1. Introduction
Primary lymphedema is a chronic condition caused by a developmental abnormality of the lymphatic system and its malfunction.[
1] Primary lymphedema is considered rare, and the estimated worldwide prevalence is about 1 in 100.000 individuals. It can manifest as an isolated disease or as part of a complex syndrome.[
2] Although primary lymphedema usually presents in childhood, it may occur at any age.[
2] The natural history of the disease is variable, and it depends not only on the underlying developmental abnormality but also on the penetrance and expression of the genetic condition. In almost 30% of primary lymphedema patients, a genetic mutation is identifiable, and it often involves the signaling pathway of vascular endothelial growth factor C.[
3] More than 20 genes have been related to lymphatic abnormalities in primary lymphedema with a high degree of genetic heterogeneity.[
3]
Primary lymphedema usually involves the lower extremities, but on rare occasions, it can affect the genitalia and upper limbs. In general, this condition affects females twice as much as males.[
4] The phenotypic entities of primary lymphedema vary in age of onset, site of edema, associated features, inheritance patterns, and underlying genetic cause.[
4,
5] Depending on the time of onset, primary lymphedema can be classified into three types: congenital lymphedema, lymphedema praecox, and lymphedema tarda.[
5] Congenital lymphedema presents at birth or in the first 2 years of life, lymphedema praecox typically presents during puberty or before the age of 35, and lymphedema tarda appears after the age of thirty-five.[
5]
The pathogenesis of most lymphatic disorders is not fully understood, and this it is an evolving area of research.[
1] According to Papendieck et al. primary lymphedema can be classified into three groups depending on the histologic and anatomical components that are affected by the developmental abnormality.[
6] It can be related to interstitial lymphatic endothelial dysplasia, lymphangiodysplasia, or lymphadenodysplasia.[
6] This classification provides the basis for a physiologic approach to primary lymphedema and dictates how to provide a comprehensive treatment taking into consideration the needs of patients.
Different physiologic procedures have been proposed in lymphatic surgery with the aim to restore lymphatic drainage. Lymphaticovenous anastomosis (LVA) is a surgical approach design to divert lymph into the venous system bypassing areas of damaged or obstructed lymphatics vessels.[
7] On the other hand, vascularized lymph node transfer (VLNT) involves the auto-transplantation of functional lymph nodes to restore physiologic lymphatic flow in a lymphedematous extremity.[
8,
9,
10] In advanced stages, lymph stasis and chronic inflammation cause alterations of the subcutaneous tissue resulting in adipogenesis and secondary fibrosis. In these cases, excisional procedures are required to enhance the results of physiologic procedures. By improving the lymphatic drainage and eliminating the densely fibrotic skin and subcutaneous tissue, the combination of physiologic and excisional procedures can address both pathophysiological components simultaneously.[
