Submitted:
25 July 2023
Posted:
25 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Study area
The biophysical characteristics
The sampling of ground cover plant species
Mammal herbivore species survey and identification
Rangeland conditions
Data analysis
Ground cover plant species analysis
Analysis of mammalian herbivores data
3. Results
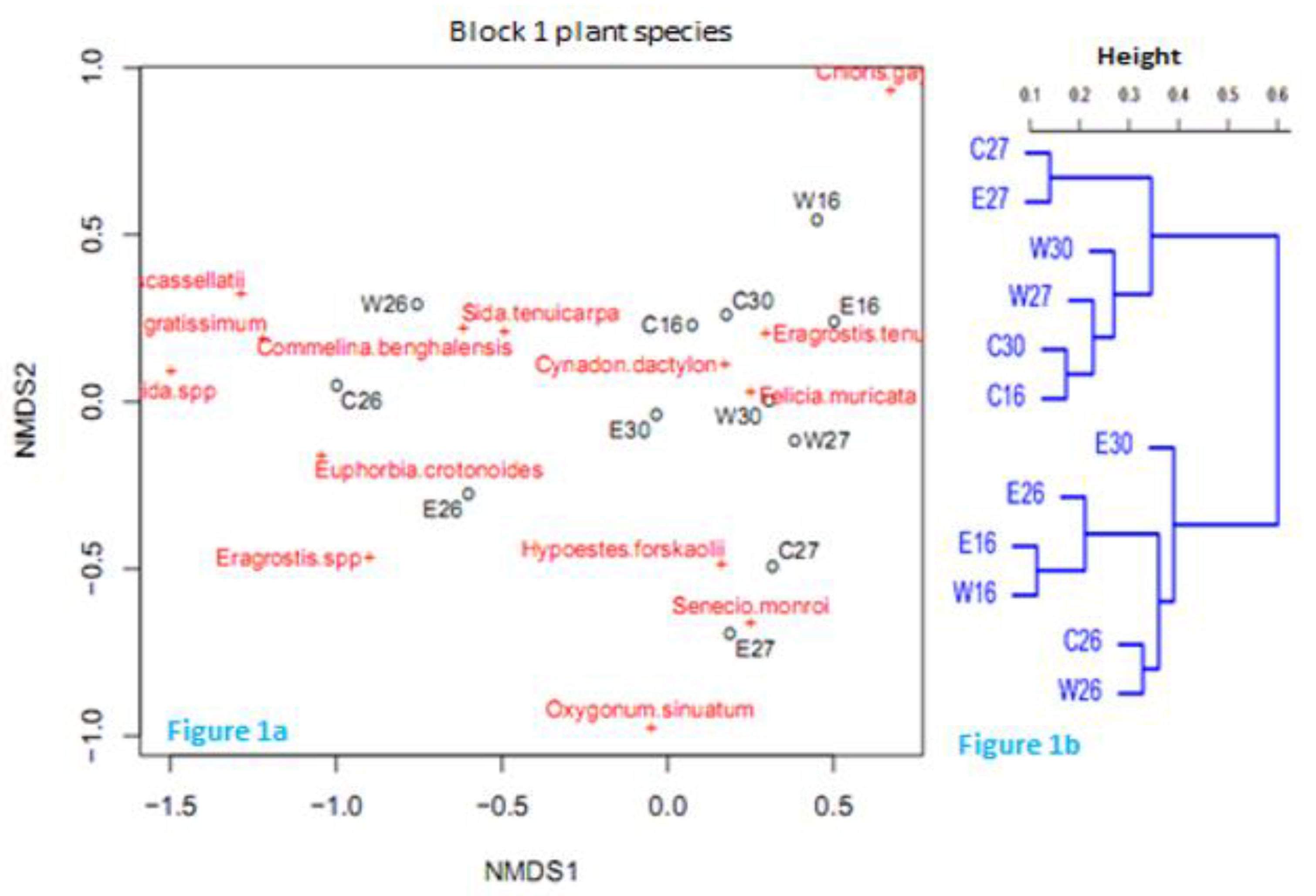
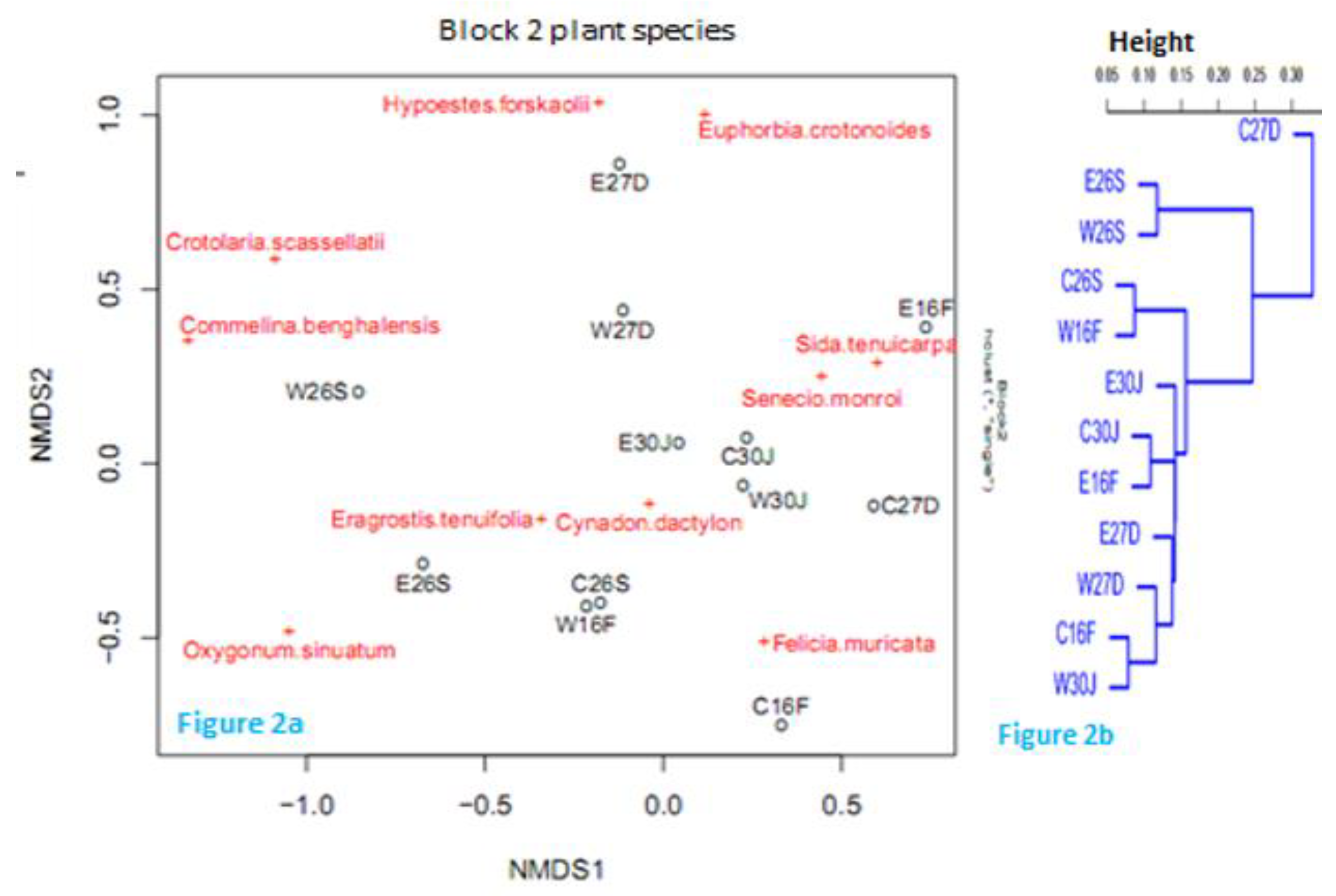
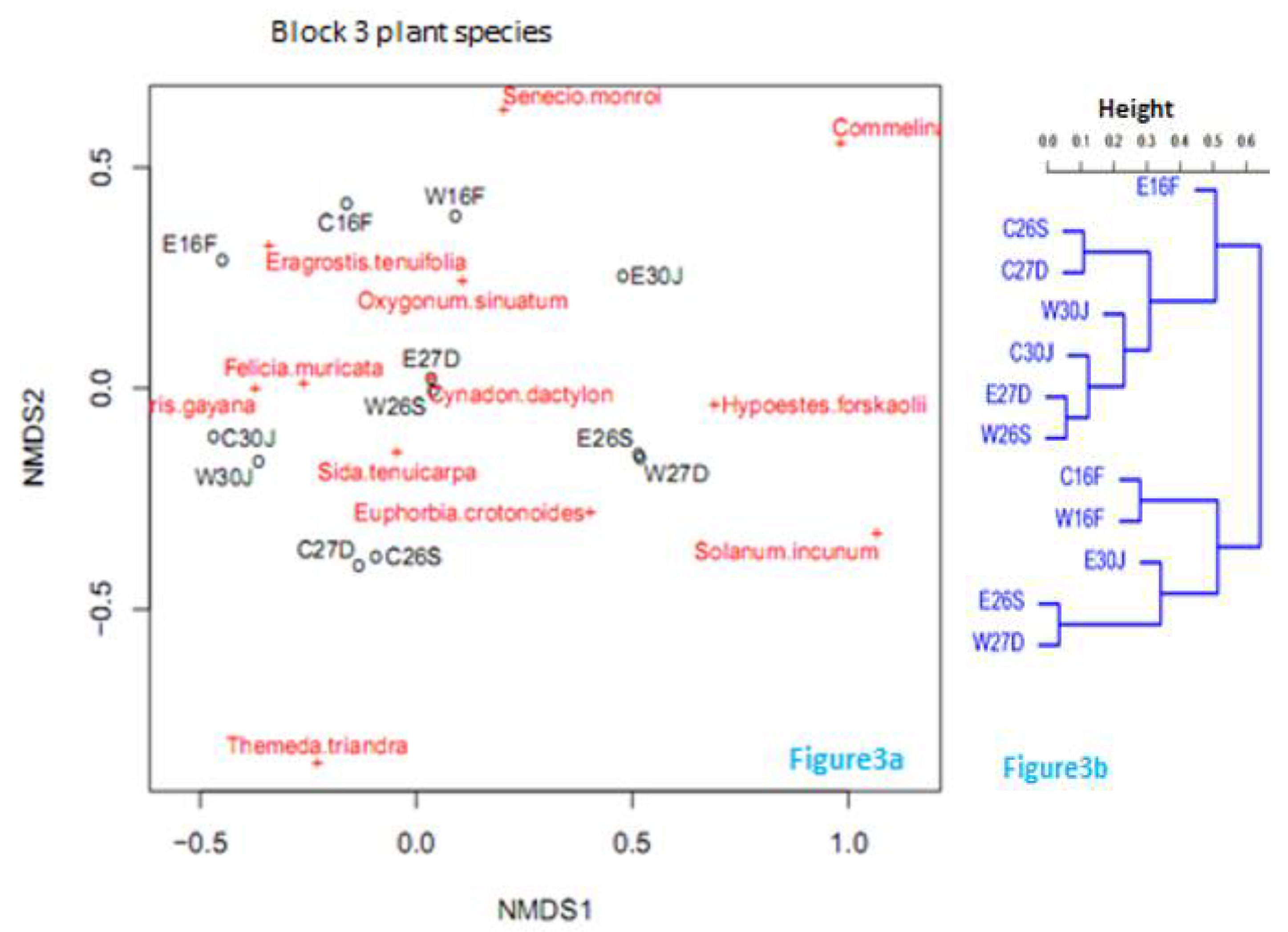
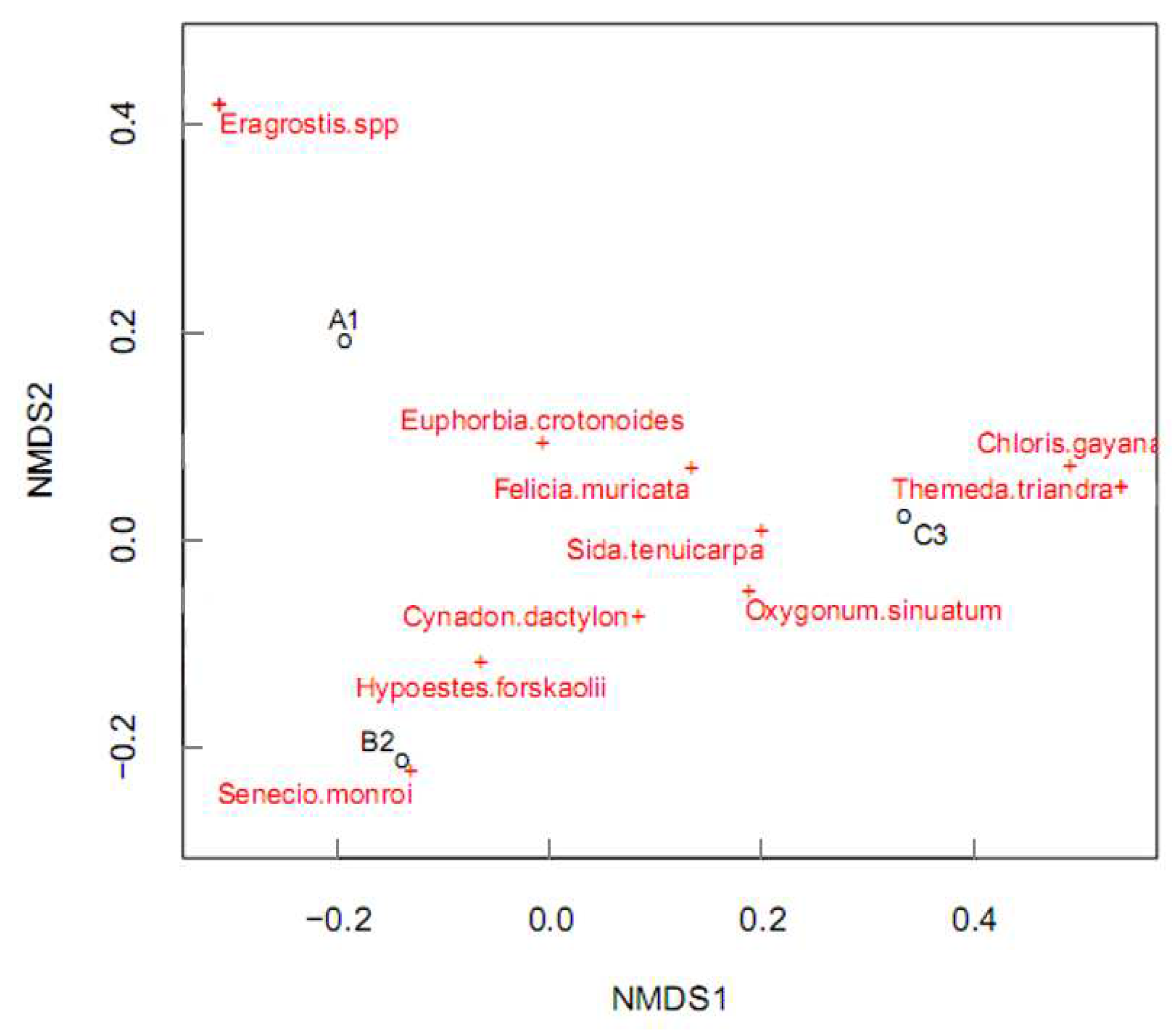
Plant species composition and distribution
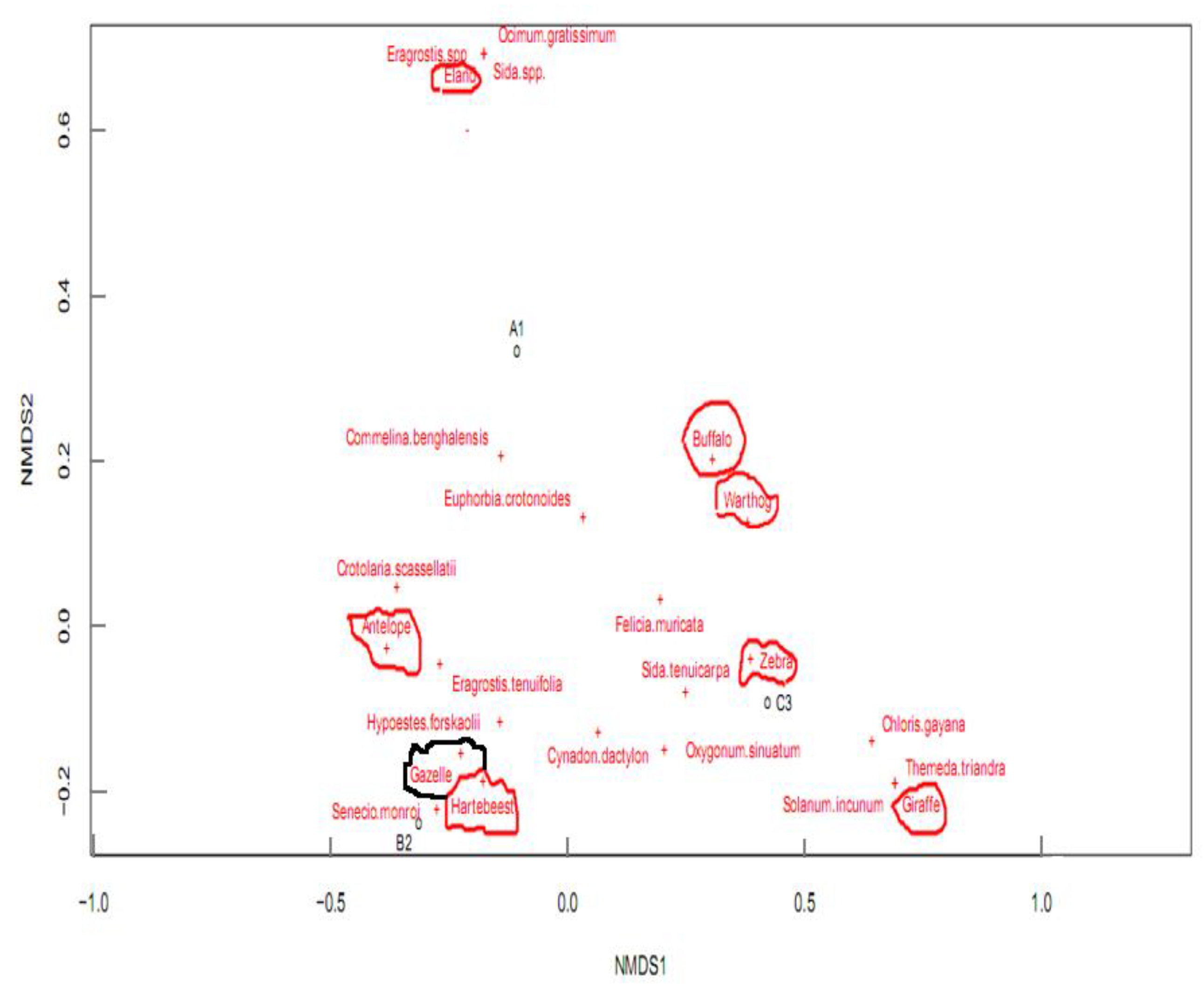
Co-occurrence of mammalian herbivores with the plant species
Vegetation attributes dynamics over time
