Submitted:
25 June 2023
Posted:
26 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Pear Fruit Samples
2.2. Near-Infrared Spectral Data Acquisition

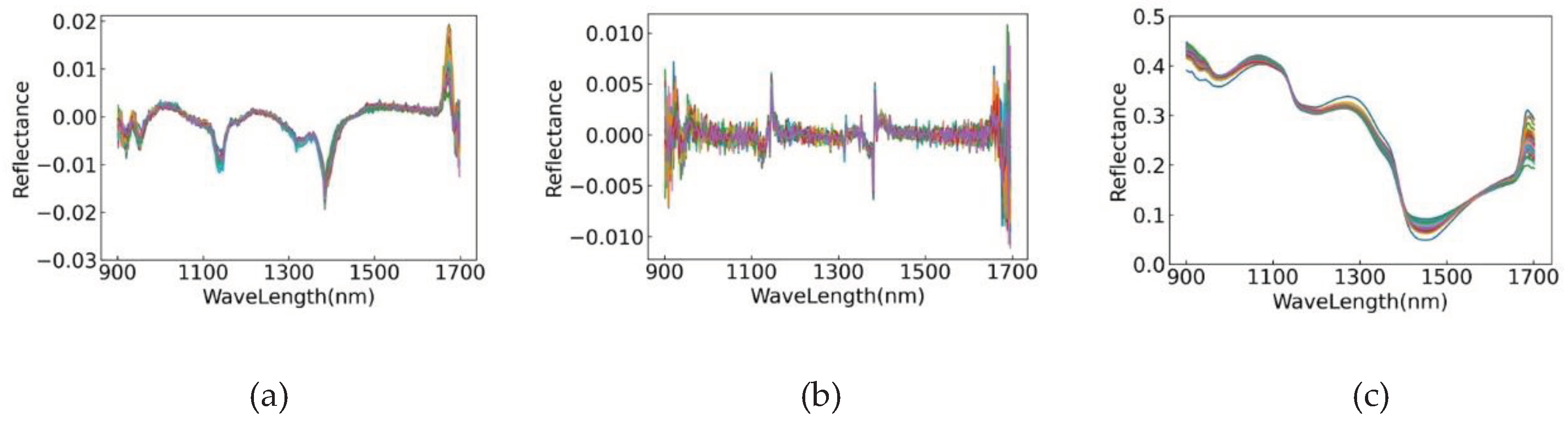
2.3. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Data Preprocessing
2.4. Characteristic Wavelength Extraction
2.5. Detection of Phosphorus Content in Pear Pulp and Peel
2.6. Establishment of Prediction Models for Phosphorus Content in the Pulp and Peel of 'Huangguan' Pear
2.7. Model Effect Evaluation Indicators
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Phosphorus Content Detection in the Pulp and Peel of 'Huangguan' Pear
3.2. Original Spectral Data Analysis
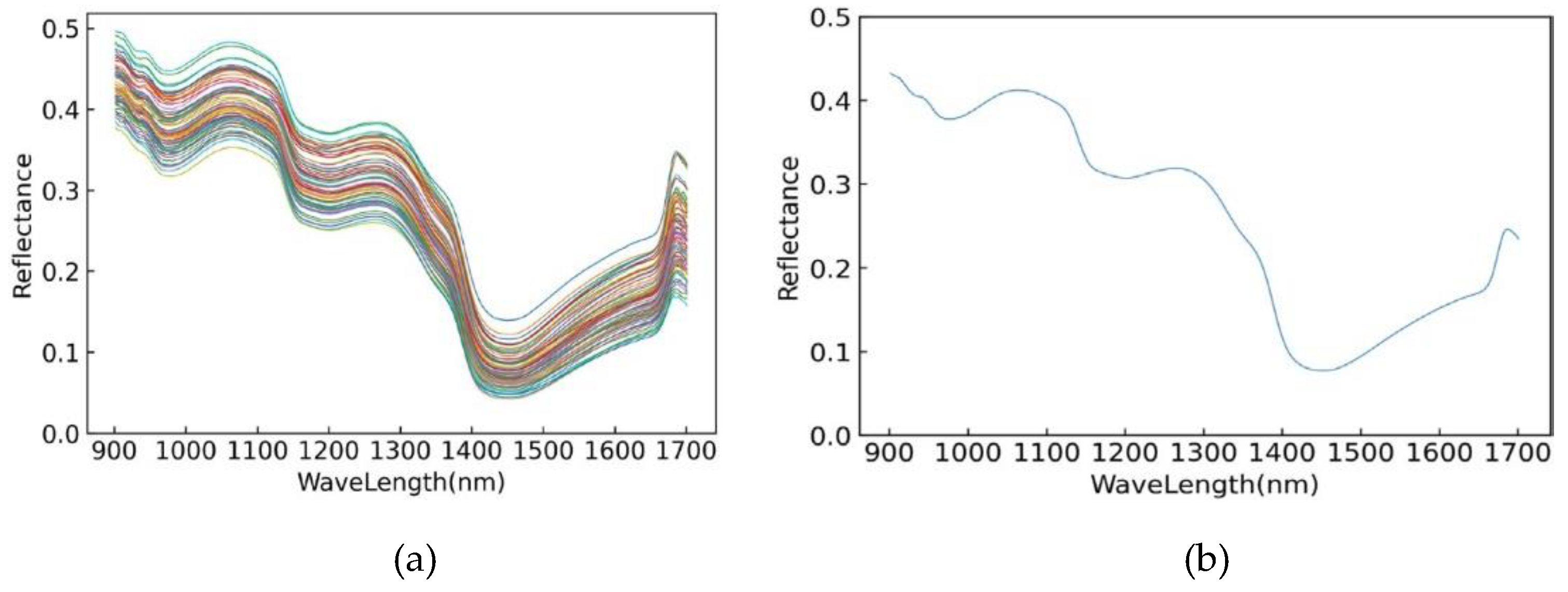
3.3. Analysis of Spectral Data Preprocessing Results
3.4. Full-Band Modelling
3.4.1. Full-Band Modelling for Pear Pulp
3.4.2. Full-Band Modelling for Pear Peel
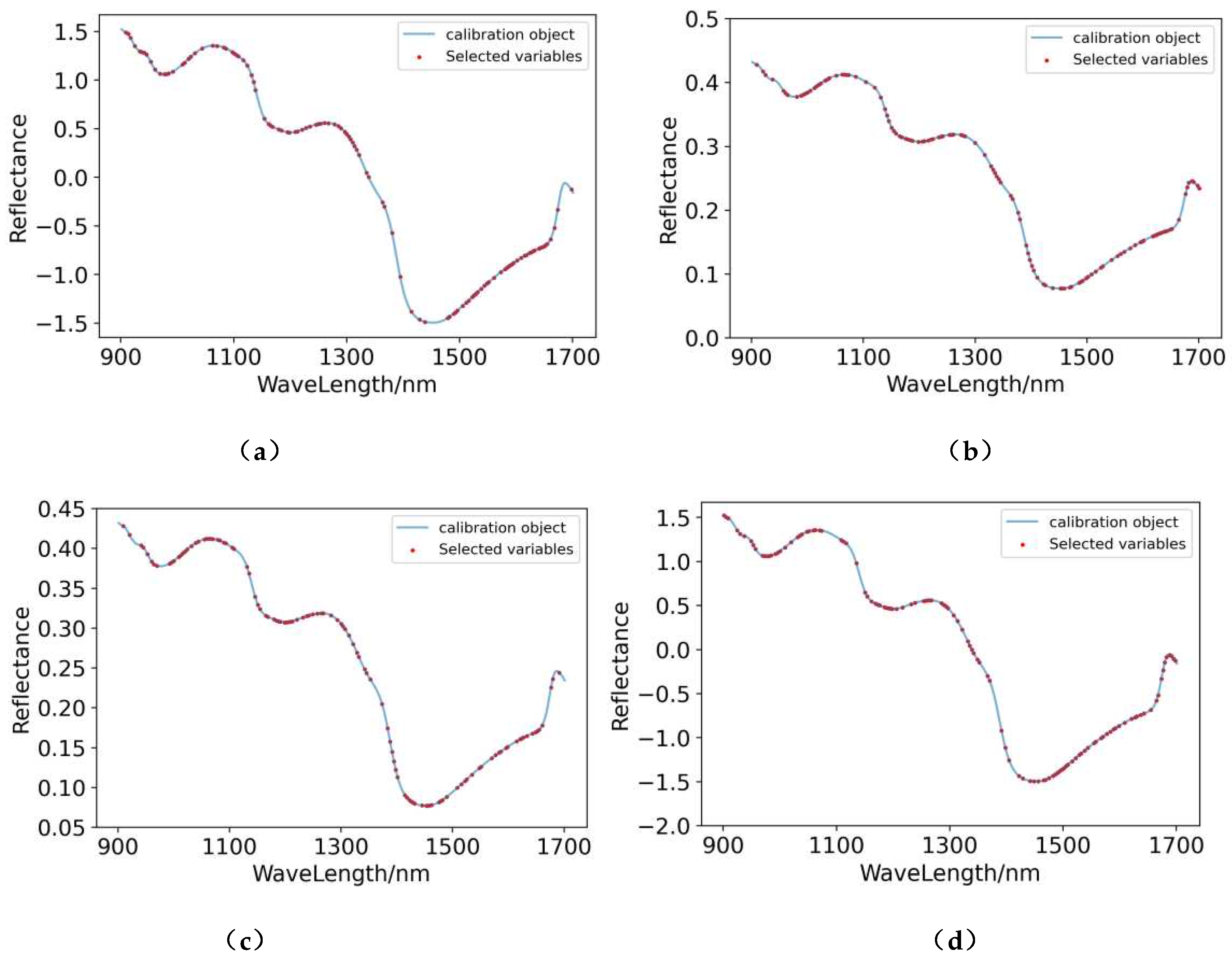
3.5. Extraction of Characteristic Wavelengths
3.5.1. Extraction of Characteristic Wavelengths for Pear Pulp
| Feature Extraction Methods | Models | Extract the Number of Characteristic Wavelengths | Specific Characteristic Band/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA | SNV-PLSR | 114 | 909.36, 913.25, 917.14, 924.89, 933.92, 937.78, 941.64, 945.50, 953.19, 960.87, 969.80, 977.45, 981.26, 985.07, 992.68, 1009.10, 1012.88, 1020.43, 1024.19, 1031.71, 1044.21, 1062.87, 1070.30, 1082.65, 1086.34, 1097.41, 1101.08, 1104.76, 1108.43, 1116.98, 1124.29, 1131.58, 1135.22, 1138.85, 1154.56, 1161.78, 1165.38, 1168.98, 1179.76, 1184.53, 1195.25, 1198.82, 1209.49, 1213.03, 1221.30, 1228.36, 1235.41, 1245.94, 1249.45, 1254.11, 1261.10, 1268.06, 1278.48, 1285.41, 1290.02, 1296.91, 1300.36, 1303.79, 1307.23, 1310.66, 1314.08, 1317.50, 1322.06, 1335.68, 1339.07, 1363.83, 1367.19, 1380.58, 1395.02, 1414.87, 1429.11, 1438.93, 1478.88, 1482.09, 1489.56, 1492.76, 1495.95, 1505.50, 1511.85, 1516.07, 1522.39, 1525.54, 1528.69, 1531.84, 1538.11, 1544.37, 1548.54, 1551.65, 1560.98, 1573.36, 1580.55, 1583.62, 1586.69, 1589.76, 1592.82, 1595.88, 1601.98, 1609.08, 1615.14, 1618.17, 1624.21, 1627.22, 1630.23, 1633.23, 1640.23, 1643.22, 1646.21, 1649.19, 1652.17, 1655.14, 1661.08, 1667.98, 1673.88, 1698.27 |
