1. Introduction
SARS-CoV-2 belongs to the family Coronaviridae, genus Betacoronavirus. The morphology and structural features of the new virus are identical to those of the other human coronaviruses. Although the mutation rate is low, the number of variants, some of which are of concern (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, omicron variants and subvariants of omicron), has increased with the prolonged spread of the virus [
1]. New threatening variants often escape infection or vaccine-induced immunity. However, whether after infection or vaccination, previously acquired immunity leads to cross-protection against severe clinical forms of disease caused by the new variants of the virus [
2,
3,
4,
5]. The quantities of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies vary widely among patients and depend on numerous factors, such as the severity of clinical presentation, age, affiliated comorbidities, patients' immunocompetence, as well as the methods used to measure specific antibody titers [
5,
6]. However, despite the differences in serological values, reinfections by the same viral variant were not as frequent. This is confirmed by numerous studies conducted after the introduction of the vaccine, which showed that seropositive individuals had a significantly lower risk of re-infection than seronegative individuals, at least six months after infection [
6,
7]. Numerous studies have demonstrated differences in the quality of the immune response following infection or vaccination based on the tracking of markers of humoral and cellular immunity [
8]. Although there are no specific correlates for the protective role of immune response, the most important marker of the efficiency of the immune response is the presence of neutralizing antibodies, namely anti-RBD epitope antibodies and anti-S1 antigen antibodies, as these two enable the virus to bind to the ACE2 receptor [
9]. Given the importance of the cellular immune response, especially CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes, for the efficient elimination of infected cells, the most common marker of the protection provided by cellular immunity is the concentration of interferon gamma [
9,
10]. Most of the licensed vaccines induce immunity against the S protein. These vaccines are mainly based on mRNA and recombinant DNA technology. All of these vaccines are designed to induce vaccine immunity against the viral S antigen of the original Wuhan strains of SARS-CoV-2 and cause no change in nucleocapsid antibody titers in immunized individuals [
11,
12,
13]. The difference between these vaccines and the Sinopharm vaccine is that the latter contains complete inactivated viral particles. Therefore, there is particular interest in tracking the immune response after immunization with the Sinopharm vaccine because it is expected to induce immunity against all viral antigens, including the nucleocapsid antigens.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
The purpose of this study was to measure humoral and cellular immune response in immunized individuals six months after receiving the 3rd dose of SARS-CoV-2 Sinopharm vaccine. All participants included in the study voluntarily signed an informed consent, completed a self-questionnaire (
Appendix A) and had their blood drawn to perform the testing. The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the Institute for Biocides and Medical Ecology, Belgrade (protocol number 05-01 468/3-1, approved on 23.02.2022).
2.2. Participant Selection and Serum Collection
All participants who met the inclusion criteria and signed the informed consent were included in the study and divided into groups based on gender, history of SARS-CoV-2 natural infection and presence of cardiovascular, pulmonary and autoimmune diseases, diseases of the endocrine and nervous system, and liver and kidney diseases.
Serum samples were obtained by collecting 4 to 6 mL of whole blood in VACUETTE® Serum Tubes (Greiner Bio-One GmbH). The blood was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min (Gyrozen, 416 centrifuge) before aliquoting the serum. Upon testing, the serum was stored at −20°C. Samples for measuring SARS-CoV-2 T-cell specific response was obtained by collecting 4 to 6 mL of whole blood in VACUETTE® Heparin Tubes (Greiner Bio-One GmbH) and processed immediately according to manufacturer’s instructions. All the samples were collected between March and June 2022.
The study involved 103 participants in total, 28 males and 75 females. Anamnestic data for participants is presented in
Table 1. Of the 103 subjects, 36 had cardiovascular diseases, 11 had endocrine diseases, 13 had allergic reactions, and 4 had lung diseases (
Table 1.). None of them were pregnant, breastfeeding, had primary and secondary immuno-deficiencies, or diseases of the hematopoietic system. Thirty-two (32) of the 36 individuals with cardiovascular diseases had hypertension, one participant had myocarditis, one pericarditis and two of them had heart valve diseases (
Table 1.).
2.3. SARS-CoV-2 Serological Analyses
In this study, we used 5 different commercial SARS-CoV-2 ELISA tests for detection of humoral immune response against SARS-CoV-2. Details about the ELISA test used in this study are shown in Supplement 1.
2.4. T-Cell Response
The SARS-CoV-2 specific T-cell response was determined by a commercial interferon gamma (IFN γ) release assay (IGRA) using the Quant-T-Cell SARS-CoV-2 (product No. ET 2606-3003) and Quant-T-Cell ELISA (product No. EQ 6841-9601) manufactured by EUROIMMUN AG, Lübeck, Germany. The specific T-cell response was quantified according to the manufacturer’s instructions with values >100 mIU/mL marked as low positive, >200 mIU/mL marked as positive and values 100-200 mIU/mL as the grey zone.
2.5 Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed according to protocols described in Hinkle et al [
14]. Groups were analyzed using analyses of variance ANOVA, post hoc compared by Tukey’s HSD t-test, and p<0.05 was considered as significant. Correlation analysis was performed by Pearson’s correlation protocol.
2.6. SARS-CoV-2 Serological Analyses
SARS-CoV-2 serology was determined with semi-quantitative and quantitative commercial ELISA test listed in
Table A1. All tests were performed according to the manufacturer's instructions using a fully automated ELISA apparatus: EuroImmun I Analyzer (for EuroImmun tests) and DS2 Dynex Technologis (for TestLine tests and Shanghai GeneoDx Biotech Co, Ltd.
3. Results
Humoral and cellular immune responses in individuals six months after receiving the third dose of the vaccine in 103 individuals who had received three doses of Sinopharm vaccine (28 males and 75 females) showed positive values of anti-SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies - neutralizing antibodies, anti-N IgG antibodies, anti-S1 IgG antibodies and cellular immune response (IFN γ) while anti-RBD IgM antibodies and anti-N IgM antibodies levels were considered negative, as the values were lower than < 18 U/mL and < 0.8.
