1. Introduction
Drug–drug interactions (DDIs) can have many adverse effects on the body. When two or more incompatible drugs are taken together, they can trigger a DDI, which can cause serious harm to the body. DDIs are therefore dangerous and can even be life-threatening when multiple drugs are used. Assessing this risk has prompted many research efforts aimed at determining whether two or more given drugs can be safely taken together. However, many diseases have complex pathological processes, and combination therapy with drugs has become an effective approach to treating diseases and relieving suffering.
In particular, when treating patients with multiple diseases [
1,
2], it is common to use a combination of two or more drugs, but drugs do not always interact with each other as expected. They may cause side effects that endanger the patient’s life. However, drug combination therapy involves a combination of multiple drugs, each typically used as a single treatment in patient populations. Since the various drugs in a drug combination can modulate the activity of different proteins, they can enhance the therapeutic effect by overcoming potential redundancies in biological processes. For example, the drug combination of venetoclax and idarubicin has recently been shown to have excellent anti-leukemia efficacy in treating acute myeloid leukemia [
3]. These two drugs act in an interactive manner, targeting complementary mechanisms simultaneously to improve cure rates [
3]. Although drug combination therapy is an effective approach to treating many diseases [
4], the major consequence of using multiple drug combinations in patients is a higher risk of side effects, which are caused by drug–drug interactions. The side effects of multiple drugs are difficult to identify manually, as it is almost impossible to test all possible drug combinations, and side effects are usually not observed in relatively few clinical trials [
5].
Furthermore, drug combination therapy is considered an increasingly serious problem affecting 15% of the US population in health care [
6]. In the US, over 177 billion is spent annually to treat side effects caused by multidrug combinations. According to statistics, 30% of adverse reactions in current reports are related to drug–drug interactions (DDIs), and side effects are also one of the main reasons for drug withdrawal from the market [
7], which can lead to a significant increase in morbidity and mortality [
1,
8]. Therefore, DDI has become a focus of clinical research (including DDI extraction [
9], DDI prediction tasks, etc.). The systematic screening of DDI candidates during clinical trials may be limited by human resources, and the rapidly growing amount of biomedical data cannot be processed even if it is available [
10], which results in unknown adverse interactions among many drugs in the market.
In medicine, the identification of DDIs is typically performed through extensive clinical trials in a drug research environment. However, testing involves using many combinations of drugs, making the whole process very expensive. Using computational methods to identify DDIs can serve as an inexpensive, fast, and rapid alternative by predicting the risk of potential DDIs by extracting knowledge from known DDIs. Drug chemistry knowledge indicates that a drug is composed of entities consisting of different functional groups (chemical substructures), which determine all their pharmacokinetic (how the organism processes it) and pharmacodynamic (how it affects the organism) properties, as well as their ultimate interactions. In existing methods that use substructure recognition to identify DDIs, each node is considered the center of a substructure, resulting in as many substructures as there are nodes. Adjacent nodes ultimately become centers of similar substructures, leading to redundancy, and a set of very similar substructures is overused, which can have many negative effects.
Over the past few decades, many machine learning and deep learning-based methods have made significant progress in identifying potential DDI risks between two drug combinations. However, most of these methods are limited in characterizing drug molecules. To address this issue, we used clustering or pooling algorithms to aggregate similar substructures and retain only one representative substructure. Therefore, we propose a new method for identifying DDIs based on substructure signature learning (DDI-SSL), which operates directly on the interaction representation between the original subgraphs of drugs to achieve more topologically preserved and physically interpretable feature extraction. Thus, substructure markers can be effectively used to aid in predicting drug–drug interactions. DDI-SSL provides the following technical contributions:
1) Improving the model’s interpretability. We use an attention mechanism to generate signal strength scores for subgraphs, and each substructure is marked with corresponding drug features weighted by learnable weights using an attention mechanism, which has the effect of producing flexible-sized and irregularly shaped substructures. Additionally, because the receptive field of message passing is variable, the model has high scalability. Both the freedom of the model and the interpretability of the model’s predictions have been significantly improved.
2) Improving the model’s generalization ability. Compared to the global molecular structure, DDI-SSL extracts useful information from local subgraphs centered on drug atoms, proposing an interaction modeling network to accurately mine the corresponding modality of drug composition individuals, thereby achieving modular representation of complex topological structures. The subgraph formula may project local structural details of the attribute graph into the subgraph signature set, reducing noise by anchoring relevant information. Meanwhile, the final representation of drugs is no longer a single vector but an expression of the connections between substructures, effectively improving the model’s generalization ability.
3) Incorporating a collaborative attention mechanism. DDI prediction between two drugs is based on the interaction score matrix learned between their substructures. However, the structural and property differences between molecules themselves can cause many irrelevant pairings, leading to the production of many unmergeable pieces of information. A collaborative attention mechanism can be used to model the mutual influence between drugs. The addition of collaborative attention effectively avoids this type of noise. This method provides an explanation for driving the DDI process and can provide domain experts with more detailed information, including which substructures may cause DDIs.
2. Related Work
Drugs are entities composed of different functional groups or chemical substructures, which determine their pharmacokinetic (how the organism processes them) and pharmacodynamic (how they affect the organism) properties, as well as the final interaction. Therefore, the processing of drugs depends on their similarity in chemical structure or other features, including their individual side effects, targets, etc. Many existing methods [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17] involve graph similarity calculations. For example, Zhang et al. [
18] established a set of prediction methods based on the similarity of 14 drugs. Later, [
17] proposed a matrix completion method for user DDI prediction, where drug similarity is used as the regularization part to preserve the manifold of drugs in a lower-dimensional space. The drawback of this assumption is that similar drugs (or general chemical entities) do not necessarily have the same biological activity [
8]. Even if they exhibit some similarity features, they may be irrelevant to the prediction task of interest.
In recent years, many deep learning methods have been proposed for drug–drug interaction (DDI) prediction [
7,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26], such as the multimodal deep autoencoder proposed by Zhang et al. [
24] and the graph autoencoder applied on a DDI network by Feng et al. [
25]. Despite the proven effectiveness of deep learning in other tasks, its potential in DDI prediction, especially in extracting features from the raw drug representation (i.e., chemical structure), has not been fully explored. Previous methods have relied solely on global structure when processing drug information, which can include irrelevant substructures and negatively affect predictions [
8,
27].
