1. Introduction
This study demonstrates for the first time the potential of neural network (NN) regression models [
1] in estimating wastewater (WW) quality parameters (BOD, COD, NH
3-N, TDS, TA, and TH) by using WW spectral reflectance as model input. The task of treating wastewater is integral in the objective of minimizing negative footprint to our environment and human health. Hence, wastewater treatment facilities exists in various systems involving water streams from industrial to municipal sectors [
2]. To maintain these facilities within their set continuous operating conditions while meeting regulatory levels of effluent streams, various parameters are monitored [
3] such as BOD, COD, NH
3-N, TDS, TA, and TH to check the quality of effluents. A common approach of monitoring is by sampling the wastewater at various locations of the treatment facility and the samples are tested immediately using readily available test kits or be brought to the laboratory to undergo various physical and chemical analysis procedures. Some of these procedures can take hours to days to be completed (COD, BOD, etc.) [
2]. The lag time in making operational decisions based on wastewater quality measurements can significantly affect the dynamics of the treatment facility amid the control systems in place [
4,
5]. Hence, a fast method of estimating wastewater quality parameters would be desirable in achieving the goal of operating a wastewater treatment facility within target operational settings. We propose in this work the use of neural network (NN) models to accelerate the estimation of WW quality parameters.
The main objective of the study is to demonstrate the potential of NN to be regression models that can estimate WW characteristic parameters at minimal prediction errors. Here are the specific questions that this paper aims to answer:
What data preprocessing tasks must be done on the WW spectral data to produce regression NN models with good prediction performance?
What are the effects of common hyperparameters in NN modeling: number of hidden layers and number of neuron units in each hidden layer?
How does the number of modelled outputs, i.e., WW parameters, affect the prediction performance of NN models?
How can hyperparameter tuning on regression NN models improve prediction performance?
There are more pertinent questions that may be asked and tested to evaluate the capabilities of NN models for regression of WW characteristic parameters due to the numerous possible ways of setting the architecture of NN models, and due to the complexities that certain WW datasets can pose. Nonetheless, the questions above set to be answered in this study should elaborate on important aspects of adopting NN models to quantitate WW characteristic parameters by modelling on WW spectral reflectance data.
2. Methodology
A schematic overview of the data analytics workflow implemented is shown in
Figure 1. The NN computations were implemented via Python codes using the Keras-TensorFlow modules for NN modeling [
6]. The hardware was a laptop computer with an Intel Core i7 (12th Gen) CPU with 2.10 GHz base speed (max speed 5.3 GHz). The Python codes organized in Jupyter Notebook files used in the data analytics workflow are made available in the online GitHub repository of the paper [
7] (URL:
https://github.com/dhanfort/WW_Spectra_NNlearning.git).
2.1. Dataset
2.1.1. WW Data Source and Structure Overview
The spectral reflectance dataset used in this study was the open-source data originally collected and published by Xing, Chen [
8]. The wastewater samples were taken from different locations in a municipal wastewater treatment facility: water inlet (Influent WW), anoxic tank, aerobic tank, sedimentation tank and water outlet (Effluent WW) under different treatment methods at a domestic sewage treatment plant [
8]. The various chemical analysis done were discussed in detail by Xing, Chen [
8]. They noted that there are two subsets of the dataset according to wastewater quality consists of high-levels and low-levels of COD, BOD and NH
3-N: (Group 1) high levels for influent WW, and (Group 2) low levels for anoxic tank, aerobic tank, sedimentation tank and water outlet (effluent WW). The collected dataset consists of wastewater spectral reflectance in the wavelength of 400 nm to 2000 nm (visible to near infrared) with the corresponding measurements of levels of BOD, COD, NH
3-N, TDS, TA, and TH, which are designated as the Targets of the learning process. There are a total of 87 data samples in the whole dataset. Details on how the measurements were made can be found in the original work [
8]. A descriptive summary of the dataset is shown in
Figure 2.
2.1.2. Training Set and Test Set
For each NN modelling, the dataset was divided into two exclusive subsets: Training set and Test set. The Training Set is used to adjust the parameters of the NN model and in computing the training cost function. The Test Set is used to compute the cost function MAE on data not seen by the NN Model during training. To keep the same training and testing datasets across all computational experiments, the random seed index was set to a constant value (see the Python code for the details). When modelling on the whole dataset, subset partitioning was 90% for training and 10% for testing. When modelling on the Influent WW dataset, dataset partitioning was 90% for training and 10% for testing. When modelling on the Group 1 (Influent WW) dataset, the dataset partitioning was 90% for training and 10% for testing. When modelling on the WW Group 2 dataset, the dataset partitioning was 80% for training and 20% for testing. The input data, which are levels of banded spectral intensity (see
Figure 1) in both training set and testing set data, were normalized by scaling using the ‘MinMaxScaler’ of the Scikit-Learn [
9]. Scaling input data to a machine learning model being trained has been shown to improve model prediction performance [
10]. Note that since the input data was the banded spectral reflectance at 400 nm, 401 nm, … ,2000 nm, with each band as a feature, each input sample is a vector of 1601 features.
2.2. NN Model Training and Testing
There are various model settings that can be specified when working with NN models. The following subsections describe the main components of the NN modelling implementation. Other details can be found in the Jupyter Notebook files of Python codes for the work [
7].
2.2.1. Learning Cost Function
The objective of the learning process in NN modelling was to minimize the cost function (or also called loss function). Among various possible metrics of machine learning with Keras-TensorFlow [
11], the mean-absolute-error (MAE) measures more directly the deviations from the true values (
Appendix A), which can be clearly interpreted as the average error in estimating the WW parameter levels. MAE
, where
= true value of the wastewater parameters in observation sample
, and
= prediction on the levels of the wastewater parameters of observation sample
by NN model. The inputs to the NN model
were the banded spectral reflectance signal designated as
; hence,
, where
are the NN model parameters configured (hyperparameters) and tuned (neuron weights) during training. Hence, the objective for each NN modelling was to minimize MAE by adjusting
via an optimization algorithm. The coefficient of determination (R
2) between the model predictions and true values was also computed to measure how well the NN models predict the true values (
Appendix A).
2.2.2. Optimization Algorithm, Learning Rate, Activation Function, and Training Epoch
The Keras-TensorFlow modules for NN modelling contains various optimization algorithms that were all used in this work during preliminary computation runs: Adadelta, Adafactor, Adagrad, Adam, AdamW, FTRL, Lion, Nadam, RMSprop, and SGD [
12]. Among these algorithms, the Adam optimizer consistently produced NN models with the best fit scores (low MAE and high R
2). Hence, the Adam optimization algorithm was used in the majority of computations. The best performance of the Adam optimizer was also achieved when the learning rate was set to 0.0001. The training epoch was set to 5000, which was found to be large enough to allow for the cost function MAE to settle at almost constant level in all of the training runs. The best activation function [
13] for the hidden layers (H1 and H2) was also determined to be the ‘ReLU’ function. The best activation function for the output layer was the ‘Linear’ function.
2.2.3. Effect of Number of Hidden Layers, Number of Neuron Units, and Outputs
To test the performance of NN models at varying number of hidden layers, and number of neurons in the hidden layers the following configurations were used: one hidden layer (H1) with low and high numbers of neuron units, and two hidden layers (H1, and H2) with the number of neuron units varied in the first layer (H1) and the number of neuron units fixed in the second layer (H2). See
Table 1 for the summary of these hidden layer configurations.
Given that there were several WW parameters being estimated (BOD, COD, NH3-N, TDS, TA, and TH), the effects of various combinations of the WW parameters being modelled as outputs were also evaluated.
