1. Introduction
The acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is characterized by acute hypoxemia (PaO2/FiO2<300mmHg) and the presence of bilateral infiltrates on chest X-ray, not explained by the presence of left atrial hypertension, and may be associated with severe hypoxemia (1).
In the literature, there are a great diversity regarding how to ventilate patients with ARDS. However, the most used approaches are based on either the ARDS Network or the Open Lung Approach (OLA) (2,3). However, if there is an adjustment of the values of positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP), this may result in alveolar derecruitment, similarly high levels of PEEP maybe associated with stress and over-distension of the pulmonary parenchyma (4).
Different ventilatory alternatives have been proposed in patients with ARDS in order to protect the lungs, improve oxigenation and eventually better outcomes (5,6). Nonethless, most of these ventilatory strategies differ from spontaneous ventilation because they have a pre-stablished ventilatory pattern, characterized by the maintenance of the respiratory rate, tidal volume and a fixed pressure ventilation (7). In this setting, it has been suggested in experimental models of ARDS that the use of variable ventilation could improve lung function and could be a very interesting and effective way to ventilate injured lungs. (8). Different approaches with satisfatory results have been proposed for the use of variable ventilation such as changes in respiratory rate, tidal volume and pressure support (9-12). Unfortunately, during the seek for the ideal ventilatory strategy we face the dilemma between collapse and overdistention. One have to choose an adequate PEEP to prevent collapse during expiration, but at the same time, it has to be lower enough to prevent overdistension of previously aerated lung regions. In this study we hypothetized that the use of oscillatory PEEP (BiPEEP) in an experimental model of ARDS is capable to improve gas exchange and reduce inflammatory response when compared to monotonous ventilation.
2. Materials and Methods
The study is conformed to the regulations of the Brazilian Code of Practice for the care and use of animals for scientific purposes and was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Hospital de Clinicas de Porto Alegre (Protocol 11-432).
Preparation of animals, anesthesia and ventilation
In this study we used 12 male pigs (Large White), weighing on average (SD) 25 kg(13) in a protocol of lung injury induced by oleic acid. The animals were divided into two groups (n = 6), ARDS group with monotonous ventilation (Control) and an oscillatory PEEP group (BiPEEP).
Following an intramuscular sedation (Ketamina 10mg/Kg and Midazolan 1mg/Kg) anesthesia was maintained with propofol, morphine, and ketamine as previously described(12).
The pigs were mechanically ventilated (Inter 7 Plus, Intermed Equipamentos Médicos Hospitalares Ltda, São Paulo, Brasil) via a size 8mm endotracheal tube using the following settings: pressure control, FiO2 1.0, inspiration to expiration ratio = 1:2, tidal volume 6 ml/kg with the initial respiratory rate adjusted to maintain an end tidal CO2 tension of 35 to 45 mmHg. The ventilatory parameters were adjusted to maintain a plateau pressure limit of 35 cm H2O. With the exception of the PEEP, the ventilation settings were not changed during the entire protocol. The control group used a fixed PEEP of 5 cmH2O. In the oscillatory bi-level PEEP group, the animals were ventilated with PEEP of 5 cmH2O which was increased to 10 cm H20 every 4 breaths. Changes in PEEP values were performed automatically, because the ventilator used allows the use of two PEEP levels and also every few respiratory cycles it must be changed.
Respiratory mechanics and lung volumes
For the evaluation of mechanical properties of the respiratory system and measures of airflow we used a flow transducer, located in the proximal portion of the endotracheal tube, the Monitor Graph Ventilation - Tracer 5® (Intermed Ltda -. São Paulo, Brazil) on the computer which recorded pressure curves (P), flow (V ') and volume (V) versus time (t); curve pressure x volume curve (compliance) and x flow volume curve, through specific software.
Arterial oxygen tension (PaO2), oxygen saturation, carbon dioxide tension were measured with a blood gas analyzer immediately after withdraw (Rapidlab 1200, Siemens, Leverkusen, Germany). PaO2 over fractional inspiratory oxygen concentration (P/F ratio) was calculated.
Hemodynamic parameters
Mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) was measured at the femoral artery. Throughout the study the animals remained in supine position. All hemodynamic pressures were zeroed at the mid axillary line at the level of the sternum and measured during end-expiration.
ARDS injury
After a set of baseline measurements, ARDS was performed by injecton of 0.15 ml/Kg oleic acid (Sigma-Aldrich®, Steinheim, Germany) in 15 mL of saline administered over 10 minutes throught the proximal end of the pulmonary artery catheter (13) until a P/F ratio of 200 to 300 mmHg was established. Noradrenaline IV was used to maintain a MAP ≥70 mmHg during the infusion of oleic acid. Intravenous fluid administration was limited to 1 ml/Kg/hour, after an initial 500 ml over a 30-minute bolus of succinylated gelatin.
