1. Introduction
Travertine/tufa refers to the secondary carbonate rocks formed at the surface by the deposition of calcium- and bicarbonate-rich springs, karst water, rivers and lake systems [
1,
2,
3,
4]. It usually developed in the Quaternary period, belonging to typical continental carbonates or nonmarine carbonates. Travertine is formed from hot water and is hard, crystalline, generally laminated and less porous carbonates. Tufa is cold water carbonate; it is generally highly porous and contains higher plant and animal remains [
3,
5,
6,
7,
8]. Travertine is gradually regarded as a geological archive of palaeohydrology, palaeoearthquakes, palaeoclimates, active tectonics, glacial processes, plateau uplift and geomorphological evolution, human activities (Anthropocene) and even the origin of life for its development of interannual layers and special production background and biomineralization [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16], which reveals great potentiality for research.
According to different CO
2 sources in sedimentary water bodies, Pentecost [
3] divides freshwater carbonates into two categories: tufa and travertine. The former is caused by atmospheric and soil CO
2 degassing and usually has a low
δ13C of −12‰~2‰. The latter is mainly caused by CO
2 degassing from the deep mantle or metamorphic origin, with a high
δ13C of −1‰~10‰. Since deep faults in the Earth directly induce or control the recharge, circulation and uplift of geothermal water, the formation and fracture of travertine is also closely related to faults and seismic activities, and its deposition sites can be used to identify active or potentially dangerous faults and seismic zones. Hancock [
17], based on fieldwork on late Quaternary thermogenic travertine in Turkey, the Aegean region of Greece, the Apennine Mountains of northern Italy and the American basin mountain area, found that travertine can reveal the characteristics and activity history of many new structures and, thus, proposed the concept of travitonics. Based on this theory, the dating of travertine produced in tectonically active sites, especially fissure-ridge-type travertine, has allowed for the reconstruction of seismic activity and its repetition [
16,
18,
19,
20,
21], and the assessment of fault spreading rates [
22], fault ages [
18,
23,
24], sliding rates [
25] and the relationship between faults and fluid properties in geothermal fields have also been studied [
26,
27]. On the other hand, there are few cases of palaeoearthquakes based on tufa, as the water source is mostly karst water, the concentration of HCO
3- is low (<6 mmol/L), and the spring water is not exposed on active faults.
Nevertheless, those tufa deposits that occur in tectonically active areas retain sedimentary abrupt layers (e.g., black beat layers and dirty tufa layers) [
28,
29] in their sedimentary profiles, which are more likely to be associated with tectonic activity or palaeoearthquakes, as tectonic activity alters karst water pathways, or earthquakes cause valley clasts debris and phytoclasts plant debris to be added to the tufa deposits [
30]. The Jiuzhaigou Sparking Lake tufa profile is a typical case. (1) Jiuzhaigou is located in the north–south seismic belt of China. On August 8, 2017, a 7.0 Ms earthquake occurred, and the mountain debris on both sides of the valley flooded into the water body and triggered the collapse of the Nuorilang Falls and Sparking Lake tufa dam break. (2) Guo Yongqiang et al. [
28] believe that the dirty tufa layers in the Sparking Lake tufa are records of flood events, while Lv Congcong et al. [
29] believe the formation of the black peat layer is the product of the synergistic effect of many factors caused by strong tectonic activities. These controversies arise from the absence of seismites similar to other sediments or seismically induced sedimentary structures (e.g., liquefaction structures, deformed structures, convoluted structures and collapse folds) [
30] during the deposition of tufa.
Previous studies have proposed that similar prehistoric events may also have exposed fine sediment particles transported by wind to the ancient Diexi Lake by large sandstorms caused by landslides in the Wenchuan earthquake and settled into sediments of nearby lakes. Based on the analysis of rare earth elements (REEs) and the morphology and particle size of quartz particles, it was determined that they originated from 26 seismic events [
30,
31,
32]. Seismic dust can also be involved in tufa deposition, (1) as in the 8.8 Ms Jiuzhaigou earthquake, landslides and collapses in valleys formed a large amount of dust, which was proved by the dust collected on the tourist trestle way in this paper; (2) these seismic dusts falling into the water body provide nucleation points or templates for tufa precipitation, which is similar to that of biodetritus providing cushion for calcite nucleation when tufa is deposited; and (3) much of these seismic dust is wind carried into the river by surface water during heavy rain after the earthquake and participates in the tufa deposition together with phytoclasts. Based on such understanding, we assume that the black peat layers and dirty tufa layers in the Sparking Lake Dam are more likely to be the products of earthquake action or that the dust formed by earthquakes is involved in the deposition of these abrupt layers.
This paper compared the mineralogy and particle size analysis of different genetic particles based on sedimentary particles in the abrupt layer of the Jiuzhaigou Sparking Lake dam, combined the analysis and interpretation of Rare Earth Elements (REE), established the different evolution models of seismic particles in tufa sediments, clarified how seismic particles in the tectonically active area participate in the process of tufa sedimentation and extracted the palaeoseismic information contained in the section with the aim of reconstructing the palaeoseismic events in the area. This study provides new methods and thoughts for the study of palaeoearthquake recordings on the tufa section in tectonically active areas, and the results can supplement and improve the previous knowledge and theory.
2. Geological setting
Jiuzhaigou is located in Zhangza Town, Jiuzhaigou County, Aba Prefecture, northwest Sichuan Province, 438 km from Chengdu, China, with an altitude of approximately 2000 m to 4750 m and an area of approximately 720 km
2. Jiuzhaigou is located in the transition zone from a subtropical monsoon climate to a continental plateau climate. It belongs to the warm temperate–middle temperate climate zone of mountain canyons, with obvious vertical zoning characteristics [
33]. Geomorphologically, Jiuzhaigou is located in the transition zone between the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau and the Sichuan Basin, which is dominated by alpine mountains and valleys [
34,
35]. It belongs to the mountainous area of the Baishui River (a tributary of the Yangtze River system) basin and presents an erosional landform landscape that is high in the south and low in the north (
Figure 1a), forming a typical alpine valley-type topography with large undulations and height differences. The valley form is a U-shaped valley combined with a V-shaped valley formed by the erosion and incision of glaciers and flowing water. Tufa is mainly distributed in Shuzhenggou, Rizegou and Zechawagou, which are Y-shaped, with a total length of 55.5 km (
Figure 1c).
Tectonically, the Jiuzhaigou Scenic Area is located at the junction of the Danba–Wenchuan tectonic sheet of the Songpan–Ganze orogenic belt and the Motianling block of the West Qinling orogenic belt [
36] (
Figure 1b), bounded by the Tazang tectonic belt, Xueshan and Minjiang faults, with the Motianling nappe of the Western Qinling orogenic belt is located in the middle. In the zone, the tectonic process is complex and faults are developed (
Figure 1c). A unique NW–SE trending fold structure formed in Jiuzhaigou, and there are four reverse faults in the NW, NNE, NE and NW. This area has undergone an evolutionary process of 395 Ma, including marine environment (Devonian~Triassic), orogenic movement (Jurassic~Cretaceous), fault basin (Neogene), Quaternary glaciation (Quaternary) and landscape development (Holocene) [
37], and this special geological and tectonic background dominates the stratigraphic spreading characteristics and tectonic development pattern of the scenic area [
38]. Identified through a field geological survey and an investigatory report by the Sichuan Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, the majority of the outcrops in Jiuzhaigou are marine carbonate formations from the Palaeozoic Devonian to the Mesozoic Triassic [
39], with the largest outcrop of Carboniferous formations (
Figure 1c). These soluble carbonate rocks are widely distributed, and various limestones (including bioclastic limestone, crystalline limestone, argillaceous limestone and siliceous limestone) and trace amounts of dolomite, slate and sandstone form the material basis of the Jiuzhaigou karst underground runoff system. The water-bearing medium of the bedrock in the zone is Carboniferous and Permian crystalline limestone with the best solubility and the siliceous limestone of Devonian strata with relatively poor solubility, forming a karst aquifer, and the metaquartz sandstone of Devonian and Triassic systems with strong water-insulating properties forming a water-insulating layer.
Figure 1.
Geological background maps of the study area: (a) map of the location of Jiuzhaigou, northwestern Sichuan Province, and the green dots represent the study area; (b) geotectonic map of Jiuzhaigou, where the green frame is the area in (c); (c) geological map of the Jiuzhaigou region [
40].
Figure 1.
Geological background maps of the study area: (a) map of the location of Jiuzhaigou, northwestern Sichuan Province, and the green dots represent the study area; (b) geotectonic map of Jiuzhaigou, where the green frame is the area in (c); (c) geological map of the Jiuzhaigou region [
40].
Jiuzhaigou is located in the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau [
41] and on the thrust fault that transports the Songpan–Ganzi Triassic flysch succession over the Yangtze Palaeozoic sedimentary cover [
42]. The eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau involving Jiuzhaigou is impacted by the northeastward extrusion of the Tibetan Plateau due to the continuous subduction of the Indian plate and is marked by strong tectonic activity [
43], resulting in frequent earthquakes, such as the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake, 2010 Yushu earthquake and the 2013 Lushan earthquake. The most recent earthquake was on August 8, 2017, which was a 7.0 Ms earthquake (33.20°N, 103.82°E) that occurred in Jiuzhaigou County [
44], triggering severe damage to the tufa landscape, resulting in the collapse of the tufa dam body in the Sparking Lake, forming a breach approximately 35 m long and 13 m high and pouring the lake water out of the dried tufa reef. The seismic dust generated by the earthquake and the outcropping of the dam body provide key samples for the dissection of the tufa sedimentary sequences.
3. Sedimentary characteristics
The study profile is located on the northwest side of the Sparking Lake dam in the Shuzhenggou Section of the Jiuzhaigou Scenic Area (N 33°12’26.04”, E 103°54’1.62”), 100 m away from the scenic road (
Figure 2a). Sparking Lake consists of an arc-shaped dam at the front and a dam at the back, which holds the lake water. The tufa reef (
Figure 2a) developed in the lake, with an altitude of 2211 m, length of 232 m, width of 134-294 m and storage capacity of 450,000 m
3.
According to the results of an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) survey and field measurement, the vertical height of the levee breach in Sparking Lake is 13 m (
Figure 2a), and it is divided into five layers from the bottom to the top, consisting of three tufa lithofacies: laminated, phytoclastic and porous biological. The three lithofacies are deposited alternately, with obvious rhythmic sedimentation characteristics. The laminated tufa is a brownish-white sublayer alternating in color (
Figure 2b), composed of light and dark dense tufa and characterized by parallel bedding, and a dense tufa layer less than 1 m is often deposited in an inorganic manner due to the action of water flow. The phytoclastic tufa is dark in color, gray and gray-black, containing impurities, such as branches and leaves, and the whole is messy, superimposed and fragile, with the thickest part reaching 4 m (
Figure 2b). The porous biological tufa is relatively bright in color and formed by algae filaments, mosses and aquatic plants. Compared with the phytoclastic tufa, its texture is hard, but it is more brittle than the laminated tufa, and the thickest part reaches 5 m (
Figure 2b).