Table 1 shows a summary of NN modelling implemented consists of 44 different computational runs. Note that the set of combinations of model outputs Y (
Table 1) does not cover all possible combinations, i.e., there are 2
6 = 64 possible Model Output(s) Y Settings; hence, resulting to (NN Model Settings) × (Model Output(s) Settings) = 4 × 64 = 256 Total Number of Modelling Settings for all possible settings of computational experiments. Rather, the choice of model output combinations was motivated by the purpose of working with a number of results, i.e., 44 sets of results, that are manageable in the discussion of key aspects of the work.
2.2.4. NN Model Hyperparameter Grid-Search
Often at the start of developing a NN model and when a very challenging dataset is encountered, the NN model settings for the optimizer, learning rate, number of neurons per hidden layer, etc., must be fine-tuned. This task focuses on finding the NN model parameters other than the weights of neuron connections in the NN Model, and this is called the hyperparameter grid-search with the main goal of improving the prediction performance of the NN model. The grid-search implemented was the full-factorial search via the Scikit-Learn module ‘GridSearchCV’ [
14], which considers all combinations of hyperparameters being tested. Hyperparameter grid-search was done during the preliminary runs to set the optimizer Adam, learning rate 0.0001, epoch of 5000, and activation function ‘ReLU’ for H1 and H2 as discussed in
Section 2.2.2.
Hyperparameter grid-search was also implemented to refine the NN modelling on the Group 2 WW subset that posed a challenge (see
Section 3.3). This task demonstrated how NN models can be subjected to tuning the hyperparameters such as optimizer algorithm, number of neuron units per hidden layer, activation function in each hidden layer and the output layer, and learning rate. The selection of the best NN model with its respective hyperparameter settings was still based on the MAE. The grid-search settings produced a total of 864 NN models evaluated (see
Section 3.3).
3. Results
Though numerous results were generated in the study, the following results sections had been organized to facilitate the discussion of the key aspects of the work.
Section 3.1 covers the results that show the need for dedicated NN models for WW stream groups.
Section 3.2 covers the results that show how the performance of NN models can be affected by the various combinations of WW parameters used as model outputs.
Section 3.3 covers the results that show how hyperparameter grid-search can improve the predictive performance of NN models.
3.1. Need for Dedicated NN Model for Wastewater Stream Groups
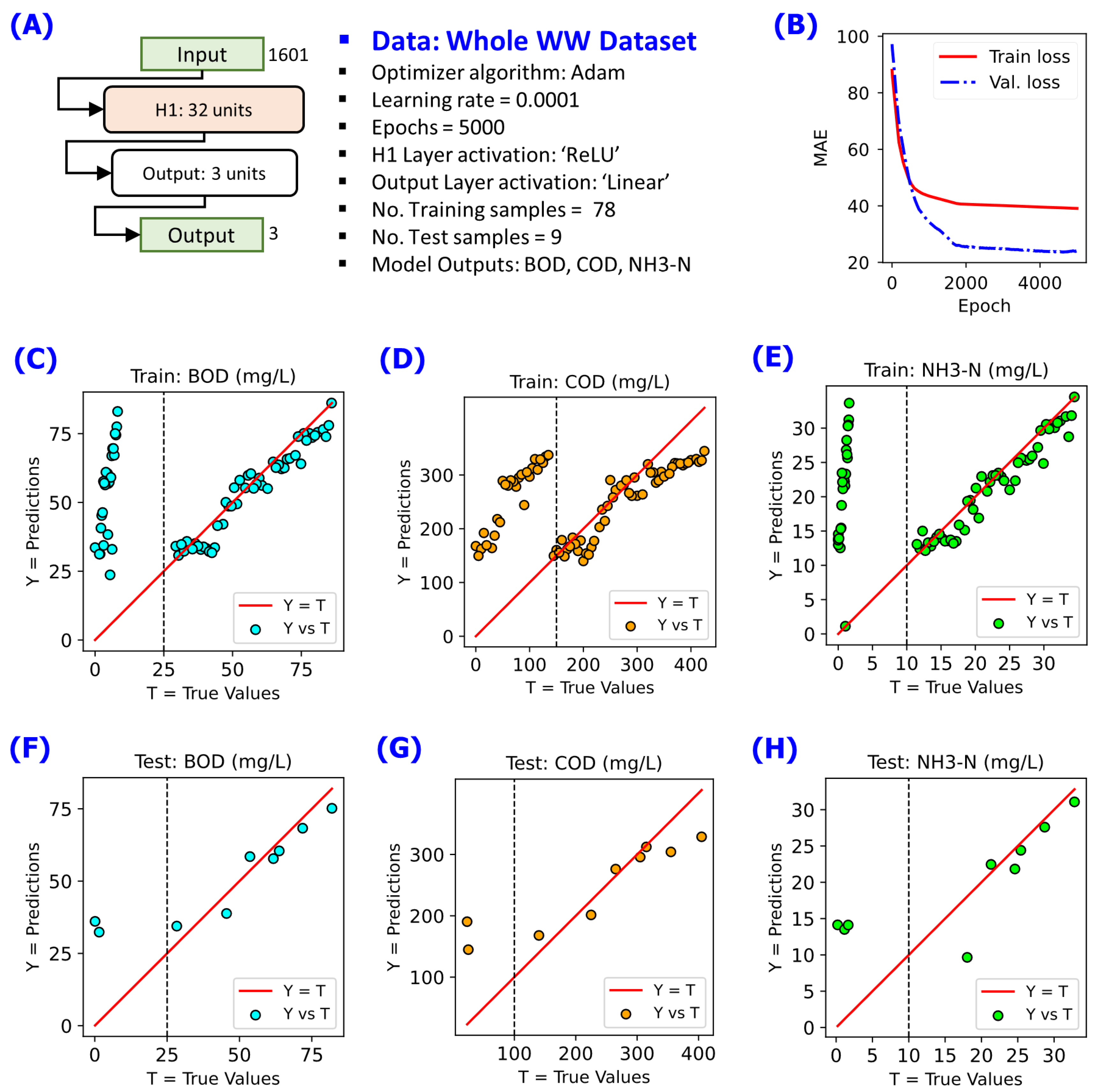
Part of the initial stage of developing the NN models was the task of determining whether the whole WW dataset can be treated as a single input array to the models. Training NN model on the whole dataset resulted into a set of predictions that show two apparent groups of the data as shown in
Figure 3 for the model outputs BOD, COD, and NH
3-N. This was an indication that the WW dataset cannot be treated as a single input array. After dividing the whole dataset into two groups according to the Group 1 WW and Group 2 WW subsets, the NN models started to achieve good prediction performance as shown in
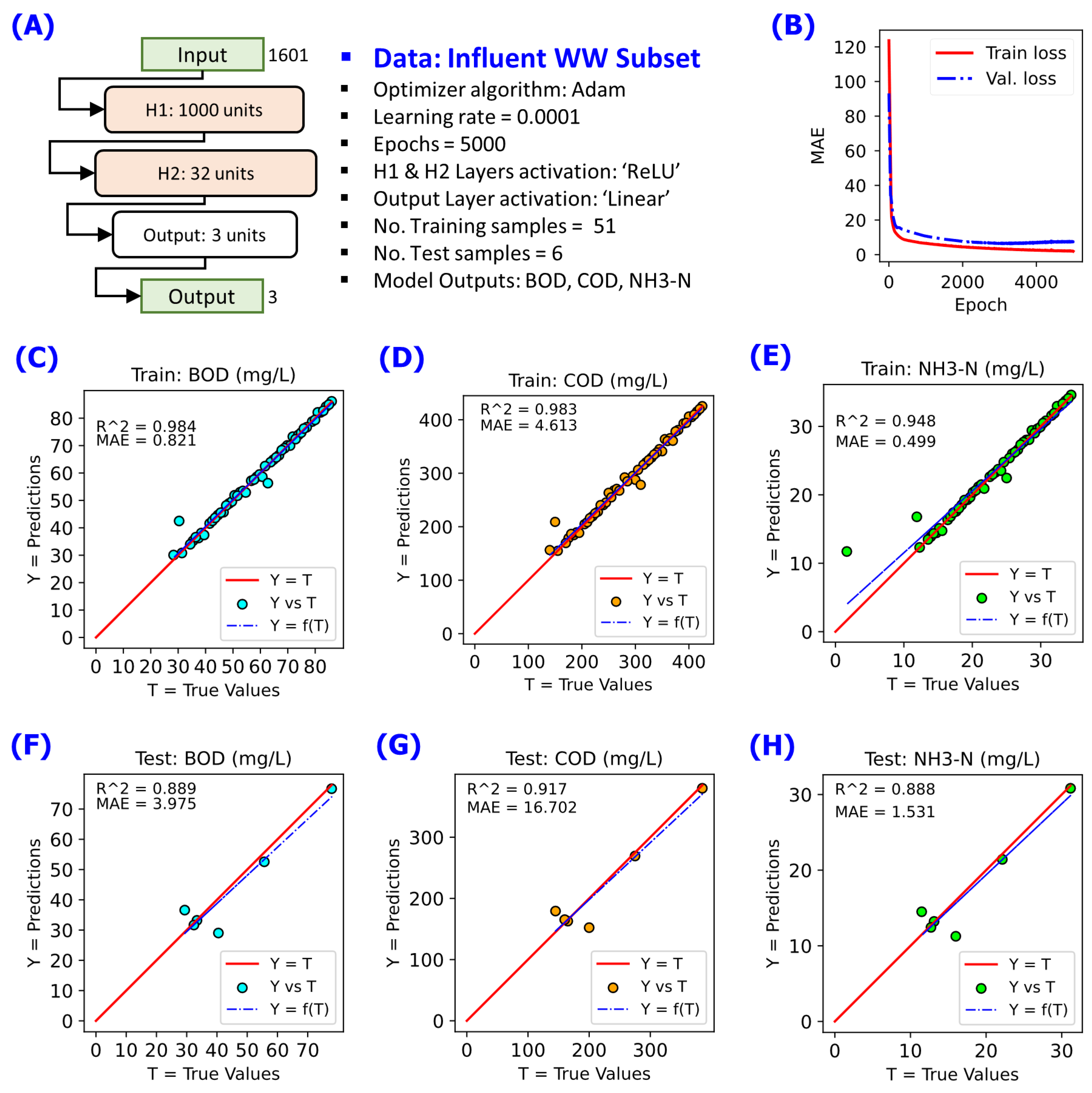
Figure 4 for the Group 1 WW (Influent WW), and
Figure 5 for the Group 2 WW. These results indicate the need for dedicated NN models for certain WW stream groups.
3.2. Challenge with Increasing Number of NN Model Output Variables
By varying the combination of WW parameters as model outputs (
Table 1), the comprehensive evaluation of NN model prediction performance was collected and the key results are shown in
Figure 6 and
Figure 7. In general, NN models trained for single output, i.e., one WW parameter estimated per NN model trained, achieved the best prediction performance in terms of the R
2 and MAE between the prediction Y and actual level T of each WW parameter (
Figure 6A–D). When more than one WW parameter is being model in an NN model, the R
2 and MAE of Y-vs-T may turn to poorer levels (
Figure 6A–D), even though increasing the number of hidden layers and the number of neuron units can be used to improve R
2 and MAE of Y-vs-T (
Figure 6D). Also, a corresponding decrease in MAE is observed, in general, with increase in the R
2 of Y-vs-T of an NN model. The MAE levels for the best NN models (
Figure 6D) can be very low as shown in
Figure 8, which is a good indication of minimizing prediction error.
3.3. Improving NN Model via Hyperparameter Grid-Search
