1. Introduction
The use of standard urine culture (SUC) that detects and quantitates classical uropathogens has been in use for over 100 years to confirm the diagnosis of an active urinary tract infection (UTI) [
1]. However, SUC has several limitations. SUC uses specific media and conditions that result in cultivating easy-to-grow microbes, like
Escherichia coli (
E. coli). However, non-
E. coli pathogens including fastidious microbes reported as important emerging uropathogens, are rarely grown [
2,
3,
4]. Recent studies using more sensitive culture techniques, such as enhanced-quantitative urine culture (EQUC), and culture-free methods, such as gene sequencing and MALDI-TOF, have led to the discovery of the uromicrobiome, which is present even in asymptomatic individuals [
2,
3,
4]. In addition, these studies have increased awareness of many additional clinically relevant microbial species, such as gram-positive organisms, fastidious microbes, and fungi, which can contribute to urinary microbiome dysbiosis in symptomatic subjects [
5].
Another disadvantage of SUC is the length of time necessary to perform the testing, which creates a delay before patients can be treated with a results-guided antimicrobial. This may result in an over-reliance on empiric therapy whereby the clinician overtreats patients lacking a true infection or treats them with the wrong antibiotic. These delays further increase the risks for poor outcomes including urosepsis. These challenges have encouraged the development of molecular tests, such as multiplex PCR (M-PCR), which have demonstrated better detection of non-
E. coli and polymicrobial UTIs and a faster turnaround time for results compared to SUC [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10].
The presence of a urinary microbiome along with the high prevalence of asymptomatic bacteriuria [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15] underscores the need for clinically relevant diagnostic tests that are both sensitive and specific for UTIs in symptomatic patients. While the identification of uropathogens in symptomatic patients is a strong indicator of infection, there remain questions about whether detected microbes are associated with a UTI. Also, symptom elucidation can be problematic in pediatric patients or in patients who are cognitively impaired. For example, in the long-term care setting there are both high rates of asymptomatic bacteriuria (up to 50%) [
14] and cognitive impairment.
With that in mind, there have been hundreds of studies looking at biomarkers as a potential tool for the identification of urinary tract infections [
16]. The innate immune system in the urinary tract consists of both resident and recruited cells expressing a variety of pattern recognition receptors that detect pathogens early and rapidly trigger a pro-inflammatory immune response to aid in bacterial clearance [
17,
18]. Uroepithelial cells secrete bacteriostatic agents, such as neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), also known as lipocalin-2 [
19,
20,
21]. In addition, resident and recruited immune cells secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukins (ILs), including IL-8, also known as chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 8 (CXCL8) [
17,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26], and IL-1β [
22,
27,
28], to further promote the response until the microbial threat is resolved [
17,
18,
29]. Soluble infection-associated biomarkers, such as NGAL, IL-8, and IL-1β, are detectable in urine and studies have demonstrated the association of these urinary biomarkers with the presence of a clinically diagnosed UTI [
16,
30,
31]. Using such biomarkers individually, or in combination, provides strong evidence of immune response to uropathogens in the urinary tract at the time of urine collection.
This study aimed to determine whether an individual biomarker or a set of biomarkers can differentiate symptomatic subjects with microbes detected in the urine from asymptomatic subjects either with microbes detected (asymptomatic bacteriuria) or without microbes detected in the urine to support the clinical diagnosis of UTI.
2. Materials and Methods
Study Design and Participants
Results from biomarker analyses, M-PCR/P-AST tests and standard urine culture (SUC) included in this study were obtained from urine samples from both asymptomatic and symptomatic cohorts. Urine samples from the asymptomatic cohort were collected between 2/28/2023 and 3/22/2023 from adult volunteers for a prospective observational study. All subjects were 60 years of age or older and provided written informed consent (Western IRB 20230847) prior to enrollment. Subjects who were pregnant, taking antibiotics for a UTI, or taking steroids were excluded. All consenting subjects completed the validated American English Acute Cystitis Symptom Score (ACSS) baseline questionnaire and provided a midstream clean-catch urine specimen [
32]. All 228 asymptomatic subjects had an ACSS sum score of ≤ 4 for the FDA-defined UTI symptoms (urinary frequency, urinary urgency, dysuria, and suprapubic pain) with no single symptom score > 1 and were included as the asymptomatic cohort.
The symptomatic cohort consisted of 583 subjects. Urine samples were collected in the Pathnostics’ clinical laboratory between 01/17/2023 and 04/24/2023 through a de-identified biorepository of adult patients with UTI symptoms and a presumptive diagnosis of UTI from a specialty urology setting. These patients were 60 years of age or older and presented to healthcare providers in urology offices from 39 U.S. states with ICD-10-CM codes consistent with UTI. The Western IRB deemed the biorepository-obtained specimens exempt from review.
All urine specimens were collected via the midstream clean catch/voided method.