| MSC-PLSR | 119 | 909.36, 921.02, 924.89, 937.78, 957.03, 960.87, 964.70, 981.26, 988.88, 992.68, 996.48, 1000.27, 1005.32, 1012.88, 1016.66, 1020.43, 1024.19, 1031.71, 1035.47, 1039.22, 1051.68, 1062.87, 1066.58, 1070.30, 1074.01, 1086.34, 1104.76, 1120.63, 1131.58, 1138.85, 1142.48, 1146.11, 1150.94, 1154.56, 1158.17, 1165.38, 1168.98, 1176.17, 1179.76, 1184.53, 1188.11, 1198.82, 1205.93, 1209.49, 1216.58, 1221.30, 1224.83, 1235.41, 1238.92, 1242.44, 1254.11, 1257.61, 1261.10, 1275.02, 1278.48, 1281.95, 1300.36, 1317.50, 1328.87, 1332.28, 1335.68, 1339.07, 1342.46, 1345.85, 1363.83, 1367.19, 1377.24, 1380.58, 1391.69, 1395.02, 1398.34, 1401.65, 1404.96, 1411.57, 1422.55, 1425.83, 1438.93, 1453.04, 1456.28, 1459.52, 1469.22, 1472.44, 1486.36, 1489.56, 1492.76, 1499.14, 1502.32, 1508.68, 1516.07, 1525.54, 1528.69, 1544.37, 1554.77, 1560.98, 1567.18, 1577.47, 1586.69, 1595.88, 1598.93, 1601.98, 1618.17, 1621.19, 1624.21, 1627.22, 1630.23, 1633.23, 1637.23, 1640.23, 1643.22, 1649.19, 1652.17, 1665.02, 1676.82, 1679.76, 1682.70, 1688.55, 1691.47, 1698.27, 1701.18 | |
| SG+MSC-PLSR | 114 | 909.36, 921.02, 941.64, 945.50, 953.19, 960.87, 964.70, 969.80, 992.68, 996.48, 1000.27, 1009.10, 1012.88, 1016.66, 1020.43, 1024.19, 1031.71, 1039.22, 1044.21, 1055.42, 1059.14, 1062.87, 1066.58, 1070.30, 1078.95, 1082.65, 1090.04, 1093.72, 1104.76, 1108.43, 1131.58, 1135.22, 1146.11, 1150.94, 1154.56, 1165.38, 1168.98, 1179.76, 1184.53, 1188.11, 1191.68, 1198.82, 1202.38, 1205.93, 1209.49, 1213.03, 1221.30, 1231.88, 1238.92, 1242.44, 1249.45, 1257.61, 1264.58, 1268.06, 1281.95, 1293.47, 1300.36, 1303.79, 1307.23, 1314.08, 1322.06, 1328.87, 1332.28, 1342.46, 1345.85, 1352.60, 1373.89, 1383.92, 1388.36, 1391.69, 1395.02, 1398.34, 1401.65, 1414.87, 1418.16, 1422.55, 1425.83, 1429.11, 1432.39, 1445.45, 1453.04, 1456.28, 1459.52, 1462.76, 1475.66, 1478.88, 1482.09, 1489.56, 1508.68, 1516.07, 1522.39, 1525.54, 1534.98, 1548.54, 1551.65, 1570.27, 1577.47, 1583.62, 1586.69, 1595.88, 1598.93, 1615.14, 1621.19, 1624.21, 1627.22, 1633.23, 1643.22, 1649.19, 1652.17, 1655.14, 1661.08, 1676.82, 1679.76, 1691.47 | |
| SG+SNV-PLSR | 108 | 905.47, 909.36, 917.14, 924.89, 945.50, 953.19, 960.87, 969.80, 981.26, 985.07, 996.48, 1005.32, 1009.10, 1016.66, 1020.43, 1024.19, 1027.96, 1031.71, 1039.22, 1047.95, 1055.42, 1070.30, 1074.01, 1082.65, 1086.34, 1090.04, 1093.72, 1116.98, 1120.63, 1150.94, 1161.78, 1165.38, 1172.58, 1176.17, 1179.76, 1184.53, 1188.11, 1191.68, 1195.25, 1202.38, 1205.93, 1213.03, 1216.58, 1221.30, 1224.83, 1228.36, 1264.58, 1268.06, 1275.02, 1278.48, 1300.36, 1310.66, 1314.08, 1328.87, 1332.28, 1345.85, 1352.60, 1370.54, 1373.89, 1380.58, 1383.92, 1391.69, 1404.96, 1414.87, 1418.16, 1422.55, 1425.83, 1429.11, 1435.66, 1462.76, 1465.99, 1472.44, 1478.88, 1482.09, 1486.36, 1489.56, 1495.95, 1519.23, 1522.39, 1528.69, 1531.84, 1534.98, 1538.11, 1544.37, 1548.54, 1551.65, 1554.77, 1557.88, 1560.98, 1567.18, 1577.47, 1580.55, 1586.69, 1598.93, 1612.11, 1615.14, 1618.17, 1621.19, 1624.21, 1633.23, 1640.23, 1646.21, 1649.19, 1658.11, 1667.98, 1670.93, 1673.88, 1676.82, 1682.70, 1688.55 |