A carbonaceous clastic layer, approximately 10~15 cm thick, is interspersed between phytoclastic tufa and porous biological tufa in the levee breach, leading to the discontinuity of the tufa deposition. Similar clastic layers are well developed in the rear dam body and tufa reefs in the lake. They are named as dirty tufa layers in the tufa reef section (
Figure 2c) [
28], which are compositionally much higher in carbonate clasts than in carbonaceous. In the rear dam body, they are represented by black peat layers (
Figure 2d), and the proportion of carbonaceous and phytoclasts in its material composition is much higher than that of carbonate debris [
29]. These rhythmic sedimentary structures and the carbonaceous clastic layer in the dam body provide samples and ideas for the study of historical geological event records and palaeoclimate changes.
4. Material and methods
The sampling location is shown in Figure. 3. The samples were taken from the settling particulate matter (
Figure 3a), fluvial sediments in the lower reaches of Panda Lake (
Figure 3b), Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments (
Figure 3c), special clastic interlayer of the Sparking Lake dam body (
Figure 3d) and collapsed limestone from mountains on both sides of the Panda Lake and Five-Colored Lake in Jiuzhaigou to demonstrate the morphological characteristics of different particulate matter and reveal the possible material source of the detrital interlayer of the dam body. In order to better identify the eolian sedimentation causes of seismic particles and reveal the palaeoseismic information contained in the tufa deposition, Ganzi loess and urban dust were also collected as references.
The mineral composition of the various samples was determined by X-ray diffractometer. The instrument model was an XPert PRO. A total of 0.5 g of sample was taken and ground thoroughly, usually to a particle size of 320 mesh, approximately 40 µm. The powder sample was prepared by the positive pressure method, setting the X-ray diffractor parameters to a 40 kV voltage, 40 mA current, 0.033° step length, 0.2° per minute integration time and 3-80° scan range. The composition of the samples was determined by semiquantitative analysis based on the lower surface reflective intensity of the identified minerals using the weighting factor method.
A laser particle size analysis was carried out using an LS13320 laser particle size analyzer produced by Beckman Coulter Company of the United States, and the measuring range of the instrument is 0.04~2000 um. Firstly, a 0.3 g sample was weighed and added to a 200 ml beaker. According to the results of the X-ray diffraction mineral composition analysis, 10 ml 10%H2O2 solution was added to the samples with high calcium carbonate content (settling particulate matter of the dam body, fluvial facies, lacustrine facies and boardwalk) and heated to fully react with the organic matter. Considering the high content of the organic matter in the samples, when there were still a few bubbles remaining, 10 ml 10%H2O2 solution was added again to continue the reaction until no bubbles were generated at which time the organic matter was completely reacted. For the samples with a high quartz content (Ganzi loess and urban dust), 10 ml 10%H2O2 solution was added and heated until only a few bubbles remained according to the pretreatment method of loess particle size analysis. Then, 10 ml 10%HCL solution was added to remove carbonates and other cements. After cooling, the beaker was filled with deionized water, and after standing still for 12 hours, the supernatant was extracted with an eyedropper. Another 10 ml of 0.05 mol/L sodium hexametaphosphate was added to the beaker as a dispersant; then, ultrasonic cleaning and shaking were carried out for 5 minutes before machine measurement.
Scanning electron microscopy is used to observe the structure, morphology and other microscopic changes of various minerals. In this experiment, tungsten filament scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to analyze the morphology of the individual mineral particles of the samples. The instrument model was an EVO18, and the main accessories included a scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) and a PP2000T freezing transmission system, and the maximum magnification was 1,000,000x.
Geochemical element measurement was completed by Guizhou Tongwei Technology Co., Ltd. The samples were digested with nitric acid, hydrochloric acid and hydrofluoric acid, which undergone at least twice as low temperature and sub-boiling purification by acid purifiers (such as an American Savillex DST-1000 and quartz secondary purifier). A high-precision inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (ICP-MS) was used for the experiment. The instrument model was an XSERIES 2. The specific gravity method was adopted for preparing the internal standard solutions of Rh, In, Re and Bi to control the experimental accuracy. The whole process was carried out at a constant temperature, constant humidity and ultra-clean environment.
The tufa chronology was completed using accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS)
14C dating at Beta Labs, USA, with the ages calibrated using IntCal13 curves and BP representing the era to 1950. The dating samples were taken from the upper phytoclastic tufa from the Sparking Lake breach dam profile, the bottom carbonaceous clastic layer and the carbonaceous clastic layer extension in the tufa reefs (
Figure 2a,b).
5. Results
5.1. Mineral Phase Results
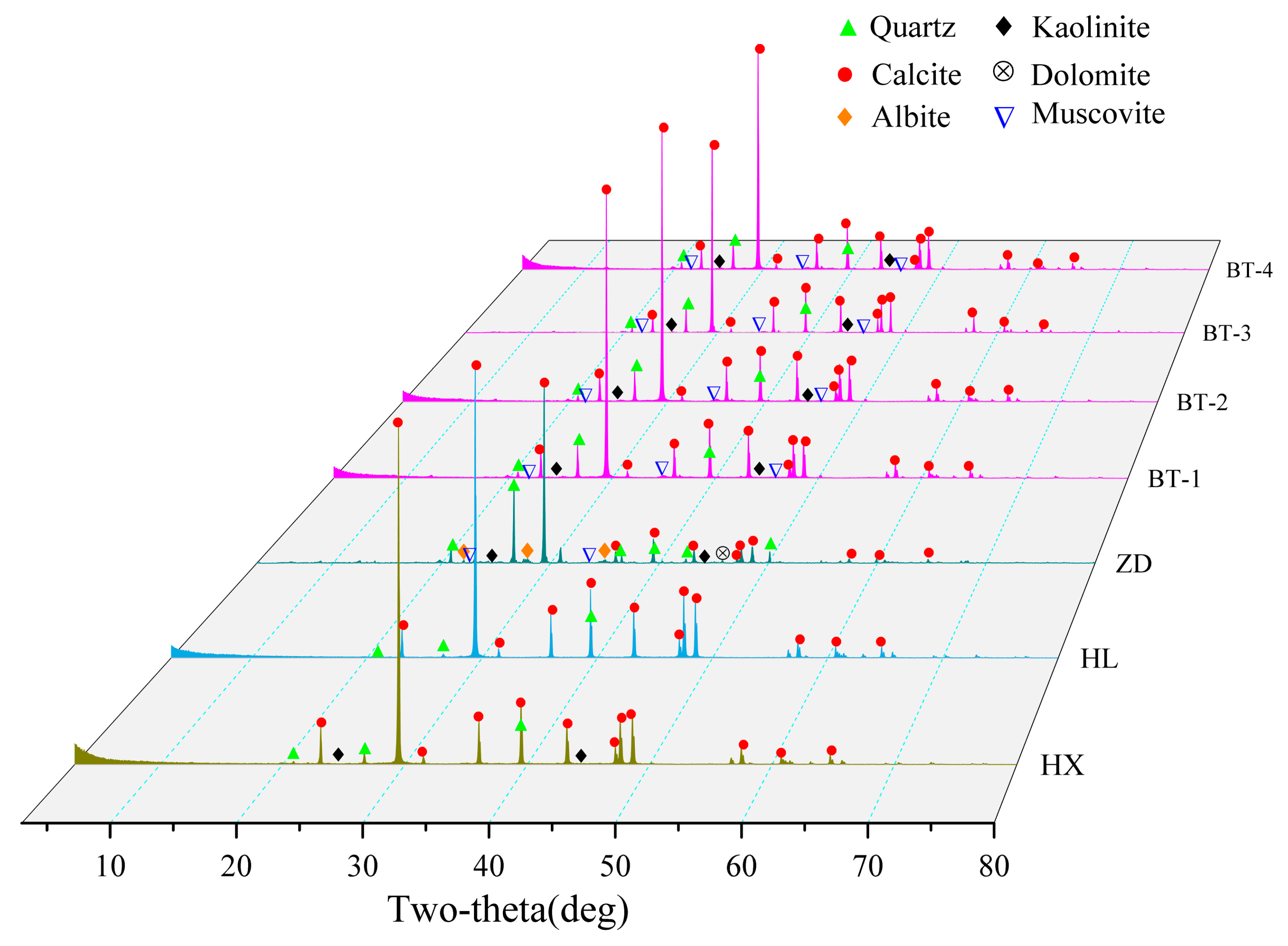
The X-ray diffraction analysis of the mineral composition was carried out on the detrital interlayer of the tufa dam body in the Sparking Lake, the settling particulate matter and sediments of lake facies of the Sparking Lake and the fluvial sediments in the lower reaches of the Panda Lake and Ganzi loess, and the diffraction patterns of the samples were compared and analyzed with the powder diffraction file (PDF) using Materials Data Jade 6.5 software, and the results are shown in
Figure 4. The mineral composition of the samples in the study area is mainly calcite, among which the compositions of the detrital interlayer of the tufa dam body in Sparking Lake, lacustrine sediments in Sparking Lake and fluvial sediments in Panda Lake include calcite, quartz, muscovite, kaolinite and other minerals. A quantitative analysis was carried out using whole peak fitting (WPF) and Rietveld refinement methods to obtain the relative content of each phase, and the results are shown in
Table 1.
The content of the mineral components in the detrital interlayers of the Sparking Lake dam is not much different, and the content of calcite is approximately 80%, followed by muscovite, and the least content is kaolinite. The calcite content in the lacustrine sediments of Sparking Lake and the fluvial sediments of the lower reaches of Panda Lake is as high as 95%, with a small amount of quartz. The sedimentary particulate matter of the plank is mainly composed of calcite and quartz (
Figure 4a). Compared with the lacustrine sediments of Sparking Lake, the fluvial sediments of the downstream Panda Lake and the detrital interlayer sediments of the dam body, the content of calcite in the plank settlement particulate matter is significantly reduced to 49.7%, but the content of quartz is significantly increased, and the content of muscovite is equivalent to that of the special interlayer sediments of the dam body while containing a small amount of kaolinite, albite and dolomite, whose composition is similar to that of limestone. The mineral composition of Ganzi loess is mainly quartz and muscovite, the content of calcite is very low at 1%, and other mineral compositions (kaolinite, albite, dolomite and chlorite) occur.
In general, the mineral compositions of the samples collected in Jiuzhaigou are generally not very different and clearly distinct from that of eolian loess, but there is obvious combination with the karst system and fluvial tufa deposition in Jiuzhaigou, and mineral evolution and regional inheritance of the particulate matter in Jiuzhaigou are shown [
45].
