Submitted:
29 June 2023
Posted:
30 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Reducing the dimensionality of the space of model input variables by optimization with Feature Selection techniques (RReliefF and Backward selection via the recursive feature elimination algorithms) and the Pareto 80/20 rule;
- Training and testing of ML models: NN, SVM and k-NN with the selection of the best delay prediction model in the LTE network using accuracy and complexity/interpretability criteria;
- Presentation of the aforementioned approaches to optimizing the number of predictors for LTE KPI predictive modeling, which is, according to the authors' knowledge and according to the review of former research papers, a particularly innovative solution given in this paper;
- Implementation of a unique methodology of indirect assessment and calculation of the value of the dependent variable based on the average number of active users in the network;
- Creation of universally applicable predictive modeling of delays in the LTE network based on real research, and a data space connected to one of the most important roads in the geo-road network of RS, BiH, was chosen for the case study.
2. Review of Relevant Published Research
- Network delay is investigated by observing a real geospatial and LTE network segment as very important factors affecting KPIs;
- The number of predictors in LTE delay examination is optimized for the first time simultaneously using three approaches for predictive modeling of delays in the LTE network;
- A complete set of 17 independent/input research variables is used and Dimensionality Reduction is explained in detail;
- The original indirect method of assessment and calculation of the values of the dependent/output variable is applied;
- The optimization of the set of input variables is modeled with Feature Selection techniques and the Pareto 80/20 rule, and the obtained results are compared according to the criteria of prediction accuracy and complexity/interpretability of the model.
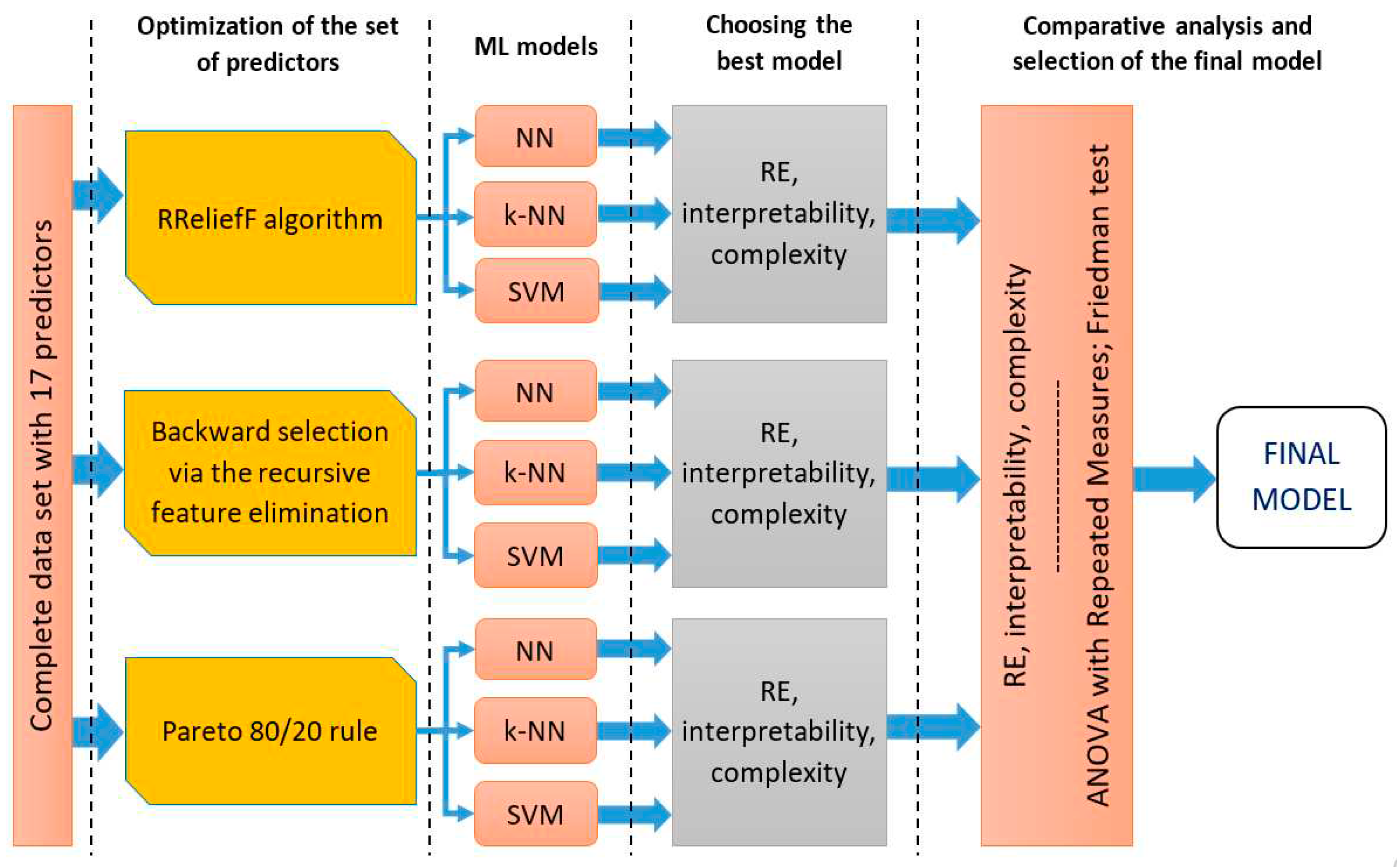
3. Materials and Methods
- Analysis of a real geospatial and network research segment in the case study;
- Data collection and analysis of independent research variables;
- Calculation of dependent variable values;
- Structuring data into input/output vectors;
- Optimization of a set of independent variables by Feature Selection techniques: RReliefF and Backward selection via the recursive feature elimination algorithms;
- Optimization of a set of independent variables by the Pareto 80/20 rule;
- Training and testing of predictive delay models over an optimized set of independent variables;
- Comparative analysis of prediction results and selection of the final model.