Two recent methods, MR-GNN [
20] and GoGNN [
28], have addressed these issues. Both utilize the powerful feature extraction capability of deep learning by directly processing the raw molecular graph representation [
29,
30,
31,
32] using graph neural networks (GNNs). They also consider the important role of substructures in DDI prediction in implicit ways. MR-GNN uses LSTM to learn a comprehensive feature representation for different drugs [
20], while GoGNN represents drugs as concatenations of different substructures [
28]. In contrast, SSI-DDI and other previous methods that use substructures to predict DDIs assume that each node is the center of a substructure, resulting in redundancy and noise from the huge differences between drug substructures.
However, these previous methods only model the similarities between drugs and do not reveal which substructures interact with each other. In contrast, our proposed method treats substructures as independent entities and learns adaptive substructures of various sizes and shapes from drug molecular graphs using substructure flags to capture the interactions between subspaces of drug properties. We then use this information to enrich the interaction between substructures and improve the embedding and model prediction. Additionally, our method characterizes DDIs using the overall probability score of drug interactions, demonstrating how to use the correlation and interaction between each substructure during DDI prediction to improve interpretability. We also use a collaborative attention mechanism to assist prediction, which improves the ability of both expert and nonexpert users to interpret the prediction results.
In addition, existing multimodal methods [
22,
33,
34] use drug features that include some chemical structures, externally introduced knowledge graphs, semantic information, etc., to assist the model in prediction by aggregating this high-order heterogeneous information. However, these methods contain considerable noise in the externally introduced heterogeneous information and ignore the complementarity between modalities. In contrast, DDI-SSL avoids using a large amount of heterogeneous information but instead explores the local substructures of drugs in depth. The subgraph formula allows the local structural details of the attribute graph to be projected onto the subgraph signature set, thereby reducing noise by anchoring relevant information and achieving modular representation of complex topological structures.
One of the most important types of methods is to enhance the transferability and generalization ability of molecular interaction prediction by introducing self-supervised contrast [
35]. Another type is to enhance the robustness of the model by constructing multivisual multiscale features [
36,
37,
38] to enhance the learning generalization ability. Both types of methods borrow from contrastive learning to maximize the mutual information of local and global contexts, including cross-level and scalar-level modules, and fuse internal and external features at different granularity levels. Among them, global representation is the representation of drug interaction graphs, and local representation is the representation of individual nodes. Although such methods construct the mutual information of global and local structures, they only apply to some scenarios, and the model needs to build a large number of positive and negative sample pairs. DDI-SSL projects the local structure of the attribute graph onto the subgraph signature set to explore local structural information. Finally, the collaborative attention mechanism is used to model the mutual influence between drugs, and the addition of collaborative attention effectively avoids the inherent heterogeneity in the structure and properties of molecules.
Another type of method is to learn some truly common substructures from molecular structures [
39,
40,
41] by reducing misleading other substructures to reduce unnecessary entity noise or balance the data distribution in a graph network. SumGNN introduces a knowledge graph [
40], which contains rich structural information but may also contain considerable noise. The algorithm generates inference paths by extracting local subgraphs to summarize subgraphs, uses transformer architecture to assign a learning weight to each edge in the subgraph by a self-attention module, and then prunes the edges in the entire subgraph according to the weight threshold. Although this type of method also uses substructures, on the one hand, the graph structure selects a knowledge graph, which requires considerable manpower. On the other hand, by extracting useful information from the local subgraphs around drugs, accurately mining the modality corresponding to the composition of drug components, and achieving modular representation of complex topological structures, DDI-SSL may project the local structural details of multiple attribute graphs onto the subgraph signature set and reduce noise by anchoring relevant information.
3. Model Framework
3.1. Problem Definition
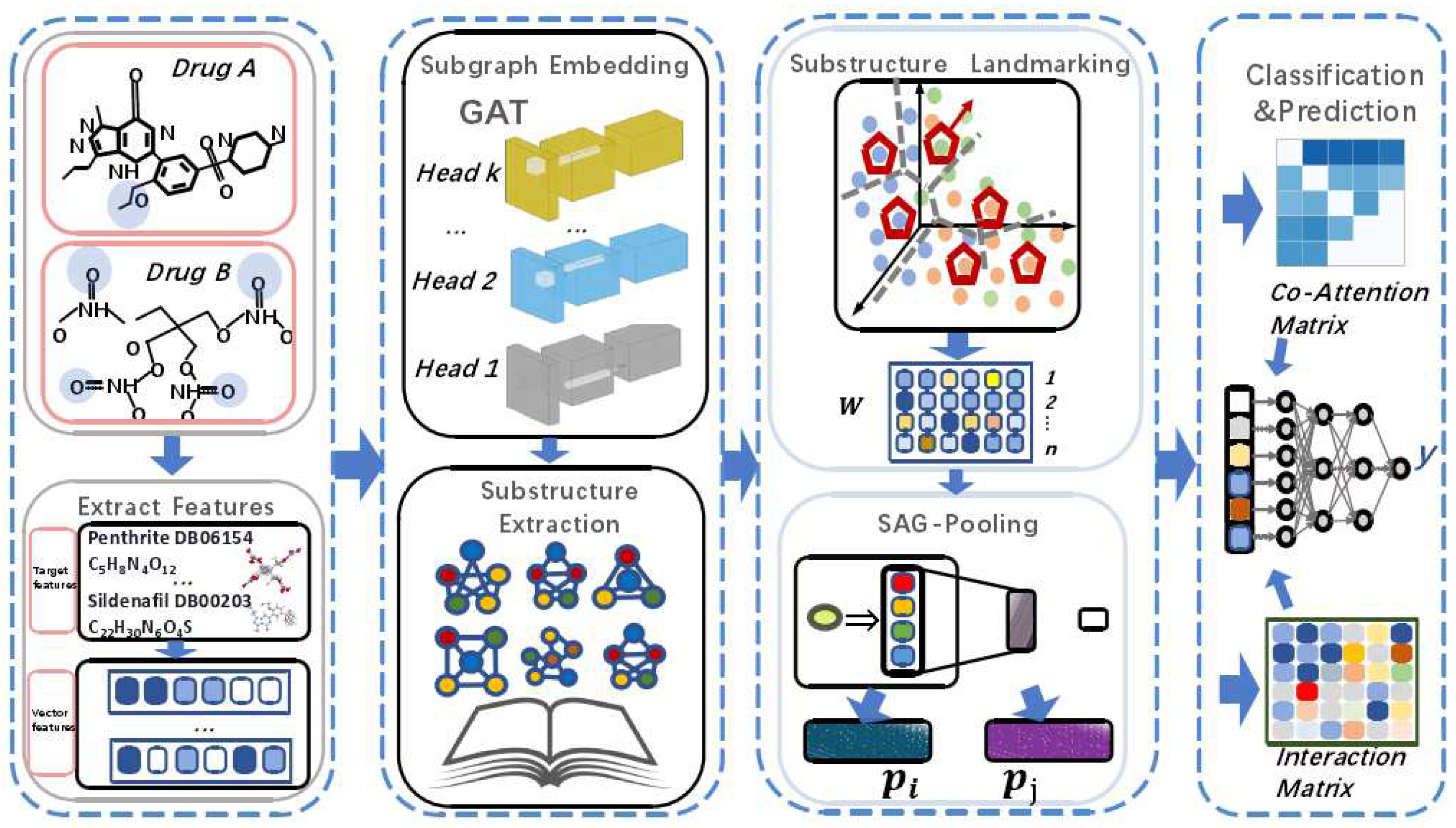
This section provides a formal definition of the problem and introduces the modules of the DDI-SSL framework in order, including input representation and computational steps. The overall framework is shown in
Figure 1.