5.2. Grain size distribution
The grain size distribution of sediments refers to the percentage of different size grains in the sediment, which is mainly controlled by the transportation medium, transportation manner, sedimentary environment and other factors. The sedimentary environment and transporting force characteristics of sediments can be studied by grain size analysis [
46]. The kurtosis and peak number of the grain size frequency curve can reflect the mode of transport, such as wind and water power, and the grain size corresponding to thick peak value of the frequency curve reflects the strength of the sedimentary dynamic [
47]. The grain sizes of the collected samples were analyzed, and based on this, a discussion of the geological significance of the grain size range of the different samples was conducted, and the sources and geological events were speculated and verified.
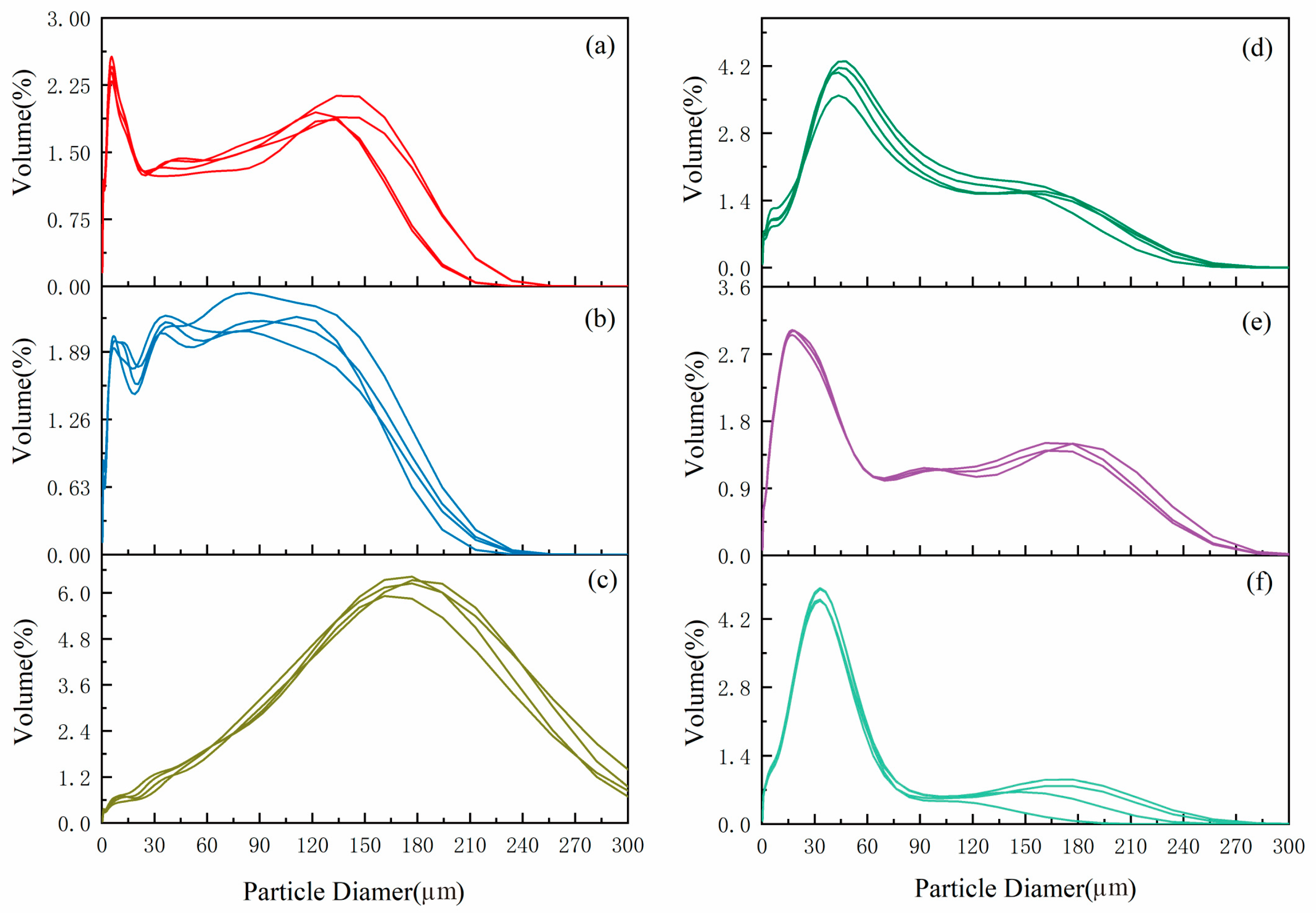
As shown in the grain size frequency curve (
Figure 5a), the grain size range of the special interlayer sediments in the Sparking Lake dam body was between 0 and 240 µm, with multiple peaks. The main peak grain size of the special interlayer sediments in the tufa dam was located on the small-ended side, with a concentrated distribution of 2-30 µm and a grain size mode of 6 µm. The kurtosis was sharp, indicating that it experienced good sorting wind transport characteristics. The subpeak grain size was located on the large-ended side, with a grain size distribution of 90~180 µm and a mode of 140 µm. The wide and flat kurtosis indicates poor sorting, displaying hydrodynamic transport characteristics. In addition, there was also a weak peak between 30 and 60 µm. The significant increase in the fine-grained components content in the sediments of the special interlayer of the tufa dam may be related to the large amount of dust or debris materials generated by large-scale landslides and landslides caused by seismic events that were transported to Sparking Lake and deposited by wind and hydrodynamic forces in a long-term time scale after the earthquake.
As shown in the grain size frequency curve (
Figure 5b), the grain sizes range of the Sparking Lake lacustrine facies sediments was also between 0 and 240 µm, and the kurtosis distribution of the curve was the same as that of the sediments of the special interlayer of the Sparking Lake tufa dam body, indicating that they have the same transporting agent and sedimentary background. The difference lies in that the fined-grain components content (2-30 µm) in sediments of the Sparking Lake lacustrine facies was lower than that of the content in sediments of the special interlayer of the dam body, and the kurtosis between 30 and 60 µm was more obvious,, indicating that the content of proximal dust increased. On the whole, Sparking Lake lacustrine facies sediments are composed of fine-to-coarse silt and fine sand, with the same content of each component and poor grain sorting. It basically corresponds to the dust and debris materials produced by the earthquake-induced collapse and landslide were finally deposited in the Sparking Lake phase after being transported over a short distance under the synergistic effect of wind and hydrodynamic forces.
The grain size frequency curve (
Figure 5c) of the fluvial sediments in the lower reaches of Panda Lake shows a normal fluvial deposition pattern and a generally normal distribution character, with a grain size mainly distributed between 120 and 240 µm and a grain size mode of approximately 180 µm. The grain size is larger than the special interlayer of the tufa dam and lacustrine sediment grains, showing strong hydrodynamic characteristics. There are weak peaks at 7 µm and 30 µm, which are speculated to be dust deposition generated by landslides on both sides of Panda Lake in the river. However, due to the high fluvial energy, only a small amount of the dust was deposited into the fluvial facies.
The trestle way grain size frequency curve between Panda Lake and Five-Colored Lake (
Figure 5d), the urban dust size frequency curve (
Figure 5e) and Ganzi loess size frequency curve (
Figure 5f) all showed obvious eolian sedimentary characteristics, and the main peak grain size was concentrated at 45 µm, 16 µm and 30 µm, respectively. The main peak grain size of the trestle way grains was significantly larger than that of the urban dust and Ganzi loess. Studies have shown that grains of size >32 µm are difficult to carry in the air over long-distance transport even under violent wind. The larger main peak grain size indicates the proximal transport attribute [
48], and the material source was mainly dust generated by the collapse of the mountains on both sides of Panda Lake. The main peaks of urban dust and Ganzi loess are sharp and well sorted, which is the result of a strong wind agent and long-distance transport.
5.3. Particle morphology
The morphological analysis of individual mineral particles is of great significance in the restoration process of geological events experienced by particulate matter. The morphological analysis of individual mineral particles under a microscope can well predict the process of evolution [
49]. Their sphericity, surface morphology and other features all contain different geological information.
The X-ray diffraction results show that calcite is the main composition of the special interlayer sediments of the Sparking Lake dam body, Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments and fluvial sediments in the lower reaches of Panda Lake. The sediments of the Jiuzhaigou trestle way are mainly composed of calcite and quartz, and the loess of Ganzi is mainly composed of quartz and muscovite. The results of the scanning electron microscopy (
Figure 6) show that the special interlayer sediments (
Figure 6a,b), sediments of the Jiuzhaigou trestle way (
Figure 6c,d), Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments (
Figure 6e,f) and Ganzi loess (
Figure 6j) had similar surface morphological characteristics. The appearance of the particles was subangular, with no obvious rounded corners, and there were a series of impact craters, fractures and grooves, suggesting that the particles in Jiuzhaigou have the same wind transport characteristics as those in Ganzi loess (
Figure 6j). The impact crater and section were also clear, indicating that the late reformation degree was low in the later stage, and the particles retained the original morphological characteristics, that is, the original particles had experienced sudden and violent impacts with each other, floated in the air for some distance and settled to the surface, and their material source was the proximal dust generated by earthquake-induced collapse and landslide. The fluvial sediments (
Figure 6g,h) in the lower reaches of Panda Lake showed an irregular shape, uneven surface and higher sphericity, with no obvious impact craters, fractures or grooves, displaying strong hydrodynamic characteristics. The provenance is weathered detrital tufa deposited after being transported by running water.
