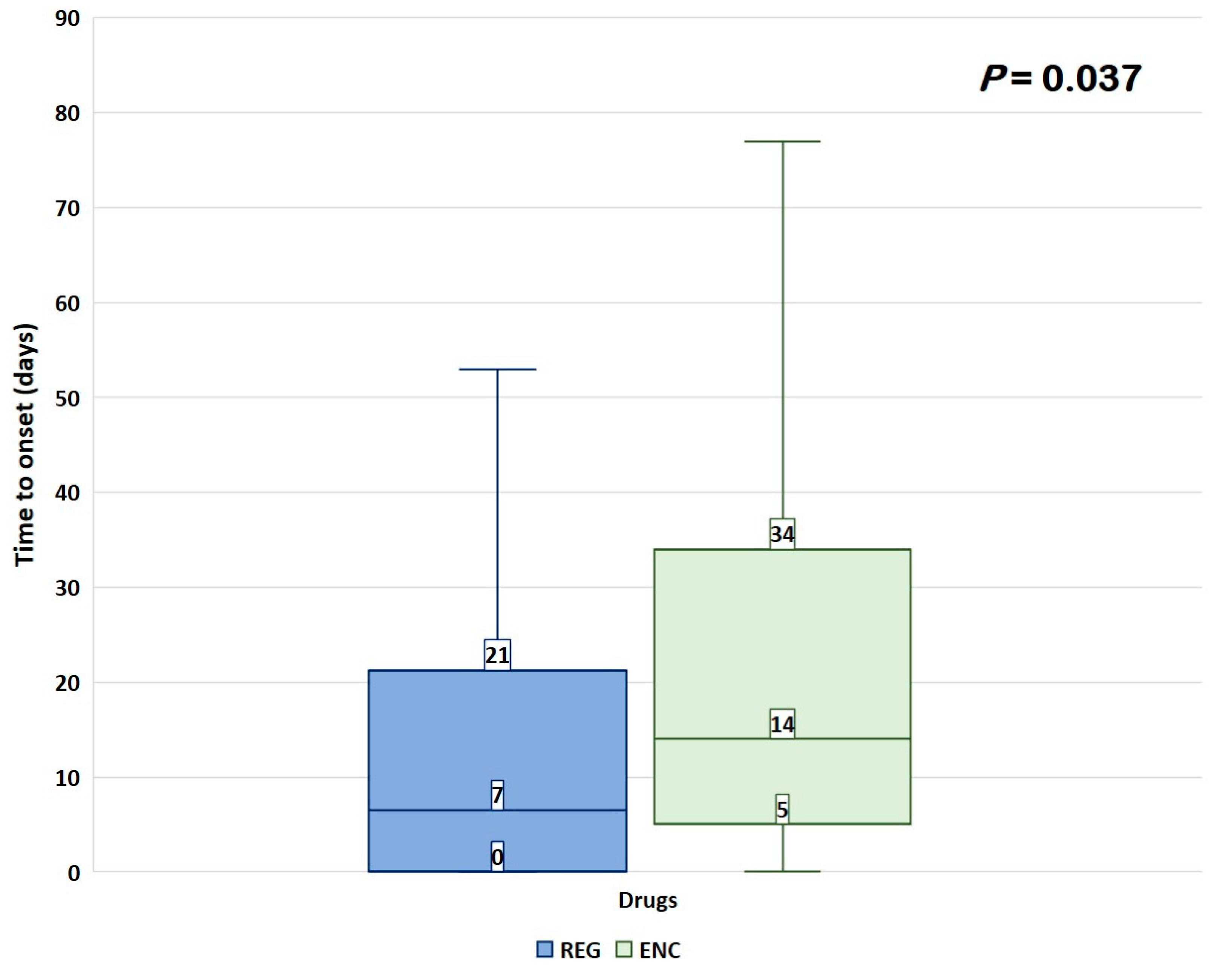
3.2. Disproportionality Analysis
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biller, L.H.; Schrag, D. Diagnosis and treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: A review. JAMA - J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021, 325, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, R.; Guo, F.; Heisser, T.; Hackl, M.; Ihle, P.; De Schutter, H.; Van Damme, N.; Valerianova, Z.; Atanasov, T.; Májek, O.; et al. Colorectal cancer incidence, mortality, and stage distribution in European countries in the colorectal cancer screening era: an international population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1002–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Brest, A.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; Lewis, D.R.; et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/Csr/1975_2017/ (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Bylsma, L.C.; Gillezeau, C.; Garawin, T.A.; Kelsh, M.A.; Fryzek, J.P.; Sangaré, L.; Lowe, K.A. Prevalence of RAS and BRAF mutations in metastatic colorectal cancer patients by tumor sidedness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 1044–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-Y.; Lin, P.-C.; Lin, H.-H.; Lin, J.-K.; Chen, W.-S.; Jiang, J.-K.; Yang, S.-H.; Liang, W.-Y.; Chang, S.-C. Mutation spectra of RAS gene family in colorectal cancer. Am. J. Surg. 2016, 212, 537–544.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, A.R.; Hamilton, S.R.; Allegra, C.J.; Grody, W.; Cushman-Vokoun, A.M.; Funkhouser, W.K.; Kopetz, S.E.; Lieu, C.; Lindor, N.M.; Minsky, B.D.; et al. Molecular Biomarkers for the Evaluation of Colorectal Cancer: Guideline From the American Society for Clinical Pathology, College of American Pathologists, Association for Molecular Pathology, and American Society of Clinical Oncology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 625–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarkavelis, G. Current and future biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2017, 30, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo; Santini; Bardasi; Cerma; Casadei-Gardini; Spallanzani; Andrikou; Cascinu; Gelsomino BRAF-Mutated Colorectal Cancer: Clinical and Molecular Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5369. [CrossRef]
- Hummel, M.; Hegewisch-Becker, S.; Neumann, J.H.L.; Vogel, A. BRAF testing in metastatic colorectal carcinoma and novel, chemotherapy-free therapeutic options. Pathologe 2021, 42, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Alfonso, P.; Muñoz Martín, A.J.; Ortega Morán, L.; Soto Alsar, J.; Torres Pérez-Solero, G.; Blanco Codesido, M.; Calvo Ferrandiz, P.A.; Grasso Cicala, S. Oral drugs in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 175883592110090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piawah, S.; Venook, A.P. Targeted therapy for colorectal cancer metastases: A review of current methods of molecularly targeted therapy and the use of tumor biomarkers in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer 2019, 125, 4139–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Food and Drug Administration Full Prescribing Information Stivarga®. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/203085lbl.pdf (accessed on Jan 30, 2023).