Given a set of drugs G, a set of interaction types , and a DDI dataset , where and , denotes the interaction type, the goal is to train a model that can determine the probability of any combination of two drugs producing an interaction type .
3.2. Input
The model takes DDI tuples as input, where both drugs and are represented as an undirected graph , where is the set of nodes, is the set of edges, denotes the interaction type, and each interaction type is represented by a matrix . Initially, simply represents the chemical structure of the drug molecule, where represents an atom with a feature vector (where F is the number of features) and represents a chemical bond between atoms and .
3.3. Substructure Graph Convolution Operator
Duvenaud [
42] and Kearnes et al. [
43] have shown that learning features from chemical entity molecules provides more information than manually extracting molecule representations (e.g., molecular fingerprints). Common methods include graph neural networks (GNNs), which are deep learning methods designed for graph-structured data. GNNs mostly consist of graph convolutional operator layers, where node features are updated through aggregation of features from neighboring nodes [
44]. In this work, GAT layers [
30] are used as the convolutional operator for node feature updating. Attention mechanisms allow the model to handle inputs of variable sizes and focus on the parts of the features that are highly correlated. A linear transformation is applied to all node features in the graph:
where
is a learnable transformation matrix from the
l-th GAT layer to the
-th GAT layer. They determine the subspaces of node features and the interactions between subspaces. We use attention mechanisms [
45] to determine the importance of each (neighboring) node
j in neighborhood
of node
i and represent it as
. This importance indicates that not all nodes
have equal relevance in updating the feature vector of node
i, so each node is assigned a learnable importance weight
. The self-importance of node
i,
, is also considered to retain some information from itself. The importance of node
j to node
i,
, is computed as follows:
In this equation,
is an activation function (used to mitigate the zero-gradient problem that may occur with the ReLU activation function), and
is a learnable weight whose inner product is
. We concatenate
and
using
1 to obtain the following equation:
T is the transpose operator, which can also be computed as the dot product, || or concatenation. The model updates node
i by aggregating all nodes in
, where each node is scaled by its importance weight
according to equation
3. This produces a preactivated feature vector:
To use this feature vector as input to the next GAT layer, an activation function is applied to capture complex nonlinear signals and generate the activation feature vector for node
i, as shown below:
Here,
is the activation function. We use the
[
46] activation function, similar to [
30]; empirically, it also performs better than the most popular
activation function.
3.3.1. Multihead Attention
DDI-SSL also utilizes a multihead attention mechanism, where each attention head interacts between specific functional subspaces. By "cross-pollinating" information between each other, it proves useful for exploring complex real-world data. We employ
c GAT layers, and for each node
s, the multihead attention representation
is obtained through equation
1 to perform parallel linear transformations. From equation
2 to equation
4, the representation
generated by the
head for node
i will be concatenated to form the activated representation
, where || denotes concatenation.
3.3.2. Normalization
We also add a LayerNorm layer after the output of each GAT layer and use the
activation function. As using a LayerNorm layer [
47] yields the best results, we also consider using it, and equation
5 becomes:
Equation
6 can be modified in the same way. At the same time, initial normalization should be applied to the input data, which are then used as a normalized preprocessed input to the model. Initially, the feature of node
i is only related to the feature of the associated atom, but under the graph convolution operation, the feature of node
i begins to be concatenated with the features of the connecting nodes. Therefore, node
i no longer represents a simple atom but a substructure containing itself and its surrounding nodes.
3.4. Substructure Extraction
Through our research, we found that the convolution operation collects information from different substructures, and each substructure updates the feature vector
(as shown in equation
5) centered around
i. Meanwhile, its preactivation vector
contains substructure information composed of nodes
. As we move from the previous layer to the next, the range of the local neighborhood expands. In addition, some nodes that are not part of the substructures are also considered in the attention equation
2, enabling the learning of correlations between different substructures.
In the GAT layer, all substructure information (represented by a single node feature vector
) is aggregated (as shown in equation
4), and each substructure is represented by a learnable parameter
, which can be understood as its importance. We use
instead of
here because we only need the current layer’s output rather than the output modified by the nonlinear layer
. Therefore, all drug substructure information
identified in the
l-th layer can be represented by the following equation:
SAGPooling [
48] is used here to determine the importance
of each node in the graph. Given the graph with
and
, SAGPooling calculates the importance vector
(whose components are the coefficients
):
SAGPooling considers the context and topological information of nodes to determine their importance in the entire graph.
3.5. Substructure Signature Learning
The purpose of learning substructure flags is to map a large number of substructure instances onto K representative subgraph patterns so that any subgraph can be reconstructed by this global "topological dictionary". This approach not only preserves the similarity between subgraphs but also provides a unified modular platform for the representation of different attribute graphs.
