1. Introduction
Rice is one of the important food crops, which solves the food security problem of about half of the world's population. Grain shape and chalkiness are important appearance qualities of rice and have a significant impact on grain weight and cooking and eating quality. Rice with good appearance quality will be accepted by more consumers and increase its commodity value.
Rice grain shape, which directly affects the 1000-grain weight and the yield, is further charactered by grain length (GL), grain width (GW), length-to-width ratio (LWR) and grain thickness (GT). Moreover, the rice grain shape also has a great influence on the appearance and milling quality of rice. For more than a decade, scientists have cloned many grain shape-related genes and analyzed the corresponding molecular mechanisms. It is generally believed that rice grain shape is a complex quantitative trait regulated by multiple genes. Currently, more than 400 grain shape-related QTL have been detected [
1], of which a number of grain shape-related genes have been cloned successfully [
2]. Among them,
GS2/
GL2,
GS3,
qGL3,
qTGW3,
GL3.3 were found to control grain length [
3,
4,
5], and
GW2,
GW5/
qSW5/
GSE5,
GS5,
GW8,
GL7/
GW7 were found to affect grain width [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10]. These genes not only regulate grain shape, but also have varying degrees of influence on 1000-grain weight and grain yield.
Chalkiness is the white opaque part in rice endosperm. According to the opaque part in the endosperm, chalkiness can be mainly divided into white-belly, white-back, and white-core. Chalkiness is also a complex quantitative trait controlled by multiple genes. A large number of rice opaque endosperm mutants were found had similar endosperm appearance with chalkiness grains, and some of the genes controlled opaque endosperm were finally identified successfully, such as
flo4/
OsPPDKB,
SSIIIa,
FLO2,
OsPK2, and so on [
11,
12,
13,
14].
flo4/
OsPPDKB encodes a chloroplast-located pyruvate phosphate double kinase (PPDK), the
flo4 mutant showed a white-core endosperm [
11].
SSIIIa/
FLO5 encodes a soluble starch synthase, which affects the amylose content, the structure of amylopectin, and the physicochemical properties of starch in rice. Compared with the wild type, the
SSIIIa/
FLO5 mutant had smaller, rounder and loosely arrangement starch granule in the central part, showing a white-core endosperm phenotype [
12]. So far, little progress has been made in revealing the mechanism of chalkiness formation by using natural resources, and only 2 chalkiness related genes have been successfully cloned.
Chalk5 was the first gene found to control chalkiness, it encodes a vacuolar membrane localized vacuolar membrane proton transporter pyrophosphatase. Higher
Chalk5 expression level greatly increased the gap formed between the starch granules and the protein body, led to the abnormal shape and spatial arrangement of the storage substances in endosperm, and resulted in the formation of chalkiness [
15].
WCR1 is the first gene found to negatively regulate the white-core rate of rice, it encodes a F-box protein [
16]. Further experimental results showed that
OsDOF17 could up-regulate the transcription of metallothionein
MT2b and inhibit the 26S proteasome-mediated MT2b degradation by directly activating
WCR1A transcription, promoting the elimination of excess ROS, delaying the PCD process of endosperm cells, and finally leading to the decrease of white-core rate of rice grain.
In this study, a genetic linkage map was constructed by using GBS sequencing technology, and QTL were primary mapped based on the grain shape and chalkiness phenotypes of the F2 and F2:3 populations. A QTL cluster affecting chalkiness was found on chromosome 6, the genetic effect of qWBR6.1, qWCR6 and qCR6 were validated in a random segregation population. The results of this study provide a basis for cloning new quality-related genes and breeding high quality rice varieties.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population development and field experiments
Two newly bred Hua 5178S and Hua 611 were used as parents to construct the genetic population, the chalkiness rate of Hua 5178S was low while Hua 611 was high. The F1 generation was generated by crossing female parent Hua 5178S (temperature-sensitive sterility line) with male parent Hua 611. The F2 generation population was planted under natural field conditions at the experimental station of Huazhong Agricultural University in Lingshui, Hainan Province in 2016, the fertility of plants was screened by using markers linked to the male sterile gene TMS5. 190 fertile plants were obtained in F2 generation for genetic map construction and phenotypic collection, and the F2:3 generation families of each plant were used for the second phenotypic collection. The F2:3 generation families were planted under natural field conditions at the experimental station of Huazhong Agricultural University in Wuhan, Hubei Province in 2017.
