1. Introduction
Passively continuous-wave mode-locked (CWML) solid-sate lasers with saturable absorbers [
1,
2,
3] have been widely used in various applications of time-resolved measurements, material processing, and other precise spectroscopies [
4,
5,
6]. Saturable absorbers, such as semiconductor saturable absorber mirror (SESAM) and carbon nanotube, can be deliberately introduced into the laser cavity to self-start mode locking by providing nonlinearity [
7,
8,
9]. Understanding the phase locking process of a large number of longitudinal cavity modes is greatly helpful for designing passively mode-locked lasers and valuable for finding the novel applications of ultrafast laser sources [
10,
11,
12,
13]. Several theoretical models have been proposed to explain the observed threshold power for the self-starting of the mode locking and to explore the buildup dynamics from the Ginzburg-Landau equation [
14,
15]. In theoretical models, the initial optical wave is generally assumed to be a single-pulse fluctuation residing on a continuous background [
16,
17,
18,
19]. However, it has been recently found that the initial multiple-pulse phase and pulse-splitting phase last for a long time in the buildup dynamics in self-starting of soliton mode-locked fiber lasers [
20]. Besides, the relaxation oscillations were observed to speed up the starting process in dissipative-soliton fiber lasers [
21]. In contrast, it is worth noting that there are no previous experimental reports on the transient process of initial pulse evolutions and the role of relaxation oscillations in passively CWML solid-state lasers. Therefore, exploring the transient pulse evolution in real-time measurements is important for understanding the starting dynamics of passively CWML solid-state lasers [
22,
23,
24,
25].
In this work, we perform the real-time measurement to explore the starting dynamics of diode-pumped passively CWML laser. The laser cavity is designed to contain only three components of a Nd:YVO4 crystal, a SESAM device, and a focusing lens to eliminate the unwanted influence on the buildup dynamics. A fast photodetector and a digital oscilloscope with 40 Giga sampling rate are used to directly measure the transient behaviors in various expanded time scales. Experimental results reveal that the laser output in the buildup process consists of a series of passively Q-switched pulses followed with a damped relaxation oscillation prior to the stable mode locking. The number of passively Q-switched pulses and the damping time of the relaxation oscillation decrease with increasing the pump power. Furthermore, the temporal traces inside the first several Q-switched envelopes clearly manifest the transient evolution of the laser output from a random set of spikes to the emergence of a single clean pulse within each round-trip period. It is indicated that the buildup time for the complete phase-locking is significantly shorter than that for the stable mode-locking. To the best of our knowledge, this result is the first direct observation for the buildup dynamics of a passively mode-locked solid-state laser with SESAM. The present real-time measurement is believed to provide useful insights into applications with temporal modulation of the pump intensity.