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alemu, M.M.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Reeves, A.; Lemon, M. Grass Species Diversity and Ground Cover of Herbs in the Grassland Plains of Nech Sar National Park, Ethiopia. J. Environ. Prot. 2017, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdo, R.M.; Holt, R. D.; Fryxell, J.M. Grazers, browsers, and fire influence the extent andspatial pattern of tree cover in the Serengeti. Ecol. App. 2009, 19(1), 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rowaily, S.L.; El-Bana, M.I.; Al-Dujain, F.A.R. Changes in vegetation composition and diversity in relation to morphometry, soil, and grazing on a hyper-arid watershed in central Saudi Arabia. Catena 2012, 97, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilly, H.; Vanderwal, J.; Schwarzkopf, L. Balancing Biodiversity and Food Production: A Better Understanding of Wildlife Response to Grazing Will Inform Off-Reserve Conservation on Rangelands. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 69(6), 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdoodt, A.; Mureithi, S.M.; Van Ranst, E. Impacts of management and enclosure age on the recovery of the herbaceous rangeland vegetation in semi-arid Kenya. J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74(9), 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, Z.S.; Hawkins, H. J.; Cramer, M.D. Implications of historical interactions between herbivory and fire for rangeland management in African savannas. Ecosphere 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandandorj, S.; Eldridge, D.J.; Travers, S.K.; Val, J.; Oliver, I. Microsite