The Guidance
® UTI M-PCR/P-AST assay (Pathnostics in Irvine, CA) includes susceptibility testing for 19 antibiotics, semi-quantification of 27 distinct uropathogenic species and 3 bacterial groups, as well as identification of 32 antibiotic-resistance genes and the ESBL phenotype. The test was performed as described previously: the first step involves DNA extraction from the subject’s urine sample using King Fisher/MagMAX™ automated DNA extraction instrument and the MagMAX™ DNA Multi-Sample Ultra Kit (Thermo Fisher, Carlsbad, CA) per the manufacturer’s instructions. Extracted DNA was mixed with a universal PCR master mix and amplified using TaqMan technology in a Life Technologies 12K Flex 112-format Open Array System (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, NC). Probes and primers were used to detect 26 bacteria/bacterial groups, fastidious and non-fastidious, and four yeast species [
7,
8,
9] listed below:
Classical uropathogens: Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, Citrobacter freundii, Citrobacter koseri, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella oxytoca, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Morganella morganii, Pantoea agglomerans, Proteus mirabilis, Providencia stuartii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus agalactiae, and Enterobacter group [including Klebsiella aerogenes (formally known as Enterobacter aerogenes) and Enterobacter cloacae].
Emerging uropathogens: Acinetobacter baumannii, Actinotignum schaalii, Aerococcus urinae, Alloscardovia omnicolens, Candida auris, Corynebacterium riegelii, Gardnerella vaginalis, Mycoplasma hominis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, coagulase negative staphylococci group (CoNS) (including Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus lugdunesis, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus), and Viridans group streptococci (VGS) (including Streptococcus anginosus, Streptococcus oralis, and Streptococcus pasteuranus).
Results of the P-AST portion of the test, an antibiotic resistance and sensitivity assay which accounts for bacterial interactions, were not included in this analysis.
Standard Urine Culture (SUC)
The SUC method was performed as previously described [
8]. Briefly, urine was vortexed, and a sterile plastic loop (1 µL) was used to inoculate blood agar plates. A sterile plastic loop (1 µL) was used also to inoculate colistin and nalidixic acid agar/MacConkey agar (CNA/MAC) plates, one loop-full of urine on the CNA side of the plate and another full loop-full on the MAC side of the plate. All plates were incubated at 35 °C in 5% CO
2 for ≥ 18 hours and then examined for evidence of growth. Per standard operating procedures plates with < 10,000 CFU/mL were reported as normal urogenital flora [
33]. For plates with growth (≥ 10,000 CFU/mL), the quantity and morphology of each organism were recorded. The maximum readable colony count using the 1 µL loop is > 100,000 CFU/mL. Colony counts were performed on blood agar plates. Species identification and colony counts were performed on CNA/MAC plates. Pathogen identification was confirmed with the VITEK 2 Compact System (bioMerieux, Durham, NC).
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
Urine levels of NGAL, IL-8, and IL-1β were analyzed according to the manufacturer’s instructions, using ELISA kits from R&D Systems/Bio-Techne (Minneapolis, MN), including human Lipocalin-2 / NGAL Quantikine ELISA Kit (Catalog number SLCN20), human IL-8 / CXCL8 Quantikine ELISA Kit (Catalog number S8000C), and human IL-1β / IL-1F2 Quantikine ELISA kit (Catalog number SLB50). OD readings at 450nm and 540nm, respectively, were measured on an Infinite M Nano + microplate reader (TECAN, Switzerland).
Statistical Analysis
Participant demographics and ICD-10-CM code breakdown were described by summary statistics (e.g., mean and standard deviation (SD) for continuous variables such as age, count, and percentage for categorical variables such as sex and ICD-10-CM code). A probit regression was fitted and plotted to describe the relationship between the density of organisms detected and the positivity (proportion of samples from symptomatic and asymptomatic cohorts with biomarker levels above the threshold) for each biomarker. Measures of biomarker clinical performance characteristics (sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, accuracy, positive likelihood ratio, and negative likelihood ratio) were calculated using the exact method. All data analyses were performed using R 4.2.2 (
https://www.r-project.org/).
To evaluate the ability of the biomarkers to differentiate UTI from non-UTI conditions, such as asymptomatic bacteriuria, we defined “Definitive UTI cases” and “Definitive non-UTI cases.” Definitive UTI cases were defined using the current standard of care diagnostic criteria of symptoms/clinical presentation combined with the presence of microorganisms in the urine above a certain density threshold and being positive by both SUC and M-PCR (“Both Detected”). Definitive non-UTI cases were defined as asymptomatic subjects regardless of the presence of detectable microbes in the urine.
Although 100,000 CFUs/mL by SUC is typically considered diagnostically significant in the US, clinical reviews and guidelines, as well as our data (publications in preparation) suggest a microbial density threshold of 10,000 cells/mL or CFUs/mL is more clinically relevant [
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39]. Thus, we performed analyses using both microbial density thresholds of positivity: Criterion 1 (10,000 cells/mL by M-PCR or CFUs/mL by SUC) and Criterion 2 (100,000 cells/mL by M-PCR or CFUs/mL by SUC).
Criterion 1 Definitions
Symptomatic cases where M-PCR detected bacterial counts of ≥ 10,000 or yeast counts > 0 cells/mL and SUC detected bacterial counts of ≥ 10,000 or yeast counts > 0 CFUs/mL.
Definitive Non-UTI Cases
All asymptomatic cases regardless of microbe identification and density.
Criterion 2 Definitions (Supplemental Data)
Definitive UTI Cases
Symptomatic cases where M-PCR detected bacterial counts of ≥ 100,000 or yeast counts > 0 cells/mL and SUC detected bacterial counts of ≥ 100,000 or yeast counts > 0 CFUs/mL.
