1. Introduction
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common and under-recognized public health problem, associated with increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality and significant increases in health and social costs [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Obesity has long been recognized as one of the most significant risk factors for OSA [
5]. Furthermore, the prevalence of OSA increases with adiposity and is greater than 50-80% for individuals who are classified as overweight or obese [
6].
OSA should be approached as a chronic disease that requires pathophysiological and clinical phenotyping, objective diagnostic testing and individualized treatment plan with Positive airway pressure (PAP) as the first-line symptomatic treatment of choice. However, PAP acceptance and compliance remain a challenging issue [
7]. Given the low compliance rates to PAP treatment, and the strong association between obesity and OSA, lifestyle interventions have emerged as complementary therapeutic choices. In line with this, the American Heart Association recommends including weight-loss-focused lifestyle interventions alongside conventional OSA treatment [
2].
Lifestyle induced weight loss has been extensively investigated as a treatment approach to reverse OSA pathogenesis and is effective in improvement in both OSA severity and OSA-related symptoms [
8,
9,
10]. The combination of PAP therapy and a 6-month behavioral dietary/lifestyle modification program based on the Mediterranean pattern was demonstrated to be effective in reducing weight and improving OSA severity, as well as providing advantageous anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and cardiometabolic outcomes in patients with OSA. [
11,
12,
13]. While weight regain is expected in the long-term, these cardiometabolic benefits appear to be sustainable even after six months following the intervention [
14].
Besides improvements in OSA severity and cardiometabolic parameters, no evaluation has been undertaken to determine the effect of diet/lifestyle interventions on objective PAP adherence. Therefore, the aim of our study was to explore the role of a 6-month diet/lifestyle intervention on treatment adherence and clinical outcomes in patients with OSA. Specifically, we evaluated the effects of a combination of PAP and weight-loss Mediterranean diet/lifestyle intervention on improving PAP adherence (hours of device use), Body mass index (ΒΜΙ), daytime symptoms, mainly sleepiness and arterial blood pressure measurements over the effect of usual (standard) care alone.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Patients
We conducted a parallel, randomized, controlled, follow up study of consecutive patients who were admitted to the Sleep Disorders Center, Department of Respiratory Medicine, University of Crete Medical School, between December 2021 and March 2022. The inclusion criteria were a) Patients aged >18 years with newly diagnosed moderate to severe OSA [apnea-hypopnea index (AHI)≥15 events/h] through an attended overnight polysomnography according to standard criteria, b) overweight and obese [BMI>25 kg/m2] c) eligible for PAP treatment with adherence data available in the 6-months after initiation of treatment and d) with an above-elementary school education. The exclusion criteria were: refusal to participate, patients on PAP treatment, current participation in a weight loss program, central sleep apnea syndromes, obesity hypoventilation syndrome, restrictive ventilator syndromes, severe congestive heart failure, a history of life-threatening arrhythmias, severe cardiomyopathy, long-term oxygen therapy, chronic kidney disease, family or personal history of mental illness, drug or alcohol abuse, severe cognitive impairment, concurrent oncological diseases, pregnancy or lactation, recent hospitalization for acute or chronic respiratory disease, history of narcolepsy or restless leg syndrome. All subjects provided written informed consent and ethical approval was provided by the University of Crete Research Ethics Committee (REC-UOC) (approval number: 158/29.11.2021).
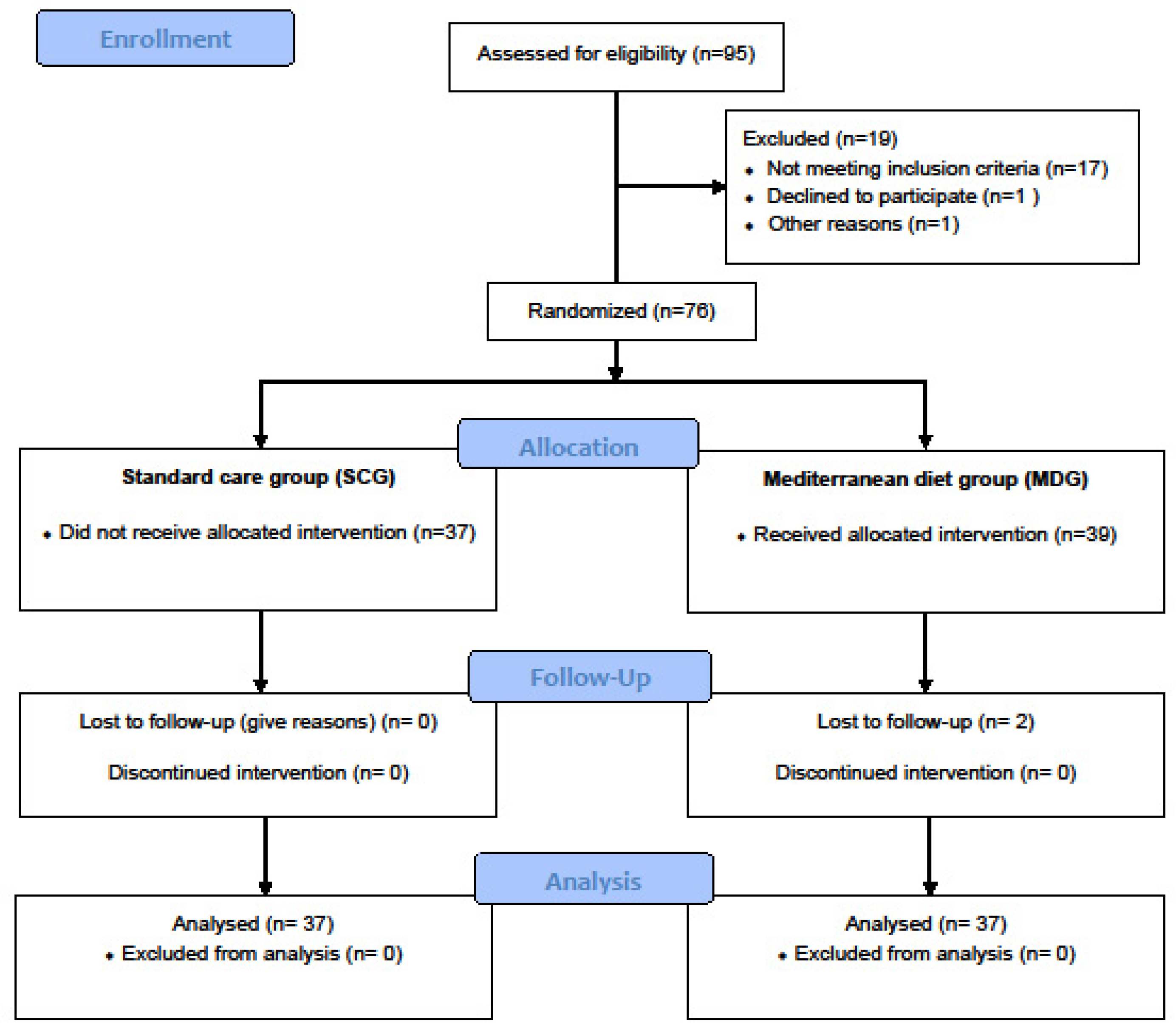
Individuals were assigned (1:1) to a usual (standard) care group (SCG, n=39) receiving usual follow-up care or an intervention group - Mediterranean diet group (MDG, n=37) with follow-up care based on an additional behavioral intervention aiming at weight loss and increasing adherence to the Mediterranean diet. (
Figure 1). The patients were blinded to the group to which they were assigned and followed for 6 months.