11,
12]
The aim of this work is to present the Primary-LYmphedema Multidisciplinary Approach (P-LYMA), a complete algorithm for the management of primary lymphedema based on the combination of conservative and surgical therapies. Furthermore, we meticulously described how physiologic and excisional procedures were chosen and performed to address the fluid and solid components of primary lymphedema.
2. Materials and Methods
After approval by the Institutional Review Board, patients with primary lymphedema of the lower limbs were enrolled in this prospective study. Exclusion criteria included concomitant vascular malformations related to the development of lymphedema, previous operations to the affected limb, or trauma involving the lower limbs. Patients with secondary lymphedema were excluded from the study.
Study Protocol
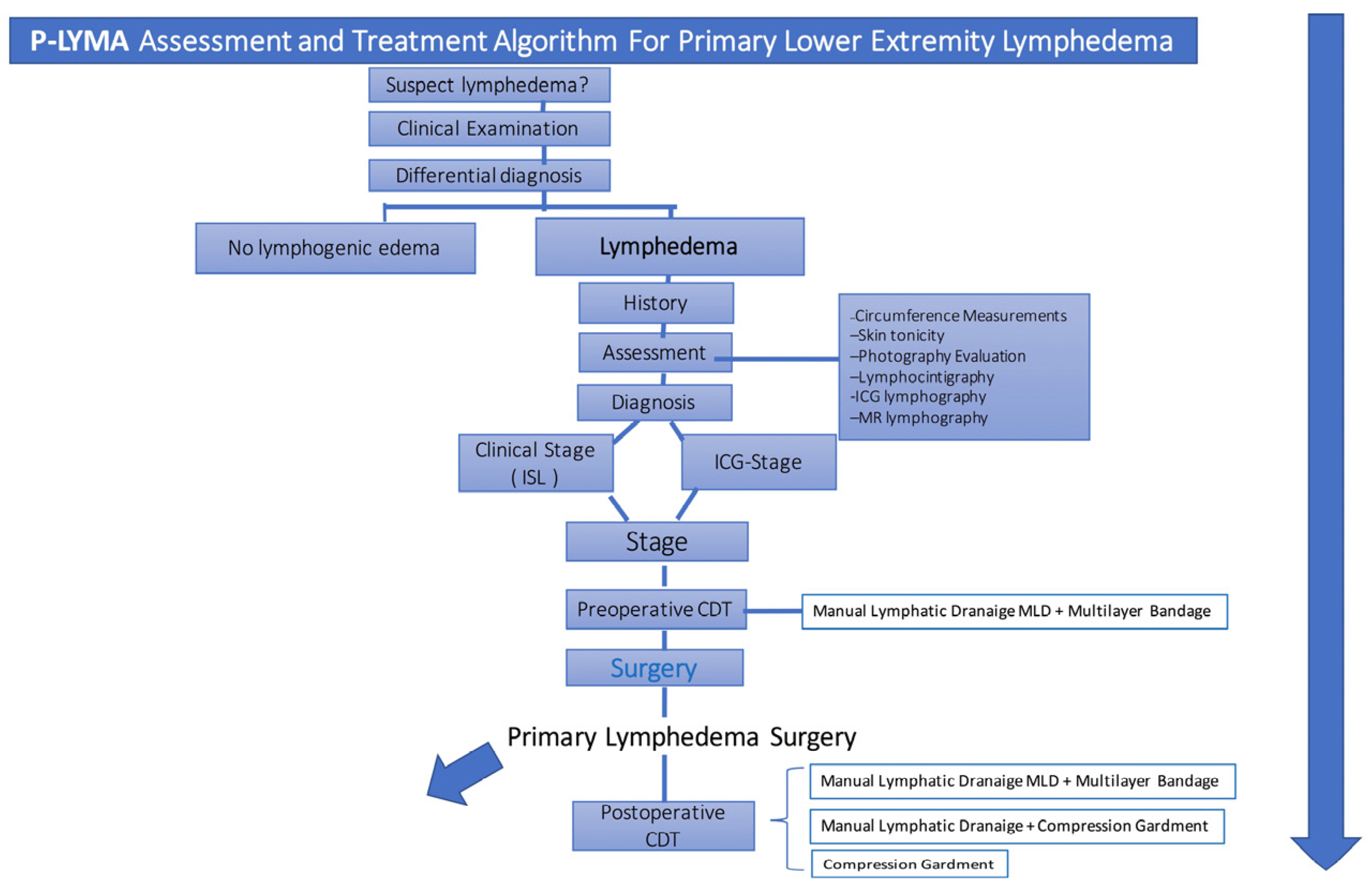
The diagnosis of primary lymphedema was done by means of the medical history and clinical evaluation. Further confirmation was determined by performing lymphoscintigraphy and ICG lymphography (
Figure 1). Additional data such as symptoms duration, prior episodes of infection, and previous conservative treatment were recorded. Circumferential limb and body weight measurements together with preoperative quality of life assessment were recorded. Circumferential measurements were taken at four levels: midfoot, ankle (at the level of the medial and lateral malleoli), 10 cm below the knee, and 10 cm above the knee.
Lymphoscintigraphy was performed on patients preoperatively to assess lymphatic drainage from lower limbs. All patients were staged according to International Society of Lymphology (ISL) system. Patients were also evaluated and stratified based on ICG lymphography. Prior to surgical treatment, all patients underwent physiotherapy with complete decongestive therapy (CDT) for 6 months which consisted of manual lymphatic drainage, multilayer bandage compression therapy, remedial exercises, and skin care. [
13] Patients who did not improve with CDT, surgical options were offered and performed based on the treatment algorithm below (
Figure 2). Postoperatively, patients received CDT.
Treatment Algorithm
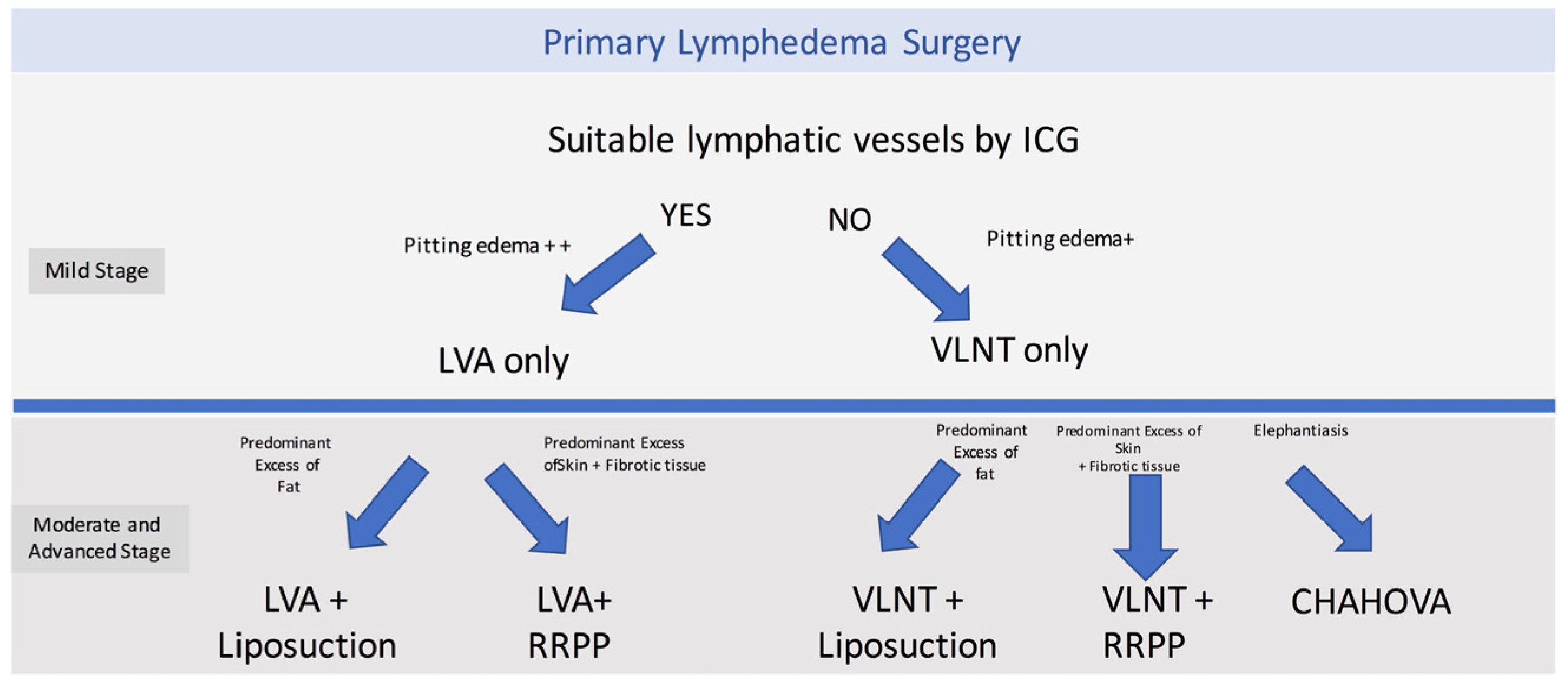
The surgical treatment options included physiologic procedures, such as LVA or VLNT; and excisional procedures such as liposuction, radical reduction with preservation of perforators (RRPP), or the combined Charles, Homan’s, and VLNT (CHAHOVA). The choice of the procedure depended on preoperative evaluation and clinical staging. LVA was performed when ICG lymphography showed areas of linear or splash patterns that were interrupted by areas of dermal backflow. Depending on the number of suitable vessels found during preoperative ICG lymphography, two or three LVAs were performed per extremity. On the other hand, if suitable lymphatics were not found on ICG lymphography, a gastroepiploic or supraclavicular VLNT was planned.
