Submitted:
29 June 2023
Posted:
30 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Mechanism of action of D2 antagonist antipsychotic medications
3. Novel target agents
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller:, P.; Lawrie, S.M.; Hodges, A.; Clafferty, R.; Cosway, R.; Johnstone, E.C. Genetic Liability, Illicit Drug Use, Life Stress and Psychotic Symptoms: Preliminary Findings from the Edinburgh Study of People at High Risk for Schizophrenia. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2001, 36, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, M.G.; Nordgaard, J.; Jansson, L.B. Genetics of Schizophrenia: Overview of Methods, Findings and Limitations. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, D.; Schmitt, A.; Kaurani, L.; Senner, F.; Papiol, S.; Malchow, B.; Fischer, A.; Schulze, T.G.; Koutsouleris, N.; Falkai, P. Childhood Trauma in Schizophrenia: Current Findings and Research Perspectives. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelot, N.; Garon-Bissonnette, J.; Jomphe, V.; Doucet-Beaupré, H.; Bureau, A.; Maziade, M. Childhood Trauma May Increase Risk of Psychosis and Mood Disorder in Genetically High-Risk Children and Adolescents by Enhancing the Accumulation of Risk Indicators. Schizophr. Bull. Open 2022, sgac017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, R.A.; Reis Marques, T.; Howes, O.D. Schizophrenia—An Overview. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messias, E.L.; Chen, C.-Y.; Eaton, W.W. Epidemiology of Schizophrenia: Review of Findings and Myths. Psychiatr. Clin. North Am. 2007, 30, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, F.J.; Ferrari, A.J.; Santomauro, D.F.; Diminic, S.; Stockings, E.; Scott, J.G.; McGrath, J.J.; Whiteford, H.A. Global Epidemiology and Burden of Schizophrenia: Findings From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadakia, A.; Catillon, M.; Fan, Q.; Williams, G.R.; Marden, J.R.; Anderson, A.; Kirson, N.; Dembek, C. The Economic Burden of Schizophrenia in the United States. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2022, 83, 22m14458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.V.; Rincón-Cortés, M.; Grace, A.A. Adolescence as a Period of Vulnerability and Intervention in Schizophrenia: Insights from the MAM Model. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 70, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, T.A. Fifty Years Chlorpromazine: A Historical Perspective. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2007, 3, 495–500. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, W.W. A History of Antipsychotic Drug Development. Compr. Psychiatry 1999, 40, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborit, H.; Huguenard, P. [Artificial hibernation by pharmacodynamic and physical means, in surgery]. J. Chir. (Paris) 1951, 67, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Casey, J.F.; Bennett, I.F.; Lindley, C.J.; Hollister, L.E.; Gordon, M.H.; Springer, N.N. Drug Therapy in Schizophrenia. A Controlled Study of the Relative Effectiveness of Chlorpromazine, Promazine, Phenobarbital, and Placebo. AMA Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1960, 2, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkes, J.; Elkes, C. Effect of Chlorpromazine on the Behavior of Chronically Overactive Psychotic Patients. Br. Med. J. 1954, 2, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, H.E.; Hanrahan, G.E. Chlorpromazine; New Inhibiting Agent for Psychomotor Excitement and Manic States. AMA Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1954, 71, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delay, J.; Deniker, P.; Harl, J.M. [Therapeutic method derived from hiberno-therapy in excitation and agitation states]. Ann. Med. Psychol. (Paris) 1952, 110, 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Hamon, null; Paraire, null; Velluz, null [Effect of R. P. 4560 on maniacal agitation]. Ann. Med. Psychol. (Paris) 1952, 110, 331–335. [Google Scholar]
- Creese, I.; Burt, D.R.; Snyder, S.H. Dopamine Receptor Binding Predicts Clinical and Pharmacological Potencies of Antischizophrenic Drugs. Science 1976, 192, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeman, P.; Lee, T.; Chau-Wong, M.; Wong, K. Antipsychotic Drug Doses and Neuroleptic/Dopamine Receptors. Nature 1976, 261, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeman, P. Dopamine Receptor Sequences. Therapeutic Levels of Neuroleptics Occupy D2 Receptors, Clozapine Occupies D4. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 1992, 7, 261–284. [Google Scholar]
- Abi-Dargham, A.; Van De Giessen, E.; Slifstein, M.; Kegeles, L.S.; Laruelle, M. Baseline and Amphetamine-Stimulated Dopamine Activity Are Related in Drug-Naïve Schizophrenic Subjects. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laruelle, M.; Abi-Dargham, A.; Van Dyck, C.H.; Gil, R.; D’Souza, C.D.; Erdos, J.; McCance, E.; Rosenblatt, W.; Fingado, C.; Zoghbi, S.S.; et al. Single Photon Emission Computerized Tomography Imaging of Amphetamine-Induced Dopamine Release in Drug-Free Schizophrenic Subjects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1996, 93, 9235–9240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laruelle, M.; Abi-Dargham, A.; Gil, R.; Kegeles, L.; Innis, R. Increased Dopamine Transmission in Schizophrenia: Relationship to Illness Phases. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 46, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gründer, G.; Cumming, P. The Dopamine Hypothesis of Schizophrenia. In The Neurobiology of Schizophrenia; Elsevier, 2016; pp. 109–124 ISBN 978-0-12-801829-3.