2.2. Data Collection
All patients underwent a detailed evaluation that included anthropometric parameters, including BMI, medical and sleep history, and comorbidities, including physician-based diagnosis for depression, smoking history and alcohol intake. Subjective daytime sleepiness, reflected by the Epworth sleepiness scale (ESS), and the patient’s level of depression Beck Depression scale (BDI) were also recorded before PAP initiation. ESS, PAP adherence (hours of device use), BMI, and arterial blood pressure measurements were also evaluated pre- and post-intervention.
2.2.1. Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS)
The ESS is currently the most widely used subjective test of daytime sleepiness in clinical practice [
15]. A score of 10 or higher represents excessive daytime sleepiness.
2.2.2. Beck Depression Inventory (BDI)
This 21-item questionnaire is a widely used and well-validated self-reported inventory of depressive symptoms [
16]. The BDI measures the severity of depressive symptoms over the preceding week. For each item, the respondent chooses one or more options rated from 0 (absence of symptoms) to 3 (most severe level). Total scores range from 0 to 63 and represent the sum of the highest level endorsed on each item. Scores below 10 are considered normal.
2.3. Follow Up—Usual (Standard) Care Group
All patients before treatment initiation attended a PAP clinic, where they were given specific counseling and education on the proper use and maintenance of PAP and underwent personalized, formal mask fitting by a specialized nurse. The total time for the appointment in the PAP clinic was 20 min/patient. Once PAP was started, patients were reviewed in the outpatient sleep clinic at 1-month and at 3-month intervals during the first year, and every 6 months thereafter. During these appointments, a clinical assessment was made, and patients were further encouraged to use the device. In addition, all patients received oral healthy lifestyle advice and counseling on physical activity and sleep habits and had the opportunity to discuss other health issues related to the condition, such as weight reduction and smoking cessation. At each visit, the compliance data were downloaded from the PAP device and reviewed by the PAP clinic nurse together with the patients. Any concerns or questions, such as pressure sores, persistent air leakage, claustrophobia, nasal congestion, and other side effects resulting from the nasal mask interface that might lead to suboptimal compliance were addressed immediately by the PAP clinic nurse. Changes in the PAP setting, nose/face mask, or circuit were made after consultation with the responsible sleep physician if necessary. In every follow-up visit, residual symptoms, including residual sleepiness, or change in patient's overall health status were recorded from the sleep nurse and sleep physician. This format adhered to a standardized approach according to our PAP clinic’s procedures [
17].
2.4. Follow Up—Intervention Group
All patients in the intervention group attended individual 60–90 min sessions weekly led by dietologist in the first month and twice/month thereafter. In this group, all the features described above for the standard group were included, plus additional visits involving intensive dietitian-led behavioral intervention aiming at weight loss and increasing adherence to the Mediterranean diet [
18]. This intervention was tailored to meet the specific needs of these patients. Guidance in physical exercise, optimal sleep length, and sleep hygiene education were also given.
Dietary behavior was assessed through the Food Frequency Questionnaire [
19] and Mediterranean Diet Score [
20] before PAP initiation. Then, a personalized Therapeutic Diet Plan was implemented in this group.
2.4.1. Food Frequency Questionnaire
The FFQ used in this study has previously been demonstrated to be reproducible and relatively valid to assess practically all food groups, as well as macronutrients and energy consumption [
19]. It includes 75 items (foods and beverages commonly consumed in Greece and dietary habits). The amounts of food consumed were expressed in grams or milliliters or in other common measures, such as slice, tablespoon or cup, representing the standard serving size. On a 6-point scale, participants were asked to report how frequently they consumed each of the meals and beverages listed in the FFQ on average over the month period preceding the study period (never/rarely, 1–3 times/month, 1–2 times/week, 3–6 times/week, 1 times/day or ≥2 times/day).