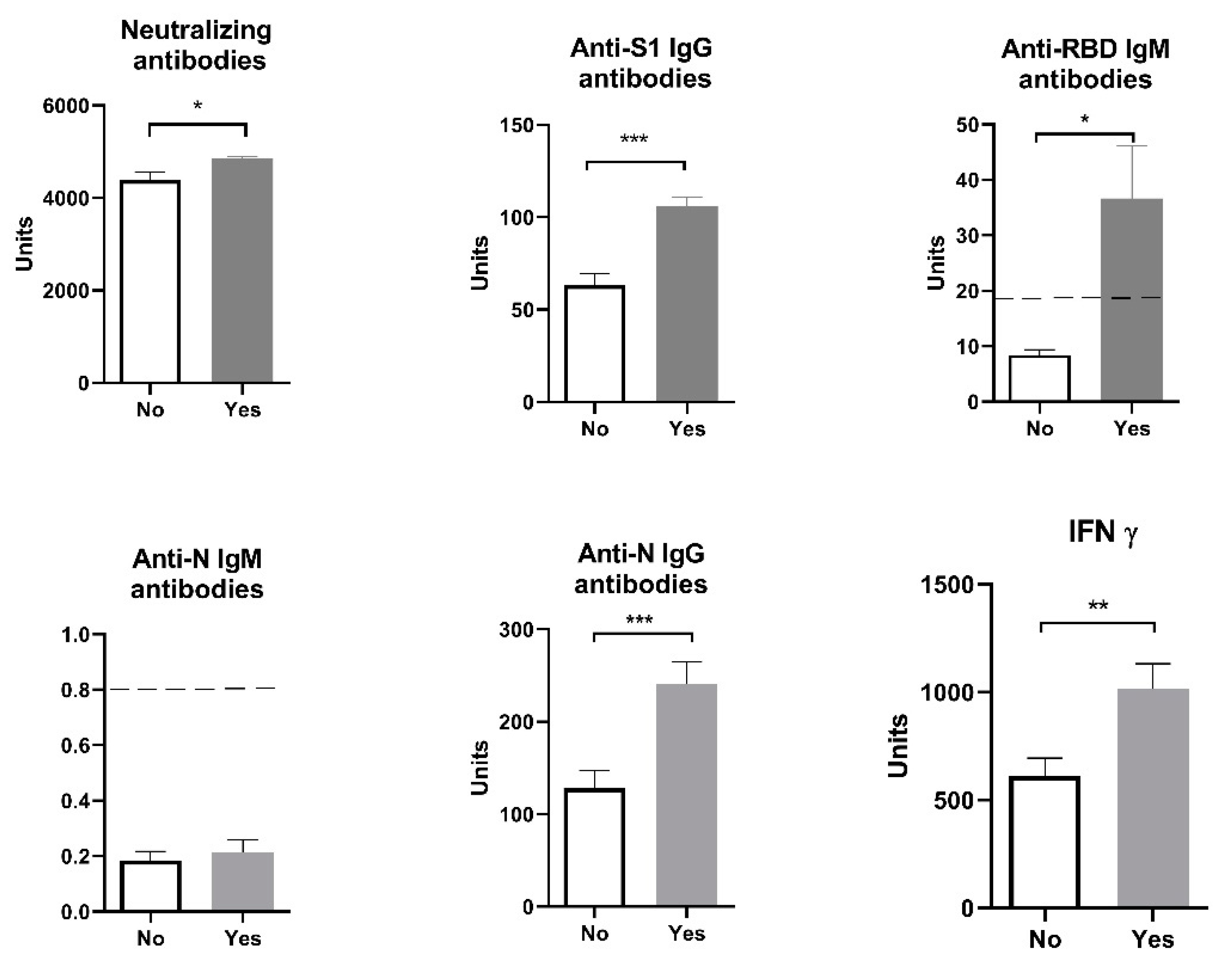
Our results showed that age (participants were divided into ten-year interval age groups: 20-30; 30-40; 40-50; 50-60) had no influence on the analyzed parameters: humoral anti-SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies - neutralizing antibodies (F=1.02, p > 0.05), anti-S1 IgG antibodies (F=0.21, p > 0.05), anti-N IgG antibodies (F=0.17, p > 0.05), and cellular immune response (IFN γ) (F=1.03, p > 0.05). When we divided all the patients by sex, the results also showed no sex difference between the analyzed parameters: humoral anti-SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing antibodies - NA (F=12.58, p > 0.05), anti-N IgG antibodies (F=1.029, p > 0.05), anti-S1 IgG antibodies (F=0.492, p > 0.05), and cellular immune response (IFN γ) (F=1.157, p > 0.05). However, levels of neutralizing antibodies, anti-S1 IgG, anti-N IgG and IFN γ are significantly higher in individuals who had COVID-19 before vaccination comparing to those who had been vaccinated but without a previous COVID-19 infection (
Figure 2). The values of anti-RBD IgM antibodies in individuals who were vaccinated following a COVID-19 infection is statistically significant and enters the positive values (>18 U/mL).
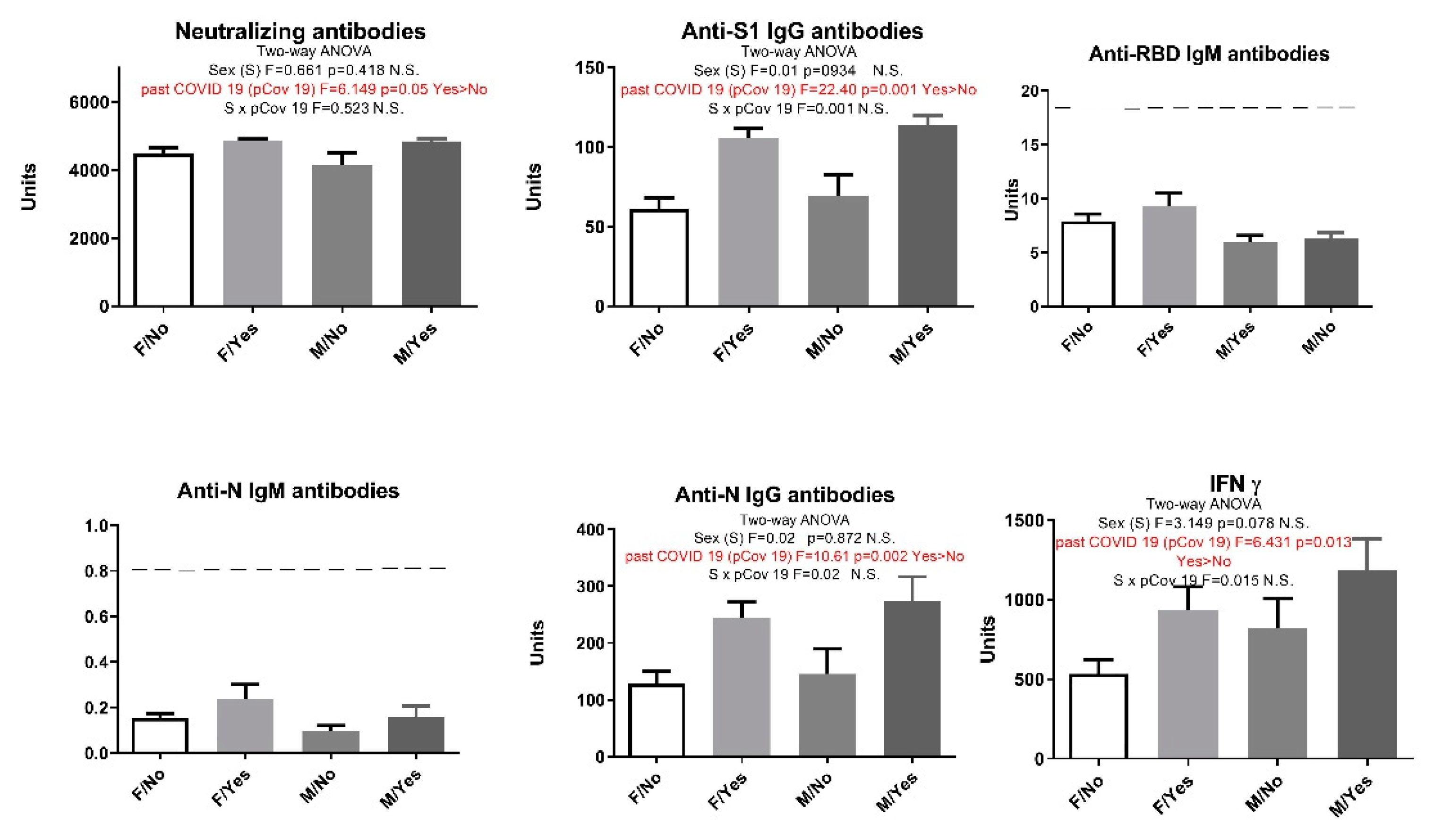
When all subjects were additionally separated by sex and previous history of COVID-19 and a two-way analysis ANOVA was performed, results showed that sex had no effect on the immune response, but in participants who have previously had COVID-19 we saw increased levels of INF γ, anti-N IgG and anti-S1 IgG antibodies (two-way ANOVA statistically significant effect of a previous infection) (
Figure 2).
Figure 1.
Humoral and cellular immune response after vaccination with 3 doses of Sinopharm vaccine based on previous COVID-19 history. No - subjects had no COVID-19; Yes - subjects had COVID-19; Below ------- negative values.