Asymptomatic Cohort
All asymptomatic cases regardless of microbe identification and density.
We previously demonstrated a 1:1 linear correlation between cells/mL reported by M-PCR and CFU/mL reported by SUC (publication in preparation). Statistical analysis between symptomatic and asymptomatic specimens used a Proportion Z-test. Statistical difference was defined as p < 0.05.
Biomarker Thresholds
Thresholds previously reported in literature were used to determine positive and negative results for the biomarkers [
18,
19] (
Table 1). Consensus biomarker positivity was defined as ≥ 2 of the 3 biomarkers measuring at or above their respective cutoff values.
3. Results
Demographics
A total of 811 unique subjects’ urine specimens, 583 from the symptomatic cohort and 228 from the asymptomatic cohort were analyzed. The subjects in the symptomatic cohort trended slightly older [mean 76.6, median 76.3, range 60.0 – 99.0 years] than subjects in the asymptomatic cohort [mean 68.8, median 67.5 years, range 60.0 - 94.0]. There were also a greater proportion of females in the symptomatic cohort (68.3%, n = 398) than in the asymptomatic cohort 55.7% (n = 127). Most symptomatic subjects had an ICD-10-CM code (
https://www.icd10data.com) of N39.0 for Urinary tract infection, site not specified (81.8%, n = 534) (
Supplemental Table S1). The asymptomatic cohort specimens were collected from volunteers from the general population and therefore, had no ICD-10-CM codes.
Training Set
There are many urine biomarkers with the potential for differentiating UTI from non-UTI conditions according to published literature [
16]. A set of five candidate markers (MMP-9, NGAL, IL8, IL6, IL1-β) were evaluated using 100 consecutive cases obtained from Urology/Urogynecology practices from patients symptomatic for UTI. Cases dual-positive by M-PCR and SUC were considered “true positive” and cases dual-negative by M-PCR and SUC were considered “true negative”. Sensitivity and Specificity results from this test cohort are summarized in
Supplemental Table S2.
From this set of five preliminary candidates, three biomarkers with the highest sensitivity (NGAL, IL-6 and IL-1β) were selected to be validated for accuracy against the cases described above in Demographics.
Correlation Relationships between Biomarker Percent Positivity and Microbial Density
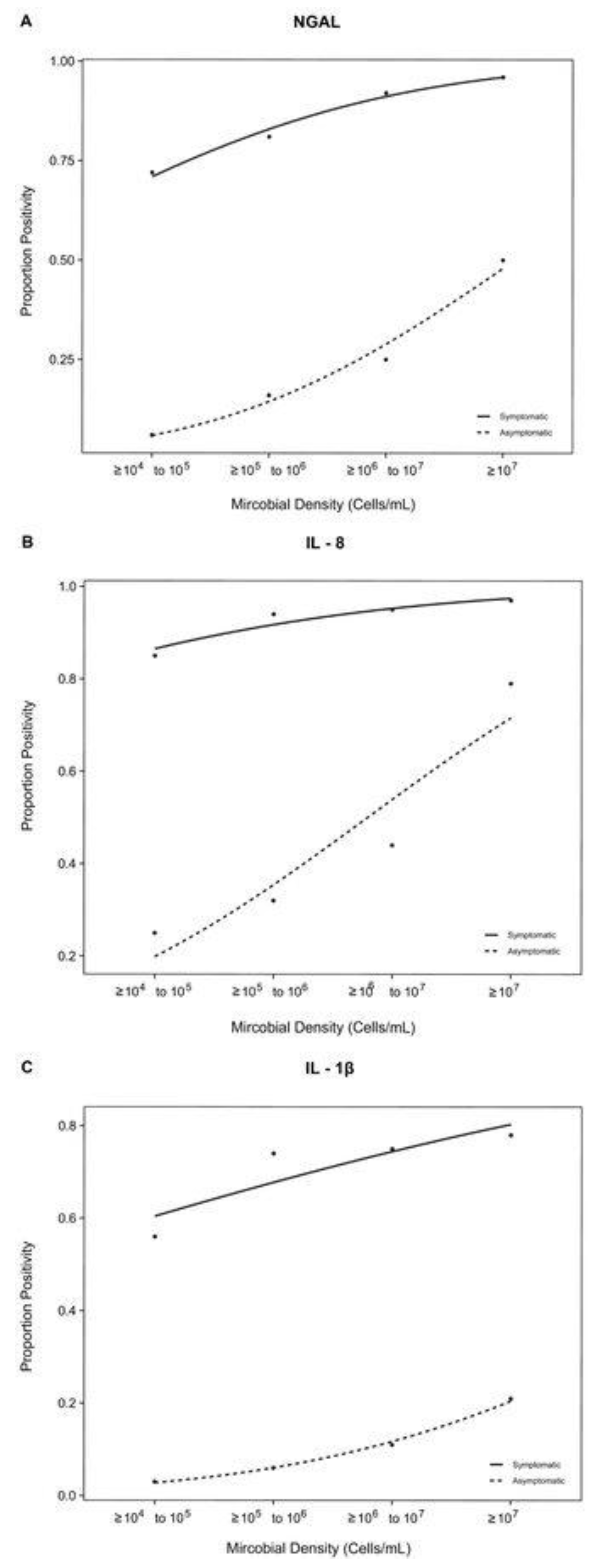
First, we examined the correlation between biomarker positivity and microbial density in both urine samples from patients symptomatic and asymptomatic subjects (
Figure 1). Each probit regression had an R
2 ≈ 1 and a p-value of < 0.0001 for all biomarkers in the symptomatic cohort and a p-value < 0.05 for all biomarkers in the asymptomatic cohort, indicating that the correlation between microbial density and biomarker positivity is statistically significant.