This is also the basis for modeling individual interactions (projection pooling mechanism) by effectively preserving the identity of subgraph individuals and avoiding information loss caused by traditional methods. We use clustering or dictionary encoding to segment
n attribute graphs into
subgraph instances and learn
K flag vectors, whose criteria are as follows: (1) high coverage, subgraph flags should faithfully reflect the distribution of subgraphs; and (2) high discriminability, the graph representation formed by subgraph flags should significantly distinguish samples of different categories. The former is achieved through dictionary reconstruction, while the latter is ensured by an end-to-end learning framework. The subgraph flag matrix
can directly represent the subgraph flags. In addition, clustering can also be implemented through nonnegative dictionaries. Let
be the subgraph flag matrix and require that all subgraph instances within the attribute graph can be reconstructed by the column vectors of
, i.e., minimizing the following reconstruction error:
where
is the reconstruction coefficient of the
i-th subgraph in the attribute graph
with respect to the subgraph symbol
. In addition, subgraph symbols can also be calculated through deep clustering. We use a clustering indicator matrix
to cluster the subgraphs of each attribute graph
, where the
-th element represents the probability that the
j-th substructure of
belongs to the
k-th subgraph symbol of
, and the form of this probability can be determined by a Gaussian or
t-distribution function, for example:
Kullback–Leibler divergence can be trained to learn the above. The objective function is:
Here, is the sparse (self-sharpening) version of . Minimizing the KL divergence above ensures that each subgraph instance is only assigned to a small number of subgraph signature points, thus forming the dictionary reconstruction code for the coefficients. The choice of the number of subgraph signatures K is controlled by the complexity of the topology. For attribute graphs with large sizes and numbers of nodes, K should be chosen to be a sufficiently large value, also known as "structural resolution".
The pooling operator of the topology-preserving graph pooling algorithm projects the local structure of each graph onto common structural signatures , and the resulting graph representation dimension depends only on the number of structural signatures K rather than the number of nodes in the attribute graph. Therefore, fixed-dimensional graph representations can be obtained for attribute graphs of different sizes while approximately maintaining the identity of individual parts (substructures) and their interconnection relationships. This operator can realize the probability distribution of the substructure distribution in the graph representation attributes of the attribute graph: the density of substructure signatures in attribute graph can be calculated as , and each row of this density can be used as a representation of each drug atom after learning.
3.6. Substructure Interaction Correlation with Collaborative Attention
After obtaining all substructure information
and
of the input drugs
and
, respectively, through subgraph signature learning layers (partial chemical substructure extraction), the importance of each pairwise interaction between the substructures of
and
, denoted as
, is considered using a collaborative attention mechanism [
30]. The calculation is given by the following equation:
Here,
is a learnable weight vector, and
and
are learnable weight matrices. Different weight matrices are used to avoid high scores for predicting similar substructures. Unlike equations
2 and
9, no activation function is used in equation
13. Additionally, negative scores are expected to occur in some noninteracting drugs. Therefore, equation
14 is used to generate lower DDI probabilities. Finally, an activation function, such as tanh, is used to obtain the predicted solution.
3.7. Prediction and Loss Function
The following equation provides the probability of predicting the interaction between a pair of drugs
and
as
r:
Here,
is the sigmoid function, and
is the learned matrix that represents the interaction type
. Equation
14 considers the probability of a pair of drugs
producing interaction
r, which is determined by the reactions between the substructures of these drugs, and each combination also has a related weighting coefficient, which is the final DDI prediction result.
The model is trained end-to-end through gradient descent using cross-entropy. The given DDI in the dataset is considered a positive sample. For each positive sample
, negative samples can be generated by replacing
and
using the strategy proposed in [
48]. The loss function
L for the entire DDI dataset is calculated as follows:
Here,
and
are both calculated using equation
14.
corresponds to the probability calculated for the positive sample, while
corresponds to the probability calculated for the associated negative sample.
3.8. The Overall Algorithm of DDI-SSL
The DDI-SSL algorithm is shown in Algorithm 1. Given input drugs
and
and interaction matrix
r, multiple nodes generate feature matrices
and
. We use GAT to perform weighted calculation of the features to obtain new representations (Line 4) and at the same time use deep clustering algorithms to train substructure markers (Lines 6-9). Lines 10-13 calculate the collaborative attention. Finally, the probability of drug interaction is generated (Lines 15-17).
|
Algorithm 1:DDI-SSL Algorithm |
 |
4. Experimental Setup and Results Analysis
4.1. Datasets
For drug–drug interaction experiments, we use four datasets: DrugBank, TwoSides, DrugComb, and DrugCombDB, and the information about these four datasets is shown in
Table 1.
DrugBank [
7]: We use the DrugBank dataset to train our DDI prediction task [
7]. This dataset contains 1706 drugs and 383,496 DDIs, with 86 general sentence structures, each describing a specific type of DDI. The training data account for 80% of the total data. Drugs are associated with their SMILES string representations [
49], which are converted to graph representations using the open-source chemistry information library RDKit. For each drug, a graph is generated, where bonds represent edges and atoms represent nodes. For each atom
v, the feature vector
H is 55-dimensional and includes (1) atomic symbol (44, one-hot representation), (2) atomic degree (number of adjacent atoms), (3) implicit valence, (4) number of free electrons, (5) hybridization mode (5, one-hot representation), (6) whether the atom is aromatic, and (7) total number of hydrogens on the atom. Each DDI pair is treated as a positive sample, and a negative sample is generated from it. In this dataset, each DDI tuple has only one interaction.
TwoSides [
19]: Given by filtering the original TwoSides adverse drug data [
1] from [
19], this dataset contains 644 drugs and 499,582 DDI interaction pairs. In contrast to the DrugBank dataset, these interactions are at the phenotype level rather than the transcript level. That is, the interactions here are just adverse effects, such as headaches, sore throats, and symptoms such as those in [
19].
DrugComb [
50]: DrugComb aims to provide free access to standardized drug combination screening results. We collected and managed high-throughput drug combination screening datasets involving 4,146 drugs tested on 288 cancer cell lines from 10 different tissues in 659,333 combinations using computational tools available on network servers.