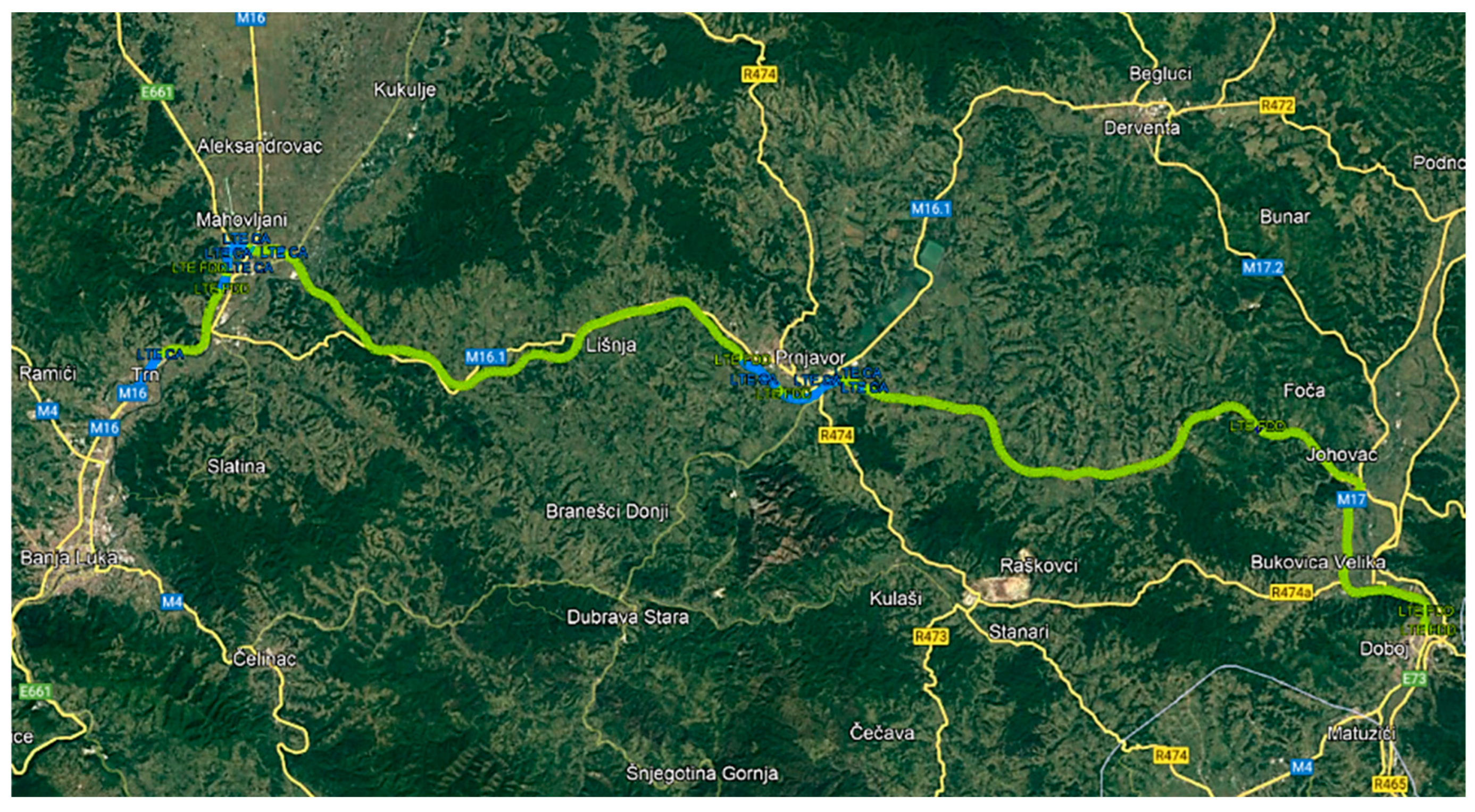
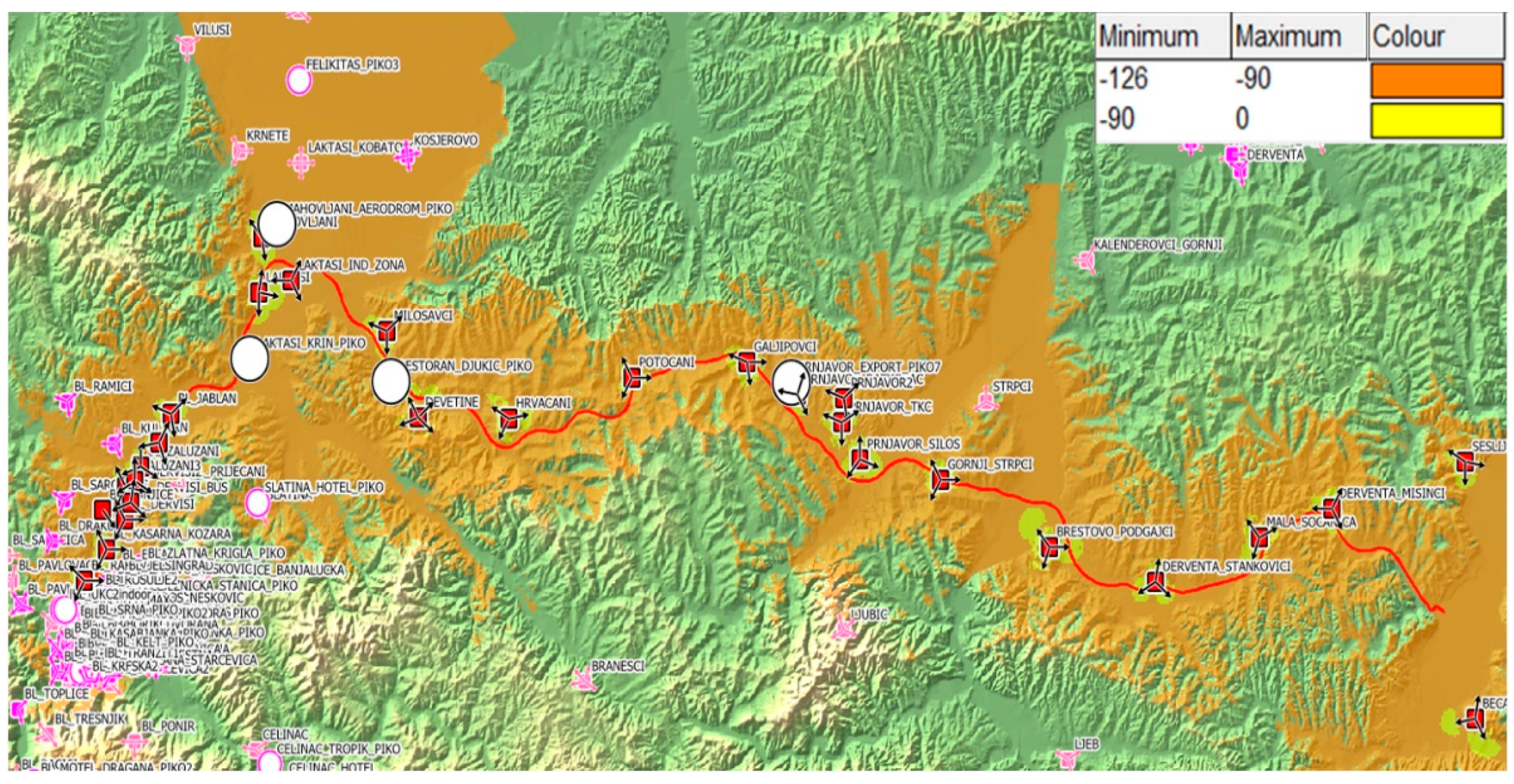
3.1. Geospatial and network research segment – a case study
- A segment of the Motorway 9th January (M9J), 72 km long, between the Jakupovci toll station, near the city of BL, and the Kladari toll station, near the town of Db;
- A segment of the M16 Main Road, about 6 km long, on the route Jakupovci – entrance to the city of BL;
- A segment of the M17 trunk road, about 10 km long, located between the Kladari toll station and the town of Db.
3.2. Analysis of independent research variables and data collection
- 15) DL.QPSK.TB.Retrans - Number of retransmitted TBs in DL SCH at Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) modulation;
- 16) DL.16QAM.TB.Retrans - Number of retransmitted TBs in DL SCH at Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) with 16 carrier states (16QAM);
- 17) DL.64QAM.TB.Retrans - Number of retransmitted TBs in DL SCH at QAM with 64 carrier states (64QAM).