- Brisch, R.; Saniotis, A.; Wolf, R.; Bielau, H.; Bernstein, H.-G.; Steiner, J.; Bogerts, B.; Braun, K.; Jankowski, Z.; Kumaratilake, J.; et al. The Role of Dopamine in Schizophrenia from a Neurobiological and Evolutionary Perspective: Old Fashioned, but Still in Vogue. Front. Psychiatry 2014, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, HJ; Janssen, PAJ The Action of Neuroleptic Drugs : A Psychiatric, Neurologic and Pharmacological Investigation; Amsterdam : North-Holland Pub. Co, 1958.
- Hippius, H. The History of Clozapine. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 1989, 99 Suppl, S3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crilly, J. The History of Clozapine and Its Emergence in the US Market: A Review and Analysis. Hist. Psychiatry 2007, 18, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, J.; Honigfeld, G.; Singer, J.; Meltzer, H. Clozapine for the Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenic. A Double-Blind Comparison with Chlorpromazine. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1988, 45, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, H.Y.; Matsubara, S.; Lee, J.C. Classification of Typical and Atypical Antipsychotic Drugs on the Basis of Dopamine D-1, D-2 and Serotonin2 PKi Values. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1989, 251, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terry, A.V. Role of the Central Cholinergic System in the Therapeutics of Schizophrenia. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2008, 6, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farde, L.; Nordström, A.L.; Wiesel, F.A.; Pauli, S.; Halldin, C.; Sedvall, G. Positron Emission Tomographic Analysis of Central D1 and D2 Dopamine Receptor Occupancy in Patients Treated with Classical Neuroleptics and Clozapine. Relation to Extrapyramidal Side Effects. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1992, 49, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, S.; Remington, G.; Jones, C.; Wilson, A.; DaSilva, J.; Houle, S.; Zipursky, R. High Levels of Dopamine D2 Receptor Occupancy with Low-Dose Haloperidol Treatment: A PET Study. Am. J. Psychiatry 1996, 153, 948–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordström, A.L.; Farde, L.; Wiesel, F.A.; Forslund, K.; Pauli, S.; Halldin, C.; Uppfeldt, G. Central D2-Dopamine Receptor Occupancy in Relation to Antipsychotic Drug Effects: A Double-Blind PET Study of Schizophrenic Patients. Biol. Psychiatry 1993, 33, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, S.; Zipursky, R.; Jones, C.; Remington, G.; Houle, S. Relationship between Dopamine D(2) Occupancy, Clinical Response, and Side Effects: A Double-Blind PET Study of First-Episode Schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2000, 157, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joel, D.; Weiner, I.; Feldon, J. Electrolytic Lesions of the Medial Prefrontal Cortex in Rats Disrupt Performance on an Analog of the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test, but Do Not Disrupt Latent Inhibition: Implications for Animal Models of Schizophrenia. Behav. Brain Res. 1997, 85, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinidis, L.; Anisman, H. Amphetamine Psychosis and Schizophrenia: A Dual Model. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1981, 5, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correll, C.U.; Rubio, J.M.; Kane, J.M. What Is the Risk-Benefit Ratio of Long-Term Antipsychotic Treatment in People with Schizophrenia? World Psychiatry Off. J. World Psychiatr. Assoc. WPA 2018, 17, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, S.; Duncan, G.E.; Marx, C.E.; Lieberman, J.A. Treatments for Schizophrenia: A Critical Review of Pharmacology and Mechanisms of Action of Antipsychotic Drugs. Mol. Psychiatry 2005, 10, 79–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
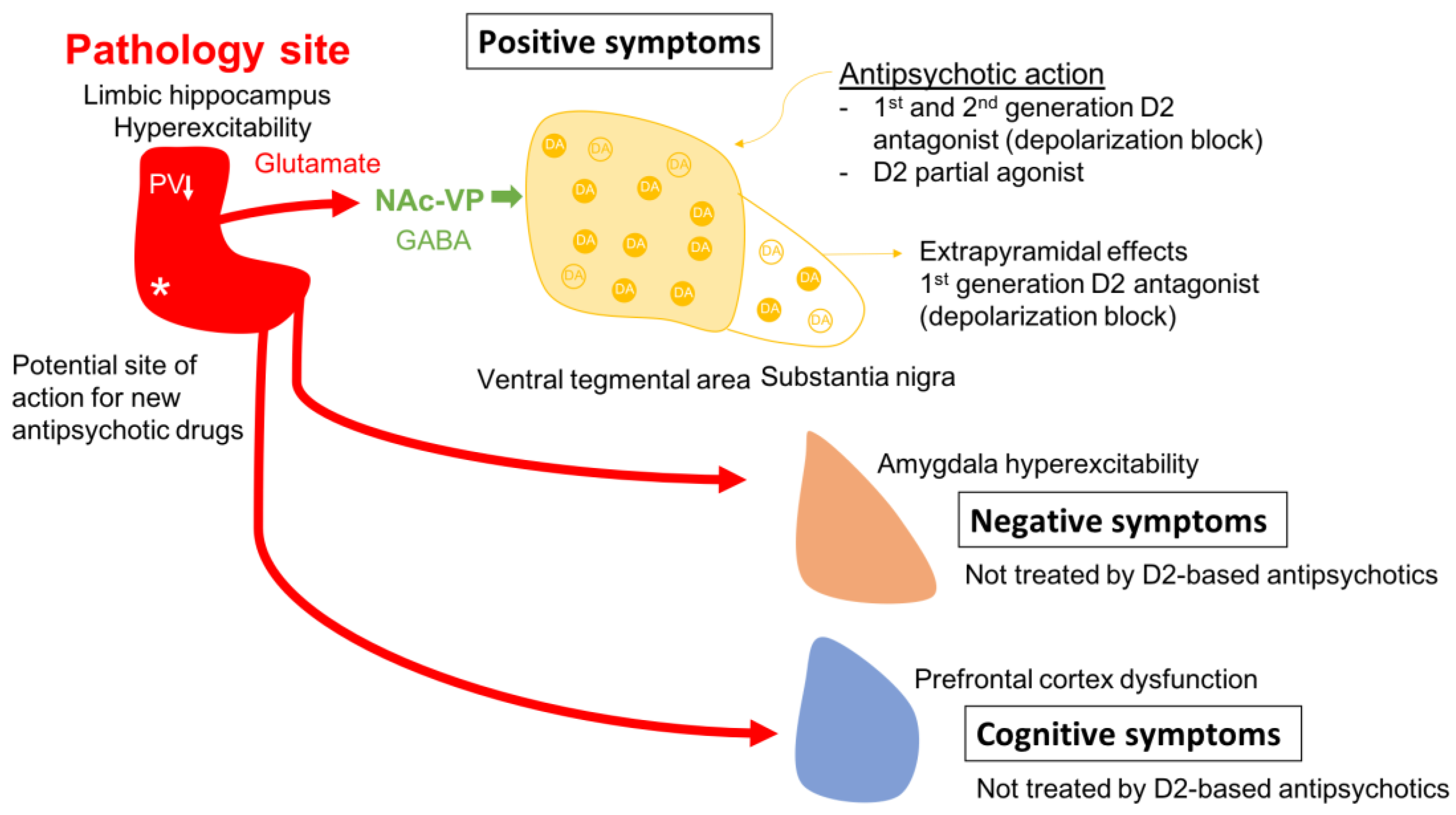
- Grace, A.A.; Bunney, B.S. Induction of Depolarization Block in Midbrain Dopamine Neurons by Repeated Administration of Haloperidol: Analysis Using in Vivo Intracellular Recording. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1986, 238, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bunney, B.S.; Grace, A.A. Acute and Chronic Haloperidol Treatment: Comparison of Effects on Nigral Dopaminergic Cell Activity. Life Sci. 1978, 23, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, A.A.; Bunney, B.S.; Moore, H.; Todd, C.L. Dopamine-Cell Depolarization Block as a Model for the Therapeutic Actions of Antipsychotic Drugs. Trends Neurosci. 1997, 20, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, A.A. The Depolarization Block Hypothesis of Neuroleptic Action: Implications for the Etiology and Treatment of Schizophrenia. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 1992, 36, 91–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, R.F.; Blaha, C.D. Chronic Haloperidol Decreases Dopamine Release in Striatum and Nucleus Accumbens in Vivo: Depolarization Block as a Possible Mechanism of Action. Brain Res. Bull. 1987, 18, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiodo, L.A.; Bunney, B.S. Typical and Atypical Neuroleptics: Differential Effects of Chronic Administration on the Activity of A9 and A10 Midbrain Dopaminergic Neurons. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1983, 3, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, F.J.; Wang, R.Y. Differential Effects of Classical and Atypical Antipsychotic Drugs on A9 and A10 Dopamine Neurons. Science 1983, 221, 1054–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J.M.; Litwin, L.C.; Sutton, E.B.; Malick, J.B. Seroquel: Electrophysiological Profile of a Potential Atypical Antipsychotic. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 1993, 112, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, R.A.; Hamilton, C.W.; Brogden, R.N.; Linkewich, J.A.; Romankiewicz, J.A.; Heel, R.C. Metoclopramide. An Updated Review of Its Pharmacological Properties and Clinical Use. Drugs 1983, 25, 451–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uliana, D.L.; Gomes, F.V.; Grace, A.A. Update on Current Animal Models for Schizophrenia: Are They Still Useful? Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2023, 36, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uliana, D.L.; Zhu, X.; Gomes, F.V.; Grace, A.A. Using Animal Models for the Studies of Schizophrenia and Depression: The Value of Translational Models for Treatment and Prevention. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 935320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, D.R. Implications of Normal Brain Development for the Pathogenesis of Schizophrenia. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1987, 44, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipska, B.K.; Jaskiw, G.E.; Weinberger, D.R. Postpubertal Emergence of Hyperresponsiveness to Stress and to Amphetamine after Neonatal Excitotoxic Hippocampal Damage: A Potential Animal Model of Schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 1993, 9, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, R.A.; Moore, J.; McEvoy, J.P.; Levin, E.D. Cognitive Effects of Neonatal Hippocampal Lesions in a Rat Model of Schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 1996, 15, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.; Grecksch, G.; Bernstein, H.G.; Höllt, V.; Bogerts, B. Social Behaviour in Rats Lesioned with Ibotenic Acid in the Hippocampus: Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 1999, 144, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grecksch, G.; Bernstein, H.G.; Becker, A.; Höllt, V.; Bogerts, B. Disruption of Latent Inhibition in Rats with Postnatal Hippocampal Lesions. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 1999, 20, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, K.Y.; Chambers, R.A.; Lipska, B.K. The Neonatal Ventral Hippocampal Lesion as a Heuristic Neurodevelopmental Model of Schizophrenia. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 204, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, H.; Jentsch, J.D.; Ghajarnia, M.; Geyer, M.A.; Grace, A.A. A Neurobehavioral Systems Analysis of Adult Rats Exposed to Methylazoxymethanol Acetate on E17: Implications for the Neuropathology of Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 60, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modinos, G.; Allen, P.; Grace, A.A.; McGuire, P. Translating the MAM Model of Psychosis to Humans. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, C.E.; Mednick, S.A.; Munk-Jorgensen, P. Exposure to Influenza Epidemics during Gestation and Adult Schizophrenia. A 40-Year Study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1990, 47, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckers, S.; Konradi, C. Hippocampal Pathology in Schizophrenia. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 529–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howes, O.D.; Kambeitz, J.; Kim, E.; Stahl, D.; Slifstein, M.; Abi-Dargham, A.; Kapur, S. The Nature of Dopamine Dysfunction in Schizophrenia and What This Means for Treatment: Meta-Analysis of Imaging Studies. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2012, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowan, S.; Lawrence, A.D.; Sales, T.; Quested, D.; Grasby, P. Presynaptic Dopaminergic Dysfunction in Schizophrenia: A Positron Emission Tomographic [ 18 F]Fluorodopa Study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2004, 61, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
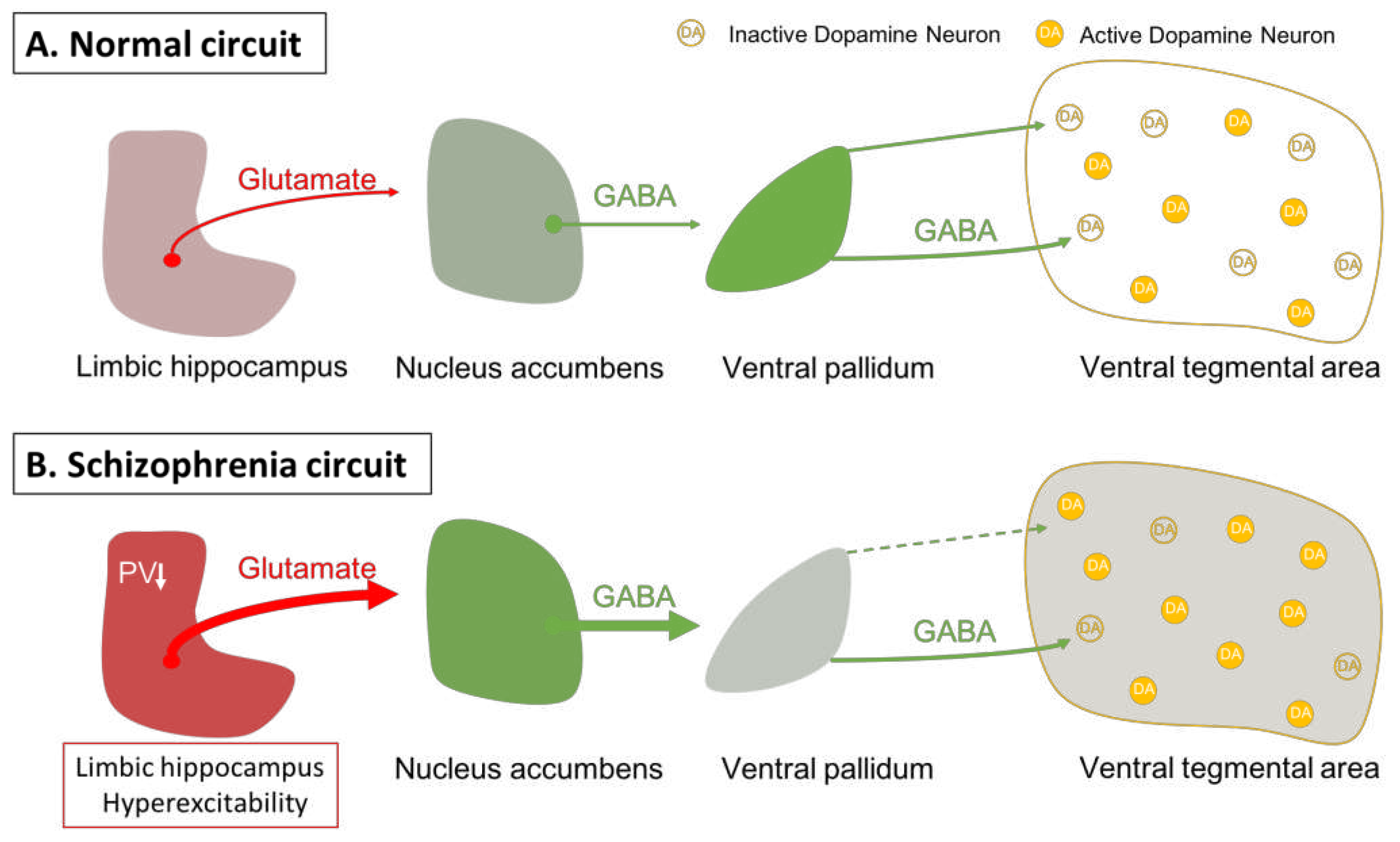