5.4. Composition of rare earth elements
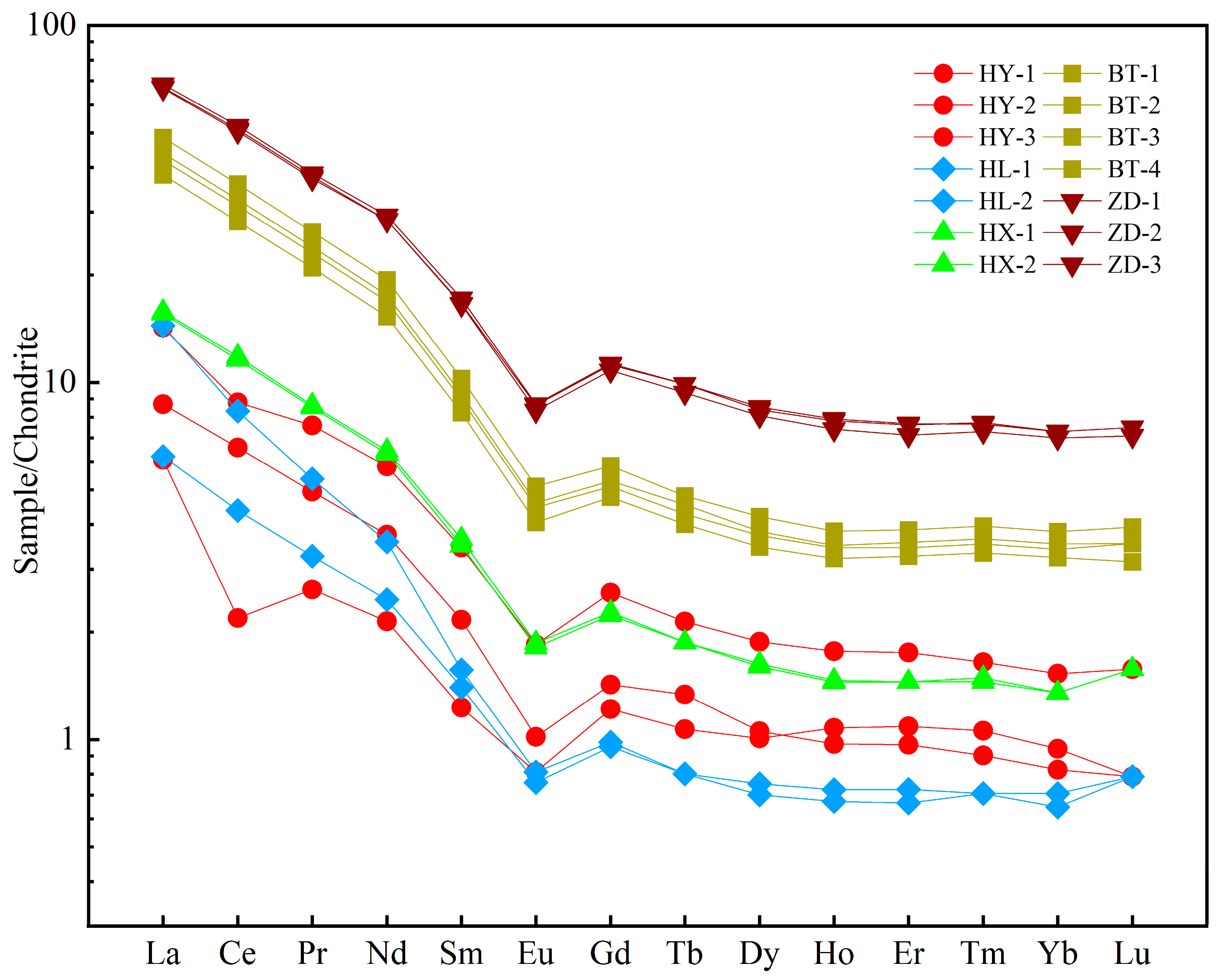
The surface morphology of the particles in Jiuzhaigou was consistent with the inheritance of the study area, as shown by the X-ray diffraction results, and the transport process, as shown by grain size analysis results, over a short distance or time. A rare earth element analysis of the particles collected in Jiuzhaigou was carried out to further demonstrate the stable identity of the provenance and correlation with the earthquake. The analysis results are shown in
Table 2. The overall content of rare earth elements in the Jiuzhaigou particulate matter was relatively low, with a total amount of rare earth elements (excluding Y) that varied from 5.26 to 76.893 ppm and an average value of 35.028 ppm, which was lower than the average value of the continental upper crust. The content of light rare earth elements (LREEs) in the study area ranged from 4.26 to 68.69 ppm, with an average of 31.63 ppm, while the abundance of heavy rare earth elements (HREEs) was low, with a total content of 0.7 to 8.20 ppm and an average of 3.39 ppm. The LREE/HREE ratio ranged from 4.29 to 14.87, with an average value of 9.45, which reflects the obvious difference between light and heavy rare earths and the characteristics of light rare earth enrichment in the study area. The (La/Yb)
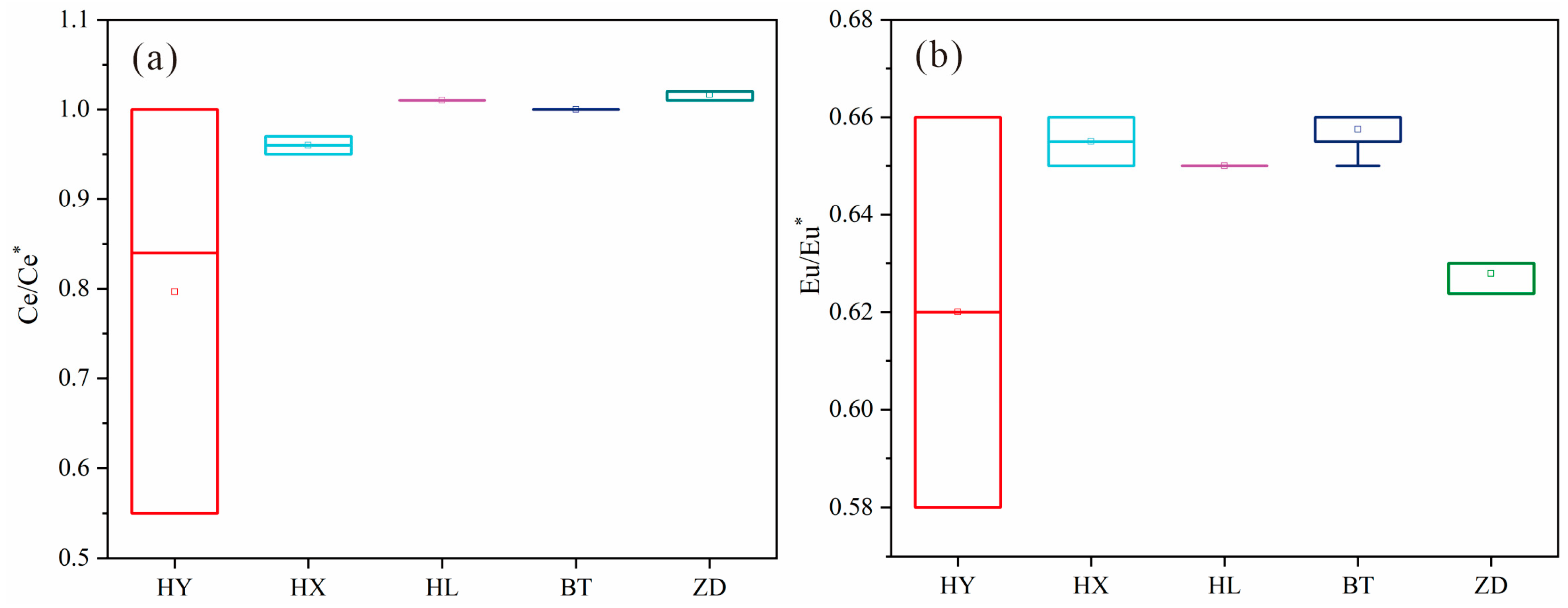
N values ranged from 6.58 to 21.33, with an average value of 11.61, indicating a distinct difference in the light and heavy rare earth elements. On the premise of chondrite standardization, the Eu/Eu* value ranged from 0.58 to 0.66, with an average value of 0.64, which is a moderate negative Eu anomaly. The Ce/Ce* value ranged from 0.55 to 1.02, with an average value of 0.96, indicating that the Ce anomaly is not obvious.
As can be seen from the Chondrite standard curve of rare earth elements (
Figure 7), only limestone and fluvial sediments show a slight negative Ce anomaly. On the whole, the REE partition patterns of the Jiuzhaigou samples were basically the same, showing an obvious right-inclined pattern. The steep curve in the La-Eu section and gentle curve in the Eu-Lu section showing enrichment of light REEs, a nonobvious fractionation of heavy REEs, and “valle” characteristics in the Eu area showing an obvious negative Eu anomaly. The overall distribution pattern (shape of the partition curve) of all particulate matter in Jiuzhaigou is basically consistent with limestone, and the results of the X-ray diffraction analysis show that the mineral composition of the Jiuzhaigou mountains particulate matter is similar to limestone, which indicates that the provenance of the supply of samples was relatively stable. The collected particulate matter in the Jiuzhaigou mountains originates from limestone, but the rare earth content of the samples was different. The general trend of the rare earth content is as follows: trestle way sedimentary particulate matter > sediment of the special interlayer of the dam body > sediment of Sparking Lake lacustrine facies > sediment of lacustrine facies in the lower reaches of Panda Lake. The parent rock characteristics and sediment types of the provenance are the main factors affecting the enrichment of rare earth elements [
50,
51]. Organic matter has the ability to enrich rare earth elements [
52], and there are differences in the organic matter content of different types of sediments. According to the map of the particulate matter collection locations in Jiuzhaigou (
Figure 3), it can be observed that the highest organic matter content was found in the deposited particulate matter of the trestle way, followed by the carbonaceous clastic layer sediments of the dam, and the organic matter content was the most important factor affecting the variation of the total rare earth content.
5.5. Chronology analysis
Precise chronological methods to investigate palaeogeological catastrophic events are particularly important, and the direct use of carbon flakes to constrain ages in
14C studies is generally accepted. In this paper,
14C dating was carried out on the phytoclastic tufa and carbonaceous clastic layer at the top and bottom of the Sparking Lake breach dam profile and the carbonaceous clastic layer in the tufa reefs in the lake, where hh1 in the tufa reefs was deposited at the same level as the carbonaceous clastic layer at the bottom of the dam. The hh1 in the tufa reefs was deposited at the same level as the carbonaceous clastic layers hh2 and hh3 at the bottom of the dam. The results of the sample dating are shown in
Table 3, with
δ13C values of -24.2 ~ -26.7‰, which are distinctly different from the epigenetic calcrete
δ13C values (-12‰ ~ -2‰) and are typical of the phytoclastic component, making them suitable for
14C dating. The ages measured for the carbonaceous clastic layer samples hh1, hh2 and hh3 at the base of the dam are consistent within the error range, with the oldest age being 1220 ± 30 a BP and the mean age being 1190 ± 30 a BP. The
14C age of hh4 at the top of the dam is 350 ± 30 a BP, which is younger than the ages of hh1, hh2 and hh3 at the base of the dam and is consistent with the tufa depositional sequence from bottom to top, reflecting the reliability and accuracy of the experiment. The
14C age of the carbonaceous clastic layer allows for an inferred palaeoearthquake date of approximately 1220 ± 30 a BP.
Based on the above experimental results, it was concluded that the mountain particles in Jiuzhaigou were not transported via a long-distance wind agent, the degree of mutual abrasion among the particles was low, and the grain size range was larger than that of eolian particles. Meanwhile, due to the short transport distance, the surface morphology and initial shape of the original particles are still relatively intact after deposition, with lower sphericity and more obvious edges and corners, mostly angular or subangular. In terms of the mineral composition, the Jiuzhaigou mountains particulate matter also bears certain regional inheritance, and the main component is calcite, which is consistent with its geological environment. Most importantly, the content and distribution of REEs confirm that the special interlayer of the dam body, fluvial sediments, lacustrine sediments and trestle way sediments in Jiuzhaigou are derived from the limestone on both sides of Panda Lake. In addition, from the chronology data, it was determined that the special interlayer of the dam formed during a geological event 1220 ± 30 a BP.
