Submitted:
17 July 2023
Posted:
18 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction:
1.1. NLR, PLR and MLR – from prognostic markers to future orchestrator of HNC multimodal approach?
2. Materials and methods:
3. Results:
| Characteristics | N (total =40) | % |
|---|---|---|
| Age at the time of diagnostic | ||
| Median (range) | 64.84 years (48-86 years). | - |
| Histology | ||
| squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) | 39 | 100 |
| Anatomical tumor site | ||
| oropharynx | 11 | 28,2 |
| oral cavity | 13 | 33,33 |
| larynx | 7 | 17,94 |
| nasopharynx | 1 | 2,55 |
| unknow priary | 2 | 5,1 |
| sinonasal | 1 | 2,55 |
| parathyroid | 1 | 2,55 |
| NLR | ||
| Mean (range) | 6.22 (1,24-69) | |
| PLR | ||
| Mean (range) | 203.17 (61.3-1775.0) | |
| MLR | ||
| Mean (range) | 0.53 (0.12-5.5) | |
| Overall survival (OS) | ||
| Median (range) | 17.92 (1-120) |
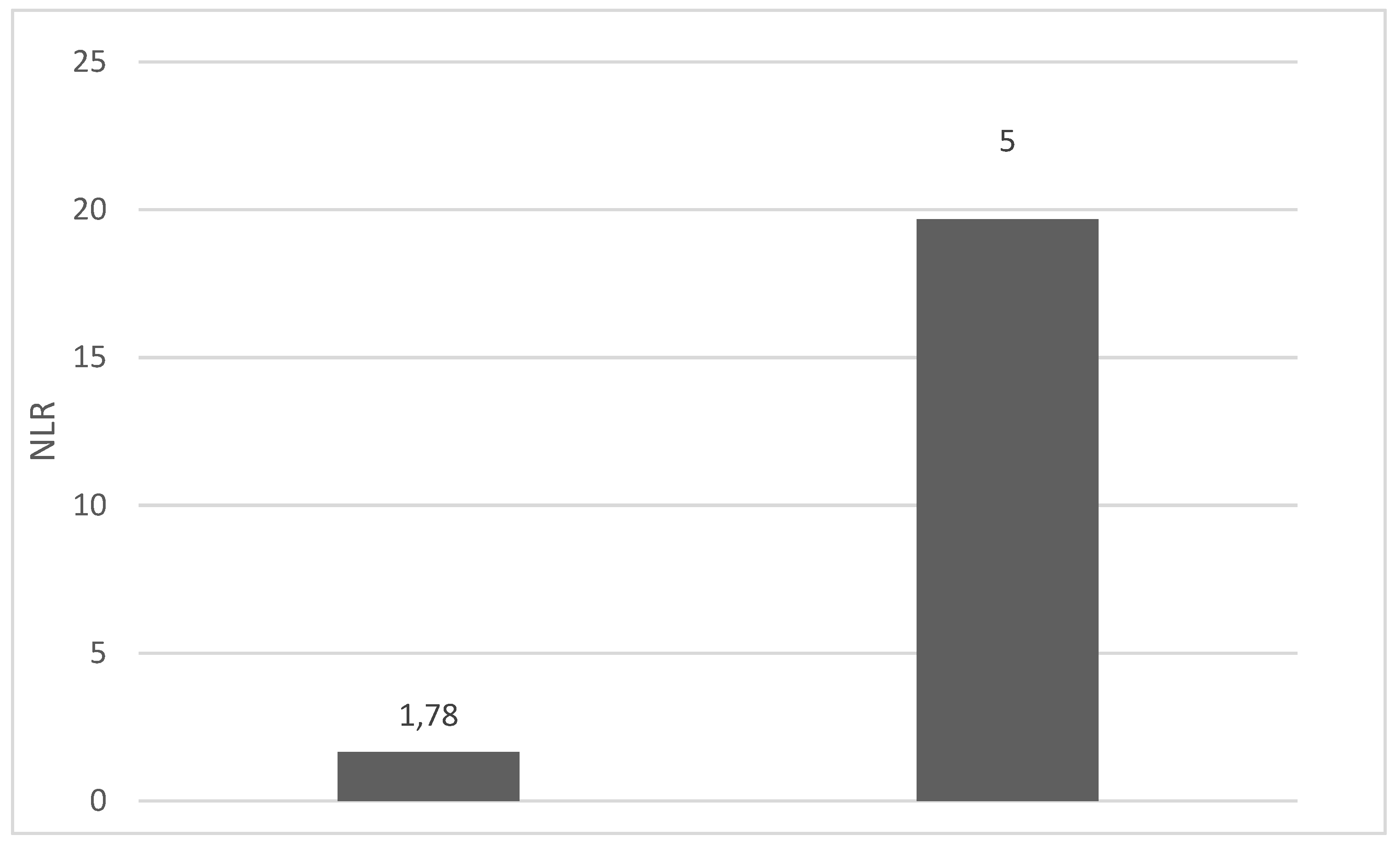
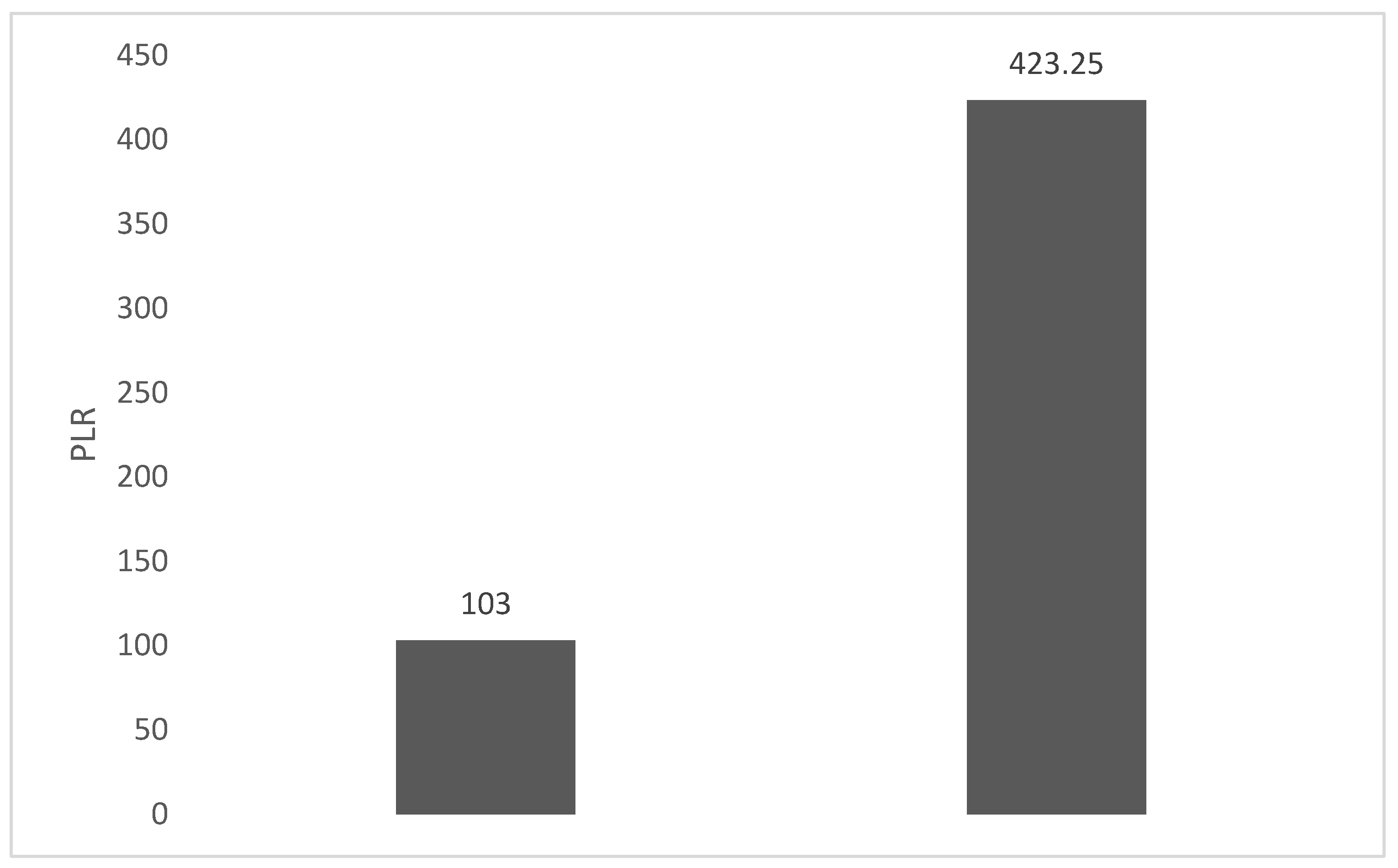
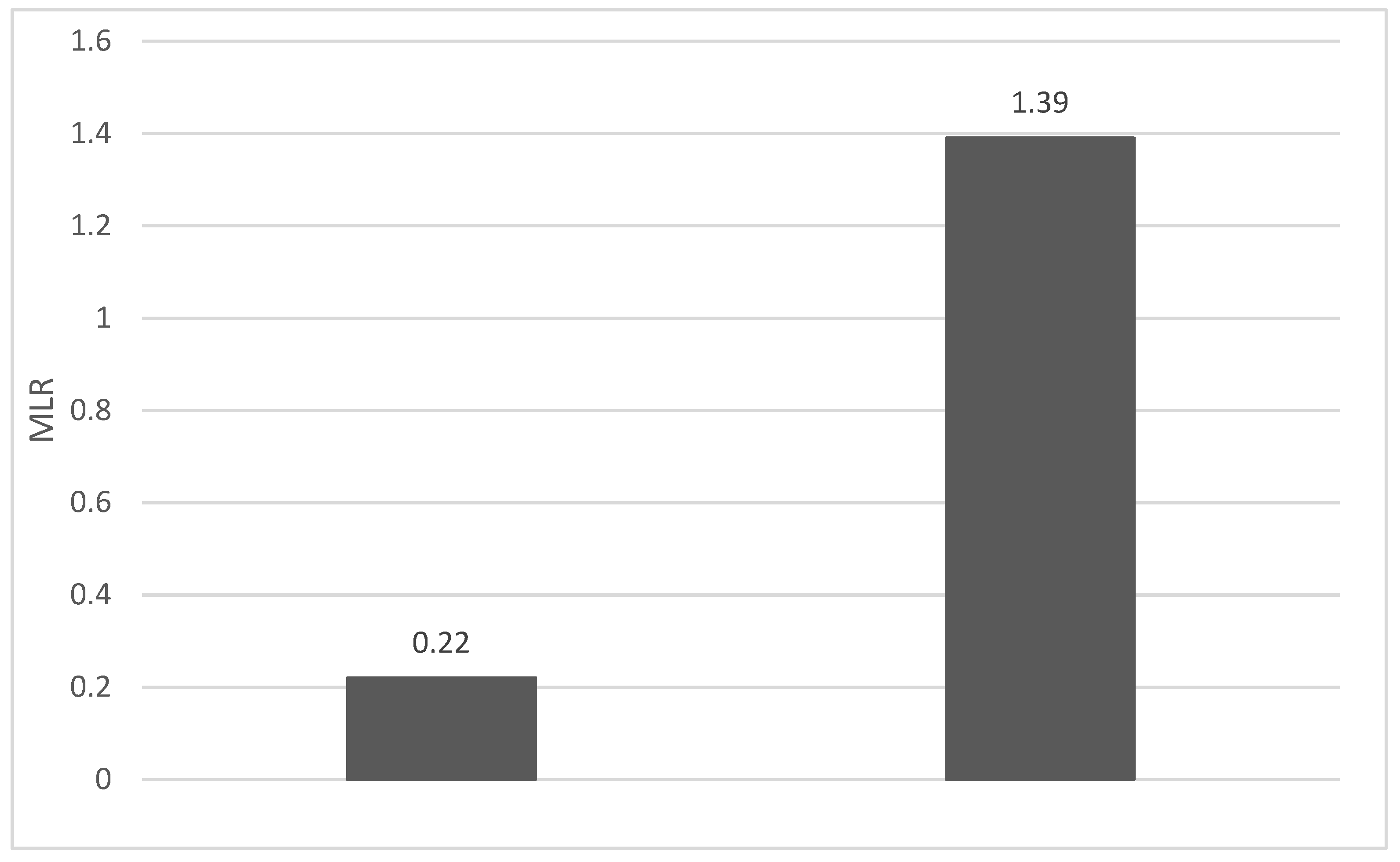
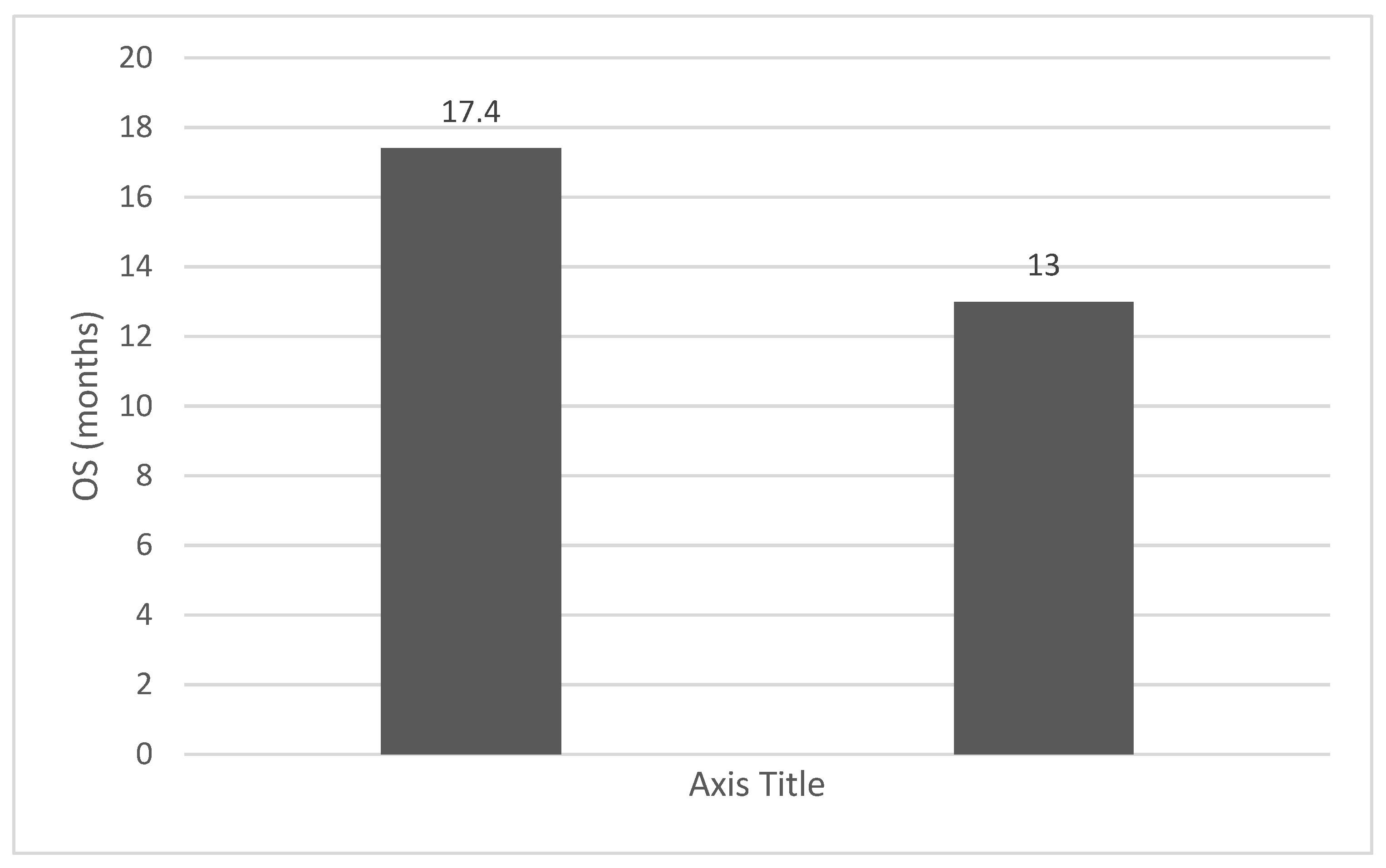
4. Discussions:
5. Conclusions:
References
- Galdiero, M.R.; Bonavita, E.; Barajon, I.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A.; Jaillon, S. Tumor associated macrophages and neutrophils in cancer. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catal O, Ozer B, Sit M, Aktas G, Erkol H. (). The role of monocyte to lymphocyt ratio in predicting me-tastasis in rectal cancer. Annals of Medical Research. 2021; 28(3), 0527–0531. Retrieved from https://www.annalsmedres.org/index.php/aomr/article/view/428.