- US Food and Drug Administration Full prescribing information Braftovi®. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/210496s006lbl.pdf (accessed on Jan 30, 2023).
- Van Cutsem, E.; Martinelli, E.; Cascinu, S.; Sobrero, A.; Banzi, M.; Seitz, J.-F.; Barone, C.; Ychou, M.; Peeters, M.; Brenner, B.; et al. Regorafenib for Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Who Progressed After Standard Therapy: Results of the Large, Single-Arm, Open-Label Phase IIIb CONSIGN Study. Oncologist 2019, 24, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabernero, J.; Velez, L.; Trevino, T.L.; Grothey, A.; Yaeger, R.; Van Cutsem, E.; Wasan, H.; Desai, J.; Ciardiello, F.; Yoshino, T.; et al. Management of adverse events from the treatment of encorafenib plus cetuximab for patients with BRAF V600E-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer: insights from the BEACON CRC study. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stammler, R.; Gallois, C.; Taieb, J.; Duong, J.-P.; Karras, A.; Thervet, E.; Lazareth, H. Acute renal failure under encorafenib, binimetinib and cetuximab for BRAF V600E–mutated colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 147, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanchoo, R.; Jhaveri, K.D.; Deray, G.; Launay-Vacher, V. Renal effects of BRAF inhibitors: a systematic review by the Cancer and the Kidney International Network. Clin. Kidney J. 2016, 9, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, A.; Jain, P.; Fradley, M.G.; Lenihan, D.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Jain, C.; Lima, M.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Oliveira, G.H.; Dowlati, A.; et al. Cardiovascular adverse events associated with BRAF versus BRAF/MEK inhibitor: Cross-sectional and longitudinal analysis using two large national registries. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 3862–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meirson, T.; Asher, N.; Bomze, D.; Markel, G. Safety of BRAF+MEK Inhibitor Combinations: Severe Adverse Event Evaluation. Cancers (Basel). 2020, 12, 1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaoka, S.; Matsui, T.; Abe, J.; Umetsu, R.; Kato, Y.; Ueda, N.; Hane, Y.; Motooka, Y.; Hatahira, H.; Kinosada, Y.; et al. Evaluation of the Association of Hand-Foot Syndrome with Anticancer Drugs Using the US Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) and Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report (JADER) Databases. YAKUGAKU ZASSHI 2016, 136, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Drug Administration FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) Public Dashboard. Available online: https://fis.fda.gov/sense/app/95239e26-e0be-42d9-a960-9a5f7f1c25ee/sheet/8eef7d83-7945-4091-b349-e5c41ed49f99/state/analysis (accessed on Jan 24, 2023).