Although the symptomatic and asymptomatic cohorts both exhibited a strong positive correlation between biomarker positivity and microbial density, the biomarker proportion positivity was considerably higher across all microbial densities in symptomatic subjects relative to asymptomatic subjects (
Figure 1A–C).
Levels of all three biomarkers (NGAL, IL, and IL-1β) are significantly lower (p < 0.0001) among all asymptomatic cohort specimens, regardless of the presence of detectable microorganisms (Definitive non-UTIs), compared to the symptomatic cohort specimens with microorganisms detected by both SUC and M-PCR (Definitive UTIs) (
Figure 2,
Table 2).
We then compared the positivity of the individual biomarkers and combinations of biomarkers against symptomatic Definitive UTI cases using two microbial density detection thresholds: criterion 1 (10,000 cells/mL by M-PCR and CFUs/mL by SUC) and criterion 2 (100,000 cells/mL by M-PCR and CFUs/mL by SUC). All asymptomatic cases were considered Definitive non-UTI cases.
Biomarker and Microbial Comparison Defined by Each Biomarker
NGAL was positive (≥ 38 ng/mL) in 82.6% of definitive UTI cases and negative in 90.8% of Definitive non-UTI cases (Table 3A). IL-8 was positive (≥ 20.6 pg/mL) in 91.2% of Definitive UTI cases and negative in 76.8% of definitive non-UTI cases (Table 3B). IL-1β was positive (≥ 12.4 pg/mL) in 69.8% of definitive UTI cases and negative in 97.9% of Definitive non-UTI cases (Table 3C).
|
Table 3A. NGAL Positivity Contingency Table for Criterion 1. |
| |
Definitive UTI |
Definitive non-UTI |
Total |
| NGAL Positive |
290 (50.1%) |
21 (3.6%) |
311 (53.7%) |
| NGAL Negative |
61 (10.5%) |
207 (30.2%) |
268 (46.3%) |
| Total |
351 (60.6%) |
228 (39.4%) |
579 (100%) |
|
Table 3B. IL-8 Positivity Contingency Table for Criterion 1. |
| |
Definitive UTI |
Definitive non-UTI |
Total |
| IL-8 Positive |
320 (55.3%) |
53 (9.1%) |
373 (64.4%) |
| IL-8 Negative |
31 (5.4%) |
175 (35.8%) |
206 (35.6%) |
| Total |
351 (60.6%) |
228 (39.4%) |
579 (100%) |
|
Table 3C. IL-1β Positivity Contingency Table for Criterion 1. |
| |
Definitive UTI |
Definitive non-UTI |
Total |
| IL-1β Positive |
245 (42.3%) |
7 (1.2%) |
252 (43.5%) |
| IL-1β Negative |
106 (18.3%) |
221 (38.2%) |
327 (56.5%) |
| Total |
351 (60.6%) |
228 (39.4%) |
579 (100%) |
A statistical analysis summary of the three biomarkers is listed in
Table 4. IL-8 had the highest sensitivity (91.2%) while IL-1β had the highest specificity (96.9%).
Biomarker and microbial comparison defined by either “Consensus” or “All three biomarkers”
“Consensus” is defined as two or more biomarkers meeting or exceeding their respective positivity thresholds (
Table 1). Consensus positivity occurred in 84.0% of Definitive UTI cases and consensus negativity occurred in 91.2% of Definitive non-UTI cases (Table 5A). All three biomarkers were positive in 66.1% of Definitive UTI cases and negative in 97.4% of Definitive non-UTI cases (Table 5B).
|
Table 5A. Biomarker Consensus Positivity Contingency Table for Criterion 1. |
| |
Definitive UTI |
Definitive non-UTI |
Total |
| Consensus Positive |
295 (50.9%) |
20 (3.4%) |
315 (54.4%) |
| Consensus Negative |
56 (9.7%) |
208 (35.9%) |
264 (45.6%) |
| Total |
351 (60.6%) |
228 (39.4%) |
579 (100%) |
|
Table 5B. All Three Biomarkers Positivity Contingency Table for Criterion 1. |
| |
Definitive UTI |
Definitive non-UTI |
Total |
| All Three Positive |
232 (40.1%) |
6 (1.0%) |
238 (41.1%) |
|
| Less than Three Positive |
119 (20.6%) |
222 (38.3%) |
341 (58.9%) |
|
| Total |
351 (60.6%) |
228 (39.4%) |
579 (100%) |
|
A summary of the statistical analysis for the biomarker combinations is listed in
Table 6. The consensus criteria of at least two biomarkers meeting or exceeding the positivity threshold performed well in terms of both sensitivity and specificity (84.9% and 91.2%, respectively). Although the combination of all three biomarkers being positive had the highest specificity (97.4%), it had lower sensitivity (66.1%).