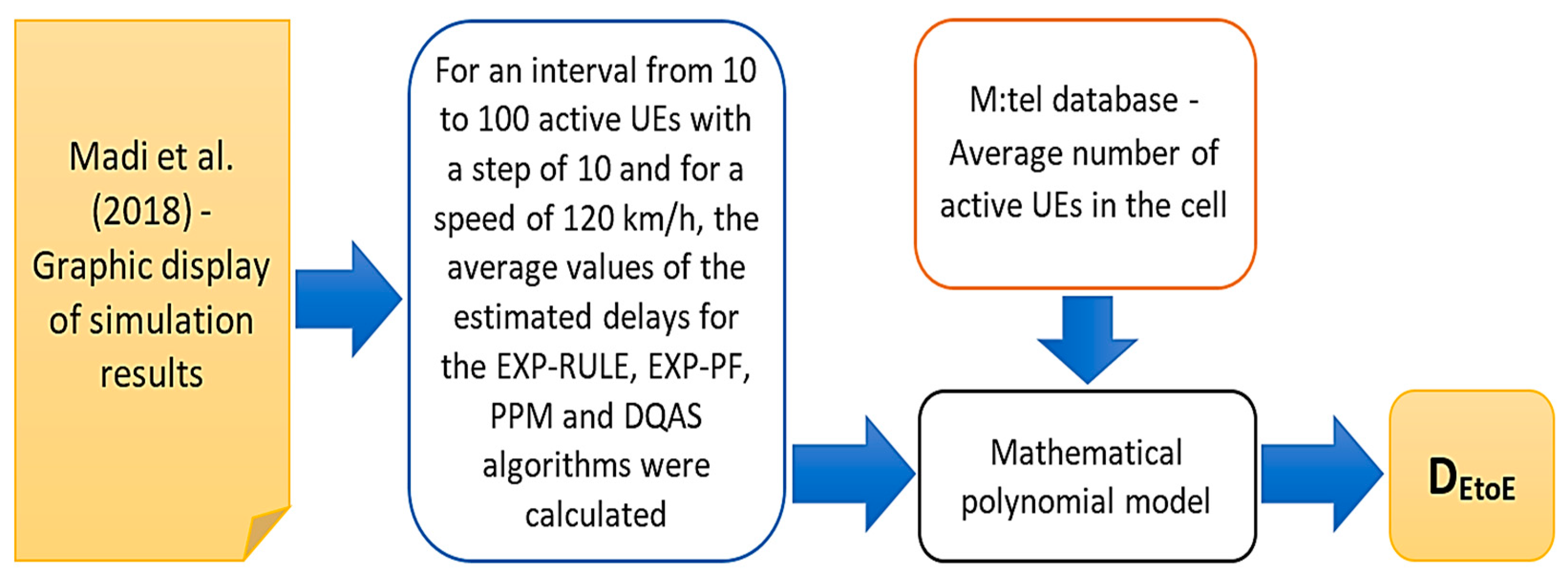
3.3. Calculation of dependent variable values
3.4. Structuring data into input/output vectors
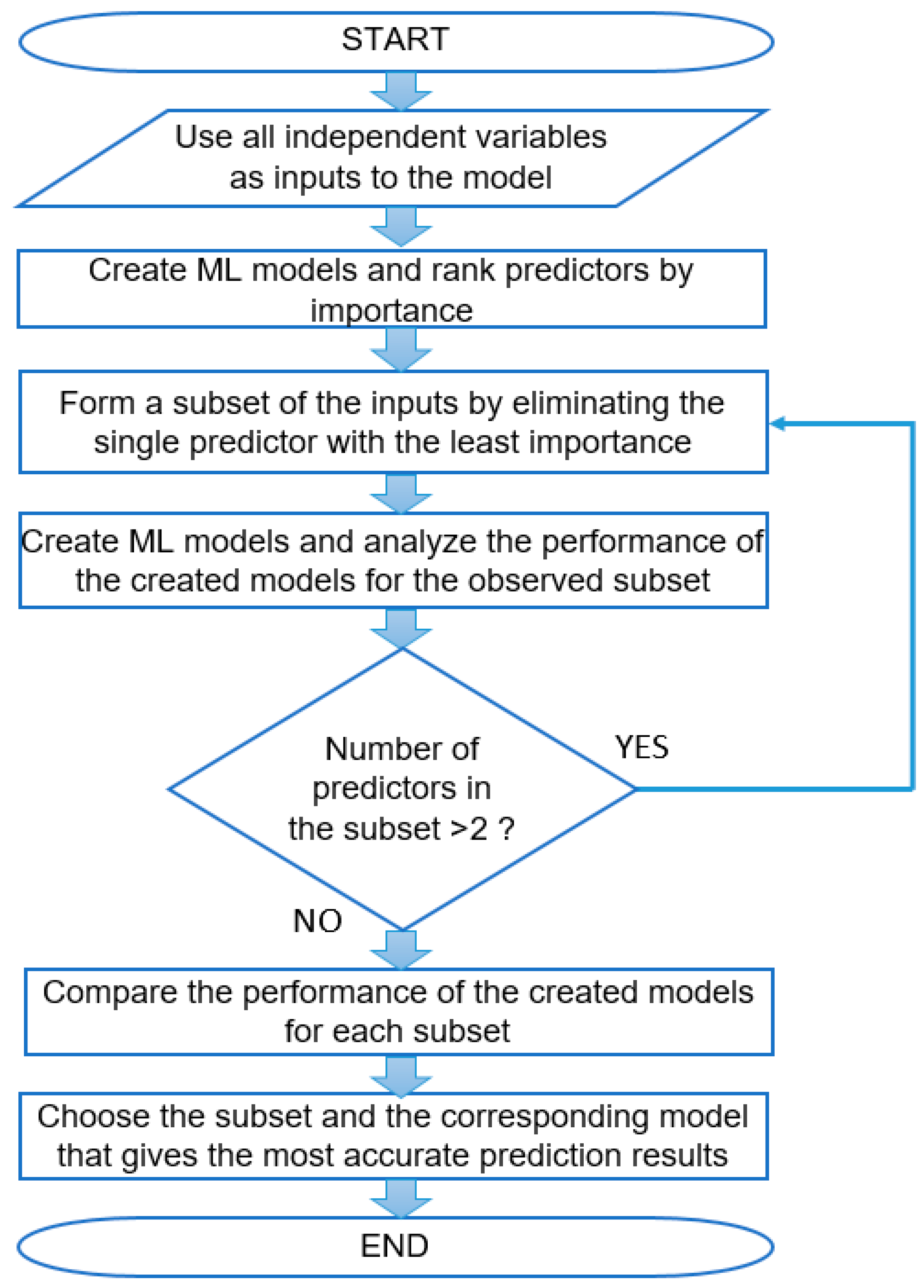
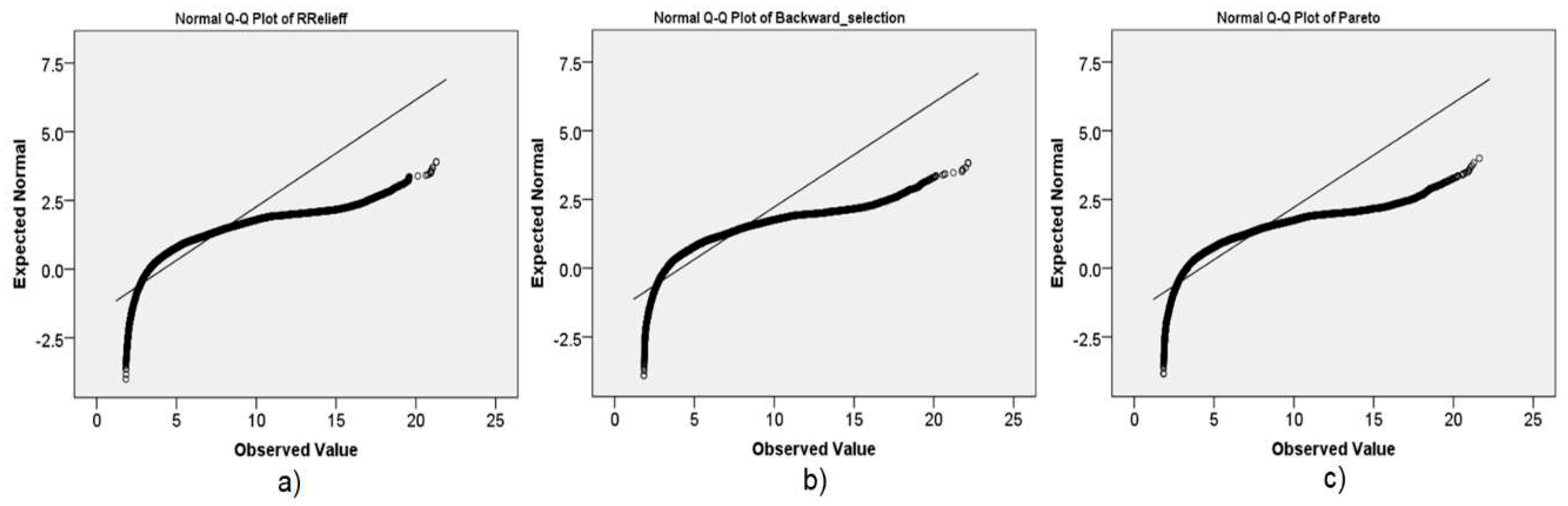
3.5. Optimization of a set of independent variables by Feature Selection techniques
- Filter technique - It is based on measuring the importance of variables based on features such as variance and relevance to the output variable. Predictors are selected according to the desired level of importance or relevance, after which an ML model is created using the selected set of inputs [26].