Depending on staging and clinical evaluation, patients were selected to received additional excisional procedures. Patients with ISL stage IIB were treated with liposuction if they presented with predominant adipose tissue deposition. On the other hand, stage III patients who presented with highly fibrotic subcutaneous tissue and recurrent skin infections, a more invasive procedure was performed (RRPP or CHAHOVA). RRPP was chosen in patients with extensive skin excess and good skin quality.[
14,
15] Conversely, the combination of Charles’ and Homan’s procedure (CHAHOVA) was used for en bloc resection of skin and subcutaneous tissue, and was performed in patients with damaged skin and indurated/fibrotic subcutaneous tissues.[
14,
15]
Patients started CDT 5 to 24 days after the procedure depending on the surgical procedure. Patients who underwent liposuction/LVA started CDT 5 days after surgery. Those who received liposuction/VLNT or RRPP/VLNT started CDT 14 days after surgery. Those who received the CHAHOVA approach started CDT 21-24 days after surgery. CDT was initially performed with continuous multilayer bandage compression therapy and sessions of manual lymphatic drainage for the first three months, three times per week.
Circumferential reduction rates were evaluated monthly during these first three months. The continuous multilayer bandage compression therapy was then transitioned into compression garments. The number of weekly sessions of manual lymphatic drainage was progressively reduced over the following three months and completed by six months after surgery.
Outcomes
Circumferential reduction rates (CRR) were recorded one month and two months after surgery. After this time, circumferential reduction rates were evaluated together alongside the Lymphedema Quality of Life Score (LeQOLiS) at 3, 6, 12, and 24 months after surgery. The CRR was defined as the difference in percentage, between the affected limb (AL) circumference and the non-affected limb (NAL) circumference, as determined with the following equation: circumference reduction rate (%) = (1 − [postoperative AL − NAL]/[preoperative AL − NAL]) × 100. Additionally, we recorded and analyzed the number of pre and postoperative episodes of cellulitis, length of stay, complications, and pre and postoperative LeQOLiS.
3. Results
Nineteen patients with primary lower extremity lymphedema were included, three patients with bilateral limb compromise and sixteen with unilateral limb compromise. Eleven patients were male (58%) and 8 female (42%). The mean age of patients at diagnosis was 28.8 ± 11.1 years while the mean BMI was 29.1 ± 5.3 kg/m2. The average symptom duration was 13.41 ± 7.97 years. Five patients had been previously treated with complete decongestive therapy (CDT) with transient good results. According to ISL staging, two patients presented with stage IIA lymphedema, four patients with stage IIB, and the thirteen with stage III. Using ICG lymphography, one limb presented with splash pattern (4.5%), seven with stardust pattern (31.8%), and fourteen with diffuse pattern (63.6%).
A total of 22 limbs were treated. One was treated with LVA (4.5%), one with VLNT (4.5%), eight with liposuction + LVA (36.4%), five with liposuction + VLNT (22.7%), two with RRPP + LVA (9%), two with RRPP + VLNT (9%), and three with the CHAHOVA procedure (13.6%). When performing VLNT, eight patients underwent gastroepiploic VLNT (72.7%) and three patients received supraclavicular VLNT (27.3%).
Hospital length of stay was one day for patients treated with LVA alone or combined with liposuction/RRPP, seven days for patients treated with VLNT alone or combined with liposuction/RRPP, and fourteen days for patients treated with the CHAHOVA approach. Two patients experienced minor complications: hematoma formation in one patient treated with liposuction and LVA, and a chronic ulcer in a patient treated with the CHAHOVA approach. The mean follow-up was 19 months (range: 12-24 months) (
Table 1).
The mean CRR calculated was 65.1% ± 10.2%, 72.8% ± 12.9%, 78.9% ± 14.0%, 78.2% ± 16.8%, 72.8% ± 19.6% at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months post-operatively (
Table 2). Only thirteen limbs were evaluated at 24 months with a mean reduction rate of 73.9% ± 28.8%. The episodes of cellulitis per year decreased from a mean of 1.9 ± 0.8 preoperative to 0.4 ± 0.6 during follow-up (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4).
In terms of CDT, transition of multilayer compression therapy into traditional compression garments was performed at 3.2 months after surgery (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6). All patients were able to resume normal daily activities, but they all maintained the use of compression garments. Patients’ quality of life was evaluated with LeQOLiS preoperatively with a mean score of 70.4 ± 11.6. LeQOLi score improved to 20.4 ± 9.6, 23.5 ± 17.4, 24.2 ± 13.9 at 3, 6 and 12 months postoperatively. Only 12 patients had a longer follow up of 24 months with a LeQOLi score of 25.3 ± 14.4 (
Table 3).
4. Discussion
Primary lymphedema still represents a challenge in lymphatic surgery as its pathophysiology is still poorly understood.[
16] Moreover, few studies focus on primary lymphedema as it is less common than secondary lymphedema.[
17,
18,
19,
20,
21] Treatment of secondary lymphedema, especially in mild cases, can still rely on a partially functional lymphatic system. Hence, the primary goal of the surgical approach is often to restore its function by locating and bypassing the disrupted area. In primary lymphedema, however, the lymphatic system is often dysfunctional at different levels due to abnormal congenital development (i.e., aplasia, hypoplasia, and hyperplasia) and is characterized by the absence of a clear surgically correctable site.[
22,
23] For this reason, primary lymphedema reconstructive approaches present many challenges as the specific characteristics of the condition may influence treatment effectiveness.