- Harpaz, R.; DuMouchel, W.; LePendu, P.; Bauer-Mehren, A.; Ryan, P.; Shah, N.H. Performance of Pharmacovigilance Signal-Detection Algorithms for the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 93, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norén, G.N.; Hopstadius, J.; Bate, A. Shrinkage observed-to-expected ratios for robust and transparent large-scale pattern discovery. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2013, 22, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhaveri, K.D.; Wanchoo, R.; Sakhiya, V.; Ross, D.W.; Fishbane, S. Adverse Renal Effects of Novel Molecular Oncologic Targeted Therapies: A Narrative Review. Kidney Int. Reports 2017, 2, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cellier, M.; Bourneau-Martin, D.; Abbara, C.; Crosnier, A.; Lagarce, L.; Garnier, A.-S.; Briet, M. Renal Safety Profile of BCR-ABL Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in a Real-Life Setting: A Study Based on Vigibase®, the WHO Pharmacovigilance Database. Cancers (Basel). 2023, 15, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filler, G.; Ramsaroop, A.; Stein, R.; Grant, C.; Marants, R.; So, A.; McIntyre, C. Is Testosterone Detrimental to Renal Function? Kidney Int. Reports 2016, 1, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Carro, C.; Draibe, J.; Soler, M.J. Onconephrology: Update in Anticancer Drug-Related Nephrotoxicity. Nephron 2023, 147, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Q.; Guo, N.; Zhou, X.; Xu, H.; Lei, S.; Fu, P.; Zhong, H. Regorafenib-induced renal-limited thrombotic microangiopathy: a case report and review of literatures. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasma, A.; Coke, H.; Mamlouk, O.; Tchakarov, A.; Mandayam, S. Lupus-Like Glomerulonephritis Associated With Regorafenib, a Multikinase Inhibitor. Kidney Med. 2021, 3, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisen, T.; Joensuu, H.; Nathan, P.D.; Harper, P.G.; Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Nicholson, S.; Bahl, A.; Tomczak, P.; Pyrhonen, S.; Fife, K.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with previously untreated metastatic or unresectable renal-cell carcinoma: a single-group phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcoraci, V.; Barbieri, M.A.; Rottura, M.; Nobili, A.; Natoli, G.; Argano, C.; Squadrito, G.; Squadrito, F. Kidney Disease Management in the Hospital Setting : A Focus on Inappropriate Drug Prescriptions in Older Patients. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.A.; Rottura, M.; Cicala, G.; Mandraffino, R.; Marino, S.; Irrera, N.; Mannucci, C.; Santoro, D.; Squadrito, F.; Arcoraci, V. Chronic Kidney Disease Management in General Practice: A Focus on Inappropriate Drugs Prescriptions. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taieb, J.; Lonardi, S.; Desai, J.; Folprecht, G.; Gallois, C.; Marques, E.P.; Khan, S.; Castagné, C.; Wasan, H. Adverse Events Associated with Encorafenib Plus Cetuximab in Patients with BRAFV600E-mutant Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: An in-depth Analysis of the BEACON CRC Study. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2023, 22, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seethapathy, H.; Bates, H.; Chute, D.F.; Strohbehn, I.; Strohbehn, S.; Fadden, R.M.; Reynolds, K.L.; Cohen, J. V.; Sullivan, R.J.; Sise, M.E. Acute Kidney Injury Following Encorafenib and Binimetinib for Metastatic Melanoma. Kidney Med. 2020, 2, 373–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, F.; Amann, K.; Daniel, C.; Klewer, M.; Büttner, A.; Büttner-Herold, M. Characteristic morphological changes in anti-VEGF therapy-induced glomerular microangiopathy. Histopathology 2018, 73, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzedine, H.; Mangier, M.; Ory, V.; Zhang, S.-Y.; Sendeyo, K.; Bouachi, K.; Audard, V.; Péchoux, C.; Soria, J.C.; Massard, C.; et al. Expression patterns of RelA and c-mip are associated with different glomerular diseases following anti-VEGF therapy. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kala, J.; Salman, L.A.; Geara, A.S.; Izzedine, H. Nephrotoxicity From Molecularly Targeted Chemotherapeutic Agents. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2021, 28, 415–428.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuma, C.; Perier-Muzet, M.; Pelletier, S.; Nouvier, M.; Amini-Adl, M.; Dijoud, F.; Duru, G.; Thomas, L.; Fouque, D.; Laville, M.; et al. New insights into renal toxicity of the B-RAF inhibitor, vemurafenib, in patients with metastatic melanoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 78, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurabielle, C.; Pillebout, E.; Stehlé, T.; Pagès, C.; Roux, J.; Schneider, P.; Chevret, S.; Chaffaut, C.; Boutten, A.; Mourah, S.; et al. Mechanisms Underpinning Increased Plasma Creatinine Levels in Patients Receiving Vemurafenib for Advanced Melanoma. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0149873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayego-Mateos, S.; Rodrigues-Diez, R.; Morgado-Pascual, J.L.; Valentijn, F.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Goldschmeding, R.; Ruiz-Ortega, M. Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Its Ligands in Kidney Inflammation and Damage. Mediators Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency Braftovi®, Summary of Product Characteristics. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/braftovi-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on Jul 5, 2023).
