Submitted:
11 July 2023
Posted:
13 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
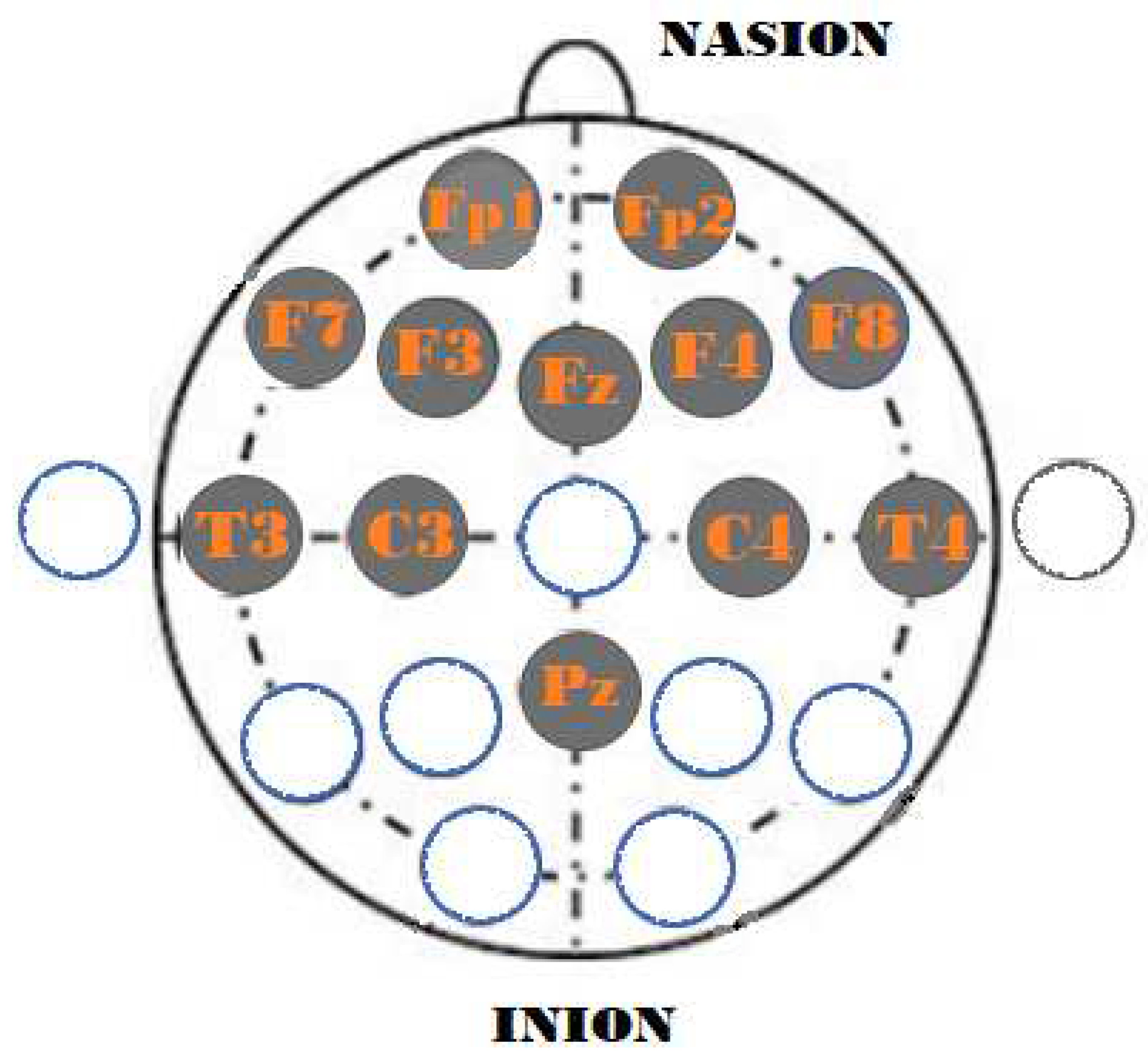
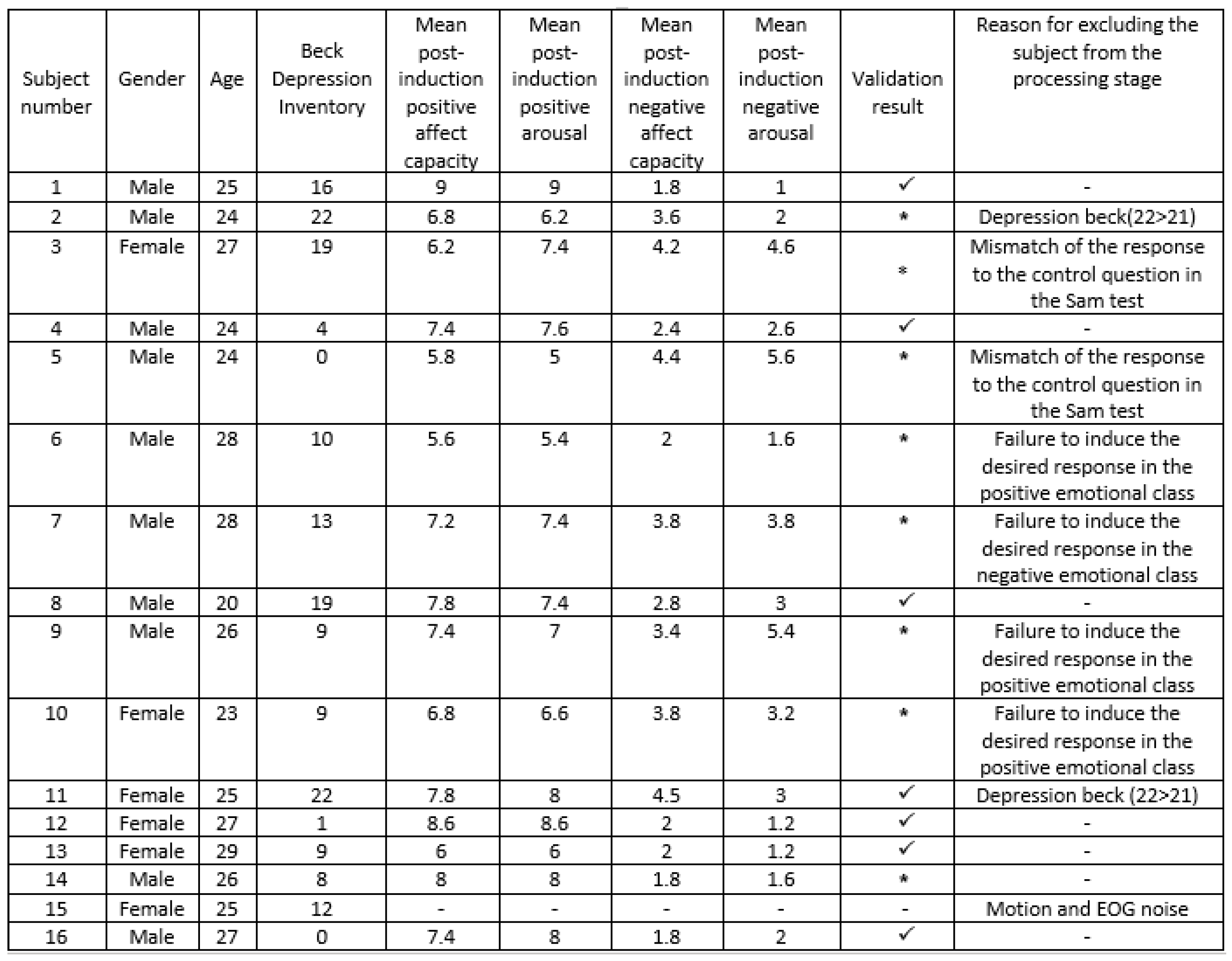
2.1. EEG Signal Acquisition
2.2. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs)
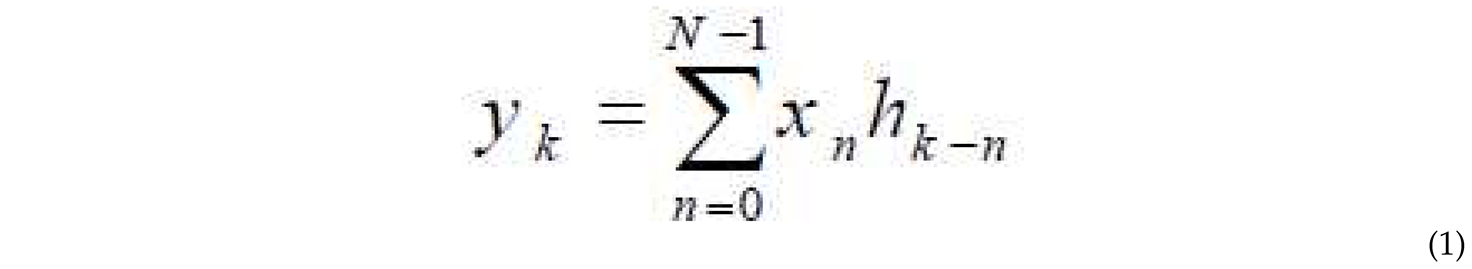 Where x is the input signal, h is the filter, N is the number of elements in x, and y is the resulting output.