2.4.2. Mediterranean Diet Score
The Mediterranean Diet Score (MedDietScore) is a 14-item validated questionnaire produced for each participant to assess their level of adherence to the Mediterranean Diet, taking into consideration their consumption of food items from nine food groups, as well as olive oil and alcoholic beverages [
20]. Each of the 14 items is scored one or zero, depending on whether participants adhere to each MedDiet component or not. The Mediterranean Diet Score has a range of 0-55, with higher values indicating greater adherence to the Mediterranean Diet.
2.5. PAP Adherence
PAP usage data included mask type (nasal or full face), number of nights on PAP, average use per night (hours), air leakage and air pressure delivered. The usage of PAP, effective pressures and residual AHI was monitored at 1, 6, 12 months after initiation, and patients were contacted by a trained sleep nurse. Patients were also encouraged to contact the telephone helpline during working hours. The humidification was defined based on patients’ feedback and was adjusted if necessary, during the follow up. In order to optimize PAP adherence unplanned visits were immediately arranged in case low adherence to PAP therapy. Regular PAP compliance was defined as using the therapy for an average of 4 hours a night for at least 70% of the nights [
21]. However, in our study for optimal PAP adherence we used the cut-off point of six hours of PAP use [
17,
22].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
A pilot study was conducted with 49 individuals to determine the sample size. With the data obtained from the pilot study, the sample size was determined as at least 63 individuals, to obtain at least 80% power to detect a significant difference in the follow-up mean hours of PAP use values between MDG and SCG, allowing for a type-I error rate of 0.05.
Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) for continuous variables if normally distributed and as median (25th-75th percentile) if not. Qualitative variables are presented as absolute number (percentage). For comparisons between groups, a two-tailed t-test for independent samples (for normally distributed data) or a Mann–Whitney U test (for non-normally distributed data) was utilized for continuous variables and the chi-square test for categorical variables. The analysis of covariance was used to test adjusted between-group differences at the end of the 6-month intervention. All models were adjusted for basic confounders, namely age and gender, baseline BMI, smoking status, questionnaires scores and co-morbidities. Analyses were additionally adjusted for weight loss (expressed as BMI difference) to test the weight-loss independent impact of the dietary/lifestyle intervention implemented on PAP adherence. Factors associated with optimal adherence (use of the device ≥6 hours) at 6 months follow up were analyzed with bivariate logistic regression after adjustment for various potential basic explanatory confounders. We checked multicollinearity among the predictors using collinearity statistics to ensure that collinearity between predictor variables was in the acceptable range as indicated by the tolerance value variance inflation factor. Age was considered continuously and categorically, as age groups of 18–59 and >60 years, BMI was also considered continuously and categorically, as BMI groups of <30 and ≥30 kg/m2. For the purpose of this analysis, the term cardiovascular disease (CVD) used, referred to any of the following conditions: coronary disease, stroke, atrial fibrillation and heart failure. Results were considered significant when p values were < 0.05. Data were analysed using SPSS software (version 25, SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL).
3. Results
Of 96 individuals with suspected OSA screened, 18 were non-eligible (mild OSA, normal weight, presence of other chronic diseases, etc.), one declined participation, and the remaining 76 were enrolled and randomized (SCG: 37, MDG: 39). After enrollment, 2 participants were excluded (lost to follow up), leaving a final sample of 74 patients for analysis (SCG: 37, MDG: 37).
3.1. Comparison of Baseline Characteristics between SCG and MDG Groups
Participants’ socio-demographic and health status characteristics are described in
Table 1. Most of the participants were men (78%), obese (77%), current or former smokers (64%) with a medium educational level. The most prevalent diseases were hypertension (49%), followed by dyslipidemia (39%), CVD (27%) and COPD (22%). There was a significantly higher proportion of men in the intervention group compared to the control group. Differences in other evaluated characteristics remained relatively insignificant between two groups, including age, other comorbidities, and smoking status (all p >0.05), except for presence of cardiovascular disease CVD (41 vs. 14%, p=0.009).
Comparison of PSG parameters of the SCG and MDG population showed no significant differences between groups (
Table 2). Although no significant difference was noted between nocturnal and diurnal symptoms (
Table 3), frequent awakenings reported were significantly higher in MDG compared to SCG (65 vs. 41%, p=0.04).
Regarding lifestyle habits, the MDG group exhibited moderate level of adherence to Mediterranean diet as evaluated by MedDietScore (29 ±5).
3.2. PAP Adherence
All patients continued to use their PAP at the end of the follow up period. Post intervention PAP use was significantly higher in the MDG group compared to SCG (6.1 ± 1.2 vs. 5.4 ± 1.4, p=0.02). Further analysis showed that this difference persisted after adjustments for age, gender, BMI, difference in BMI, ESS, difference in ESS, BDI score, OSA severity, and comorbidities (5.2 vs. 6.1, p=0.03). Moreover, diet/lifestyle intervention was one of the most significant predictive factors for optimal PAP adherence (OR = 5.458, 95% CI = 1.144-26.036, p=0.03) (
Table 4).