Figure 1.
Humoral and cellular immune response after vaccination with 3 doses of Sinopharm vaccine based on previous COVID-19 history. No - subjects had no COVID-19; Yes - subjects had COVID-19; Below ------- negative values.
Figure 2.
Humoral and cellular immune response after vaccination with 3 doses of Sinopharm vaccine based on sex and previous COVID-19 history. F/No - women who did not have COVID-19; F/Yes - women who had COVID-19; M/No - men who did not have COVID-19; M/Yes - men who had COVID-19. N.S. Not significant; Below ------- negative values.
Figure 2.
Humoral and cellular immune response after vaccination with 3 doses of Sinopharm vaccine based on sex and previous COVID-19 history. F/No - women who did not have COVID-19; F/Yes - women who had COVID-19; M/No - men who did not have COVID-19; M/Yes - men who had COVID-19. N.S. Not significant; Below ------- negative values.
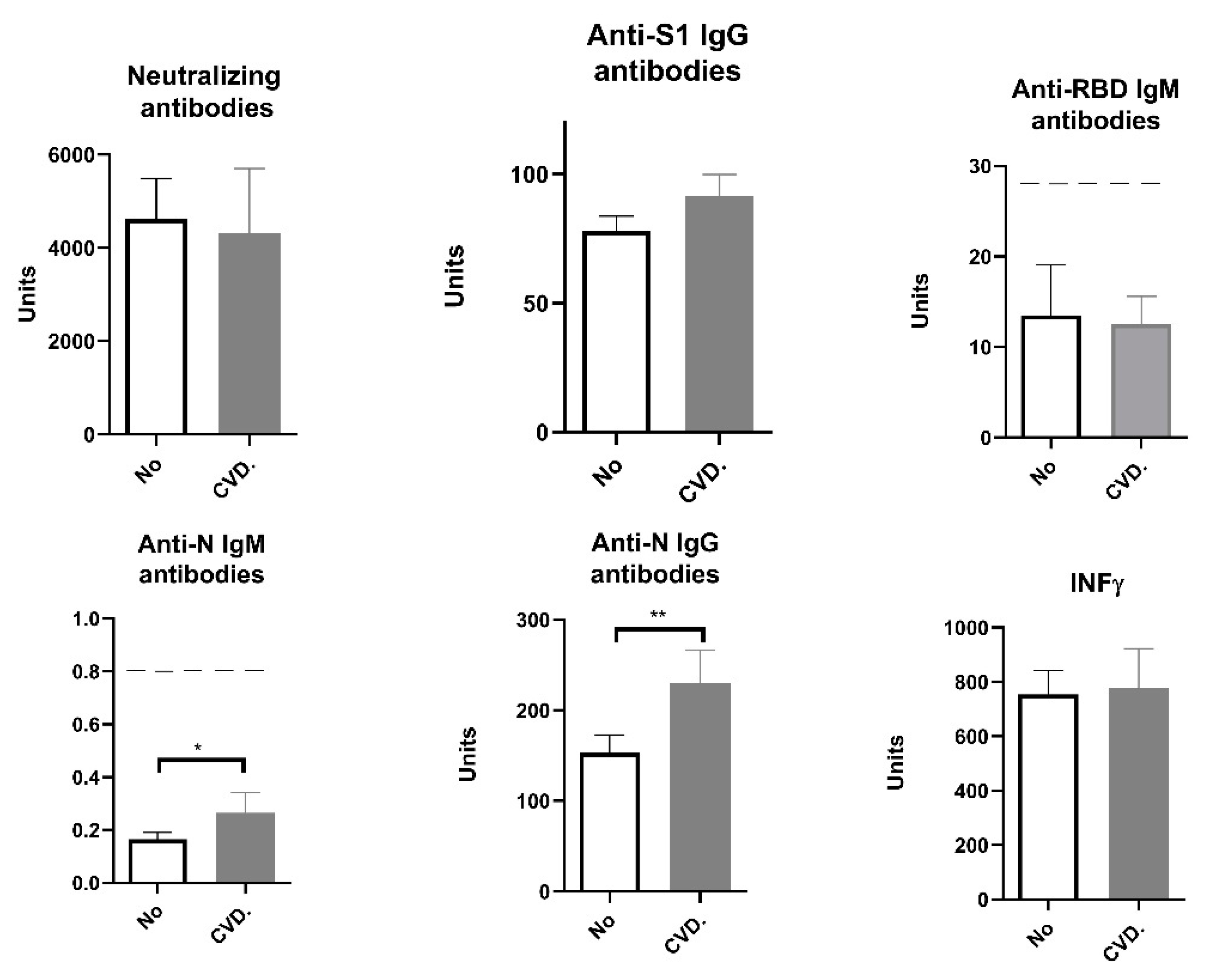
Some of the participants included in our study suffered from cardiovascular diseases (CVD). So when we divided the participants into those with and those without cardiovascular diseases, statistical analysis showed that participants with CVD produced elevated anti-N IgG levels (
Figure 3). Although IgM values were below the positivity threshold, in subjects with cardiovascular diseases we saw higher anti-N IgM antibody levels to the extent which is statistically significant (
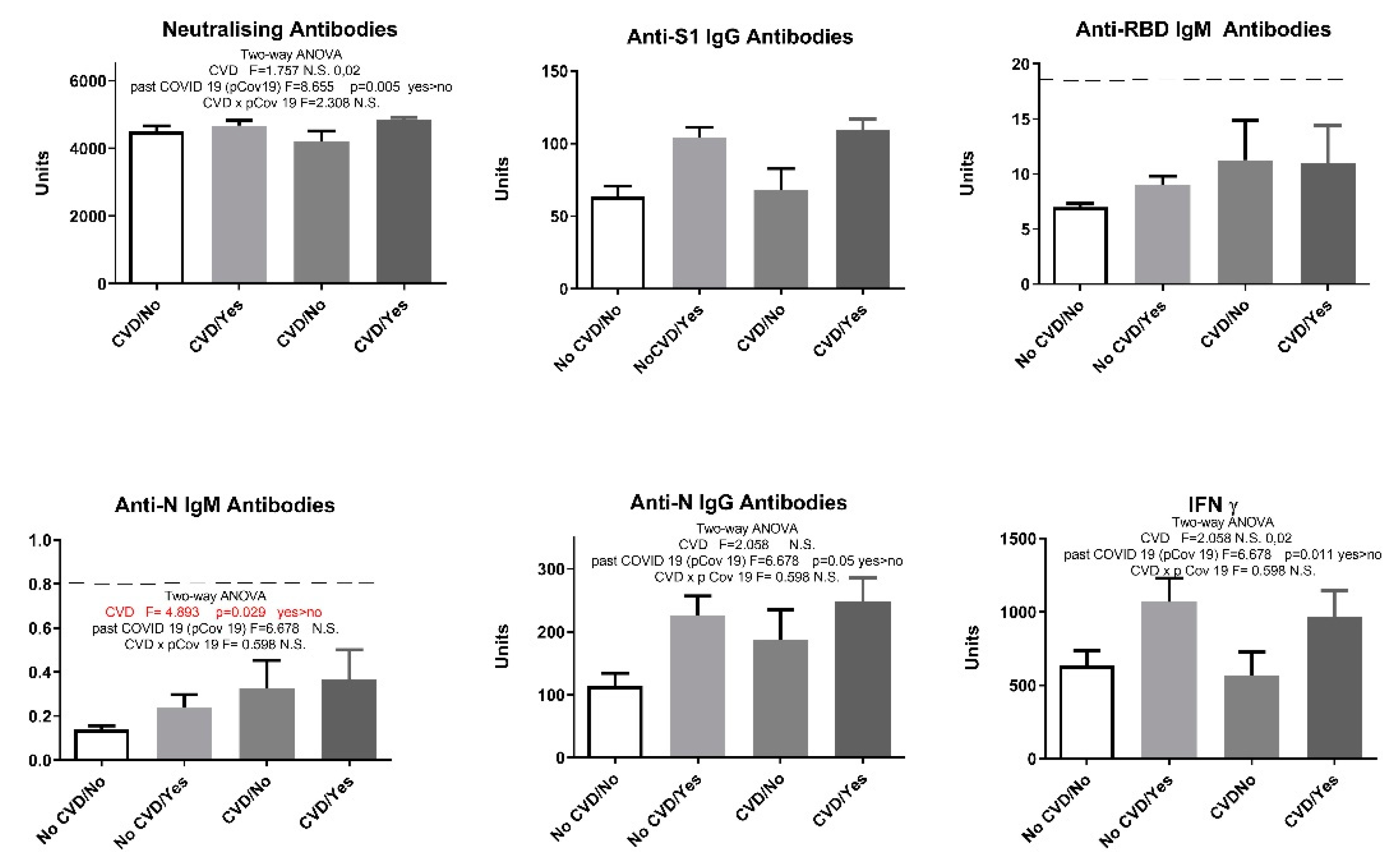
Figure 3). Interestingly, after adding previous history of COVID-19 as a second parameter and performing a two-way analysis ANOVA, participants with cardiovascular diseases showed a statistically significant increase only in anti-N IgM levels regardless whether they had had the infection or not. (
Figure 4).