Where x is the input signal, h is the filter, N is the number of elements in x, and y is the resulting output.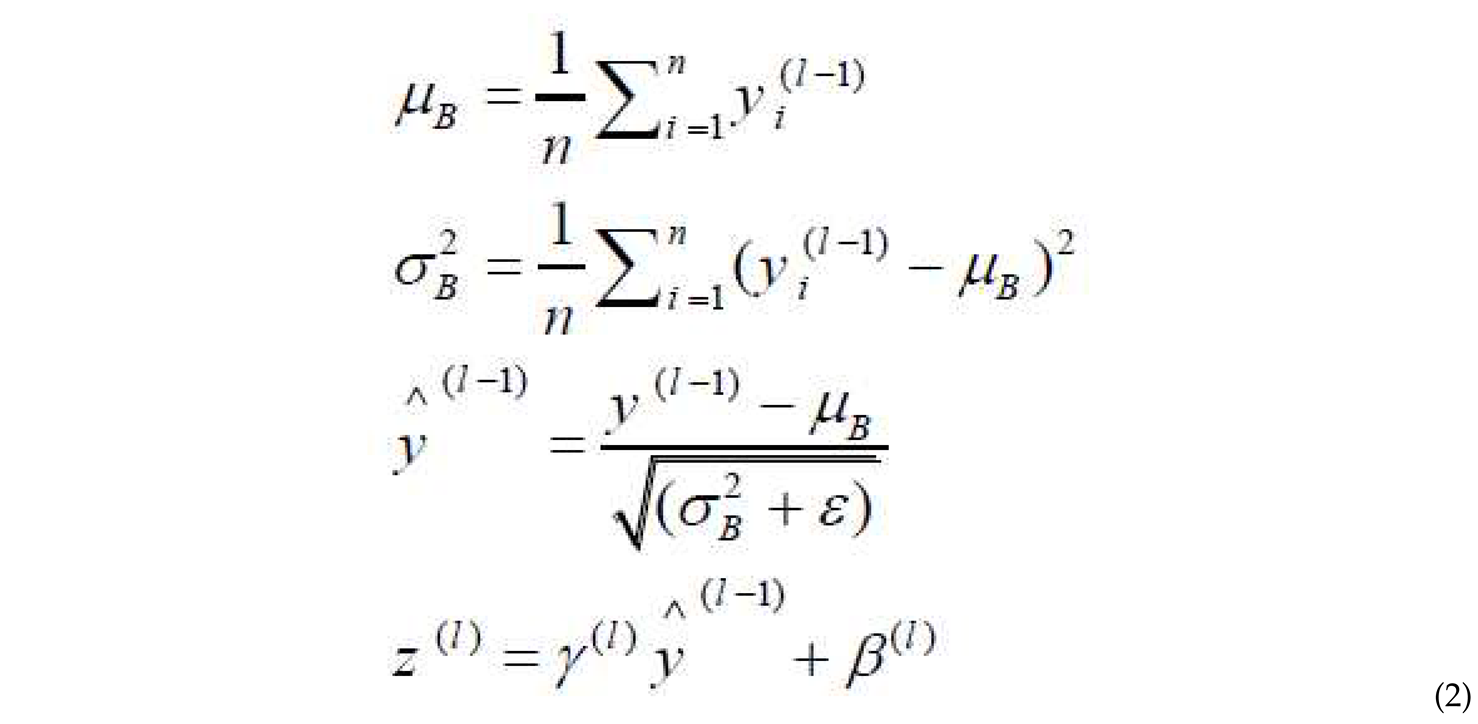 where and are the mean and variance of the batch, is a small constant for numerical stability, I layer number, input vector to the normalization layer, output vector from normalization to a neuron, and are parameters for scaling and shifting the normalized output.
where and are the mean and variance of the batch, is a small constant for numerical stability, I layer number, input vector to the normalization layer, output vector from normalization to a neuron, and are parameters for scaling and shifting the normalized output.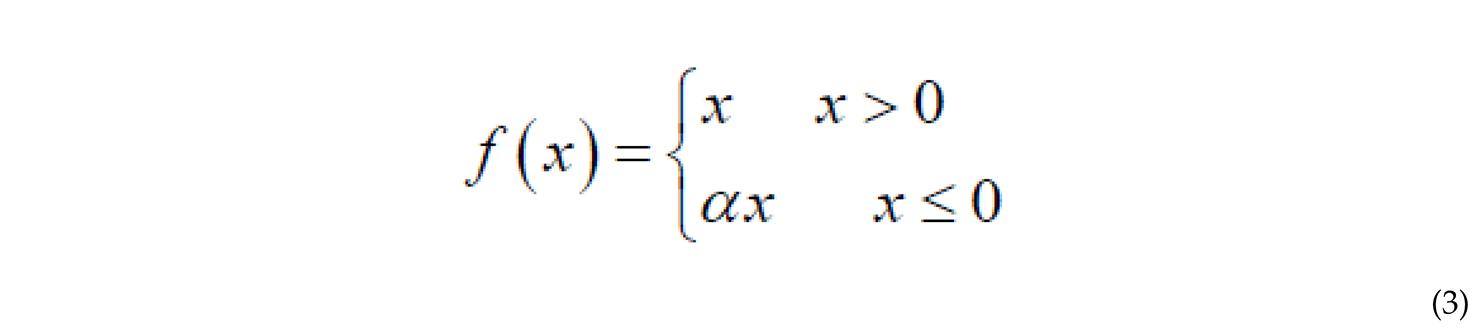
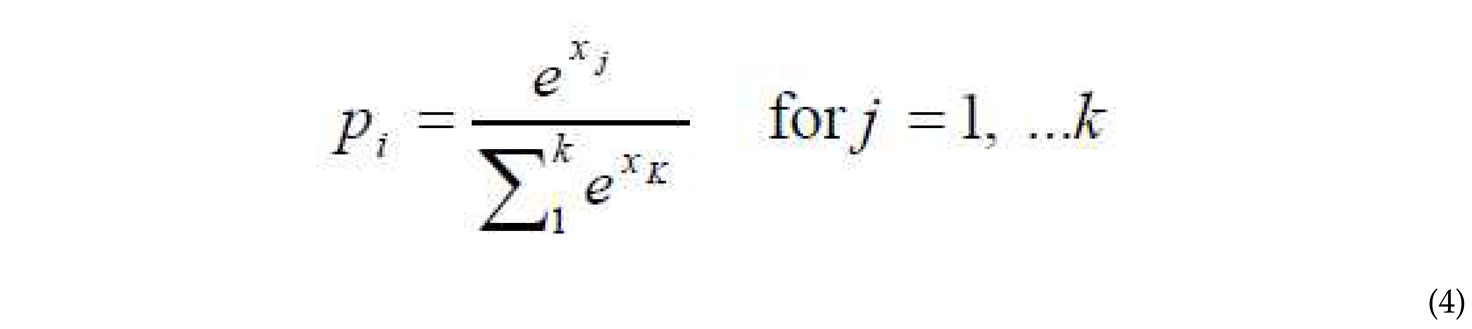 where x is the input to the network and p is the output vector representing the probabilities between 0 and 1, with their sum equal to 1.
where x is the input to the network and p is the output vector representing the probabilities between 0 and 1, with their sum equal to 1.2.2.1. Long Short-Term Memory Network(LSTM)
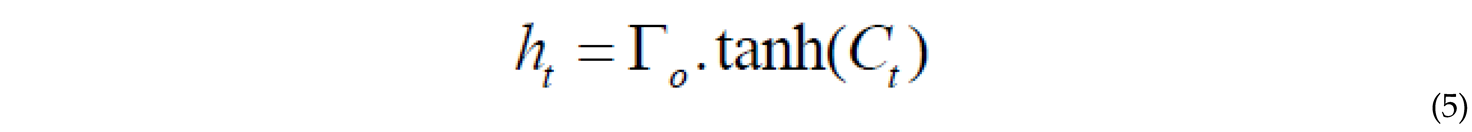
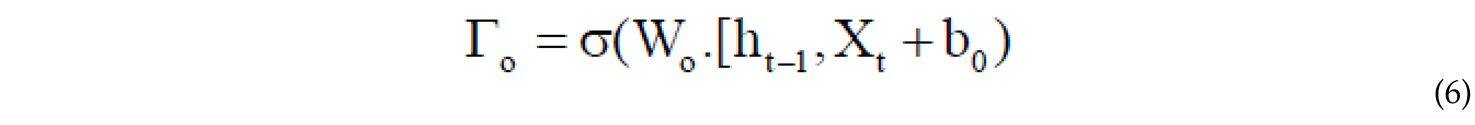
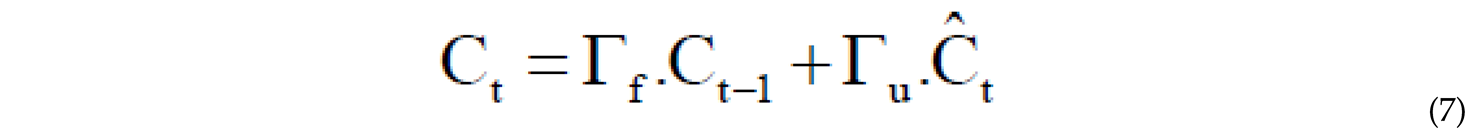
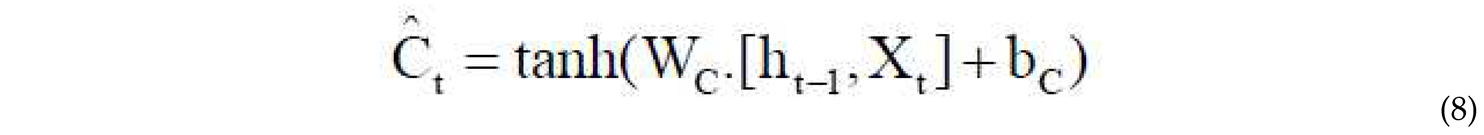
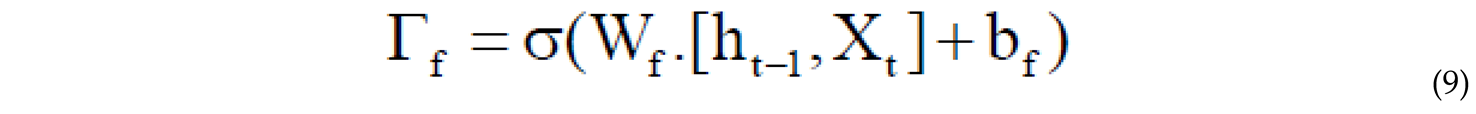
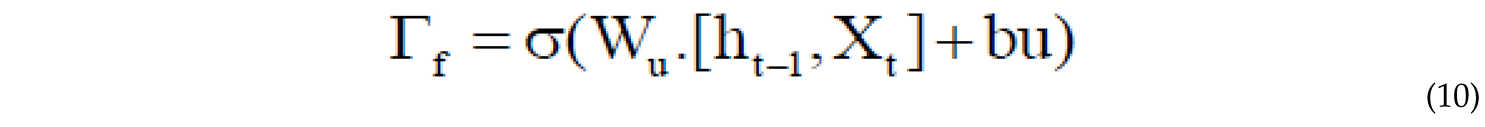
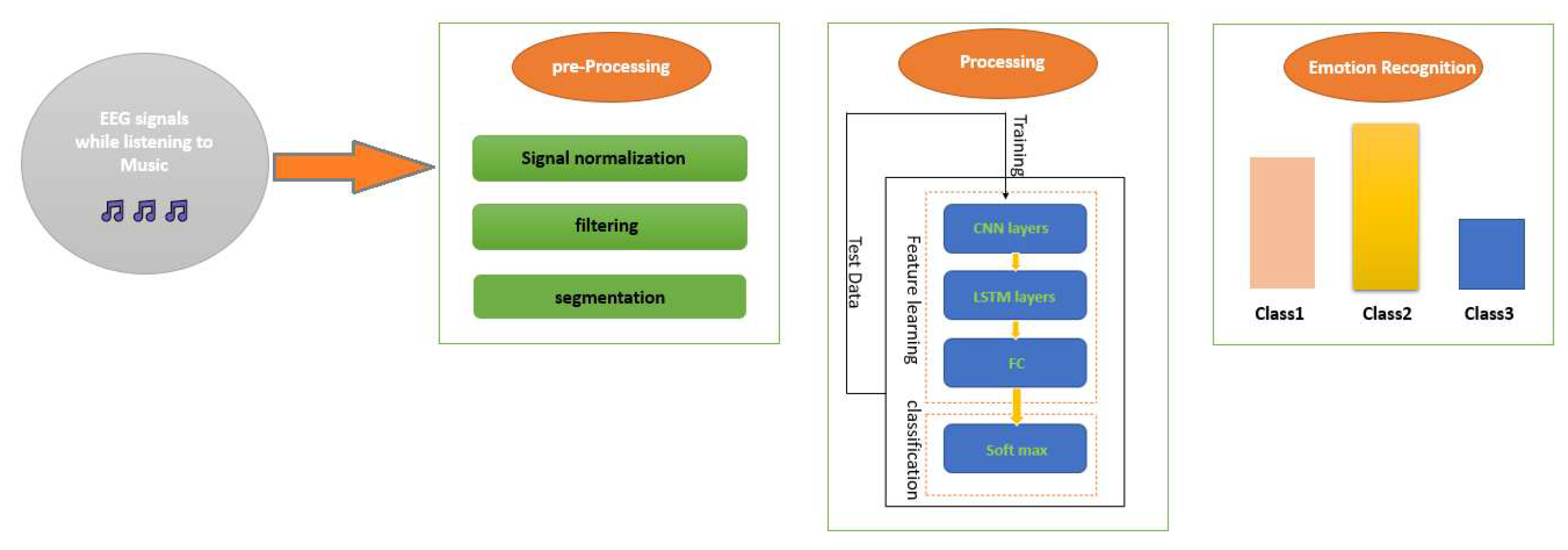
3. Proposed method
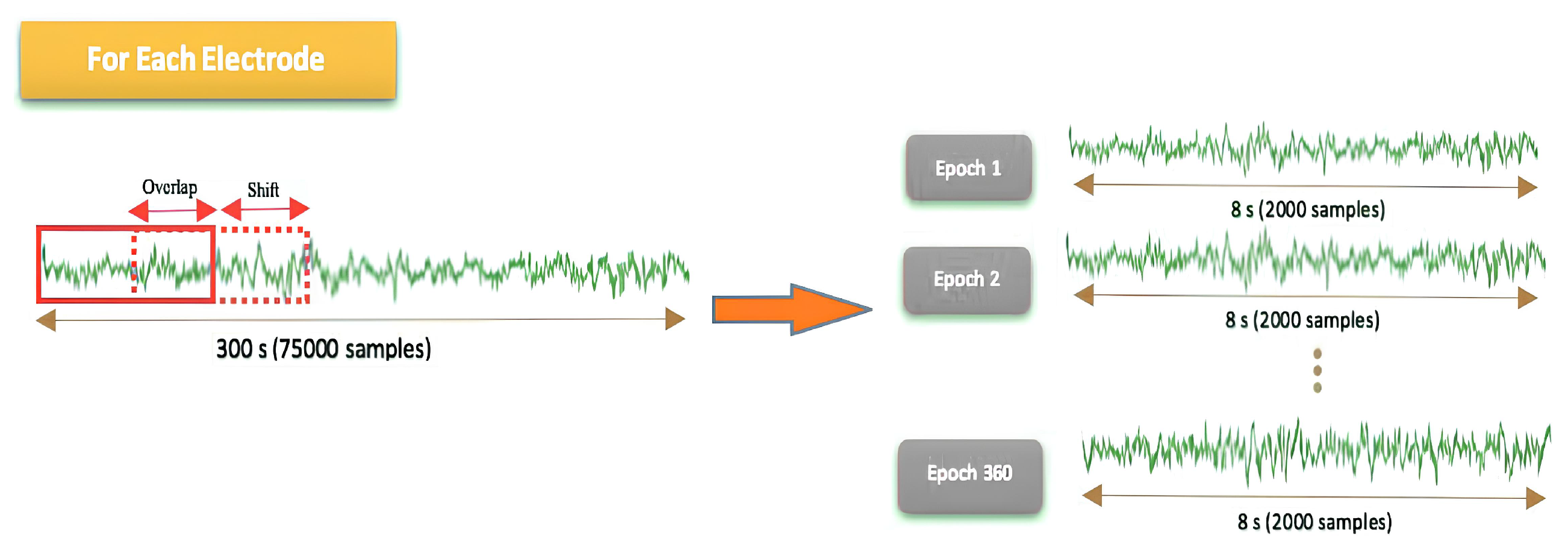
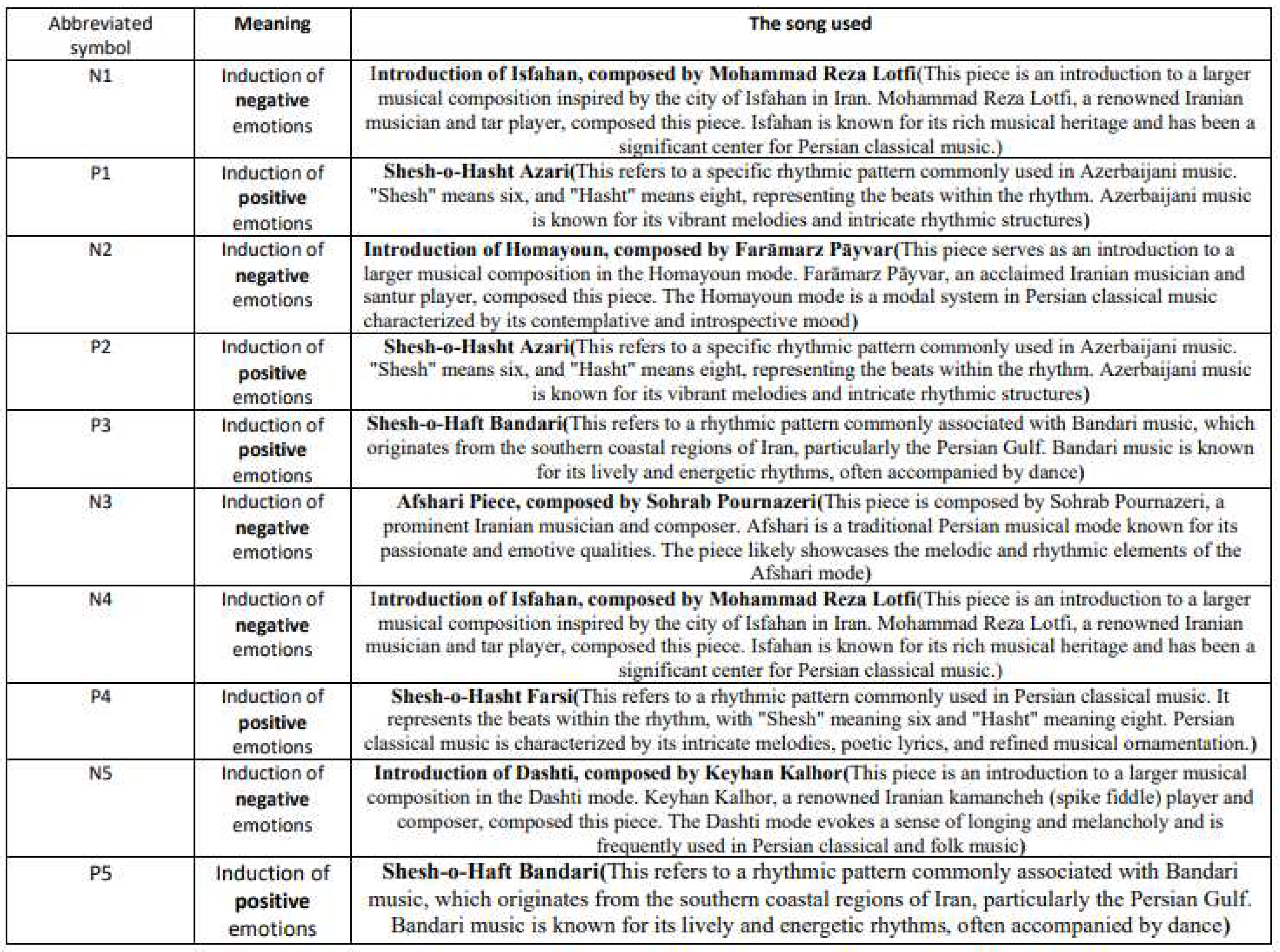
3.1. Data Preprocessing
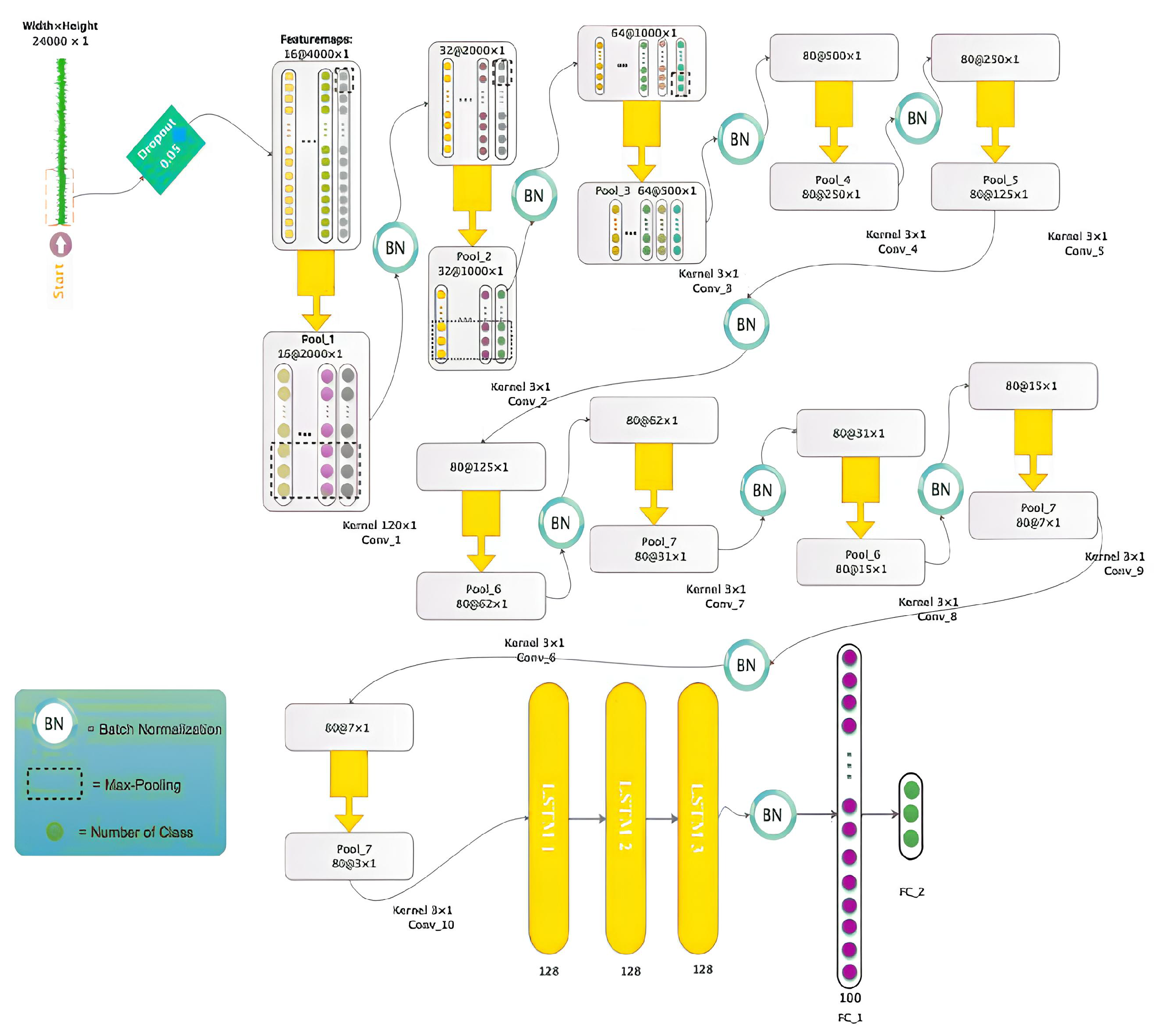
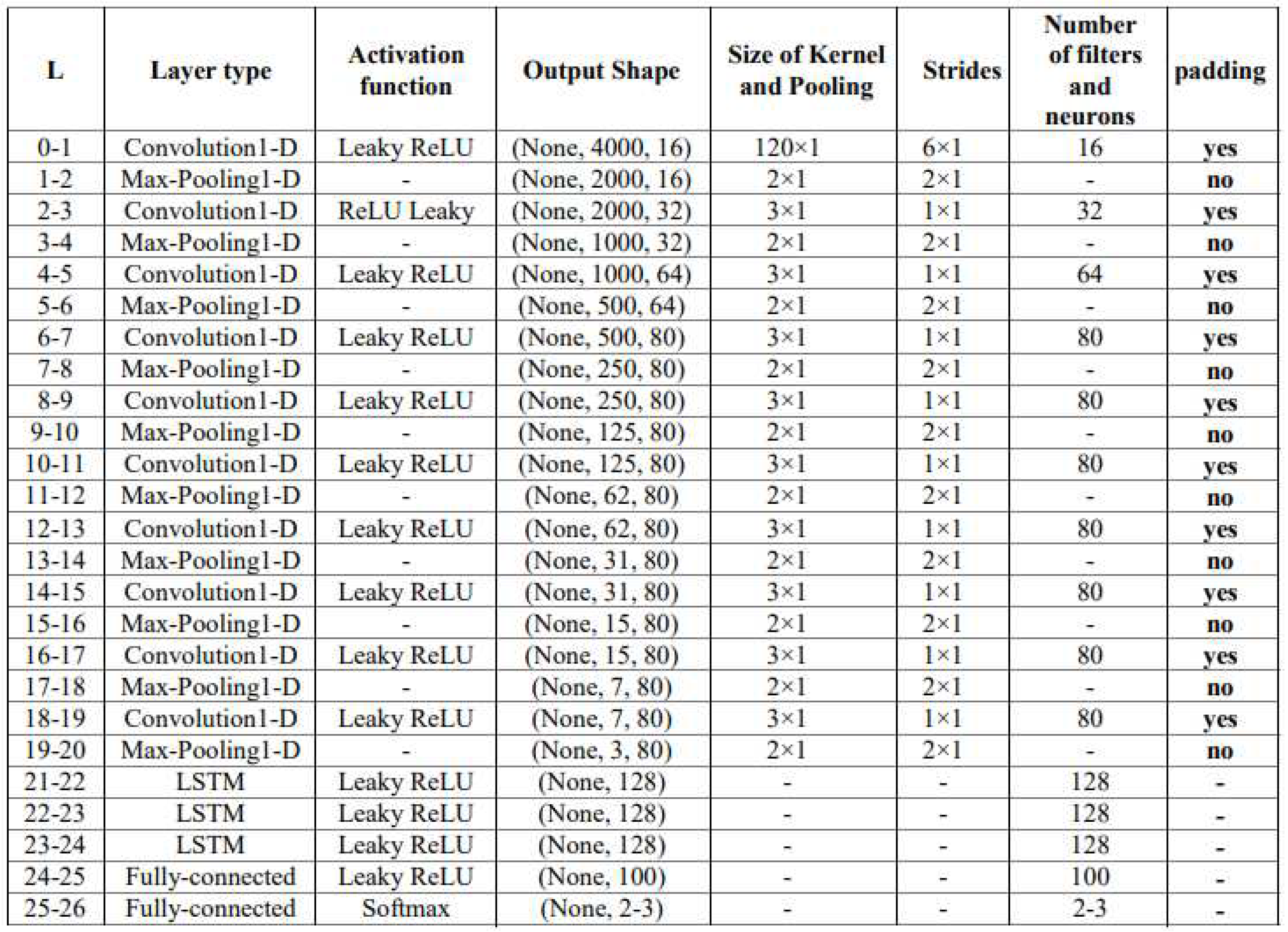
3.2. Proposed Deep Neural Network Architecture