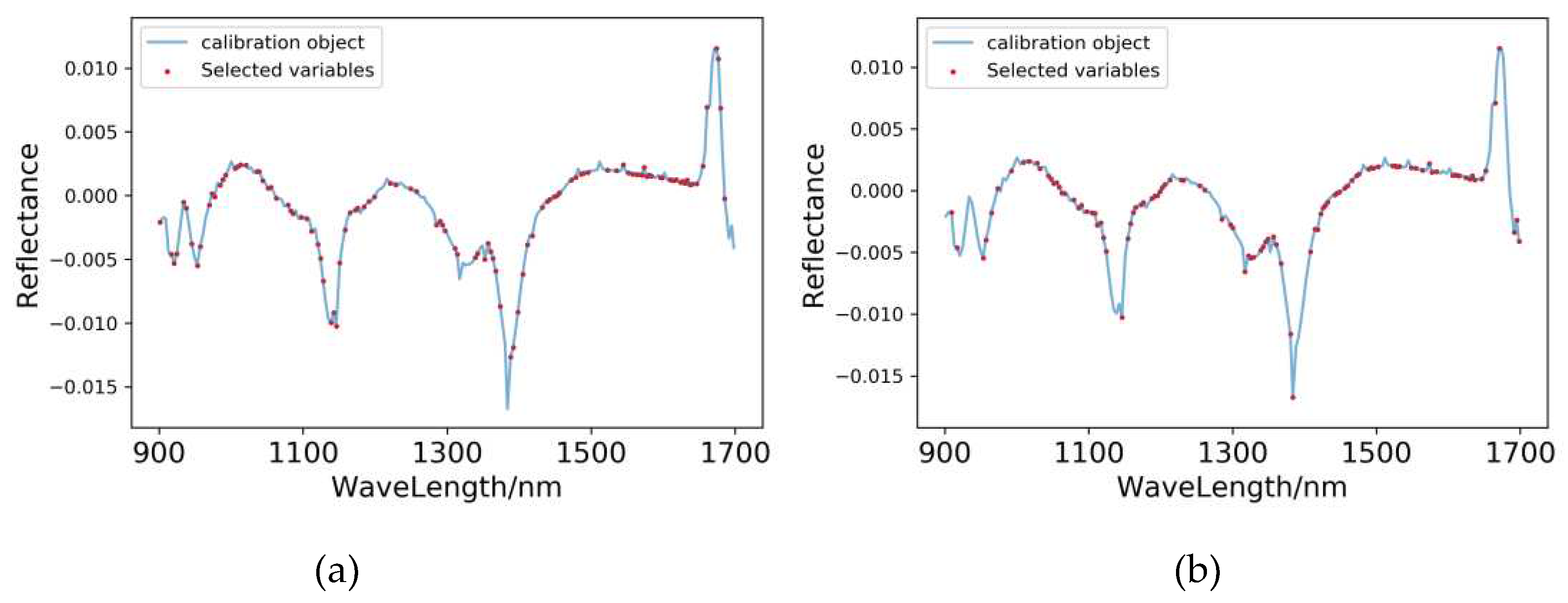
3.5.2. Extraction of Characteristic Wavelengths for Pear Peel
| Feature Extraction Methods | Models | Extract the Number of Characteristic Wavelengths | Specific Characteristic Band/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA | FD-PLSR | 111 | 901.57, 917.14, 924.89, 941.64, 953.19, |
| 957.03, 960.87, 964.70, 969.80, 981.26, | |||
| 988.88, 992.68, 1005.32, 1009.10, 1016.66, | |||
| 1024.19, 1027.96. 1051.68, 1059.14, 1062.87, | |||
| 1070.30, 1074.01, 1078.95, 1090.04, 1101.08, | |||
| 1108.43, 1116.98, 1124.29, 1135.22, 1146.11, | |||
| 1158.17, 1176.17, 1179.76, 1209.49, 1213.03, | |||
| 1216.58, 1221.30, 1249.45, 1257.61, 1261.10, | |||
| 1268.06, 1278.48, 1285.41, 1290.02, 1296.91, | |||
| 1307.23, 1310.66, 1322.06, 1335.68, 1357.10, | |||
| 1363.83, 1367.19, 1373.89, 1377.24, 1380.58 , | |||
| 1395.02, 1401.65, 1404.96, 1408.27, 1418.16, | |||
| 1422.55, 1425.83, 1429.11, 1432.39, 1442.19, | |||
| 1448.70, 1456.28, 1459.52, 1462.76, 1472.44, | |||
| 1489.56, 1492.76, 1495.95, 1499.14, 1505.50, | |||
| 1516.07, 1525.54, 1531.84, 1538.11, 1541.25, | |||
| 1548.54, 1551.65, 1554.77, 1567.18, 1570.27, | |||
| 1583.62, 1592.82, 1609.08, 1615.14, 1618.17, | |||
| 1621.19 ,1624.21, 1627.22, 1637.23, 1643.22, | |||
| 1655.14, 1661.08, 1665.02, 1673.88, 1691.47, | |||
| 1695.36, | |||
| SG+MSC+FD-PLSR | 111 | 909.36, 913.25, 921.02, 930.06, 933.92, | |
| 937.78, 941.64, 953.19, 957.03, 969.80, | |||
| 973.63, 977.45, 981.26, 985.07, 992.68, | |||
| 1016.66, 1020.43, 1027.96, 1035.47, 1039.22, | |||
| 1044.21, 1047.95, 1051.68, 1055.42, 1062.87, | |||
| 1066.58, 1070.30, 1086.34, 1093.72, 1112.10, | |||
| 1116.98, 1120.63, 1124.29, 1138.85, 1150.94, | |||
| 1172.58, 1176.17, 1179.76, 1184.53, 1191.68, | |||
| 1209.49, 1213.03, 1221.30, 1235.41, 1242.44, | |||
| 1245.94, 1249.45, 1254.11, 1264.58, 1268.06, | |||
| 1271.54, 1275.02, 1278.48, 1285.41, 1290.02, | |||
| 1296.91, 1314.08, 1317.50, 1322.06, 1325.47, | |||
| 1339.07, 1357.10, 1360.47, 1367.19, 1383.92, | |||
| 1388.36, 1395.02, 1401.65, 1414.87, 1422.55, | |||
| 1425.83, 1429.11, 1438.93, 1445.45, 1448.70, | |||
| 1456.28, 1462.76, 1472.44, 1482.09, 1489.56, | |||
| 1495.95, 1502.32, 1508.68, 1511.85, 1522.39, | |||
| 1531.84, 1534.98, 1541.25, 1554.77, 1557.88, | |||
| 1567.18, 1577.47, 1589.76, 1592.82, 1609.08, | |||
| 1618.17, 1621.19, 1624.21, 1627.22, 1630.23, | |||