6. Discussion
6.1. Sedimentary model of seismogenic dust particles in tufa of Jiuzhaigou
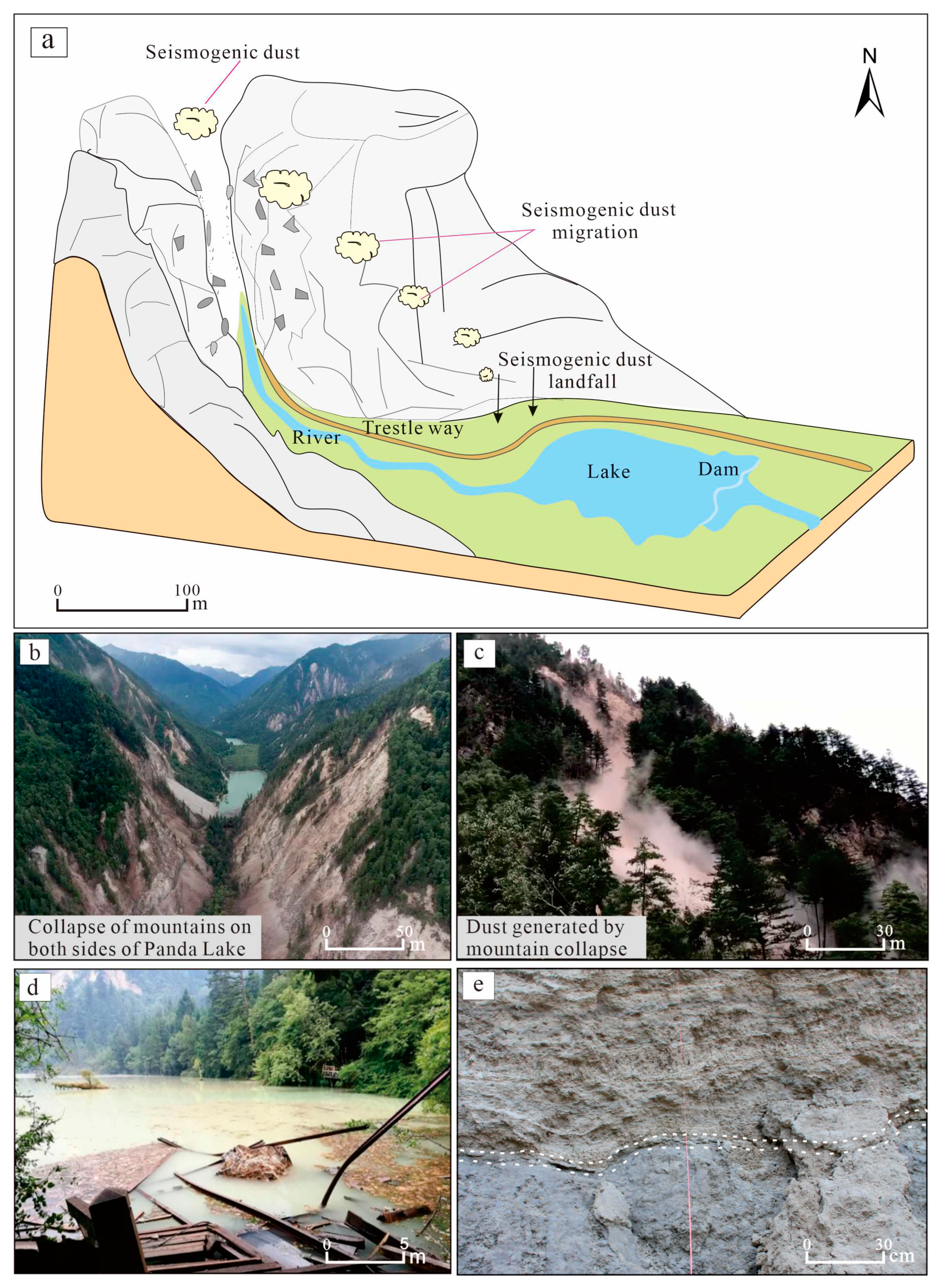
Earthquakes cause mountain collapses and landslides, and the clasts form a large amount of dust (even dust storms) while rolling down [
53]. These dusts are not transported over long distances and will often settle in close proximity, so mountain slopes or gullies are the main deposition sites. Based on a site survey of the Jiuzhaigou earthquake and a related image survey of the earthquake, this paper reconstructed the dust formation of the quake and modeled the formation and deposition process of the seismic mountain particulate matter taking sedimentary dynamics into consideration (
Figure 8).
The earthquake triggered the collapse of mountains on both sides of the front edge of Panda Lake, forming a large amount of mountain dust (
Figure 8b,c). Fine dust was suspended in the air for a certain distance and settled on the trestle way between Panda Lake and Five-Colored Lake or on the surface near the collapse area (
Figure 8a). Heavy rainfall over a certain time scale after earthquakes (e.g., surface runoff formed by clast flows in the days after the Wenchuan earthquake and Jiuzhaigou earthquake) [
54] transported these scattered particles to the river course, and a large number of particles led to a significant increase in water turbidity (
Figure 8d). Eventually, these dust or clasts generated by earthquakes were transported by river water and accumulated in the dam body together with phytoclasts to form a carbonaceous classical layer, as evidenced by the high content of phytoclasts in these layers (
Figure 2c) or rich organic matter (
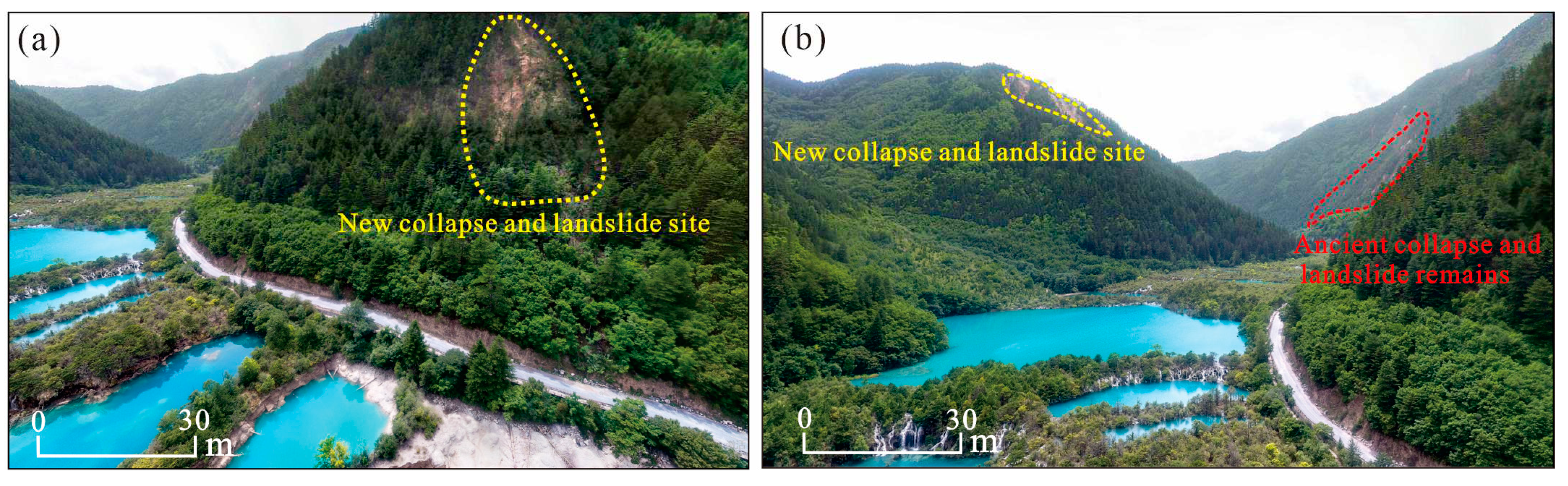
Figure 2b,d). For the carbonaceous clastic layer of the Sparking Lake dam body, its formation mode is the same as the above mode, but the clast source is the source of seismogenic dust particles generated in Shuzhenggou in the previous earthquake. The reasons for this are as follows: (1) many collapses and landslides also occurred in the Sparking Lake and Shuzhenggou waterfall area (
Figure 9a,b) during this earthquake, forming seismogenic dust storms; (2) the palaeo-collapse and palaeo-landslide bodies developed in the Sparking Lake and Shuzhenggou waterfall area (
Figure 9b), which can generate seismogenic dust particles from previous earthquakes. Similarly, after sedimentation and post-earthquake rainstorm transport, these clasts accumulated in the Sparking Lake dam body to form a special discontinuity layer (
Figure 8e).
From the section of the Sparking Lake dam body collected from the 8.8 Ms earthquake, there was a mode similar to the transport and accretion deposition of detrital particles (
Figure 2c,d); that is, when detrital particles were transported to the dam body by the water body, there were carbon dioxide losses due to the fact of hydrodynamic changes, and these detritals were similar to the biological residues that provided nucleation sites for calcite crystals [
45], forming micrite tufa. Therefore, it is more heterogeneous in mineral composition compared to lacustrine and fluvial tufas. The quartz content is also relatively high [
29] (
Figure 4,
Table 1). As for the thickness of the carbonaceous classical layer, it is usually less than 20 cm, mostly 5-10 cm, and this thickness can be reached because of the mixed pthytoclasts. Compared with the normal sedimentary layers of the dam body tufa (laminated tufa, phytoclastic tufa and algae and moss tufa (
Figure 2b), all with a thickness of more than 50 cm), the deposition rate was lower, which can better represent the characteristics of the sedimentary interlayer of geological events.
6.2. Palaeoseismic characterization of morphology and geochemistry of mountain particles
6.2.1. Indication of mineral composition
According to the X-ray diffraction results, the compositions of the samples collected in Jiuzhaigou were mainly composed of calcite (
Figure 4,
Table 1), containing a small amount of quartz, which is consistent with the local provenance conditions. According to geological records [
55] and field investigation, the composition of the mountains on both sides of the front of Panda Lake is Carboniferous and Permian limestone with a small amount of sandstone (
Figure 1c). The earthquake caused the limestone to collapse, forming limestone clast dust and subsiding near the ground on the trestle way at the foot of the mountain. The sampling location of the particulate matter on the trestle way was just below the collapsed hills on both sides of Panda Lake (
Figure 8a,b), and the particle composition is consistent with the mineral composition of limestone. In prehistoric earthquakes, the sedimentary pattern of clastic intercalations in the Sparking Lake dam body is also as described above. In addition to calcite, quartz accounts for 18.8% of the mineral composition of the trestle sample (ZD) (
Table 1), which is related to a small amount of sandstone interbedded in the mountain stratum. Apart from this, the lowest quartz content in the dam samples (BT) (6.7% on average) was found in the lacustrine (HX) and fluvial samples (HL). The quartz content of the carbonaceous clastic layer was close to that of the seismogenic dust particles, indicating that its origin is related to that of similar seismic particles at the perimeter of Sparking Lake. The mineralogical composition of the Sparking lakebed sediments (HX) consists of calcite precipitated by carbonate supersaturation in the water column due to the fact of inorganic and biological interactions [
56], as well as containing a small amount of quartz, which may also be associated with a similar source of seismic particulate matter. Therefore, mineralogical constraints on prehistoric earthquakes can be provided based on the mineralogical composition, combining the geological setting with the sedimentary model of the seismogenic dust particles in tufa and comparing the compositional analysis of the sediments in various depositional environments (e.g., river course, lake bottom and dam body).