Experimental protocol
All 12 pigs received oleic acid. The experimental protocol provides that 15 minutes after the induction of the lesion, arterial blood gas analysis is performed to assess the P/F ratio, and the protocol is started only when it is at values between 300 and 200. Otherwise, it takes 10 minutes for a new blood gas analysis and confirmation of injury. Analysis of respiratory mechanics, ventilatory parameters and arterial blood gases were performed after stabilization of the animals (post-induction), after the animals were evaluated for 180 minutes and during this period the measurements were made every 30 minutes until the end of the evaluation period. At the end of the observation period the animals were sacrificed by exsanguination and, we collected tissue samples from the upper and lower portion of the left lungs.
Oxidative Stress - Assessment of Lipid Peroxidation
The thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) technique consists of heating the homogenate with thiobarbituric acid to produce a colored product that is subsequently measured at 535 nm using a spectrophotometer. The change in the color is due to the presence of malondialdehyde and other substances produced from lipid peroxidation in the biological material. Briefly, 0.25 ml of 10% trichloroacetic acid (TCA), 0.10 ml of homogenate, 0.067 ml of 0.67% thiobarbituric acid (TBA), and 0.033 ml of distilled water were added to a tube, stirred, and heated at 100°C. After the tubes cooled, 0.20 ml of n-butyl alcohol was added to extract the pigment. The tubes were then stirred and centrifuged for 10 minutes at 1110 g. A 0.20 ml aliquot of the supernatant was added to a 96-well plate. The absorbance of the samples was quantified on a spectrophotometer at 535 nm. The TBARS concentration was expressed in nmol/mg of protein (14).
Antioxidant Enzymes - Determination of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD)
The technique used to measure SOD was based on the level of inhibition caused by the reaction of the enzyme with O−2. We used adrenaline in an alkaline medium to produce adrenochrome and O−2 (15). In a 96-well plate, we measured the SOD activity in the reaction medium (50 mM glycine-NaOH, pH 10) and in three samples containing different concentrations of homogenate. After the addition of 10.5 μl of epinephrine (60 mM, pH 2.0), the reaction was monitored for 2 min at 480 nm. The enzymatic activity was expressed in the units SOD/mg of protein.
Interleukin Analysis
After the samples were thawed, a 96-well plate was coated with monoclonal antibodies against IL-8 and IL-17a. The wells were filled with either 100 µl of homogenized lung (diluted 1:2), 100 µl of positive or negative controls, or 100 µl of recombinant IL-8 or IL-17a at concentrations established by the manufacturer (Creative Biomart, NY, USA). Then, 100 µl of polyclonal anti-IL-8 and anti-IL-17a conjugated to peroxidase was added to the wells, and the samples were incubated for 3 h at room temperature. Following the incubation, the plate was washed four times with a detergent solution. The color change was then induced by adding hydrogen peroxide (0.02%) and tetramethylbenzene (2%). The reaction was interrupted 30 min later using sulfuric acid (1 M). The color intensity was assessed by obtaining optical density measurements using an ELISA automatic reader (Titertek Multiskan®) at a wavelength of 450 nm. The IL-8 and IL-17a concentrations in the homogenized lung samples were calculated based on the results of a standard curve.
Histological analisys
The lung tissue specimens were fixed in formalin and dehydrated, cleared, and embedded in paraffin. The specimens were cut into 5-μm serial sections and stained with hematoxylin-eosin. The same regions were sampled in all groups. A pathologist blinded to the experimental protocol and the region of sampling performed quantitative analysis by light microscopy. Each sample was examined under both low and high power fields. At least four sections were obtained from each block, and 20 fields were randomly selected and analyzed for each section. The severity of histological lesions was assessed using a histologic score (18) based on six parameters: intraalveolar edema, hyaline membrane formation, hemorrhage, recruitment of granulocytes into the air spaces, focal alveolar collapse or consolidation, and epithelial desquamation or necrosis of the airways or alveoli. Each parameter was evaluated semi quantitatively using the following scale: 0, absent; 1, mild; 2, moderate; and 3, prominent. In addition, the percentage of the involved area of each histological specimen was estimated (0-100%) to quantify the histological changes (16).
Statistics
The sample size calculation with a confidence interval of 95% for the experimental groups was performed. Normal distributions of means tests were performed for statistical tests. The groups were compared using an analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a post hoc Tukey test performed using SPSS® version 19.0 (Statistical Package for Social Science). In the case of unequal variances or an abnormal distribution, a nonparametric Kruskal Wallis test was performed, followed by Mann-Whitney U-tests for intergroup comparisons. The results are represented as the means ± standard deviation. The statistical significance level was set at p<0.05.
3. Results
There were no significant differences between the groups in terms of mechanical ventilation only from Baseline Control to 30 minutes Control regarding airway resistance (
Table 1). The groups were not different at baseline, and similar changes in heart rate, PAP and end tidal CO2 increased in both groups after OA infusion (
Table 2).
