1. Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) accounts for the largest proportion of primary liver cancers. It is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide [
1]. Between 2000 and 2014, the incidence rates of liver cancer increased by 2.6% in men and by 3.0% in women [
2]. Although the overall cancer mortality rate has decreased since the 1990s, the liver cancer mortality rate has increased by 43% from 2000 to 2016 [
3]. Hepatitis B virus infection is the most common cause of HCC, followed by hepatitis C virus infection, alcohol consumption, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [
4]. Recent advancements in medical technologies, including vaccination and antiviral therapies, have increased the number of patients with NAFLD due to obesity and metabolic syndrome [
5,
6]. Consequently, there has been an increased interest and studies on the detection and prevention of HCC due to NAFLD and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and the difference between NAFLD and HCCs due to other etiologies [
4].
Recently, the IMbrave150 study demonstrated that the immune checkpoint inhibitor atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (AB) was superior to sorafenib in overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) outcomes; as a result, it has been approved as the first-line treatment for unresectable locally advanced or metastatic HCC since May 2020 [
7]. Several patients have been treated with combination therapy with positive results. Multiple studies have reported comparable results between AB combination therapy and lenvatinib. Between 2022 and 2023, studies by Kim et al. and Su et al. revealed a comparative OS between patients with unresectable HCC treated with AB and lenvatinib [
8,
9]. Lenvatinib has comparable outcomes with AB combination therapy. In fact, in 2022, Casadei-Gardini et al. and Rimini et al. suggested comparable OS in patients with advanced HCC treated with lenvatinib than with AB combination therapy [
10,
11].
Another treatment option for unresectable locally advanced HCC is hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy (HAIC), which is commonly used in East Asia [
12]. Approximately 8% of the patients initially diagnosed with HCC are treated with HAIC [
13]. It achieves high concentrations of chemotherapy agents directly to the liver, thus decreasing systemic toxicity and increasing delivery of the agent to malignant intrahepatic lesions [
14]. In 2019, Sung et al. demonstrated that intrahepatic tumor reduction elicited by HAIC prolonged the survival of patients with unresectable HCC, regardless of portal vein invasion or extrahepatic metastasis [
15]. In 2021, Lee et al. suggested comparable OS and PFS between patients treated with lenvatinib and HAIC [
16]. In 2020, Ueshima et al. demonstrated that in patients with macrovascular invasion without extrahepatic metastasis, HAIC had superior OS than sorafenib [
17]. Hatooka et al. suggested that HAIC might be superior to sorafenib as a first-line treatment before AB combination therapy was recognized as the first-line chemotherapy regimen for advanced HCC [
18]. Choi et al. demonstrated that in advanced HCC with portal vein invasion, HAIC was significantly superior to sorafenib [
19]. In addition, most recently, a meta-analysis by Zhang et al. also suggested that HAIC was superior to sorafenib in advanced HCC with portal vein invasion [
20]. Our institute recognized the need to compare the prognoses of patients treated with AB combination therapy and HAIC.
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Population
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Catholic University of Korea (approval number: XC23TIDI0015) and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. We enrolled patients diagnosed with HCC who were treated with AB combination therapy and HAIC between January 2018 and January 2023 at Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital and Eunpyeong St. Mary’s Hospital. We retrospectively reviewed the hospital records of the enrolled patients who received AB combination therapy (n=77) and HAIC therapy (n=174). Patients were diagnosed with HCC based on the imaging criteria of the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease and 2022 Korean Liver Cancer Association and National Cancer Center Korea practice guidelines [
21,
22]. Most patients had Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage C. Some patients had BCLC stage B but did not have indications for locoregional therapy (trans-arterial chemoembolization-refractory or infiltrative nature).