- Kumarasamy C, Sabarimurugan S, Madurantakam RM, Lakhotiya K, Samiappan S, Baxi S, Nachimuthu R, Gothandam KM, Jayaraj R. Prognostic significance of blood inflammatory biomarkers NLR, PLR, and LMR in cancer-A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jun;98(24):e14834.
- Misiewicz, A.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V. Fashionable, but What is Their Real Clinical Usefulness? NLR, LMR, and PLR as a Promising Indicator in Colorectal Cancer Prognosis: A Systematic Review. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, ume 16, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarasamy, C.; Tiwary, V.; Sunil, K.; Suresh, D.; Shetty, S.; Muthukaliannan, G.K.; Baxi, S.; Jayaraj, R. Prognostic Utility of Platelet–Lymphocyte Ratio, Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratio and Monocyte–Lymphocyte Ratio in Head and Neck Cancers: A Detailed PRISMA Compliant Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, J.P.; Sánchez-Canteli, M.; Triantafyllou, A.; de Bree, R.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Franchi, A.; Hellquist, H.; Saba, N.F.; Stenman, G.; Takes, R.P.; et al. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheeth, N.; Patil, N. Biomarkers in Head and Neck Cancer an Update. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 71, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.; Lan, C.; Yan, J.; Xie, Y.; Gray, T.; Amirkhan, R.H.; E Dowell, J. ERCC1 expression and outcomes in head and neck cancer treated with concurrent cisplatin and radiation. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Li, H.; Ding, S.; Zhou, J. NLR, PLR, LMR and MWR as diagnostic and prognostic markers for laryngeal carcinoma. . 2022, 14, 3017–3027. [Google Scholar]
- Seetohul, Y.B.; Singh, V.; Jain, R.K.; Chaudhary, A.K. Prognostic Value of Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet–Lymphocyte Ratio in Head and Neck Malignancies. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 72, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu Xiu-Ping, Tian Tian, Chen Liang-Si, Luo Xiao-Ning, Lu Zhong-Ming, Zhang Si-Yi, Chen Shao-Hua. Prognostic values of preoperative NLR and PLR in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcino-ma.Translational Cancer Research; Vol 7, No 2 (April 28, 2018). 28 April.
- Liao, L.-J.; Hsu, W.-L.; Wang, C.-T.; Lo, W.-C.; Cheng, P.-W.; Shueng, P.-W.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Lin, Y.-C. Prognostic impact of pre-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A retrospective study of 180 Taiwanese patients. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2017, 43, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewczyński, A.; Jabłońska, B.; Mazurek, A.M.; Mrochem-Kwarciak, J.; Mrowiec, S.; Śnietura, M.; Kentnowski, M.; Kołosza, Z.; Składowski, K.; Rutkowski, T. Comparison of Selected Immune and Hematological Parameters and Their Impact on Survival in Patients with HPV-Related and HPV-Unrelated Oropharyngeal Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-K.; Kim, M.W.; Choi, I.S.; Moon, U.Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Sohn, I.; Kim, S.; Jeong, H.-S. Optimal cutoff of pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in head and neck cancer patients: a meta-analysis and validation study. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Dai, Y.; Hu, G. High pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of poor survival prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck 2018, 41, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zeng, H.; Yang, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Kuang, C.; Zhu, S.; Wang, M.; Ma, X. Survival and prognostic analysis of preoperative inflammatory markers in patients undergoing surgical resection for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setakornnukul, J.; Chanvimalueng, W.; Patumanond, J.M.; Thephamongkhol, K.M. Cutoff point of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for predicting survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Medicine 2021, 100, e27095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojaxhiu, B.; Templeton, A.J.; Elicin, O.; Shelan, M.; Zaugg, K.; Walser, M.; Giger, R.; Aebersold, D.M.; Pra, A.D. Relation of baseline neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio to survival and toxicity in head and neck cancer patients treated with (chemo-) radiation. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, Y.; Oya, R.; Kitamiura, T.; Ashida, N.; Shimizu, K.; Takemura, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Uno, A. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in head and neck cancer: A meta-analysis. Head Neck 2017, 40, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, Y.; Oya, R.; Kitamiura, T.; Ashida, N.; Shimizu, K.; Takemura, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Uno, A. Platelet count and platelet-lymphocyte ratio as prognostic markers for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Meta-analysis. Head Neck 2018, 40, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, Y.; Oya, R.; Takemoto, N.; Inohara, H. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: Meta-analysis. Head Neck 2022, 44, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarella, M.A.; Mannard, E.; Silva, S.D.; Zeitouni, A. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in head and neck cancer prognosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck 2018, 40, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassouli, A.; Saliba, J.; Castano, R.; Hier, M.; Zeitouni, A.G. Systemic inflammatory markers as independent prognosticators of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2013, 37, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szilasi, Z.; Jósa, V.; Zrubka, Z.; Mezei, T.; Vass, T.; Merkel, K.; Helfferich, F.; Baranyai, Z. Neutrophil-To-Lymphocyte and Platelet-To-Lymphocyte Ratios as Prognostic Markers of Survival in Patients with Head and Neck Tumours—Results of a Retrospective Multicentric Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2020, 17, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tham, T.; Olson, C.; Khaymovich, J.; Herman, S.W.; Costantino, P.D. The lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio as a prognostic indicator in head and neck cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngology 2018, 275, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-H.; Chou, W.-C.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chang, K.-P.; Liao, C.-T.; Ho, T.-Y.; Yeh, C.-M.; Liu, C.-J.; Hung, S.-P.; et al. Prognostic significance of dynamic changes in lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio in patients with head and neck cancer treated with radiotherapy: results from a large cohort study. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 154, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turri-Zanoni, M.; Salzano, G.; Lambertoni, A.; Giovannardi, M.; Karligkiotis, A.; Battaglia, P.; Castelnuovo, P. Prognostic value of pretreatment peripheral blood markers in paranasal sinus cancer: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio. Head Neck 2016, 39, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, T.; Takahashi, H.; Sano, D.; Matsuoka, M.; Hyakusoku, H.; Hatano, T.; Hiiragi, Y.; Oridate, N. Fibrinogen and Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Survival in Patients with Advanced Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Anticancer. Res. 2018, 38, 5321–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, E.; Barros, J.; Salgado, I.; Millán, A.; Vilares, M.; Zagalo, C.; Gomes, P. Pretreatment Blood Markers in the Prediction of Occult Neck Metastasis: A 10-Year Retrospective Study. Cureus 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Tian, T.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, W. Prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in laryngeal cancer: What should we expect from a meta-analysis? Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 945820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourilovitch, M.; Galarza–Maldonado, C. Could a simple biomarker as neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio reflect complex processes orchestrated by neutrophils? J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2023, 6, 100159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahorec, R. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, past, present and future perspectives. Bratisl. Med J. 2021, 122, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Wu, F.; Zhang, L. Prognostic Significance of Pretreatment Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet−to−Lymphocyte Ratio, or Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Endometrial Neoplasms: A Systematic Review and Meta−analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 734948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.; Xu, R.; Lu, T.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, P.; Qu, L.; Zhang, S.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L. The MLR, NLR, PLR and D-dimer are associated with clinical outcome in lung cancer patients treated with surgery. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, C.-H.; Bhoo-Pathy, N.; Ng, K.-L.; Jabir, R.S.; Tan, G.-H.; See, M.-H.; Jamaris, S.; A Taib, N. Utility of pre-treatment neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio as prognostic factors in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huszno, J.; Kołosza, Z.; Mrochem-Kwarciak, J.; Telka, E.; Jochymek, B.; Miszczyk, L. Role of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-lymphocyte ratio, lymphocyte-monocyte ratio and platelets in prognosis of patients with prostate cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lin, Z.; Zeng, M.; Shi, P.; Cao, Y.; Chen, F. Compare the Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of MLR, NLR and PLR in CRC Patients. Clin. Lab. 2021, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursu, R.G.; Luchian, I.; Ghetu, N.; Costan, V.V.; Stamatin, O.; Palade, O.D.; Damian, C.; Iancu, L.S.; Porumb-Andrese, E. Emerging Oncogenic Viruses in Head and Neck Cancers from Romanian Patients. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursu, R.G.; Danciu, M.; Spiridon, I.A.; Ridder, R.; Rehm, S.; Maffini, F.; McKay-Chopin, S.; Carreira, C.; Lucas, E.; Costan, V.-V.; et al. Role of mucosal high-risk human papillomavirus types in head and neck cancers in Romania. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0199663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonacera, A.; Stancanelli, B.; Colaci, M.; Malatino, L. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio: An Emerging Marker of the Relationships between the Immune System and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Investigated ratio(s) as biomarker(s) | Anatomical site of cancer/hystology | Number of case | Results/conclusion | Cuoff value(s) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLR, PLR, LMR, monocyte-to-white blood cell ratio (MWR) | laryngeal carcinoma | 50 | NLR, PLR, LMR, and MWR could be used as prognostic and diagnostic markers in laryngeal cancer; their combination increases the accuracy of the prediction. | Li et al., 2022 | |
| NLR, PLR | not specified | 170 hystological confirmed cases+80 case in control group | Increased NLR and PLR values is correlated with poor prognostic | Seetohul et al., 2019 | |
| NLR, PLR | laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | 290 | preoperative NLR and PLR can be prognostic markers, the accuracy increases if they are used in combination | 2,22 for NLR and 114 for PLR | Tu et al., 2018 |
| NLR | nasopharyngeal carcinoma | 190 | A high NLR is identified as a poor prognostic factor for nasopharyngeal cancer in Taiwan | 3,6 | Liao et al., 2018 |
| NLR, PLR, MLR, systemic immune inflammation (SII) index | HPV-Related and HPV-Unrelated Oropharyngeal Cancer | 127 | Studied immune ratios could be stratification factors in both HPV− and HPV+ cases | NLR >2,13, SII >448 for OS andNLR >2.29), SII >462.58 for DFS | Brewczyński et al., 2021 |
| NLR | HNSCC | 25 studies in 24 articles, 1536 cases | pretreatment NLR values below 2 and above 6 could be more conclusive biomarkers of prognosis | NLR < 2, 2 to 6, and ≥ 6 | Cho et al., 2018 |
| NLR, PLR | HNSCC | 28 cohorts involving 6847 cases | high pretreatment NLR predicted poor OS, DFS and cancer specifical survival. PLR not associated with OS or DFS | Yang et al., 2019 | |
