Submitted:
19 July 2023
Posted:
21 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials Collection and Authentication

2.2. Extraction
2.3. Phytochemical Screening
2.4. Determination of α- Amylase Inhibition Activity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Molecular Docking
2.7. Toxicity Profiling
3. Results
3.1. Percentage Yield
3.2. Phytochemical Screening
| S.N. | Test | Result | |
| 1. | Alkaloids | Mayer’s test | + |
| Wagner’s test | + | ||
| Hager’s test | + | ||
| 2. | Glycosides | Brontrager’s test | + |
| 3. | Carbohydrates | Molish’s test | _ |
| 4. | Reducing sugar | Benedicts test | _ |
| 5. | Tannins | Potassium dichromate test | + |
| 6. | Phenol | Ferric chloride test | + |
| 7. | Flavonoids | Ferric chloride test | + |
| 8. | Saponins | Foam test | + |
| 9. | Amino acids | Ninhydrine test | _ |
| 10. | Steroids and terpenoids | Salkoski test | + |
3.3. Alpha-Amylase Inhibitory Activity
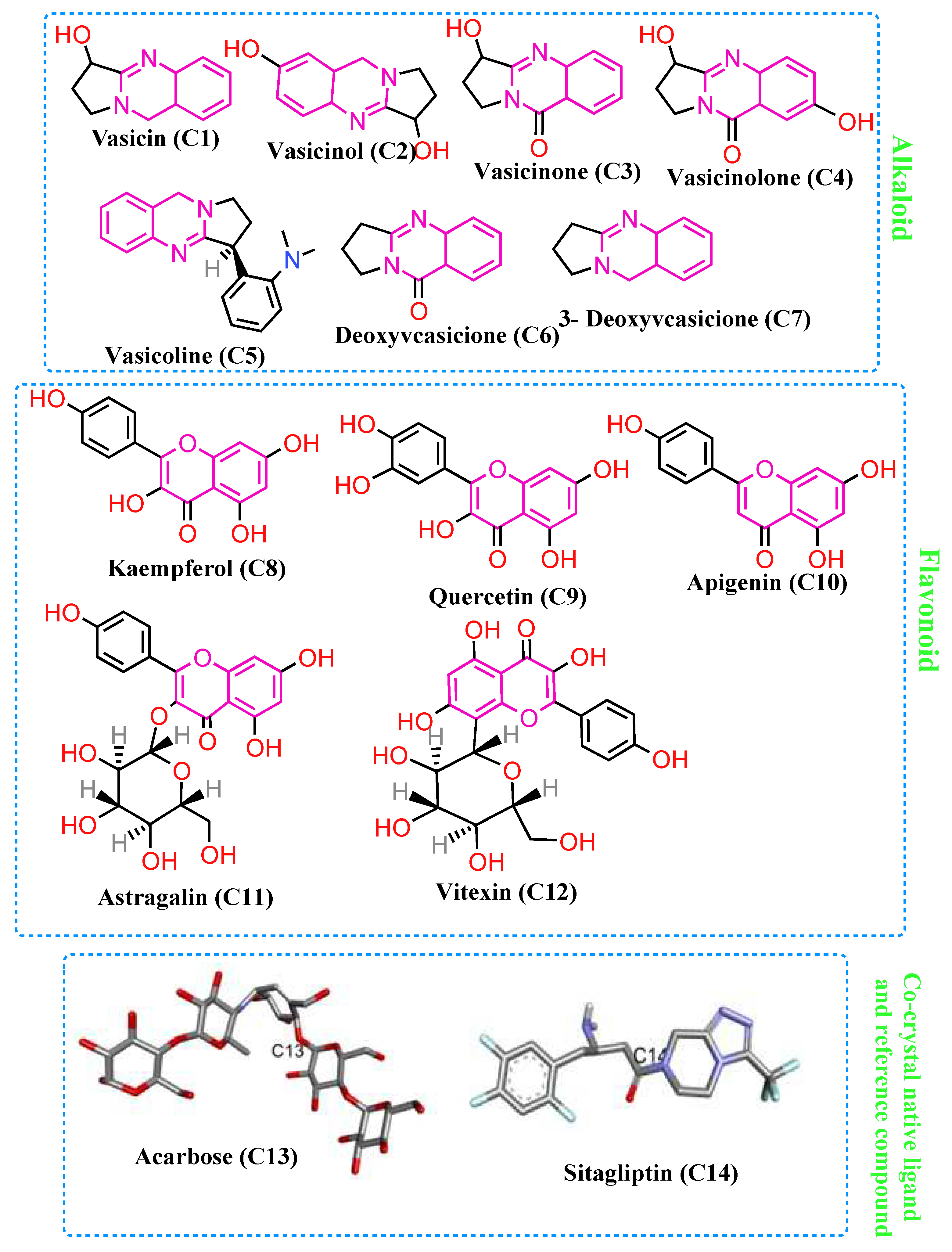
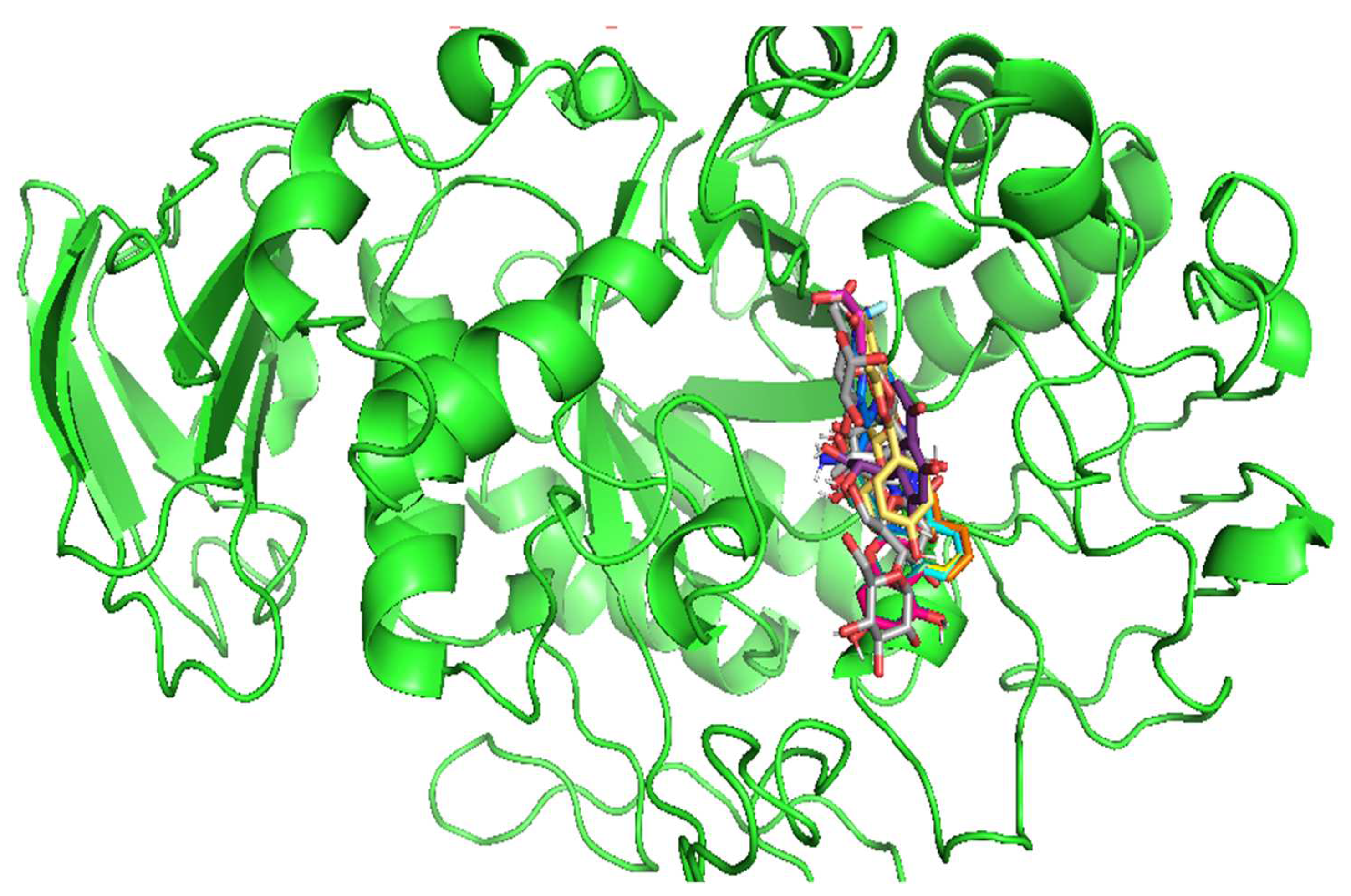
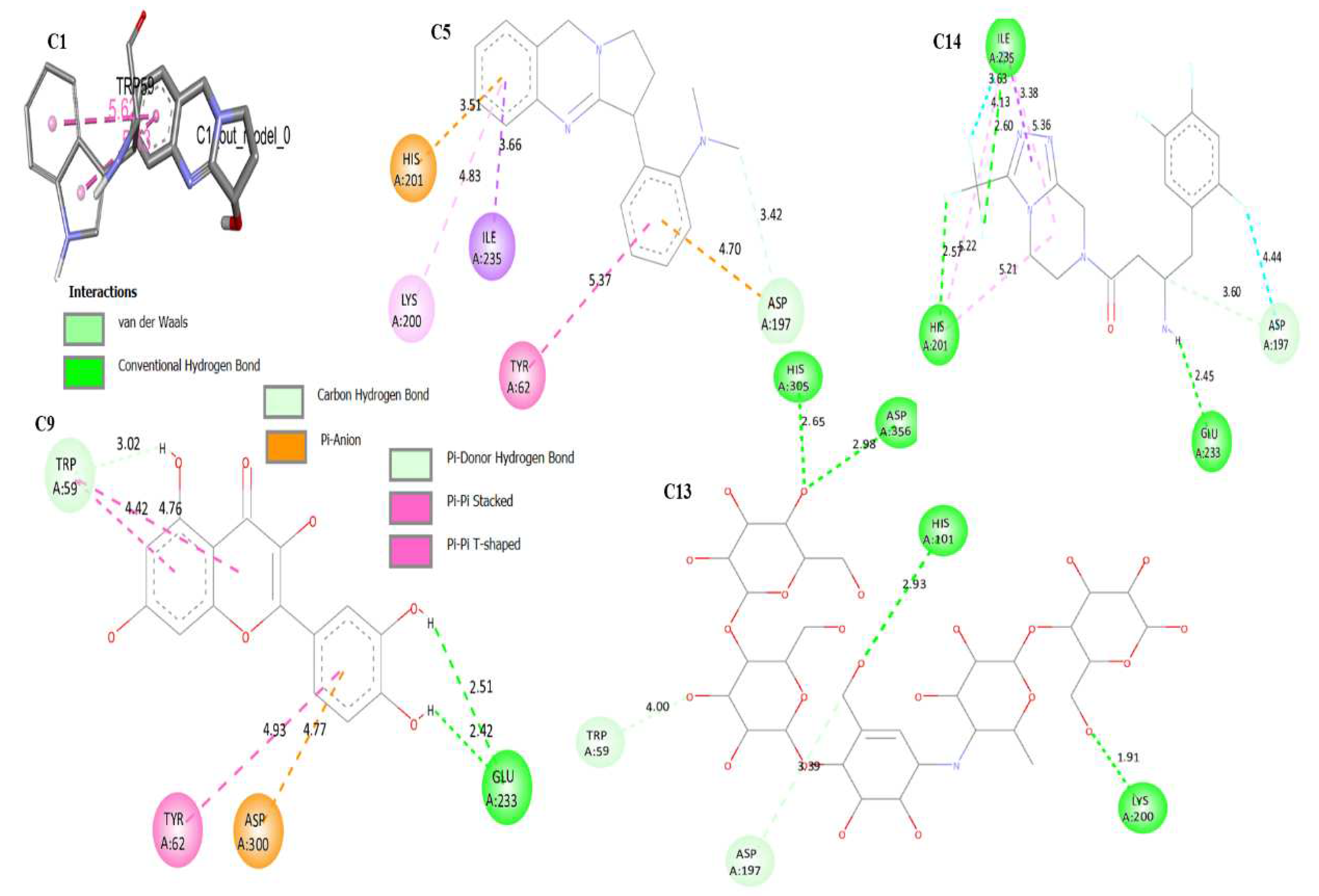
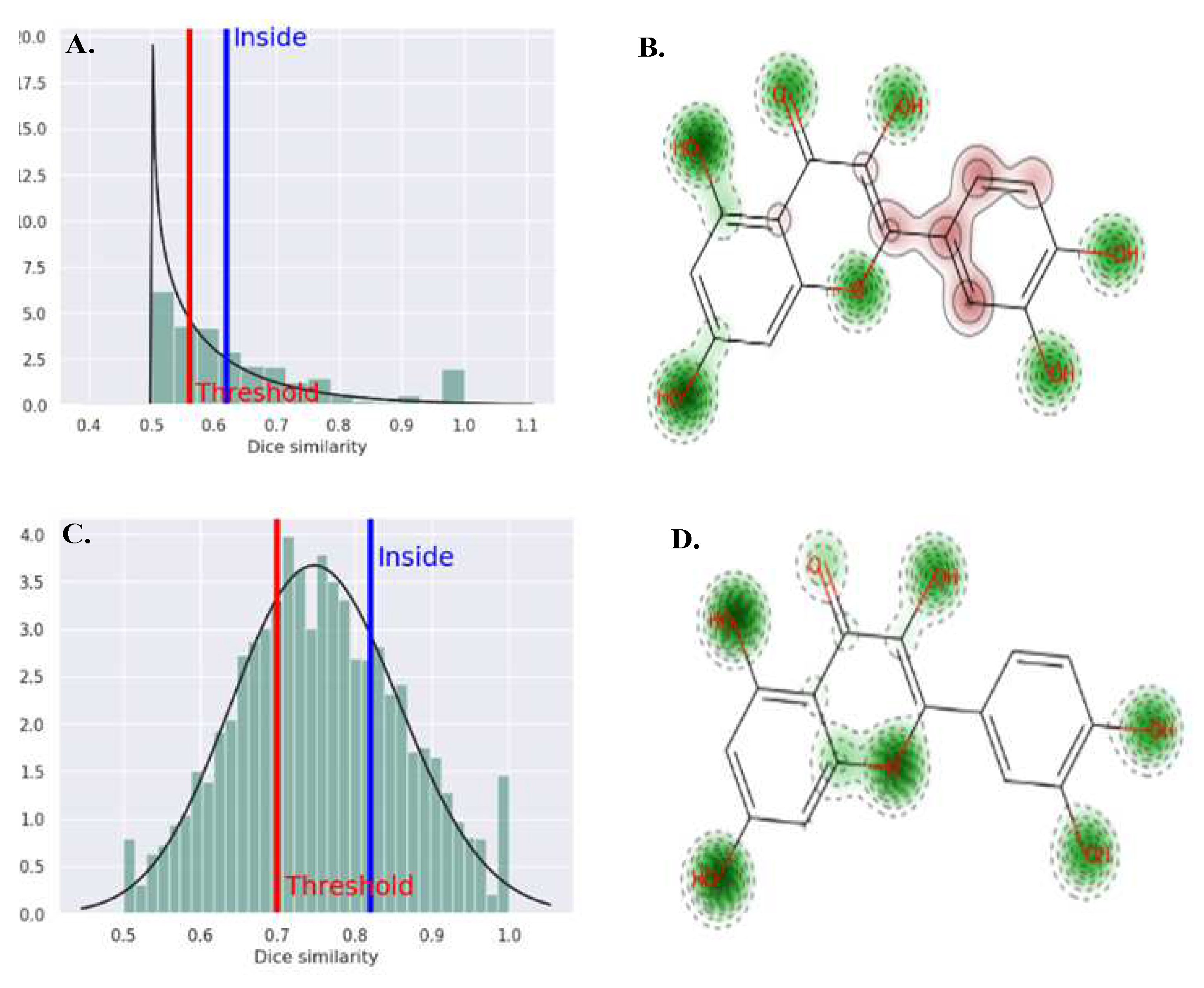
3.4. Molecular Docking
3.5. Toxicity Profiling Analysis
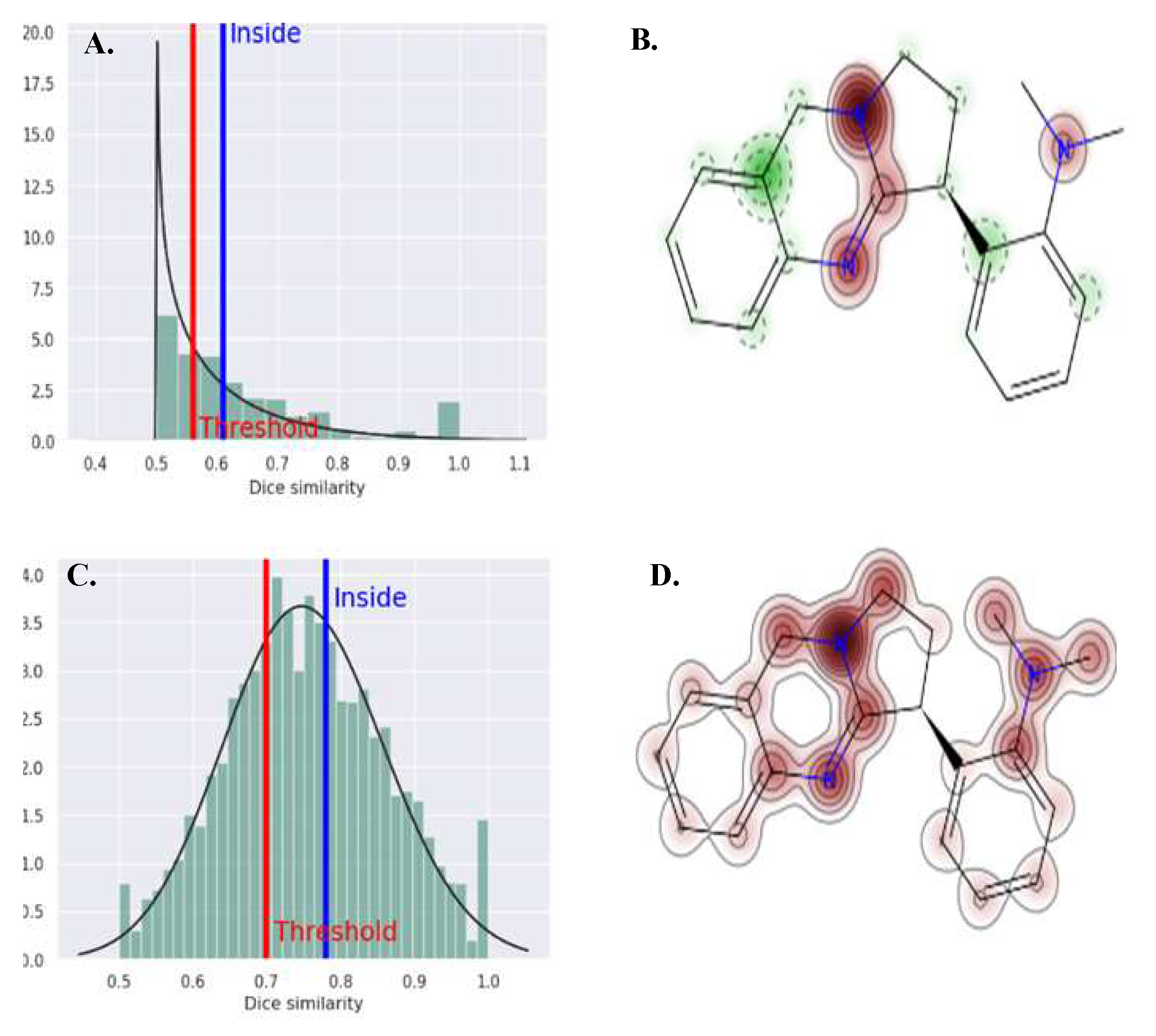