2.2. Treatment Protocol
AB combination therapy protocol consisted of 1200 mg of atezolizumab and 15 mg/kg of bevacizumab [
23]. HAIC consisted of 60 mg/m
2/day of cisplatin and 500 mg/m
2/day of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU). Both 5-FU and cisplatin were infused at days 1–2, and only 5-FU was infused at day 3 [
24]. HAIC was administered via infusion through an injection port, which was installed at initial therapy. The port consisted of a catheter that ended at the common or proper hepatic artery and a chemoport installed in the subcutaneous pocket of the inguinal region. The port was kept throughout the treatment.
2.3. Endpoints and Response Evaluation
The primary endpoints were OS (time from initial treatment to death from any cause) and PFS (time from initial treatment to disease progression according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors [RECIST] version 1.1, or death from any cause). The secondary endpoints were the objective response rate (ORR) (percentage of complete response [CR] or partial response [PR]) and disease control rate (DCR) (percentage of CR or PR, or stable disease [SD]). All patients were evaluated by computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging at diagnosis and initial treatment and were evaluated every 4–9 weeks according to the RECIST version 1.1. Adverse events were recorded according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, and adverse events above grade 3 were included.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
We calculated the OS and PFS of all enrolled patients using Kaplan–Meier analysis. To compensate for any existing confounding variables, we continued with a propensity score matching (PSM) analysis. After PSM, the OS and PFS of the matched groups were calculated and compared. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 23.0 software (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). The Kaplan–Meier method was used for survival analyses, including OS and PFS, and differences were examined using the log-rank test. Cox regression analyses were performed to identify factors associated with survival outcomes, and factors with P<0.05 in univariate analysis were included in multivariate analysis. The therapeutic efficacy was shown by the ORR and DCR using the chi-squared test. Statistical significance was defined as P-values <0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
The baseline characteristics are presented in
Table 1. A total of 72 patients received AB combination therapy, and 179 patients received HAIC. There were no significant differences in age, sex, etiology of malignancy, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance score between the two groups. However, there was a significant difference in BCLC stage, Child–Pugh class, serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level, tumor size, portal vein invasion, metastasis, and previous treatments between the two groups. Patients treated with AB were of a significantly more progressed BCLC stage (P=0.027) than those treated with HAIC, but patients treated with AB had better Child–Pugh scores (P=0.008) than those treated with HAIC. Patients treated with HAIC had significantly higher serum AFP levels and larger tumor sizes (P=0.012 and P=0.042 respectively) than those treated with AB. Patients treated with HAIC had significantly more portal vein invasion and less distant metastasis (P=0.028 and P<0.001 respectively) than those treated with AB. Our data revealed that significantly more patients treated with HAIC had previous treatment history.
Naturally, PSM was performed to compensate for these confounding variables. We analyzed our data using PSM with the following factors: sex, age, etiology, ECOG performance status scores, BCLC stage, Child–Pugh scores, and metastasis (caliper=0.2). In total, 62 pairs of patients were matched by PSM. A comparative analysis of the two groups of baseline characteristics showed no significant differences in possible confounding factors between the two groups (
Table 2).
3.2. Treatment Responses
Treatment responses of the enrolled patients are shown in
Table 3. In patients receiving AB, the median OS and PFS periods were 170 days and 149.5 days, respectively. In patients treated with HAIC, the median OS and PFS periods were 185 days and 138 days, respectively. Of the patients who received AB, 3 (4.17%) achieved CR, 22 (30.56%) PR, 32 (44.44%) SD, and 15 (20.83%) progressive disease (PD). Among the patients who received HAIC, 10 (5.59%) achieved CR, 30 (16.76%) PR, 127 (70.95%) SD, and 11 PD. Our statistical analysis showed a significant difference between the two groups (
Table 3, P<0.001). In the AB therapy group, 25 (34.72%) patients showed an objective response, and 57 (79.17%) patients achieved disease control. In the HAIC group, 40 (22.35%) patients showed an objective response, and 167 (97.09%) patients achieved disease control.