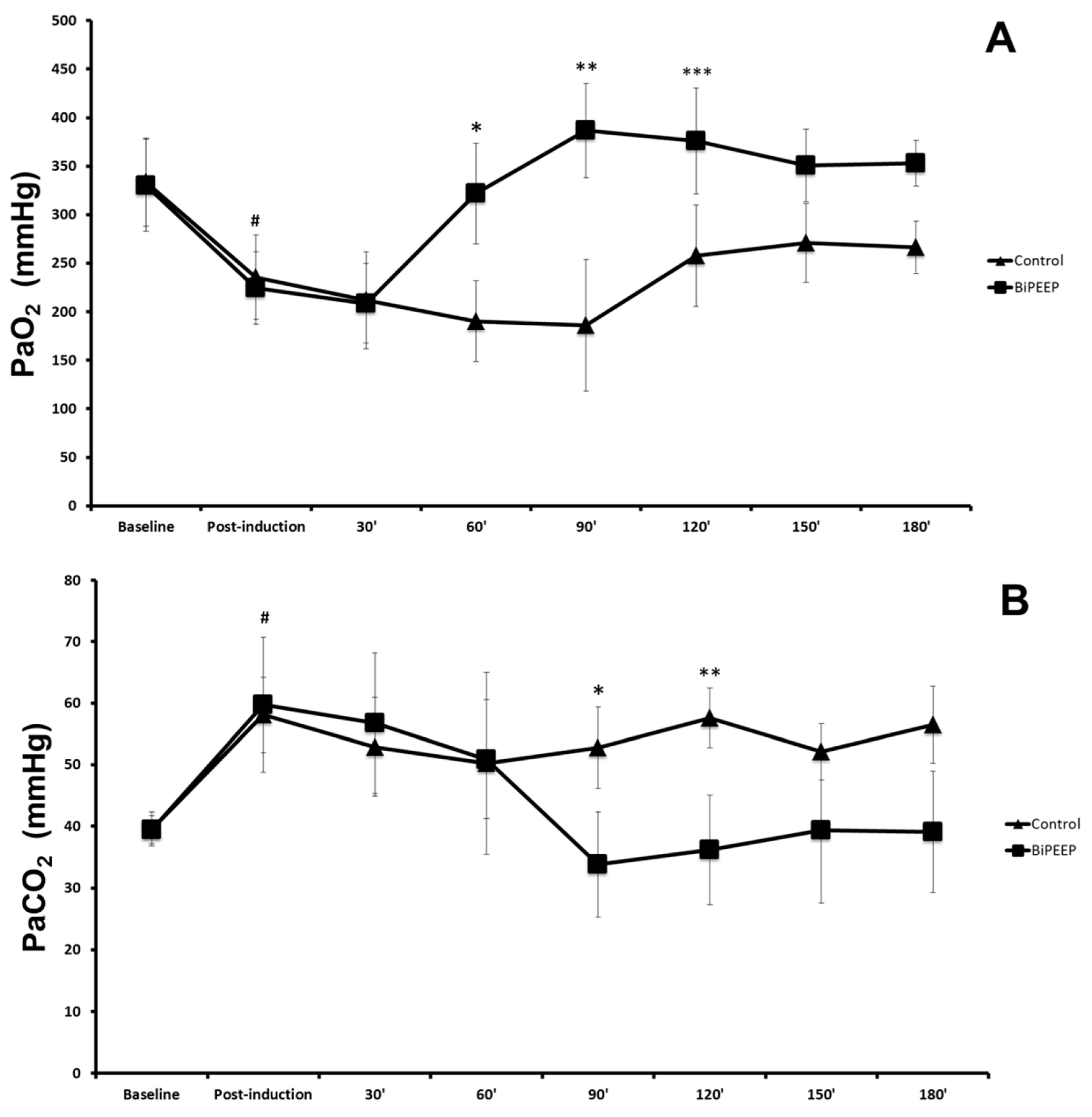
There was a significant difference in arterial oxygen pressure (PaO
2) in baseline control compared to post-induction control and baseline BiPEEP compared to post-induction BiPEEP (p <0.05). PaO
2 in the BiPEEP group was significantly different to the control group at the times 60, 90 and 120 minutes (p <0.001). The post-induction period of BiPEEP was significantly different to the 60 minutes BiPEEP (p <0.05) and the periods of 90, 120, 150 and 180 minutes (p <0.001). A significant reduction was demonstrate in the 30, 60 and 90 minutes periods of the contrl in relation to the baseline control (p<0.01) (
Figure 1A). The blood pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO
2) was significantly lower at baseline control compared to post-induction control (p <0.05). The same finding was observed in BiPEEP group. In the control group at 90 (p<0.05) and 120 (p<0.01) minutes, PaCO
2 was significantly higher compared to BiPEEP group. At times 90 (p <0.001), 120 (p <0.01), 150 and 180 minutes (p <0.05) the use of BiPEEP significantly reduced PaCO
2 values when compared to post-induction BiPEEP (
Figure 1B).