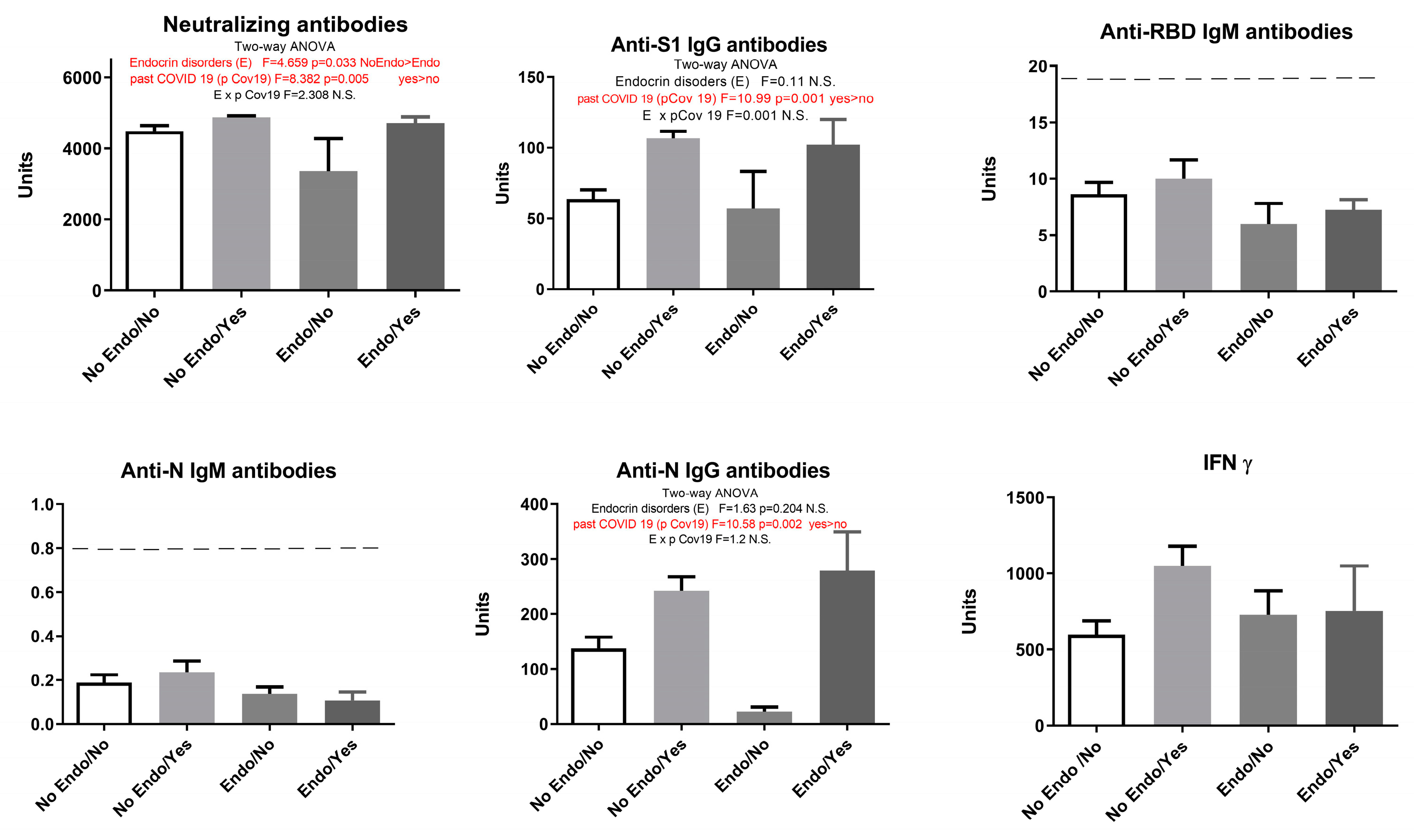
Our study showed that endocrine disorders had no influence on the observed parameters: humoral anti-SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies - neutralizing antibodies (F=2.91, p > 0.05), anti-S1 IgG antibodies (F=1.33, p > 0.05), anti-N IgG antibodies (F=1.095, p > 0.05), and cellular immune response (IFN γ) (F=2.069, p > 0.05). However, when COVID-19 overcome was added as a second parameter, results showed that endocrine disorders attenuated the elevation of neutralizing antibodies in vaccinated individuals with no history of COVID-19 (
Figure 5).