3.3. Effect of Diet Intervention on Anthropometric and Daytime Symptoms Parameters
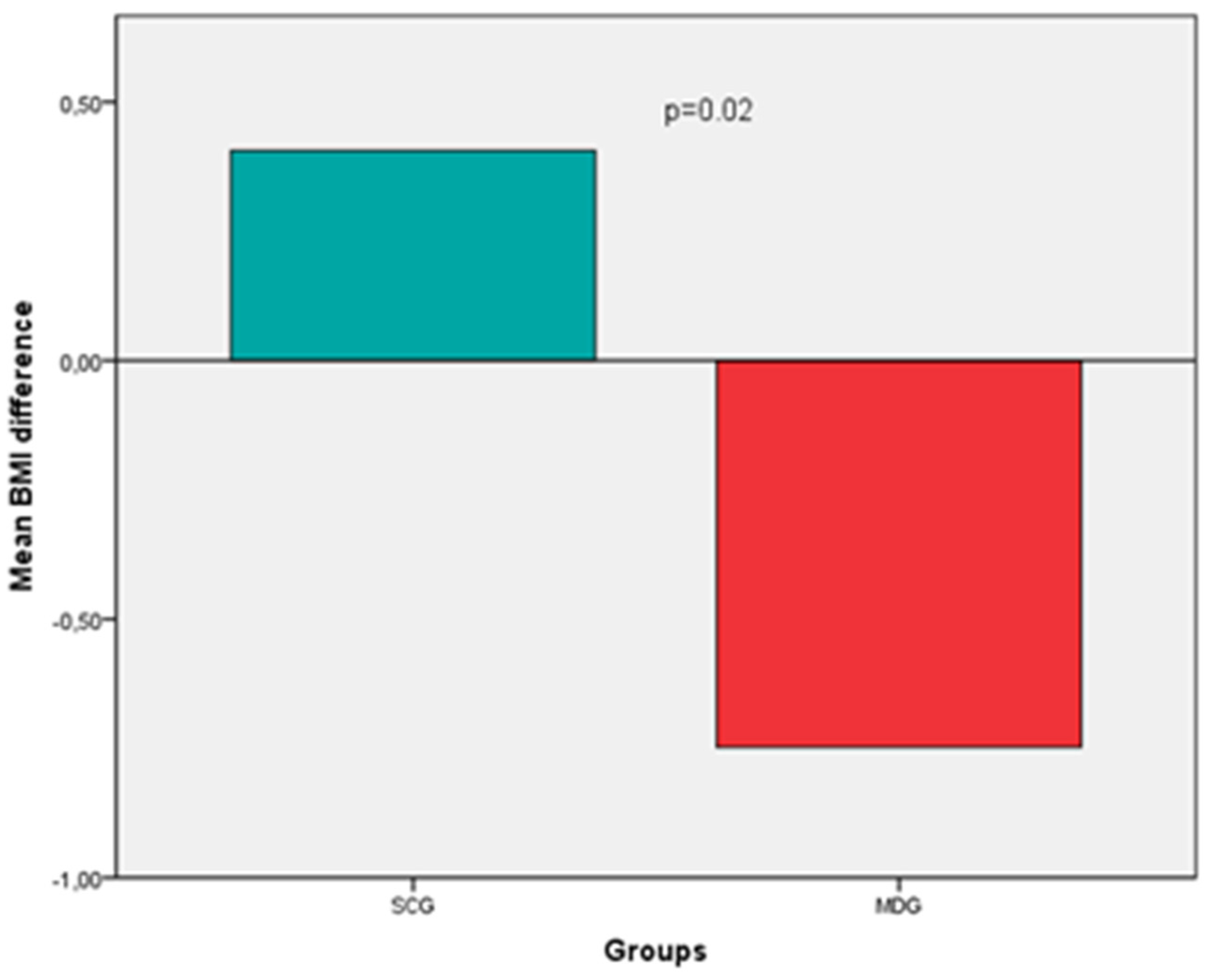
Regarding BMI, an increase was noted in the SCG group, whereas a decrease (improvement) in the MDG, (0.41 ± 1.8 vs. -0.75 ± 1.3, p=0.02) (
Figure 2). Specifically, at the 6-month follow-up, patients in the SCG exhibited a mean weight gain of 1.6% of their baseline body weight, while those in the MDG a loss equal to 1.5% (p=0.04). BMI difference, although attenuated, persisted after adjustments for age, gender, BMI, ESS, BDI score, OSA severity, PAP adherence and comorbidities (0.23 vs. -0.55, p=0.31).
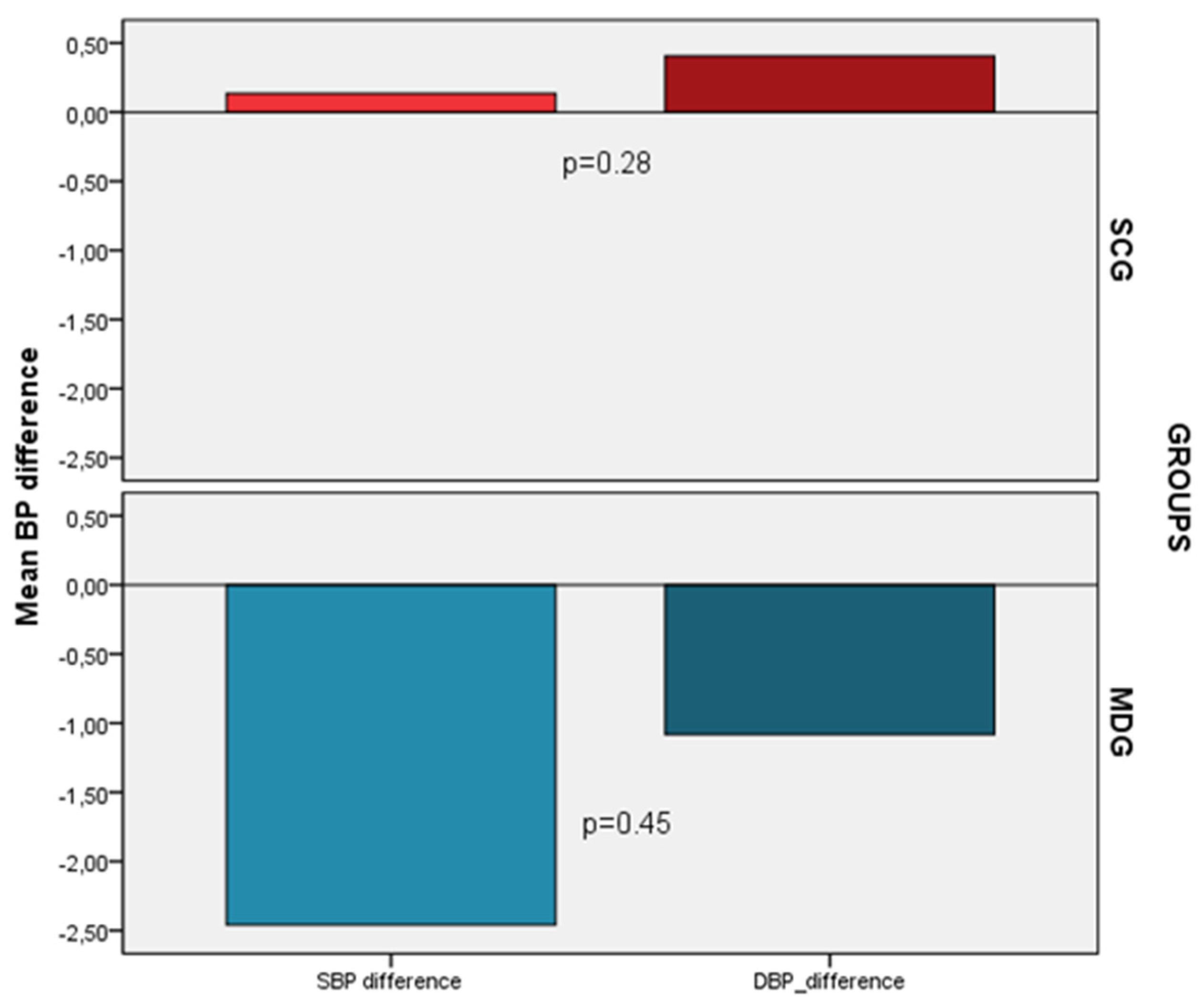
Despite the decrease noticed only in the MDG (SBP -2.5 ± 11, DBP -1.1 ± 7.6) compared to SCG (SBP 0.14 ± 9.2, DBP 0.40 ± 9.2) in blood pressure measurements after the 6 months follow period, these changes were not statistically significant (p=0.28 and p=0.45, respectively) (