The present study evaluated the results of the application of an algorithm of treatment for primary lower limb lymphedema. Nineteen patients were included in the study, with a total of twenty-two limbs treated. The treatment protocol associated pre and postoperative CDT with a combined surgical approach in order to address both the lymphatic drainage and the degeneration of the subcutaneous tissues and skin. Lymphatic drainage was improved by performing physiologic procedures (LVA or VLNT), while fibrotic adipose tissue changes were treated by reducing the burden to the limbs through excisional procedures (liposuction, RRPP, CHAHOVA).
Several authors have contrasting opinions regarding the suitability of certain physiologic procedures, such as LVA, in primary lymphedema patients. According to O’Brien, 80% of patients affected by primary lymphedema present with aplastic or hypoplastic distal superficial lymphatics. This would represent a contraindication to LVA and would limit its use to primary lymphedema patients who have only proximal obliteration of lymphatic channels, which are only 10% of the total according to their experience.[
24]
On the other hand, other authors advocate that suitable lymphatics for LVA can be found in 84% of primary lymphedema patients.[
18] In our experience, the wide range of different clinical conditions that can be found in patients affected by primary lymphedema strongly alters the surgical outcomes. Therefore, a complete algorithm which comprises multiple diagnostic and treatment levels is necessary to address these patients.
It is important to highlight the significance of CDT as the primary and long-lasting treatment for these patients. CDT aims to increase fluid transfer through residual functioning lymphatics, thereby reducing limb volumes and preventing disease progression caused by chronic inflammation, recurrent skin infections, and fibrosis of the subcutaneous tissues. CDT is composed of two phases: the intensive phase, aimed to reach the goals of the treatment (improve the lymphatic drainage), and the maintenance phase, aimed to help preserve the current lymphodynamic properties of postoperative results.[
13,
25,
26,
27] In our study, all patients underwent CDT for six months before surgery. While CDT did not prevent surgery in our patients, it is an integral part of treatment as it helps improve the patients’ preoperative condition and prevents disease progression.
According to recent trends in lymphedema surgery, procedures performed in these patients can be divided into physiologic and excisional - with the general concept that physiologic surgery allows us to achieve better results in milder cases and earlier stages of the disease, whereas excisional procedures are more beneficial in complex and severe cases.[
28,
29] In our practice, we often combine a physiologic procedure to an excisional procedure in the same patient.[
30] The concept behind this approach is that primary lymphedema patients are characterized by a long-lasting condition of a progressive dysfunctional lymphatic system that inevitably evolves into a chronic disorder. Therefore, in these patients we enhance results by addressing both aspects of the disease.
Physiologic procedures are aimed at improving the system’s capability of draining the lymphatic fluid, whereas the excisional procedures allow the removal of the excess adipose and/or fibrotic tissue already formed and tissue that will not respond to physiologic treatment alone. Only in two patients with early-stage lymphedema (Stage IIA) a single physiologic procedure was performed as an excess of fat or fibrotic tissue was not identified upon clinical evaluation. The P-LYMA algorithm also aims at directing surgeons’ choice regarding the appropriate procedure to perform in each patient. However, part of the decision-making is based on the experience of the surgeon.
Currently, the most commonly performed physiologic procedures are LVA and VLNT. According to literature, preoperative evaluation of primary lymphedema patients with lymphoscintigraphy or ICG lymphography is essential to determine which procedure would be more beneficial.[
31,
32] Hara et al. (2015) conducted a study in which they found that preoperative ICG lymphography revealing a stardust or diffuse dermal backflow pattern in the distal aspect of the lower limb is indicative of hypoplasia in the lymphatic vessels. Based on these findings, it is suggested that in such cases, VLNT may be a more favorable treatment option compared to LVA.[
17] Other studies have shown similar results in secondary lymphedema patients.[
33] The P-LYMA algorithm follows this approach. Furthermore, we selected the physiologic treatment according to ICG lymphography. Patients with wide areas of dermal backflow and no suitable lymphatics were addressed with VLNT.
VLNT is a very common procedure for lymphedema patients with many studies reporting satisfying results in secondary lymphedema patients.[
8,
34,
35,
36] Becker et al. evaluated the effectiveness of VLNT in patients affected by primary lymphedema and reported that all cases with distal limb lymphedema experienced a reduction in the circumferences of the limbs while in 46% of patients the limb circumference was normalized.[
20] Bolletta et al. also published an article on the adequate results of the combined approach of gastroepiploic VLNT and liposuction in patients affected by Milroy disease, a particular form of primary lymphedema.[
37]
The use of suction-assisted lipectomy in lymphedema patients has been evaluated in many studies and found to be effective in reducing the excess adipose tissue in the subcutaneous layer caused by adipogenesis and chronic inflammation.[
38,
39] This procedure, however, may not be very effective in advanced stages of disease with skin redundancy, fibrosis of the subcutaneous tissue, and recurrent infections. A more radical approach is required in these cases. One such approach is RRPP. The combination of this excisional procedure with VLNT has previously been evaluated by our senior author.[
11] Advantages of RRPP when compared to liposuction include the removal of the hardened fibrotic tissue and safe redundant skin reduction by preservation of perforators that allow us to maintain sufficient blood supply to the skin. On the other hand, chronic lymphedema can alter not only the subcutaneous tissue, that becomes fibrotic, but also the overlying skin and the underlying deep fascia.[
40] The difficulties that arise in keeping clean the thick, papillomatous skin together with bacterial colonization, and local immune system compromise associated with the disease require a treatment that addresses not only limb size but also the frequent infections.[
41,
42]
The CHAHOVA approach combines multiple procedures such as the Charles’ procedure, Homans’ procedure, and VLNT.[
12] This procedure is highly invasive with frequently voiced concerns related to the aesthetic outcome. While the appearance of the limb is significantly altered by the procedure, accurate postoperative care can improve the aesthetic results by reducing the rates of skin grafts loss, functional joint contracture, and hypertrophic scarring. Moreover, in most of these patients, as the preoperative condition drastically reduces the function of the limb, size improvement and improved contour of the extremity are perceived as being much more important than limb aesthetics. This was confirmed in the current stud, as those treated with the CHAHOVA approach reported a significant improvement in quality of life seen by the data collected with the LeQOLiS. This observation was also related to the significant reduction in the number of episodes of cellulitis which were frequent in these patients before surgery. We achieved this by treating the toes which represented the major source of infection as well as improving lymphatic function by transferring the lymph node flap at the distal aspect of the limb.