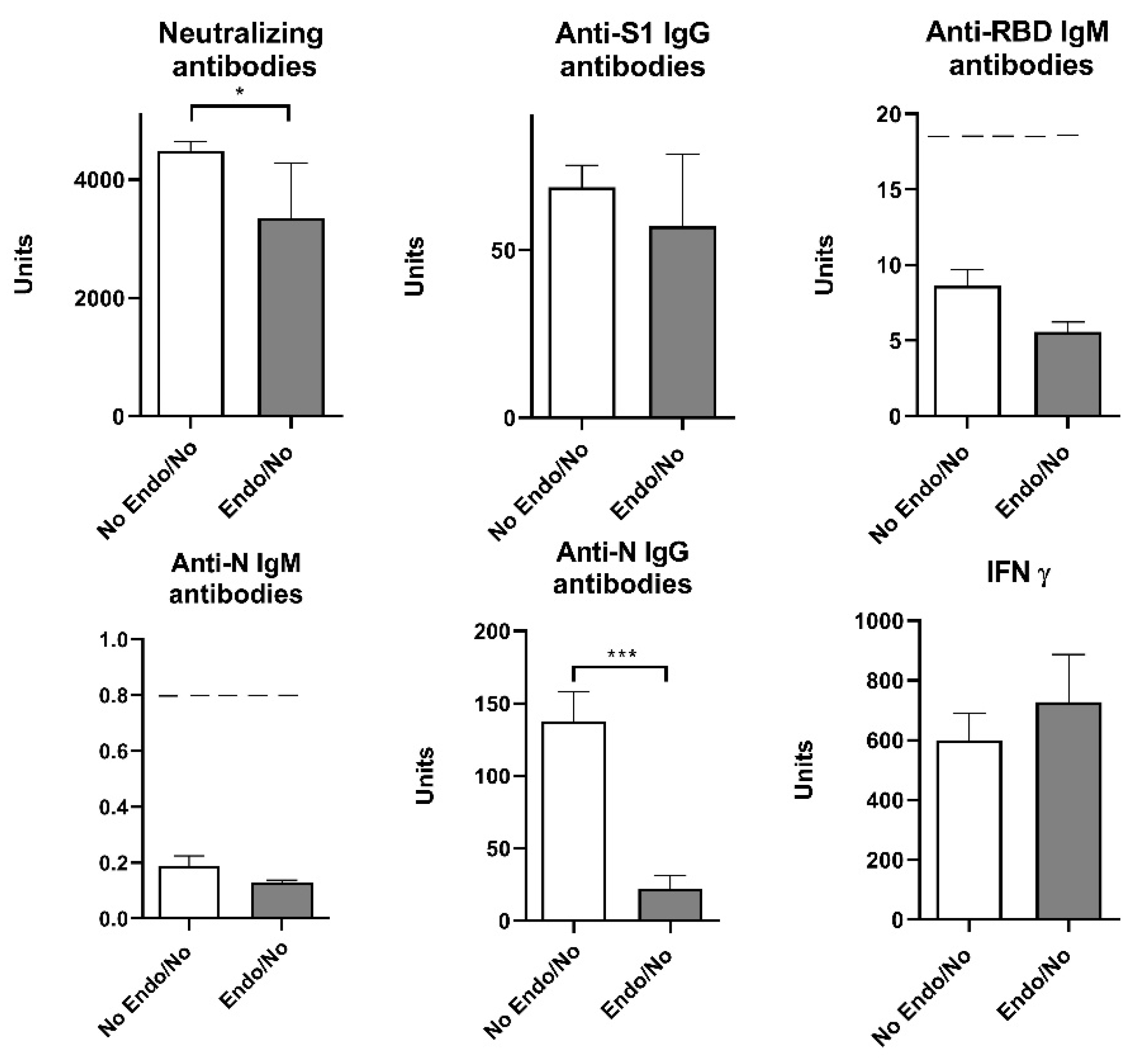
Our results showed that previous COVID-19 overcome elevated neutralizing antibodies, IgG S1 and IgG N humoral response (
Figure 5). Since the presence of endocrine disorders and the prior history of COVID-19 showed no significance at the level of neither humoral nor cellular response, with the exception of neutralizing antibodies, we singled out the group of subjects who have not had COVID-19 and divided them into two groups - with and without endocrine disorders. Statistical T-test showed that neutralizing antibodies and anti-N IgG humoral parameters decreased significantly in Endo/No group, implying that subjects with endocrine disorders who were vaccinated with Sinofarm vaccine and had no prior history of COVID-19 had a lower humoral response than the vaccinated subjects with endocrine disorders (
Figure 6).
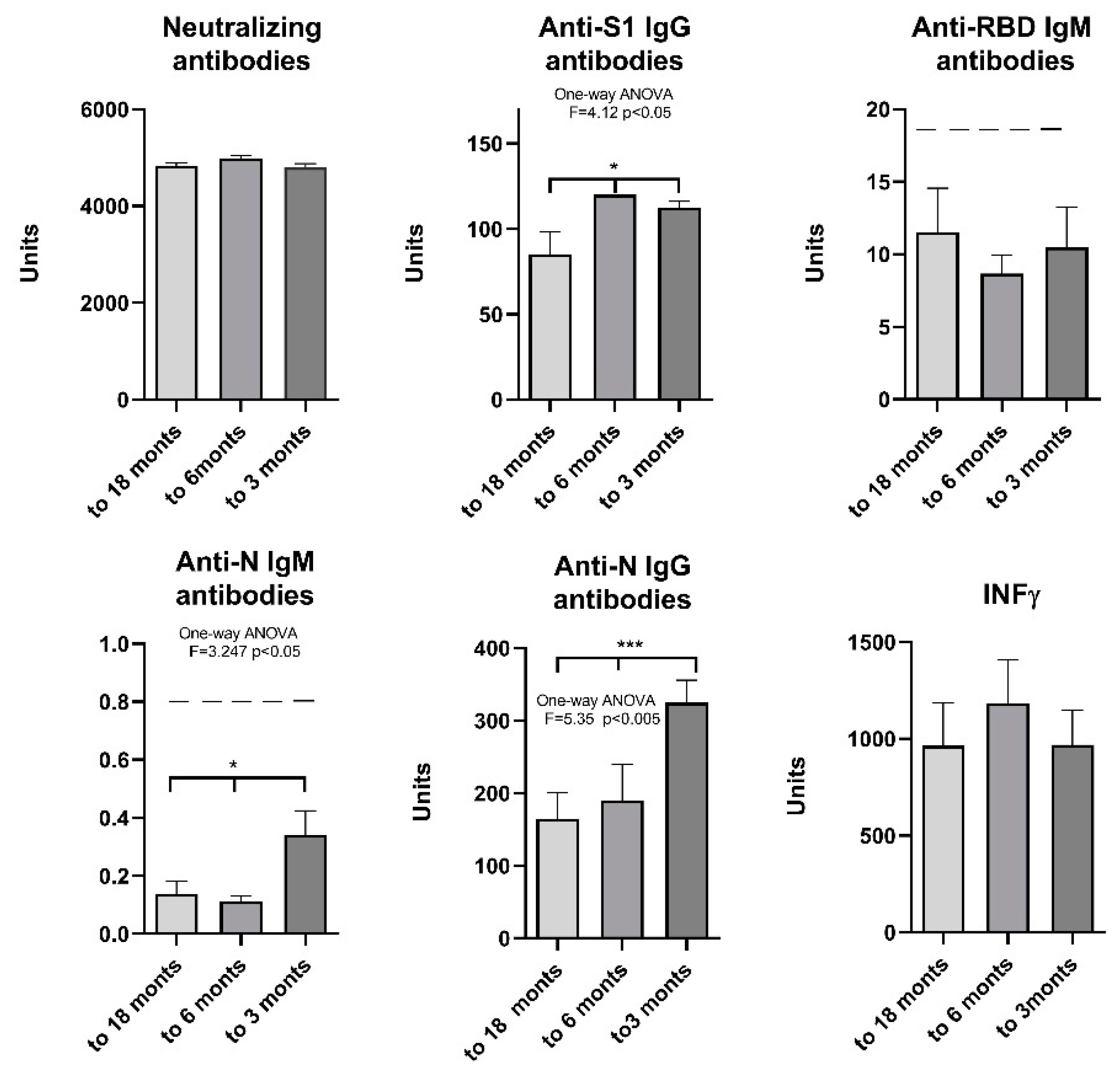
To determine the extent of change in antibody levels over time, participants were divided into 3 subgroups based on the period elapsed between the last clinical presentation of COVID-19 symptoms and the time of testing (up to 3 months, 3 to 6 months and up to 18 months since the last symptoms). The results show that there is no decrease in neutralizing antibodies and IFN γ 3, 6 and 18 months after COVID-19, while there is a significant decrease in anti-S1 IgG 6 months after and anti-N IgG 18 months after COVID-19. The significance was also confirmed for anti-N IgM levels, although the value was below the threshold (
Figure 7).