2. Experimental setup
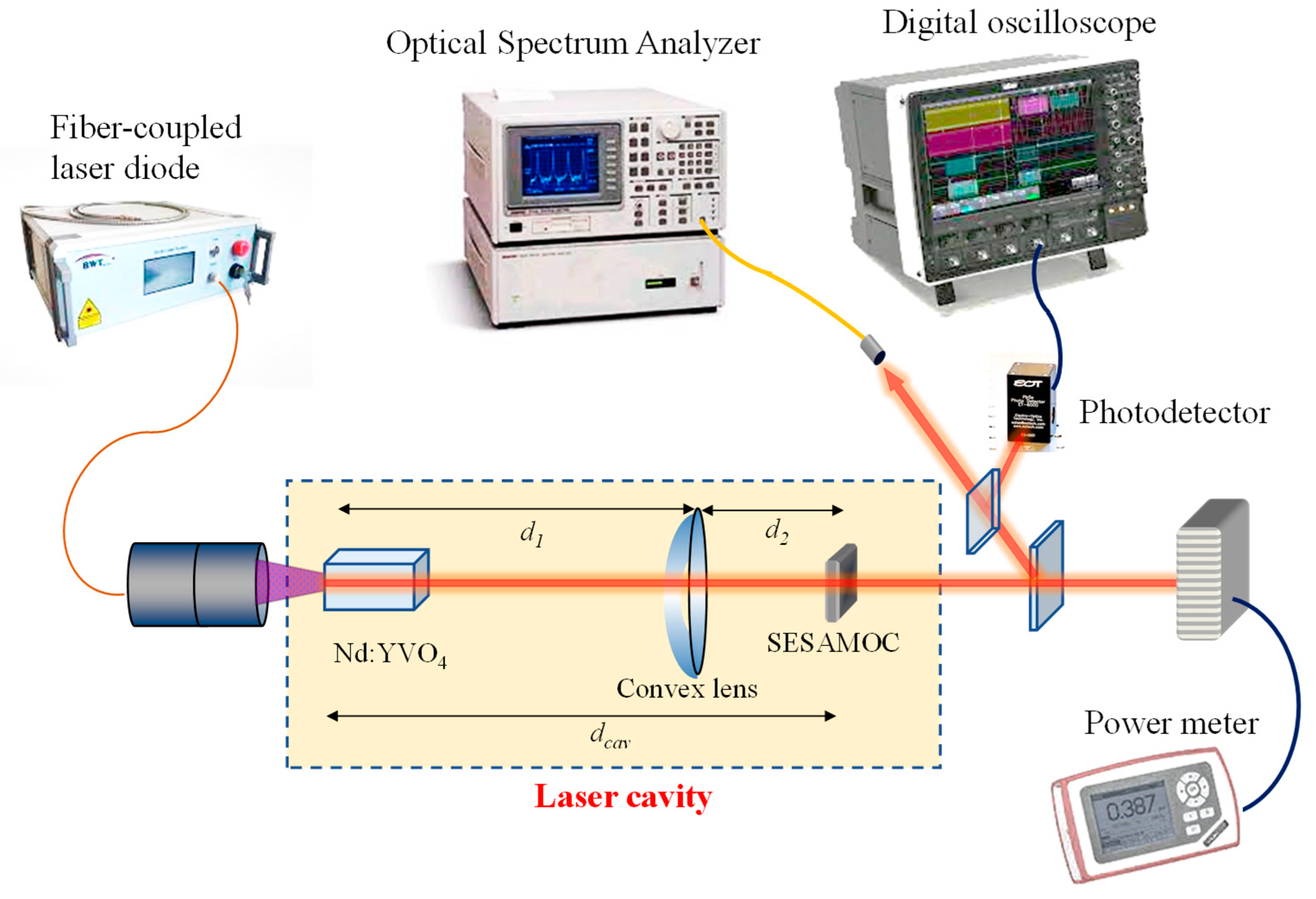
Figure 1 shows the experimental setup of passively mode-locked solid-state laser for exploring the buildup dynamics in the turn-on process. To investigate the transient dynamics purely arising from the gain medium and saturable absorber, the laser cavity was designed to comprise only three components of a Nd:YVO
4 crystal, a SESAM device and a focusing lens. The pump source was a fiber-coupled semiconductor laser with wavelength at 808 nm, where the fiber had a core diameter of 200 μm and a numerical aperture of 0.16. The gain medium was a
a-cut 0.35 at.% Nd:YVO
4 crystal with a dimension of 3 × 3 × 8 mm
3. One facet of the Nd:YVO
4 crystal was a plane surface that was coated as a rear mirror with high reflection (HR) at 1064 nm (reflectance > 99.8%) and high transmission at 808 nm (transmittance > 95%). The other facet of the laser crystal with a wedged angle of 0.5° for avoiding the internal etalon effect had an anti-reflection (AR) coating at 808 nm and 1064 nm (reflectance < 0.2 %). The Nd:YVO
4 crystal wrapped with indium foil was mounted in water-cooled copper block with temperature held at 20
oC. The saturable absorber was a SESAM device that was simultaneously designed as an output coupler, abbreviated as SESAMOC [
4,
5]. The SESAM device was monolithically grown on an undoped GaAs substrate with the method of metalorganic chemical vapor deposition. The SESAMOC was composed of 10 pairs distributed Bragg reflectors (DBRs) that was formed by AlAs/GaAs quarter-wavelength layers with the effective reflectivity of approximately 96.5 % at 1064 nm. The absorbing material of the SESAMOC was made of two 8-nm In
0.34Ga
0.66As quantum well that provided an effective modulation depth of 0.8 % with the saturable fluence of 100 μJ∕cm
2. Furthermore, the back side of the 350-μm GaAs substrate was coated for AR at 1064 nm (reflectance < 0.5 %). The SASEMOC device was soldered on a copper holder with temperature maintained at 20
oC. A focusing lens with a focal length of
f = 100 mm was used to satisfy the criterion of self-starting CWML cavity. The both sides of the focusing lens were coated for AR at 1064 nm (reflectance < 0.5 %). Experimental optical spectra were measured using a Michelson interferometer-based Fourier spectrometer (Advantest Q8347) with a resolution up to 0.003 nm. Temporal characteristics of mode-locked pulses were measured using a high-speed InGaAs photodetector (Electro-optics Technology Inc. ET-3500 with rise time 35 ps), whose output signal was recorded using a digital oscilloscope (Teledyne LeCroy, Wave Master 820Zi-A) with a 20 GHz electrical bandwidth and the sampling rates of 25 ps. Besides, the output signal detected by the photodetector was also connected to an RF spectrum analyzer (Agilent, 8563EC) with a bandwidth of 26.5 GHz to measure the output power spectrum. The second-order autocorrelation traces were measured using a commercial autocorrelator (APE pulse check, Angewandte Physik and Elektrnic GmbH) to analyze the effective pulse width.