and grazing intensity drive infiltration in a semiarid woodland. Ecohydrology 2017, 10(4), 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanentzap, A. J.; Coomes, D.A. Carbon storage in terrestrial ecosystems: Do browsing and grazing herbivores matter? Biol. Rev. 2012, 87(1), 72–94. [CrossRef]
- Al-Rowaily, S.L.; El-bana, M.I.; Al-bakre, D.A.; Assaeed, A.M.; Hegazy, A.K.; Ali, M.B. Effects of open grazing and livestock exclusion on floristic composition and diversity in the natural ecosystem of Western Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22(4), 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staver, A.C.; Bond, W.J. Is there a “browse trap”? Dynamics of herbivore impacts on trees and grasses in an African savanna. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 595–602. [Google Scholar]
- Burkepile, D.E.; Fynn, R.W.S.; Thompson, D.I.; Lemoine, N.P.; Koerner, S.E.; Eby, S.; Smith, M. D. Herbivore size matters for productivity–richness relationships in African savannas. J. Ecol. 2017, 105(3), 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giljohann, K.M.; Mccarthy, M.A.; Tozer, M.G.; Regan, T.J.; Keith, D.A.; Kelly, L.T. Interactions between rainfall, fire, and herbivory drive resprouter vital rates in a semi-arid ecosystem. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, S.; Gul, S.; Shah, M.H.; Hussain, F.; Ahmad, S.; Islam, M.; Yaqoob, M. Influence of grazing exclosure on vegetation biomass and soil quality. ISWCR. 2017, 5(2), 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawuoro, S.O.; Koech, O.K.; Karuku, G.N.; Mbau, J.S. Plant species composition and diversity depending on piospheres and seasonality in the southern rangelands of Kenya. Ecol. Process. 2017, 6(1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, C.N.; Barton, PS.; Sato, C.F.; Wood, J.T.; Macgregor, C.I.; Lindenmayer, DB. Herbivory and fire interact to affect forest understory habitat, but not its use by small vertebrates. Anim. Conserv. 2016, 19(1), 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiringe, J.W. A Vegetation and Large herbivore survey in Hell’s Gate National Park, Naivasha, Kenya. 1990.
- Mutia, T. M. Short Course IV on Exploration for Geothermal Resources. 2009.(11), 1–9.