Based on the results in the previous sections, the Influent WW (Group 1 WW) parameters can be modelled at good levels of fitness (high R
2 and low MAE) using a NN model (
Figure 6 and
Figure 7) consists of two hidden layers with 1000 units in the first layer (H1) and 32 units in the second layer (H2). However, using the same NN model for the Group 2 WW data subset, which is the WW subset for anoxic tank, aerobic tank, sedimentation tank and water outlet (effluent WW), did not perform as well, which can be seen in
Figure 5 (for other results, see
Supplementary Materials section for results spreadsheet). A possible solution to this issue, which is also an opportunity to demonstrate the flexibility of NN modelling approach, is the evaluation of hyperparameters beyond those used above, i.e., learning optimizer other than Adam, learning rate other than 0.0001, varied number of neurons in H1 and H2, etc. The hyperparameter grid-search implemented is summarized in
Table 2 with the corresponding best setting determined after the grid-search based on scoring using MAE.
Figure 8 shows pertinent graphical results after training the NN model consists of the best settings from the hyperparameter grid-search (
Table 2 column 2).
4. Discussion
First, we address the main questions posed in the introduction of the paper (
Section 4.1). Then we put into perspective the significance and possible future directions of the research work (
Section 4.2).
4.1. Answers to the Main Questions of the Study
Question 1: What data preprocessing tasks must be done on the WW spectral data to produce regression NN models with good prediction performance?
Based on the results shown in
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5, the WW dataset of a treatment facility may need to be grouped according to WW strength levels (high strength for Group 1 WW and low strength of Group 2 WW) for better performance of NN models. The apparent grouping of data in the plots of Y-vs-T for the whole WW dataset as shown in
Figure 3 was an interesting trend from a NN model trained for regression. Such grouping trends usually arise in classification type of NN modelling. The grouping trends in
Figure 3 indicates how the performance of a NN model can be good only when the data array being used as input has been properly preprocessed, which, in this case, was a simple grouping of the data into subsets according to the WW strength (Group 1 WW and Group 2 WW). Another preprocessing done implemented in this study was the scaling of the banded spectral reflectance data before feeding them as input to the NN models (see
Section 2.1.2). Scaling the input features allows for each feature, which is the spectral band in this case, to have standardized levels between 0 to 1 and this usually improves NN model training [
10].
Question 2: What are the effects of common hyperparameters in NN modeling: number of hidden layers and number of neuron units in each hidden layer?
The effects of the number of hidden layers and the neuron units are shown on
Figure 6 and
Figure 7 for the influent WW (Group 1 WW). In general, the higher the number of neuron units in a hidden layer results to better prediction performance. The same trend can also be seen for the effect of the number of hidden layers. This, however, does not mean that large number of hidden layers and neuron units always results to better model performance. Other studies have shown that large numbers of hidden layers and neuron units can result to overfitting of the model on the training set with the consequence of having poor prediction performance on the test set [
15]. So, the number of hidden layers and neuron units must be set accordingly perhaps with guidance from hyperparameter grid-search (
Section 3.3).
Question 3: How does the number of modelled outputs, i.e., WW parameters, affect the prediction performance of NN models?
In general, the NN models have their best prediction performance when the modelled output variable is a single WW parameter, i.e., BOD only, COD only, etc. as shown in
Figure 6 and
Figure 7. As more WW parameters are assigned as NN model output variables, the prediction performance can degrade. The implication of this finding is that the same spectral reflectance input data can be fed to separate NN models with each model assigned to a WW parameter to be estimated. This setup can be easily implemented in a computer running NN models. If the performance of a combination of WW parameters as outputs is acceptable, then NN models with multiple outputs may also be run for estimation.
Question 4: How can hyperparameter tuning on regression NN models improve prediction performance?