3. Analysis of cavity mode sizes
As shown in Fig. 1,
d1 is the effective optical length between the HR side of the laser crystal and the focusing lens, and
d2 is the effective optical length between the focusing lens and the output plane of the SESAMOC. By using the ABCD matrix method, the cavity mode radius at the HR side of Nd:YVO
4 crystal can be derived as
where
l is the laser wavelength. On the other hand, the cavity mode radius at the output plane of the SESAMOC can be found to be
In experiment, the distances of d1 and d2 are designed be 460 and 125 mm, respectively. Substituting the values of f, d1, and d2 into Eqs. (1) and (2), the mode radii w1 and w2 can be calculated to be approximately 203 and 53 μm, respectively. The optical length of the laser cavity is approximately 585 mm corresponding to the repetition rate of 256 MHz.
4. Results and discussion
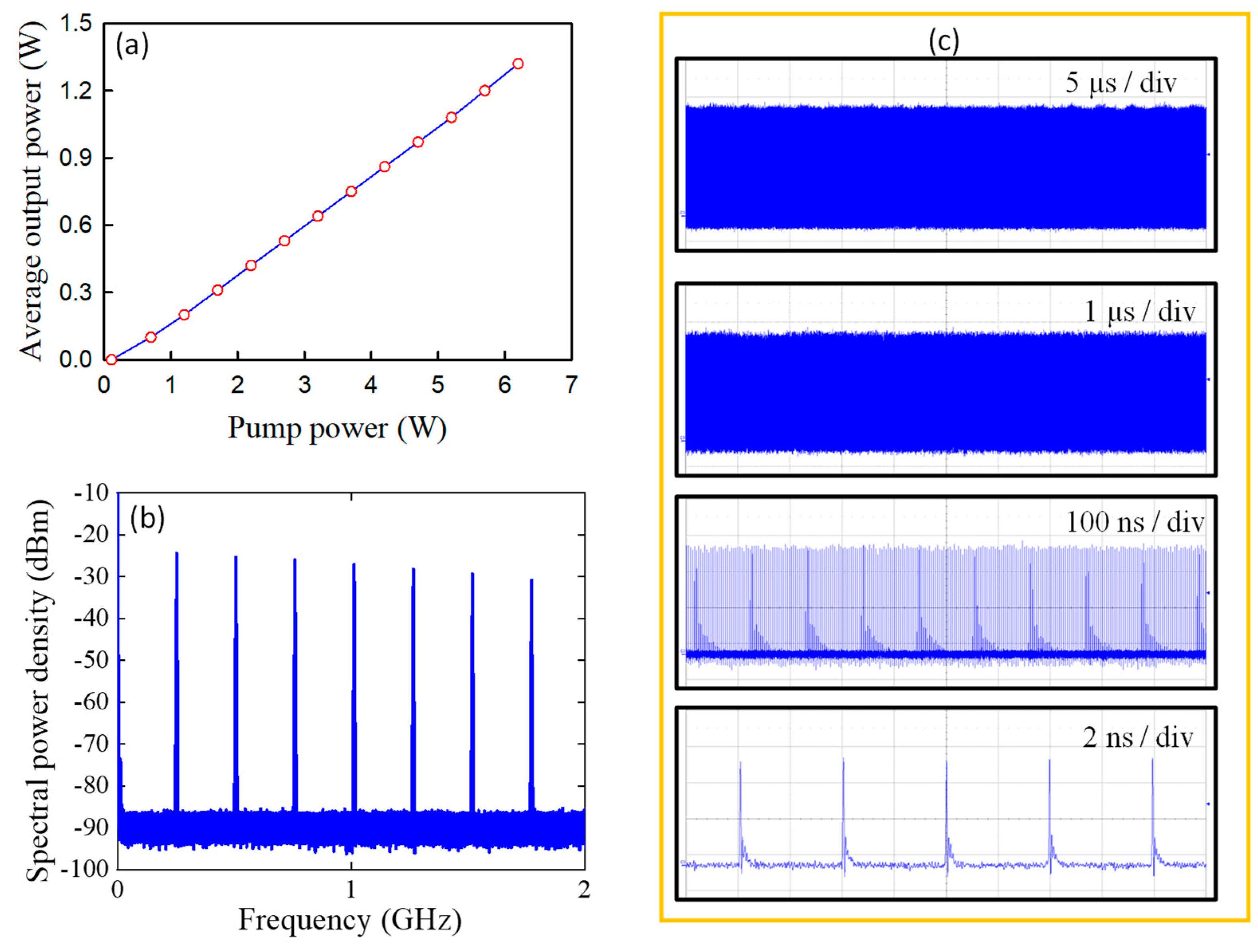
Figure 2(a) shows the average output power versus the pump power for the laser operation. At a pump power of 6.3 W, the output power for stable passive mode-locking is approximately 1.3 W, corresponding to the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 20.6 %. The pump power for lasing threshold was found to be around 0.1 W, whereas pump power as high as 1.2 W was required for stable mode-locking.