| 1637.23, 1640.23, 1643.22, 1646.21, 1652.17, | |||
| 1661.08, 1665.02, 1670.93, 1673.88, 1676.82, | |||
| 1685.63 |
3.6. Characteristic Wavelength Modelling
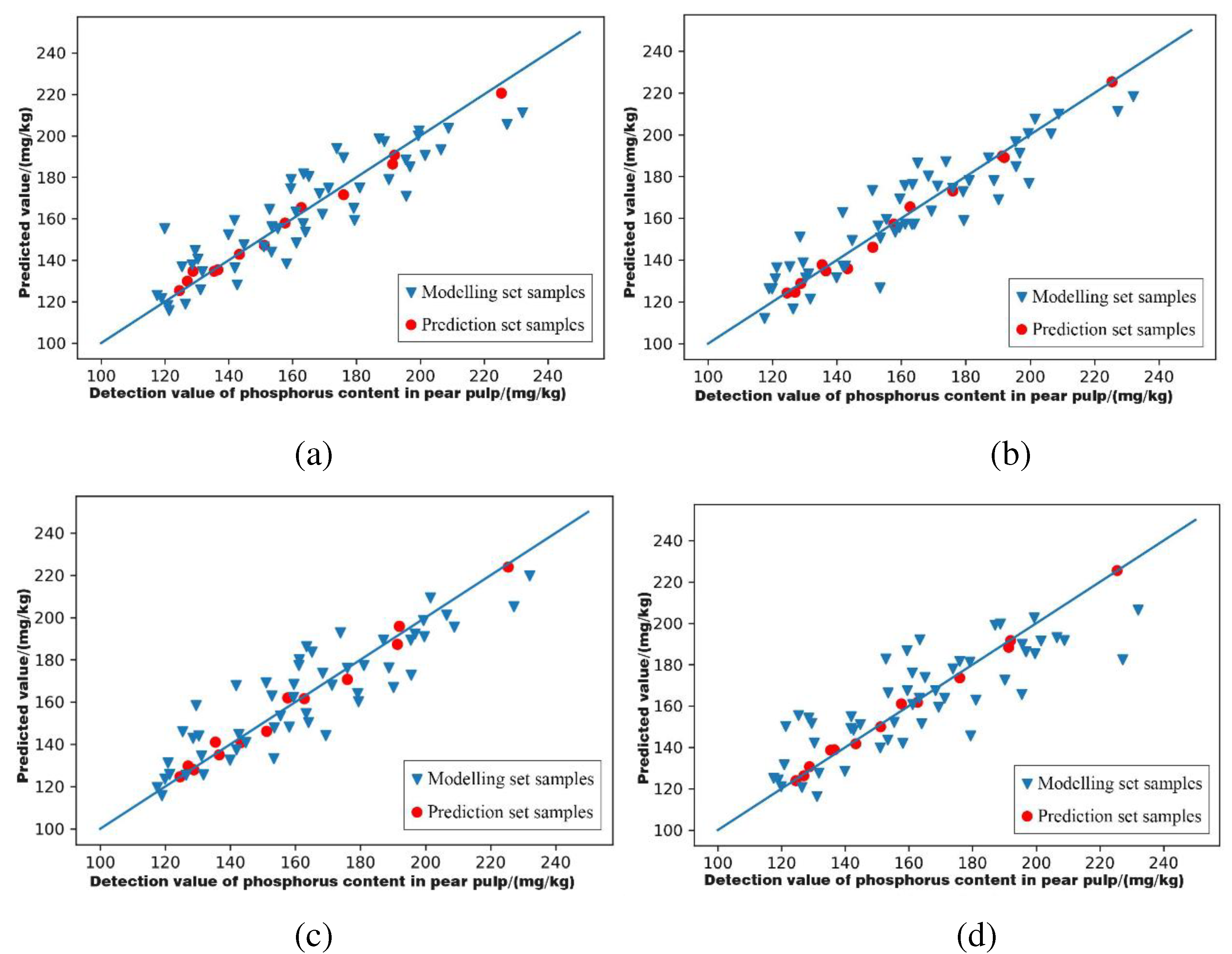
3.6.1. Characteristic Wavelength Modelling of Phosphorus Content in Pear Pulp
| Feature Extraction Methods | Models | Modelling Set | Prediction Set | Level of Models | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R² | RPD | R² | RPD | |||
| GA | SNV-PLSR | 0.806 | 1.690 | 0.988 | 6.483 | A |
| MSC-PLSR | 0.843 | 1.857 | 0.989 | 7.041 | A | |
| SG+MSC-PLSR | 0.786 | 1.619 | 0.987 | 6.152 | A | |
| SG+SNV-PLSR | 0.672 | 1.351 | 0.995 | 10.447 | A | |
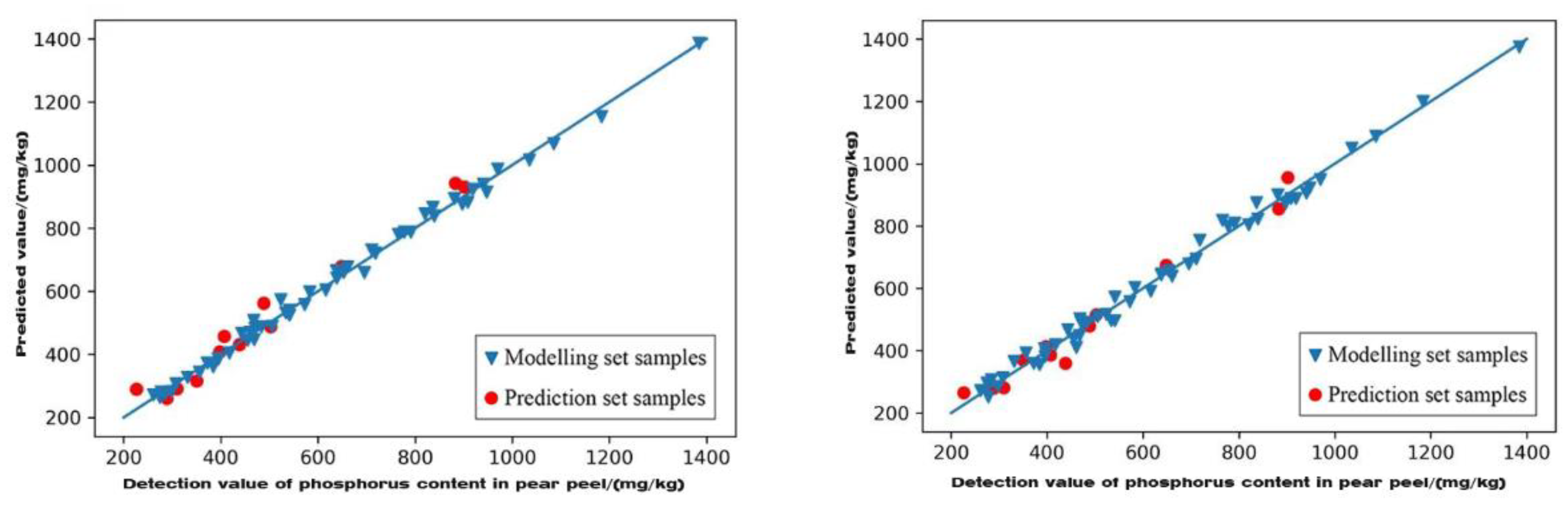
3.6.2. Characteristic Wavelength Modelling of Phosphorus Content in Pear Peel
| Feature Extraction Methods | Models | Modelling Set | Prediction Set | Level of Models | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RPD | R2 | RPD | |||
| GA | FD-PLSR | 0.986 | 5.997 | 0.959 | 3.529 | A |
| SG+MSC+FD-PLSR | 0.991 | 7.47 | 0.974 | 4.414 | A | |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raese, J.T. Phosphorus deficiency symptoms in leaves of apple and pear trees as influenced by available soil phosphorus. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 2002, 33, 461–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, R.; Glisic, I.; Radovanovic, M.; Milosevic, N.; Milosevic, T. Response of pear trees to different fertilization treatment. Mitteilungen Klosterneuburg 2022, 72, 102–117. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.-R.; Li, P.; Wen, J.-H.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.-J.; Yin, D.-H.; Lian, H.-Z. Determination of arsenic species in mainstream cigarette smoke based on inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Spectroscopy Letters 2018, 51, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ge, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, B.; Liang, A. Determination of tungsten in bulk drug substance and intermediates by ICP-AES and ICP-MS. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis 1999, 19, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, L.; Xu, Z.-y.; Hang, W.; Huang, B.-l. Recent Technical and Application Development of Atomic Spectrometry in China. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis 2019, 39, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, G.R.; Evans, C.D.; Kwolek, W.F. Copper in edible oils: trace amounts determined by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society 1971, 48, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Chow, C.W.K.; Fabris, R.; Liu, J.; Jin, B. Applications of Online UV-Vis Spectrophotometer for Drinking Water Quality Monitoring and Process Control: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, L.; Pumpanen, J.; Keinanen, M.; Laudon, H.; Ojala, A.; Palviainen, M.; Kiirikki, M.; Neitola, K.; Berninger, F. Assessment of a portable UV-Vis spectrophotometer's performance in remote areas: Stream water DOC, Fe content and spectral data. Data in brief 2021, 35, 106747–106747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bec, K.B.; Huck, C.W. Advances in Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Related Computational Methods. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, F.; Fumagalli, M. Near infrared spectroscopy: what applications? La Pediatria medica e chirurgica : Medical and surgical pediatrics 2002, 24, 419–421. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.T.; Yuan, H.F.; Lu, W.Z. Development of modern near infrared spectroscopic techniques and its applications. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis 2000, 20, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, H.-b.; Shen, C.-w.; Chen, Q.-w.; Dong, C.-x.; Xu, Y.-c. Determination of Nitrogen Concentration in Fresh Pear Leaves by Visible/Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy. Agronomy Journal 2014, 106, 1867–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.C.A.; Morgano, M.A.; Ferreira, M.M.C.; Milani, R.F. Quantification of mineral composition of Brazilian bee pollen by near infrared spectroscopy and PLS regression. Food Chemistry 2019, 273, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lastras, C.; Revilla, I.; Gonzalez-Martin, M.I.; Vivar-Quintana, A.M. Prediction of fatty acid and mineral composition of lentils using near infrared spectroscopy. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2021, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fu, X.-p.; Ying, Y.-b. Effect of humidity on detection of near-infrared spectra. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis 2007, 27, 2197–2199. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, A.-x.; Tang, X.-j.; Zhang, Z.-h.; Liu, J.-h. Optimizing Savitzky-Golay Parameters and Its Smoothing Pretreatment for FTIR Gas Spectra. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis 2016, 36, 1340–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.S. Salient Chromagram Extraction Based on the Savitzky-Golay Filter for Cover Song Identification. Journal of Multimedia Information System 2022, 9, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Song, H.; Guo, L.; Guang, P.