- Wrapper technique – Model training is performed using a selected subset or the entire set of independent variables, and then individual predictors are added or removed based on a certain criterion that measures the change in model performance. Model training and testing are repeated until predefined stopping criteria are met [26].
- Embedded technique – Assessing the importance of the predictor is in this case an integral part of a model training process.
3.5.1. RRelieff algorithm
- Wj is the weighting coefficient of the predictor Fj;
- Wdy is the weighting coefficient for different values of the dependent variable y;
- Wdj is the weighting coefficient for different predictor values Fj;
- Wdy∧dj is the weighting coefficient for different values of y and different values of the predictor Fj [31].
3.5.2. Backward selection via the recursive feature elimination algorithm
- -
- DEtoEi is a calculated end-to-end delay value for the i-th input/output vector,
- -
- DPREDi is a prediction value of DEtoEi, and
- -
- DAVGi is the arithmetic mean of the variable DEtoEi.
3.6. Optimization of a set of independent variables by the Pareto 80/20 rule
3.7. Creating predictive models using the ML method of automatic modeling
3.8. Comparative analysis of prediction results and selection of the final model
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Predictive ML models created over a set of predictors optimized by the RReliefF algorithm
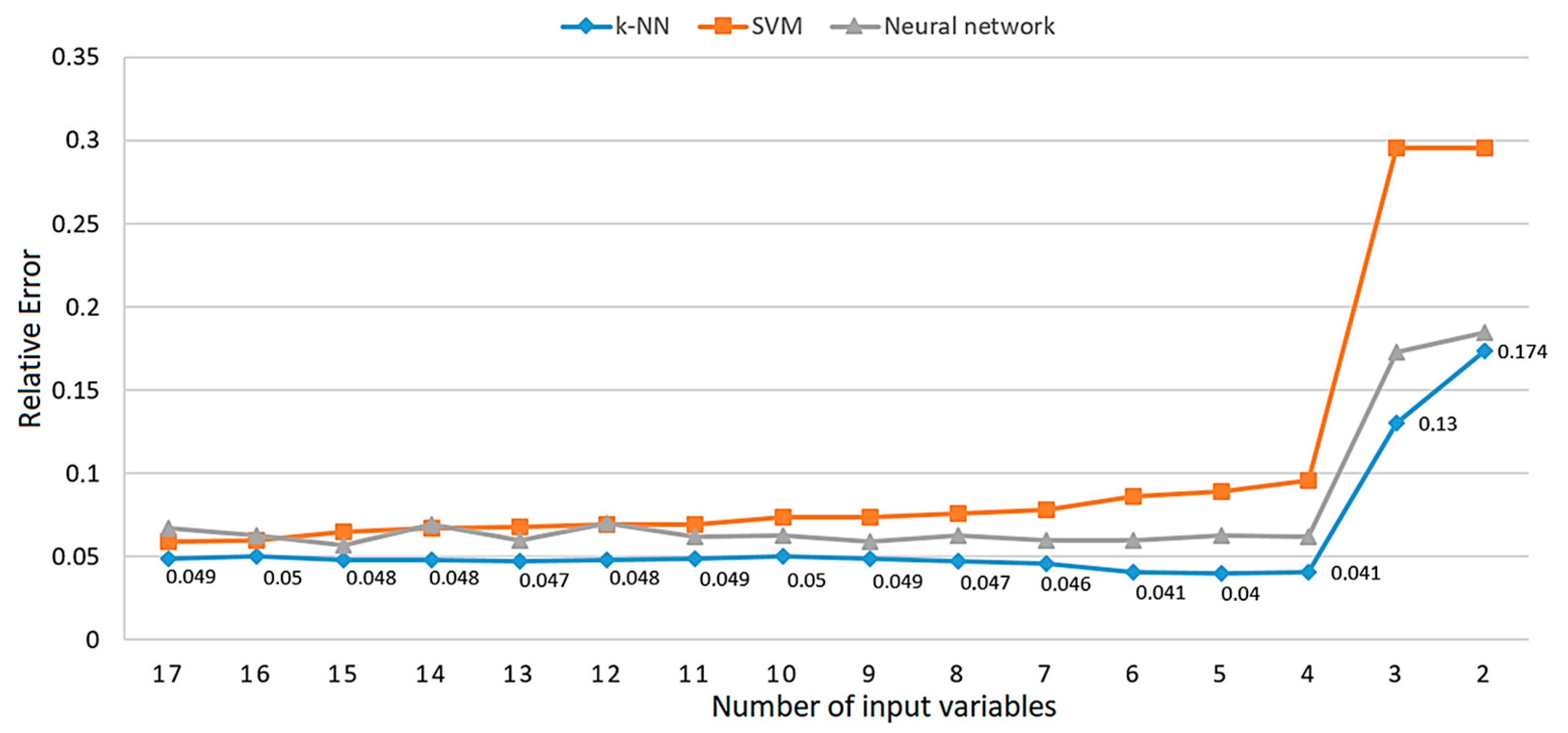
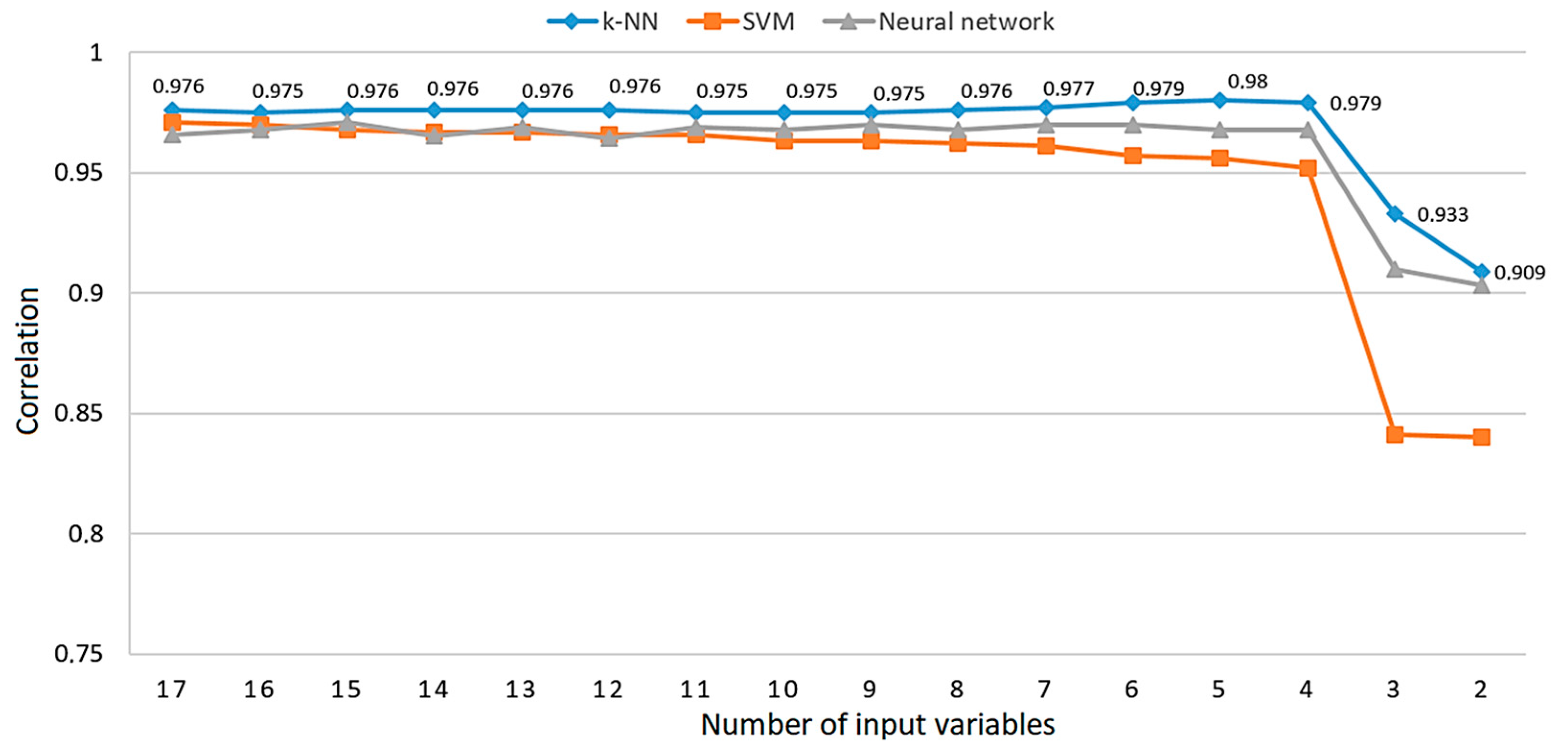
4.2. ML predictive models created over a set of predictors optimized by the Backward selection via the recursive feature elimination algorithm
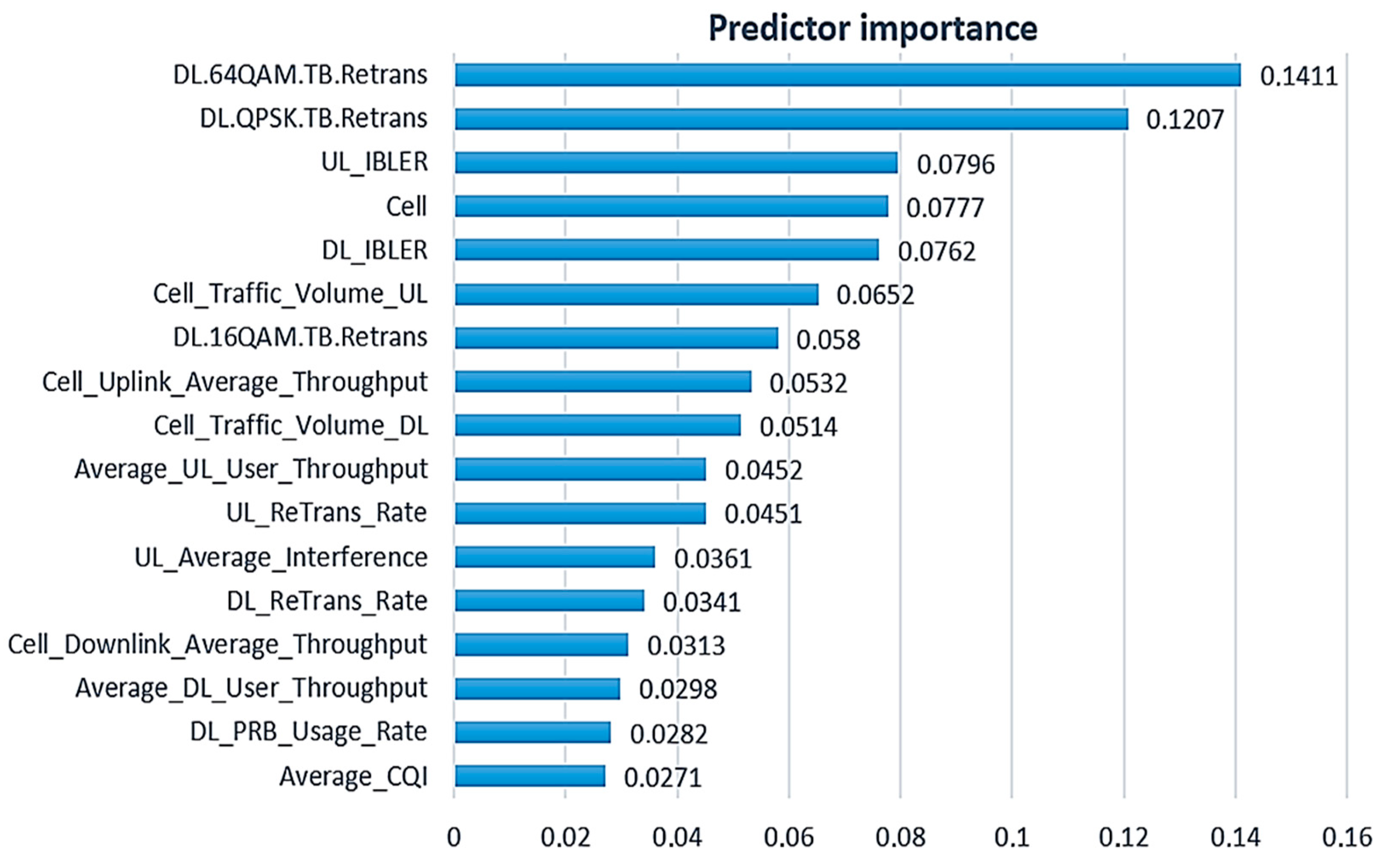
4.3. Predictive ML models created over a set of predictors optimized by the Pareto 80/20 rule
4.4. Comparative analysis of results using statistical methods and selection of the final model
-
H0: µ1 = µ2 = µ3, where µ1, µ2 and µ3 are the arithmetic means of delay prediction values for k-NN models selected as the best solutions in the approach based on the RRelieff algorithm, Backward selection via the recursive feature elimination algorithm, and the Pareto 80/20 rule, respectively. In other words, this hypothesis represents the assumption that there are no significant statistical differences in the arithmetic means of the delay prediction results for the three observed models.In contrast, the alternative hypothesis can be stated as follows:
- H1: There are significant statistical differences in the prediction results between at least two models, i.e. two optimization approaches.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banjanin, M.K.; Maričić, G.; Stojčić, M. Multifactor Influences on the Quality of Experience Service Users of Telecommunication Providers in the Republic of Srpska, Bosnia and Herzegovina. International Journal for Quality Research 2022, 17, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjanin, M.K.; Stojčić, M.; Danilović, D.; Ćurguz, Z.; Vasiljević, M.; Puzić, G. Classification and Prediction of Sustainable Quality of Experience of Telecommunication Service Users Using Machine Learning Models. Sustainability 2022, 14, 17053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesbahi, N.; Dahmouni, H. Delay and jitter analysis in LTE networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Communications (WINCOM), Fez, Morocco, 26-29 October 2016; IEEE; pp. 