Hyperparameter tuning can boost the performance of a machine learning model such as NN model [
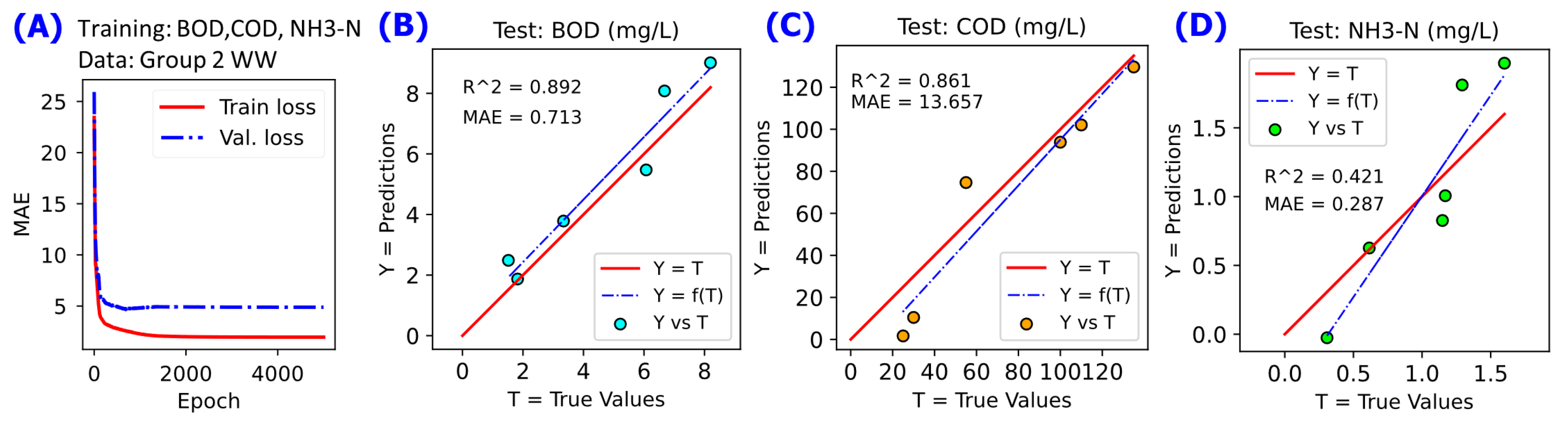
16]. The challenge with WW data subset of Group 2 WW is apparent in
Figure 5F–H, which shows that even though the NN model can have good performance on the Training set, the prediction performance of the model on the Test set may be very poor. One obvious limitation in the Group 2 WW subset data is the fewer number of observations (with 28 samples) compared to the Group 1 WW subset (with 57 samples). Machine learning models such as NN models improve in their prediction capabilities with increasing number of observations used in training. Given that this limitation on number of observations was limited by the source of the data, hyperparameter grid-search was the only approach left to try to improve the NN model performance on Group 2 WW subset. The results of the hyperparameter grid-search for improved prediction performance shown in
Table 2 and
Figure 8 indicate that there was an improvement in terms of higher R
2 values and lower MAE values compared to that of
Figure 5F–H. Even though the Y-vs-T R
2 and MAE in
Figure 8 for Group 2 WW are not close to those of the Group 1 WW shown in
Figure 6D, the improvements compared to those in
Figure 5F–H, are good indications of the potential of hyperparameter grid-search to improve NN models.
4.2. Perspective
The use of spectral reflectance has been a common technique in remote sensing such as low-orbit satellites designed to study earth’s water [
17,
18] and atmospheric data [
19]. Though such applications are in a large-scale aggregation of signals from the sources of spectral reflectance, they inspired the concept of also applying spectral reflectance in small-scale systems such as soil [
20,
21] and wastewater [
8] systems. The processing of such spectral data to estimate target variables poses a challenge in terms of the speed of data analytics when implemented in a process control system for a wastewater treatment facility and similar systems that can benefit from immediate signal conversion to system variable values. Unlike the analysis done by the originators of the dataset [
8], the use of NN models in this study eliminates the intermediate steps of fitting the raw spectral data to structured models of data filters, which usually result to loss of information from the original spectral signal. The NN models account for all signal features during the training stage.
After a NN model is trained, the estimation of the wastewater parameter levels when the spectral data is fed to the model takes just milliseconds to execute in a laptop computer of decent hardware specifications such as the one used in this work. An envisioned practical setup can be with the use of smaller hardware that can run such computations. With the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) in various systems, hardware dedicated to running AI programs with small physical size has been recently developed by leading companies such as NVIDIA with their Jetson Nano for implementing AI in mobile platforms [
22]. Such innovations in hardware can be leveraged to implement NN models integrated with off-the-shelf sensors of reflectance in the range of the spectral wavelength 400nm-2000nm used in the WW samples for the collection of the dataset [
8] used in this study. The traditional wired sensors connected to a centralized control room where the NN model estimations are run can also be a default implementation setup. The NN-enabled sensor system, however, will not totally eliminate the traditional WW sample-based chemical analysis method. Such sample chemical analysis will still be done but at less frequent occurrences to make sure that the NN model is within reasonable accuracy. The chemical analysis data will also be added to the training dataset where the NN model can be re-trained to refine the model parameters for better estimation.
Finally, an important consideration in using the proposed approach of using NN models trained on WW spectral reflectance is the acceptable range of error on the model output for a particular application.
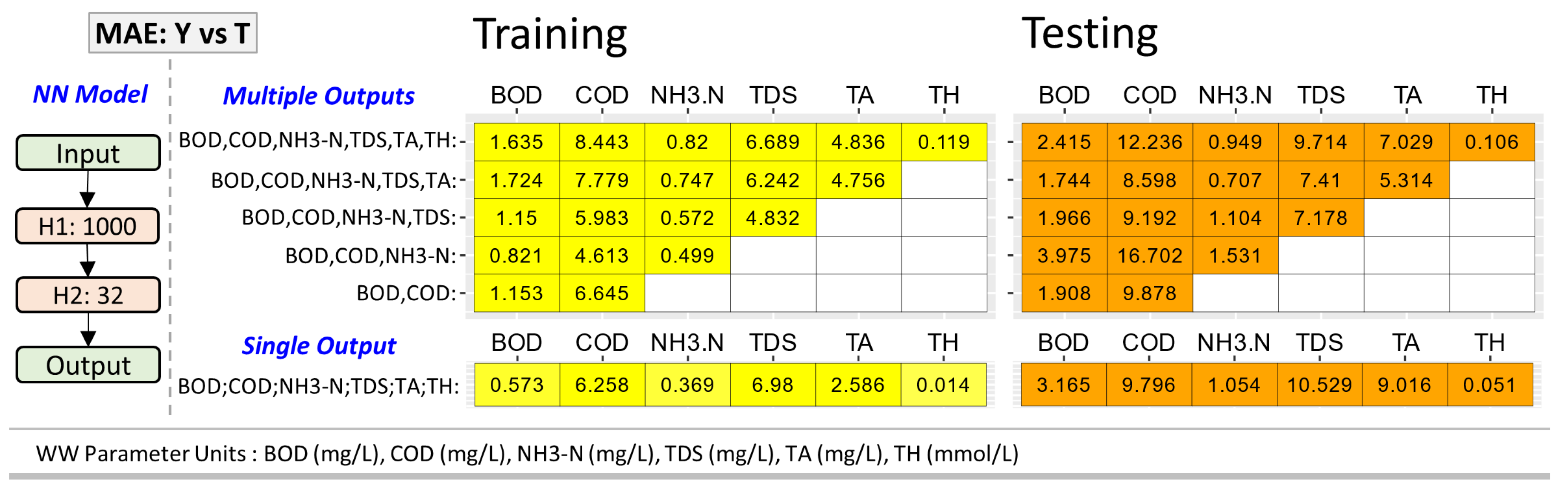
Figure 7 shows a summary of the MAE for various NN models. The MAE values represent the average error around the true values T by the estimate Y from the NN model. These errors may be acceptable in the process control system of a WW treatment facility, but these may not be acceptable errors for purposes requiring more stringent limits of error on WW parameters such as scheduled measurements according to regulatory agencies like US-EPA [
2]. Such more stringent WW analysis should still use the established chemical analysis for the various WW parameters amid longer analysis time. Hence, there is a trade-off between tolerance for error and the speed of spectral signal conversion to WW parameter levels via NN models.