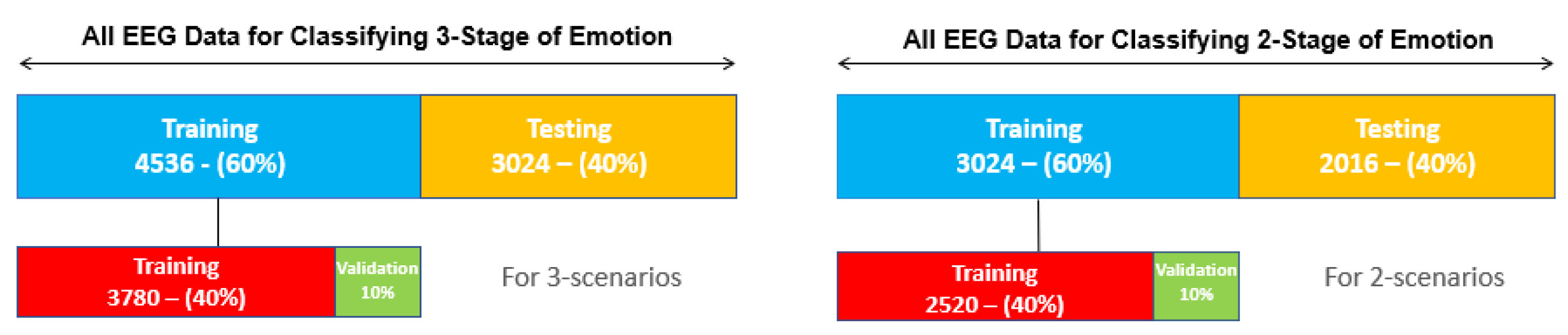
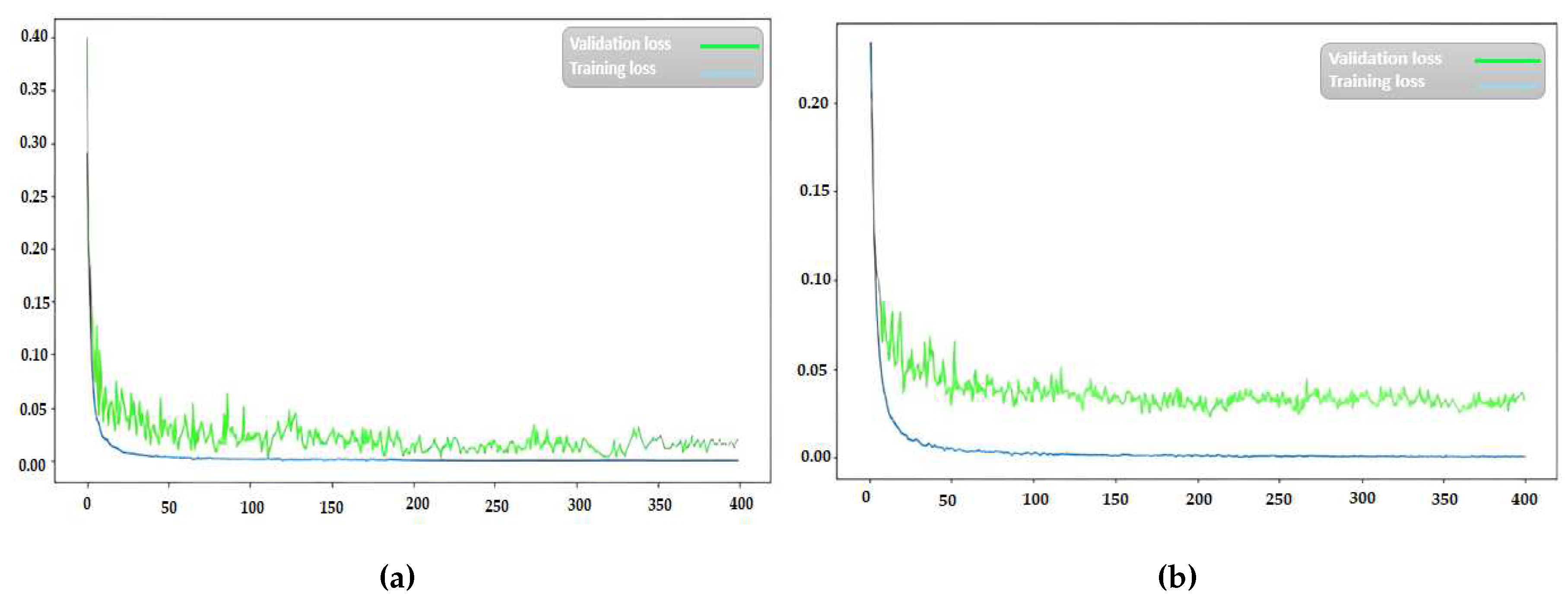
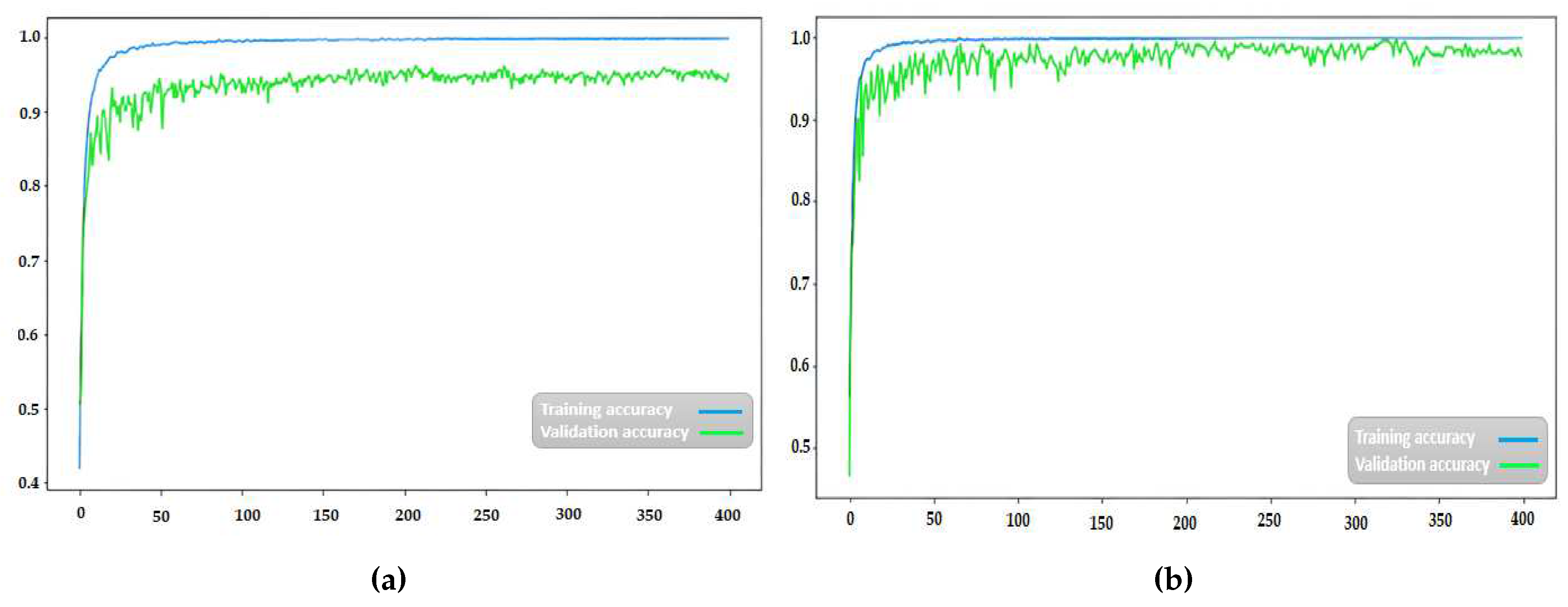
3.3. Training of the Proposed Deep Neural Network
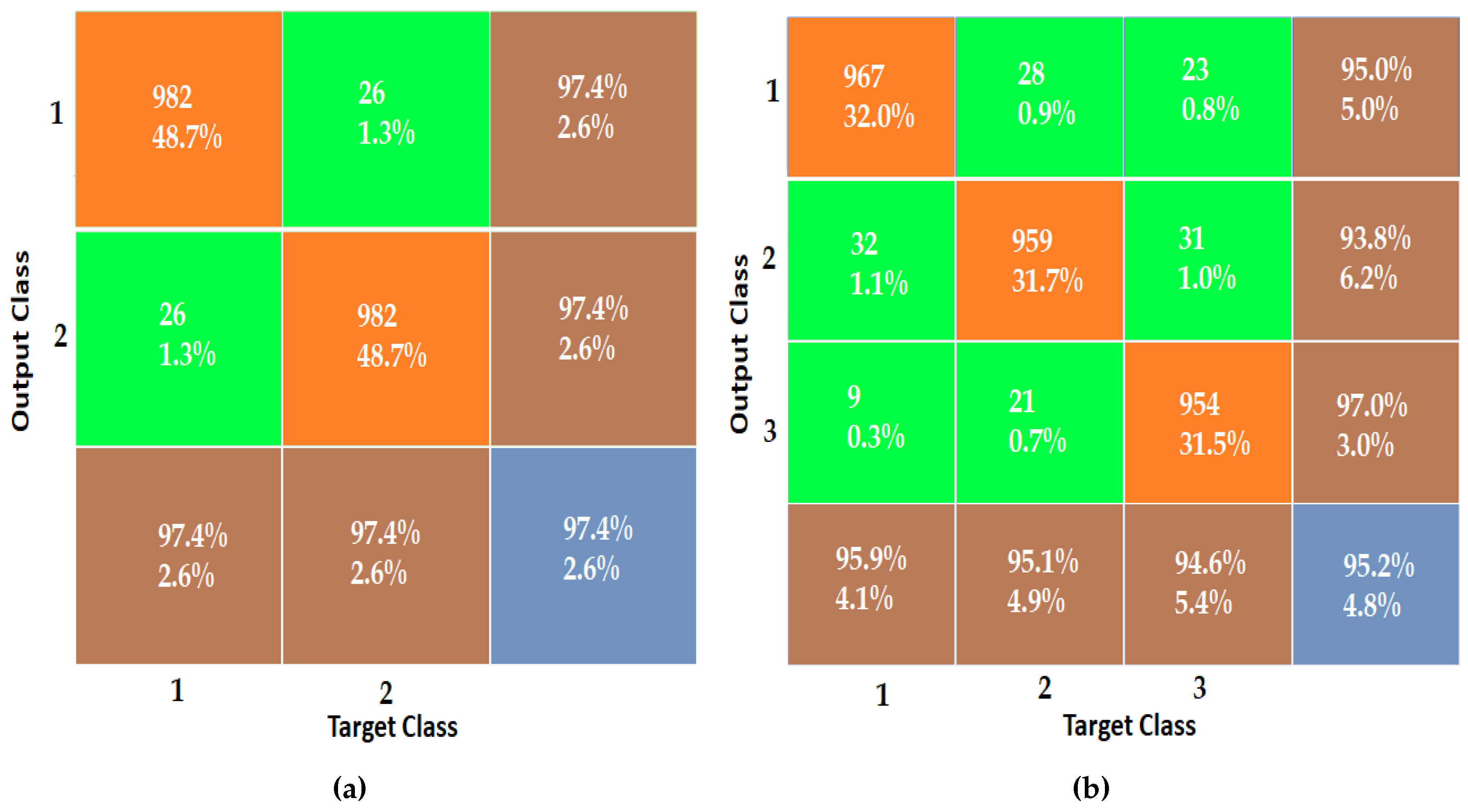
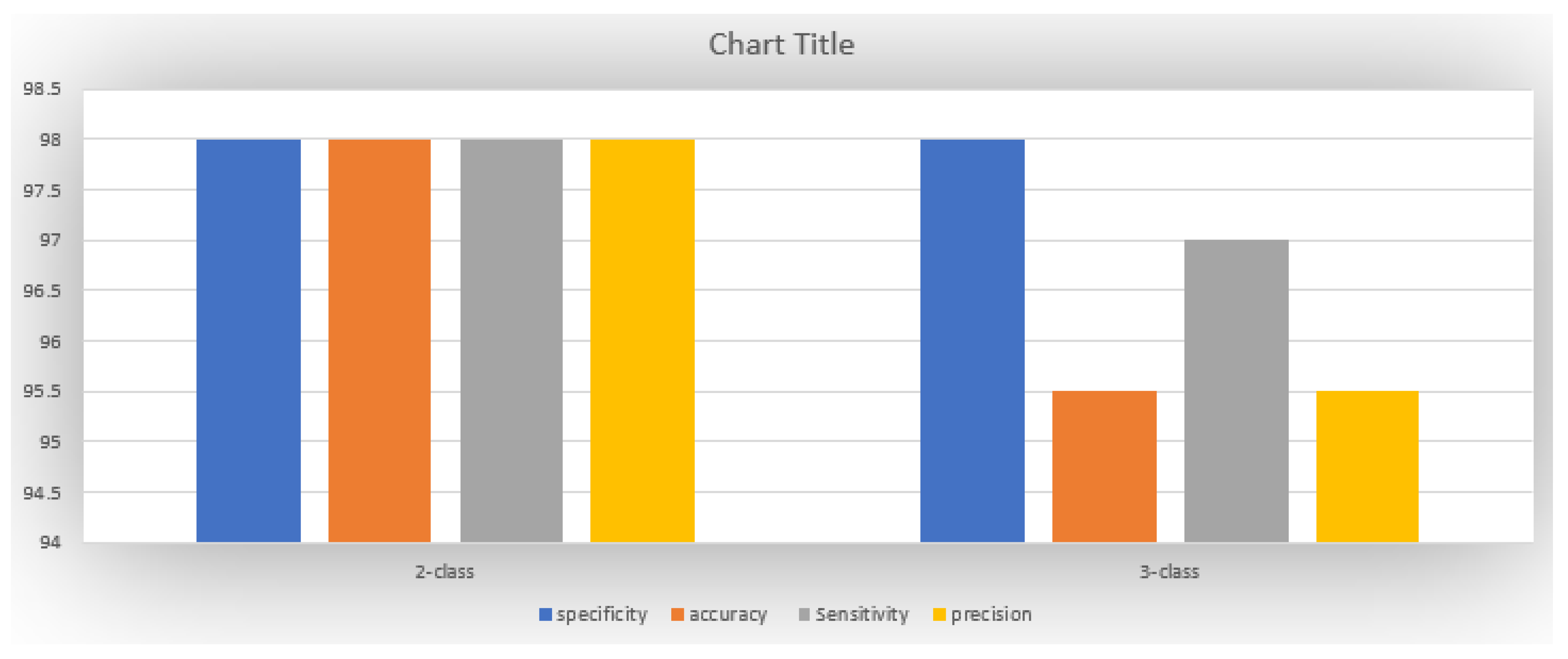
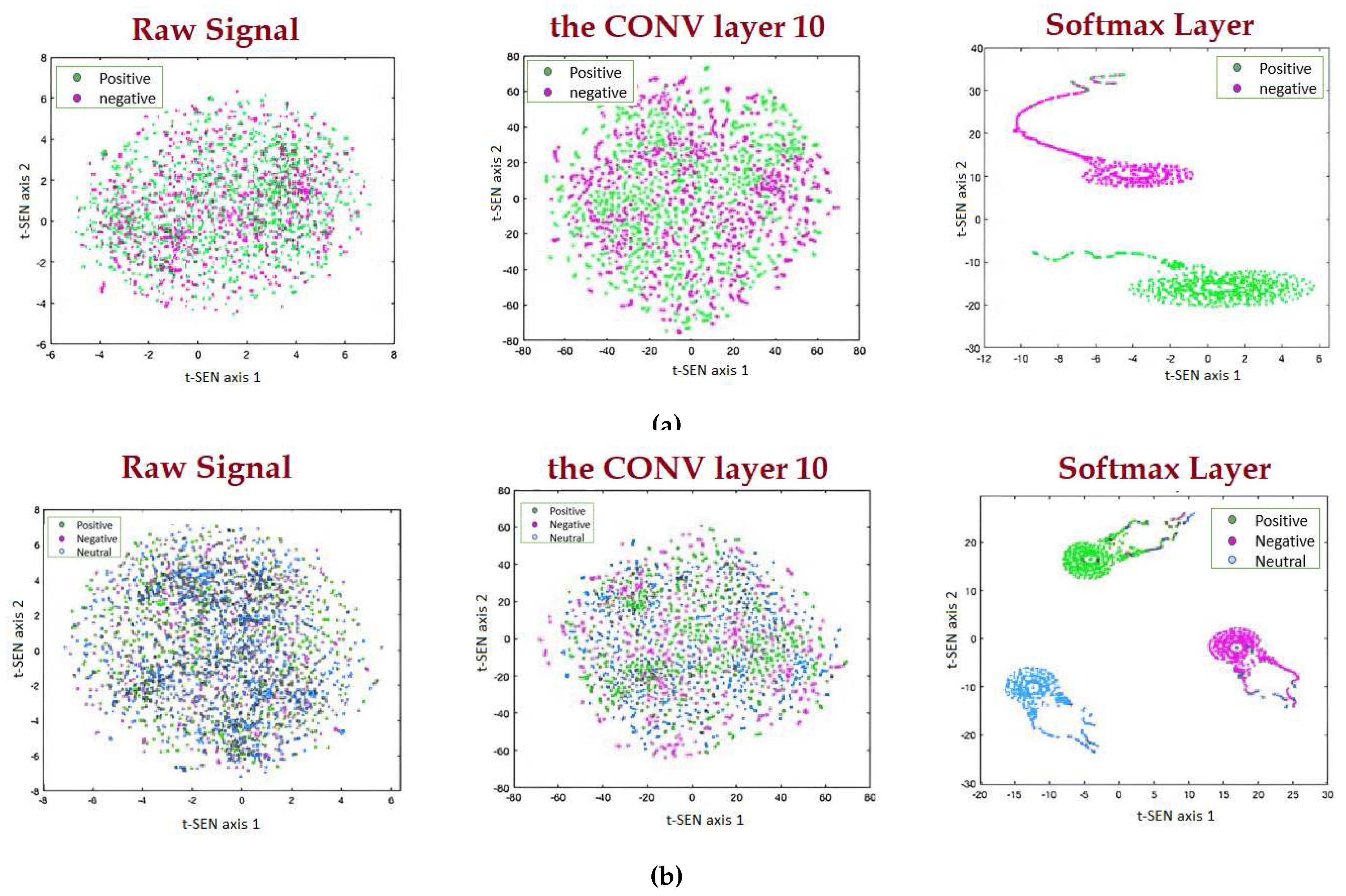
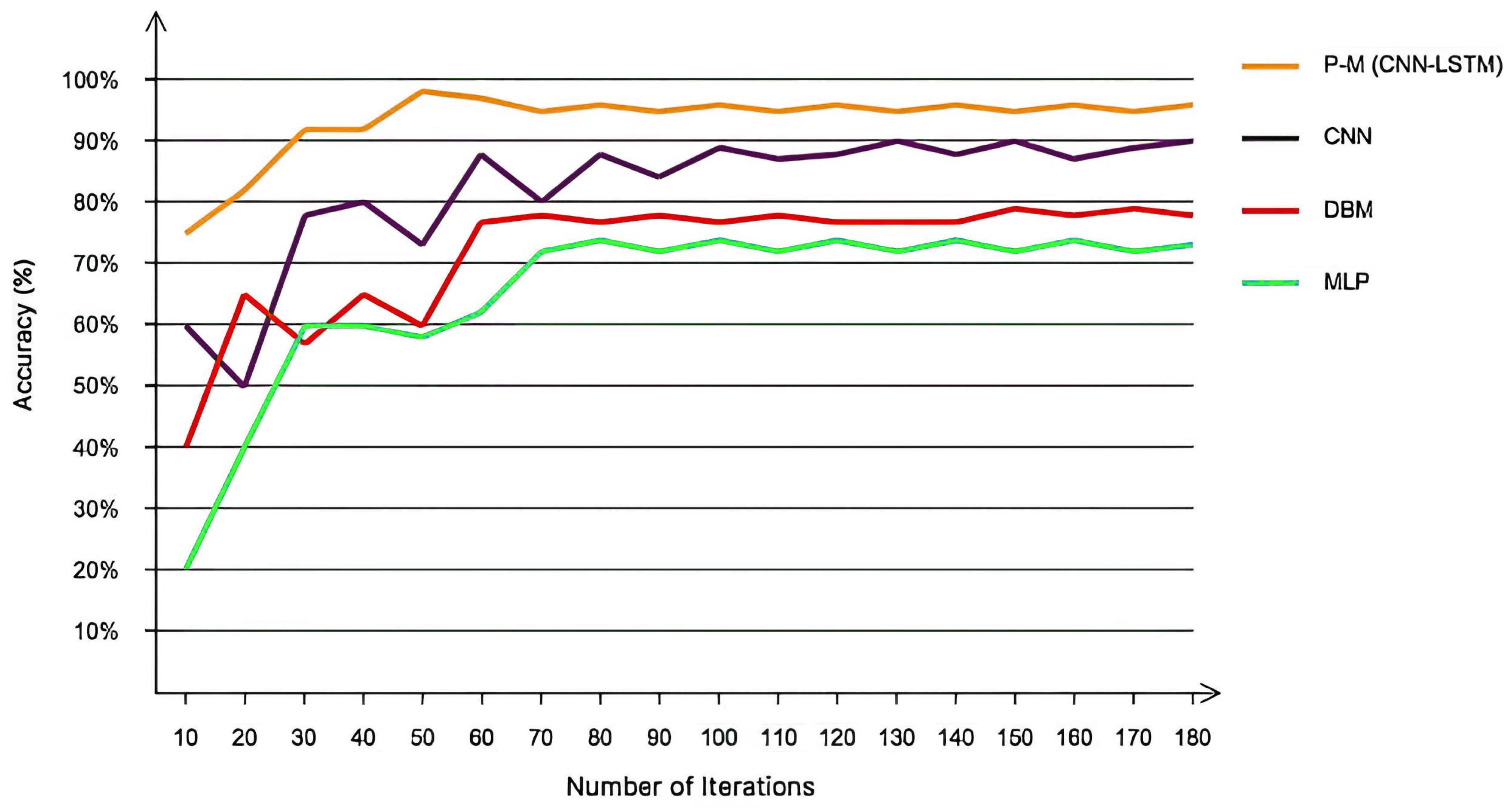
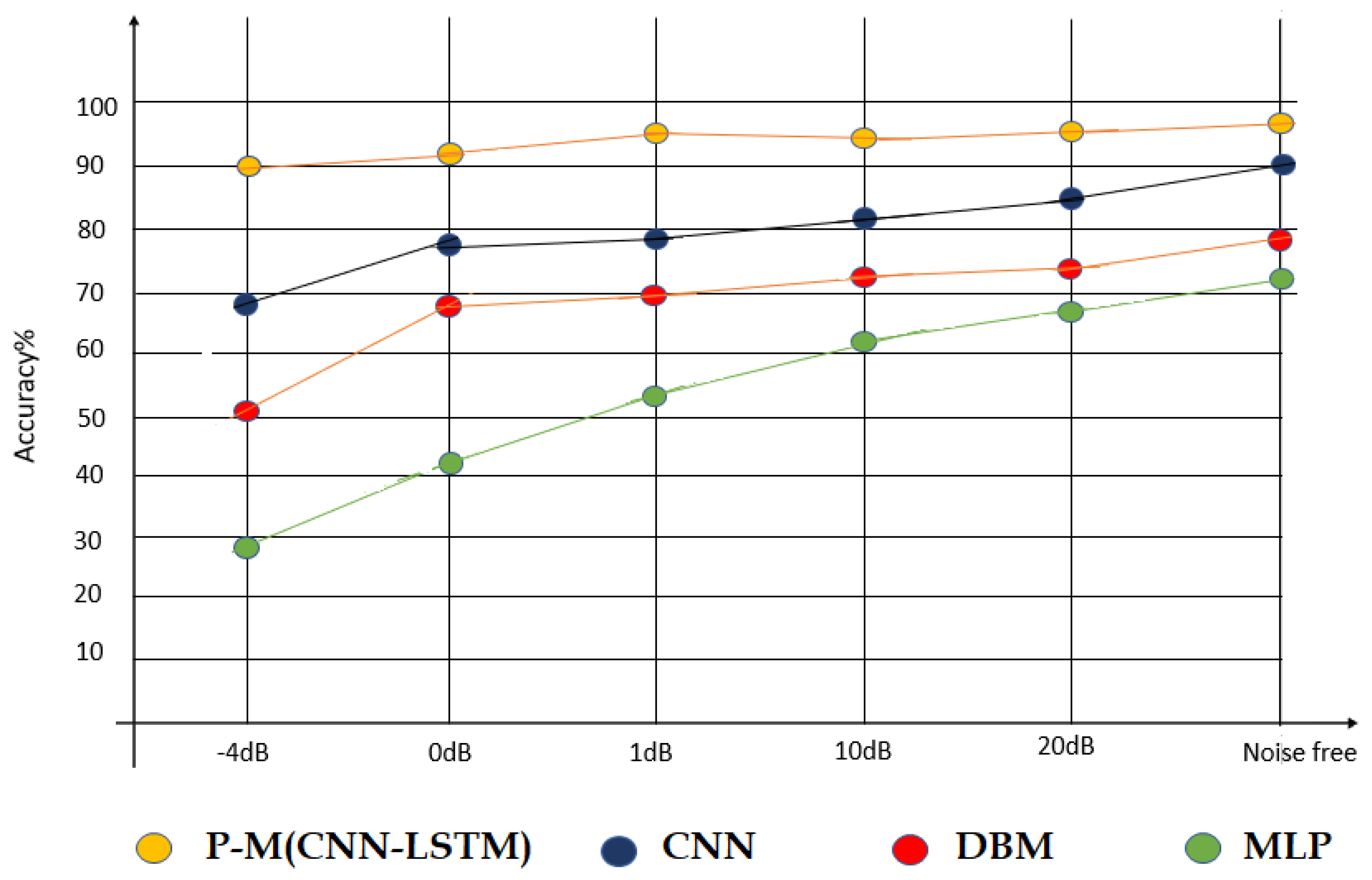
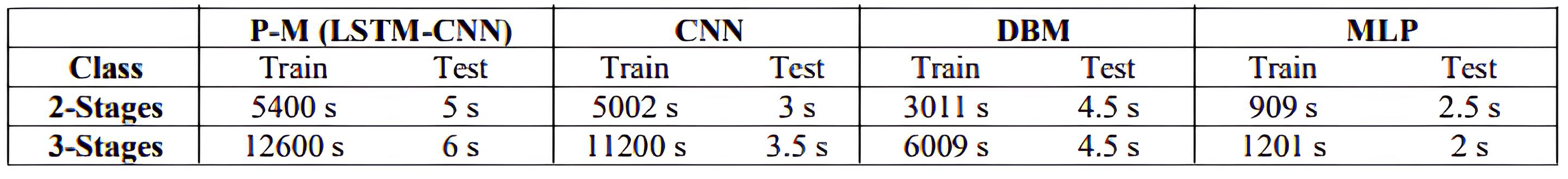
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusion
References
- Rad, N.F.; Yousefi-Koma, A.; Tajdari, F.; Ayati, M. Design of a novel three degrees of freedom ankle prosthesis inspired by human anatomy. 2016 4th International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (ICROM). IEEE, 2016, pp. 428–432. [CrossRef]
- Paydarfar, S.; Abbasi, M.A.; Hashemi, A.; Taheri, S.; Bandehpour, M.; Mosaffa, N. Serum Level of Antibodies Against Novel Acinetobacter Baumannii OmpA-selected Peptides in ICU Staff: Promise for the Future of Vaccine Development. Iranian Journal of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology 2023, pp. 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Paydarfar, S.; Hashemi, A.; Abbasi, M.A.; Bakhtiari, A.; Tajik, F.; Mosaffa, N.; others. Investigation of preformed design Acinetobacter Baumannii outer membrane protein A peptide vaccine candidate in reaction with serum antibodies from ICU staffs members. Research in Medicine: Journal of Research in Medical Sciences 2020, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, Z. EEG signal processing and feature extraction; Springer, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Sanei, S. Adaptive processing of brain signals; John Wiley & Sons, 2013.