4. Discussion
M-PCR has been previously demonstrated to be superior to SUC at detecting non-
E. coli microorganisms and/or polymicrobial infections [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10]. Failure to detect and correctly identify these organisms can result in many UTIs remaining undiagnosed and untreated or being sub-optimally treated based on culture results, potentially prolonging symptoms in patients and resulting in potential complications. To provide clarity on whether M-PCR-detected microorganisms are clinically and diagnostically relevant, it is useful to have biomarkers indicating active immune responses to infection, rather than solely relying on the presence of microorganisms. This study examined three potential biomarkers for UTI in Definitive UTI cases, along with Definitive non-UTI cases that included asymptomatic bacteriuria, to evaluate the usefulness of biomarkers in differentiating UTI from non-UTI patients.
The three biomarkers selected for this study, NGAL, IL-8, and IL-1β, are integral in the innate response to pathogens in the urinary tract [
31,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44]. As with any measurement of biomarkers, care in selection, interpretation, and use must be taken. For example, NGAL can be secreted both in response to infection and impaired renal function [
16,
45]. Additionally, many biomarkers, are impacted by intrinsic host factors such as age, sex, urinary abnormalities, genetic polymorphisms, and comorbid conditions which affect expression levels and responses to infection [
46,
47,
48].
To determine if these three biomarkers were sensitive and specific indicators for UTIs, this study measured them in both Definitive UTI cases (symptomatic cases, diagnosed in a Urology/Urogynecology specialty setting, with uropathogens identified above threshold values by both SUC and M-PCR) and in Definitive non-UTI control cases (asymptomatic based on FDA-defined criteria included in a Symptom Score Analysis)). The Definitive non-UTI cases included asymptomatic individual with detected microbes (asymptomatic bacteriuria). Previous studies had reported the presence of asymptomatic bacteriuria at lower prevalence and primarily in post-menopausal women (up to 5% of healthy pre-menopausal women, up to 25% of post-menopausal women, and up to 1% of healthy adult males) [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. In this study, more than half of this control group (52%, n = 119) had had microbial detection at densities ≥ 10,000 cells/mL by either SUC
or M-PCR, and 22% had microbial detection at densities ≥ 10,000 cells/mL by both SUC
and M-PCR (n = 51) (
Supplemental Figure S1, Supplemental Table S11). This relatively high prevalence of microorganisms in urine specimens from our asymptomatic cohort underscores the importance of practicing diagnostic stewardship such as implementing clinical testing only for the indicated population of symptomatic cases of presumed UTI and the value of having these types of biomarkers [
49].
The biomarkers exhibited excellent specificity (>75% individually and > 90% for consensus) indicating that urine specimens positive for infection-associated biomarkers are highly likely to be associated with cases of active UTIs. There was also a strong correlation between microbe density and rising positivity levels, with high positivity levels in symptomatic patients appearing even at 10,000 cells/mL and CFU/mL in symptomatic patients. Positivity levels for asymptomatic cases remained low even at 100,000 cells/mL and CFU/mL, though there was some increase observed with rising microbe density.
The consensus biomarker positivity criteria showed very high sensitivity and specificity for UTIs, with specificity and NPV above 90%. This makes it a valuable tool to differentiate true UTI cases from asymptomatic bacteriuria and other false-positive differential diagnoses when establishing an objective “truth” for the comparison of existing and novel diagnostic test methods. This is especially important since the current “gold standard” test, SUC, is known to have significant limitations, including low sensitivity for non-E. coli organisms and polymicrobial infections, making it an unreliable source of diagnostic “truth.”
The measurement of urinary biomarkers, individually or in combination, may also prove valuable as a supportive tool for the clinical diagnostic workup of suspected UTIs, especially in patients unable to clearly communicate their symptoms, such as pediatric patients and patients with cognitive impairment. Leukocyte esterase (LE) dipstick analysis is often employed in clinics as part of the diagnostic workup for UTI, even though the specificity is usually too low to be useful as an individual test (specificity range 9-59%, PPV is 86% and NPV is 72%.) [
31,
42,
43,
50]. In contrast, the biomarker consensus criteria has a sensitivity of 84.0%, a specificity of 91.2%, a PPV of 93.7%, and an NPV of 78.8%, using a microbial density threshold of ≥ 10,000 cells/mL or CFUs/mL. It also has a sensitivity of 90.2%, a specificity of 91.2%, a PPV of 91.7%, and a NPV of 89.7% using a higher microbial density threshold of ≥ 100,000 cells/mL or CFUs/mL (
Supplemental Data).