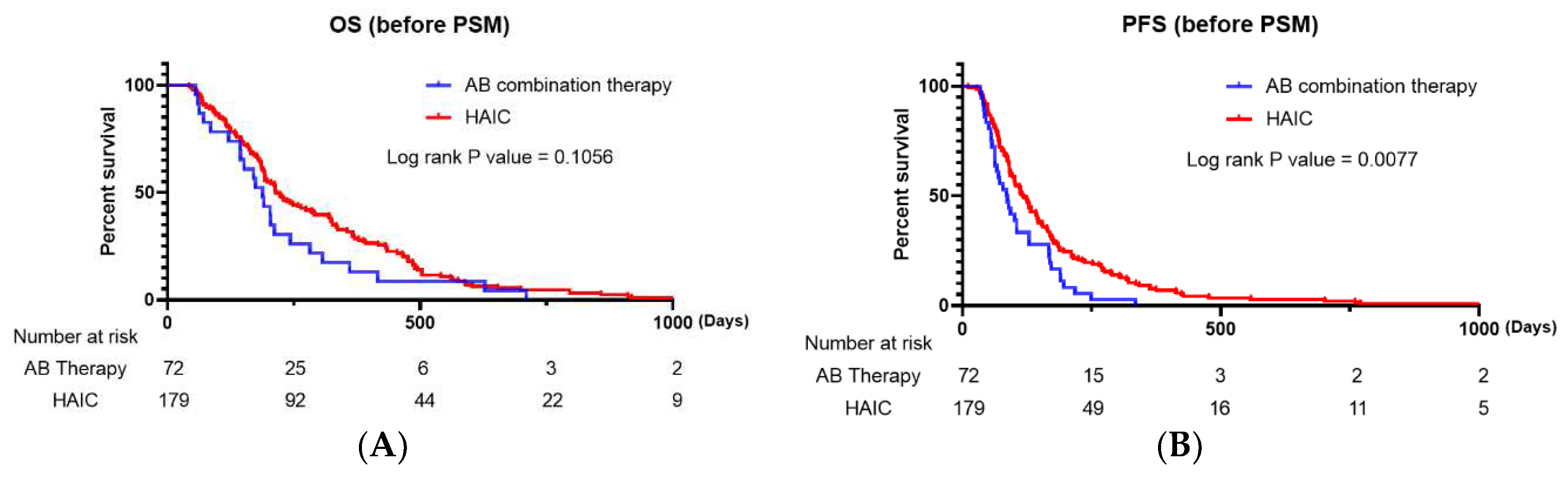
There was a significant difference in the DCR (P=0.001) but no significant difference in the ORR (P=0.137) between the two groups. When we compared the Kaplan–Meier survival curve for PFS and OS, the HAIC group had a significantly longer PFS than the AB therapy group (P=0.0077), and there was no significant difference in OS (P=0.1056) between the two groups (
Figure 1A and 1B).
However, when we analyzed the baseline characteristics between the two therapy groups, there were significant differences in terms of BCLC stage, Child–Pugh class, serum AFP level, tumor size, portal vein invasion, distant metastasis, and previous treatment (
Table 2).