- Scherer, K.R. What are emotions? And how can they be measured? Social science information 2005, 44, 695–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaff, K.; Schultz, T. Towards emotion recognition from electroencephalographic signals. 2009 3rd international conference on affective computing and intelligent interaction and workshops. IEEE, 2009, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Murugappan, M.; Rizon, M.; Nagarajan, R.; Yaacob, S.; Zunaidi, I.; Hazry, D. EEG feature extraction for classifying emotions using FCM and FKM. International journal of Computers and Communications 2007, 1, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Tajdari, M.; Pawar, A.; Li, H.; Tajdari, F.; Maqsood, A.; Cleary, E.; Saha, S.; Zhang, Y.J.; Sarwark, J.F.; Liu, W.K. Image-based modelling for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: mechanistic machine learning analysis and prediction. Computer methods in applied mechanics and engineering 2021, 374, 113590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, A.; Khodayari, A.; Kamali, A.; Tajdari, F.; Hosseinkhani, N. New fuzzy solution for determining anticipation and evaluation behavior during car-following maneuvers. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of automobile engineering 2018, 232, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodayari, A.; Ghaffari, A.; Kamali, A.; Tajdari, F. A new model of car following behavior based on lane change effects using anticipation and evaluation idea. Iranian Journal of Mechanical Engineering Transactions of the ISME 2015, 16, 26–38. [Google Scholar]