5. Conclusions
Using symptomatic subjects’ urine specimens in which SUC and M-PCR results agreed on the presence of uropathogens, we demonstrated the association of NGAL, IL-8, and IL-1β, with Definitive UTI cases. A consensus criterion with ≥ 2 of the biomarkers meeting the positivity thresholds showed a good balance of sensitivity (90.2%), specificity (91.2%), and accuracy (90.7%). Therefore, this biomarker consensus is an excellent supportive diagnostic tool for resolving the presence of active UTI, particularly if SUC and M-PCR results disagree. These biomarkers can be used as an important supplemental tool to determine if a case is a UTI when the microbial detection and identification diagnostic test has significant limitations in sensitivity or when it is unclear whether the detected microorganism(s) can cause disease.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org. Supplemental Table S1: ICD-10-CM codes for the symptomatic cohort; Supplemental Table S2: Sensitivity and specificity of candidate biomarkers; Supplemental Table S3A: NGAL and IL-8 Positivity Contingency Table; Supplemental Table S3B: NGAL and IL-1β Positivity Contingency Table; Supplemental Table S3C: IL-8 and IL-1β Positivity Contingency Table; Supplemental Table S4: Combination of two biomarkers performance comparisons in the presence of microorganisms detected at both ≥ 104 cells/mL by M-PCR and ≥ 104 CFUs/mL by SUC; Supplemental Table S5A: NGAL Positivity Contingency Table for Criterion 2; Supplemental Table S5B: IL-8 Positivity Contingency Table for Criterion 2; Supplemental Table S5C: IL-1β Positivity Contingency Table for Criterion 2; Supplemental Table S6: Biomarker performance comparisons in the presence of microorganisms detected at both ≥ 105 cells/mL by M-PCR and ≥ 104 CFUs/mL by SUC; Supplemental Table S7A: Biomarker Consensus Positivity Contingency Table for Criterion 2; Supplemental Table S7B: All Three Biomarkers Positivity Contingency Table for Criterion 2; Supplemental Table S8: Biomarker “Consensus” and triple combination performance comparisons in the presence of microorganisms detected at both ≥ 105 cells/mL by M-PCR and CFUs/mL by SUC; Supplemental Table S9A: NGAL and IL-8 Positivity Contingency Table; Supplemental Table S9B: NGAL and IL-1β Positivity Contingency Table; Supplemental Table S9C: IL-8 and IL-1β Positivity Contingency Table; Supplemental Table S10: Biomarker combination performance comparisons in the presence of microorganisms detected at both ≥ 105 cells/mL by M-PCR and CFUs/mL by SUC; Supplemental Figure S1: Asymptomatic Microbial Density; Supplemental Table S11: Asymptomatic Subjects with Positive Microbial Detection (> 10,000 CFU or cells/mL for bacteria/bacterial groups).
Author Contributions
Mohit Mathur and David Baunoch; Data curation, Marzieh Akhlaghpour, Richard Festa, Michael Percaccio, Jesus Magallon, Mariana Remedios-Chan, Alain Rosas and David Baunoch; Formal analysis, Jimin Wang and Yan Jiang; Funding acquisition, David Baunoch; Investigation, Natalie Luke and Richard Festa; Methodology, Natalie Luke, Mohit Mathur and David Baunoch; Project administration, Emery Haley, Natalie Luke and Richard Festa; Resources, David Baunoch; Software, Richard Festa, Michael Percaccio and Jimin Wang; Supervision, Natalie Luke and Richard Festa; Validation, Richard Festa; Visualization, Emery Haley; Writing – original draft, Marzieh Akhlaghpour, Emery Haley and Laura Parnell; Writing – review & editing, Emery Haley, Laura Parnell, Natalie Luke, Mohit Mathur, Lori Anderson and David Baunoch. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Pathnostics.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by WIRB-Copernicus Group (WCG® IRB) (protocol code: 20230847; date of approval: February 27, 2023). Ethical review and approval were waived for the symptomatic cohort in this study due to the use of deidentified samples from a biobank repository.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all asymptomatic subject volunteers involved in the study. Patient consent was waived for the symptomatic cohort in this study due to the use of deidentified samples from a biobank repository.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy concerns.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Max Murphy, Jasmine Nguyen, Kelli Eugenio, Tim Cho, and Annie Ngo for their contributions toward generating the data presented in this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
MA, EH, NL, MM, RF, MP, JM, MR, AR, LA, and DB are employees of Pathnostics, and JW, YJ, and LP are paid consultants of Pathnostics.