Figure 3). However, after adjusting for confounders a significant decrease in SBP (-5.5 vs. 2.8, p=0.014) and DBP (-4.0 vs. 2.5, p=0.01) was noted in the MDG compared to SCG.
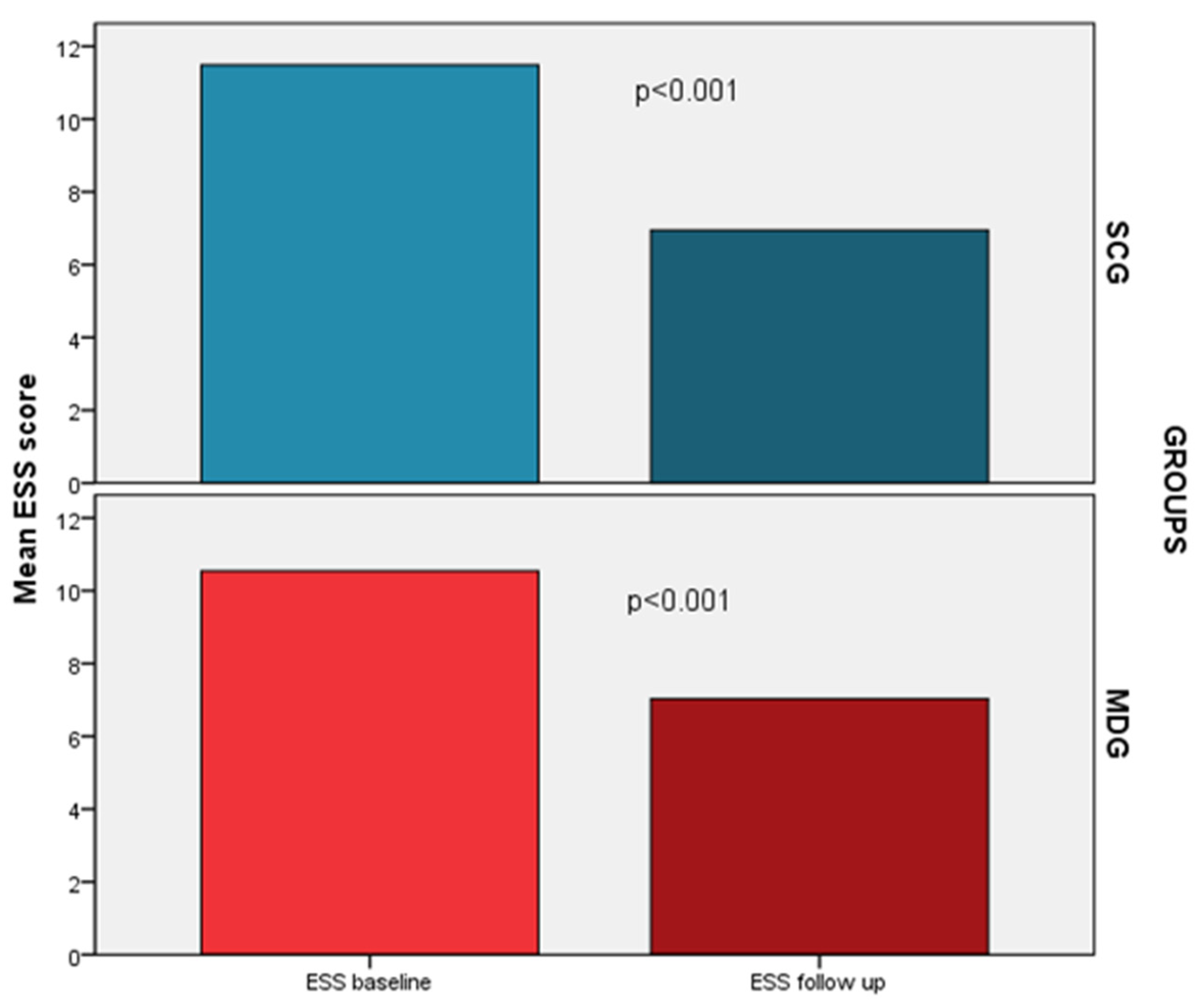
A significant decrease in ESS was also noted in both groups; nevertheless, no group had a significant predominance in this improvement (-4.5 vs. -3.5, p=0.19), even after adjustment for confounders (
Figure 4). In addition, both groups presented a significant decrease in the proportion of patients with excessive daytime sleepiness (SCG: 19% vs. 62%, p<0.001, MDG: 16% vs. 54%, p<0.001). Residual sleepiness at the end of the follow up period did not differ between groups (16 vs. 19%, p=0.76).