| NLR, MLR, PLR, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and l actate dehydrogenase (LDH) | laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | 361 | elevated preoperative NLR, PLR, MLR and ALP are predictors of worst survival; NLR and postoperative MLR were identified as independent prognostic markers | Chen et al., 2018 | |
| NLR | nasopharyngeal carcinoma | 463 | A value off NLR=3 is an independent poor prognostic factor | 3 | Setakornnukul et al., 2021 |
| NLR, PLR | head and neck cancer patients treated with (chemo-) radiation | 186 | Higher NLR is associated with OS but not associated with recurrence-free survival (LRFS), distant recurrence-free survival (DRFS), and acute toxicity acita de grad ≥ 2; PLR was not correlated with outcome or toxicity | Bojaxhiu et al., 2016 | |
| NLR | HNSCC | 3770 | Elevated NLR predicts worse outcomes | Takenaka et al., 2017 | |
| Platelet count and PLR | HNSCC | 8 studies including 4096 patients and 9 studies including 2327 patients | Elevated platelet count and PLR are associated with poor prognosis | Takenaka et al., 2018 | |
| NLR | HNSCC | 14 studies involving 929 | The NLR predicts treatment results in immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) | Takenaka et al., 2022 | |
| NLR | HNSCC | 24 articles and 6479 cases | An elevated NLR is a predictor for a poor OS | Mascarella et al., 2018 | |
| NLR, PLR | HNSCC | 273 | PLR and NLR independent predictors of mortality and recurrence respectively | Rassouli et al., 2015 | |
| NLR, PLR | HNSCC | 156 | NLR higher than the threshold is associated with an unfavorable evolution. NLR is an independent predictor of five-year overall survival. Neither PLR nor NLR are correlated with tumor recurrence | NLR =3,9 | Szilasi et al., 2020 |
| lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR) | HNSCC | 4260 | An elevated LMR may be a predictor of favorable prognosis | Tham et al., 2018 | |
| LMR | HNC | 1431 | Dynamic delta-LMR during radiotherapy is a simple and inexpensive marker for freedom from metastasis and OS | Lin et al. 2020 | |
| NLR,PLR | paranasal sinus | 215 | NLR and PLR are independent prognostic factors of DFS. Higher pretreatment NLR and PLR are related to poor prognosis. | NLR =2.6; PLR =156.9 | Turri-Zanoni et al., 2017 |
| Fibrinogen (F) and NLR; F-NLR score | hypopharyngeal carcinoma | 111 | F-NLR score could stratify patients into prognostic groups | Kuwahara et al., 2018 | |
| NLR, MLR | early-stage (T1-T2) oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) of the tongue | 102 | NLR, MLR indepnednt predictor of o | NLR=2,96 | Ventura et al., 2021 |
| NLR, PLR | laryngeal cancer. | 5716 patients from 20 studies | higher NLR predict poor PFS and os and higher PLR predict poor OS | Hu et al., 2022 | |
| NLR, PLR, NLR/PLR relationship | Laryngeal carcimoma | 5716 patients from 20 studies | NLR is associated with poor OS, PFS, and DFS; Higher PLR is a marker of poor OS | Hu et al., 2022 |
| NLR | PLR | MLR | OS (months) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.07 | 110.71 | 0.36 | 12 |
| 2.74 | 83.69 | 0.41 | 6 |
| 1.25 | 74.06 | 0.14 | 15 |
| 1.24 | 61.63 | 0.22 | 42 |
| 4.57 | 201.55 | 0.46 | 4 |
| 3.03 | 127.91 | 0.39 | 15 |
| 1.83 | 78.98 | 0.22 | 23 |
| 4.44 | 244.14 | 0.78 | 3 |
| 15.50 | 139.58 | 0.76 | 78 |
| 2.51 | 188.72 | 0.22 | 6 |
| 2.01 | 183.14 | 0.18 | 6 |
| 1.88 | 88.63 | 0.14 | 4 |
| 1.48 | 70.43 | 0.13 | 18 |
| 8.91 | 142.34 | 0.81 | 13 |
| 1.40 | 88.44 | 0.18 | 37 |
| 5.04 | 379.33 | 0.23 | 11 |
| 2.36 | 182.23 | 0.14 | 9 |
| 1.67 | 89.63 | 0.12 | 13 |
| 31.85 | 392.75 | 0.73 | 7 |
| 4.33 | 160.91 | 0.34 | 1 |
| 3.71 | 107.14 | 0.43 | 11 |
| 2.56 | 170.00 | 0.19 | 8 |
| 8.61 | 146.50 | 1.00 | 11 |
| 7.31 | 327.94 | 0.84 | 11 |
| 2.75 | 111.71 | 0.33 | 13 |
| 1.39 | 143.59 | 0.30 | 17 |
| 1.37 | 201.34 | 0.46 | 21 |
| 9.22 | 247.59 | 0.60 | 16 |
| 2.97 | 118.70 | 0.30 | 3 |
| 6.98 | 214.29 | 0.85 | 45 |
| 2.69 | 331.18 | 0.15 | 11 |
| 69.00 | 1775.00 | 5.50 | 1 |
| 1.63 | 117.50 | 0.25 | 3 |
| 4.10 | 155.69 | 0.45 | 3 |
| 2.78 | 87.04 | 0.37 | 120 |
| 4.74 | 174.14 | 0.50 | 69 |
| 4.96 | 131.37 | 0.56 | 3 |
| 2.34 | 137.21 | 0.30 | 8 |
| 3.56 | 136.92 | 0.38 | 17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