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, H.; Yang, M. Detection of adulteration in Chinese honey using NIR and ATR-FTIR spectral data fusion. Spectrochimica Acta Part a-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2020, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, H.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Q. Quantitative detection of zearalenone in wheat grains based on near-infrared spectroscopy. Spectrochimica Acta Part a-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2022, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Yuan, K.; Xiao, W.; Wu, J.; Shi, C.; Xia, J.; Chu, G.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, G. A local pre-processing method for near-infrared spectra, combined with spectral segmentation and standard normal variate transformation. Analytica Chimica Acta 2016, 909, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chang, Q.-R.; Guo, M.; Xing, D.-X.; Yuan, Y.-S. Detection of leaf nitrogen content of summer corn using visible/near infrared spectra. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves 2011, 30, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dol, I.; Knochen, M.; Vieras, E. Determination of lithium at ultratrace levels in biological fluids by flame atomic emission spectrometry. Use of first-derivative spectrometry. The Analyst 1992, 117, 1373–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Sheng, L.Q.; Tong, H.W.; Jin, Z.X.; Liu, S.M. Determination of benzo(a)pyrene in cigarette mainstream smoke by second-order-derivative synchronous fluorescence. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis 2005, 25, 1627–1629. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ai, N.; Jiang, Y.; Omar, S.; Wang, J.; Xia, L.; Ren, J. Rapid Measurement of Cellulose, Hemicellulose, and Lignin Content in Sargassum horneri by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Characteristic Variables Selection Methods. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.-y.; Zou, X.-b.; Zhao, J.-w.; Yin, X.-p.; Chen, Z.-w. A New Method of Characteristic Wavelength Sub-Range Selection of Near Infrared Spectroscopy. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis 2010, 30, 3199–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.M.; Gemperline, P.J. Wavelength selection and optimization of pattern recognition methods using the genetic algorithm. Analytica Chimica Acta 2000, 423, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patchava, K.C.; Benaissa, M.; Behairy, H. Improving the prediction performance of PLSR using RReliefF and FSD for the quantitative analysis of glucose in Near Infrared spectra. Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Annual International Conference 2015, 2015, 2379–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W.; Laird, D.A.; Mausbach, M.J.; Hurburgh, C.R. Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy-principal components regression analyses of soil properties. Soil Science Society of America Journal 2001, 65, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shidhani, S.; Rehman, N.U.; Mabood, F.; Al-Broumi, M.; Hussain, H.; Hussain, J.; Csuk, R.; Al-Harrasi, A. Quantification of Incensole in Three Boswellia Species by NIR Spectroscopy Coupled with PLSR and Cross-Prediction by HPLC. Phytochemical Analysis 2018, 29, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Lin, M.; Xu, T. Epilepsy Seizures Prediction Based on Nonlinear Features of EEG Signal and Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Mu, L.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, J.; Wu, S.; Lin, L. New strategy of sample set division in spectroscopy analysis--SWNW. Infrared Physics & Technology 2021, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetto, G.; Nava, G.; Ambrosini, V.G.; Comin, J.J.; Kaminski, J. THE PEAR TREE RESPONSE TO PHOSPHORUS AND POTASSIUM FERTILIZATION. Revista Brasileira De Fruticultura 2015, 37, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-z.; Min, S.-g.; Liu, X. Study on the methods and applications of near-infrared spectroscopy chemical pattern recognition. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis 2007, 27, 1299–1303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
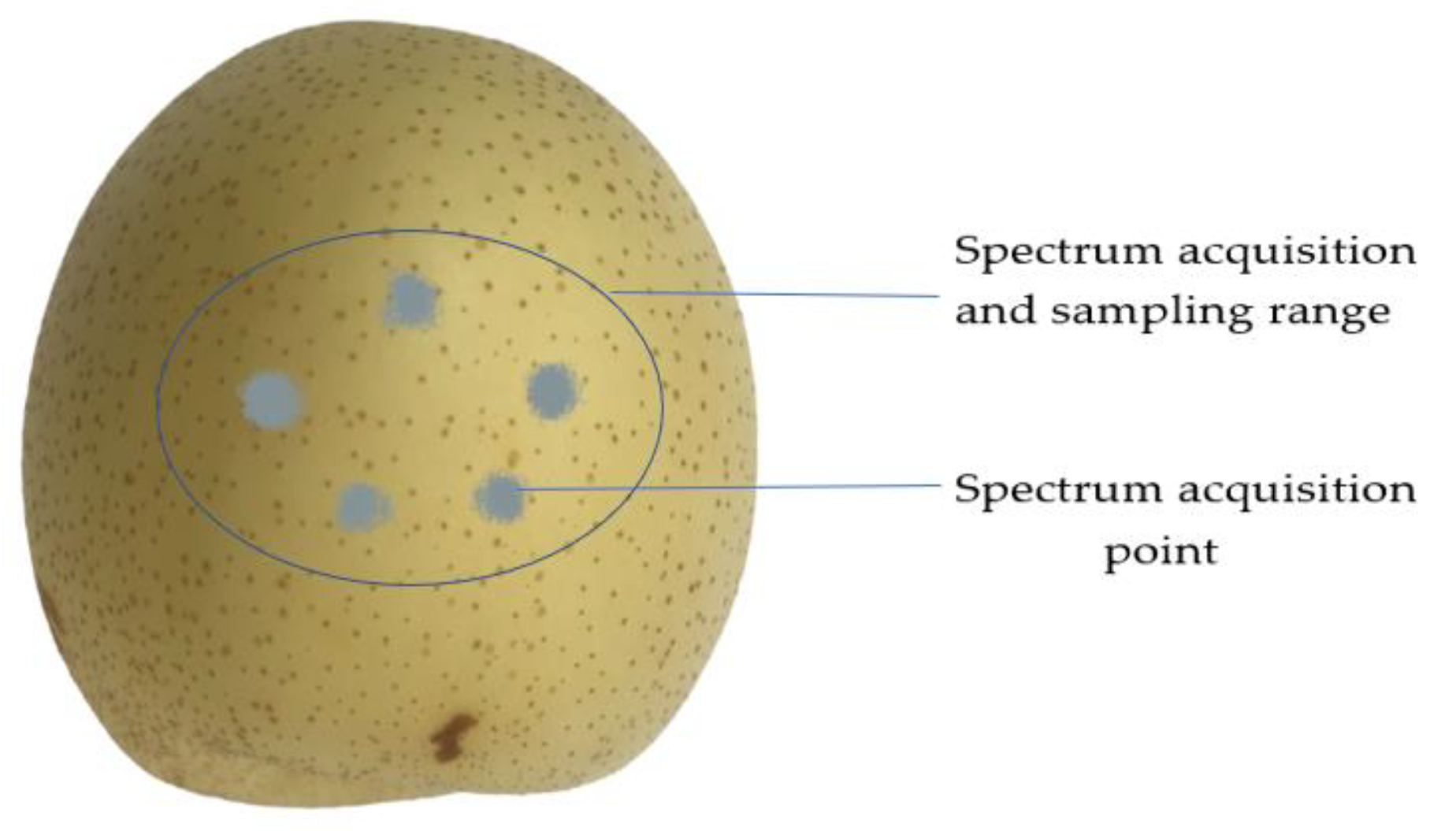

| Sets | Sample Size | Maximum (mg/kg) |
Minimum (mg/kg) |
Average (mg/kg) |
Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Totals | 65 | 232.00 | 117.55 | 161.69 | 29.18 |
| Modelling set(pulp) | 52 | 232.00 | 117.55 | 162.67 | 29.02 |
| Prediction set(pulp) | 13 | 225.32 | 124.50 | 157.78 | 29.49 |
| Modelling set(peel) | 52 | 1384.45 | 261.10 | 628.97 | 258.81 |
| Prediction set(peel) | 13 | 226.50 | 901.85 | 471.10 | 208.90 |
| Modelling Methods for Phosphorus Content of Pear Pulp | Preprocessing Methods | Modelling Set | Prediction Set | Level of Models | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R² | RPD | R² | RPD | |||
| PLSR | Original | 0.412 | 1.097 | 0.621 | 1.276 | C |
| SNV | 0.887 | 2.165 | 0.836 | 1.821 | B | |
| FD | 0.730 | 1.462 | 0.479 | 1.140 | C | |
| MSC | 0.877 | 2.087 | 0.787 | 1.622 | B | |