- Muthoni, F.K.; Groen, T.A.; Skidmore, A.K.; Oel, P. Van. Ungulate herbivory overrides rainfall impacts on herbaceous regrowth and residual biomass in a key resource area. J. Arid Environ. 2014, 101, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hodd, M. East Africa handbook: the travel guide. Footprint Travel Guides, 2002,152.
- Spichiger, R.E.; Savolainen, V.; Figeat, M.; Jeanmonod, D. Systematic Botany of Flowering Plants. In CRC Press. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyekho, F.N.; Barrion, A.T.; Khan, Z.R. A Primer on grass identification and their uses in Kenya. 2004. 1–86.
- Bonham, C.D.; Mergen, D.E.; Montoya, S. Plant Cover Estimation: A Contiguous Daubenmire Frame. Rangel. Ecol. Manag 2018, 26(1), 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Daubenmire Method. Daubenmire Method 2003, 6(1), 1–3.
- Spellerberg, I.A.N.F.; Fedor, P.J. A tribute to Claude Shannon (1916 – 2001) and a plea for more rigorous use of species richness, species diversity and the “ Shannon – Wiener ” Index. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2003, (12), 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindt, R. Package “ BiodiversityR.”2016. 3(12).
- Team, R. C. R: A language and environment for statistical computing, version 3.3. 1. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2016.
- Ashafa, A.O.T.; Grierson, D.S.; Afolayan, A.J. Foliar Micromorphology of Felicia muricata Thunb., A South African Medicinal Plant. PJBS. 2008, 13(11), 1713–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masters, R.A.; Sheley, R.L. Synthesis Paper : Principles and practices for managing rangeland invasive plants. J. Range Manag 2001, 54(5). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimiti, D.W.; Riginos, C.; Belnap, J. Low-cost grass restoration using erosion barriers in degraded African rangeland. Restor. Ecol. 2017, 25(3), 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, V.; Baltzinger, C.; Chevalier, R.; Corcket, E.; Dumas, Y.; Sonia, P.; Ulrich, E. Ungulates increase forest plant species richness to the benefit of non-forest specialists. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, (3), 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shackleton, S.E.; Shackleton, R.T. Local knowledge regarding ecosystem services and disservices from invasive alien plants in the arid Kalahari, South Africa. J. Arid Environ. 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’soka, J. Creel, S.; Becker, M. S.; Murdoch, J. D. Ecological and anthropogenic effects on the density of migratory and resident ungulates in a human-inhabited protected area. Afr. J. Ecol. 2017, 55(4), 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.T.; Horst, S. Desertification and livestock grazing: The roles of sedentarization, mobility, and rest. Pastoralism. 2011, 1(1), 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutllot, F.; Rambal, S.; Joffre, R. Simulating climate change impacts on fire frequency and vegetation dynamics in a Mediterranean-type ecosystem. 2002, 423–437. [Google Scholar]
- Angassa, A. Effects of grazing intensity and bush encroachment on herbaceous species and rangeland conditions in southern Ethiopia. Land Degrad Dev. 2014, 451(5), 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuldt, A.; Ebeling, A.; Kunz, M.; Staab, M.; Guimarães-steinicke, C.; Bachmann, D.; Eisenhauer, N. Consumer communities across ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mramba, R.P.; Andreassen, H.P.; Skarpe, C. Browsing and plant traits in nutrient-rich and nutrient-poor savannas in Tanzania. J. Trop. Ecol. 2017, 33(5), 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiage, L.M. Perspectives on the assumed causes of land degradation in the rangelands of Sub-Saharan Africa. Prog Phys Geogr 2013, 37(5), 664–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiballa, A.K.; Elhaj, G.O. Relationship between grazing intensity and distance from water points. Sudan University of Science and Technology. 2006, 7(1), 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, S. Natural Desert and Human Controlled Landscapes: Remote Sensing of LULC Response to Drought. 2014.