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, J.I.A.Y.; Pang, W.L.; Wong, S.K.; Chan, K.Y. Enhanced exponential rule scheduling algorithm for real-time traffic in LTE network. International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE) 2020, 10, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojčić, M.; Banjanin, M.K.; Vasiljević, M.; Stjepanović, A.; Ćurguz, Z. PCA modeling of extraction and selection of variables influencing LTE network delay in urban mobility conditions. Paper presented at International Conference on Advances in Traffic and Communication Technologies ATCT 2023, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina., 11-12 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- ETSI TS 123 107 v12.0.0; Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE.; Quality of Service (QoS) concept and architecture. European Telecommunications Standards Institute: Sophia Antipolis Cedex, France, 2014. Available online: https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_ts/123100_123199/123107/12.00.00_60/ts_123107v120000p.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- Kumar, V.; Minz, S. Feature selection: A literature review. SmartCR 2014, 4, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Luo, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, S. Feature selection in machine learning: A new perspective. Neurocomputing 2018, 300, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đukić, A.; Bjelošević, R.; Stojčić, M.; Banjanin, M.K. Network Model of Multiagent Communication of Traffic Inspection for Supervision and Control of Passenger Transportation in Road and City Traffic. In Proceedings of the Croatian Society for Information, Communication and Electronic Technology – MIPRO 2023 46th (Hybrid) Convention, Opatija, Croatia, 22-26 May 2023; pp. 1352–1357. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Figueroa, L.; Schepker, H.F.; Jiru, J. QoS evaluation and prediction for C-V2X communication in commercially-deployed LTE and mobile edge networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 91st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Spring), Antwerp, Belgium, 25-28 May 2020; IEEE; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Feng, M.; Krunz, M.; Volos, H. Latency prediction for delay-sensitive v2x applications in mobile cloud/edge computing systems. In Proceedings of the GLOBECOM 2020-2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 7-11 December 2020; IEEE; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Khan, J.Y. A predictive resource allocation algorithm in the LTE uplink for event based M2M applications. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 2015, 14, 2433–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatouni, A.S.; Soro, F.; Giordano, D. A machine learning application for latency prediction in operational 4g networks. In In Proceedings of the 2019 IFIP/IEEE Symposium on Integrated Network and Service Management (IM), Arlington, VA, USA, 8-12 April 2019; IEEE; pp. 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhohov, R.; Minovski, D.; Johansson, P.; Andersson, K. Real-time performance evaluation of LTE for IIoT. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 43rd Conference on Local Computer Networks (LCN), Chicago, IL, USA, 1-4 October 2018; IEEE; pp. 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.K.; Tang, C.L. QoS-aware downlink packet scheduling for LTE networks. Computer Networks 2013, 57, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.K.; Hsu, C.W.; Kuo, T.H.; Lin, M.T. A LTE downlink scheduling mechanism with the prediction of packet delay. In Proceedings of the 2015 Seventh International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks, Sapporo, Japan, 7-10 July 2015; IEEE; pp. 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasri, M.; Hamdi, M. LTE QoS parameters prediction using multivariate linear regression algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd conference on innovation in clouds, internet and networks and workshops (ICIN), Paris, France, 19-21 February 2019; IEEE; pp. 