- Tajdari, F.; Kabganian, M.; Rad, N.F.; Khodabakhshi, E. Robust control of a 3-dof parallel cable robot using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. 2017 Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (IRANOPEN). IEEE, 2017, pp. 97–101. [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Toulkani, N.E.; Zhilakzadeh, N. Intelligent optimal feed-back torque control of a 6dof surgical rotary robot. 2020 11th Power Electronics, Drive Systems, and Technologies Conference (PEDSTC). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Ghaffari, A.; Khodayari, A.; Kamali, A.; Zhilakzadeh, N.; Ebrahimi, N. Fuzzy control of anticipation and evaluation behaviour in real traffic flow. 2019 7th International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (ICRoM). IEEE, 2019, pp. 248–253. [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Ebrahimi Toulkani, N. Implementation and intelligent gain tuning feedback–based optimal torque control of a rotary parallel robot. Journal of Vibration and Control 2022, 28, 2678–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Tajdari, M.; Rezaei, A. Discrete time delay feedback control of stewart platform with intelligent optimizer weight tuner. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). IEEE, 2021, pp. 12701–12707. [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Toulkani, N.E.; Nourimand, M. Intelligent architecture for car-following behaviour observing lane-changer: Modeling and control. 2020 10th International Conference on Computer and Knowledge Engineering (ICCKE). IEEE, 2020, pp. 579–584. [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Golgouneh, A.; Ghaffari, A.; Khodayari, A.; Kamali, A.; Hosseinkhani, N. Simultaneous intelligent anticipation and control of follower vehicle observing exiting lane changer. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2021, 70, 8567–8577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, N.F.; Ayati, M.; Basaeri, H.; Yousefi-Koma, A.; Tajdari, F.; Jokar, M. Hysteresis modeling for a shape memory alloy actuator using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. 2015 3Rd RSI international conference on robotics and mechatronics (ICROM). IEEE, 2015, pp. 320–324. [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F. Adaptive time-delay estimation and control of optimized Stewart robot. Journal of Vibration and Control, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, M.; Tajdari, F.; Shirzadian, P.; Pawar, A.; Wardak, M.; Saha, S.; Park, C.; Huysmans, T.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; others. Next-generation prognosis framework for pediatric spinal deformities using bio-informed deep learning networks. Engineering with Computers 2022, 38, 4061–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Huysmans, T.; Song, Y. Non-rigid registration via intelligent adaptive feedback control. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F. ; others. Optimal and adaptive controller design for motorway traffic with connected and automated vehicles 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jenke, R.; Peer, A.; Buss, M. Feature extraction and selection for emotion recognition from EEG. IEEE Transactions on Affective computing 2014, 5, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Huysmans, T.; Yang, Y.; Song, Y. Feature preserving non-rigid iterative weighted closest point and semi-curvature registration. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2022, 31, 1841–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, T.; Huysmans, T.; Elkhuizen, W.S.; Tajdari, F.; Song, Y. Posture-invariant three dimensional human hand statistical shape model. Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering 2021, 21, 031006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Eijck, C.; Kwa, F.; Versteegh, C.; Huysmans, T.; Song, Y. Optimal position of cameras design in a 4D foot scanner. International design engineering technical conferences and computers and information in engineering conference. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2022, Vol. 86212, p. V002T02A044. [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Kwa, F.; Versteegh, C.; Huysmans, T.; Song, Y. Dynamic 3d mesh reconstruction based on nonrigid iterative closest-farthest points registration. International design engineering technical conferences and computers and information in engineering conference. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2022, Vol. 86212, p. V002T02A051. [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, M.; Tajdari, F.; Pawar, A.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.K. 2D to 3D volumetric reconstruction of human spine for diagnosis and prognosis of spinal deformities. Conference: 16th US national congress on computational mechanics, 2021.