DrugCombDB [
51]: DrugCombDB covers 191,391 dual drug combinations, 2,956 unique drugs, and 112 cancer cell line samples.
4.2. Baselines
We compared our model with state-of-the-art methods that share some common features: (1) using molecular graphs as input; (2) integrating drug substructure information in some way during the learning process; and (3) considering the role of substructures in predicting drug–drug interactions (DDIs).
DeepDDI [
7] incorporates structural similarity profiles in the representation learning process and uses the Jaccard coefficient to predict DDI.
DeepSynergy [
52] uses chemical and genetic information as input and is applied to predict drug synergy.
MHCADDI [
26] uses a collaborative attention mechanism to integrate drug combination information.
MR-GNN [
20] captures different-sized structures of each drug using each graph convolutional layer of the nodes. These representations are then fed into a recurrent neural network for joint representation learning of a drug pair to make predictions.
CASTER [
52] uses an end-to-end dictionary learning framework to encode drug chemical structures.
SSI-DDI [
39] treats each node’s hidden feature as a substructure and computes the interaction between these substructures to ultimately determine the DDI.
EPGCN-DS [
53] achieves drug structure permutation invariance using a graph convolutional network and DeepSets.
DeepDrug [
54] learns graph representations of drugs and proteins using graph convolutional networks, e.g., residual structures, to optimize training.
GCN-BMP [
55] stacks multiple graph convolutional layers (a total of L layers) to learn representations of each node in the graph and constructs an attention-based graph pooling layer.
DeepDDS [
56] identifies cancer drug combinations using a deep learning model based on either graph convolutional networks or attention mechanisms.
MatchMaker [
57] uses drug chemical structure information to predict in a deep learning framework.
We reproduced these methods using PyTorch and made minor modifications to some of them to achieve better performance under fair comparison.
4.3. Experimental Settings
As shown in
Figure 1, the model learns drug pair representations by sharing GAT weights, achieved by reusing the same layers for both drugs. The algorithm consists of 4 GAT layers, each with
C multihead modules, set to 2, where each attention head calculates a 32-dimensional intermediate feature, resulting in the final output of the GAT layers being transformed into a 64-dimensional hidden feature vector. Following the GAT layers are LayerNorm layers and ELU activation functions. The LayerNorm layer is directly applied to the input data. Each interaction type
is represented by a learnable matrix
. The model uses the Adam optimizer [
58] to train on batches of 1024 DDI data, with weight decay set to 5e-4. A learning rate with exponential decay over time is designed as
, where
t is the epoch number, and the number of epochs is set to 200.
In this setting, the DDI tuples are randomly split into training (80% of data) and testing (20% of data) sets with the same proportion of interaction types. This process is repeated three times to generate three sets of randomly split datasets. Our proposed method and the settings for all baseline models are shown in
Table 2, where each model is trained and tested on each of the three datasets. The average and standard deviation of the results for each model from the three experiments are reported in
Table 3.
4.4. Experimental Implementation
The model is implemented using PyTorch, and the experiments were run on an NVIDIA RTX 3090 GPU with the Ubuntu operating system.
4.5. Experimental Results
In this experiment, DDI-SSL uses the following metrics: ACC, AUC-ROC, and F1-score. For the multiclass models (MR-GNN and DeepDDI), the microaverage measure of AUC is considered. Each method is run on the same split of the dataset. For MR-GNN, the original code provided by the authors is reused. DeepDDI and MHCADDI methods are also reimplemented according to the settings given in their respective original papers. The scores obtained by each method for each metric are shown in the bottom row of