Figure 2(b) shows the measured power spectral density at a pump power of 3.0 W for a representative case of the experimental results. The power spectral density reveals a signal-to-noise ratio higher than 60 dB, indicating the excellent quality of stable mode locking.
Figure 2(c) shows the measured oscilloscope traces at four different time spans ranging from 20 ns to 50 μs to display the good stability and CW mode locking. From the autocorrelation trace, the real pulse duration of CW mode locking was estimated to be approximately 20 ps based on the assumption of the Gaussian-shaped profile.
To explore the buildup dynamics, the pump source of the laser diode was electronically operated at a pump duration of 500 μs with a pump frequency of 1 kHz. The pump-on duration of 500 μs is sufficiently long to observe the pulse evolution. Besides, the pump-off cycle of 500 μs is also long enough to clean up the residual population density, since the upper-state lifetime
tf is approximately 90 μs. The laser output was directly measured by using a digital oscilloscope with 40 Giga sampling rate with a fast photodetector. Based on thorough experimental observations, it is confirmed that under the optimal cavity alignment the buildup process of the mode locking mainly depended on the pumping strength, rather insensitive to environmental perturbations, such as air flow, acoustic noise, and thermal variations. Consequently, experimental results could be utterly reproducible.
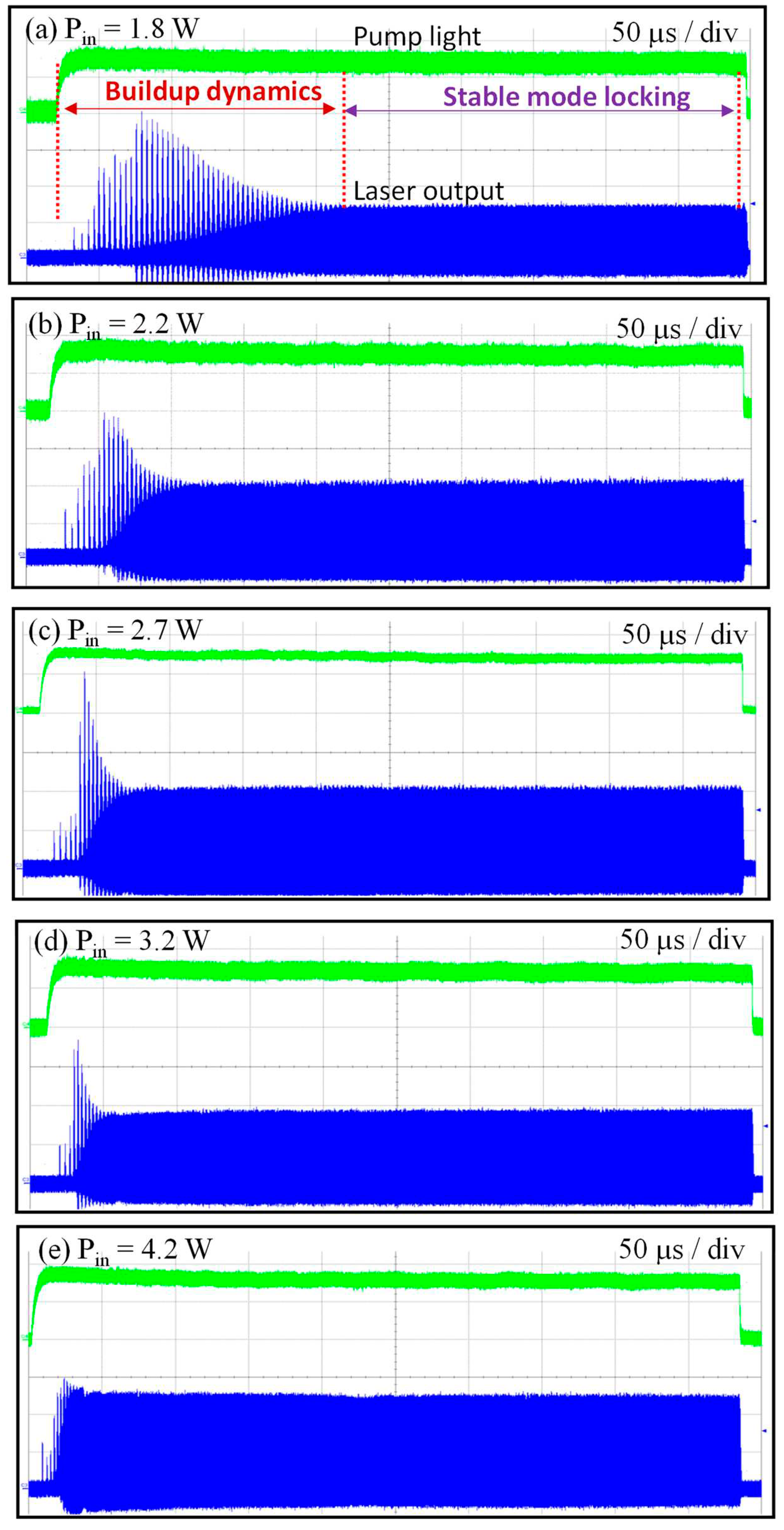