5. Conclusions
Neural network (NN) models may accelerate the estimation of wastewater quality parameters (BOD, COD, NH3-N, TDS, TA, and TH) at minimal estimation error by using WW spectral reflectance as input data. The WW dataset in a treatment facility may need to be grouped according to WW stream strength for best NN model training and prediction. Various model hyperparameter settings can be configured to improve the prediction performance of NN models on WW quality parameters.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.L.B.F., and W.S.; methodology, D.L.B.F., and A.T.; software, D.L.B.F. and A.T.; formal analysis, D.L.B.F., A.P.M., W.S., E.R., R.H., W.H. and M.Z.; data curation, D.L.B.F.; project administration, D.L.B.F.; funding acquisition, D.L.B.F., A.T., and M.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the Louisiana Space Grant Consortium (LaSPACE) through the LURA sub-award PO-0000206339 under the main NASA grant number 80NSSC20M0110.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
We thank the supportive staff and students of the Department of Chemical Engineering and the Energy Institute of Louisiana at the University of Louisiana at Lafayette. We are also grateful to LaSPACE for supporting students who pursue research in STEM projects.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A. Pertinent Equations
A.1. Mean-Absolute-Error (MAE)
where
= true value of the wastewater parameters in observation sample
, and
= prediction on the levels of the wastewater parameters of observation sample
by NN model.
A.2. Coefficient of Determination (R2)
where
and
and
.
Note that can have negative values when the optimal model with prediction is worse than the mean of the true values , i.e., when .
References
- Liu, W.K., Z. Gan, and M. Fleming, Deep Learning for Regression and Classification, in Mechanistic Data Science for STEM Education and Applications, W.K. Liu, Z. Gan, and M. Fleming, Editors. 2021, Springer International Publishing: Cham. p. 171-214.
- US-EPA. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES): Municipal Wastewater. 2023; Available from: https://www.epa.gov/npdes/municipal-wastewater.
- Zhang, S., et al., Improved model-free adaptive predictive control method for direct data-driven control of a wastewater treatment process with high performance. Journal of Process Control, 2022. 110: p. 11-23.
- Li, F., Z. Su, and G.-m. Wang, An effective integrated control with intelligent optimization for wastewater treatment process. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 2021. 24: p. 100237. [CrossRef]
- Han, H.-G., et al., Hierarchical nonlinear model predictive control with multi-time-scale for wastewater treatment process. Journal of Process Control, 2021. 108: p. 125-135. [CrossRef]
- TensorFlow. Module: tf.keras. 2023 [cited 2023 2 July 2023]; Available from: https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras.
- Fortela, D.L.B. GitHub Repositpry: Neural Network Regression Modelling on Wastewater Spectral Reflectance. 2023 [cited 2023 2 July 2023]; Available from: https://github.com/dhanfort/WW_Spectra_NNlearning.git.
- Xing, Z., et al., Quantitative estimation of wastewater quality parameters by hyperspectral band screening using GC, VIP and SPA. PeerJ, 2019. 7: p. e8255.
- Scikit-Learn. Module: sklearn.preprocessing.MinMaxScaler. 2023 [cited 2023 2 July 2023]; Available from: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.preprocessing.MinMaxScaler.html.
- Scikit-Learn. Module: 6.3. Preprocessing data. 2023 [cited 2023 2 July 2023]; Available from: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/preprocessing.html.
- TensorFlow. Module: tf.keras.losses. 2023 [cited 2023 2 July 2023]; Available from: https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/losses.
- TensorFlow. Module: tf.keras.optimizers. 2023 [cited 2023 2 July 2023]; Available from: https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/optimizers.
- TensorFlow. Module: tf.keras.activations. 2023 [cited 2023 2 July 2023]; Available from: https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/activations.
- Scikit-Learn. Module: sklearn.model_selection.GridSearchCV. 2023 [cited 2023 2 July 2023]; Available from: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.model_selection.GridSearchCV.html.
- Goodfellow, I., Y. Bengio, and A. Courville, Deep Learning. 2016: MIT Press.
- Louis, O., Hyperparameter Tuning with Python: Boost your machine learning model’s performance via hyperparameter tuning. 2022: Packt Publishing. 1.
- Han, L. and D.C. Rundquist, Comparison of NIR/RED ratio and first derivative of reflectance in estimating algal-chlorophyll concentration: A case study in a turbid reservoir. Remote Sensing of Environment, 1997. 62(3): p. 253-261. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., C. Giardino, and L. Li Water Optics and Water Colour Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing, 2017. 9. [CrossRef]
- Joiner, J., et al., Use of Hyper-Spectral Visible and Near-Infrared Satellite Data for Timely Estimates of the Earth’s Surface Reflectance in Cloudy and Aerosol Loaded Conditions: Part 1–Application to RGB Image Restoration Over Land With GOME-2. Frontiers in Remote Sensing, 2022. 2.
- Wenjun, J., et al., In situ measurement of some soil properties in paddy soil using visible and near-infrared spectroscopy. PloS one, 2014. 9(8): p. e105708. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z., Y. Li, and H. Feng, Modeling soil cation concentration and sodium adsorption ratio using observed diffuse reflectance spectra. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 2016. 96(4): p. 372-385. [CrossRef]
- NVIDIA. NVIDIA Jetson Nano. 2023 [cited 2023 10 July 2023]; Available from: https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/autonomous-machines/embedded-systems/jetson-nano/.