4. Discussion
Our study assessed the impact of dietary/lifestyle intervention along with usual care on PAP adherence, BMI, BP measurements and sleepiness in moderate to severe OSA patients. The intervention demonstrated significant and clinically meaningful improvements in PAP adherence, BMI, BP measurements in the intervention compared to the control group, independently of age, gender, BMI, weight loss, baseline level of sleepiness, depressive symptoms, OSA severity and comorbidities and even though participants were enrolled in the study for a period of six months.
This is the first study demonstrating the favorable effect of incorporating a dietary/lifestyle intervention in combination with standard care towards objective PAP adherence, in Greece. The findings suggest that providing intensive support with increased time spent in the MDG group may prove beneficial in enhancing PAP compliance, irrespective of weight loss. While previous studies, with comparable follow up times, have investigated the impact of diet and lifestyle interventions alongside usual care on various OSA severity and cardiometabolic parameters, there has been no objective evaluation of PAP adherence [
13,
14,
23,
24,
25]. Only self-reported PAP adherence was reported in a limited number of studies [
13,
14,
24,
25]. Compared to our study, Georgoulis et al found a lower self-reported average PAP use of roughly 4 hours/day [
13]. Likewise, they observed a greater PAP compliance in the Mediterranean lifestyle group when compared to the Mediterranean diet alone and standard care group six months following the intervention [
14]. Although Schiavo et al in a similar study investigating the effect of a low-calorie ketogenic diet combined with PAP therapy on OSA and cardiometabolic parameters acknowledged that they monitored adherence to PAP treatment through a wireless router linked to the device, they did not provide relevant data [
26].
Despite recommendations [
27] and studies indicating better clinical outcomes [
28] with diet-induced weight loss as part of OSA treatment, interventions targeting weight loss through lifestyle changes are underutilized. Indeed, based on MeditDietScore we found medium adherence to Mediterranean Diet in our patients, indicating that non-conventional management was not regarded as an essential component of care from the patient point of view. Furthermore, another challenge was the lack of specific educational skills from health care professionals to support diet/lifestyle interventions or promote behavior change in these patients. Optimizing OSA treatment is crucial for clinicians, but many fail to recognize the importance of incorporating diet and lifestyle interventions into their treatment plans. Thus, our study has the potential to raise awareness regarding the importance of diet and lifestyle among OSA patients who are overweight or obese. Our results also demonstrated that the Mediterranean diet/lifestyle intervention contributed to improvements in BMI and BP measurements compared with standard care. These benefits were evident even after adjustment for confounders, suggesting that the Mediterranean lifestyle can lead to cardiovascular benefits beyond weight loss in these patients. These findings are noteworthy as they align with prior research indicating more weight loss in patients following diet/lifestyle intervention than standard care [
12,
13,
14,
23,
26]. Although the weight loss achieved in our study was below the recommended 5% - 10% for managing obesity and achieving health benefits, even a slight reduction in weight was seen as beneficial for health, particularly among patients with OSA [
13,
29,
30]. Another study we conducted involved randomly assigning 40 obese individuals with OSA undergoing PAP treatment to either a weight-loss Mediterranean diet or a weight-loss prudent diet for 6 months. The group on the Mediterranean diet showed more significant weight loss, but the results were not statistically significant due to a small number of participants (27). In the MIMOSA RCT conducted recently, a dietary/lifestyle intervention also based on the Mediterranean pattern was combined with PAP treatment for OSA patients, resulting in a notable improvement in weight reduction, OSA severity, and related symptoms when compared to standard care alone [
12,
28] .
At present, the prescription of PAP remains the first-line treatment for patients with moderate to severe OSA. However, effectiveness is dependent on the patient’s usage. Consequently, it is essential to take into account diet/lifestyle intervention as an added strategy in the treatment of OSA. These interventions provide a non-invasive approach that may also help to address PAP's adherence issues. Combining diet and exercise has been found to be an effective intervention in mitigating OSA severity [
28], therefore, it is probable that lower pressures will be required in the PAP machine [
33], making it easier for patients to tolerate high PAP pressures. In support of this, evidence suggests that patients diagnosed with OSA frequently encounter distress and are incapable of tolerating heightened PAP pressures, thus abandoning PAP devices [
34]. Furthermore, our intervention group had more regular contact with the same health professional specialized in dietetics, which was advantageous for PAP adherence, as previously reported [
17]. - Consequently, implementing diet and lifestyle interventions on a regular basis is valuable in treating OSA and must consistently implemented in all OSA patients.