Figure 3a–e show the oscilloscope traces for the transient turn-on behavior measured at different pump powers in the time span of 500 ms. The transient feature of the buildup process can be found to comprise a series of passively Q-switched pulses followed with damped relaxation oscillations. The number of passively Q-switched pulses can be clearly seen to decrease with increasing the pump strength. From the results shown in Fig. 3, the buildup time for the stable mode-locking,
tML, can be identified as the duration from the turn-on time of the pump power to the end of the damped relaxation oscillation. Referring to
tf = 90 ms, the buildup time
tML decreases from a few times to a fraction of the upper-level lifetime for the pump power increasing from 1.5 to 5.0 W.
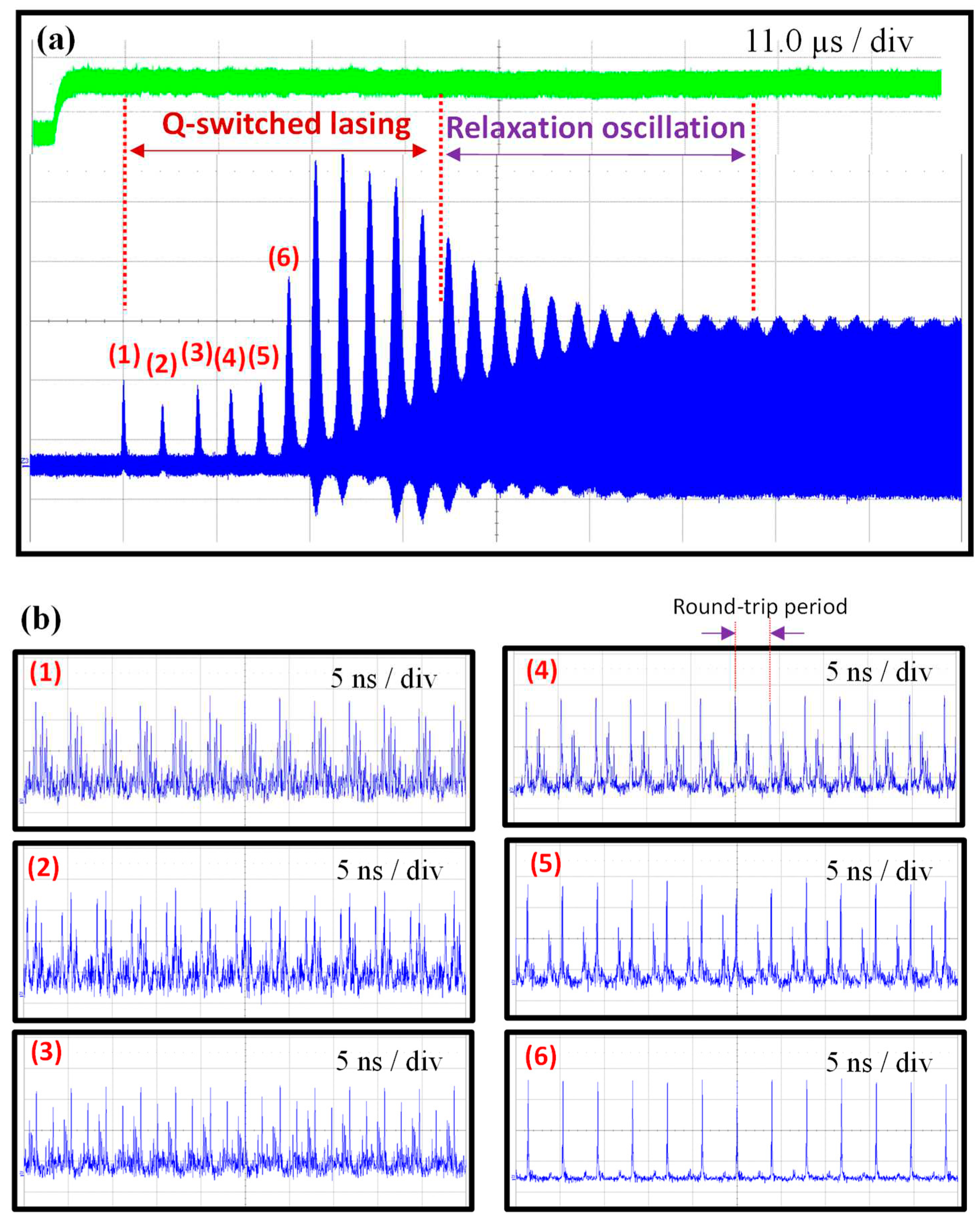
The formation process for the phase locking in the transient turn-on dynamics can be comprehended from the temporal characteristics inside the passively Q-switched envelopes.
Figure 4(a) shows the oscilloscope traces for the transient dynamics measured at a pump power of 2.6 W in a time span of 55 μs. It can be found that each passively Q-switched pulse is approximately a fraction of a microsecond wide and spaced a few microseconds apart. After growing to a maximum, the Q-switched pulses are gradually transformed into a quasi-sinusoidal relaxation oscillation, then damping to the stable mode locking. The phase locking process between lasing longitudinal modes in the buildup dynamics can be further explored by looking into the temporal behaviors inside the Q-switched envelopes. The six plots