According to our protocol, patients are encouraged to start CDT as soon as they are diagnosed and to continue this treatment in the postoperative period. Since primary lymphedema patients are characterized by a genetically determined deficient lymphatic system, we strongly believe that the results of surgical treatment can be enhanced when combined with CDT. All our patients were evaluated throughout the follow-up and we observed that the circumference reduction rates kept improving over time. We believe this is the result of the cumulative effect of the partial lymphatic restoration and the application of decongestive therapy. In our experience, even though patients experienced improvement as seen by the CRR and it was possible to progressively reduce the use of compression garments, we suggest that patients do not discontinue its use to maintain their results. In primary lymphedema the lymphatic system is affected by developmental disorders resulting in the inability of surgical procedures to completely restore the system. For this reason, the use of compression garments remains a useful tool to preserve results over time.
While a limitation of this study is the small number of patients treated, it is important to remember that primary lymphedema is less common than secondary lymphedema. Moreover, some of the patients, especially in the very early stages, are responsive to conservative treatment and are not, at least initially, addressed with surgery. To our knowledge this is the first study that presents a complete algorithm that combines different approaches and techniques for primary lower extremity lymphedema patients.
Figure 1.
Assessment and Treatment Algorithm. Primary-Lymphedema Multidisciplinary Approach (P-LYMA) for patients with lower extremity lymphedema. CDT: Complete Decongestive Therapy, ISL: International Society of Lymphology.
Figure 1.
Assessment and Treatment Algorithm. Primary-Lymphedema Multidisciplinary Approach (P-LYMA) for patients with lower extremity lymphedema. CDT: Complete Decongestive Therapy, ISL: International Society of Lymphology.
Figure 2.
P-LYMA Surgical Algorithm for Primary Lymphedema. LVA: Lymphaticovenous anastomosis, VLNT vascularized lymph node transfer, RRRP: radical reduction with preservation of perforators, CHAHOVA Charles’, Homans’ and vascularized lymph node transfer procedures.
Figure 2.
P-LYMA Surgical Algorithm for Primary Lymphedema. LVA: Lymphaticovenous anastomosis, VLNT vascularized lymph node transfer, RRRP: radical reduction with preservation of perforators, CHAHOVA Charles’, Homans’ and vascularized lymph node transfer procedures.
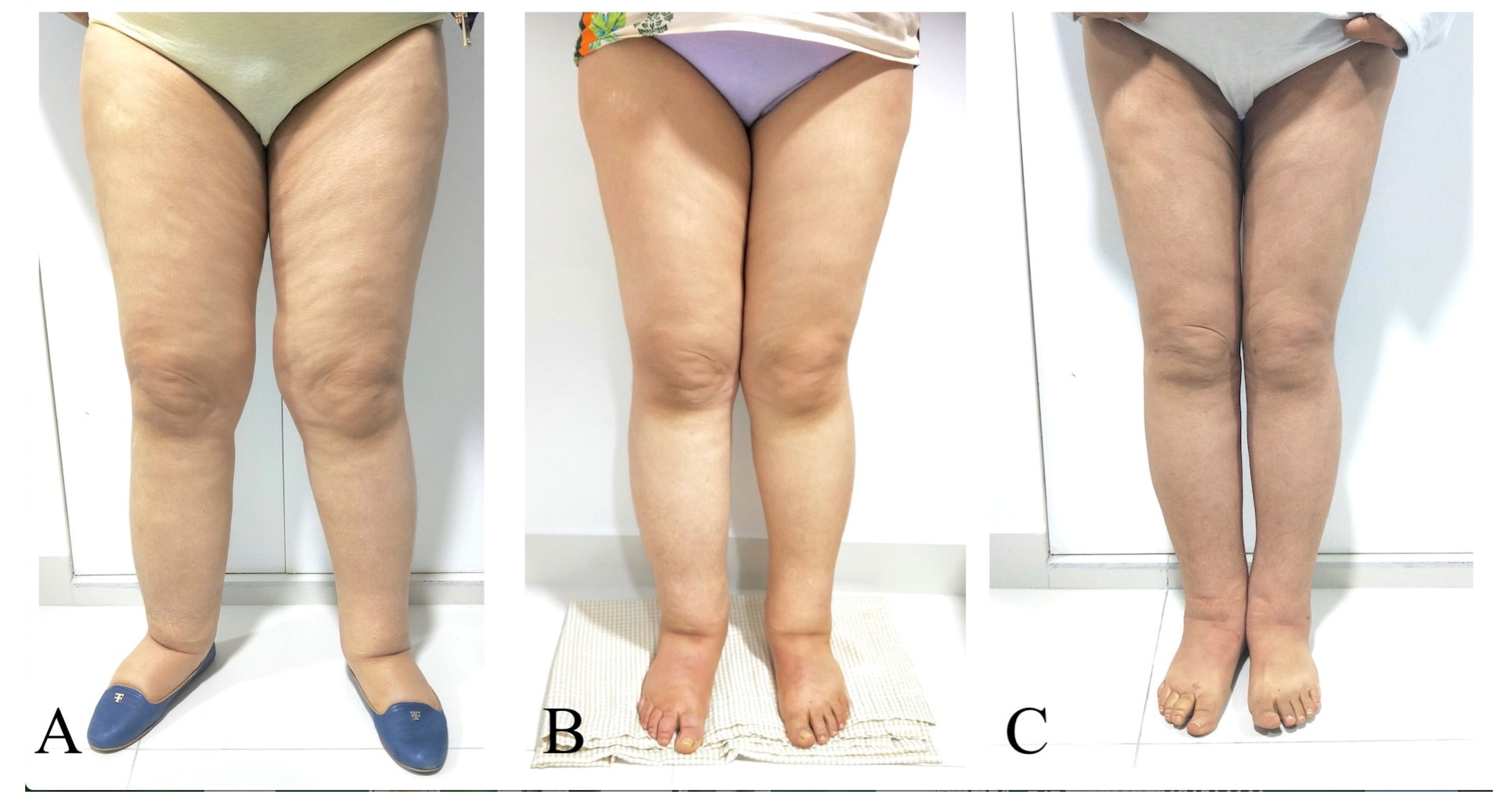
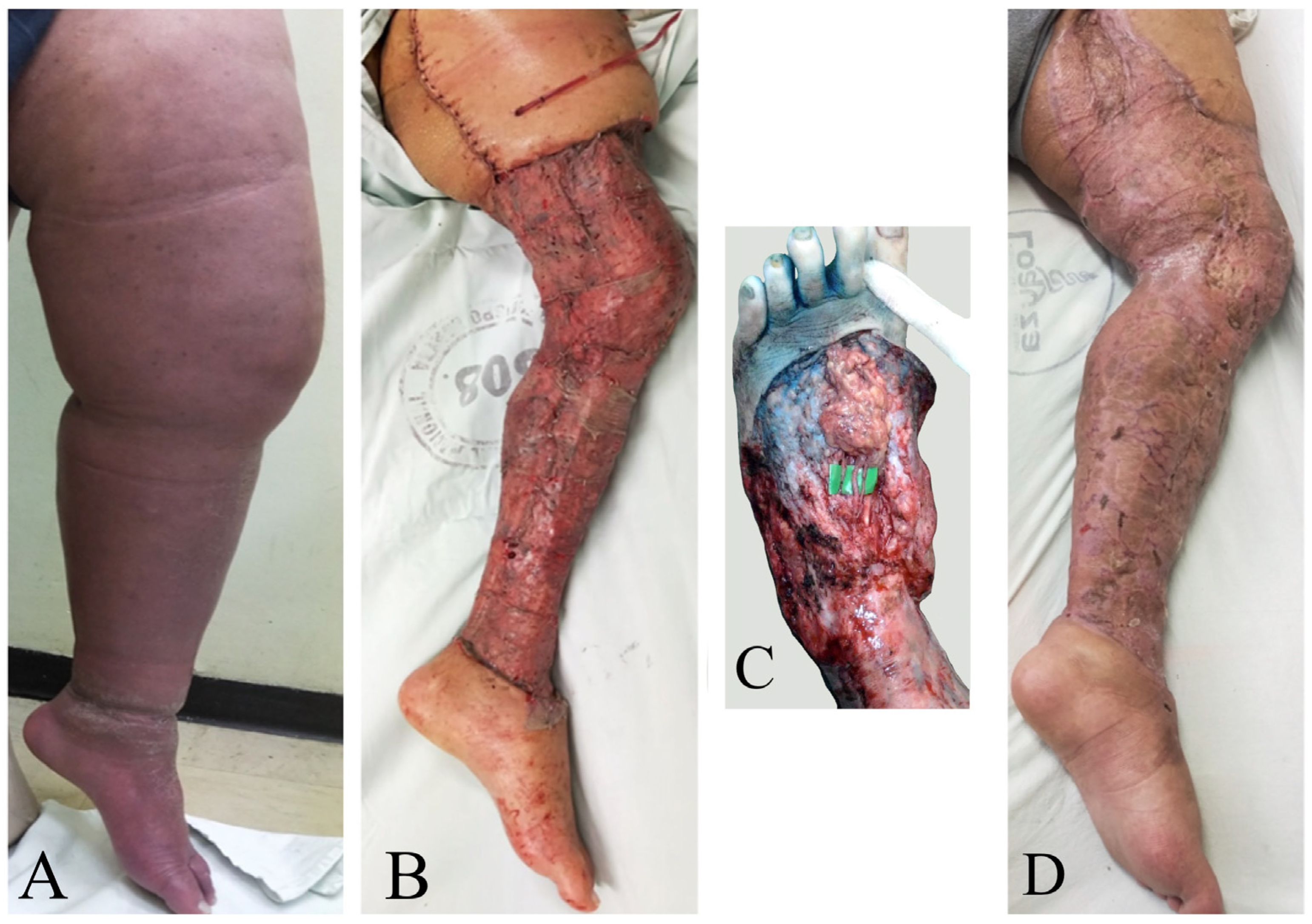
Figure 3.
A 45-year-old woman with primary bilateral lower extremity lymphedema who underwent VASER-assisted liposuction and distal LVA according to P-LYMA algorithm. (A) Preoperative picture. (B) Preoperative picture at 6 months post complete decongestive therapy (CDT) showing improvement in the lymphatic drainage. (C) Postoperative picture at 24 months of follow-up showing drastically significant improvement and decrease in the size of the affected limb. During the period of follow-up, the patient completed 6 months of CDT, after which it was discontinued and replaced by single compression garment. At two-years of follow-up post P-LYMA treatment, the reduction rate of the limb circumference was 85, 77, 84, and 74% above the knee, below the knee, above the ankle, and at the foot level, respectively.
Figure 3.