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kharroubi, AT. Diabetes mellitus: The epidemic of the century. World J Diabetes. 2015, 6, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha DB, Budhathoki P, Sedhai YR, et al. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Nepal from 2000 to 2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis. F1000Research. 2021, 10, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhi S, Nayak AK, Behera A. Type II diabetes mellitus: a review on recent drug-based therapeutics. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlén AD, Dashi G, Maslov I, et al. Trends in Antidiabetic Drug Discovery: FDA Approved Drugs, New Drugs in Clinical Trials and Global Sales. Front Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyedemi SO, Oyedemi BO, Ijeh II, Ohanyerem PE, Coopoosamy RM, Aiyegoro OA. Alpha-Amylase Inhibition and Antioxidative Capacity of Some Antidiabetic Plants Used by the Traditional Healers in Southeastern Nigeria. Sci World J. 2017, 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalli S, Hassikou R, Arahou M. An ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants used for diabetes treatment in Rabat, Morocco. Heliyon. 2019, 5, e01421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhury A, Duvoor C, Reddy Dendi VS. Clinical Review of Antidiabetic Drugs: Implications for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management. Front Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindu J, Narendhirakannan RT. Role of medicinal plants in the management of diabetes mellitus: a review. 3 Biotech. 2019, 9, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Salleh NH, Zulkipli IN, Mohd Yasin H. Systematic Review of Medicinal Plants Used for Treatment of Diabetes in Human Clinical Trials: An ASEAN Perspective. Zarrelli A, ed. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med. 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin Z, Zhang W, Feng F, Zhang Y, Kang W. α-Glucosidase inhibitors isolated from medicinal plants. Food Sci Hum Wellness. 2014, 3, 136–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary S, Kaurav H, Chaudhary G. Adhatoda Vasica (Vasapatra): A Review Based Upon Its Medicinal Properties. Int J Res Ayurveda Pharm. 2021, 12, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla S, Ahirwal L, Bajpai VK, Huh YS, Han Y-K. Growth Inhibitory Effects of Adhatoda vasica and Its Potential at Reducing Listeria monocytogenes in Chicken Meat. Front Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikhitha JN, Swathy KS, Chandran RP. In vitro anticancer activity of ethanol extract of Adhatoda vasica Nees on human ovarian cancer cell lines. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogole L, Omwoyo W, Mtunzi F. Phytochemical screening, anti-oxidant activity and α-amylase inhibition study using different extracts of loquat (Eriobotrya japonica) leaves. Heliyon. 2020, 6, e04736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul R, Jan SU, Faridullah S, Sherani S, Jahan N. Preliminary Phytochemical Screening, Quantitative Analysis of Alkaloids, and Antioxidant Activity of Crude Plant Extracts from Ephedra intermedia Indigenous to Balochistan. Sci World J. 2017, 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubale S, Kebebe D, Zeynudin A, Abdissa N, Suleman S. Phytochemical Screening and Antimicrobial Activity Evaluation of Selected Medicinal Plants in Ethiopia. J Exp Pharmacol. 2023, 15, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazeem MI, Mayaki AM, Ogungbe BF, Ojekale AB. In-vitro studies on Calotropis procera leaf extracts as inhibitors of key enzymes linked to diabetes mellitus. Iran J Pharm Res. 2016, 15, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Amin Mir M, Sawhney SS, S Jassal MM. In-vitro antidiabetic studies of various extracts of Taraxacum officinale. Pharma Innov J. 2015, 4, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar Singh Scholar S, Ram Patel J, Dangi A, et al. A complete over review on Adhatoda vasica a traditional medicinal plant. J Med Plants Stud. 2017, 017, 175–180.