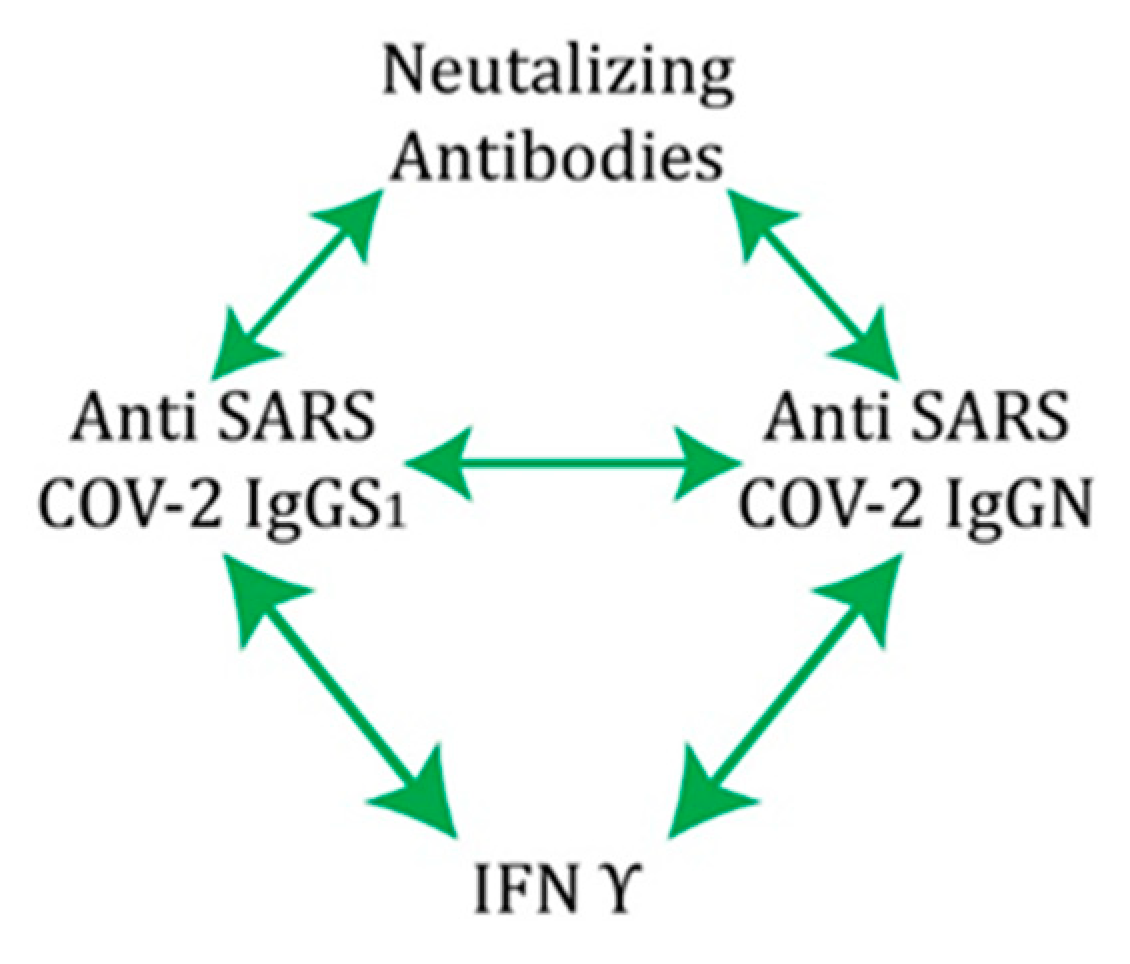
Correlation analysis performed on the complete sample showed that, in vaccinated individuals, significant positive correlations exist between humoral and cellular markers of immunity: neutralizing antibodies, anti-S1 IgG, anti-N IgG and interferon γ, suggesting a unique coordinated response specific for COVID-19 (
Table 2).
4. Discussion
To determine the biomarkers of acquired immunity after infection and after vaccination, viral antigens that could potentially induce a strong type-specific immune response were studied. Among the four structural proteins of coronaviruses (S, E, M, N), the two most abundant structural proteins of coronaviruses are the S and N antigens. The surface spike S glycoprotein is crucial for the initial step of infection, as it mediates entry of the virus by binding to the host ACE2 receptor and fusing the virus-host membrane. The S antigen consists of the S1 and S2 subunits. The epitopes for the neutralizing antibodies and the epitopes for the cellular immune response are located within the S1 subunit and the RBD domain [
15,
16]. The N protein is immunodominant and is highly expressed in infected cells. Within the N antigen, there are epitopes for the cellular immune response of CD4- and CD8-positive T lymphocytes, as well as epitopes targeted by non-neutralizing antibodies [
17].
Therefore, most tests measuring the efficiency of the immune response are based on these two antigens. Antibodies produced during infection with different human coronaviruses (HcoV-OC43, HcoV-HKU1, HcoV-229E, HcoV-NL63), especially from the same genus, are known to have a potential for cross-reactivity [
18]. For example, the S protein of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV, which are phylogenetically closely related, have an amino acid sequence identity of approximately 77%. Such a high degree of sequence similarity suggests the possibility of cross-reactive epitopes between these two viruses. In order to examine proteins for possible cross-immunity with other human coronaviruses, the conserved and variable regions of the S and N antigens were analysed. Antibodies against the S1 and RBD domains of the S protein were found to be hypervariable and subtype-specific. This is in contrast to the N antigen and the S2 subunit of the S antigen, which are highly conserved in human coronaviruses. However, antibodies against N and S2 antigens formed during previous infections with human coronaviruses cannot protect against SARS-CoV-2 infection [
6,
18,
19]. Serological evidence of a specific immune response to the S and N antigens was of paramount importance in diagnosing the infection. Because most vaccines are designed to elicit only an immune response to the S antigen, tests that detect the presence of neutralizing antibodies are most commonly used to monitor the effectiveness of vaccine immunity [
20,
21,
22]. However, the Sinopharm vaccine elicits a response to all single antigens (including the S and N antigens), so determining the serological profile in infected and vaccinated individuals is of great interest. According to literature, the efficacy of inactivated COVID-19 vaccines is 70-80% after two administrations [
23,
24]. Therefore, a third booster dose was recommended, which according to our results induced long-term immunity against the original virus variant. Using biomarkers of humoral and cellular immunity as indicators, we found that all recipients of three doses of Sinopharm vaccine developed an effective humoral and cellular response regardless of gender and age.
Biomarkers of humoral and cellular immunity were analysed separately in vaccinated individuals with COVID-19. These individuals have a hybrid immunity consisting of natural and vaccine-generated immunity. In the literature, this type of "hybrid immunity" is referred to as superior immunity. Individuals who acquire natural immunity through infection and are subsequently vaccinated develop stronger immunity to SARS-CoV-2 [
23,
24,
25]. Many authors emphasise the importance of memory immunity. It has been shown that the number of memory B cells is increased 5-10-fold in hybrid immunity compared to natural infection or vaccination alone [
33]. According to the data found in the literature, prior infection alone and prior infection in combination with prior vaccination provide high and sustained protection against hospitalisation or severe disease [
26]. Since there are few data in the scientific literature on serological status after vaccination with the Sinopharm vaccine, we considered our results in the light of serological markers detected after vaccination with an mRNA vaccine. After one dose of mRNA vaccine, humoral immunity is 10-45 times higher in people who have already undergone infection than in people who have not been infected [
27,
28]. Administration of the second dose results in a threefold increase in antibodies in non-immune individuals, but does not have this effect in individuals with previous infection. Individuals who have been fully vaccinated with two doses of an mRNA vaccine and have undergone prior infection have six times higher antibody levels than individuals who have undergone only natural infection or have been fully vaccinated. Vaccination of previously infected individuals has also been shown to result in significantly higher levels of cross-neutralizing antibodies than fully vaccinated individuals.