- Makris, K.; Spanou, L. Acute Kidney Injury: Definition, Pathophysiology and Clinical Phenotypes. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2016, 37, 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Mielczarek, Ł.; Brodziak, A.; Sobczuk, P.; Kawecki, M.; Cudnoch-Jędrzejewska, A.; Czarnecka, A.M. Renal toxicity of targeted therapies for renal cell carcinoma in patients with normal and impaired kidney function. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 723–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.; Schwarz, K.; Kriz, W.; Miettinen, A.; Reiser, J.; Mundel, P.; Holthöfer, H. Involvement of Lipid Rafts in Nephrin Phosphorylation and Organization of the Glomerular Slit Diaphragm. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzedine, H.; Escudier, B.; Lhomme, C.; Pautier, P.; Rouvier, P.; Gueutin, V.; Baumelou, A.; Derosa, L.; Bahleda, R.; Hollebecque, A.; et al. Kidney Diseases Associated With Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF). Medicine (Baltimore). 2014, 93, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ollero, M.; Sahali, D. Inhibition of the VEGF signalling pathway and glomerular disorders. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankalakunti, M.; Siddini, V.; Bonu, R.; Prakash, G.; Babu, K.; Ballal, H.; Jha, P. Sunitinib induced nephrotic syndrome and thrombotic microangiopathy. Indian J. Nephrol. 2013, 23, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bax; Lotesoriere; Sironi; Capelli Review and Comparison of Cancer Biomarker Trends in Urine as a Basis for New Diagnostic Pathways. Cancers (Basel). 2019, 11, 1244. [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Leslie, S.; Reddivari, A. Dysuria. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549918/ (accessed on Jul 5, 2023).
- Barbieri, M.A.; Sorbara, E.E.; Russo, G.; Cicala, G.; Franchina, T.; Santarpia, M.; Silvestris, N.; Spina, E. Neuropsychiatric Adverse Drug Reactions with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: An Analysis from the European Spontaneous Adverse Event Reporting System. Cancers (Basel). 2023, 15, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raschi, E.; Moretti, U.; Salvo, F.; Pariente, A.; Cosimo Antonazzo, I.; De Ponti, F.; Poluzzi, E. Evolving Roles of Spontaneous Reporting Systems to Assess and Monitor Drug Safety . Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.79986 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Barbieri, M.A.; Sorbara, E.E.; Cicala, G.; Santoro, V.; Cutroneo, P.M.; Franchina, T.; Spina, E. Adverse Drug Reactions with HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Treatment: An Analysis from the Italian Pharmacovigilance Database. Drugs - Real World Outcomes 2022, 9, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.A.; Sorbara, E.E.; Cicala, G.; Santoro, V.; Cutroneo, P.M.; Franchina, T.; Santarpia, M.; Silvestris, N.; Spina, E. Safety profile of tyrosine kinase inhibitors used in non-small-cell lung cancer: An analysis from the Italian pharmacovigilance database. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1005626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagieła, J.; Bartnicki, P.; Rysz, J. Nephrotoxicity as a complication of chemotherapy and immunotherapy in the treatment of colorectal cancer, melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wynsberghe, M.; Flejeo, J.; Sakhi, H.; Ollero, M.; Sahali, D.; Izzedine, H.; Henique, C. Nephrotoxicity of Anti-Angiogenic Therapies. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palleria, C.; Leporini, C.; Chimirri, S.; Marrazzo, G.; Sacchetta, S.; Bruno, L.; Lista, R.; Staltari, O.; Scuteri, A.; Scicchitano, F.; et al. Limitations and obstacles of the spontaneous adverse drugs reactions reporting: Two “challenging” case reports. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2013, 4, S66–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | Renal cases (n = 379) |
Other reports (n = 4,605) |
P value | Total (n = 4,984) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, n (%) | ||||
| Male | 230 (60.7) | 2,384 (51.8) | 0.006 | 2,614 (52.4) |
| Female | 141 (37.2) | 1,991 (43.2) | 2,132 (42.8) | |
| Not specified | 8 (2.1) | 230 (5.0) | 238 (4.8) | |
| Median age (Q1-Q3), years | 65 (55-71) | 64 (56-71) | 0.886 | 64 (56-71) |
| Age group, n (%) | ||||
| Adult | 170 (44.9) | 1,990 (43.3) | 0.494 | 2,160 (43.3) |
| 18-29 years | 0 (0.0) | 26 (0.6) | 0.197 | 26 (0.5) |
| 30-49 years | 40 (10.6) | 399 (8.7) | 439 (8.8) | |
| 50-64 years | 130 (34.3) | 1,565 (34.0) | 1,695 (34.0) | |
| Elderly | 170 (44.9) | 1,830 (39.8) | 2000 (40.1) | |
| 65-75 years | 125 (33.0) | 1,283 (27.9) | 0.449 | 1,408 (28.3) |
| 76-85 years | 42 (11.1) | 487 (10.6) | 529 (10.6) | |
| >85 years | 3 (0.8) | 60 (1.3) | 63 (1.3) | |
| Missing | 39 (10.3) | 785 (17.0) | 824 (16.5) | |
| Reporter type, n (%) | ||||
| Consumer | 184 (48.5) | 1,941 (42.1) | 0.025 | 2,125 (42.6) |
| Healthcare professional | 194 (51.2) | 2,617 (56.8) | 2,811 (56.4) | |
| Not specified | 1 (0.3) | 47 (1.0) | 48 (1.0) | |
| Reporter Country, n (%) | ||||
| Africa | 1 (0.3) | 34 (0.7) | 0.457 | 35 (0.7) |
| Asia | 98 (25.9) | 1,063 (23.1) | 0.244 | 1,161 (23.3) |
| Europe | 75 (19.8) | 783 (17.0) | 0.190 | 858 (17.2) |
| North America | 177 (46.7) | 2,199 (47.8) | 0.734 | 2,376 (47.7) |
| Oceania | 4 (1.1) | 49 (1.1) | 0.987 | 53 (1.1) |
| South America | 12 (3.2) | 141 (3.1) | 0.910 | 153 (3.1) |
| Not specified | 12 (3.2) | 336 (7.3) | - | 348 (7.0) |
| Serious, n (%) | 370 (97.6) | 4,122 (89.5) | <0.001 | 4,492 (90.1) |
| Outcome, n (%) | ||||
| Died | 78 (20.6) | 970 (21.1) | 0.876 | 1,048 (21.0) |
| Disabled | 5 (1.3) | 53 (1.2) | 0.964 | 58 (1.2) |
| Hospitalized | 150 (39.6) | 1,273 (27.6) | <0.001 | 1,423 (28.6) |
| Life threatening | 15 (4.0) | 96 (2.1) | 0.028 | 111 (2.2) |
| Non-serious | 9 (2.4) | 483 (10.5) | <0.001 | 492 (9.9) |
| Other outcomes | 122 (32.2) | 1,727 (37.5) | 0.045 | 1,849 (37.1) |
| Required intervention | 0 (0.0) | 3 (0.1) | - | 3 (0.1) |