- Lodge, D.J.; Grace, A.A. Aberrant Hippocampal Activity Underlies the Dopamine Dysregulation in an Animal Model of Schizophrenia. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 11424–11430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Reynolds, G.P. A Selective Decrease in the Relative Density of Parvalbumin-Immunoreactive Neurons in the Hippocampus in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2002, 55, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konradi, C.; Yang, C.K.; Zimmerman, E.I.; Lohmann, K.M.; Gresch, P.; Pantazopoulos, H.; Berretta, S.; Heckers, S. Hippocampal Interneurons Are Abnormal in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2011, 131, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodge, D.J.; Behrens, M.M.; Grace, A.A. A Loss of Parvalbumin-Containing Interneurons Is Associated with Diminished Oscillatory Activity in an Animal Model of Schizophrenia. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 2344–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, K.M.; Grace, A.A. Corresponding Decrease in Neuronal Markers Signals Progressive Parvalbumin Neuron Loss in MAM Schizophrenia Model. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 17, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floresco, S.B.; Todd, C.L.; Grace, A.A. Glutamatergic Afferents from the Hippocampus to the Nucleus Accumbens Regulate Activity of Ventral Tegmental Area Dopamine Neurons. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 4915–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.F.; Wagner, H.N.; Tune, L.E.; Dannals, R.F.; Pearlson, G.D.; Links, J.M.; Tamminga, C.A.; Broussolle, E.P.; Ravert, H.T.; Wilson, A.A.; et al. Positron Emission Tomography Reveals Elevated D2 Dopamine Receptors in Drug-Naive Schizophrenics. Science 1986, 234, 1558–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tost, H.; Alam, T.; Meyer-Lindenberg, A. Dopamine and Psychosis: Theory, Pathomechanisms and Intermediate Phenotypes. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, A.; Conn, P.J. The Hippocampo-Prefrontal Pathway: A Possible Therapeutic Target for Negative and Cognitive Symptoms of Schizophrenia. Future Neurol. 2015, 10, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, P.; Grace, A.A. Synaptic Interactions among Excitatory Afferents to Nucleus Accumbens Neurons: Hippocampal Gating of Prefrontal Cortical Input. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 3622–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, P.; Lewis, B.L.; Weinberger, D.R.; Lipska, B.K. Neonatal Hippocampal Damage Alters Electrophysiological Properties of Prefrontal Cortical Neurons in Adult Rats. Cereb. Cortex N. Y. N 1991 2002, 12, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
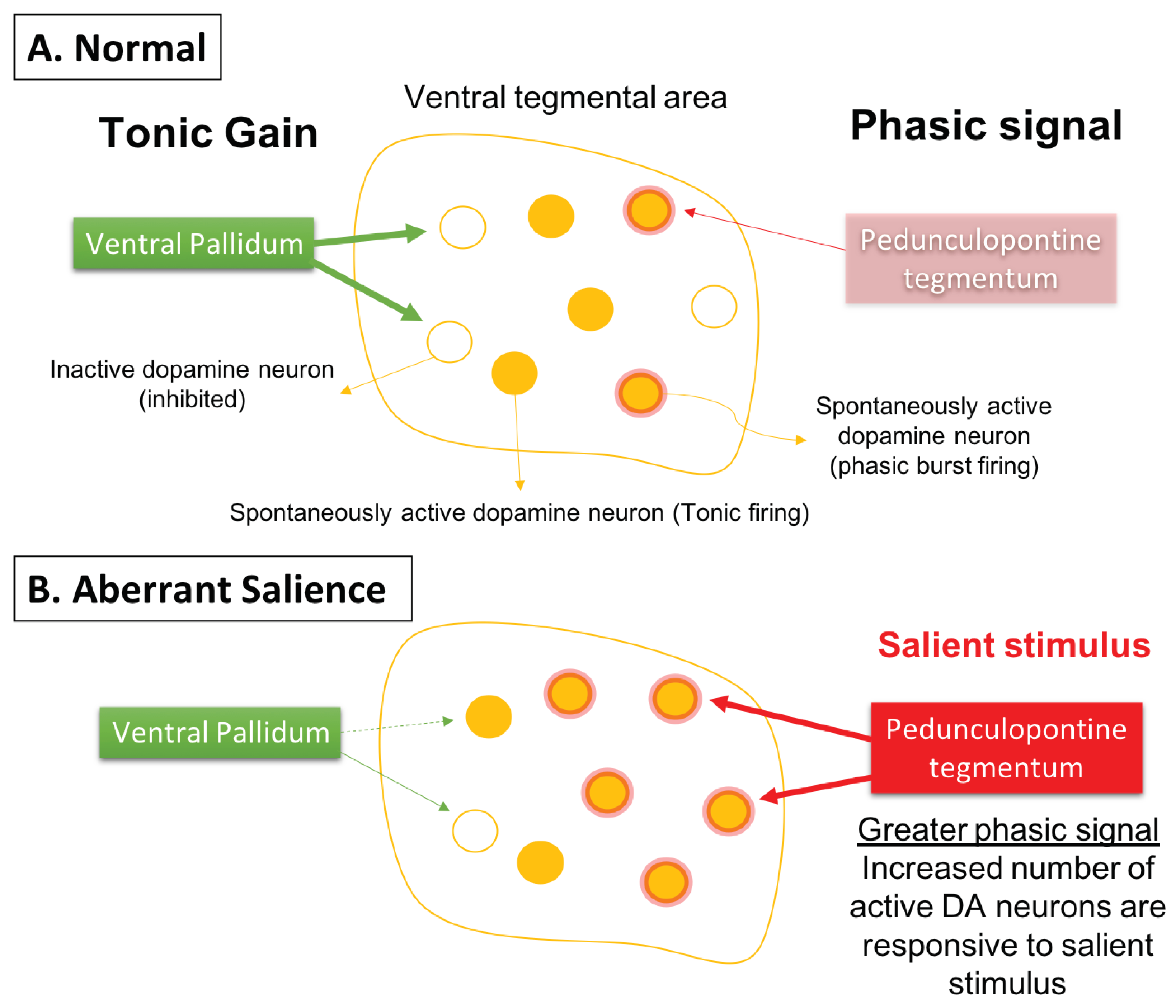
- Kapur, S. Psychosis as a State of Aberrant Salience: A Framework Linking Biology, Phenomenology, and Pharmacology in Schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenschein, S.F.; Gomes, F.V.; Grace, A.A. Dysregulation of Midbrain Dopamine System and the Pathophysiology of Schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, A.A. Dysregulation of the Dopamine System in the Pathophysiology of Schizophrenia and Depression. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, K.M.; Cook, J.M.; Poe, M.M.; Grace, A.A. Prior Antipsychotic Drug Treatment Prevents Response to Novel Antipsychotic Agent in the Methylazoxymethanol Acetate Model of Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2014, 40, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, S.; Arenovich, T.; Agid, O.; Zipursky, R.; Lindborg, S.; Jones, B. Evidence for Onset of Antipsychotic Effects within the First 24 Hours of Treatment. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, P.M.; Correll, C.U. The Acute Efficacy of Antipsychotics in Schizophrenia: A Review of Recent Meta-Analyses. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 8, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, P.M.; Brain, C.; Scott, J. Nonadherence with Antipsychotic Medication in Schizophrenia: Challenges and Management Strategies. Patient Relat. Outcome Meas. 2014, 5, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, P.; Masopust, J.; Kopeček, M. Dopamine Receptor Partial Agonists: Do They Differ in Their Clinical Efficacy? Front. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 781946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, K.D.; Molski, T.F.; Xu, C.; Ryan, E.; Tottori, K.; Kikuchi, T.; Yocca, F.D.; Molinoff, P.B. Aripiprazole, a Novel Antipsychotic, Is a High-Affinity Partial Agonist at Human Dopamine D2 Receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenschein, S.F.; Gill, K.M.; Grace, A.A. State-Dependent Effects of the D2 Partial Agonist Aripiprazole on Dopamine Neuron Activity in the MAM Neurodevelopmental Model of Schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 44, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leucht, S.; Pitschel-Walz, G.; Abraham, D.; Kissling, W. Efficacy and Extrapyramidal Side-Effects of the New Antipsychotics Olanzapine, Quetiapine, Risperidone, and Sertindole Compared to Conventional Antipsychotics and Placebo. A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Schizophr. Res. 1999, 35, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, R.S.E.; Sweeney, J.A.; Gu, H.; Hamer, R.M.; Perkins, D.O.; McEvoy, J.P.; Lieberman, J.A. Effects of Olanzapine, Quetiapine, and Risperidone on Neurocognitive Function in Early Psychosis: A Randomized, Double-Blind 52-Week Comparison. Am. J. Psychiatry 2007, 164, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keefe, R.S.E.; Bilder, R.M.; Davis, S.M.; Harvey, P.D.; Palmer, B.W.; Gold, J.M.; Meltzer, H.Y.; Green, M.F.; Capuano, G.; Stroup, T.S.; et al. Neurocognitive Effects of Antipsychotic Medications in Patients with Chronic Schizophrenia in the CATIE Trial. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorick-Kehn, L.M.; Johnson, B.G.; Knitowski, K.M.; Salhoff, C.R.; Witkin, J.M.; Perry, K.W.; Griffey, K.I.; Tizzano, J.P.; Monn, J.A.; McKinzie, D.L.; et al. In Vivo Pharmacological Characterization of the Structurally Novel, Potent, Selective MGlu2/3 Receptor Agonist LY404039 in Animal Models of Psychiatric Disorders. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2007, 193, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberati, D.; Moreau, J.-L.; Lengyel, J.; Hauser, N.; Mory, R.; Borroni, E.; Pinard, E.; Knoflach, F.; Schlotterbeck, G.; Hainzl, D.; et al. Glycine Reuptake Inhibitor RG1678: A Pharmacologic Characterization of an Investigational Agent for the Treatment of Schizophrenia. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menniti, F.S.; Chappie, T.A.; Schmidt, C.J. PDE10A Inhibitors-Clinical Failure or Window Into Antipsychotic Drug Action? Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 600178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnenschein, S.F.; Grace, A.A. The MGluR2/3 Agonist Pomaglumetad Methionil Normalizes Aberrant Dopamine Neuron Activity via Action in the Ventral Hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020, 45, 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska, A.; Świerczek, A.; Wyska, E.; Gawalska, A.; Bucki, A.; Pawłowski, M.; Chłoń-Rzepa, G. Advances in Discovery of PDE10A Inhibitors for CNS-Related Disorders. Part 1: Overview of the Chemical and Biological Research. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umbricht, D.; Alberati, D.; Martin-Facklam, M.; Borroni, E.; Youssef, E.A.; Ostland, M.; Wallace, T.L.; Knoflach, F.; Dorflinger, E.; Wettstein, J.G.; et al. Effect of Bitopertin, a Glycine Reuptake Inhibitor, on Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Proof-of-Concept Study. JAMA Psychiatry 2014, 71, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macek, T.A.; McCue, M.; Dong, X.; Hanson, E.; Goldsmith, P.; Affinito, J.; Mahableshwarkar, A.R. A Phase 2, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study of the Efficacy and Safety of TAK-063 in Subjects with an Acute Exacerbation of Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2019, 204, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinon, B.J.; Millen, B.A.; Zhang, L.; McKinzie, D.L. Exploratory Analysis for a Targeted Patient Population Responsive to the Metabotropic Glutamate 2/3 Receptor Agonist Pomaglumetad Methionil in Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 78, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.H.; Kinon, B.J.; Baygani, S.; Millen, B.A.; Velona, I.; Kollack-Walker, S.; Walling, D.P. A Long-Term, Phase 2, Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label, Comparative Safety Study of Pomaglumetad Methionil (LY2140023 Monohydrate) versus Atypical Antipsychotic Standard of Care in Patients with Schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry 2013, 13, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugarski-Kirola, D.; Iwata, N.; Sameljak, S.; Reid, C.; Blaettler, T.; Millar, L.; Marques, T.R.; Garibaldi, G.; Kapur, S. Efficacy and Safety of Adjunctive Bitopertin versus Placebo in Patients with Suboptimally Controlled Symptoms of Schizophrenia Treated with Antipsychotics: Results from Three Phase 3, Randomised, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group, Placebo-Controlled, Multicentre Studies in the SearchLyte Clinical Trial Programme. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.P.; Banerjee, A.; Dawra, V.; Boyer, S.; Schmidt, C.J.; DeMartinis, N. Phosphodiesterase 10A Inhibitor Monotherapy Is Not an Effective Treatment of Acute Schizophrenia. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 39, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.H.; Zhang, L.; Millen, B.A.; Kinon, B.J.; Gomez, J.-C. Pomaglumetad Methionil (LY2140023 Monohydrate) and Aripiprazole in Patients with Schizophrenia: A Phase 3, Multicenter, Double-Blind Comparison. Schizophr. Res. Treat. 