A 45-year-old woman with primary bilateral lower extremity lymphedema who underwent VASER-assisted liposuction and distal LVA according to P-LYMA algorithm. (A) Preoperative picture. (B) Preoperative picture at 6 months post complete decongestive therapy (CDT) showing improvement in the lymphatic drainage. (C) Postoperative picture at 24 months of follow-up showing drastically significant improvement and decrease in the size of the affected limb. During the period of follow-up, the patient completed 6 months of CDT, after which it was discontinued and replaced by single compression garment. At two-years of follow-up post P-LYMA treatment, the reduction rate of the limb circumference was 85, 77, 84, and 74% above the knee, below the knee, above the ankle, and at the foot level, respectively.
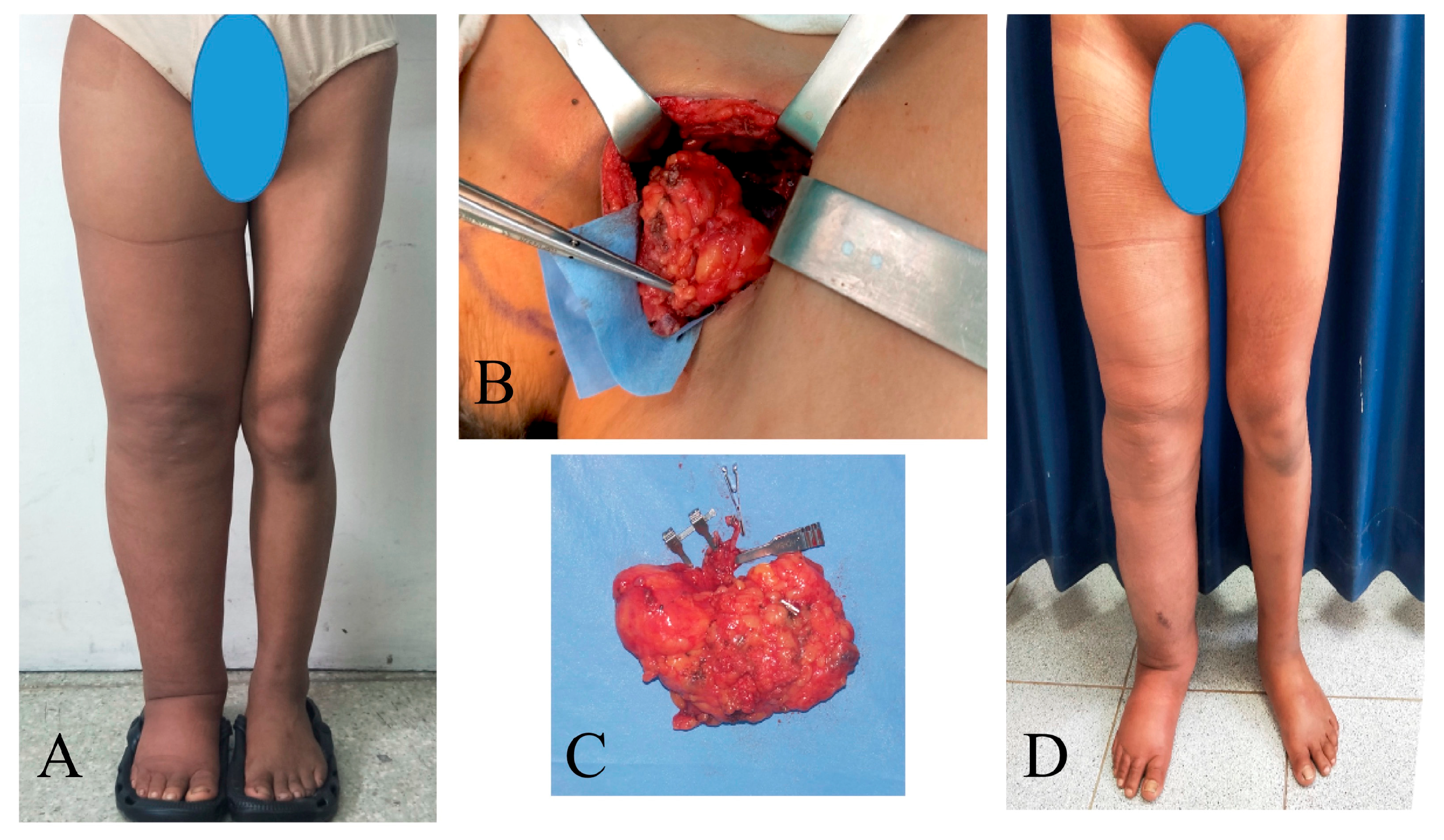
Figure 4.
A 23-year-old woman with primary right lower extremity lymphedema who underwent simultaneous VASER-assisted liposuction and distal LVA. (A) Preoperative picture. (B) Postoperative picture at 7 days post-op. (C) Postoperative picture at 24 months of follow-up. (D) The patient completed 6 months of complete decongestive therapy, then started to wear compression garments.
Figure 4.
A 23-year-old woman with primary right lower extremity lymphedema who underwent simultaneous VASER-assisted liposuction and distal LVA. (A) Preoperative picture. (B) Postoperative picture at 7 days post-op. (C) Postoperative picture at 24 months of follow-up. (D) The patient completed 6 months of complete decongestive therapy, then started to wear compression garments.
Figure 5.
Example of a multilayered garments used preoperatively and for the first 4 months postoperatively.
Figure 5.
Example of a multilayered garments used preoperatively and for the first 4 months postoperatively.
Figure 6.
Picture shows patient with left lower extremity lymphedema using multilayer garment. This was used in all patients as part of the P-LYMA protocol during the preoperative period and 3 to 4 months postoperative.
Figure 6.
Picture shows patient with left lower extremity lymphedema using multilayer garment. This was used in all patients as part of the P-LYMA protocol during the preoperative period and 3 to 4 months postoperative.
Table 1.
Primary lymphedema patients treated with P-LIMA algorithm: preoperative data and procedures.
Table 1.