with labels (1)-(6) in Fig. 4(b) show the temporal traces in a time span of 50 ns measured from the intensities inside the first six Q-switched envelopes shown in Fig. 4(a), respectively. From the left-hand column of Fig. 4(b) for the first three Q-switched pulses, the laser output can be seen to consist not of single clean pulses but of a random set of spikes, essentially a noise-like feature, with the spikes distributed throughout the entire round-trip period. Nevertheless, it can be found that the signal output is still strictly periodic in time, that is, it repeats exactly after one cycle. The signature of random spikes within each round-trip cycle indicates that the laser output consists of a large number of longitudinal modes with random phases, regardless of whether the amplitude distribution is random or more orderly. Precisely, the laser output in the first three Q-switched pulses can be called a case of mode coupling that does not achieve the phase locking. From the right-hand column of Fig. 4(b) for the Q-switched pulses with labels (4)-(6), the transient evolution of phase locking can be clearly observed. From the plot (6) in Fig. 4(b), the laser output has already displayed a single clean pulse within each round-trip period. In other words, the lasing longitudinal modes have been arrayed all in phase to reach a phase-locked situation. The buildup time for the complete phase-locking,
tPL, can be ascertained as the duration from the turn-on time of the pump power to the emergence of a single clean pulse within each round-trip period.