References
- Flores-Mireles, A.L.; Walker, J.N.; Caparon, M.; Hultgren, S.J. Urinary Tract Infections: Epidemiology, Mechanisms of Infection and Treatment Options. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2015, 13, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, C.; Rantell, A.; Cardozo, L.; Jacobson, S.K.; Anding, R.; Kirschner-Hermanns, R.; Greenwell, T.; Swamy, S.; Malde, S.; Abrams, P. How Can We Improve Investigation, Prevention and Treatment for Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections—ICI-RS 2018. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2019, 38, S90–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, T.K.; Hilt, E.E.; Dune, T.J.; Mueller, E.R.; Wolfe, A.J.; Brubaker, L. Urine Trouble: Should We Think Differently about UTI? Int. Urogynecology J. 2018, 29, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, T.K.; Dune, T.; Hilt, E.E.; Thomas-White, K.J.; Kliethermes, S.; Brincat, C.; Brubaker, L.; Wolfe, A.J.; Mueller, E.R.; Schreckenberger, P.C. The Clinical Urine Culture: Enhanced Techniques Improve Detection of Clinically Relevant Microorganisms. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2016, 54, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreland, R.B.; Choi, B.I.; Geaman, W.; Gonzalez, C.; Hochstedler-Kramer, B.R.; John, J.; Kaindl, J.; Kesav, N.; Lamichhane, J.; Lucio, L.; et al. Beyond the Usual Suspects: Emerging Uropathogens in the Microbiome Age. Frontiers in Urology 2023, 3, 1212590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollstedt, A.; Baunoch, D.; Wolfe, A.; Luke, N.; Wojno, K.J.; Cline, K.; Belkoff, L.; Milbank, A.; Sherman, N.; Haverkorn, R.; et al. Bacterial Interactions as Detected by Pooled Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (P-AST) in Polymicrobial Urine Specimens. J Surgical Urology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baunoch, D.; Luke, N.; Wang, D.; Vollstedt, A.; Zhao, X.; Ko, D.S.C.; Huang, S.; Cacdac, P.; Sirls, L.T. Concordance Between Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Susceptibility in Symptomatic Urinary Tract Infections. Infect Drug Resist 2021, 14, 3275–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojno, K.J.; Baunoch, D.; Luke, N.; Opel, M.; Korman, H.; Kelly, C.; Jafri, S.M.A.; Keating, P.; Hazelton, D.; Hindu, S.; et al. Multiplex PCR Based Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Analysis Compared to Traditional Urine Culture in Identifying Significant Pathogens in Symptomatic Patients. Urology 2020, 136, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollstedt, A.; Baunoch, D.; Wojno, K.J.; Luke, N.; Cline, K.; Belkoff, L.; Sirls, L. Multisite Prospective Comparison of Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction Testing with Urine Culture for Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infections in Symptomatic Patients. Journal of Surgical Urology 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Daly Utilization of M-PCR and P-AST for Diagnosis and Management of Urinary Tract Infections in Home-Based Primary Care. JOJ Urology & Nephrology 2020. [CrossRef]
- Nicolle, L.E. Asymptomatic Bacteriuria When to Screen and When to Treat. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 2003, 17, 367–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhanel, G.G.; Harding, G.K.M.; Nicolle, L.E. Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1990, 13, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolle, L.E. Asymptomatic bacteriuria in the elderly. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 1997, 11, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colgan, R.; Nicolle, L.E.; McGlone, A.; Hooton, T.M. Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Adults. Am. Fam. Physician 2006, 74, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luu, T.; Albarillo, F.S. Asymptomatic Bacteriuria: Prevalence, Diagnosis, Management, and Current Antimicrobial Stewardship Implementations. Am. J. Med. 2022, 135, e236–e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosman, I.S.; Roić, A.C.; Lamot, L. A Systematic Review of the (Un)Known Host Immune Response Biomarkers for Predicting Recurrence of Urinary Tract Infection. Frontiers Medicine 2022, 9, 931717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, S.N.; Miao, Y. The Nature of Immune Responses to Urinary Tract Infections. Nat Rev Immunol 2015, 15, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, L.L.; Ingersoll, M.A. The Immune Response to Infection in the Bladder. Nat Rev Urol 2020, 17, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigedal, M.; Marstad, A.; Haug, M.; Damås, J.K.; Strong, R.K.; Roberts, P.L.; Himpsl, S.D.; Stapleton, A.; Hooton, T.M.; Mobley, H.L.T.; et al. Lipocalin 2 Imparts Selective Pressure on Bacterial Growth in the Bladder and Is Elevated in Women with Urinary Tract Infection. J Immunol 2014, 193, 6081–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichino, M.; Kuroyanagi, Y.; Kusaka, M.; Mori, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Shiroki, R.; Kurahashi, H.; Hoshinaga, K. Increased Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase Associated Lipocalin Levels in a Rat Model of Upper Urinary Tract Infection. J Urology 2009, 181, 2326–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flo, T.H.; Smith, K.D.; Sato, S.; Rodriguez, D.J.; Holmes, M.A.; Strong, R.K.; Akira, S.; Aderem, A. Lipocalin 2 Mediates an Innate Immune Response to Bacterial Infection by Sequestrating Iron. Nature 2004, 432, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsson, P.; Hang, L.; Wullt, B.; Irjala, H.; Svanborg, C. Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression and Cytokine Responses in the Human Urinary Tract Mucosa. Infect Immun 2004, 72, 3179–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, R.; Säve, S.; Persson, K. Adenosine Triphosphate Induced P2Y2 Receptor Activation Induces Proinflammatory Cytokine Release in Uroepithelial Cells. J Urology 2012, 188, 2419–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Säve, S.; Persson, K. Extracellular ATP and P2Y Receptor Activation Induce a Proinflammatory Host Response in the Human Urinary Tract. Infect Immun 2010, 78, 3609–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.C.; Mukaida, N.; Ishiyama, S.; Tokue, A.; Kawai, T.; Matsushima, K.; Kasahara, T. Elevated Interleukin-8 Levels in the Urine of Patients with Urinary Tract Infections. Infect Immun 1993, 61, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambite, I.; Rydstrom, G.; Schwaderer, A.; Hains, D. The Genetics of Urinary Tract Infections and the Innate Defense of the Kidney and Urinary Tract. J Pediatric Genetics 2015, 05, 025–032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamatsu, K.; Hannan, T.J.; Guest, R.L.; Kostakioti, M.; Hadjifrangiskou, M.; Binkley, J.; Dodson, K.; Raivio, T.L.; Hultgren, S.J. Dysregulation of Escherichia Coli α-Hemolysin Expression Alters the Course of Acute and Persistent Urinary Tract Infection. Proc National Acad Sci 2015, 112, E871–E880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, S.Y.; Sullivan, M.J.; Ipe, D.S.; Smith, J.P.; Cripps, A.W.; Ulett, G.C. Pathogenesis of Streptococcus Urinary Tract Infection Depends on Bacterial Strain and β-Hemolysin/Cytolysin That Mediates Cytotoxicity, Cytokine Synthesis, Inflammation and Virulence. Sci Rep-uk 2016, 6, 29000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Xie, X.; Chen, H. The Immune Responses to Different Uropathogens Call Individual Interventions for Bladder Infection. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 953354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, N.; Juthani-Mehta, M. Novel Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infection—A Systematic Review. Biomark Insights 2009, 4, BMI.S3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, J.; Wullt, B.; Naber, K.G.; Köves, B. Biomarkers in Urinary Tract Infections—Which Ones Are Suitable for Diagnostics and Follow-Up? Gms Infect Dis 8 Doc24. [CrossRef]
- Alidjanov, J.F.; Naber, K.G.; Pilatz, A.; Wagenlehner, F.M. Validation of the American English Acute Cystitis Symptom Score. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfeir, M.M.; Hooton, T.M. Practices of Clinical Microbiology Laboratories in Reporting Voided Urine Culture Results. Clin Microbiol Infec 2018, 24, 669–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, R.H.; Shapiro, E.D.; Andriole, V.T.; Davis, R.J.; Stamm, W.E. Evaluation of New Anti-Infective Drugs for the Treatment of Urinary Tract Infection. Clin Infect Dis 1992, 15, S216–S227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovelius, B.; Mårdh, P.-A.; Bygren, P. Urinary Tract Infections Caused by Staphylococcus Saprophyticus: Recurrences and Complications. J Urology 1979, 122, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNulty, C. PHE/NHS Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infections. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/927195/UTI_diagnostic_flowchart_NICE-October_2020-FINAL.pdfov.uk) (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Kouri, T.; Fogazzi, G.; Gant, V.; Hallander, H.; Hofmann, W.; Guder, W.G. European Urinalysis Guidelines. Scand J Clin Laboratory Investigation 2000, 60, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, F.J. Quantitative Urine Culture in Patients with Urinary Tract Infection and Bacteremia. Am J Clin Pathol 1986, 85, 616–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunin, M. (Ed.) Urinary Tract Infections: Detection, Prevention, and Management; Lea & Febiger: Philadelphia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki, A.; Medzhitov, R. Regulation of Adaptive Immunity by the Innate Immune System. Science 2010, 327, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Nascimento, L.; Massari, P.; Wetzler, L.M. The Role of TLR2 in Infection and Immunity. Front Immunol 2012, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadalla, A.A.H.; Friberg, I.M.; Kift-Morgan, A.; Zhang, J.; Eberl, M.; Topley, N.; Weeks, I.; Cuff, S.; Wootton, M.; Gal, M.; et al. Identification of Clinical and Urine Biomarkers for Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Sci Rep-uk 2019, 9, 19694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, N.; Martin, J.M.; Hoberman, A.; Skae, M.; Milkovich, L.; McElheny, C.; Hickey, R.W.; Gabriel, L.V.; Kearney, D.H.; Majd, M.; et al. Biomarkers That Differentiate False Positive Urinalyses from True Urinary Tract Infection. Pediatr Nephrol 2020, 35, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, N.; Martin, J.M.; Hoberman, A.; Skae, M.; Milkovich, L.; Nowalk, A.; McElheny, C.; Hickey, R.W.; Kearney, D.; Majd, M.; et al. Host and Bacterial Markers That Differ in Children with Cystitis and Pyelonephritis. J Pediatrics 2019, 209, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarajan, P. Neutrophil Gelatinase-associated Lipocalin (NGAL): A New Marker of Kidney Disease. Scand J Clin Laboratory Investigation 2008, 68, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif-Askari, F.S.; Sharif-Askari, N.S.; Guella, A.; Alabdullah, A.; Sheleh, H.B.A.; AlRawi, A.M.H.; Haddad, E.S.; Hamid, Q.; Halwani, R.; Hamoudi, R. Blood Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Urine IL-8 Levels Predict the Type of Bacterial Urinary Tract Infection in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Infect Drug Resist 2020, 13, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundstedt, A.-C.; Leijonhufvud, I.; Ragnarsdottir, B.; Karpman, D.; Andersson, B.; Svanborg, C. Inherited Susceptibility to Acute Pyelonephritis: A Family Study of Urinary Tract Infection. J Infect Dis 2007, 195, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, M.; Jodal, U.; Agace, W.; Hellström, M.; Mårild, S.; Rosberg, S.; Sjöström, M.; Wettergren, B.; Jönsson, S.; Svanborg, C. Interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8 in children with febrile urinary tract infection and asymptomatic bacteriuria. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1996, 174, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messacar, K.; Parker, S.K.; Todd, J.K.; Dominguez, S.R. Implementation of Rapid Molecular Infectious Disease Diagnostics: The Role of Diagnostic and Antimicrobial Stewardship. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2017, 55, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmiemann, G.; Kniehl, E.; Gebhardt, K.; Matejczyk, M.M.; Hummers-Pradier, E. The Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infection. Deutsches Ärzteblatt Int 2010, 107, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).