Families with heterozygous genotypes in each QTL interval were selected for genetic effect validation, and each family consist of 190 individuals. All families were planted under natural field conditions at the experimental station of Huazhong Agricultural University in Wuhan, Hubei Province in 2019.
Seedlings of 25~30 days after sowing were transplanted with a single plant spacing of 16.5 cm and 26.4 cm between rows in the field. Field management followed local practices.
2.2. Phenotyping
Before phenotyping, harvested seeds were dried and stored at room temperature for at least three months. About 200-300 mature seeds per plant were selected and scanned on a BenQ scanner to generate high-resolution images. Then the images were analyzed by SmartGrain software to obtain the grain length, grain width, length-to-width ratio and seed number performance. At the end of the scan, all the scanned seeds were weighed and the 1000-grain weight was calculated according to the number of seeds.
After examining the grain shape of each plant, the seeds were dehulled into brown rice, and the number of chalkiness grains was recorded with the naked eye on a cold light lamp. WBR is the proportion of white-belly brown rice to the total number of brown rice, WCR is the proportion of white-core brown rice to the total number of brown rice, and the chalkiness rate (CR) is the ratio of chalkiness brown rice to the total number of brown rice.
2.3. Genotyping and linkage map construction
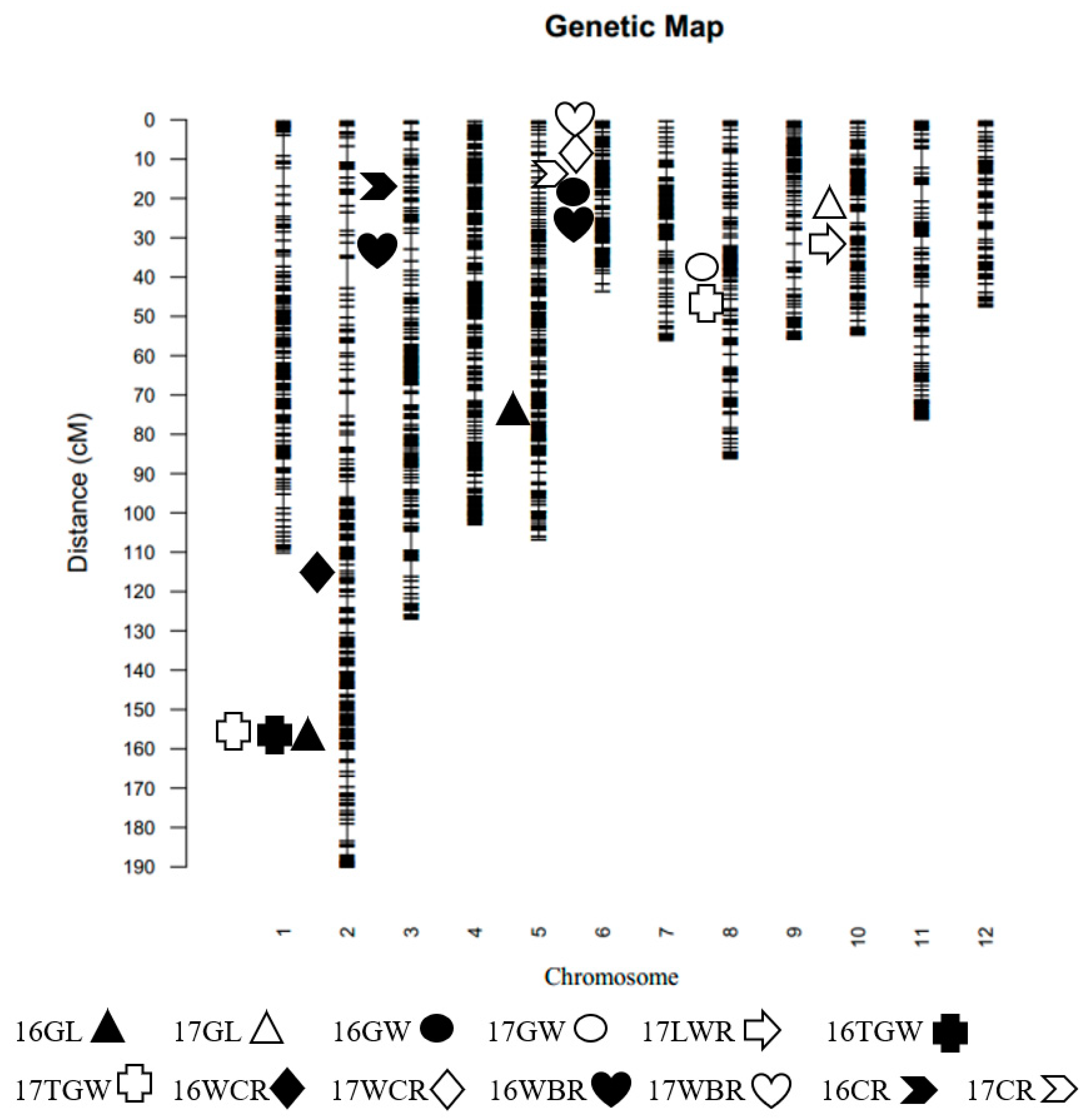
Genotyping of F
2 population was carried out by GBS sequencing technology. There were 1985 polymorphisms between Hua611 and Hua5178S (
Figure 2). The linkage map of this population was constructed by R Programming Language. QTL analysis was conducted by composite interval mapping using WinQTLCart V2.5. A LOD (log likelihood) value of 2.5 was used as the threshold for claiming the putative main-effect QTL. The peak points were considered to the positions of QTL.
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic data of parents and RIL populations
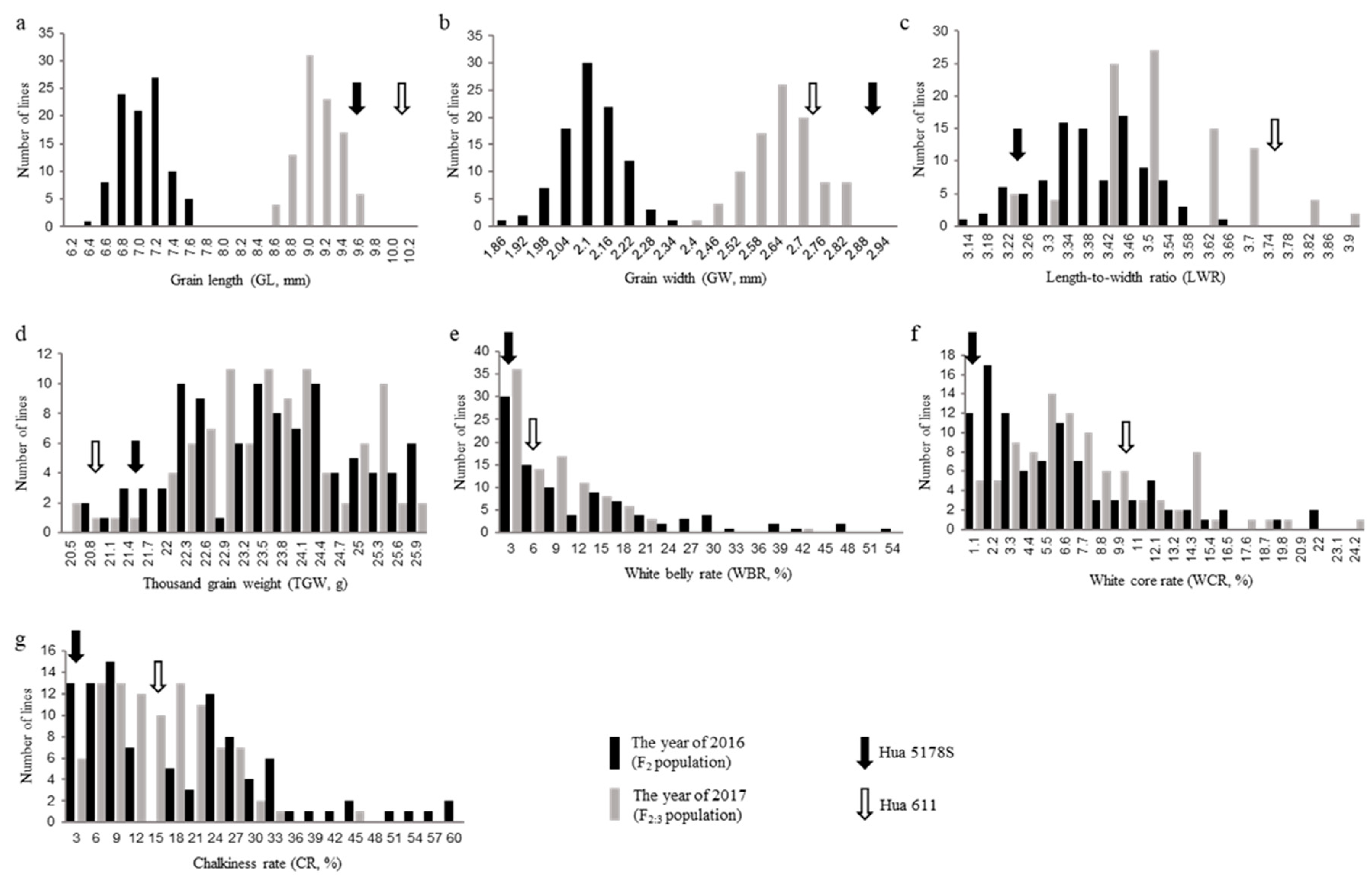
Both parents have slender grains, but there are still some differences. Compared with Hua 611, Hua 5178S has shorter and wider grain shape, and heavier 1000-grain weight in 2016 (
Figure 1a-d and
Table 1). In the progeny populations, the grain length and grain width of F
2 population were significantly smaller than that of F
2:3, but there the 1000-grain weight showed stable in different populations (
Figure 1a-d and
Table 1).
The chalkiness performance of parents and progeny populations were analyzed. In the year of 2016, the white-belly rate, white-core rate and total chalkiness rate of Hua 5178S was 1.45%, 0.72% and 2.17% respectively, while those in Hua 611 was 5.56%, 10.10% and 15.66% respectively (
Figure 1e-g and
Table 1). The white belly rate, white core rate, and chalkiness rate of two populations showed non-normal distributions, and widely ranged than parents (
Figure 1e-g and
Table 1).
Correlation analysis was conduct for grain shape and chalkiness relate traits (
Table 2). Both grain length and grain width displayed significantly positively correlated with 1000-grain weight in different populations. Length-to-width ratio showed significantly negatively correlation with the grain width but significantly positively correlation with the grain length. White-belly rate, white-core rate and chalkiness rate have extremely significantly positively correlation with each other. White belly rate displayed significantly positively correlate with grain width in the F
2 population while there was no significant correlation between chalkiness-related traits and grain shape-related traits in the F
2:3 population.
3.2. QTL mapping
The genetic linkage map was constructed by using 1985 bins identified from the sequencing data of 190 F
2 individuals (
Figure 2). A total of 15 QTL were detected on 6 chromosomes in two populations, and genetic variations explained by each QTL ranged from 10.7% to 46.48% (
Table 3).