Primary lymphedema patients treated with P-LIMA algorithm: preoperative data and procedures.
| Patient |
Age |
Gender |
BMI |
Affected Lower Limb |
ISL stage |
ICG pattern |
Duration of symptoms (years) |
Previous CDT |
LeQOLiS |
Physiologic procedure |
Excisional procedure |
| 1 |
29 |
F |
27.5 |
Left |
III |
Diffuse |
13 |
No |
70 |
VLNT (SC) |
SAL |
| 2 |
45 |
F |
29.4 |
Left |
III |
Diffuse |
20 |
Irregular |
86 |
LVA |
SAL |
| Right |
III |
Diffuse |
20 |
Irregular |
LVA |
SAL |
| 3 |
16 |
M |
22.4 |
Right |
III |
Diffuse |
2 |
No |
76 |
LVA |
SAL |
| 4 |
35 |
F |
30.0 |
Right |
III |
Stardust |
28 |
No |
82 |
VLNT (SC) |
SAL |
| 5 |
23 |
M |
22.8 |
Right |
II-B |
Stardust |
8 |
Irregular |
85 |
LVA |
SAL |
| 6 |
16 |
M |
24.5 |
Left |
III |
Diffuse |
14 |
No |
66 |
VLNT (GE) |
RRPP |
| 7 |
33 |
F |
31.0 |
Left |
III |
Diffuse |
30 |
Irregular |
64 |
LVA |
RRPP |
| 8 |
15 |
M |
19.2 |
Left |
II-B |
Stardust |
2 |
No |
66 |
VLNT (GE) |
- |
| 9 |
21 |
M |
32.0 |
Left |
III |
Diffuse |
15 |
No |
56 |
VLNT (SC) |
SAL |
| 10 |
15 |
M |
18.8 |
Right |
II-A |
Stardust |
3 |
No |
76 |
LVA |
SAL |
| 11 |
19 |
F |
28.4 |
Left |
III |
Diffuse |
16 |
Irregular |
56 |
VLNT (GE) |
SAL |
| Right |
III |
Diffuse |
15 |
Irregular |
VLNT (GE) |
SAL |
| 12 |
45 |
M |
35.2 |
Left |
III |
Diffuse |
25 |
Irregular |
52 |
VLNT (GE) |
RRPP |
| 13 |
42 |
M |
32.4 |
Right |
III |
Diffuse |
8 |
No |
65 |
LVA |
RRPP |
| 14 |
36 |
M |
34.4 |
Right |
III |
Diffuse |
15 |
No |
88 |
VLNT (GE) |
CHAHOVA |
| 15 |
39 |
F |
30.4 |
Left |
III |
Diffuse |
10 |
No |
90 |
VLNT (GE) |
CHAHOVA |
| Right |
III |
Stardust |
11 |
No |
|
VLNT (GE) |
CHAHOVA |
| 16 |
42 |
M |
30.2 |
Left |
III |
Stardust |
12 |
No |
66 |
LVA |
SAL |
| 17 |
23 |
F |
24.8 |
Right |
II-B |
Stardust |
5 |
No |
68 |
LVA |
SAL |
| 18 |
37 |
F |
32.4 |
Left |
II-A |
Splash |
18 |
No |
57 |
LVA |
- |
| 19 |
17 |
M |
18.6 |
Left |
II-B |
Diffuse |
5 |
No |
68 |
LVA |
SAL |
| Average |
28.8 |
|
29.0 |
|
|
|
13.4 |
|
70,4 |
|
|
| SD |
11.1 |
|
5.1 |
|
|
|
7.9 |
|
11,6 |
|
|
Table 2.
Data collected prior to surgical treatment and at 12 months and 24 months after P-LYMA treatment.
Table 2.
Data collected prior to surgical treatment and at 12 months and 24 months after P-LYMA treatment.
| Variable |
Pre-operative |
Post-operative
12 months |
Post-operative
24 months |
| Circumferential reduction rate (%) |
|
72.8 ± 19.6 |
73.9 ± 28.8 |
| Lymphedema Quality of Life Score |
70.4 ± 11.6 |
24.2 ± 13.9 |
25.3 ± 14.4 |
| Infection occurrence rate |
1.9 ± 0.8 |
|
0.4 ± 0.6 |
Table 3.
Lymphedema Quality of Life Score collected prior to surgical treatment and at 3, 6, 12 and 24 months after P-LYMA treatment. (Quality of Life, QOL).
Table 3.
Lymphedema Quality of Life Score collected prior to surgical treatment and at 3, 6, 12 and 24 months after P-LYMA treatment. (Quality of Life, QOL).
| Patient |
Lymphedema QoL Score
Pre-operative |
Lymphedema QoL Score
Post-op 3 months |
Lymphedema QoL Score Post-op 6 months |
Lymphedema QoL Score
Post-op 12 months |
Lymphedema QoL Score Post-op 24 months |
| 1 |
70 |
35 |
30 |
40 |
32 |
| 2 |
86 |
20 |
22 |
20 |
20 |
| 3 |
76 |
44 |
55 |
66 |
66 |
| 4 |
82 |
25 |
78 |
|
|
| 5 |
85 |
15 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
| 6 |
66 |
20 |
22 |
25 |
22 |
| 7 |
64 |
18 |
10 |
18 |
|
| 8 |
66 |
29 |
30 |
33 |
|
| 9 |
56 |
10 |
15 |
18 |
22 |
| 10 |
76 |
6 |
6 |
8 |
|
| 11 |
56 |
10 |
12 |
14 |
|
| 12 |
52 |
20 |
25 |
27 |
|
| 13 |
65 |
14 |
12 |
12 |
16 |
| 14 |
88 |
18 |
22 |
24 |
24 |
| 15 |
90 |
18 |
18 |
20 |
22 |
| 16 |
66 |
22 |
18 |
20 |
16 |
| 17 |
68 |
14 |
12 |
20 |
24 |
| 18 |
57 |
15 |
18 |
22 |
32 |
| 19 |
68 |
35 |
34 |
40 |
|
| Average |
70,4 ± 11,6 |
20,4 ± 9,6 |
23,5 ±17,4 |
24,2 ± 13,9 |
25,3 ± 14,4 |