| SD | 0.728 | 1.459 | 0.359 | 1.071 | C | |
| SG | 0.412 | 1.097 | 0.621 | 1.276 | C | |
| LG | 0.443 | 1.116 | 0.454 | 1.122 | C | |
| SG+MSC | 0.877 | 2.087 | 0.787 | 1.622 | B | |
| SG+SNV | 0.887 | 2.165 | 0.836 | 1.821 | B | |
| SG+MSC+FD | 0.640 | 1.302 | 0.488 | 1.146 | C | |
| SG+MSC+SD | 0.741 | 1.491 | 0.378 | 1.080 | C | |
| SG+SNV+FD | 0.647 | 1.311 | 0.488 | 1.146 | C | |
| SG+SNV+SD | 0.647 | 1.311 | 0.488 | 1.146 | C | |
| GBRT | Original | 0.784 | 1.610 | 0.159 | 1.013 | C |
| SNV | 0.874 | 2.057 | 0.228 | 1.027 | C | |
| FD | 0.997 | 13.737 | 0.258 | 1.035 | C | |
| MSC | 0.999 | 14.857 | 0.358 | 1.071 | C | |
| SD | 0.965 | 3.827 | 0.217 | 1.024 | C | |
| SG | 0.784 | 1.610 | 0.159 | 1.013 | C | |
| LG | 0.784 | 1.610 | 0.129 | 1.008 | C | |
| SG+MSC | 0.999 | 7.098 | 0.358 | 1.071 | C | |
| SG+SNV | 0.874 | 2.057 | 0.228 | 1.027 | C | |
| SG+MSC+FD | 0.985 | 5.743 | 0.118 | 1.007 | C | |
| SG+MSC+SD | 0.948 | 3.141 | 0.629 | - | ||
| SG+SNV+FD | 0.992 | 8.166 | 0.240 | 1.030 | C | |
| SG+SNV+SD | 0.156 | 1.000 | 0.037 | - | ||
| Modelling Methods for Phosphorus Content of Pear Peel | Preprocessing Methods | Modelling Set | Prediction Set | Level of Models | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R² | RPD | R² | RPD | |||
| PLSR | Original | 0.417 | 1.100 | 0.404 | 1.093 | C |
| SNV | 0.791 | 1.634 | 0.436 | 1.111 | C | |
| FD | 0.716 | 1.432 | 0.708 | 1.416 | B | |
| MSC | 0.741 | 1.489 | 0.486 | 1.144 | C | |
| SD | 0.664 | 1.337 | 0.582 | 1.230 | C | |
| SG | 0.417 | 1.100 | 0.404 | 1.093 | C | |
| LG | 0.411 | 1.097 | 0.393 | 1.088 | C | |
| SG+MSC | 0.741 | 1.489 | 0.486 | 1.144 | C | |
| SG+SNV | 0.791 | 1.634 | 0.436 | 1.111 | C | |
| SG+MSC+FD | 0.826 | 1.774 | 0.738 | 1.482 | B | |
| SG+MSC+SD | 0.622 | 1.277 | 0.501 | 1.155 | C | |
| SG+SNV+FD | 0.826 | 1.774 | 0.536 | 1.185 | C | |
| SG+SNV+SD | 0.622 | 1.277 | 0.502 | 1.156 | C | |
| GBRT` | Original | 0.999 | 22.366 | 0.493 | 1.199 | C |
| SNV | 0.998 | 15.819 | 0.253 | 1.034 | C | |
| FD | 0.999 | 22.366 | 0.432 | 1.109 | C | |
| MSC | 0.999 | 22.366 | 0.333 | 1.061 | C | |
| SD | 0.999 | 22.366 | 0.512 | 1.173 | C | |
| SG | 0.943 | 3.005 | 0.423 | 1.199 | C | |
| LG | 0.992 | 7.922 | 0.275 | 1.040 | C | |
| SG+MSC | 0.999 | 22.366 | 0.333 | 1.061 | C | |
| SG+SNV | 0.984 | 5.613 | 0.251 | 1.033 | C | |
| SG+MSC+FD | 0.999 | 22.366 | 0.313 | 1.053 | C | |
| SG+MSC+SD | 0.999 | 22.366 | 0.332 | 1.060 | C | |
| SG+SNV+FD | 0.905 | 2.351 | 0.313 | 1.053 | C | |
| SG+SNV+SD | 0.973 | 4.333 | 0.264 | 1.037 | C | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