Table 3. The DDI-SSL algorithm performs well on all three datasets, including DrugBank, where it shows improvement in scores. Although DeepSynergy exhibits high AUC performance on the DrugBank dataset, its metrics are not very reliable due to the imbalanced nature of the dataset. Even with very low true positive rates, multiclass classifiers often have high AUC scores. DDI-SSL also has a very high AUC score, indicating that it not only distinguishes interacting and noninteracting drugs but also has high accuracy.
Moreover, on the TwoSides and DrugComb datasets, DDI-SSL outperforms most other methods in terms of F1-score and AUC.
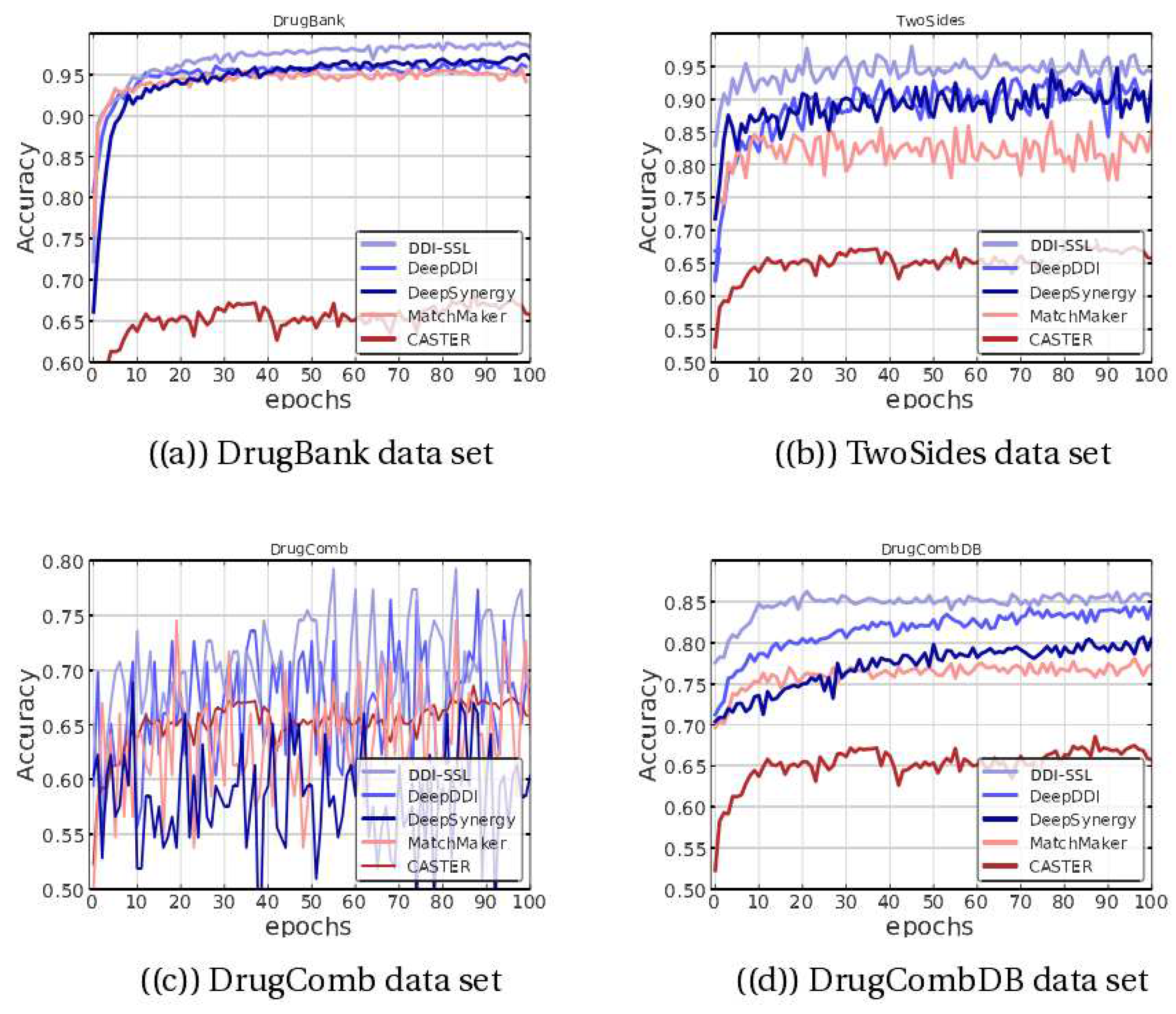
Figure 2 shows the accuracy (ACC) of different methods on the test set. On the DrugBank dataset, the DDI-SSL method shows improvement over DeepDDI, DeepSynergy, and others and converges more smoothly, ultimately approaching 100% accuracy. On the TwoSides dataset, the accuracy is significantly improved, and the convergence is also faster. On the DrugComb dataset, the performance is more oscillatory, and since multiple methods have oscillating ACC curves on this dataset, it suggests that the dataset itself has significant differences in distribution. Additionally, we found that DDI-SSL still has high accuracy on the DrugCombDB dataset, indicating that the model has strong stability on this type of dataset.
4.5.1. The Effect of Collaborative Attention
To investigate the interaction between substructure interaction and cooperative attention, the impact of removing the cooperative attention layer was examined.
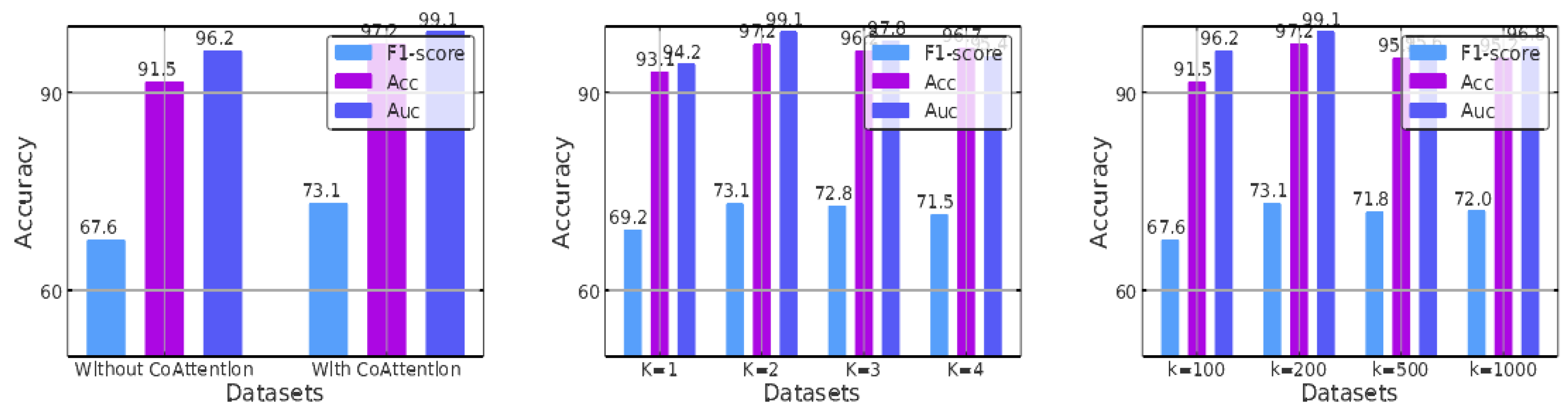
Figure 3(a) shows the AUC, ACC, and F1-score results obtained with and without the cooperative attention layer on the DrugBank validation set. It can be seen that the combination of cooperative attention does improve performance: under the same number of attention heads and markers, using cooperative attention leads to an improvement, and its removal causes a decline. This is because when matching the substructures of two different molecules, the structural and property differences between the molecules themselves can cause many irrelevant pairings, resulting in much unmergeable information. The addition of cooperative attention allows such noise to be effectively avoided.
4.5.2. The Effect of Multihead Attention
The experiment also compared the effect of different numbers of attention heads on the results. As shown in
Figure 3(b), the model performed best when the number of attention heads was two. Multiple attention heads allow exploration of different feature subspaces, which can improve the generalization performance of graph neural networks. When pursuing multihead attention, the computation of each head can be parallelized, giving the algorithm a special advantage. However, as the number of attention heads increases, the prediction results do not improve but gradually decrease, indicating that information interference reaches saturation.
4.5.3. The Effect of Number of Substructure Markers
In our experiments, we varied the number of substructures, denoted as K, to study its impact on the results. Specifically, we set
K to 100, 200, 500, and 1000. As shown in
Figure 3(c), we found that the model performed best when
K was set to 200. As the number of substructures increased beyond this point, the performance did not improve but rather gradually decreased. Therefore, if
K is too small (resulting in underfitting) or too large (resulting in overfitting), the accuracy may decrease. Generally, the optimal performance can be achieved when
K is approximately its median value.
5. Conclusion and Discussion
We propose a novel method, called DDI-SSL, for identifying drug–drug interactions (DDIs) by learning substructure patterns, which can effectively assist in predicting drug side effects.