In our study, participants who had COVID-19 infection prior to vaccination and were fully vaccinated with three doses of Sinopharm vaccine showed a statistically significant increase in all types of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies, particularly anti-S1 IgG and anti-N IgG. The titer of NA antibodies is also higher in the group of participants with previous infection, as is IFN γ. Our results confirm the importance of hybrid immunity, which provides the greatest and most durable protection based on humoral biomarkers. A certain number of participants, especially those who had COVID-19 infection immediately before and after vaccination, showed positive anti-RBD IgM antibodies. The presence of subtype-specific IgM antibodies is probably due to the fact that the viral variant contained in the vaccine differs from the variant that caused the infection, which stimulates the de novo production of IgM antibodies.
According to the literature, cardiovascular disease, especially hypertension, is an important cofactor for severe COVID-19 [
29,
30,
31,
32]. About 85% (27 of 32) of the patients with hypertension included in our study use ACE inhibitors as part of their treatment. However, in our study, there was no statistically significant difference in markers of humoral and cellular immune response between patients with cardiovascular disease and other participants, except for IgM N, which was higher in CVD patients (
Figure 4).
Endocrine disorders also affect the efficacy of the immune response [
33,
34,
35]. According to our study, patients with endocrine disorders show a statistically significant impairment of the humoral immune response after vaccination, with lower values for all tested antibodies (NA, anti-S1 IgG, anti-N IgG), which means that subjects with endocrine disorders have a lower humoral response after Sinofarm vaccination. However, in the group of participants with a history of COVID-19 infection and endocrine disorders, these differences were lost and there was no difference in humoral and cellular markers.
Overall, these results show that individuals with previous COVID-19 infection who were vaccinated with three doses of inactivated vaccine had hybrid immunity. This means that participants with hybrid immunity have the best adoptive immunity, probably against both the original strain and the variants in question. The titre of NA and IFNγ remained unchanged in our group of participants studied, but the anti-S1 IgG and anti-N IgG antibodies showed a statistically significant decrease in titre when sampled 18 months after infection. Our results confirm the findings that the inactivated Sinopharm vaccine induces effective production of neutralizing antibodies, as do the mRNA- and vector-based vaccines. Natural immunity, together with vaccine-generated immunity against SARS-CoV-2, is clearly involved in protection against COVID-19 reinfection. The results also point to the contribution of the T-cell response to protection, particularly immunological memory as a source of protective immunity. Correlation analysis also showed that immunity was established through positive cooperativity between IgGS1 and IgGN, which stimulate each other as well as NA and IFNγ through independent and separate pathways (
Figure 8). According to our results, this connection represents the main pathway for the establishment of protection in COVID-19 hybrid immunity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.D.; K.Š.; and M.V.; methodology, M.V.; and A.V.; validation, A.V., M.V. and Z.Z.; formal analysis, M.V.; investigation, M.V.; resources, K.Š.; data curation, D.B.; writing—original draft preparation, T.J. and A.N-K.; writing—review and editing, T.J. D.B; and A.N-K; funding acquisition, D.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by Institutional Ethics Committee of the Institute for Biocides and Medical Ecology, Belgrade (protocol number 05-01 468/3-1, approved on 23.02.2022.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are not available due to ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
Gratitude to all the staff of the Institute for Biocides and Medical Ecology who contributed to the realisation of this study through their work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest to publish the results.
Appendix A
Participant self-questionnaire
All participants who gave their informed consent voluntarily filled out a self-questionnaire with the following inquiries:
History of previous SARS-CoV-2 infections with the date on which the symptoms appeared or date of the last positive PCR result
History of vaccination (date and name of 1st, 2nd and 3rd dose of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine)
Diseases of the cardiovascular system (hypertension, ischemic heart disease, heart failure, heart valve diseases, myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis, deep vein thrombosis, etc.)
Diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, Cushing's syndrome, etc.)
Diseases of the nervous system (cerebrovascular diseases, stroke, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, polyneuropathy, neuroborreliosis, etc.)
Liver diseases (hepatitis B, hepatitis C, cirrhosis, etc.)
Autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic sclerosis, etc.)
Pulmonary diseases (asthma, COPD, emphysema, pulmonary hypertension, etc.)
Kidney diseases (hypertensive nephropathy, diabetic nephropathy, hydronephrosis, chronic renal insufficiency, etc.)
The presence of allergic reactions (atopy, allergic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, allergic asthma, etc.)
Primary and secondary immunodeficiencies (yes or no, and which)
Severe diseases of the hematopoietic system (yes or no, and which)
Oncological diseases (yes or no, and which)
Pregnancy and breastfeeding status
Appendix B
Table A1.
Commercial test used for detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.
Table A1.
Commercial test used for detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.
| |
Commercial ELISA Name |
Purpose of Detection |
Reference Values |
Automated System |
|
anti-SARS-CoV-2neutralizing antibodies –NA
|
Novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Detection Kit (ELISA) Shanghai GeneoDx Biotech Co, Ltd |
neutralizing antibodies
(NA) |
<79 U/mL: negative
≥79 to <81 U/mL: borderline
≥81 U/mL: positive |
DYNEX DS2®, Dynex Technologies |
|
anti-SARS-CoV-2IgG S1
|
Anti-SARS-CoV-2 QuantiVac ELISA (IgG), EUROIMMUN AG, Lübeck, Germany |
IgG antibodies against S1 (including RBD) |
<8 RU/mL: negative
≥8 to <11 RU/mL: borderline
≥11 RU/mL: positive |
EuroImmun I Analyzer |
|
anti-SARS-CoV-2IgM N
|
Anti-SARS-CoV-2 NCP ELISA (IgМ), EUROIMMUN AG, Lübeck, Germany |
IgM antibodies against the nucleocapsid protein (N) |
Ratio <0.8: negative
Ratio ≥ 0.8 to <1.1: borderline
Ratio ≥1.1: positive |
EuroImmun I Analyzer |
|
anti-SARS-CoV-2IgG N
|
EIA Covid-19 NP IgG, TestLine Clinical Diagnostics |
IgG antibodies against the nucleocapsid protein (N) |
<18 U/mL: negative
≥8 to <22 U/mL: borderline
≥22 U/mL: positive |
DYNEX DS2®, Dynex Technologies |
|
anti-SARS-CoV-2IgM RBD
|
EIA Covid-19 RBD IgM, TestLine Clinical Diagnostics |
IgM antibodies against RBD domain |
<18 U/mL: negative
≥8 to <22 U/mL: borderline
≥22 U/mL: positive |
DYNEX DS2®, Dynex Technologies |
References
- Amicrone, M.; Aves, M.J.; Isidoro, J.; Zé-Zé, L.; Durate, S.; Vieira, R.; Guimar, R.; Gpmes, J.P.; Gordo, I. Mutation rate of SARS-CoV-2 and emergence of mutators during experimental evolution. Evol Med Public Health 2022, 10(1), 142–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dearlove, B.; Lewitus, E.; Bai, H.; Rolland, M. A SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate would likely match all currently circulating variants. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 23652–23662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, D.; Bruel, T.; Grzelak, L.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Staropoli, I.; Porrot, F.; Planchais, C.; Buchrieser, J.; Rajah, M. M.; Bishop, E.; et al. Sensitivity of infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 variants to neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.F.; Moustsen-Helms, I.R.; Schelde, A.B.; Gram, M.A.; Emborg, H.D.; Nielsen, J.; Hansen, C.H.; Andersen, M.A.; Meaidi, M.; Wohlfahrt, J.; et al. Vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 reinfection during periods of Alpha, Delta, or Omicron dominance: A Danish nationwide study. PloS Med. 2022, 19, e1004037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaebler, C.; Wang, Z.; Lorenzi, J.C.C., Muecksch; Tokuyama, M.; Cho, A.; Jankovic, M.