The main strengths of the current study are the design (RCT) and implementation of a diet and lifestyle intervention readily adaptable to real-world clinical practice. On the other hand, the study has some limitations that deserve comments. Since it was a real-life implementation of a diet/lifestyle program, the results can only be generalized to patients who are motivated to participate in such a program and not to all OSA patients. Furthermore, it was a single-center trial in a primarily male patient population. Additionally, this study was carried out at the second wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, which resulted in small sample size. Besides that, a 6-month period was insufficient to determine long-term intervention effects and benefits maintenance. Future, large-scale studies therefore may need to consider these factors.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion our results provide evidence that overweight/obese patients with moderate-to-severe OSA can benefit significantly in terms of PAP adherence, BP and BMI control from behavioral interventions aiming at weight loss through the adoption of appropriate food and lifestyle practices. Therefore, it is essential to consider such type of intervention as an add-on approach for OSA management. However, additional evidence is needed from studies, including larger number of patients with longer-term follow-ups to explore the influence of diet/lifestyle interventions on OSA, and especially on the long-term sequelae.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.T. and I.B.; methodology, E.D.; software, I.B.; validation, I.B.., S.S. and I.T.; formal analysis, I.B..; investigation, E.D..; data curation, E.M. and V.M.; writing—original draft preparation, I.B.; writing—review and editing, I.B..; visualization, I.T.; supervision, S.S and S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the University of Crete Research Ethics Committee (REC-UOC) (approval number: 158/29.11.2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Benjafield, A. V.; Ayas, N. T.; Eastwood, P. R.; Heinzer, R.; Ip, M. S. M.; Morrell, M. J.; Nunez, C. M.; Patel, S. R.; Penzel, T.; Pépin, J. L.; Peppard, P. E.; Sinha, S.; Tufik, S.; Valentine, K.; Malhotra, A. Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of obstructive sleep apnoea: a literature-based analysis. Lancet Resp medicine 2019, 7, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeghiazarians, Y.; Jneid, H.; Tietjens, J. R.; Redline, S.; Brown, D. L.; El-Sherif, N.; Mehra, R.; Bozkurt, B.; Ndumele, C. E.; Somers, V. K. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 144, e56–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost & Sullivan; American Academy of Sleep Medicine. Hidden health crisis costing America billions: underdiagnosing and undertreating obstructive sleep apnea draining health care system. Published Aug. 8, 2016.
- Knauert, M.; Naik, S.; Gillespie, M. B.; Kryger, M. Clinical consequences and economic costs of untreated obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2015, 1, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.R. The complex relationship between weight and sleep apnoea. Thorax 2015, 70, 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareli, A. E.; Cantor, C. R.; Williams, N. N.; Korus, G.; Raper, S. E.; Pien, G.; Hurley, S.; Maislin, G.; Schwab, R. J. Obstructive sleep apnea in patients undergoing bariatric surgery--a tertiary center experience. Obes Surg 2011, 21, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, T.E.; Grunstein, R.R. Adherence to continuous positive airway pressure therapy: the challenge to effective treatment. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2008, 5, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, K.; Neovius, M.; Lagerros, Y. T.; Harlid, R.; Rössner, S.; Granath, F.; Hemmingsson, E. Effect of a very low energy diet on moderate and severe obstructive sleep apnoea in obese men: a randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2009, 339, b4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomilehto, H. P.; Seppä, J. M.; Partinen, M. M.; Peltonen, M.; Gylling, H.; Tuomilehto, J. O.; Vanninen, E. J.; Kokkarinen, J.; Sahlman, J. K.; Martikainen, T.; Soini, E. J.; Randell, J.; Tukiainen, H.; Uusitupa, M.; Kuopio Sleep Apnea Group. Lifestyle intervention with weight reduction: first-line treatment in mild obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2009, 179, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmach-Mardas, M.; Brajer-Luftmann, B.; Kuśnierczak, M.; Batura-Gabryel, H.; Piorunek, T.; Mardas, M. Body Mass Index Reduction and Selected Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Meta-Analysis. J Clin Med 2021, 10, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgoulis, M.; Yiannakouris, N.; Kechribari, I.; Lamprou, K.; Perraki, E.; Vagiakis, E.; Kontogianni, M. D. Cardiometabolic Benefits of a Weight-Loss Mediterranean Diet/Lifestyle Intervention in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: The "MIMOSA" Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgoulis, M.; Yiannakouris, N.; Tenta, R.; Fragopoulou, E.; Kechribari, I.; Lamprou, K.; Perraki, E.; Vagiakis, E.; Kontogianni, M. D. A weight-loss Mediterranean diet/lifestyle intervention ameliorates inflammation and oxidative stress in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: results of the "MIMOSA" randomized clinical trial. Eur J Nutr 2021, 60, 3799–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgoulis, M.; Yiannakouris, N.; Kechribari, I.; Lamprou, K.; Perraki, E.; Vagiakis, E.; Kontogianni, M. D. Dose-response relationship between weight loss and improvements in obstructive sleep apnea severity after a diet/lifestyle interventions: secondary analyses of the "MIMOSA" randomized clinical trial. J Clin Sleep Med 2022, 18, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgoulis, M.; Yiannakouris, N.; Kechribari, I.; Lamprou, K.; Perraki, E.; Vagiakis, E.; Kontogianni, M. D. Sustained improvements in the cardiometabolic profile of patients with obstructive sleep apnea after a weight-loss Mediterranean diet/lifestyle intervention: 12-month follow-up (6 months post-intervention) of the "MIMOSA" randomized clinical trial. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2023, 33, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, M.W. A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness:the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 1991, 14, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Garbin, M.G. Psychometric properties of the Beck depression inventory: twenty-five years of evaluation. Clin Psychol Rev 1988, 8, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouloukaki, I.; Giannadaki, K.; Mermigkis, C.; Tzanakis, N.; Mauroudi, E.; Moniaki, V.; Michelakis, S.; Siafakas, N. M.; Schiza, S. E. Intensive versus standard follow-up to improve continuous positive airway pressure compliance. Eur Respir J 2014, 44, 1262–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayram, S.Ş.; Aktaş, N. Mediterranean diet and frequently used indexes for measuring Mediterranean diet quality. International Eurasian congress on "natural nutrition and healthy life' 12-15 July (2018). In Proceedings book. M. R. Karaman, N. Artık, N. Şanlıer (Eds.). Ankara University Institute of Food Safety "Pelin Ofset; Press”.