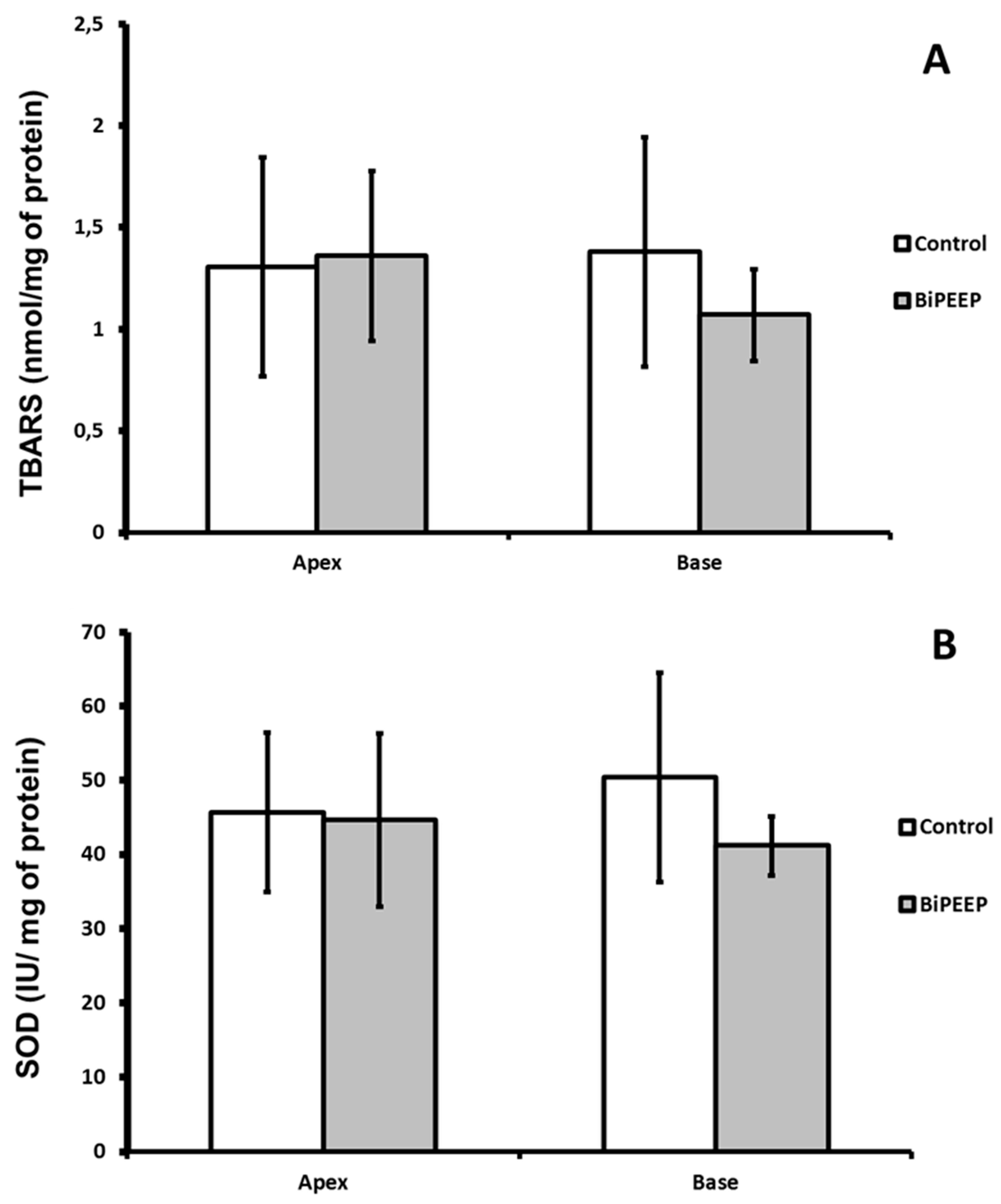
There were not significant differences between groups at the quantity of lipid peroxidation products. The TBARS quantification was slightly lower in the BiPEEP base lung sample than in the BiPEEP apex sample, but the difference was not significant (
Figure 2A). The activity of superoxide dismutase did not change significantly between the groups (
Figure 2B).