2014, 2014, 758212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servonnet, A.; Samaha, A.-N. Antipsychotic-Evoked Dopamine Supersensitivity. Neuropharmacology 2020, 163, 107630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Grace, A.A. Amygdala Hyperactivity in MAM Model of Schizophrenia Is Normalized by Peripubertal Diazepam Administration. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 41, 2455–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Grace, A.A. Sex- and Exposure Age-Dependent Effects of Adolescent Stress on Ventral Tegmental Area Dopamine System and Its Afferent Regulators. Mol. Psychiatry 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, K.M.; Lodge, D.J.; Cook, J.M.; Aras, S.; Grace, A.A. A Novel A5GABA(A)R-Positive Allosteric Modulator Reverses Hyperactivation of the Dopamine System in the MAM Model of Schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 36, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velligan, D.I.; Weiden, P.J.; Sajatovic, M.; Scott, J.; Carpenter, D.; Ross, R.; Docherty, J.P. Expert Consensus Panel on Adherence Problems in Serious and Persistent Mental Illness The Expert Consensus Guideline Series: Adherence Problems in Patients with Serious and Persistent Mental Illness. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2009, 70 Suppl 4, 1–46; quiz 47–48.
- Lacro, J.P.; Dunn, L.B.; Dolder, C.R.; Leckband, S.G.; Jeste, D.V. Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Medication Nonadherence in Patients with Schizophrenia: A Comprehensive Review of Recent Literature. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2002, 63, 892–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cramer, J.A.; Rosenheck, R. Compliance with Medication Regimens for Mental and Physical Disorders. Psychiatr. Serv. Wash. DC 1998, 49, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieslehto, J.; Tiihonen, J.; Lähteenvuo, M.; Tanskanen, A.; Taipale, H. Primary Nonadherence to Antipsychotic Treatment Among Persons with Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2022, 48, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, R.; Turolla, A.; Chinellato, G.; Roy, A.; Hartman, R.D. Phase 2 Results Indicate Evenamide, a Selective Modulator of Glutamate Release, Is Associated with Remarkable Clinically Important Long-Term Efficacy When Added to an Antipsychotic in Patients with Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia (TRS). Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2023, pyad035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolato, M.; Faravelli, L.; Anand, R. T36. THE ANTIPSYCHOTIC-LIKE PROPERTIES OF EVENAMIDE (NW-3509) REFLECT THE MODULATION OF GLUTAMATERGIC DYSREGULATION. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44, S126–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, D.J.; Grace, A.A. Amphetamine Activation of Hippocampal Drive of Mesolimbic Dopamine Neurons: A Mechanism of Behavioral Sensitization. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 7876–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, I.M.; Whitaker, C.; White, W. Amphetamine-Induced Hyperlocomotion in Rats: Hippocampal Modulation of the Nucleus Accumbens. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