First, we analyze that previous methods relying on global structures may lead to inaccurate results in handling drug information. We use a self-attention mechanism to generate signal strength scores for subgraphs, and each substructure is marked with corresponding drug features weighted by learnable weights, which can produce flexible-sized and irregularly shaped results. Due to the variable receptive field of message passing, our method has high scalability. Moreover, we accurately extract information from local drug subgraphs to identify the corresponding modules of the composed individuals. Subgraph formulas allow the projection of local structural details of attribute maps onto subgraph signature sets, which reduces noise by anchoring relevant information, thereby achieving modular representation of complex topological structures. Finally, we model the mutual influence between drugs by introducing a cooperative attention mechanism, which effectively avoids noise in molecular structures and properties. Comprehensive experiments on DDI datasets demonstrate the improvement of the DDI-SSL model and the contribution of each improvement point.
Future research will leverage message passing and other methods to capture the topological relationships and semantic information of larger-scale protein atoms and bonds by representing nodes and edges in graph networks. In addition to drug–drug interactions, research in the field of graph neural networks has also made progress in learning protein structure and predicting temporal dynamics. However, challenges remain in protein dynamics prediction tasks, such as the need to dynamically capture complex structural spatiotemporal changes and use long-range correlations at different time scales. To better understand the physiological mechanisms behind protein dynamics, a new interaction modeling graph neural network framework that captures long-range dynamic spatiotemporal correlations is urgently needed to provide prediction and interpretation for protein dynamics research in target interactions.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Guangxi Key Laboratory of Trusted Software (no. KX202037), the Project of Guangxi Science and Technology (no. GuiKeAD 20297054), and the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation Project (no. 2020GXNSFBA297108).
References
- Tatonetti, N.P.; Ye, P.P.; Daneshjou, R.; Altman, R.B. Data-driven prediction of drug effects and interactions. Science Translational Medicine 2012, 4, 125ra31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Jeng, E.E.; Hess, G.T.; Morgens, D.W.; Li, A.; Bassik, M.C. Synergistic drug combinations for cancer identified in a CRISPR screen for pairwise genetic interactions. Nature Biotechnology 2017, 35, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.; Ruvolo, V.; Mu, H.; Leverson, J.D.; Nichols, G.; Reed, J.C.; Konopleva, M.; Andreeff, M. Synthetic lethality of combined Bcl-2 inhibition and p53 activation in AML: mechanisms and superior antileukemic efficacy. Cancer cell 2017, 32, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebler, D.C.; Guengerich, F.P. Elucidating mechanisms of drug-induced toxicity. Nature reviews Drug discovery 2005, 4, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, M.; Yang, J.; Karan, C.; Menden, M.P.; Costello, J.C.; Tang, H.; Xiao, G.; Li, Y.; Allen, J.; Zhong, R.; et al. A community computational challenge to predict the activity of pairs of compounds. Nature biotechnology 2014, 32, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, F.R.; Grizzle, A.J. Drug-related morbidity and mortality: updating the cost-of-illness model. Journal of the American Pharmaceutical Association (1996) 2001, 41, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.Y.; Kim, H.U.; Lee, S.Y. Deep learning improves prediction of drug–drug and drug–food interactions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2018, 115, E4304–E4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, R.B.; Holladay, M.W. The Organic Chemistry of Drug Design and Drug Action (Third Edition); Academic Press, 2014.
- Zhang, T.; Leng, J.; Liu, Y. Deep learning for drug-drug interaction extraction from the literature: a review. Briefings Bioinform. 2020, 21, 1609–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitebread, S.; Hamon, J.; Bojanic, D.; Urban, L. Keynote review: in vitro safety pharmacology profiling: an essential tool for successful drug development. Drug Discovery Today 2005, 10, 1421–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Mao, K.T.; Shi, J.Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, Z.; Dong, K.; Yiu, S.M. Predicting and understanding comprehensive drug-drug interactions via semi-nonnegative matrix factorization. BMC Systems Biology 2018, 12, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, A.; Stein, G.Y.; Oron, Y.; Ruppin, E.; Sharan, R. INDI: a computational framework for inferring drug interactions and their associated recommendations. Molecular Systems Biology 2012, 8, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, P.; Qu, X.A.; Sanseau, P.; Yang, L. Systematic prediction of drug combinations based on clinical side-effects. Scientific reports 2014, 4, 7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Cui, H.; Huang, T.; Wang, D.; Lian, B.; Li, W.; Qin, G.; Chen, L.; Xie, L. Prediction of synergistic anti-cancer drug combinations based on drug target network and drug induced gene expression profiles. Artificial intelligence in medicine 2017, 83, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastrin, A.; Ferk, P.; Leskošek, B. Predicting potential drug-drug interactions on topological and semantic similarity features using statistical learning. PloS one 2018, 13, e0196865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdousi, R.; Safdari, R.; Omidi, Y. Computational prediction of drug-drug interactions based on drugs functional similarities. Journal of biomedical informatics 2017, 70, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Yue, X. Manifold regularized matrix factorization for drug-drug interaction prediction. Journal of biomedical informatics 2018, 88, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, F.; Luo, F.; Tian, G.; Li, X. Predicting potential drug-drug interactions by integrating chemical, biological, phenotypic and network data. BMC bioinformatics 2017, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitnik, M.; Agrawal, M.; Leskovec, J. Modeling polypharmacy side effects with graph convolutional networks. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i457–i466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wang, P.; Chen, L.; Tao, J.; Zhao, J. Mr-gnn: Multi-resolution and dual graph neural network for predicting structured entity interactions. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.09558, arXiv:1905.09558 2019.
- Huang, K.; Xiao, C.; Hoang, T.N.; Glass, L.; Sun, J. CASTER: Predicting Drug Interactions with Chemical Substructure Representation. In Proceedings of the AAAI 2020; pp. 702–709.
- Deng, Y.; Xu, X.; Qiu, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, S. A multimodal deep learning framework for predicting drug–drug interaction events. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 4316–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Xiao, C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, F. Drug Similarity Integration Through Attentive Multi-view Graph Auto-Encoders. In Proceedings of the IJCAI 2018; pp. 3477–3483.