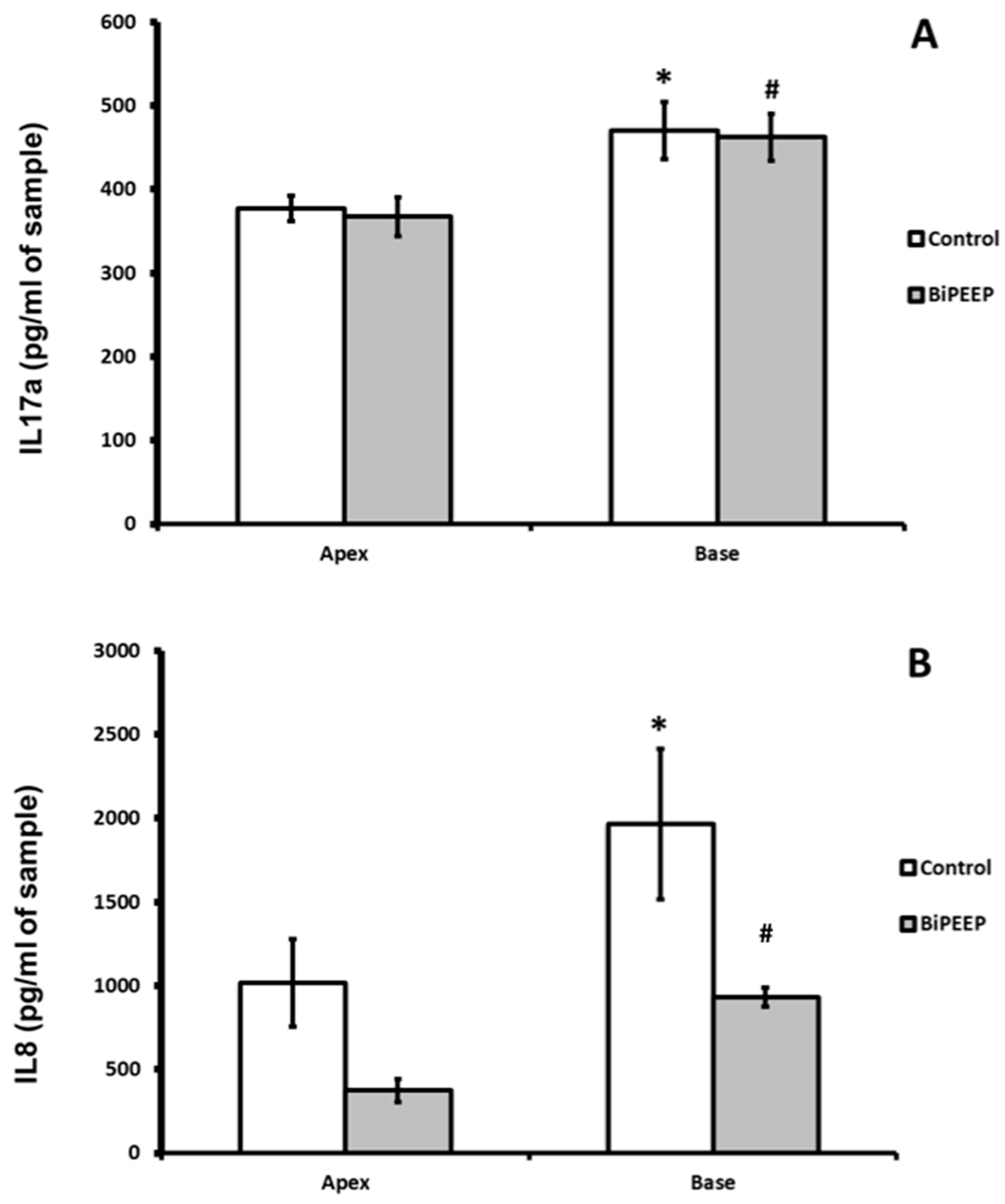
Interleukin 17a (IL-17a) showed no significant difference between control and BiPEEP groups. There was a significantly difference (p <0.01) between the apex and base lung samples of each group (
Figure 3A). Interleukin 8 (
Figure 3B) demonstrated a significant increase in the control lung base when compared to BiPEEP base lung sample (p<0.001). The apex of BiPEEP presented a significant reduction in IL8 in comparison to control (p<0.01). In both groups there was a significant difference from the apex to the base of the lungs (p<0.01).
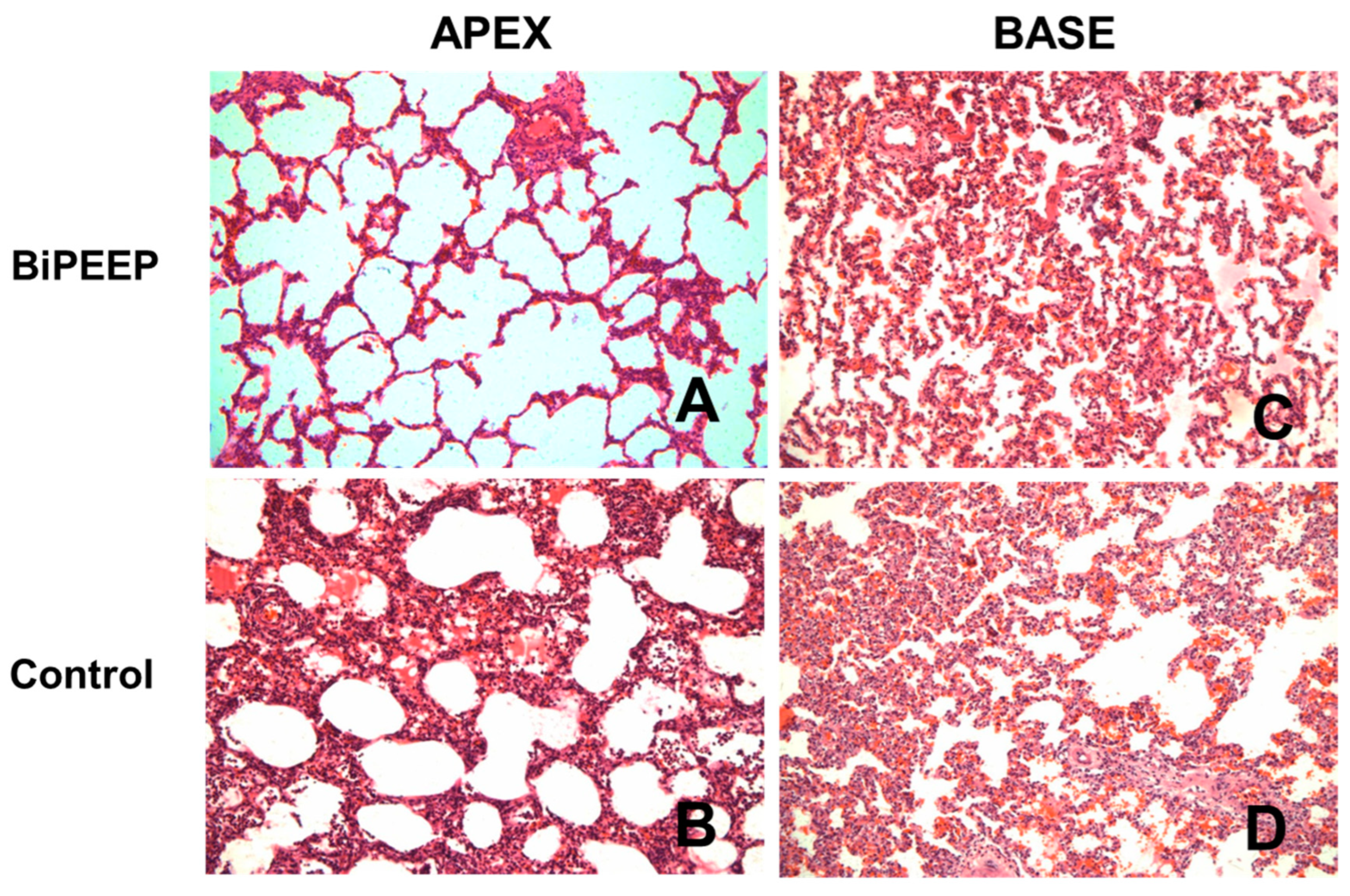
The histopathological analysis (
Figure 4) of the control group showed changes in lung morphology characterized by cellular infiltrates, a thickening of the alveolar septae and atelectasis, which were attenuated in BiPEEP group (p<0.05), whereas both groups presented greater alteration in the lung bases (p<0.01). However, the BiPEEP group presented less morphological alteration then the control group (p<0.05).
4. Discussion
When compared monotonous ventilation with BiPEEP, the main findings of the study were: (1) the use of a ventilatory strategy with two levels of PEEP resulted in improved gas exchange; (2) the oscillating PEEP showed reduced inflammatory response assessed by IL8; (3) less structural abnormalities when using two levels of PEEP. This study, comparing the two levels of PEEP with conventional ventilation, is the first report in the literature using this ventilatory strategy in an experimental model of ARDS induced by oleic acid.
In this study, the ARDS induced by oleic acid resulted in the reduction of the PaO2/FiO2 ratio in both groups, as reported by Schuster (17). However, it should be pointed out that the option of this model was related to the group's experience in the use of the same, being evident in the literature different models of induction, as well as the experimental models (18,19).
Variable ventilation (VV) was evaluated in experimental studies, which demonstrate beneficial effects of this strategy in respiratory mechanics, gas exchange and pulmonary function in models with and without lung injury (20). However, there are only three clinical studies that have evaluated this approach, and the objectives as well as the outcomes evaluated are different on those studies (21-23).