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Hicks, S.; Riegler, M.A.; Elmokashfi, A. Predicting High Delays in Mobile Broadband Networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 168999–169013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjanin, M.K.; Stojčić, M.; Drajić, D.; Ćurguz, Z.; Milanović, Z.; Stjepanović, A. Adaptive Modeling of Prediction of Telecommunications Network Throughput Performances in the Domain of Motorway Coverage. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loshakov, V.A.; Al-Janabi, H.D.; Al-Zayadi, H.K. Adaptive control signal parameters in LTE technology with MIMO. Telecommunications Problems 2012, 2, 78–90, UDC 621.396. http://openarchive.nure.ua/handle/document/430.
- Ren, J.; Zhang, X.; Xin, Y. Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network to Recognize LTE Uplink Interference. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Marrakesh, Morocco, 15-18 April 2019; IEEE; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
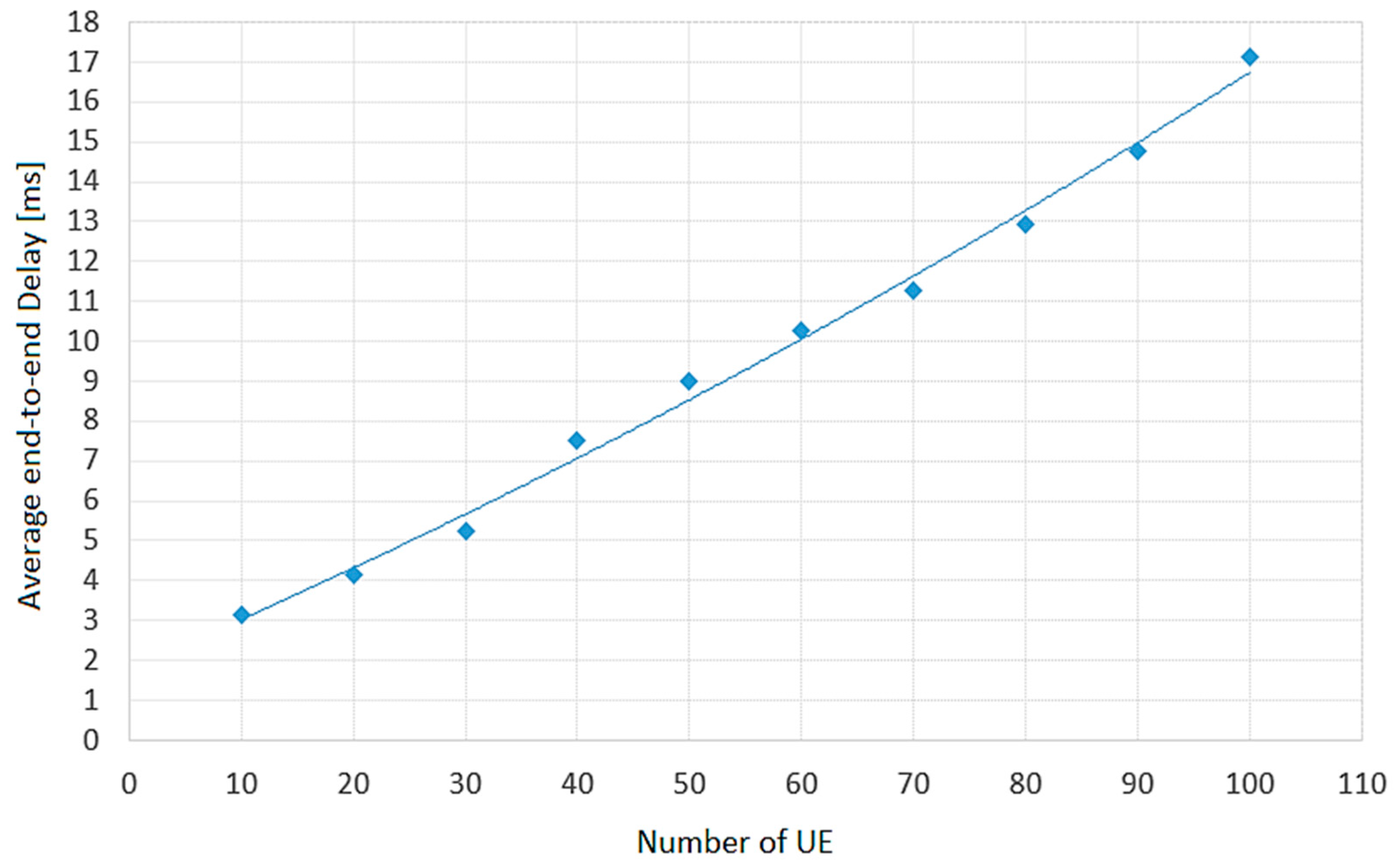
- Madi, N.K.; Hanapi, Z.M.; Othman, M.; Subramaniam, S.K. Delay-based and QoS-aware packet scheduling for RT and NRT multimedia services in LTE downlink systems. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking 2018, 180, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Johnson, K. Feature Engineering and Selection: A Practical Approach for Predictive Models, 1st ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, Florida, 2019; ISBN 978-1-13-807922-9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Cheng, K.; Wang, S.; Morstatter, F.; Trevino, R.P.; Tang, J.; Liu, H. Feature selection: A data perspective. ACM computing surveys (CSUR) 2017, 50, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wah, Y.B.; Ibrahim, N.; Hamid, H.A.; Abdul-Rahman, S.; Fong, S. Feature Selection Methods: Case of Filter and Wrapper Approaches for Maximising Classification Accuracy. Pertanika Journal of Science & Technology 2018, 26, 329–340. [Google Scholar]
- MathWorks. Introduction to Feature Selection. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/stats/feature-selection.html (accessed on 27 March 2023).
- Kira, K.; Rendell, L.A. A practical approach to feature selection. In Proceedings of the Machine learning proceedings, Aberdeen, Scotland, 1-3 July 1992; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kira, K.; Rendell, L.A. The feature selection problem: Traditional methods and a new algorithm. In Proceedings of the tenth national conference on Artificial intelligence - AAAI ’92, San Jose, California, 12-16 July 1992; pp. 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Kononenko, I. Estimating Attributes: Analysis and extensions of RELIEF. In Machine Learning: ECML-94; Bergadano, F., De Raedt, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; Volume 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robnik-Šikonja, M.; Kononenko, I. An adaptation of Relief for attribute estimation in regression. In Proceedings of the Machine learning: Proceedings of the fourteenth international conference (ICML’97), Nashville, Tennessee, USA, 8-12 July 1997; pp. 296–304.
- MathWorks. Relief. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/stats/relieff.html (accessed on 24 April 2023).