- Kumar M, Dandapat S, Kumar A, Sinha MP. Pharmacological Screening of Leaf Extract of Adhatoda vasica for Therapeutic Efficacy. Glob J Pharmacol. 2014, 8, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad Q, Sammi S, Mehmood A, Naveed K, Azeem K, Ayub A. Phytochemical analysis and antimicrobial activity of adhatoda vasica leaves. Pure Appl Biol. 2020, 9, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar BS, Anuragh S, Kammala AK, Ilango K. Computer Aided Drug Design Approach to Screen Phytoconstituents of Adhatoda vasica as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Enzyme. Life. 2022, 12, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams LK, Zhang X, Caner S. The amylase inhibitor montbretin A reveals a new glycosidase inhibition motif. Nat Chem Biol. 2015, 11, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa S, Nargund SL, Biradar MS. Molecular Design and In-Silico Analysis of Trisubstituted Benzimidazole Derivatives as Ftsz Inhibitor. J Chem. 2023, 2023, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurus R, Begum A, Williams LK. Alternative Catalytic Anions Differentially Modulate Human alpha-Amylase Activity and Specificity. Biochemistry. 2008, 47, 3332–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott O, Olson AJ. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem. 2009, 31, 21334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger D, de Groot BL. Ligand docking and binding site analysis with PyMOL and Autodock/Vina. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2010, 24, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa S, Nargund SL, Biradar MS, Banerjee J, Karati D. In-silico investigation and drug likeliness studies of benzimidazole congeners: The new face of innovation. Informatics Med Unlocked. 