| Year of reporting, n (%) | ||||
| 2012 | 6 (1.6) | 75 (1.6) | 0.946 | 81 (1.6) |
| 2013 | 40 (10.6) | 619 (13.4) | 0.129 | 659 (13.2) |
| 2014 | 33 (8.7) | 477 (10.4) | 0.352 | 510 (10.2) |
| 2015 | 47 (12.4) | 491 (10.7) | 0.336 | 538 (10.8) |
| 2016 | 41 (10.8) | 316 (6.9) | 0.006 | 537 (7.2) |
| 2017 | 38 (10.0) | 437 (9.5) | 0.802 | 475 (9.5) |
| 2018 | 50 (13.2) | 416 (9.0) | 0.010 | 466 (9.3) |
| 2019 | 34 (9.0) | 366 (7.9) | 0.544 | 400 (8.0) |
| 2020 | 25 (6.6) | 458 (9.9) | 0.043 | 483 (9.7) |
| 2021 | 34 (9.0) | 515 (11.2) | 0.216 | 549 (11.0) |
| 2022 | 31 (8.2) | 435 (9.4) | 0.470 | 466 (9.3) |
| Primary suspect drug | ||||
| ENC | 26 (6.9) | 462 (10.0) | 0.046 | 488 (9.8) |
| REG | 353 (93.1) | 4,143 (90.0) | 4,496 (90.2) |
| Preferred Term | ENC | REG | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | ROR (95% CI) | IC (IC025-IC075) | Unexpected | N | ROR (95% CI) | IC (IC025-IC075) | Unexpected | ||
| Renal Impairment | 3 | 2.35 (0.75-7.31) | 53 | 4.16 (3.17-5.45) | 1.39 (1.12-1.66) | Yes | 56 | ||
| AKI | 11 | 3.79 (2.09-6.90) | 1.32 (0.72-1.91) | Yes | 43 | 1.46 (1.08-1.97) | 0.37 (0.07-0.67) | Yes | 54 |
| Chromaturia | 44 | 12.00 (8.92-16.16) | 2.36 (2.06-2.66) | Yes | 44 | ||||
| Renal Failure | 2 | NA | 38 | 1.66 (1.20-2.28) | 0.49 (0.17-0.81) | Yes | 40 | ||
| Proteinuria | 29 | 11.01 (7.64-15.86) | 2.24 (1.87-2.60) | No | 29 | ||||
| Urinary Retention | 27 | 4.99 (3.42-7.28) | 1.53 (1.15-1.91) | Yes | 27 | ||||
| Dysuria | 4 | 6.50 (2.43-17.39) | 1.86 (0.88-2.85) | Yes | 19 | 3.06 (1.95-4.81) | 1.06 (0.61-1.52) | Yes | 23 |
| Haematuria | 22 | 3.29 (2.16-5.00) | 1.14 (0.72-1.56) | No | 22 | ||||
| Renal Disorder | 1 | NA | 19 | 2.72 (1.73-4.26) | 0.95 (0.50-1.40) | Yes | 20 | ||
| Urinary Incontinence | 13 | 2.46 (1.43-4.24) | 0.85 (0.30-1.39) | Yes | 13 | ||||
| Hydronephrosis | 1 | NA | 10 | 8.70 (4.67-16.19) | 1.85 (1.23-2.47) | Yes | 11 | ||
| Pollakiuria | 2 | NA | 8 | 1.18 (0.59-2.36) | 10 | ||||
| Renal Pain | 2 | NA | 6 | 4.08 (1.83-9.10) | 1.19 (0.39-1.99) | No | 8 | ||
| Nephrolithiasis | 1 | NA | 6 | 0.95 (0.43-2.11) | 7 | ||||
| Nephrotic Syndrome | 7 | 5.73 (2.73-12.03) | 1.47 (0.73-2.21) | No | 7 | ||||
| Anuria | 6 | 3.48 (1.56-7.76) | 1.07 (0.27-1.87) | Yes | 6 | ||||
| Nocturia | 6 | 3.39 (1.52-7.55) | 1.05 (0.25-1.85) | Yes | 6 | ||||
| Oliguria | 5 | 3.25 (1.35-7.81) | 0.99 (0.11-1.87) | Yes | 5 | ||||
| Urinary Tract Obstruction | 5 | 9.16 (3.81-22.04) | 1.66 (0.78-2.54) | Yes | 5 | ||||
| Haemorrhage Urinary Tract | 4 | 11.23 (4.21-29.96) | 1.66 (0.68-2.64) | No | 4 | ||||
| Micturition Urgency | 4 | 2.28 (0.86-6.08) | 4 | ||||||
| Prerenal Failure | 4 | 22.13 (8.29-59.11) | 1.89 (0.91-2.87) | Yes | 4 | ||||
| Urine Odour Abnormal | 4 | 4.61 (1.73-12.28) | 1.19 (0.21-2.17) | Yes | 4 | ||||
| Bladder Disorder | 3 | 1.96 (0.63-6.09) | 3 | ||||||
| CKD | 3 | 0.23 (0.07-0.72) | 3 | ||||||
| Micturition Disorder | 3 | 5.78 (1.86-17.95) | 1.23 (0.10-2.37) | Yes | 3 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