When analyzing respiratory mechanics variables, we observed a significant increase in airway resistance 30 minutes after induction in the control group, and no change in the BiPEEP group. Contrary to our findings, several experimental studies have demonstrated improvement in respiratory mechanics in experimental models of ARDS using VV a possible explanation for this may be the variable of choice for these levels of PEEP (20). Boker et al. (24) compared the use of conventional ventilation to VV during a 5-hour in porcine model of ARDS, with VT and RR being non-fixed variables, and demonstrated improvement in respiratory mechanics, gas exchange and reduction of the shunt fraction. This finding may be associated with the variable of variability used by the authors, the VT, because they are generated randomly, thus reaching the critical pressure of alveolar opening resulting in the opening of non-ventilated lung regions. We demonstrated the existence of hemodynamic changes (HR, PAP and ETCO2) only after induction with AO, this finding can be evidenced in a similar way by Boker et al. (24), which demonstrated a significant increase in hemodynamic variables immediately after induction of lung injury, remaining high in the other periods.
We demonstrated that the use of two levels of PEEP is able to improve oxygenation as well as the reduction of PaCO2, these findings corroborate with several experimental studies in ARDS that demonstrated improvement in gas exchange with VV (11, 24-32). The beneficial effects of variability reported in this study are similar to those previously described by Lefevre et al. (33) and Mutch et al. (34). In these studies, breath rate was randomly varied about a given value and VT was adjusted to keep minute ventilation constant during oleic acid-induced lung injury and unilateral lung collapse. In both cases, a single level of variability was applied and resulted in a significant increase in lung compliance and PaO2 in comparison with conventional ventilation. Nam et al. (35) demonstrated that variability had no beneficial effects over conventional ventilation. This observation suggests that factors other than variability per se can be important for conferring beneficial effects on lung physiology in this setting.