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W. Predicting drug-drug interactions using multi-modal deep auto-encoders based network embedding and positive-unlabeled learning. Methods 2020, 179, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.H.; Zhang, S.W.; Shi, J.Y. DPDDI: a deep predictor for drug-drug interactions. BMC bioinformatics 2020, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deac, A.; Huang, Y.H.; Veličković, P.; Liò, P.; Tang, J. Drug-drug adverse effect prediction with graph co-attention. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.00534, arXiv:1905.00534 2019.
- Jia, J.; Zhu, F.; Ma, X.; Cao, Z.W.; Li, Y.X.; Chen, Y.Z. Mechanisms of drug combinations: interaction and network perspectives. Nature reviews Drug discovery 2009, 8, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Lian, D.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, L.; Lin, X. Gognn: Graph of graphs neural network for predicting structured entity interactions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.05537, arXiv:2005.05537 2020.
- Defferrard, M.; Bresson, X.; Vandergheynst, P. Convolutional Neural Networks on Graphs with Fast Localized Spectral Filtering. In Proceedings of the NIPS 2016; pp. 3837–3845.
- Velickovic, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Liò, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph Attention Networks. In Proceedings of the ICLR 2018.
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-Supervised Classification with Graph Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the ICLR 2017.
- Gilmer, J.; Schoenholz, S.S.; Riley, P.F.; Vinyals, O.; Dahl, G.E. Neural Message Passing for Quantum Chemistry. In Proceedings of the ICML 2017, Vol. 70, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp.; pp. 1263–1272.
- Lin, X.; Quan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ma, T.; Zeng, X. KGNN: Knowledge Graph Neural Network for Drug-Drug Interaction Prediction. In Proceedings of the IJCAI 2020; pp. 2739–2745.
- Lyu, T.; Gao, J.; Tian, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J. MDNN: A Multimodal Deep Neural Network for Predicting Drug-Drug Interaction Events. In Proceedings of the IJCAI 2021; pp. 3536–3542.
- Zhao, C.; Liu, S.; Huang, F.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W. CSGNN: Contrastive Self-Supervised Graph Neural Network for Molecular Interaction Prediction. In Proceedings of the IJCAI 2021; pp. 3756–3763.
- Wang, Y.; Min, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, J. Multi-view Graph Contrastive Representation Learning for Drug-Drug Interaction Prediction. In Proceedings of the WWW 2021; pp. 2921–2933.
- Fu, H.; Huang, F.; Liu, X.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, W. MVGCN: data integration through multi-view graph convolutional network for predicting links in biomedical bipartite networks. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, T.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Song, B.; Zeng, X. MUFFIN: multi-scale feature fusion for drug–drug interaction prediction. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 2651–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamabo, A.K.; Yu, H.; Shi, J.Y. SSI–DDI: substructure–substructure interactions for drug–drug interaction prediction. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2021, 22, bbab133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, K.; Zhang, C.; Glass, L.M.; Sun, J.; Xiao, C. SumGNN: multi-typed drug interaction prediction via efficient knowledge graph summarization. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 2988–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.; Hu, Z.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, S. Learning Unknown from Correlations: Graph Neural Network for Inter-novel-protein Interaction Prediction. In Proceedings of the IJCAI 2021; pp. 3677–3683.
- Huang, K.; Xiao, C.; Glass, L.M.; Sun, J. MolTrans: molecular interaction transformer for drug–target interaction prediction. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvenaud, D.; Maclaurin, D.; Aguilera-Iparraguirre, J.; Gómez-Bombarelli, R.; Hirzel, T.; Aspuru-Guzik, A.; Adams, R.P. Convolutional Networks on Graphs for Learning Molecular Fingerprints. In Proceedings of the NIPS 2015; pp. 2224–2232.
- Kearnes, S.; McCloskey, K.; Berndl, M.; Pande, V.; Riley, P. Molecular graph convolutions: moving beyond fingerprints. Journal of computer-aided molecular design 2016, 30, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.L.; Hannun, A.Y.; Ng, A.Y.; et al. Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In Proceedings of the Proc. icml, Vol. 30; 2013; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Proceedings of the NIPS 2017; pp. 5998–6008.
- Lee, J.; Lee, I.; Kang, J. Self-Attention Graph Pooling. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML 2019, 9-15 June 2019, Long Beach, California, USA, Vol. 97, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp.; pp. 3734–3743.
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J.; Chen, Z. Knowledge Graph Embedding by Translating on Hyperplanes. In Proceedings of the AAAI 2014; pp. 1112–1119.
- Zagidullin, B.; Aldahdooh, J.; Zheng, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Saad, J.; Malyutina, A.; Jafari, M.; Tanoli, Z.; Pessia, A.; et al. DrugComb: an integrative cancer drug combination data portal. Nucleic acids research 2019, 47, W43–W51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Zou, B.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Deng, L. DrugCombDB: a comprehensive database of drug combinations toward the discovery of combinatorial therapy. Nucleic acids research 2020, 48, D871–D881. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Preuer, K.; Lewis, R.P.; Hochreiter, S.; Bender, A.; Bulusu, K.C.; Klambauer, G. DeepSynergy: predicting anti-cancer drug synergy with Deep Learning. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1538–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Wang, F.; Elemento, O.; Zhou, J. Structure-Based Drug-Drug Interaction Detection via Expressive Graph Convolutional Networks and Deep Sets (Student Abstract). In Proceedings of the AAAI 2020; pp. 13927–13928.
- Yin, Q.; Cao, X.; Fan, R.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, R.; Zeng, W. DeepDrug: A general graph-based deep learning framework for drug-drug interactions and drug-target interactions prediction. bioRxiv, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, J. GCN-BMP: investigating graph representation learning for DDI prediction task. Methods 2020, 179, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Shen, S.; Deng, L.; Liu, H. DeepDDS: deep graph neural network with attention mechanism to predict synergistic drug combinations. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2022, 23, bbab390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuru, H.I.; Tastan, O.; Cicek, A.E. MatchMaker: a deep learning framework for drug synergy prediction. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics 2021, 19, 2334–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weininger, D. SMILES, a chemical language and information system. 1. Introduction to methodology and encoding rules. Journal of chemical information and computer sciences 1988, 28, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).