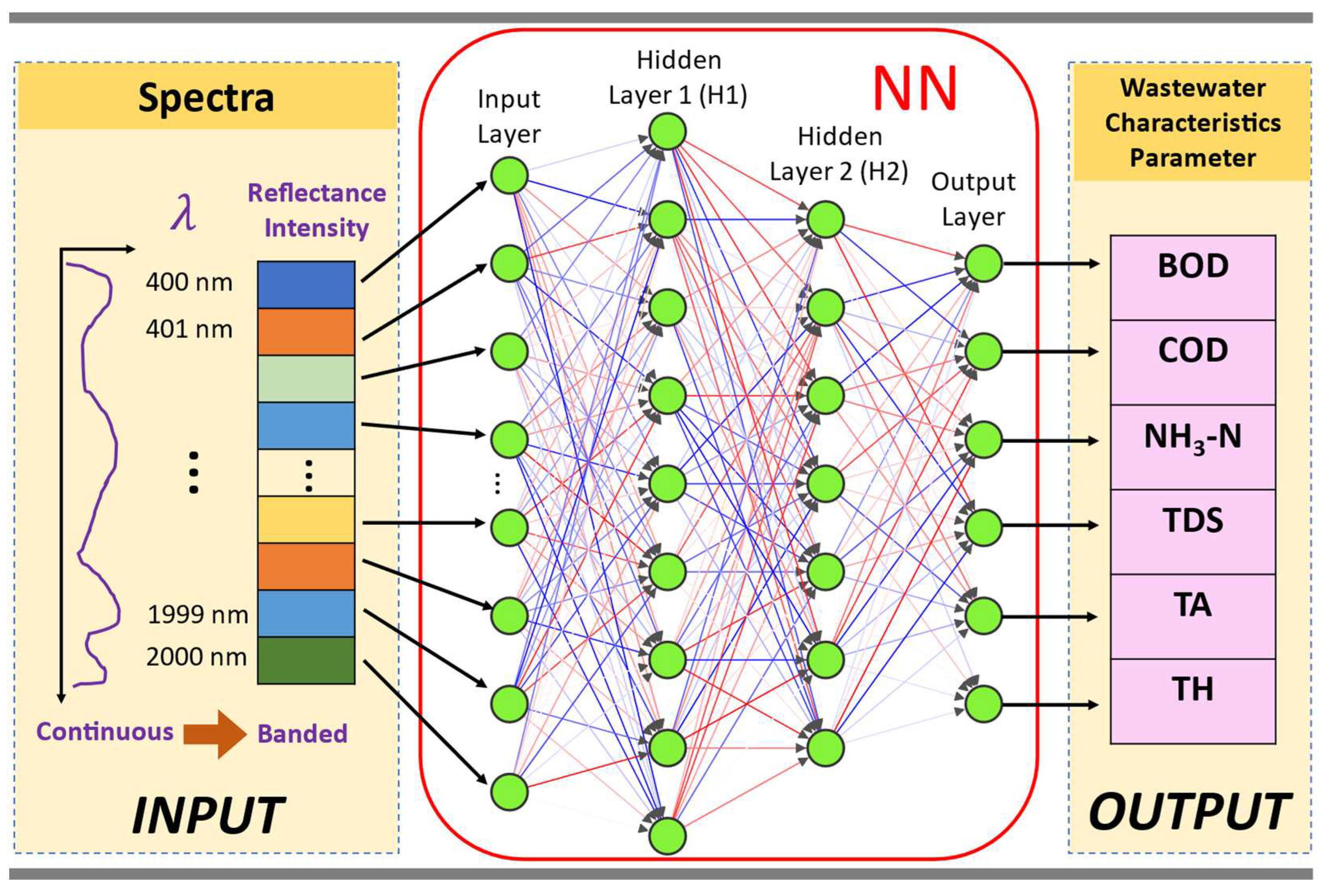
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the data analytics workflow implemented in this work. The wastewater spectral reflectance in the wavelength range of 400 nm to 2000 nm raw signal in continuous form is banded into 1-nm interval. Then the banded signal is used as input data to train the neural network (NN) model with the levels of wastewater parameters (BOD, COD, NH3-N, TDS, TA, and TH) as target outputs.
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the data analytics workflow implemented in this work. The wastewater spectral reflectance in the wavelength range of 400 nm to 2000 nm raw signal in continuous form is banded into 1-nm interval. Then the banded signal is used as input data to train the neural network (NN) model with the levels of wastewater parameters (BOD, COD, NH3-N, TDS, TA, and TH) as target outputs.
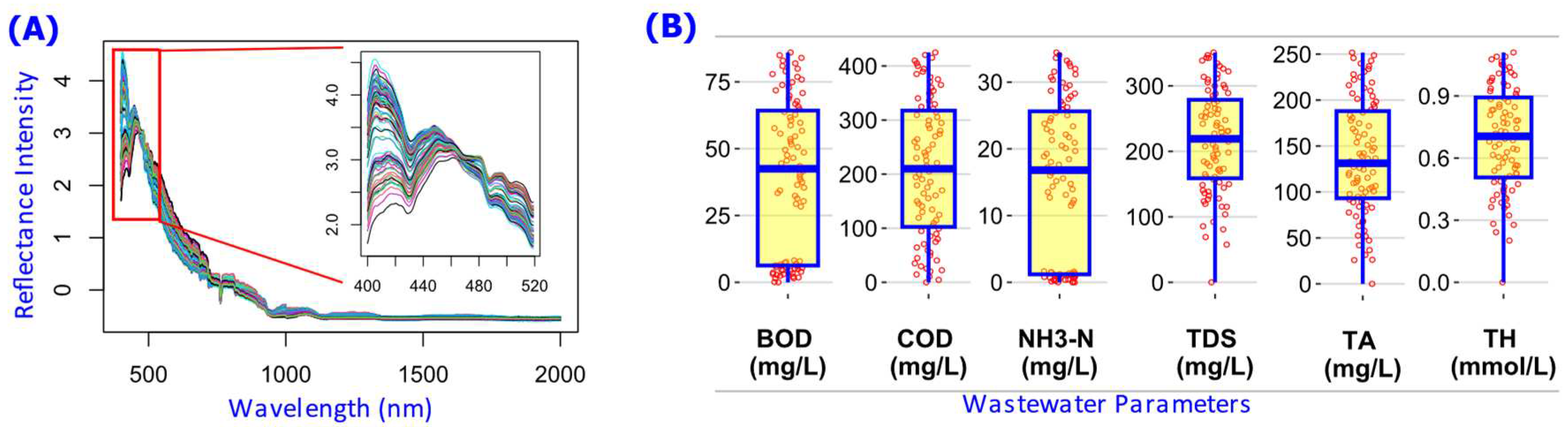
Figure 2.
Descriptive statistics of the wastewater spectral and quality parameters dataset. (
A) Plot of all the wastewater samples reflectance intensity over wavelength (nm), which is the input data to the NN models. (
B) Boxplots of the levels of wastewater parameters, which is the output data in training the NN models. The dataset is an open-source data originally collected by Xing, Chen [
8].
Figure 2.
Descriptive statistics of the wastewater spectral and quality parameters dataset. (
A) Plot of all the wastewater samples reflectance intensity over wavelength (nm), which is the input data to the NN models. (
B) Boxplots of the levels of wastewater parameters, which is the output data in training the NN models. The dataset is an open-source data originally collected by Xing, Chen [
8].
Figure 3.
Illustration on the need to train NN model dedicated to a wastewater stream group. One NN model may not be able to capture all trends as indicated by the two apparent groups in the prediction-versus-actual plots. Results of training, validation, and testing of the NN model with 1 hidden layer of 32 units of neurons. Annotated red solid line shows the reference relation Y = T. (A) NN model configuration implemented, (B) changes of cost function MAE during the training for 5000 epochs, (C) Y-vs-T of the training data for BOD, (D) Y-vs-T of the training data for COD, (E) Y-vs-T of the training data for NH3-N, (F) Y-vs-T of the test data for BOD, (G) Y-vs-T of the test data for COD, (H) Y-vs-T of the test data for NH3-N.
Figure 3.
Illustration on the need to train NN model dedicated to a wastewater stream group. One NN model may not be able to capture all trends as indicated by the two apparent groups in the prediction-versus-actual plots. Results of training, validation, and testing of the NN model with 1 hidden layer of 32 units of neurons. Annotated red solid line shows the reference relation Y = T. (A) NN model configuration implemented, (B) changes of cost function MAE during the training for 5000 epochs, (C) Y-vs-T of the training data for BOD, (D) Y-vs-T of the training data for COD, (E) Y-vs-T of the training data for NH3-N, (F) Y-vs-T of the test data for BOD, (G) Y-vs-T of the test data for COD, (H) Y-vs-T of the test data for NH3-N.