- Jirayucharoensak, S.; Pan-Ngum, S.; Israsena, P.; others. EEG-based emotion recognition using deep learning network with principal component based covariate shift adaptation. The Scientific World Journal 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Huysmans, T.; Yao, X.; Xu, J.; Song, Y. 4D Feet: Registering Walking Foot Shapes Using Attention Enhanced Dynamic-Synchronized Graph Convolutional LSTM Network. Computer Vision, 2023, pp. 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Roncoli, C.; Papageorgiou, M. Feedback-based ramp metering and lane-changing control with connected and automated vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2020, 23, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F. Online set-point estimation for feedback-based traffic control applications. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Nie, D.; Lu, B.L. Emotional state classification from EEG data using machine learning approach. Neurocomputing 2014, 129, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, H.; Ma, L.; Liu, Q.; Xu, R.; Li, H. Music-evoked emotion recognition based on cognitive principles inspired EEG temporal and spectral features. International journal of machine learning and cybernetics 2019, 10, 2439–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Chen, S.; others. Distinguishing different emotions evoked by music via electroencephalographic signals. Computational intelligence and neuroscience 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keelawat, P.; Thammasan, N.; Numao, M.; Kijsirikul, B. Spatiotemporal emotion recognition using deep CNN based on EEG during music listening. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.09719, arXiv:1910.09719 2019. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Qiu, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. Emotion recognition from multi-channel EEG through parallel convolutional recurrent neural network. 2018 international joint conference on neural networks (IJCNN). IEEE, 2018, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Han, J.; Min, K. A multi-column CNN model for emotion recognition from EEG signals. Sensors 2019, 19, 4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P. Emotion recognition from spatiotemporal EEG representations with hybrid convolutional recurrent neural networks via wearable multi-channel headset. Computer Communications 2020, 154, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Roncoli, C.; Bekiaris-Liberis, N.; Papageorgiou, M. Integrated ramp metering and lane-changing feedback control at motorway bottlenecks. 2019 18th European Control Conference (ECC). IEEE, 2019, pp. 3179–3184. [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Ramezanian, H.; Paydarfar, S.; Lashgari, A.; Maghrebi, S. Flow metering and lane-changing optimal control with ramp-metering saturation. 2022 CPSSI 4th International Symposium on Real-Time and Embedded Systems and Technologies (RTEST). IEEE, 2022, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Roncoli, C. Adaptive traffic control at motorway bottlenecks with time-varying fundamental diagram. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2021, 54, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Khodabakhshi, E.; Kabganian, M.; Golgouneh, A. Switching controller design to swing-up a two-link underactuated robot. 2017 IEEE 4th International Conference on Knowledge-Based Engineering and Innovation (KBEI). IEEE, 2017, pp. 0595–0599. [CrossRef]
- Minnoye, A.L.; Tajdari, F.; Doubrovski, E.L.; Wu, J.; Kwa, F.; Elkhuizen, W.S.; Huysmans, T.; Song, Y. Personalized product design through digital fabrication. International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2022, Vol. 86212, p. V002T02A054. [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Kabganian, M.; Khodabakhshi, E.; Golgouneh, A. Design, implementation and control of a two-link fully-actuated robot capable of online identification of unknown dynamical parameters using adaptive sliding mode controller. 2017 Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (IRANOPEN). IEEE, 2017, pp. 91–96. [CrossRef]
- Tajdari, F.; Toulkani, N.E.; Zhilakzadeh, N. Semi-real evaluation, and adaptive control of a 6dof surgical robot. 2020 11th Power Electronics, Drive Systems, and Technologies Conference (PEDSTC). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Koen, B.D. Devotional music and healing in Badakhshan, Tajikistan: Preventive and curative practices; The Ohio State University, 2003.
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep learning. Book in preparation for MIT Press. URL!` http://www. deeplearningbook. org 2016, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Srivastava, N.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors. arXiv preprint arXiv:1207.0580, arXiv:1207.0580 2012. [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. International conference on machine learning. pmlr, 2015, pp. 448–456.
- Konar, A. Computational intelligence: principles, techniques and applications; Springer Science & Business Media, 2006.
- Phan, H.; Andreotti, F.; Cooray, N.; Chén, O.Y.; De Vos, M. Automatic sleep stage classification using single-channel eeg: Learning sequential features with attention-based recurrent neural networks. 2018 40th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC). IEEE, 2018, pp. 1452–1455. [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural computation 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
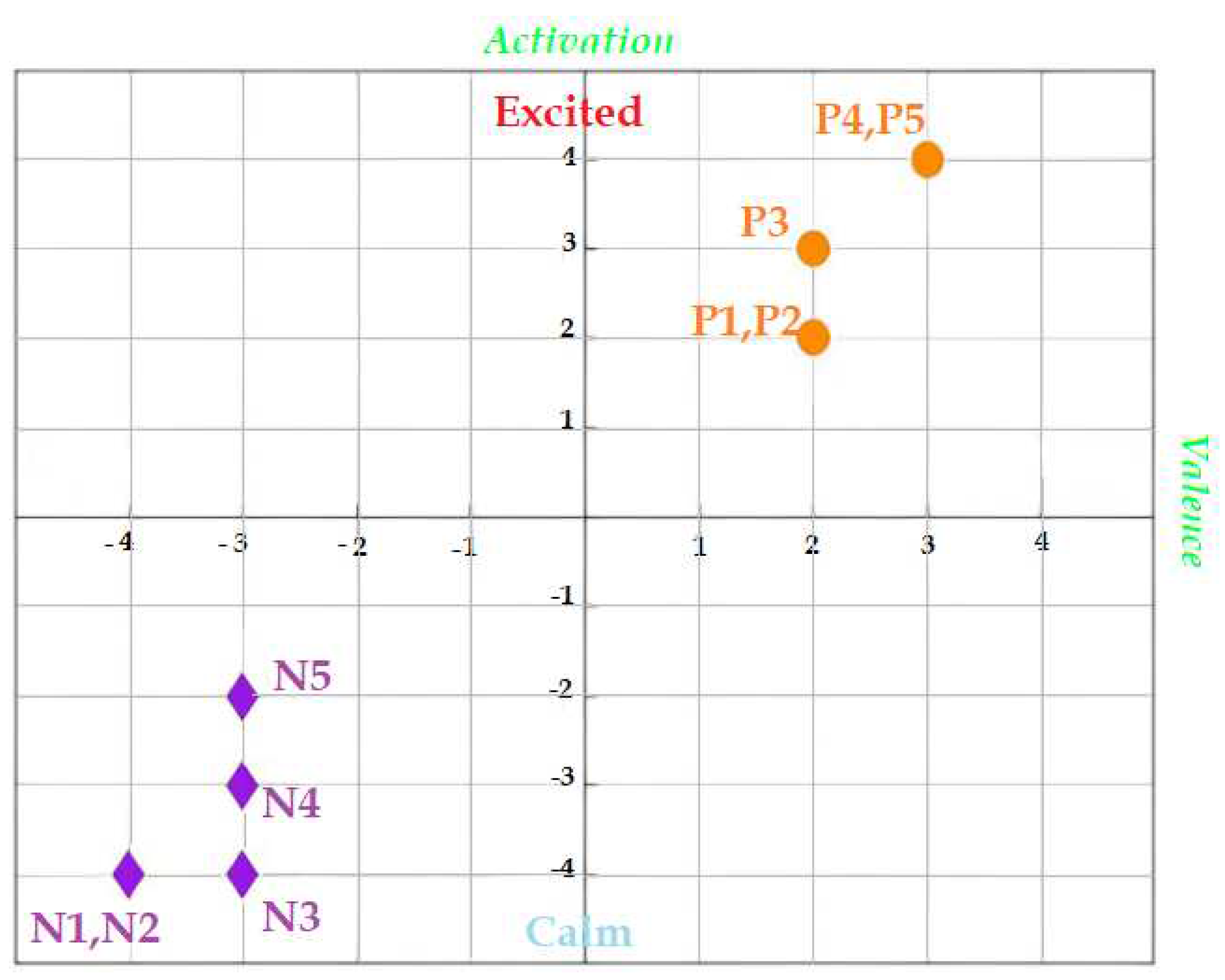
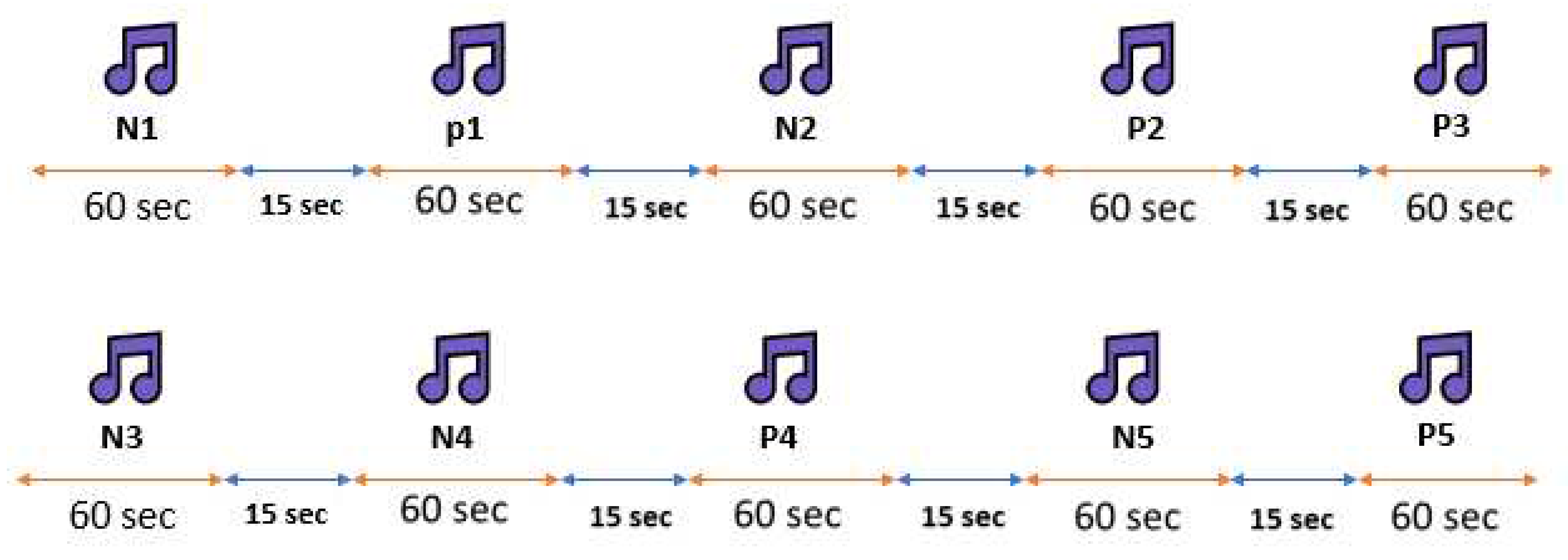
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