Three QTL for grain length were detected in two populations (
Figure 2,
Table 3).
qGL2 located between M02259 and M02344 on chromosome 2, explained 46.48% of the phenotypic variation in 2016.
qGL5 was detected between M05249 and M05252 on chromosome 5, explained 14.14% of the phenotypic variation in 2016.
qGL10 was narrowed between M10147 and M10157 on chromosome 10, explained 15.24% of the phenotypic variation in 2017. Two grain width QTL were detected, explained 21.25% and 19.14% of phenotypic variation, respectively (
Figure 2,
Table 3). Two 1000-grain weight QTL were detected, and
qTGW2 was repeatedly detected in two populations, explained 17.15% and 20.94% of phenotypic variation in F
2 and F
2:3 populations, respectively (
Figure 2,
Table 3).
Seven QTL for chalkiness were detected in two populations and the phenotypic variation explained by each QTL ranged from 10.70% to 34.64% (
Figure 2,
Table 3).
qWCR2 was detected between M02213 and M02215 on chromosome 2, explained 10.70% of the phenotypic variation in 2016. Both
qWBR3 and
qCR3 located on chromosome 3, explained 25.33% and 34.64% of the phenotypic variation in 2016 respectively.
qWBR6.1 was found in the interval between M0633 and M0642 on chromosome 6, explained 12.56% of the phenotypic variation in 2017.
qWBR6.2 was detected between M0683 and M0696 on chromosome 6, explained 17.90% of the phenotypic variation in 2016.
qWCR6 and
qCR6 were found located in the same interval between M0653 and M0665 on chromosome 6, explained 24.48% and 28.82% of the phenotypic variation in 2017, respectively.
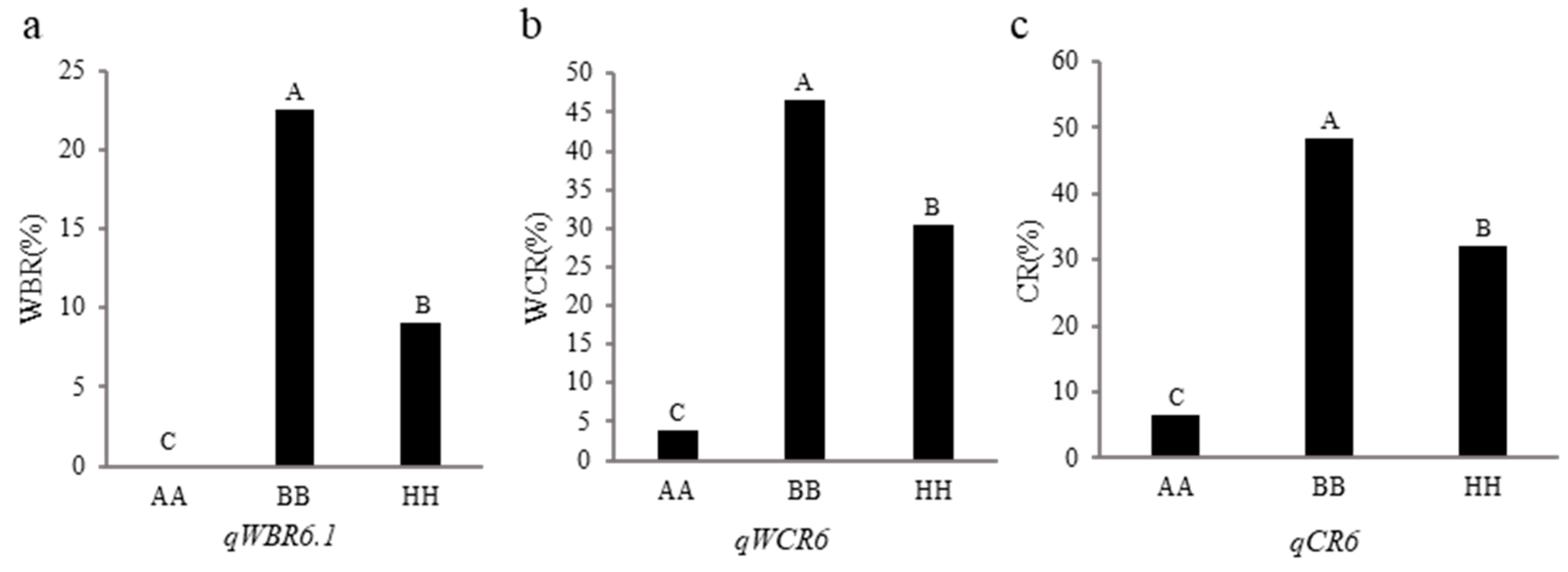
3.3. Validation of qWBR6.1, qWCR6 and qCR6
A gene cluster affecting white-belly rate, white-core rate and chalkiness rate was found on chromosome 6, and there were no related genes reported before.