2023, 38, 101213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biradar MS, Nargund SL, Thapa S. Synthesis and Cytotoxicity Assay of Aniline Substituted Thienopyrimidines for Anti-Colorectal Cancer Activity. Results Chem. 2023, 5, 100926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadhoush F, Sadeghi M, Pourfarzam M. Biochemical changes in blood of type 2 diabetes with and without metabolic syndrome and their association with metabolic syndrome components. J Res Med Sci. 2015, 20, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariadoss AVA, Sivakumar AS, Lee C-H, Kim SJ. Diabetes mellitus and diabetic foot ulcer: Etiology, biochemical and molecular based treatment strategies via gene and nanotherapy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadayat K, Marasini BP, Gautam H, Ghaju S, Parajuli N. Evaluation of the alpha-amylase inhibitory activity of Nepalese medicinal plants used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Clin Phytoscience. 2020, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao H, Huang Y-N, Gao B, Li P, Inagaki C, Kawabata J. Inhibitory effect on α-glucosidase by Adhatoda vasica Nees. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 965–972. [CrossRef]
- Rudrapal M, Vallinayagam S, Aldosari S. Valorization of Adhatoda vasica leaves: Extraction, in vitro analyses and in silico approaches. Front Nutr. 2023, 10, 1161471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulfraz M, Ahmad A, Asad MJ. Antidiabetic activities of leaves and root extracts of Justicia adhatoda linn against alloxan induced diabetes in rats. African J Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 6101–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulfatai U, Uba S, Abdullahi B, Muhammad U, Ibrahim T. Molecular design and docking analysis of the inhibitory activities of some α _ substituted acetamido - N - benzylacetamide as anticonvulsant agents. SN Appl Sci. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Pham TNH, Nguyen TH, Tam NM. Improving Ligand-Ranking of AutoDock Vina by Changing the Empirical Parameters. J Comput Chem. 2022, 43, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen NT, Nguyen TH, Pham TNH. Autodock Vina Adopts More Accurate Binding Poses but Autodock4 Forms Better Binding Affinity. J Chem Inf Model. 