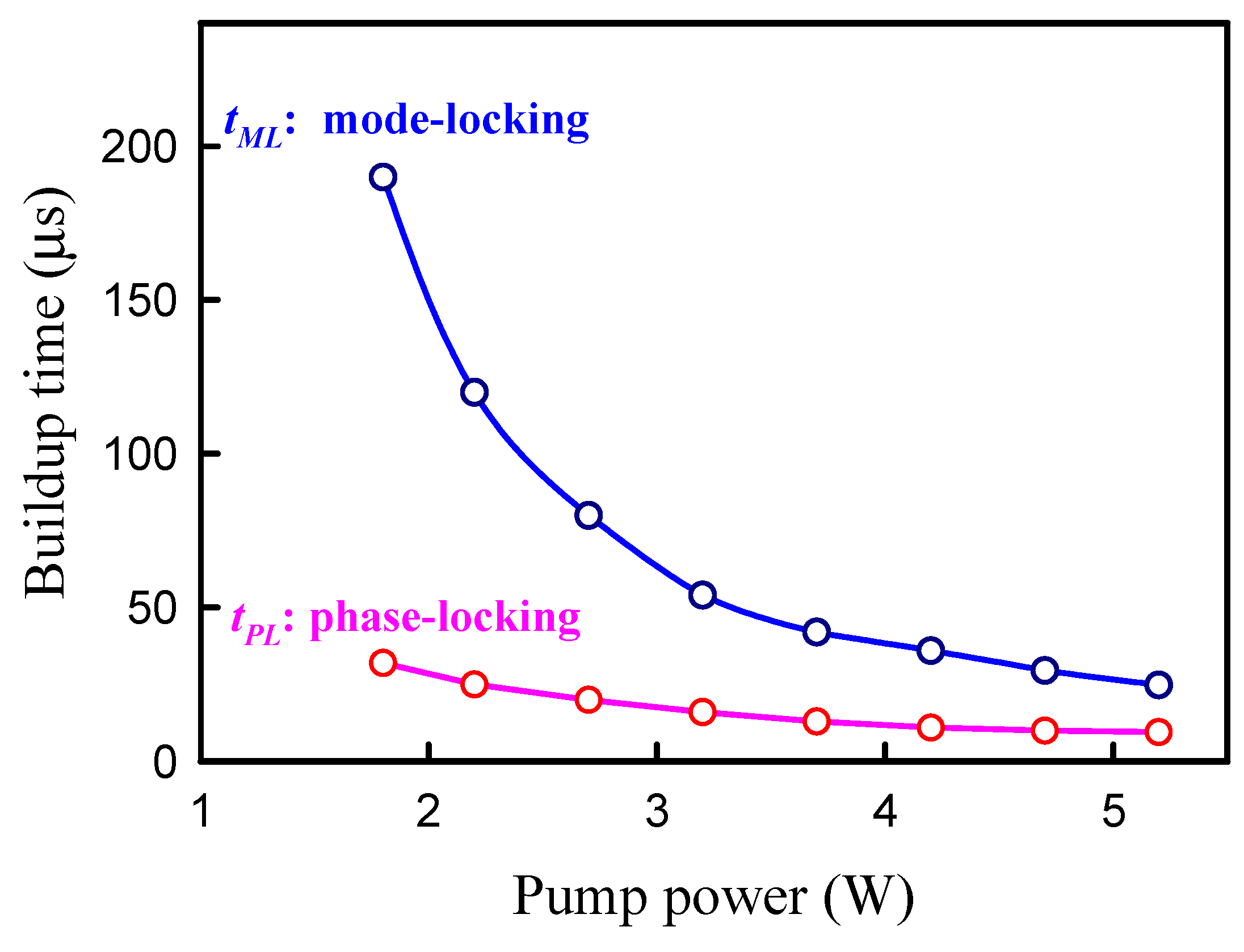
Figure 5 shows the experimental results for the buildup times
tPL and
tML versus the pump power. Clearly, the buildup time
tPL for the complete phase-locking is significantly shorter than the time
tML for the stable mode-locking.
5. Conclusions
In summary, we have explored the buildup dynamics of diode-pumped passively mode-locked solid-state laser by means of the real-time measurement with temporal sampling rate up to 40 GHz. We have designed the laser cavity comprising only three components to ensure the transient dynamics purely arising from the gain medium and saturable absorber. The laser output in the buildup process was observed to exhibit a number of passively Q-switched pulses followed with a damped relaxation oscillation prior to the stable mode locking. The buildup time for the stable mode locking was found to decrease from a few times to a fraction of the upper-level lifetime for the pump power increasing from slightly to far above lasing threshold. Furthermore, we have experimentally confirmed that the laser output has already displayed single clean mode-locked pulses inside the first several Q-switched envelopes, which indicates that the buildup rate for the complete phase-locking is substantially faster than that for the stable mode-locking. It is believed that the present real-time exploration can offer important information for practical applications with temporal modulation of the pump intensity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.-W.C. and Y.-F.C.; validation, P.-W.C. and H.-C.L.; formal analysis, P.-W.C. and Y.-F.C.; resources, Y.-H.H. and X.-W.C.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.-F.C.; writing—review and editing, P.-W.C., H.-C.L. and Y.-F.C.; supervision, Y.-F.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (contract number 109-2112-M-009-015-MY3).