6.2.2. Indication of mineral grain size and morphological characteristics
Generally, grain size parameters have certain discriminative significance for the genesis and sedimentary environment [
57], but in view of the complexity of the sedimentary environment and the diversity of influencing factors, it is usually necessary to conduct a comprehensive analysis of various grain size parameters. According to the size of the detrital particles and the action of the transporting agent, 2 µm and 63 µm were used as the dividing lines of the clay/silt and silt/sand, respectively [
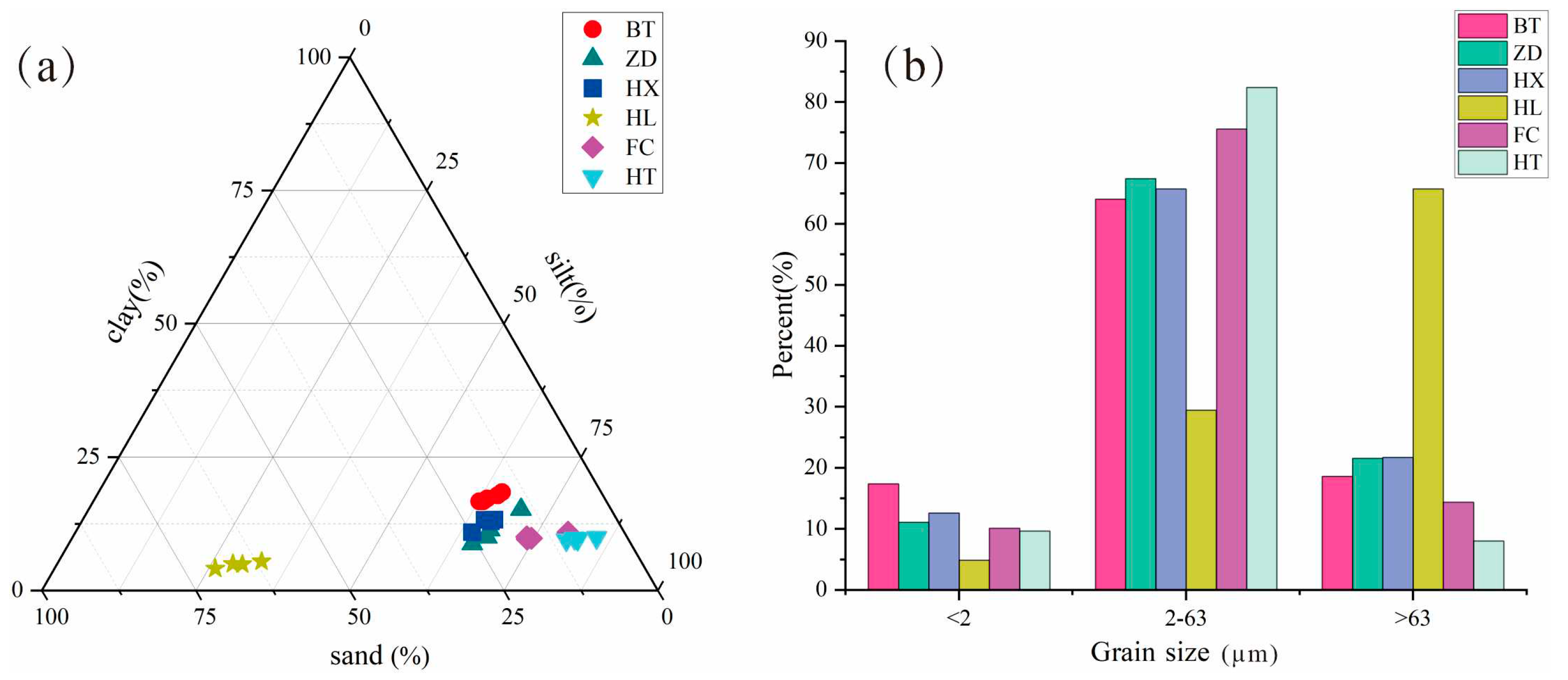
58]. A triangulation diagram of the sediment size (
Figure 10a) shows that the sediment of the fluvial facies is mainly sand, while the other samples are mainly silt. In terms of the grain size ratio at different levels (
Figure 10b), the content of clay is less than 20%. The silt contents of the Sparking Lake dam body, downstream trestle way of Panda Lake, and Sparking Lake lacustrine sediment were similar, ranging from 65% to 70%, while that of urban dust and Ganzi loess were higher than 75%, and the silt content of the fluvial facies was approximately 30% at the lowest level. Moreover, the grain size frequency curve analysis also shows that the fluvial sediments displayed typical fluvial sedimentary characteristics (
Figure 5) and strong hydrodynamic transport characteristics. The Panda Lake downstream trestle way, Ganzi loess and urban dust show obvious wind transport characteristics. The transporting agent of each sediment particle can be explored in accordance with the percentage of the content of silt. The Sparking Lake dam body, downstream trestle way of Panda Lake, and the lacustrine sediment of Sparking Lake should have a similar deposition dynamic mechanism, that is, the result of the synergistic effect of wind transport and water transport.
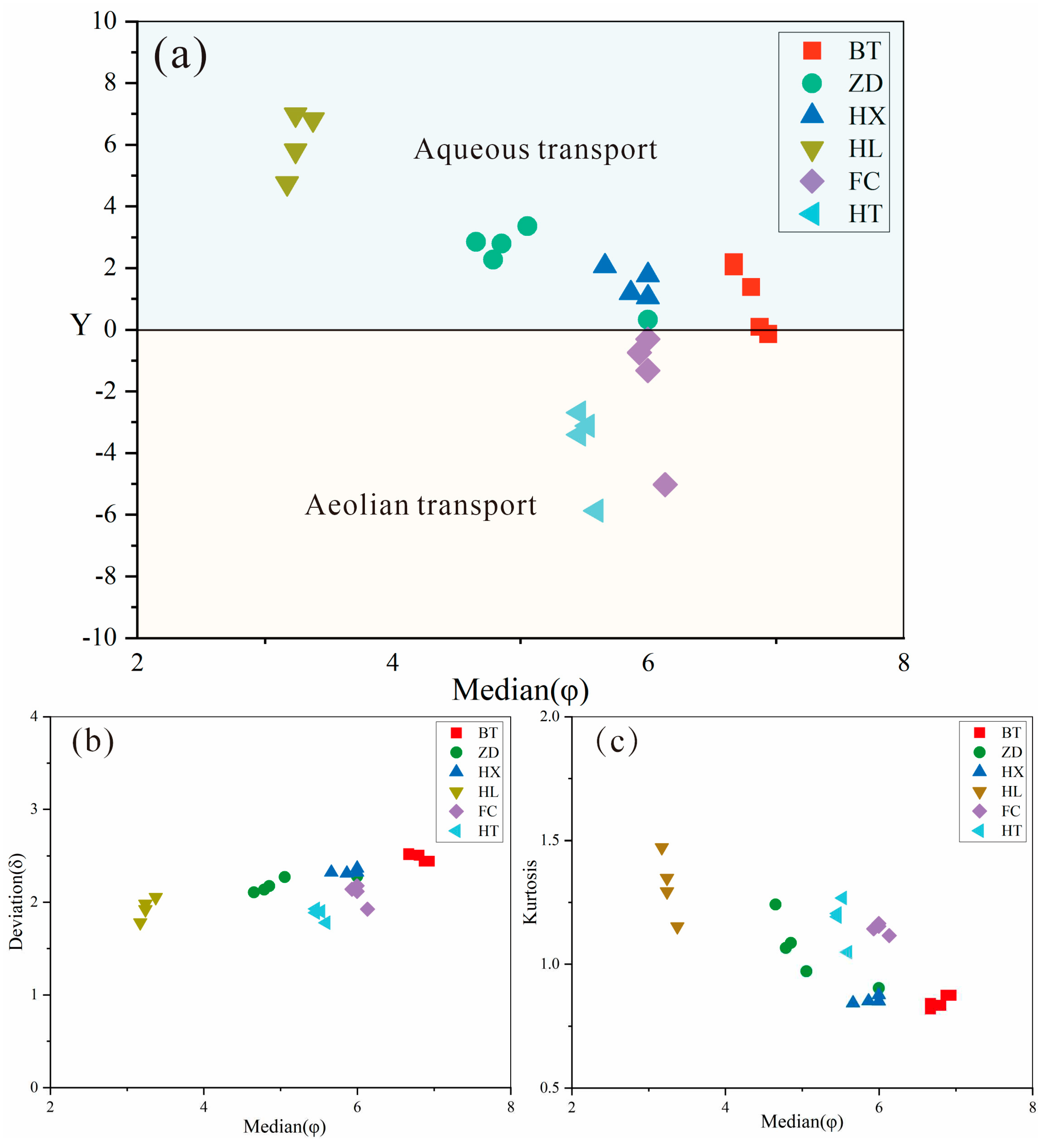
Research shows that particles of 5~6 φ (corresponding to 10~50 µm) float easily in the air and are the main objects for wind suspension transport. As the particle size becomes larger, the transport coefficient becomes smaller, which leads to the weakening of air floating performance. Particles with a size less than 4 φ (larger than 63 µm) cannot be suspended in the air and are generally transported by saltation [
59]. Through a comprehensive statistical analysis of the sediment grain size parameters, the environmental indexes of different depositional environments and processes can be determined. The discriminant function for identifying the depositional environment (Y = -3.5688 Md + 3.7016 δ2 - 2.0766 SK + 3.1135 Kg, where Md is the median grain size, δ is the standard deviation, SK is the skewness, and Kg is the kurtosis) was used to calculate the discriminant values of the Jiuzhaigou particulates and the Ganzi loess (
Figure 11). Previous studies show that the discriminant function of typical eolian sediments is negative, while most of the aqueous sediments are positive [
60,
61]. The results of the calculation (
Figure 11a) show that the plotting results of the Ganzi loess and urban dust fall in the negative range, indicating the characteristics of wind transport, which is consistent with the actual transporting agent. Fluvial sediment is a typical aqueous sedimentary model, and its discriminant value falls in the range of aqueous sedimentation, and the discriminant value reflects the strength of the sedimentary dynamics. Although most of the samples from the Sparking Lake dam body, lacustrine facies and trestle way fall in the aqueous sedimentary range, most of them were distributed near the range of a zero-discriminant value, and a small amount of particulate matter from the dam body and trestle way fall in the boundary of sedimentary environments or the eolian sedimentary range. The individual particle results under scanning electron microscopy (
Figure 6) show that all particles in Jiuzhaigou were deposited by close-range transport. The samples transported by rivers showed increased sphericity and gradually blurred and smooth surface features, such as fractures (
Figure 6f,g,h), but the original particle characteristics were still retained, in general. These characteristics indicate that the sediment samples at the dam body, the lacustrine facies of Sparking Lake and the trestle way are the result of joint transportation by wind and water agents. A scatterplot of the standard deviation of samples (
Figure 11b) and kurtosis (
Figure 11c) reflects that the dam body, lacustrine facies, trestle way, urban dust and Ganzi loess have similar sedimentary environment characteristics, to a certain extent, and are obviously different from those of fluvial sediments.