Treatment responses of matched patients via PSM are shown in
Table 4. In the AB therapy group, 2 (3.22%) patients achieved CR, 19 (26.39%) PR, 29 (40.28%) SD, and PD. In the HAIC group, 4 (6.45%) patients achieved CR, 11 (17.74%) PR, 41 (66.13%) SD, and 5 (8.06%) PD (
Table 3). After PSM, no significant difference was observed between the two groups in terms of treatment response (P=0.068). There were also no significant differences between the two groups regarding ORR and DCR (
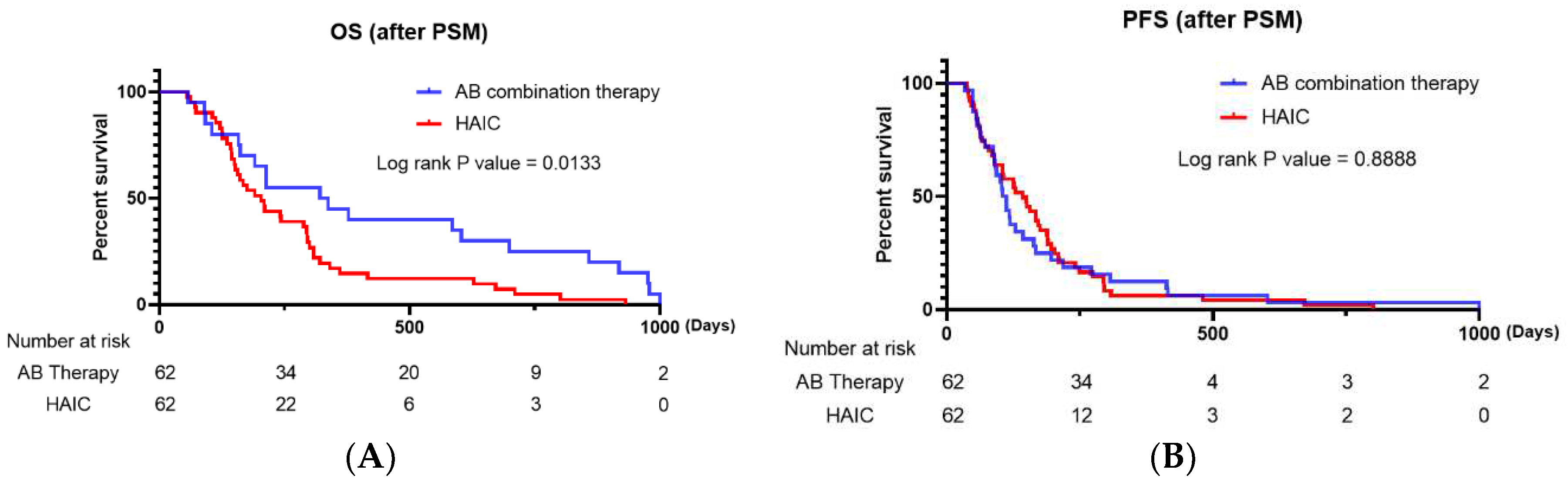
Table 3, P=0.326 and P=0.213, respectively). The analysis revealed no significant difference in PFS between the two groups (
Figure 2B, P=0.6017). However, the AB therapy group had a significantly longer OS than the HAIC group (
Figure 2A, P=0.0133).
3.3. Factors Associated with Survival Outcomes
We analyzed the factors associated with OS and PFS of all enrolled patients with univariate and multivariate analyses using the Cox proportional hazards model (
Table 5). Factors from the univariate analysis with a P-value <0.05 were included in the multivariate analysis. In the univariate analyses regarding OS, the patients’ performance, represented by ECOG performance status ≤1, absence of metastasis, and patients’ liver function, represented by Child–Pugh class were factors associated with favorable OS. In the multivariate analyses, Child–Pugh class A (hazard ratio [HR], 0.389; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.276–0.549; P<0.001) was a significant factor associated with OS. In the univariate analyses regarding PFS, Child–Pugh class A was a factor associated with favorable PFS; distant metastasis was associated with poor PFS. In the multivariate analyses, Child–Pugh class A (HR, 0.410; 95% CI, 0.295–0.571; P<0.001) was significantly associated with favorable PFS, and distant metastasis (HR, 1.721; 95% CI, 1.261–2.353; P=0.001) was significantly associated with poor PFS.
3.4. Adverse events
We also assessed the adverse events that occurred during treatment in both groups (
Table 6). Significantly more adverse events occurred in the HAIC therapy group than in the AB combination therapy group. The most common adverse event in the HAIC therapy group was hyperbilirubinemia.
4. Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, no study has compared AB combination therapy and HAIC in patients with advanced HCC. This was a real-world study that compared first-line systemic chemotherapy for unresectable HCC with the less popular locoregional chemotherapy, HAIC. AB therapy is the first-line chemotherapy currently used to treat patients with unresectable advanced HCC; durvalumab plus tremelimumab is currently not available in South Korea, and if the treatment is not feasible, sorafenib or lenvatinib can be considered [
25]. After the IMBrave150 trial demonstrated that AB therapy was superior in OS and PFS to sorafenib chemotherapy in patients with advanced HCC, several studies regarding AB therapy have been conducted. Cheon et al. confirmed the efficacy and safety of AB therapy in Korean patients and noted inferior outcomes in patients with elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio [
26]. Fulgenzi et al. also confirmed the safety and efficacy of AB therapy and pointed out that the presence of portal vein invasion and higher albumin-bilirubin grade were correlated with poor prognosis [
27]. Recently, Casadei-Gardini et al. suggested that there was no significant difference in OS between AB therapy and lenvatinib [
28]. Interestingly, Persano et al. reported higher ORR in patients treated with lenvatinib compared with those treated with AB therapy [
29]. D’Alessio et al. published a notable study confirming the safety of AB combination therapy in patients with liver functions of Child–Pugh classes A and B [
30]. HAIC is a locoregional chemotherapy technique that does not involve embolization; thus, it can be considered a type of systemic chemotherapy directly infused to the liver [12,31-33]. In 2014, Song et al. revealed the comparative OS and time to progression between patients with advanced HCC with portal vein tumor thrombosis treated with sorafenib and HAIC [
34]. Considering these results, our institute acknowledged the need to compare the prognoses of patients with unresectable HCC treated with AB therapy and HAIC.
Our study, which included all enrolled patients, revealed that there was no significant difference between the HAIC and AB therapy groups in terms of OS and ORR (P=0.1056 and P=0.137, respectively). However, HAIC was significantly superior to AB in terms of PFS and DCR (P<0.05). Regarding confounding factors resulting from differences in baseline characteristics, PSM analysis was performed, and 62 propensity score-matched enrolled patients were analyzed. After PSM analysis, our results revealed no significant difference in PFS between patients who received AB and HAIC (P=0.6017); however, patients who received AB therapy had significantly longer OS than those who received HAIC therapy. After PSM analysis, there were no significant differences in ORR and DCR between the two therapies.
There may be questions regarding the large difference between the results before and after PSM analysis. Before propensity matching, there were significant differences between patients treated with HAIC and AB, including Child–Pugh scores, serum AFP level, tumor size, portal vein invasion, and distant metastasis. More patients treated with HAIC had BCLC stages A and B. AFP levels and tumor size were significantly higher in patients treated with HAIC than in those treated with AB, which may be because several terminal patients are palliatively treated with HAIC despite worse liver function. Portal vein invasion was more present in patients treated with HAIC than in those treated with AB, possibly because HAIC is more preferred in patients with portal vein invasion [
34]. Distant metastasis occurred in a significantly larger proportion of patients in the AB therapy group than in the HAIC therapy group as systemic chemotherapy is preferred over locoregional therapy in patients with distant metastases. To compensate for confounding variables, we performed PSM analyses. In total, 62 matches were selected, and the results were compared. After PSM analysis, the results were less surprising and acceptable. AB combination therapy has been confirmed as the first-line chemotherapy for patients with advanced HCC because of its safety and efficacy, and its results have been duplicated [
35].
The limitation of this study includes its retrospective design. Several enrolled patients were previously treated with other therapies before being treated with AB therapy or HAIC; therefore, confounding variables may have affected our data and results, and temporal relationships may have been missed.
5. Conclusions
Patients treated with AB have a significantly longer OS than those treated with HAIC. A prospective cohort study with a meticulous design can help elucidate accurate differences between the current first-line systemic chemotherapy, AB therapy, and HAIC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.-S.S.; methodology, P.-S.S. and J.-H.K.; software, H.-S.C. and J.-S.Y.; validation, P.-S.S, and J.-H.K.; formal analysis, P.-S.S., J.-H.K., and J.-S.Y.; investigation, J.-H.K.; resources, J.-S.O. and C.-H.C.; data curation, J.-W.H. and H.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, J.-H.K.; writing—review and editing, J.-H.K.; visualization, J.-W.J. H.N., and C.-W.K.; supervision, S.B., J.-Y.C., and S.-K.Y.; project administration, P.-S.S., H.-J.C., S.K., and J.A; funding acquisition, P.-S.S. and J.A.