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Oliveira, T.Y.; et al. Evolution of antibody immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 591, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breathnach, A.S.; Riley, P.A.; Cotter, M.P.; Houston, A.C.; Habibi, M.S.; Planche, T.D. Prior COVID-19 significantly reduces the risk of subsequent infection, but reinfections are seen after eight months. J Infect 2021, 82, e11–e12.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemaitelly, H.; Nagelkerke, N.; Ayoub, H.H.; Coyle, P.; Tang, P.; Yassine, H.M.; Al-Khatib, H.A.; Smatti, M.K.; Hasan, M.R.; Al-Kanaani, Z.; et al. Duration of immune protection of SARS-CoV-2 natural infection against reinfection. J Travel Med 2022, 29, taac109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pušnik, J.; Monzon-Posadas, W.O.; Zorn, J.; Peters, K.; Baum, M.; Proksch, H.; Schlüter, B.C.; Alter, G.; Menting, T. Streeck, H.. SARS-CoV-2 humoral and cellular immunity following different combinations of vaccination and breakthrough infection. Nature Communications 2023, 14, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudellari, M. How the Coronavirus infects our cells. Nature 2021, 595, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grifoni, A.; Weiskopf, D.; Ramirez, S.I.; Mateus, J .; Dan, J.M.; Moderbacher, C.R.; Rawlings, S.A.; Sutherland, A.; Premkumar, L.; Jadi, R.S.; et al. Targets of T cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus in humans with COVID-19 disease and unexposed individuals. Cell 2020, 181, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagan, N.; Barda, N.; Kepten, E.; Miron, O.; Perchik, S.; Katz, M.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Lipsitch, M.; Reis, B.; and Balicer, R.D. BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine in a nationwide mass vaccination setting. N Engl J Med 2021, 384, 1412–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhi, S. A.; Vicky, B.; Cutland, C.L.; Voysey, M.; Koen, A.L.; Fairlie, L.; Padayachee, S. D.; Dheda, K.; Barnabas, S.L.; Bhorat, Q.E.; et al. Efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Covid-19 Vaccine against the B.1.351 Variant. N. Engl. J. Med 2021, 384, 1885–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, V.J.; Foulkes, S.; Saei, A.; Andrews, N.; Oguti, B.; Charlett, A.; Wellington, E.; Stowe, J.; Gillson, N.; Atti, A.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine coverage in health-care workers in England and effectiveness of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine against infection (SIREN): a prospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet 2021, 397, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkle, E.D.; Wiersma, W.; Jurs, G.S. Applied Statistics for Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.-F.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.-W. Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2020, 41, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilocca, B.; Soggiu, A.; Sanguinetti, M.; Musella, V.; Britti, D.; Bonizzi, L.; Urbani, A.; Roncada, P. Comparative computational analysis of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein epitopes in taxonomically related coronaviruses. Microbes Infect. 2020, 22, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grifoni, A.; Sidney, J.; Zhang, Y.; Scheuermann, R.H.; Peters, B.; Sette, A. A sequence homology and bioinformatic approach can predict candidate targets for immune responses to SARS-CoV-2. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, S.M; Ansari, A.M.; Frater, J.; Klenerman, P.; Dunachie, S.; Barnes, E.; Ogbe, A. The impact of pre-existing crossreactive immunity on SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccine responses. Nat Rev Immunol 2023, 23, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.K.P.; Cohen, C.A.; Cheng, S.M.S.; Chen, C.; Kwok, K.-O.; Yiu, K.; Chan, T-O.; Bull, M.; Ling, K.C.; Dai, Z.; et al. Comparison of the immunogenicity of BNT162b2 and CoronaVac COVID-19 vaccines in Hong Kong. Respirology 2022, 27, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premikha, M.; Chiew, C.J.; Wei, W.E.; Leo, Y.-S.; Ong, B.; Chien Lye, D.; Lee, V.J.; Tan, B.K. Comparative effectiveness of mRNA and inactivated whole virus vaccines against COVID-19 infection and severe disease in Singapore. Clin Infect Dis 2022, 75, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ella, R.; Reddy, S.; Blackwelder, W.; Potdar, V.; Yadav, P.; Sarangi, V.; Aileni, V.K.; Kanungo, S.; Rai, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; S., *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Reddy, P.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and lot-to-lot immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (BBV152): interim results of a randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 2173–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordström, P.; Ballin, M.; Nordström, A. Risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection and COVID-19 hospitalisation in individuals with natural and hybrid immunity: a retrospective, total population cohort study in Sweden. Lancet Infect Dis 2022, 22, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, V.J.; Foulkes, S.; Charlett, A.; Atti, A.; Monk, E.J.M.; Simmons, R.; Wellington, E.; Cole, M.J.; Saei, A.; Oguti, B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection rates of antibody-positive compared with antibody-negative health-care workers in England: a large, multicentre, prospective cohort study (SIREN). Lancet 2021, 397, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobrovitz, N.; Ware, H.; Ma, X.; Li, Z.; Hosseini, R.; Li, Z.; Hosseini, R.; Cao, C.; Selemon, A.; Whelan, M.; et al. Protective effectiveness of previous SARS-CoV-2 infection and hybrid immunity against the omicron variant and severe disease: a systematic review and meta-regression. Lancet infect Dis 2023, 23, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Guan, F.; Condotti, F.; Benlagha, K.; Chen, S.; Guan, F.; Candotti, F.; Benlagha, K.; Camara, N.O.S.; Herrada, A.A.; et al. The role of B cells in COVID-19 infection and vaccination. Front Immunol. 2022, 13, 988536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, A.; Theel, E.S. Immunity to SARS-CoV-2: What do we know and should we be testing for it. JCV 2022, 60(6), e00482-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygorian, L.; Pulendran, B. The immunology of SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccines. Seminars in Immunology 2020, 50, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellini, R.; Venuti, A.; Pimpinelli, F.; Abril, E.; Blandino, G.; Campo, F.; Conti, L.; De Virgilio, A.; De Marco, F.; Di Domenico, E.G.; et al. Initial observations on age, gender, BMI and hypertension in antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine. Eclinicalmedicine 2021, 36, 100928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ielapi, N.; Licastro, L.; Provenzano, M.; Andreucci, M.; Franciscis, S.; Serra, R. Cardiovascular disease as a biomarker for an increased risk of COVID-19 infection and related poor prognosis. Biomark. Med. 2020, 14(9), 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiga, M.; Wang, D.W.; Han, Y.; Lewis, D.B.; Wu, J.C. COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease: from basic mechanisms to clinical perspectives. Nat. Rev. Cardiol 2020, 17, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.K.; Zidar, D.A.; Bristow, M.R.; Cameron, S.J.; Chan, T.; Harding III, C.V.; Kwon, D.H.; Singh, T.; Tilton, J.C.; Tsai, E.J.; Tucker, N.R.; Barnard, J.; Loscalzo, J. COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1214–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barron, E.; Bakhai, C.; Kar, P.; Weaver, A.; Bradley, D.; Ismail, H.; Knighton, P.; Holman, N.; Khunti, K.; Sattar, N.; Wareham, N.J.; Young, B.; Valabhji, J. Associations of type 1 and type 2 diabetes with COVID-19-related mortality in England: a wholepopulation study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Li, M.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, C.; Qin, R.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Du, K.; Zhao, L.; Fan, H.; Luo, S.; De, Hu. Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2020, 36, e3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornstein, S.R.; Rubino, F.; Khunti, K.; Mingrone, G.; Hopkins, D.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Boehm, B.; Amiel, S.; Holt, R. I.; Skyler, J.S.; et al. ; Practical recommendations for the management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2020, 8, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).