In conclusion, the proportion of silt content and the discriminant function of the sedimentary environment all intuitively show that the particles of the dam body, lacustrine facies and trestle way were the result of a combination of wind and aqueous transport. The individual particle minerals appeared to have a certain abrasion phenomenon and lacked obvious impact craters due to the fact of short-distance transport. The grain size characteristics of the sediments from the bottom of Sparking Lake and the interlayer of the dam body were similar to that of the dust or detritus generated by earthquake-induced mountain collapse, which proves that the dust or detritus from an earthquake can be deposited at the lake bottom or accumulated in the dam body after being transported by running water, finally forming a discontinuity layer that is different from conventional hydrodynamic deposition.
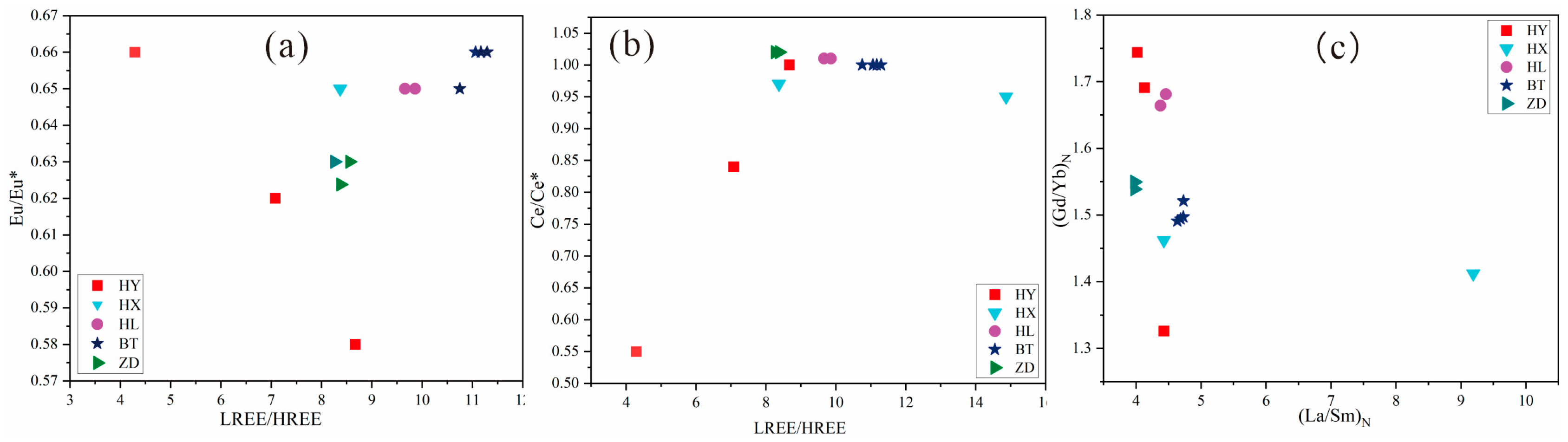
6.2.3. Indication of rare earth elements and Rb, Sr, Ba composition on source of components
Rare earth elements often coexist together in nature due to the fact of their similar chemical properties. In the process of external transport, deposition and metamorphism, the REE composition and distribution pattern of weathered products experience few changes. Therefore, the REE composition characteristics in sediments are mainly controlled by source rocks in the provenance area, and rare earth elements are often used as provenance tracers of sediments. The results show that the Eu and Ce depletion and enrichment anomalies of the particulate matter in Jiuzhaigou have strong similarity characteristics. The ratio of La
N/Sm
N and Gd
N/Yb
N can reflect the internal differentiation of the sediment LREEs and HREEs. The scatter distributions of Eu/Eu* and Ce/Ce* relative LREE/HREE ratios (
Figure 12a,b) and La
N/Sm
N and Gd
N/Yb
N (
Figure 12c) of particulate matter in Jiuzhaigou all displayed centralized distribution characteristics and were concentrated in the limestone scatter distributions range. This indicates the consistency of the provenance and inheritance of the geochemical characteristics of the regional parent rocks. The relatively small spatial differentiation of Eu/Eu* and Ce/Ce* ratios of the particulate matter in Jiuzhaigou (
Figure 13a,b) indicates stable sedimentary environment characteristics, which basically receive no affection from remote provenance. It can be concluded that the interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body is mainly from proximal dust or detritus. The overall distribution pattern of rare earth elements is consistent (
Figure 7), and the total rare earth content has obvious characteristics of continental margin marine sedimentation [
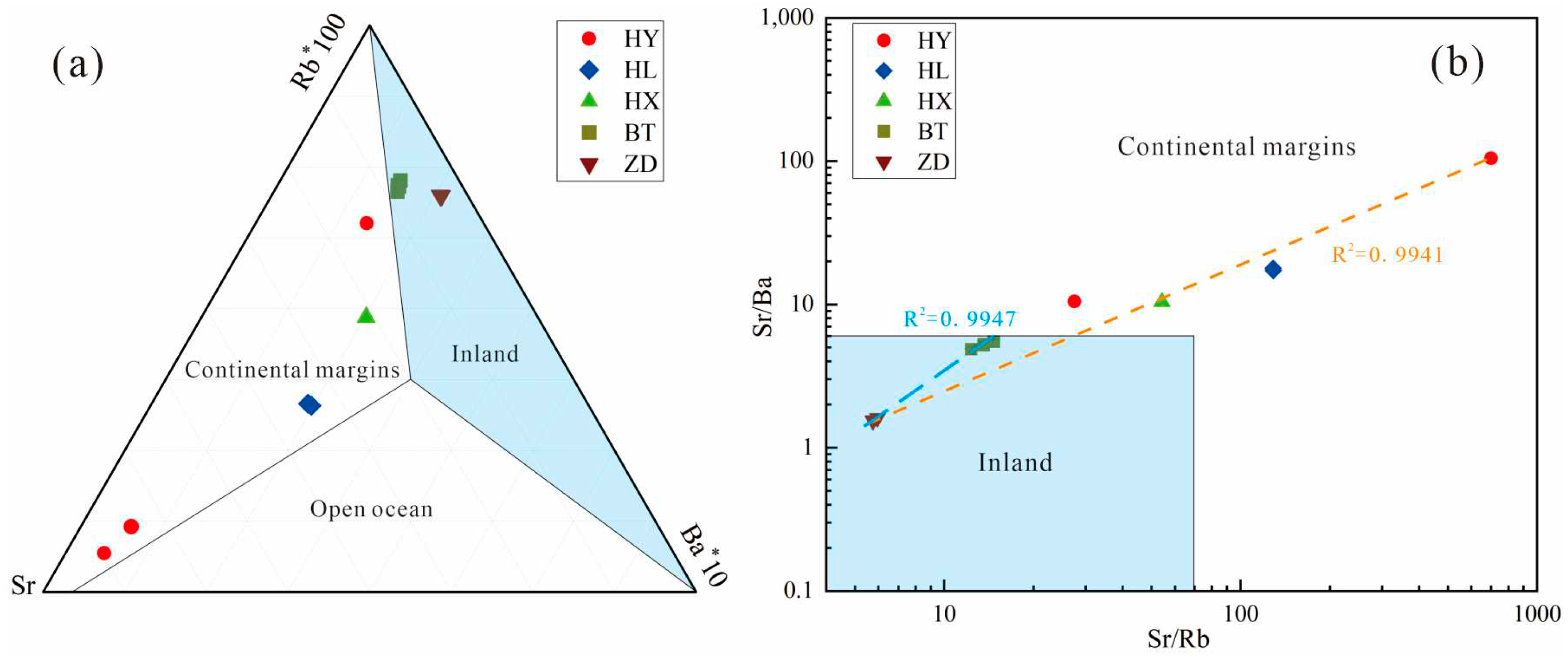
62]. Furthermore, the Rb-Sr-Ba triangles diagram show the continental margin marine sedimentary characteristics of the Limestone (HY), fluvial sediments in the lower reaches of Panda Lake (HL), and lacustrine sediments of the Sparking Lake (HX) (
Figure 14a), suggesting that the source of the tufa in Jiuzhaigou was derived from the Devonian-Triassic carbonate strata. Undersaturated karst water is formed after groundwater circulated in these layers. After outcropping and flowing through different landforms, the tufa is deposited due to the change of hydrodynamic conditions and the supersaturation of biological action and, therefore, on the whole it has a consistent pattern of partition. The Sr/Ba-Sr/Rb diagram shows an overall strong correlation (R
2 = 0.9941) for particulate matter in Jiuzhaigou (
Figure 14b), indicating the stability and homogeneity of the material sources, which are all derived from Limestone. A higher correlation (R
2 = 0.9947) was found between the trestle way (ZD) and the special interlayer of the Sparking Lake dam body (BT), suggesting a seismogenic origin for the special interlayer of the Sparking Lake dam body.
The total REE content of limestone is relatively low, while that of others is relatively high, which indicates that secondary carbonate rocks (tufa) may have a greater REE enrichment capacity and is closely related to biological participation (template and respiration). Even the content of the trestle way particles is the highest, the composition of rare earth elements can reflect the single source of provenance in the same background, and it can well distinguish the specific geological processes of different origin in the same background.
Based on the above results, it can be confirmed that the interlayer sediment of the dam body is of seismic origins rather than fluvial. The specific deposition process is that earthquakes of 1220 ± 30 a BP caused geological phenomena such as the collapse of the steep slope on both sides of the Sparking Lake due to the fact of prehistoric earthquakes which caused the dust raised by the collapse colliding violently with each other. Some particles fell to cover the mountain slope and the watercourse, and other particles fell into the water and then were carried by river to be deposited in different places, and finally deposited into the dam body, showing a special interlayer distinct from the normal flow sedimentary layer. The interlayer of the tufa dam body deposited eventually records the corresponding earthquake information, so that the study of tufa sediment profile can reconstruct the palaeoearthquake recorded in the dam body.
7. Conclusion
The sedimentary characteristics of the special interlayer of Sparking Lake tufa in Jiuzhaigou are obviously different from those of the conventional sedimentary layer of flows. Through a comparative thinking approach, this paper focused on the comparative petrographic, mineralogical, geochemical and chronological studies of the interlayered sediments of the dam body and other genetic samples to obtain homologous information and diagenetic links. The palaeoseismic benefits of the discontinuity layers in the dam body were also explored by combining the tufa sedimentary dynamics with the subsidence of earthquake disasters, and the palaeoseismic information contained in the section was extracted. This paper provides new ideas for reconstructing palaeoseismic events in Jiuzhaigou. The main innovative research results are as follows:
(1) The mountain particles in Jiuzhaigou have specific mineralogical and petrographic characteristics. According to the results of the X-ray diffraction, laser particle size analysis and scanning electron microscopy, the mineral composition of the mountain particles in Jiuzhaigou is basically calcite, the particle size is large, single particles are mostly angular or subangular and the fracture morphology observed under single particle microscope is uneven, indicating the dust lifting characteristics of seismic hazards.