2020, 60, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhong CH, Riyaphan J, Lin SH, Chia YC, Weng CF. Screening alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase inhibitors from natural compounds by molecular docking in silico. BioFactors. 2015, 41, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabil-Adam A, Ashour ML, Tamer TM, Shreadah MA, Hassan MA. Interaction of Jania rubens Polyphenolic Extract as an Antidiabetic Agent with α-Amylase, Lipase, and Trypsin: In Vitro Evaluations and In Silico Studies. Catalysts 2023, 13, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim AM, Mohammed N, Ghazi R. In vitro and In silico Analysis of Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Fruit Powder as Pancreatic Lipase and α-Amylase Inhibitor. J Phys Conf Ser. 2020, 1665, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colerangle, JB. Preclinical Development of Nononcogenic Drugs (Small and Large Molecules). In: A Comprehensive Guide to Toxicology in Nonclinical Drug Development. Elsevier 2017, 1, 659–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães D, Noro J, Loureiro A. Increased Encapsulation Efficiency of Methotrexate in Liposomes for Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy. Biomedicines. 2020, 8, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreck K, Melzig MF. Traditionally Used Plants in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: Screening for Uptake Inhibition of Glucose and Fructose in the Caco2-Cell Model. Front Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
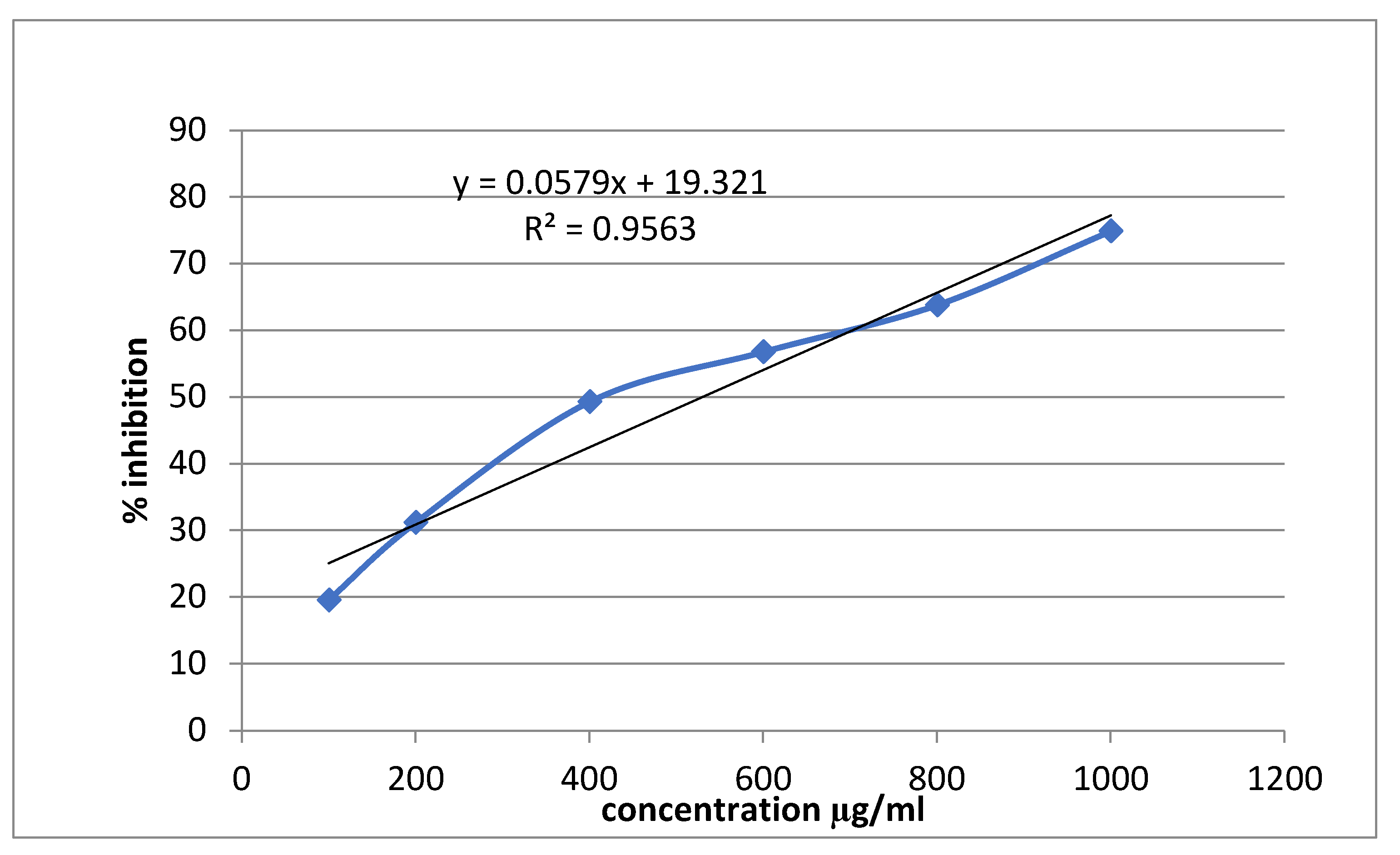
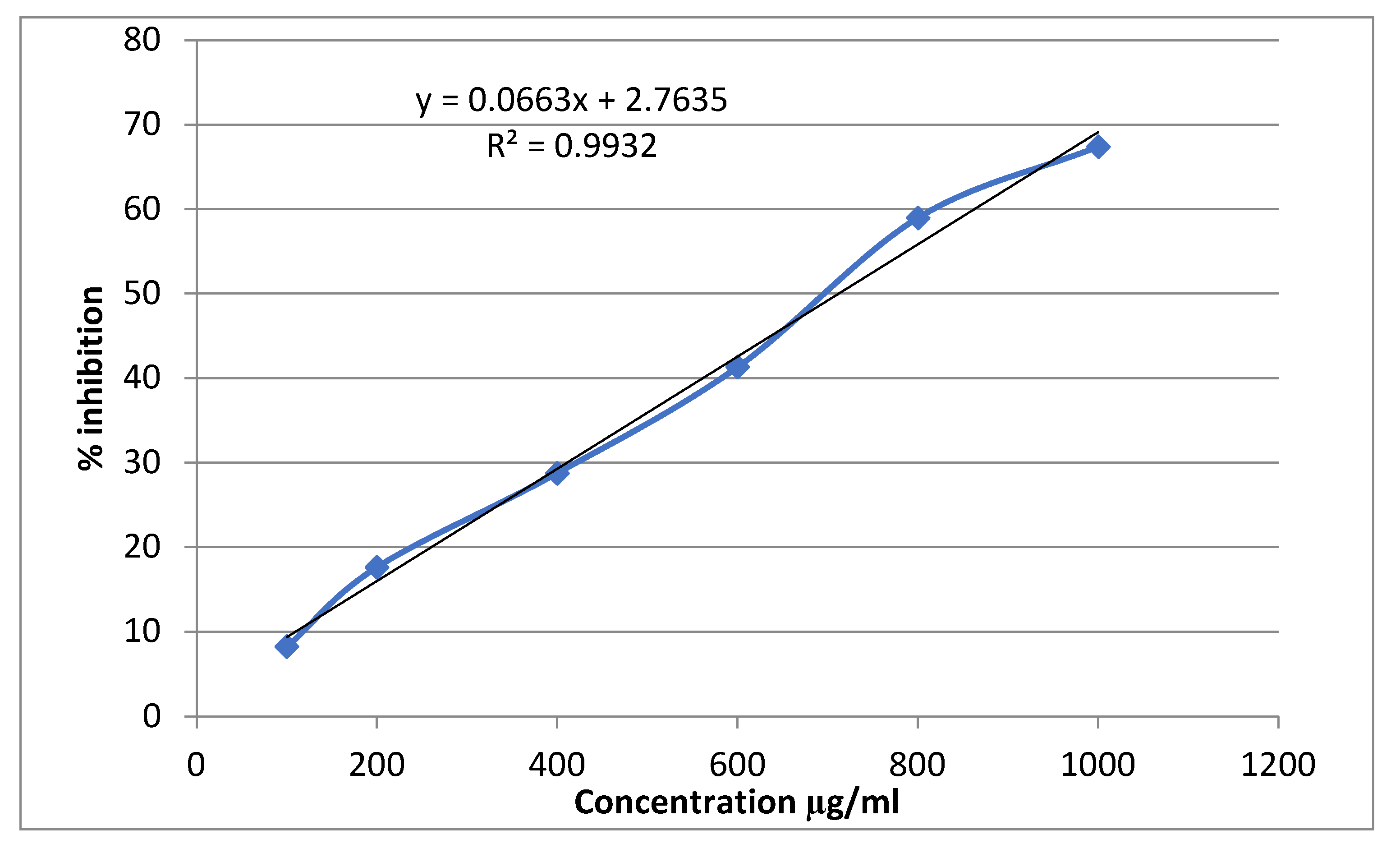
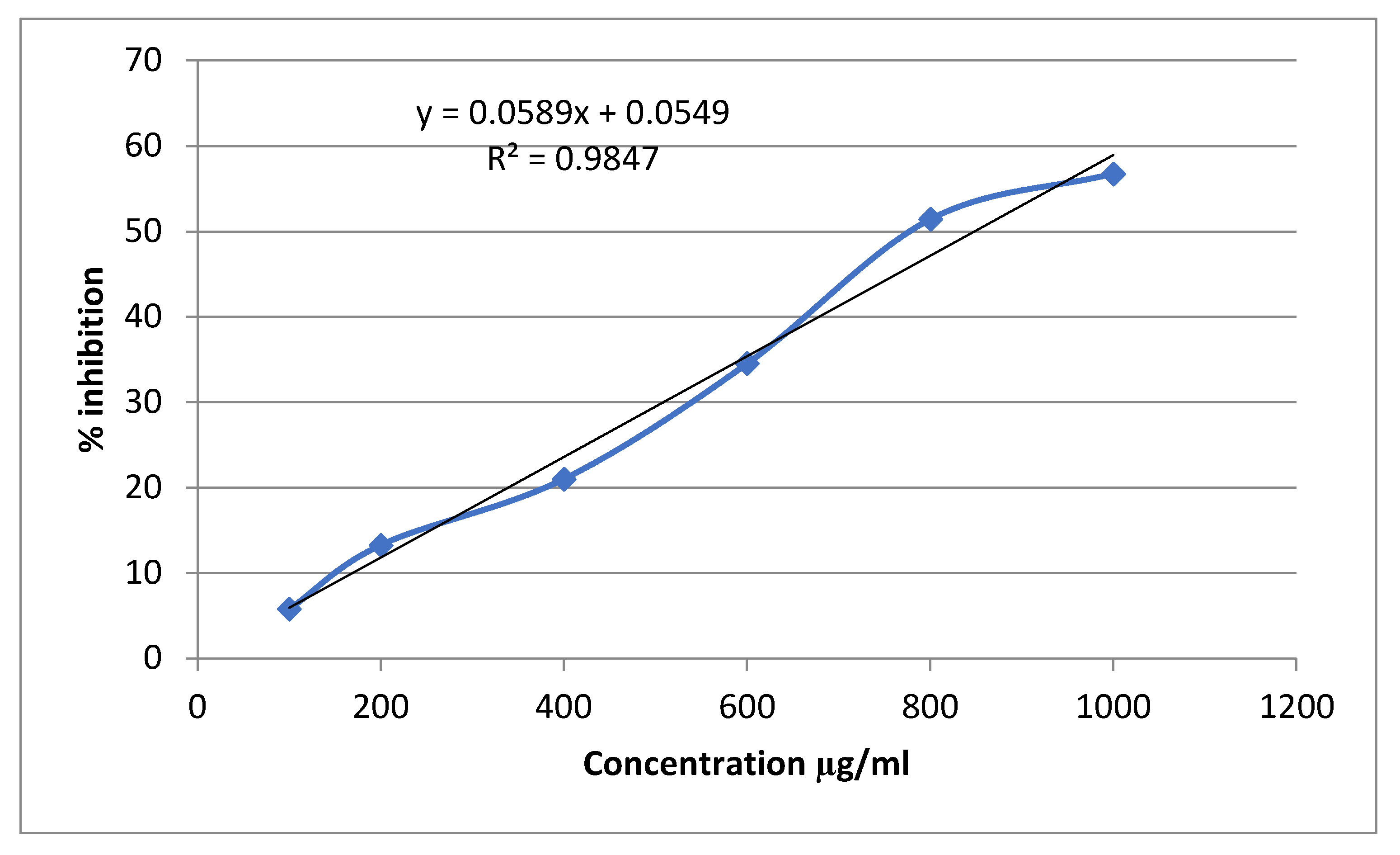
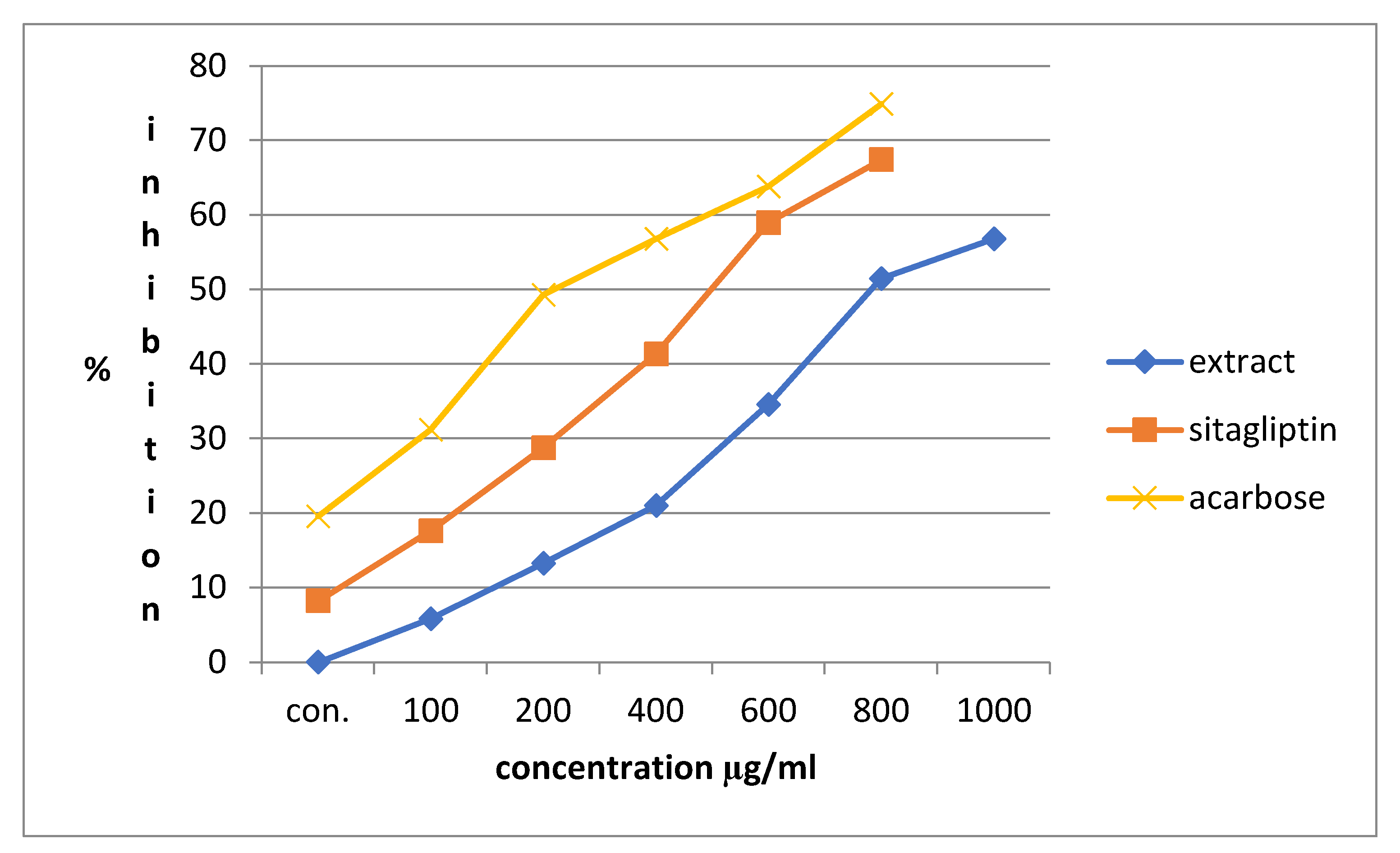
| Conc (mg/ml) | Alpha amylase inhibition | |||||