Data Availability Statement
All of the data reported in the paper are presented in the main text. Any other data will be provided on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, C.J.; Wai, P.K.A.; Menyuk, C.R. Self-starting of passively mode-locked lasers with fast saturable absorbers. Opt. Lett. 1995, 20, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haus, H.A. Mode-Locking of Lasers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2000, 6, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Crespo, J.M.; Akhmediev, N.; Town, G. Continuous-wave versus pulse regime in a passively mode locked laser with a fast saturable absorber. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2002, 19, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picqué, N.; Hänsch, T.W. Frequency comb spectroscopy. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, K.C.; Gandhi, H.H.; Mazur, E.; Sundaram, S.K. Ultrafast laser processing of materials: a review. Adv. Opt. Photon. 2015, 7, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diddams, S.A.; Vahala, K.; Udem, T. Optical frequency combs: Coherently uniting the electromagnetic spectrum. Science 2020, 369, eaay3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, U. Recent developments in compact ultrafast lasers. Nature 2003, 424, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernysheva, M.; Rozhin, A.; Fedotov, Y.; Mou, C.; Arif, R.; Kobtsev, S.M.; Dianov, E.M.; Turitsyn, S.K. Carbon nanotubes for ultrafast fibre lasers. Nanophotonics 2017, 6, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafailov, W.S.E.U.; Cataluna, M.A. Mode-locked quantum-dot lasers. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herink, G.; Jalali, B.; Ropers, C.; Solli, D.R. Resolving the build-up of femtosecond mode-locking with single-shot spectroscopy at 90 MHz frame rate. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cui, Y. Revealing the behavior of soliton buildup in a mode-locked laser. Adv. Photon. 2019, 1, 016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pang, M. Revealing the buildup dynamics of harmonic mode-locking states in ultrafast lasers. Laser Photon. Rev. 2019, 13, 1800333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Popa, D.; Akhmediev, N. Revealing the Transition Dynamics From Q Switching to Mode Locking in a Soliton Laser. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 093901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, M.; Gat, O. Pulse growth dynamics in laser mode locking. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 011801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunov, I.M.; Georgiev, Z.D.; Arabadzhiev, T.N. Transitions of stationary to pulsating solutions in the complex cubic-quintic Ginzburg-Landau equation under the influence of nonlinear gain and higher-order effects. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 97, 052215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haus, H.A.; Ippen, E.P. Self-starting of passively mode-locked lasers. Opt. Lett. 1991, 16, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausz, F.; Brabec, T.; Spielmann, Ch. Self-starting passive mode locking. Opt. Lett. 1991, 16, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausz, F.; Brabec, T. Passive mode locking in standing-wave laser resonators. Opt. Lett. 1993, 18, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, J. Starting dynamic, self-starting condition and mode-locking threshold in passive, coupled-cavity or Kerr-lens mode locked solid-state lasers. Opt. Comm. 1993, 98, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L.; Cao, T.; Qin, X.; Ning, H.; Yan, J.; Hu, K.; Guo, Z.; Peng, J. Optimal conditions for self-starting of soliton mode-locked fiber lasers with a saturable absorber. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 2376–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ouzounov, D.G.; Wise, F.W. Starting dynamics of dissipative-soliton fiber laser. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 2403–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Liu, R.; Zhao, S.; Yang, K.; Li, D.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y. Simulation of the passively mode-locked laser with a SESAM. Optik 2012, 123, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waritanant, T.; Major, A. High efficiency passively mode-locked Nd:YVO4 laser with direct in-band pumping at 914 nm. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 12851–12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waritanant, T.; Major, A. Discretely selectable multiwavelength operation of a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror mode-locked Nd:YVO4 laser. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 3331–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Liu, X.; Song,Y. ; Wang, C.; Cao, M.; Yan, A.; Wang, Z. LD end-pumped Nd: YVO4 high energy high beam quality 1064 nm picosecond laser with a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror. Optik 2018, 175, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).