- Urbanowicz, R.J.; Meeker, M.; La Cava, W.; Olson, R.S.; Moore, J.H. Relief-based feature selection: Introduction and review. Journal of biomedical informatics 2018, 85, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyon, I.; Weston, J.; Barnhill, S.; Vapnik, V. Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Machine learning 2002, 46, 389–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okorie, O.; Salonitis, K.; Charnley, F.; Turner, C. A systems dynamics enabled real-time efficiency for fuel cell data-driven remanufacturing. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 2018, 2, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugh, J. Engineering Design, Planning, and Management, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States, 2021; ISBN 978-0-12-821055-0. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Sendhoff, B. Pareto-based multiobjective machine learning: An overview and case studies. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews) 2008, 38, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Mazumder, J.; Park, J.; Kim, S. Ranked feature-based laser material processing monitoring and defect diagnosis using k-NN and SVM. Journal of Manufacturing Processes 2020, 55, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Eckert, C.; Teredesai, A. Interpretable machine learning in healthcare. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACM international conference on bioinformatics, computational biology, and health informatics, Washington DC, USA, 29 August-1 September 2018; pp. 559–560. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, T.A.; Zahid, M.S.M.; Ali, W. A review of interpretable ML in healthcare: Taxonomy, applications, challenges, and future directions. Symmetry 2021, 13, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dherin, B.; Munn, M.; Rosca, M.; Barrett, D. Why neural networks find simple solutions: The many regularizers of geometric complexity. In Proceedings of the Thirty-sixth Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems-NeurIPS, New Orleans Convention Center, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; Volume 35, pp. 2333–2349. [Google Scholar]
- Stiglic, G.; Kocbek, P.; Fijacko, N.; Zitnik, M.; Verbert, K.; Cilar, L. Interpretability of machine learning-based prediction models in healthcare. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery 2020, 10, e1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morocho-Cayamcela, M.E.; Lee, H.; Lim, W. Machine learning for 5G/B5G mobile and wireless communications: Potential, limitations, and future directions. IEEE access 2019, 7, 137184–137206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Bang, C.S. Application of artificial intelligence in gastroenterology. World journal of gastroenterology 2019, 25, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, M.; Hartig, F. Machine learning and deep learning—A review for ecologists. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 2023, 14, 994–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhang, Q.; Liao, X.; Chen, Y. An interpretable machine learning framework for modelling human decision behavior. arXiv preprint 2019, arXiv:1906.01233. [Google Scholar]
- Nesvijevskaia, A.; Ouillade, S.; Guilmin, P.; Zucker, J.D. The accuracy versus interpretability trade-off in fraud detection model. Data & Policy 2021, 3, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.Z.I.; Turin, T.C. Variable selection strategies and its importance in clinical prediction modelling. Family medicine and community health 2020, 8, e000262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Ren, Y.; Chen, K.C.; Hanzo, L. Thirty years of machine learning: The road to Pareto-optimal wireless networks. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2020, 22, 1472–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Guindani, M.; Grieco, S.F.; Chen, L.; Holmes, T.C.; Xu, X. Beyond t test and ANOVA: Applications of mixed-effects models for more rigorous statistical analysis in neuroscience research. Neuron 2022, 110, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali, A.; Valipour, A. Identification and selection of building façade's smart materials according to sustainable development goals. Sustainable Materials and Technologies 2020, 26, e00213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ref. No. | Models and techniques | Regression/ Classification |