| Percentage inhibition of Acarbose | IC50 (μg/ml) | Percentage inhibition of Sitagliptin | IC50 (μg/ml | Percentage inhibition of Extract | IC50 (μg/ml | |
| 0.1 | 19.56522±0.0063 | 529.861 | 8.21256±0.0028 | 712.466 | 5.797101±0.0028 | 847.964 |
| 0.2 | 31.15942±0.0035 | 17.63285±0.0021 | 13.28502±0.0021 | |||
| 0.4 | 49.27536±0.0028 | 28.74396±0.0007 | 21.01449±0.0070 | |||
| 0.6 | 56.76329±0.0049 | 41.30435±0.0035 | 34.54106±0.0021 | |||
| 0.8 | 63.76812±0.0028 | 58.9372±0.0028 | 51.44928±0.0049 | |||
| 1 | 74.87923±0.0056 | 67.3913±0.0049 | 56.76329±0.0035 | |||
| Compound Code | 4W93 | ||
| Binding energy (Kcal/mol) | Amino acid | RMSD value (Å) | |
| C1 | -5.9 | Ala169, Lys178, Trp59 | 1.386 |
| C2 | -6.2 | Tyr151, Lys200, Ala198, Ile235, His201 | 1.334 |
| C3 | -6.3 | Trp59, Tyr62 | 1.271 |
| C4 | -6.3 | Ala198, Lys200, Ile235, His201, Tyr151 | 1.302 |
| C5 | -8.3 | Asp197, Tyr62, Ile235, Lys200, His201 | 0.925 |
| C6 | -6.4 | Tyr62, His299, Trp58 | 1.254 |
| C7 | -5.9 | Trp59, Tyr62 | 1.223 |
| C8 | -7.7 | Asp197, 300, 356, Trp59, Tyr 62 | 1.497 |
| C9 | -8.0 | Trp59, Tyr62, Asp300, Glu233 | 1.425 |
| C10 | -7.9 | Tyr62, Asp356, His299, Glu233 | 1.595 |
| C11 | -7.4 | Tyr151, His299, Ile151, Glu233 | 1.896 |
| C12 | -7.8 | Glu233, Ile235, Lys200, His201, Leu162 | 1.338 |
| C13 | -8.6 | Trp59, Lys200, Asp356, His101,305 | 0.856 |
| C14 | -8.5 | Ile235, His201, Glu233, Asp197 | 1.392 |
| Compound code | Acute Inhalation Toxicity | Acute Oral Toxicity | ||
| Prediction | Confidence | Prediction | Confidence | |
| C1 | + | 55.0 % | + | 81.0% |
| C2 | - | 54.0% | + | 68.0% |
| C3 | - | 60.0% | + | 75.0% |
| C4 | - | 75.0% | + | 56.0% |
| C5 | + | 69.0% | + | 91.0% |
| C6 | - | 58.0% | + | 72.0% |
| C7 | + | 75.0% | + | 90.0% |
| C8 | - | 68.0% | - | 70.0% |
| C9 | - | 69.0% | - | 72.0% |
| C10 | - | 66.0% | - | 73.0% |
| C11 | - | 77.0% | - | 66.0% |
| C12 | - | 76.0% | - | 75.0% |
| C13 | - | 78.0% | - | 96.0% |
| C14 | - | 70.0% | - | 69.0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