Funding
This work was partly supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (2021R1C1C1005844) and the Research Fund of Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital of The Catholic University of Korea (to P.S.S.). This work was also supported by the Basic Science Research Program through an NRF grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (grant number: NRF-2019R1A2C3005212 to J.A.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Boards of The Catholic Medical Center (XC23TIDI0015). This study conformed to the ethical guidelines of the Helsinki Declaration.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from each patient prior to enrollment.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Villanueva, A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2019, 380, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Ward, E.M.; Johnson, C.J.; Cronin, K.A.; Ma, J.; Ryerson, B.; Mariotto, A.; Lake, A.J.; Wilson, R.; Sherman, R.L.; et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, 1975-2014, Featuring Survival. J Natl Cancer Inst 2017, 109, djx030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J. Trends in liver cancer mortality among adults aged 25 and over in the United States, 2000-2016. NCHS Data Brief 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Daher, D.; Dahan, K.S.E.; Singal, A.G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Liver Cancer 2023, 23, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, W.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, S.; Lim, J.H.; Lee, M.W.; Park, C.H.; Yoon, S.K. Obesity and the risk of primary liver cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Mol Hepatol 2021, 27, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Tsutsumi, T.; Nakano, D.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Torimura, T. MAFLD enhances clinical practice for liver disease in the Asia-Pacific region. Clin Mol Hepatol 2022, 28, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.L.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Lim, H.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; et al. Updated efficacy and safety data from IMbrave150: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab vs. sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2022, 76, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Cheon, J.; Kim, H.; Kang, B.; Ha, Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Hwang, S.G.; Chon, Y.E.; Chon, H.J. Atezolizumab/bevacizumab vs. lenvatinib as first-line therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A real-world, multi-center study. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.W.; Teng, W.; Lin, P.T.; Jeng, W.J.; Chen, K.A.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Chen, W.T.; Ho, M.M.; Hsieh, C.H.; Wang, C.T.; et al. Similar efficacy and safety between lenvatinib versus atezolizumab plus bevacizumab as the first-line treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med 2023, 12, 7077–7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei-Gardini, A.; Rimini, M.; Rimassa, L.; Burgio, V.; Kudo, M.; Tada, T.; Shimose, S.; Suda, G.; Yoo, C.; Cheon, J.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus lenvatinib or sorafenib in non-viral unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: An international study. J Clin Oncol 2022, 40, 4069–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimini, M.; Rimassa, L.; Ueshima, K.; Burgio, V.; Shigeo, S.; Tada, T.; Suda, G.; Yoo, C.; Cheon, J.; Pinato, D.J.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus lenvatinib or sorafenib in non-viral unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: an international propensity score matching analysis. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.; Liu, T.H.; Shao, Y.Y.; Liu, K.L.; Liang, P.C.; Lin, Z.Z. Revisiting hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.S.; Lee, H.A.; Kim, H.Y.; Sinn, D.H.; Lee, D.H.; Hong, S.K.; Cho, J.-Y.; Choi, J.; Chang, Y.; Kong, H.-J.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma in Korea: An analysis of the 2015 Korean nationwide cancer registry. J Liver Cancer 2021, 21, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obi, S.; Sato, S.; Kawai, T. Current status of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy. Liver Cancer 2015, 4, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, P.S.; Yang, K.; Bae, S.H.; Oh, J.S.; Chun, H.J.; Nam, H.C.; Jang, J.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Yoon, S.K. Reduction of intrahepatic tumour by hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy prolongs survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res 2019, 39, 3909–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Han, J.W.; Sung, P.S.; Lee, S.K.; Yang, H.; Nam, H.C.; Yoo, S.H.; Lee, H.L.