qWBR6.1,
qWCR6 and
qCR6 were selected for genetic validation. The F
4 random segregating populations of three QTL were constructed and genotyped by two flank markers, and then the phenotypic differences among different genotypes were compared. As shown in
Figure 3,
qWBR6.1 locus from Hua 5178S increased white-belly rate by approximately 22.53% in the segregating population,
qWCR6 or
qCR6 locus from Hua 5178S increased white-core rate and white-belly rate by 42.75% and 41.87%, respectively. These results show that both three loci have an effect on chalkiness, and have application potential in decreasing chalkiness of rice.
4. Discussion
Rice grain shape is a trait of great application value. At present, many grain shape genes have been cloned.
GS2/
GL2 can positively regulate rice grain shape and ear length, increased expression of
GS2/
GL2 lead to larger and more cells, result in an increase in 1000-grain weight [
4]. In this study,
qGL2 and
qTGW2 were co-located at the same locus and positively regulated grain length and 1000-grain weight. The interval of
qGL2 and
qTGW2 contains the
GS2/
GL2 locus, which indicates that the candidate genes of
qGL2 and
qTGW2 are likely to be
GS2, but further confirmation is needed.
GS3,
GW5,
GW2 are the main genes affecting grain shape [
3,
6,
7], but no grain shape-related QTL were found at these loci, which could be that the function of these genes did not differ between parents. In addition, some new QTL that affecting grain shape and 1000-grain weight were found on chromosomes 6, 8 and 10, but the functions of these QTL need to be further verified.
Chalkiness is caused by an inhomogeneous arrangement of starch granules and proteomes in the endosperm, which has a great negative effect on rice quality.
Chalk5 controls the formation of chalkiness in the endosperm by affecting the formation of protein bodies [
15].
FLO4,
FLO5,
FLO2 regulate chalkiness by affecting starch synthesis [
11,
12,
13]. Up to now, no chalkiness gene has been cloned on chromosome 6. In this study, some QTL with significant effect on chalkiness were found on chromosome 6, most of which were co-mapped in the interval of 3.3Mb-4.2Mb and 5.3Mb-6.5Mb. This result laid a foundation for the discovery of chalkiness genes on chromosome 6. The appearance quality of rice is very important because rice with less chalkiness has higher economic value and is more popular. Although some genes affecting grain shape and chalkiness have been found, the regulatory networks need to be further explored. In this study, 15 QTL related to grain shape and chalkiness were mapped. In addition,
qWBR6.1 and
qWCR6/
qCR6 were found had great effect on chalkiness. Our research provides a wealth of QTL resources for rice quality improvement. Simultaneously, it also provides a foundation for fine mapping related functional genes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. and Y.H.; methodology, Y.W., D.X. and Y.H.; investigation, Y.W., W.D., H.S., M.Z.; resources, Y.H., D.X., G.G. and Q.Z.; writing-original draft preparation, Y.W.; writing-review and editing, Y.W., Y.H. and H.S.; supervision, Y.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U21A20211), the Ministry of Science and Technology (2021YFF1000200), the science and technology major program of Hubei Province (2021ABA011) and China Agriculture Research System (CARS-01-01).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the support from National Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement, Huazhong Agricultural University.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Huang, R. , Jiang, L., Zheng, J., Wang, T., Wang, H., Huang, Y., Hong, Z. Genetic bases of rice grain shape: so many genes, so little known. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D. , Zhang, C., Li, Q., Liu, Q. Genetic control of grain appearance quality in rice. Biotechnol Adv. 2022, 60, 108014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C. , Xing, Y., Mao, H., Lu, T., Han, B., Xu, C., Li, X., Zhang, Q. GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P. , Zhang, W., Wang, Y., He, Q., Shu, F., Liu, H., Wang, J., Wang, J., Yuan, L., Deng, H. OsGRF4 controls grain shape, panicle length and seed shattering in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2016, 58, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, D. , Zhou, H., Liu, R., Dan, W., Li, P., Wu, B., He, Y. GL3. 3, a novel QTL encoding a GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase, epistatically interacts with GS3 to produce extra-long grains in rice. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 754–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X, Huang, W. , Shi, M., Zhu, M., Lin, H. A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, J. , Gu, S., Wan, X., Gao, H., Guo, T., Su, N., Lei, C., Zhang, X., Cheng, Z., Guo, X., Wang, J., Jiang, L., Zhai, H., Wan, J. Isolation and initial characterization of GW5, a major QTL associated with rice grain width and weight. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y. , Fan, C., Xing, Y., Jiang, Y., Luo, L., Sun, L., Shao, D., Xu, C., Li, X., Xiao, J., He, Y., Zhang, Q. Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1266–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S. , Wu, K., Yuan, Q., Liu, X., Liu, Z., Lin, X., Zeng, R., Zhu, H., Dong, G., Qian, Q. Control of grain size, shape, and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y. , Miao, J., Gu, H., Peng, X., Leburu, M., Yuan, F., Gu, H., Gao, Y., Tao, Y., Zhu, J., Gong, Z., Yi, C., Gu, M., Yang, Z., Liang, G. Natural Variations in SLG7 Regulate Grain Shape in Rice. Genetics 2015, 201, 1591–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.G. , Park, S., Matsuoka, M., An, G. White-core endosperm floury endosperm-4 in rice is generated by knockout mutations in the C4-type pyruvate orthophosphate dikinase gene (OsPPDKB). Plant J. 2005, 42, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryoo, N. , Yu, C., Park, C., Baik, M., Park, M., Cho, H., Bhoo, H., An, G., Hahn, R., Jeon, S. Knockout of a starch synthase gene OsSSIIIa/Flo5 causes white-core floury endosperm in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, K.C. , Kusano, H., Koizumi, K., Yamakawa, H., Hakata, M., Imamura, T., Fukuda, M., Naito, N., Tsurumaki, Y., Yaeshima, M., Tsuge, T., Matsumoto, K., Kudoh, M., Itoh, E., Kikuchi, S., Kishimoto, N., Yazaki, J., Ando, T., Yano, M., Aoyama, T., Sasaki, T., Satoh, H., Shimada, H. A Novel Factor FLOURY ENDOSPERM2 Is Involved in Regulation of Rice Grain Size and Starch Quality. Plant Cell. 2010, 22, 3280–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y. , Li, S., Jiao, G., Sheng, Z., Wu, Y., Shao, G., Xie, L., Peng, C., Xu, J., Tang, S., Wei, X., Hu, P. OsPK2 encodes a plastidic pyruvate kinase involved in rice endosperm starch synthesis, compound granule formation and grain filling. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1878–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y. , Fan, C., Xing, Y., Yun, P., Luo, L., Yan, B., Peng, B., Xie, W., He, Y., Zhang, Q. Chalk5 encodes a vacuolar H+-translocating pyrophosphatase influencing grain chalkiness in rice. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B. , Yun, P., Zhou, H., Xia, D., Gu, Y., Li, P., Yao, J., Zhou, Z., Chen, J., He, Y. Natural variation in WHITE-CORE RATE 1 regulates redox homeostasis in rice endosperm to affect grain quality. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 1912–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).