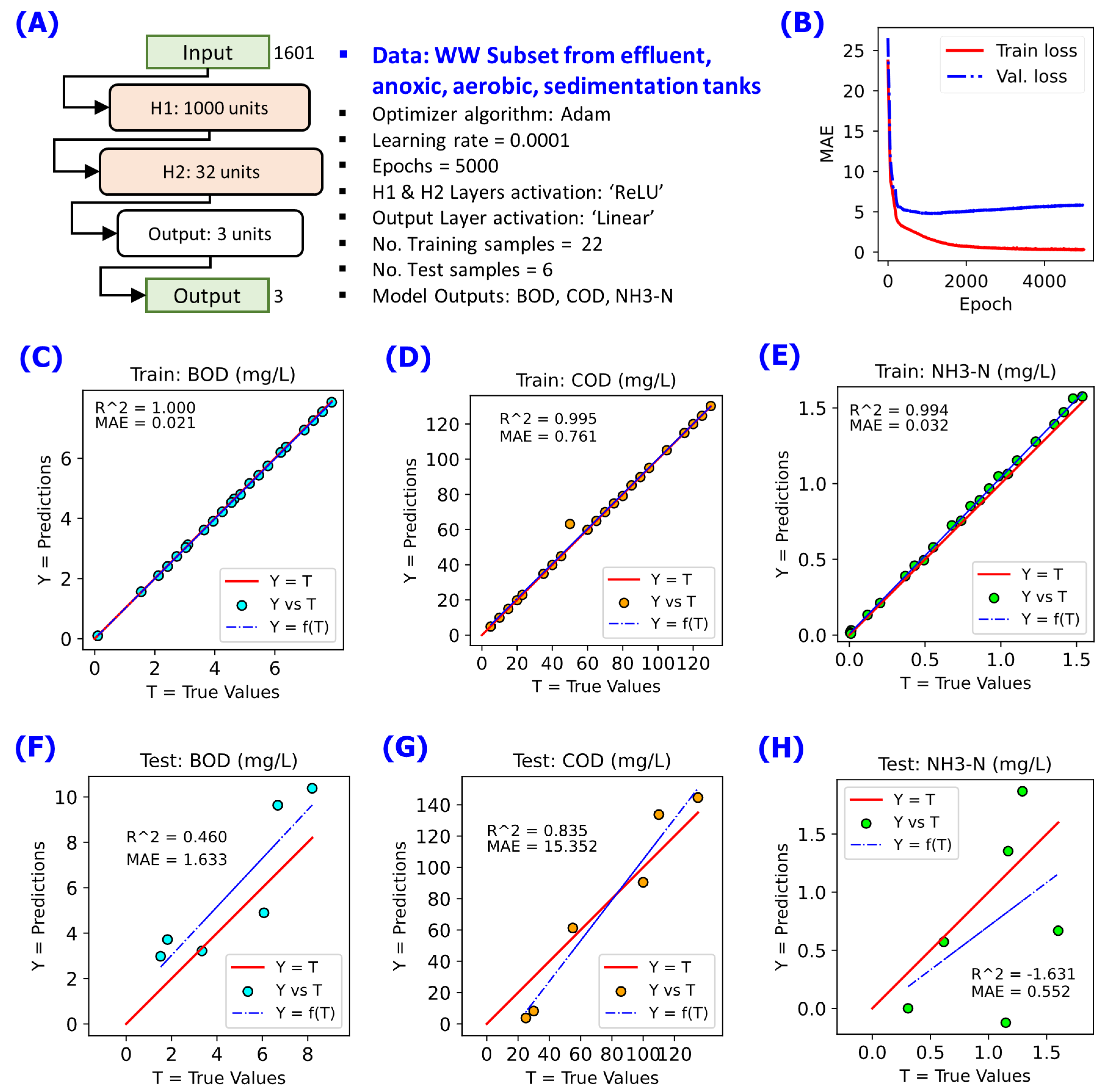
Figure 4.
NN modelling on the data subset for Group 1 WW (Influent WW) using 2 hidden layers consists of 1000 neuron units in first hidden payer H1 and 32 neuron units in second hidden payer H2. A linear fit Y = f(T) in blue dashed line is annotated to compare with reference line Y = T in red solid line. (A) NN model configuration implemented, (B) changes of cost function MAE during the training for 5000 epochs, (C) Y-vs-T of the training data for BOD, (D) Y-vs-T of the training data for COD, (E) Y-vs-T of the training data for NH3-N, (F) Y-vs-T of the test data for BOD, (G) Y-vs-T of the test data for COD, (H) Y-vs-T of the test data for NH3-N.
Figure 4.
NN modelling on the data subset for Group 1 WW (Influent WW) using 2 hidden layers consists of 1000 neuron units in first hidden payer H1 and 32 neuron units in second hidden payer H2. A linear fit Y = f(T) in blue dashed line is annotated to compare with reference line Y = T in red solid line. (A) NN model configuration implemented, (B) changes of cost function MAE during the training for 5000 epochs, (C) Y-vs-T of the training data for BOD, (D) Y-vs-T of the training data for COD, (E) Y-vs-T of the training data for NH3-N, (F) Y-vs-T of the test data for BOD, (G) Y-vs-T of the test data for COD, (H) Y-vs-T of the test data for NH3-N.
Figure 5.
NN modelling on the data subset for Group 2 WW subset using 2 hidden layers consists of 1000 neuron units in first hidden payer H1 and 32 neuron units in second hidden payer H2. A linear fit Y = f(T) in blue dashed line is annotated to compare with reference line Y = T in red solid line. (A) NN model configuration implemented, (B) changes of cost function MAE during the training for 5000 epochs, (C) Y-vs-T of the training data for BOD, (D) Y-vs-T of the training data for COD, (E) Y-vs-T of the training data for NH3-N, (F) Y-vs-T of the test data for BOD, (G) Y-vs-T of the test data for COD, (H) Y-vs-T of the test data for NH3-N.
Figure 5.
NN modelling on the data subset for Group 2 WW subset using 2 hidden layers consists of 1000 neuron units in first hidden payer H1 and 32 neuron units in second hidden payer H2. A linear fit Y = f(T) in blue dashed line is annotated to compare with reference line Y = T in red solid line. (A) NN model configuration implemented, (B) changes of cost function MAE during the training for 5000 epochs, (C) Y-vs-T of the training data for BOD, (D) Y-vs-T of the training data for COD, (E) Y-vs-T of the training data for NH3-N, (F) Y-vs-T of the test data for BOD, (G) Y-vs-T of the test data for COD, (H) Y-vs-T of the test data for NH3-N.