A possible factor responsible for the effectiveness of the use of BiPEEP in relation to gas exchange is the effects related to alveolar recruitment and derecruitment. This is evident in the study by Ma et al. (36) in which this hypothesis was tested in a computational pulmonary model. The model also showed that recruitment/derecruitment dynamics contribute to the relative efficacy of variable ventilation, providing lung units open more rapidly than they close, once a critical opening or closing pressure threshold has been crossed. We conclude that the dynamics of recruitment and derecruitment in the lung may be important factors responsible for the benefits of VV compared with CV (37).
In our study, we observed a significant reduction of the IL-8 values in the BiPEEP group. Unfortunately, the same finding was not observed regarding IL-17a. Boker et al. observed that the concentration of interleukin-8 (IL-8) in the tracheal aspirate after 5 hours of VV was lower compared to conventional mechanical ventilation, although with similar findings in pulmonary edema (24). Corroborating observations, Arold et al. (37) demonstrated that, after 3 hours of VV in guinea pigs without lung injury, there was a reduction in the concentrations of IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) in bronchoalveolar lavage.
Thammanomai et al. (4) investigated the physiological consequences of variable ventilation in a mouse model of ALI and showed it to be superior to conventional ventilation in terms of lung mechanical function and biomarkers of injury. The possible explanation for the beneficial effects of VV is due to the use of a non-linear system, which is similar to biological variability of the respiratory system. These modes may increase VT based on the nonlinear characteristics of collapsed (8) and normal (36) alveoli. There are thus two main epiphenomena, which are the basis for improvement of pulmonary function during VV, recruitment and stabilization of lung regions, improving gas exchange; and improvement in the corresponding ventilation-perfusion.
5. Conclusions
Our study showed that the use of mechanical ventilation with bi-oscillatory level (BiPEEP) improves the parameters of ventilatory mechanics and gas exchange, as well as reduced the inflammatory parameters through the lower expression of IL-8. As a consequence, histopathological changes were reduced in the use of BiPEEP.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: The Berlin Definition. The ARDS Definition Task Force. JAMA. 2012;307(23):2526-2533.
- The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1301-1308.
- Lachmann B. Open up the lung and keep the lung open. Intensive Care Med 1992;18:319–321. [CrossRef]
- Thammanomai A, Hueser LE, Majumdar A, Bartolak-Suki E, Suki B. Design of a new variable-ventilation method optimized for lung recruitment in mice. J Appl Physiol 104: 1329–1340, 2008.
- Villagrá A, Ochagavía A, Vatua S, Murias G, DelMar Fernández M, Lopez Aguilar J, Fernández R, Blanch L. Recruitment maneuvers during lung protective ventilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. CareMed. 2002;65:165–170.
- Amato MB, Barbas CS, Medeiros DM, Magaldi RB, Schettino GP, Lorenzi-Filho G, Kairalla RA, Deheinzelin D, Munoz C, Oliveira R, Takagaki TY, Carvalho CR. Effect of a protective-ventilation strategy on mortality in the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl Med1998;338:347–354.
- Tobin MJ, Mador MJ, Guenther SM, Lodato RF, Sackner MA. Variability of resting respiratory drive and timing in healthy subjects. J Appl Physiol 1988;65:309–317. [CrossRef]
- Suki B, Alencar AM, Sujeer MK, Lutchen KR, Collins JJ, Andrade JS Jr, Ingenito EP, Zapperi S, Stanley HE. Life-support system benefits from noise. Nature 1998;393:127–128. [CrossRef]
- Gama de Abreu M, Spieth PM, Pelosi P, Carvalho AR, Walter C, Schreiber-Ferstl A et al. Noisy pressure support ventilation: A pilot study on a new assisted ventilation mode in experimental lung injury. Crit Care Med 2008; 36:818–827. [CrossRef]
- Lefevre GR, Kowalski SE, Girling LC, Thiessen DB, Mutch AC. Improved arterial oxygenation after oleic acid lung injury in the pig using a computer-controlelled mechanical ventilation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996;154:1567–1572.
- Arold SP, Mora R, Lutchen KR, Ingenito EP, and Suki B. Variable tidal volume ventilation improves lung mechanics and gas exchange in a rodent model of acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165: 366–371, 2002. [CrossRef]
- Regli A, Hockings LE, Musk GC, Roberts B, Noffsinger B, Singh B, van Heerden PV. Commonly applied positive end-expiratory pressures do not prevent functional residual capacity decline in the setting of intra- abdominal hypertension: a pig model. Crit Care 2010, 14:R128. [CrossRef]
- Julien M, Hoeffel JM, Flick MR. Oleic acid lung injury in sheep. J Appl Physiol. 1986;60(2):433-40. [CrossRef]
- Buege, J.A. and S.D. Aust, Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol, 1978. 52: p. 302-10.