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, S.W.; et al. Comparative analysis of lenvatinib and hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A multi-center, propensity score study. J Clin Med 2021, 10, 4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueshima, K.; Ogasawara, S.; Ikeda, M.; Yasui, Y.; Terashima, T.; Yamashita, T.; Obi, S.; Sato, S.; Aikata, H.; Ohmura, T.; et al. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy versus sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatooka, M.; Kawaoka, T.; Aikata, H.; Inagaki, Y.; Morio, K.; Nakahara, T.; Murakami, E.; Tsuge, M.; Hiramatsu, A.; Imamura, M.; et al. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy followed by sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HICS 55): An open label, non-comparative, phase II trial. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Chung, W.J.; Bae, S.H.; Song, D.S.; Song, M.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Yim, H.J.; Jung, Y.K.; Suh, S.J.; Park, J.Y.; et al. Randomized, prospective, comparative study on the effects and safety of sorafenib vs. hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2018, 82, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ouyang, D.; Huang, Z.; Che, X. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy versus sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: An updated meta-analysis and systematic review. Front Oncol 2023, 13, 1085166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korean Liver Cancer Association (KLCA) and National Cancer Center (NCC) Korea. 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Liver Cancer 2023, 23, 1–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, H.; Niizeki, T.; Nagamatsu, H.; Ueshima, K.; Nomura, T.; Kuzuya, T.; Kasai, K.; Kooka, Y.; Hiraoka, A.; Sugimoto, R.; et al. Survival benefit of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy over sorafenib in the treatment of locally progressed hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J Hepatol 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, J.; Yoo, C.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.W.; Lee, M.A.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, I.; Oh, S.B.; Hwang, J.E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in Korean patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int 2022, 42, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulgenzi, C.A.M.; Cheon, J.; D'Alessio, A.; Nishida, N.; Ang, C.; Marron, T.U.; Wu, L.; Saeed, A.; Wietharn, B.; Cammarota, A.; et al. Reproducible safety and efficacy of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab for HCC in clinical practice: Results of the AB-real study. Eur J Cancer 2022, 175, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei-Gardini, A.; Rimini, M.; Tada, T.; Suda, G.; Shimose, S.; Kudo, M.; Cheon, J.; Finkelmeier, F.; Lim, H.Y.; Rimassa, L.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus lenvatinib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a large real-life worldwide population. Eur J Cancer 2023, 180, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, M.; Rimini, M.; Tada, T.; Suda, G.; Shimose, S.; Kudo, M.; Cheon, J.; Finkelmeier, F.; Lim, H.Y.; Rimassa, L.; et al. Clinical outcomes with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab or lenvatinib in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicenter real-world study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessio, A.; Weinmann, A.; Galle, P.R.; Fulgenzi, C.A.M.; Bettinger, D.; Bengsch, B.; Vogel, A.; Balcar, L.; Scheiner, B.; Navaid, M.; et al. Real-world use of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and Child-Pugh A and B cirrhosis. J Clin Oncol 2022, 40, 393–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.J. Hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2015, 21, 3843–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.E.; Suh, S.J.; Yim, H.J.; Seo, Y.S.; Yoon, E.L.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Yim, S.Y.; Kim, H.R.; Kang, S.H.; et al. Comparison of sorafenib versus hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy-based treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Gut Liver 2021, 15, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Osaki, Y.; Kita, R.; Kimura, T. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan. Cancers (Basel) 2012, 4, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.S.; Song, M.J.; Bae, S.H.; Chung, W.J.; Jang, J.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.Y.; Yim, H.J.; Cho, S.B.; et al. A comparative study between sorafenib and hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. J Gastroenterol 2015, 50, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessio, A.; Fulgenzi, C.A.M.; Nishida, N.; Schönlein, M.; von Felden, J.; Schulze, K.; Wege, H.; Gaillard, V.E.; Saeed, A.; Wietharn, B.; et al. Preliminary evidence of safety and tolerability of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and Child-Pugh A and B cirrhosis: A real-world study. Hepatology 2022, 76, 1000–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).