- Shiponeni, N.N.; Milton, S.J. Seed dispersal in the dung of large herbivores: implications for restoration of Renosterveld shrubland old fields. 2006. 3161–3175. [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.W.; Sheley, R.L. A Conceptual Framework for Preventing the Spatial Dispersal of Invasive Plants. 2007, (4), 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Plant Species | Sampling Block | 9/26/2018 | 12/27/2018 | 1/30/2019 | 2/16/2019 | Total counts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cynodon dactylon (N) | Block 1 | 2832 | 1354 | 1634 | 2560 | 8380 |
| Block 2 | 3050 | 1292 | 1838 | 1462 | 7642 | |
| Block 3 | 973 | 966 | 701 | 687 | 3327 | |
| Felicia muricata (INV) | Block 1 | 129 | 411 | 491 | 265 | 1296 |
| Block 2 | 20 | 22 | 32 | 36 | 110 | |
| Block 3 | 675 | 673 | 756 | 729 | 2833 | |
| Eragrostis tenuifolia (N) | Block 1 | 93 | 99 | 460 | 420 | 1072 |
| Block 2 | 339 | 49 | 105 | 150 | 643 | |
| Block 3 | 5 | 5 | 33 | 41 | 84 | |
| Sida tenuicarpa (INV) | Block 1 | 78 | 0 | 6 | 2 | 86 |
| Block 2 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 19 | 26 | |
| Block 3 | 186 | 176 | 219 | 32 | 613 | |
| Chloris gayana (N) | Block 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| Block 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Block 3 | 134 | 182 | 141 | 244 | 701 | |
| Euphorbia crotonoides (N) | Block 1 | 421 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 428 |
| Block 2 | 0 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 28 | |
| Block 3 | 70 | 94 | 44 | 0 | 208 | |
| Senecio monroi (INV) | Block 1 | 0 | 67 | 35 | 0 | 102 |
| Block 2 | 0 | 111 | 164 | 30 | 305 | |
| Block 3 | 0 | 0 | 31 | 19 | 50 | |
| Hypoestes forskaolii (INV) | Block 1 | 10 | 230 | 6 | 0 | 246 |
| Block 2 | 0 | 64 | 0 | 0 | 64 | |
| Block 3 | 17 | 20 | 12 | 0 | 49 | |
| Oxygonum sinuatum (N) | Block 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| Block 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | |
| Block 3 | 13 | 20 | 6 | 21 | 60 | |
| Crotolaria scassellatii (N) | Block 1 | 47 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 47 |
| Block 2 | 16 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 17 | |
| Block 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Commelina benghalensis (N) | Block 1 | 32 | 0 | 8 | 2 | 42 |
| Block 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | |
| Block 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | |
| Ocimum gratissimum (INV) | Block 1 | 32 | 0 | 8 | 2 | 42 |
| Block 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | |
| Block 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 | |
| Eragrostis spp. (N) | Block 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Block 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Block 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Themeda triandra (N) | Block 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Block 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Block 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| Solanum incunum (INV) | Block 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Block 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Block 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| Sida spp. (INV) | Block 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Block 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Block 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mammalian Herbivore Species | Common Name | Block 1 | Block 2 | Block 3 | Total counts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equus quagga | Zebra | 47 | 3 | 457 | 507 |
| Eudorcas thomsonii | Gazelle | 45 | 66 | 20 | 131 |
| Phacochoerus africanus | Warthog | 26 | 0 | 73 | 99 |
| Alcelaphus buselaphus | Hartebeest | 15 | 31 | 16 | 67 |
| Syncerus caffer | Buffalo | 8 | 0 | 11 | 19 |
| Taurotragus oryx | Eland | 18 | 0 | 0 | 18 |
| Aepyceros melampus | Antelope | 5 | 3 | 0 | 8 |
| Giraffa Camelopardalis | Giraffe | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 164 | 103 | 578 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