- Misra HP, Fridovich I. The role of superoxide anion in the autoxidation of epinephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3170-5.
- ARAUJO, Luiz Felipe Lopes et al. Effect of the systemic administration of methylprednisolone on the lungs of brain-dead donor rats undergoing pulmonary transplantation. Clinics. 2014, v. 69, n. 2, p. 128-133. [CrossRef]
- Schuster DP. ARDS: clinical lessons from the oleic acid model of acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 149: 245–260, 1994. [CrossRef]
- Reiss LK, Uhlig U, Uhlig S. Models and mechanisms of acute lung injury caused by direct insults. Eur J Cell Biol. 2012 Jun-Jul;91(6-7):590-601. [CrossRef]
- Matute-Bello G, Frevert CW, Martin TR. Animal models of acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008 Sep;295(3):L379-99.
- Fontela PC, Prestes RB, Forgiarini LA Jr, Friedman G. Variable mechanical ventilation. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 2017 Jan-Mar;29(1):77-86. [CrossRef]
- Boker A, Haberman CJ, Girling L, Guzman RP, Louridas G, Tanner JR, et al. Variable ventilation improves perioperative lung function in patients undergoing abdominal aortic aneurysmectomy. Anesthesiology. 2004;100(3):608-16. [CrossRef]
- Spieth PM, Güldner A, Huhle R, Beda A, Bluth T, Schreiter D, et al. Short- term effects of noisy pressure support ventilation in patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. Crit Care. 2013;17(5):R261. [CrossRef]
- Wang R, Chen J, Wu G. Variable lung protective mechanical ventilation decreases incidence of postoperative delirium and cognitive dysfunction during open abdominal surgery. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(11):21208-14.
- Boker A, Graham MR, Walley KR, McManus BM, Girling LG, Walker E, et al. Improved arterial oxygenation with biologically variable or fractal ventilation using low tidal volumes in a porcine model of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165(4):456-62. [CrossRef]
- Thammanomai A, Hueser LE, Majumdar A, Bartolák-Suki E, Suki B. Design of a new variable-ventilation method optimized for lung recruitment in mice. J Appl Physiol (1995). 2008;104(5):1329-40. [CrossRef]
- Bellardine CL, Hoffman AM, Tsai L, Ingenito EP, Arold SP, Lutchen KR, et al. Comparison of variable and conventional ventilation in a sheep saline lavage lung injury model. Crit Care Med. 2006;34(2):439-45. [CrossRef]
- Mutch WA, Harms S, Lefevre GR, Graham MR, Girling LG, Kowalski SE. Biologically variable ventilation increases arterial oxygenation over that seen with positive end-expiratory pressure alone in a porcine model of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2000;28(7):2457-64. [CrossRef]
- Funk DJ, Graham MR, Girling LG, Thliveris JA, McManus BM, Walker EK, et al. A comparison of biologically variable ventilation to recruitment manoeuvres in a porcine model of acute lung injury. Respir Res. 2004;5:22. [CrossRef]
- Spieth PM, Carvalho AR, Pelosi P, Hoehn C, Meissner C, Kasper M, et al. Variable tidal volumes improve lung protective ventilation strategies in experimental lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;179(8):684-93. [CrossRef]
- Ruth Graham M, Goertzen AL, Girling LG, Friedman T, Pauls RJ, Dickson T, et al. Quantitative computed tomography in porcine lung injury with variable versus conventional ventilation: Recruitment and surfactant replacement. Crit Care Med. 2011;39(7):1721-30. [CrossRef]
- Thammanomai A, Hamakawa H, Bartolák-Suki E, Suki B. Combined effects of ventilation mode and positive end-expiratory pressure on mechanics, gas exchange and the epithelium in mice with acute lung injury. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53934. [CrossRef]
- Samary CS, Moraes L, Santos CL, Huhle R, Santos RS, Ornellas DS, et al. Lung Functional and Biologic Responses to Variable Ventilation in Experimental Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(7):e553-62. [CrossRef]
- Lefevre GR, Kowalski SE, Girling LG, Thiessen DB, Mutch WA. Improved arterial oxygenation after oleic acid lung injury in the pig using a computer-controlled mechanical ventilator. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996;154:1567–1572. [CrossRef]
- Mutch WA, Harms S, RuthGraham M, Kowalski SE, Girling LG, Lefevre GR. Biologically variable or naturally noisy mechanical ventilation recruits atelectatic lung. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;162:319–323. [CrossRef]
- Nam AJ, Brower RG, Fessler HE, Simon BA. Biologic variability in mechanical ventilation rate and tidal volume does not improve oxygenation or lung mechanics in canine oleic acid lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;161:1797–1804.
- Ma B, Suki B, Bates JH. Effects of recruitment/derecruitment dynamics on the efficacy of variable ventilation. J Appl Physiol 110: 1319 –1326, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Arold SP, Suki B, Alencar AM, Lutchen KR, Ingenito EP. Variable ventilation induces endogenous surfactant release in normal guinea pigs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003;285(2):L370-5. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).