Service/ Application |
Dimensionality reduction methods and techniques |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10] | NN, Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) with Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neurons, Random Forest (RF), SVM |
Classification | C-V2X | Maximum Dependency (MD) algorithm |
| [11] | LSTM; k-medoids classification, Epanechnikov Kerne, Moving average functions |
Regression and Classification |
Delay-sensitive V2X Applications in Mobile Cloud/Edge Computing Systems |
- |
| [12] | Mathematical models | Regression | M2M uplink communication | - |
| [13] | Logistic Regression (LR), SVM, Decision Tree (DT) | Classification | Operational 4G Networks Services | Random Forest |
| [14] | Artificial Neural Networks, Decision Tree, Ensemble modeling: Bagging technique with a Decision Tree | Regression | IIoT | Lag features, Window features |
| [15] | Mathematical models, PPM, virtual queues | Regression | Real time services | - |
| [16] | Mathematical models, PPM, virtual queues | Regression | Real time services | - |
| [17] | Multivariate linear regression technique | Regression | LTE services | - |
| [18] | Logistic regression, Random forest, Light gradient-boosting machine (LightGBM), Ensemble | Classification | 4G and 5G services | - |
| Mean | StDev | Var | Min | Median | Max | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
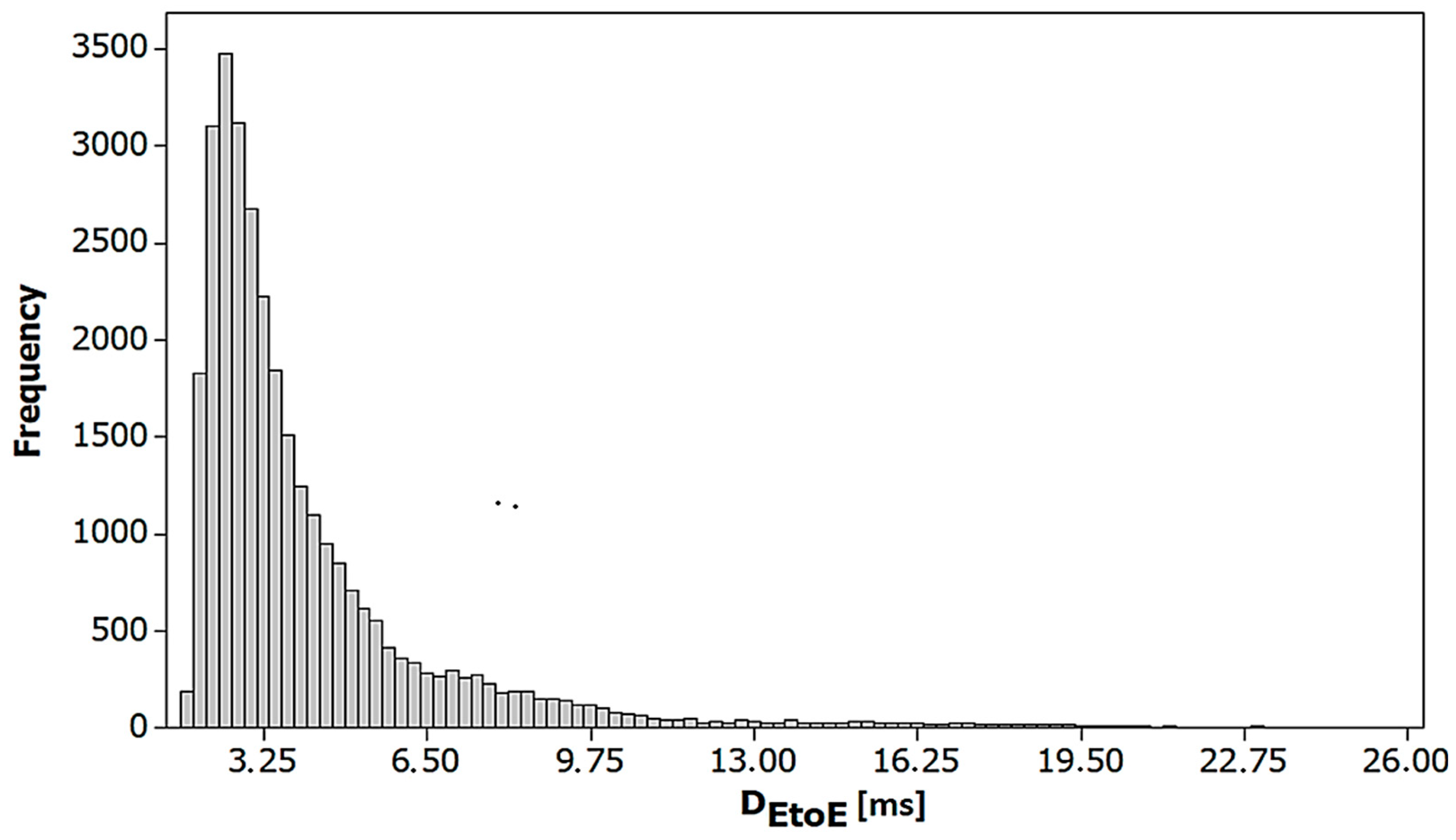
| 4.1503 | 2.6520 | 7.0329 | 1.8081 | 3.2516 | 25.8282 | 2.81 | 10.17 |
| Rank | Independent variable or Predictor | Predictor weighting coefficients for individual values of k | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k=10 | k=15 | k=20 | ||
| 1 | DL.16QAM.TB.Retrans | 0.0061 | 0.0065 | 0.007 |
| 2 | DL.QPSK.TB.Retrans | 0.006 | 0.0064 | 0.0067 |
| 3 | Cell_Traffic_Volume_UL | 0.0041 | 0.0044 | 0.0045 |
| 4 | DL_PRB_Usage_Rate | 0.0037 | 0.004 | 0.0043 |
| 5 | Cell_Traffic_Volume_DL | 0.0033 | 0.0035 | 0.0038 |
| 6 | UL_Average_Interference | 0.0028 | 0.0031 | 0.0033 |
| 7 | DL.64QAM.TB.Retrans | 0.0027 | 0.0028 | 0.0029 |
| 8 | Cell | 0.0024 | 0.0025 | 0.0027 |
| 9 | UL_IBLER | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.0012 |
| 10 | UL_ReTrans_Rate | 0.0009 | 0.001 | 0.0011 |
| 11 | Cell_Uplink_Average_Throughput | 0.0006 | 0.0006 | 0.0007 |
| 12 | Average_UL_User_Throughput | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| 13 | Average_CQI | -0.0008 | -0.0008 | -0.0009 |
| 14 | DL_ReTrans_Rate | -0.0013 | -0.0013 | -0.0014 |
| 15 | DL_IBLER | -0.0015 | -0.0016 | -0.0017 |
| 16 | Cell_Downlink_Average_Throughput | -0.0019 | -0.002 | -0.0021 |
| 17 | Average_DL_User_Throughput | -0.0027 | -0.0029 | -0.003 |
| Model | RE | Correlation |
|---|---|---|
| 1. k-NN | 0.109 | 0.944 |
| 2. NN | 0.159 | 0.917 |
| 3. SVM | 0.205 | 0.893 |
| An approach to optimization of a set of input variables | ML model selected | Number of inputs | RE | Kolmogorov-Smirnov | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic | df | Sig. | ||||
| RReliefF algorithm | k-NN | 6 | 0.109 | 0.188 | 31143 | 0.000 |
| Backward selection via the recursive feature elimination algorithm | k-NN | 4 | 0.041 | 0.191 | 31143 | 0.000 |
| Pareto 80/20 rule | k-NN | 11 | 0.049 | 0.189 | 31143 | 0.000 |
| N | 31143 |
| Chi-Square | 268.019 |
| df | 2 |
| Asymp. Sig. | 0.000 |
| Pairs for comparison | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| RReliefF - Pareto 80/20 rule | Backward selection via the recursive feature elimination - RReliefF | Backward selection via the recursive feature elimination - Pareto 80/20 rule | |
| Z | -3.077 | -7.848 | -18.727 |
| Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