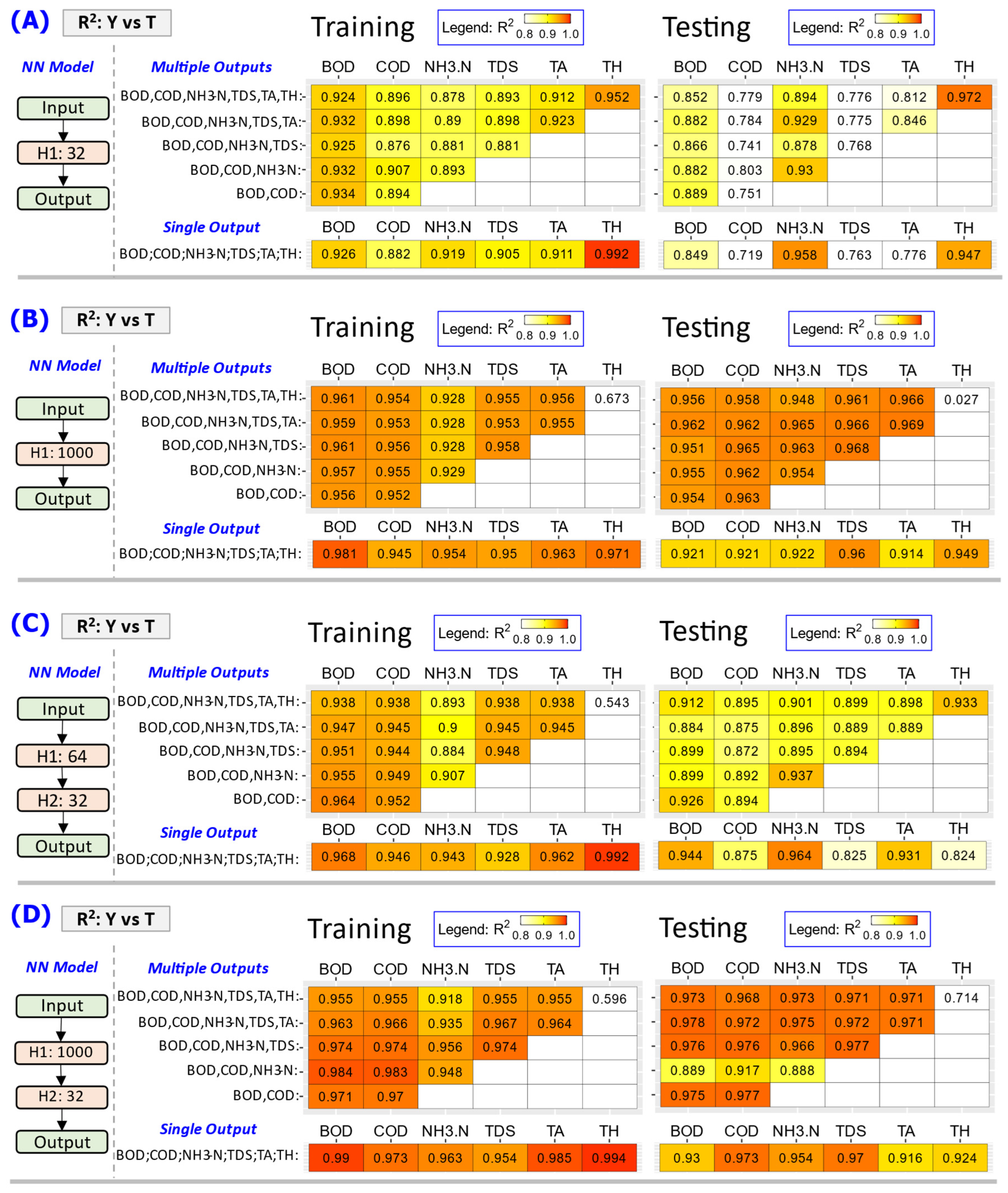
Figure 6.
Summary of R2 values between target T values and predicted Y values of the Influent WW (Group 1 WW) parameters from training and testing of NN model at varying model configurations and model output combinations. Color fill represents the R2 values with red being closest to 1.0 and no color fill for the R2 values lower than 0.8. (A) using NN model with 1 hidden layer (H1) of 32 neuron units, (B) using NN model with 1 hidden layer (H1) of 1000 neuron units, (C) using NN model with 2 hidden layers: 64 neurons units in first (H1) and 32 neuron units in second (H2), (D) using NN model with 2 hidden layers: 1000 neurons units in first (H1) and 32 neuron units in second (H2).
Figure 6.
Summary of R2 values between target T values and predicted Y values of the Influent WW (Group 1 WW) parameters from training and testing of NN model at varying model configurations and model output combinations. Color fill represents the R2 values with red being closest to 1.0 and no color fill for the R2 values lower than 0.8. (A) using NN model with 1 hidden layer (H1) of 32 neuron units, (B) using NN model with 1 hidden layer (H1) of 1000 neuron units, (C) using NN model with 2 hidden layers: 64 neurons units in first (H1) and 32 neuron units in second (H2), (D) using NN model with 2 hidden layers: 1000 neurons units in first (H1) and 32 neuron units in second (H2).
Figure 7.
Summary of mean-absolute-error (MAE) between target T values and predicted Y values of the Influent WW (Group 1 WW) parameters from training and testing of NN model with 2 hidden layers: 1000 neurons units in first (H1) and 32 neuron units in second (H2).
Figure 7.
Summary of mean-absolute-error (MAE) between target T values and predicted Y values of the Influent WW (Group 1 WW) parameters from training and testing of NN model with 2 hidden layers: 1000 neurons units in first (H1) and 32 neuron units in second (H2).
Figure 8.
NN modelling on the data for Group 2 WW subset using the NN model configured using the best settings from the hyperparameter grid-search (see
Table 2). A linear fit Y = f(T) in blue dashed line is annotated to compare with reference line Y = T in red solid line. (
A) cost function MAE value during the training for 5000 epochs, (
B) Y-vs-T of the test data for BOD, (
C) Y-vs-T of the test data for COD, (
D) Y-vs-T of the test data for NH
3-N.
Figure 8.
NN modelling on the data for Group 2 WW subset using the NN model configured using the best settings from the hyperparameter grid-search (see
Table 2). A linear fit Y = f(T) in blue dashed line is annotated to compare with reference line Y = T in red solid line. (
A) cost function MAE value during the training for 5000 epochs, (
B) Y-vs-T of the test data for BOD, (
C) Y-vs-T of the test data for COD, (
D) Y-vs-T of the test data for NH
3-N.
Table 1.
Summary of NN modelling run settings implemented in the study.
Table 1.
Summary of NN modelling run settings implemented in the study.
| NN Model Settings |
Model Output(s) Y Settings |
(1) 1 Hidden Layer: H1 w/ 32 neuron units
(2) 1 Hidden Layer: H1 w/ 1000 neuron units
(3) 2 Hidden Layers: H1 w/ 64 neuron units; H2 w/ 32 neuron units
(4) 2 Hidden Layers: H1 w/ 1000 neuron units; H2 w/ 32 neuron units |
Multiple Outputs:
(1) BOD, COD, NH3-N, TDS, TA, TH (all)
(2) BOD, COD, NH3-N, TDS, TA
(3) BOD, COD, NH3-N, TDS
(4) BOD, COD, NH3-N
(5) BOD, COD
Single Output:
(6) BOD; (7) COD; (8) NH3-N; (9) TDS; (10) TA; (11) TH |
| Total Number of Modelling Settings = (NN Model Settings) × (Model Output(s) Settings) = 4 × 11= 44 |
Table 2.
Hyperparameter grid-search levels used to determine the best NN model hyperparameters for training on the Group 2 WW dataset (WW data subset for anoxic tank, aerobic tank, sedimentation tank and WW effluent).
Table 2.
Hyperparameter grid-search levels used to determine the best NN model hyperparameters for training on the Group 2 WW dataset (WW data subset for anoxic tank, aerobic tank, sedimentation tank and WW effluent).
| NN Model Hyperparameter Grid-Search Settings |
Best NN Model Hyperparameter Setting |
| Optimizer: [‘Adam’, ‘Adadelta’, ‘SGD’] |
Optimizer: ‘Adam’ |
| Activation function in H1: [‘ReLU’, ‘Linear’] |
Activation function in H1: ‘Linear’ |
| Activation function in H2: [‘ReLU’, ‘Linear’] |
Activation function in H2: ‘ReLU’ |
| Activation function in output layer: [‘ReLU’, ‘Linear’] |
Activation function in output layer: ‘Linear’ |
| Number of neuron units in H1: [1600, 1000, 64] |
Number of neuron units in H1: 1000 |
| Number of neuron units in H2: [64, 32, 9] |
Number of neuron units in H2: 32 |
| Learning rate*: [0.00001, 0.0001, 0.001, 0.01] |
Learning rate*: 0.0001 |
Total hyperparameter grid-search settings with full-factorial grid via Scikit-Learn ‘GridSearchCV’ = 864
Epoch for each setting NN model training = 5000 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).