- Bountziouka, V.; Bathrellou, E.; Giotopoulou, A.; Katsagoni, C.; Bonou, M.; Vallianou, N.; Barbetseas, J.; Avgerinos, P. C.; Panagiotakos, D. B. Development, repeatability and validity regarding energy and macronutrient intake of a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire: methodological considerations. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2012, 22, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotakos, D. B.; Pitsavos, C.; Arvaniti, F.; Stefanadis, C. Adherence to the Mediterranean food pattern predicts the prevalence of hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes and obesity, among healthy adults; the accuracy of the MedDietScore. Prev Med 2007, 44, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kribbs, N. B.; Pack, A. I.; Kline, L. R.; Smith, P. L.; Schwartz, A. R.; Schubert, N. M.; Redline, S.; Henry, J. N.; Getsy, J. E.; Dinges, D. F. Objective measurement of patterns of nasal CPAP use by patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1993, 147, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, T. E.; Maislin, G.; Dinges, D. F.; Bloxham, T.; George, C. F.; Greenberg, H.; Kader, G.; Mahowald, M.; Younger, J.; Pack, A. I. Relationship between hours of CPAP use and achieving normal levels of sleepiness and daily functioning. Sleep 2007, 30, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro-Barrera, A.; Amaro-Gahete, F. J.; Guillén-Riquelme, A.; Jurado-Fasoli, L.; Sáez-Roca, G.; Martín-Carrasco, C.; Buela-Casal, G.; Ruiz, J. R. Effect of an Interdisciplinary Weight Loss and Lifestyle Intervention on Obstructive Sleep Apnea Severity: The INTERAPNEA Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open 2022, 5, e228212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igelström, H.; Åsenlöf, P.; Emtner, M.; Lindberg, E. Improvement in obstructive sleep apnea after a tailored behavioural sleep medicine intervention targeting healthy eating and physical activity: a randomised controlled trial. Sleep Breath 2018, 22, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spörndly-Nees, S.; Åsenlöf, P.; Lindberg, E.; Emtner, M.; Igelström, H. Effects on obstructive sleep apnea severity following a tailored behavioral sleep medicine intervention aimed at increased physical activity and sound eating: an 18-month follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Sleep Med 2020, 16, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, L.; Pierro, R.; Asteria, C.; Calabrese, P.; Di Biasio, A.; Coluzzi, I.; Severino, L.; Giovanelli, A.; Pilone, V.; Silecchia, G. Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet with Continuous Positive Airway Pressure to Alleviate Severe Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Patients with Obesity Scheduled for Bariatric/Metabolic Surgery: a Pilot, Prospective, Randomized Multicenter Comparative Study. Obes Surg 2022, 32, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudgel, D. W.; Patel, S. R.; Ahasic, A. M.; Bartlett, S. J.; Bessesen, D. H.; Coaker, M. A.; Fiander, P. M.; Grunstein, R. R.; Gurubhagavatula, I.; Kapur, V. K.; Lettieri, C. J.; Naughton, M. T.; Owens, R. L.; Pepin, J. L.; Tuomilehto, H.; Wilson, K. C.; American Thoracic Society Assembly on Sleep and Respiratory Neurobiology. The role of weight management in the treatment of adult obstructive sleep apnea. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2018, 198, e70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokou, A.; Eleftheriou, A.; Tsigalou, C.; Apessos, I.; Nena, E.; Dalamaga, M.; Voulgaris, A.; Steiropoulos, P. Effect of the Implementation of a Structured Diet Management Plan on the Severity of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Systematic Review. Curr Nutr Rep 2023, 12, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M. D.; Ryan, D. H.; Apovian, C. M.; Ard, J. D.; Comuzzie, A. G.; Donato, K. A.; Hu, F. B.; Hubbard, V. S.; Jakicic, J. M.; Kushner, R. F.; Loria, C. M.; Millen, B. E.; Nonas, C. A.; Pi-Sunyer, F. X..; Stevens, J.; Stevens, V. J.; Wadden, T. A.; Wolfe, B. M.; Yanovski, S. Z.; Jordan, H. S.; et al. Obesity Society. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. In Circulation; 2014; Volume 129, pp. S102–S138. [Google Scholar]
- Yumuk, V.; Tsigos, C.; Fried, M.; Schindler, K.; Busetto, L.; Micic, D.; Toplak, H.; Obesity Management Task Force of the European Association for the Study of Obesity. Obesity Management Task Force of the European Association for the Study of Obesity. European Guidelines for obesity management in adults. Obes Facts 2015, 8, 402–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papandreou, C.; Schiza, S. E.; Bouloukaki, I.; Hatzis, C. M.; Kafatos, A. G.; Siafakas, N. M.; Tzanakis, N. E. Effect of Mediterranean diet versus prudent diet combined with physical activity on: a randomised trial. Eur Respir J 2012, 39, 1398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgoulis, M.; Yiannakouris, N.; Kechribari, I.; Lamprou, K.; Perraki, E.; Vagiakis, E.; Kontogianni, M. D. The effectiveness of a weight-loss Mediterranean diet/lifestyle intervention in the management of obstructive sleep apnea: results of the “MIMOSA” randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr 2021, 40, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankford, D.A.; Proctor, C.D.; Richard, R. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) changes in bariatric surgery patients undergoing rapid weight loss. Obes Surg 2005, 15, 336–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri, M.; Grunstein, R.R. Clinical side effects of continuous positive airway pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Respirology 2020, 25, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).