(2) The source of the interlayer sediments of the dam body is earthquake. The tufa sedimentary dynamics analysis shows that seismic particles were transported and deposited near the ground by aeolian formation and accumulated in the tufa dam body by rainfall. The comparative analysis of particle size, morphology and mineral composition proves the potentiality of seismic particle accumulation in the dam body. The dams in the Rizegou and Shuzhenggou gully systems are characterized by the accretion of particles from the adjacent mountains, as evidenced by the detrital interlayers in the Sparking Lake dam. All types of particulate matter sources in Jiuzhaigou came from earthquake collapse.
(3) Geochemical analyses and chronology data indicate that the provenance of various particles in the same area is stable, indicating the homology of the sedimentation of terrestrial carbonate rocks in the karst system. Combined with mineralogy and grain size morphology, the interlayer particles in the tufa sedimentary section have the potential application of palaeoearthquake archives, and the AMS 14C age of the charcoal layer at the base of the Sparking Lake dam identifies a prehistoric seismic extreme event that occurred around 1220 ± 30 a BP. Therefore, the earthquake mountain disaster particles in tufa bedding can be linked with palaeoearthquakes, and the special interlayers in the tufa section can be used for the reconstruction of palaeoearthquakes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Fudong Wang and Shengwen Jing; methodology, Xueqin Zhao, Faqin Dong; software, Shengwen Jing, Zijian Zhou; validation, Fudong Wang, Shengwen Jing and Guoqing Huang; formal analysis, Shengwen Jing; investigation, Guoqing Huang; resources, Fudong Wang; data curation, Shengwen Jing; writing—original draft preparation, Shengwen Jing; writing—review and editing, Shengwen Jing,Fudong Wang, Enrico Capezzuoli, Andrea Brogi; visualization, Shengwen Jing, Fudong Wang; supervision, Junhao Li, Guoqing Huang; project administration, Fudong Wang, Xueqin Zhao; funding acquisition, Fudong Wang, Hanchao Jiang. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 41973053);.The Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Earthquake Dynamics, Institute of Geology, Seismological Bureau of China (grant no.LED2019B05); the Sichuan Province Overseas High-end Talent Introduction Project (grant no.22RCYJ0060); The Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Mountain Disasters and Surface Processes of China Academy of Sciences (grant no.19zd3105); The Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Loess and Quaternary Geology, Institute of Earth Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant no.SKLLQG1620). The Open Fund of Guangxi Key Science and Technology Innovation Base on Karst Dynamics(grant no.KDL&Guangxi202302).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Jiuzhaigou Administration for their support and assistance in the field work to ensure the smooth conduct of the study, to Guizhou Tongwei Test Technology co., Ltd for the accurate analysis of rare earth elements, and to Yunzhou Xu, Jiachuan Yu and Congcong Lv for their valuable comments during the writing of the paper. Many thanks to the academic editors and the three peer reviewers for their constructive suggestions to improve the quality of the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ford, T.D.; Pedley, H.M. A review of tufa and travertine deposits of the world. Earth-Sci Rev 1996, 41, 117–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H, M.P. Classification and environmental models of cool freshwater tufas. Sediment Geol 1990, 68, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentecost, A. Travertine. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media: 2005; p 1-445.
- Wang, F.; Zhao, X.; Dong, F.; Capezzuoli, E.; Malov, A.I.; Du, J. Classification of Alpine-type travertine in Jiuzhaigou valley on the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Carsologica Sinica 2021, 40, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capezzuoli, E.; Gandin, A.; Pedley, M. Decoding tufa and travertine (fresh water carbonates) in the sedimentary record: The state of the art. Sedimentology 2014, 61, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaisaoğlu, S.; Orhan, H. Sedimentology and geochemistry of the Kavakköy Travertine (Konya, central Turkey). Carbonate Evaporite 2018, 33, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedley, H.M. Classification and environmental models of cool freshwater tufas. Sediment Geol 1990, 68, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koşun, E. Facies characteristics and depositional environments of Quaternary tufa deposits, Antalya, SW Turkey. Carbonate Evaporite 2012, 27, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sembroni, A.; Molin, P.; Soligo, M.; Tuccimei, P.; Anzalone, E.; Billi, A.; Franchini, S.; Ranaldi, M.; Tarchini, L. The uplift of the Adriatic flank of the Apennines since the Middle Pleistocene: New insights from the Tronto River basin and the Acquasanta Terme Travertine (central Italy). Geomorphology 2020, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, S.C.; Karlstrom, K.E.; Love, A.J.; Crossey, L.J.; Polyak, V.J.; Asmerom, Y.; Meredith, K.T.; Crow, R.; Keppel, M.N.; Habermehl, M.A. Uranium series dating of Great Artesian Basin travertine deposits: Implications for palaeohydrogeology and palaeoclimate. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 2018, 490, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C., M.M.; S., A.M.; Z., W.; L., H.D.; A., D.J.; D., D.; R., H.W.; F., S. Permanent human occupation of the central Tibetan Plateau in the early Holocene. Science 2017, 355, 64–67. [CrossRef]
- Zaihua, L.; Hongchun, L.; Chengfeng, Y.; Naijung, W.; Hailong, S. Thickness and stable isotopic characteristics of modern seasonal climate-controlled sub-annual travertine laminas in a travertine-depositing stream at Baishuitai, SW China: implications for paleoclimate reconstruction. Environmental Geology 2006, 2, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis L, F.C.B.A. Plateau versus fissure ridge travertines from Quaternary geothermal springs of Italy and Turkey: Interactions and feedbacks between fluid discharge, paleoclimate, and tectonics. Earth-Science Reviews. 2013, 123, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradzinski M, W.W.D.M. Earthquake-affected development of a travertine ridge. Sedimentology 2014, 61, 238–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.J.J. Climatic controls on travertine deposition in southern Tibet during the late Quaternary. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 2022, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunel, E.; Karabacak, V. Determination of horizontal extension from fissure-ridge travertines: A case study from the Denizli Basin, southwestern Turkey. Geodin Acta 2005, 18, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock P L, C.R.M.L. Travitonics: Using travertines in active fault studies. J Struct Geol 1999, 21, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabacak, V.; Uysal, I.T.; Mutlu, H.E.A. Physics - Geophysics; Findings from Eskisehir Osmangazi University Update Knowledge of Geophysics (Are U-th Dates Correlated With Historical Records of Earthquakes? Constraints From Coseismic Carbonate Veins Within the North Anatolian Fault Zone). Chemicals & Chemistry 2019, 38, 2431–2448. [Google Scholar]
- T, W.R.; B, G.L.; D, S.W.; S, M.P. Reading a 400,000-year record of earthquake frequency for an intraplate fault. P Natl Acad Sci Usa 2017, 114, 4893–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, B.; Enrico, C.; Volkan, K.; Cihat, A.M.; Lianchao, L. Fissure Ridges: A Reappraisal of Faulting and Travertine Deposition (Travitonics). Geosciences 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matera, P.F.; Ventruti, G.; Zucchi, M.; Brogi, A.; Capezzuoli, E.; Liotta, D.; Yu, T.; Shen, C.; Huntington, K.W.; Rinyu, L. Geothermal fluid variation recorded by banded Ca-carbonate veins in a fault-related, fissure ridge-type travertine depositional system (Iano, southern Tuscany, Italy). Geofluids 2021, 2021, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KUMAR, K.R.; ACHUTHA, K.P. U-Th age evidence from carbonate veins for episodic crustal deformation of Central Anatolian Volcanic Province. Quaternary Sci Rev 2017, 177, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogi, A.; Capezzuoli, E.; Aqué, R.; Branca, M.; Voltaggio, M. Studying travertines for neotectonics investigations: Middle–Late Pleistocene syn-tectonic travertine deposition at Serre di Rapolano (Northern Apennines, Italy). Int J Earth Sci 2010, 99, 1383–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogi, A.; Liotta, D.; Capezzuoli, E.; Al, E. (Bagno Vignoni-Val d’Orcia area, Italy). Geothermics 2020, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Karabacak, V.; Ring, U.; Uysal, I.T. Earth Sciences; The off-fault deformation on the North Anatolian Fault Zone and assessment of slip rate from carbonate veins. Chemicals & Chemistry 2020, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogi, A.; Capezzuoli, E.; Moretti, M.; Olvera-García, E.; Matera, P.F.; Garduno-Monroy, V.; Mancini, A. Earthquake-triggered soft-sediment deformation structures (seismites) in travertine deposits. Tectonophysics 2018, 745, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogi, A.; Capezzuoli, E.; Kele, S.; Baykara, M.O.; Shen, C. Key travertine tectofacies for neotectonics and palaeoseismicity reconstruction: effects of hydrothermal overpressured fluid injection. J Geol Soc London 2017, 174, 679–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongqiang, G.; Yonggang, G.; Peng, C.; Xiaoqing, C.; Peini, M.; Tao, L.; Liang, Z. Early and mid-Holocene hydroclimate change recorded in tufa deposits in the Jiuzhaigou gully, eastern Tibetan Plateau. Catena 2021, 196, 278–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Al, E. Insights into Alpine-Karst-Type Tufa Deposits in Geological Environmental Records: A Case Study of the Calcareous Tufa Profile of the Jiuzhaigou Natural Reserve on the Eastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Minerals-Basel 2023, 13, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanchao, J.; Ning, Z.; Yanhao, L.; Xiaolin, M.; Hongyan, X.; Wei, S.; Siqi, Z.; Gaozhong, N. A continuous 13.3-ka record of seismogenic dust events in lacustrine sediments in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Sci Rep-Uk 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.C.M.X. Provenance and earthquake signature of the last deglacial Xinmocun lacustrine sediments at Diexi, East Tibet. Geomorphology 2014, 204, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Jiang, H. Geochemical composition of the last deglacial lacustrine sediments in East Tibet and implications for provenance, weathering, and earthquake events. Quatern Int 2015, 430, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henck, A.; Taylor, J.; Lu, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Grub, B.; Breslow, S.J.; Robbins, A.; Elliott, A.; Hinckley, T.; et al. Anthropogenic hillslope terraces and swidden agriculture in Jiuzhaigou National Park, northern Sichuan, China. Quaternary Res 2009, 73, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, F.; Wu, C.; Li, S. Radioactivity of Nuorilang waterfall travertine dam in Jiuzhaigou valley,Sichuan Province and its implication for the sedimentary environment. Carsologica Sinica 2021, 40, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Dai, Q.; Rao, H.; Wang, F.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, B.; Alexander, I.M.; Enrico, C.; et al. Comparative study on microbial deposition of travertine in Huanglong scenic area and Yellowstone National Park. Carsologica Sinica 2021, 40, 264–272. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, J. A system study on the geological environment and water cycle at the Jiuzhaigou Valley. Master Degree Thesis Type, Southwest Jiaotong University, Sichuan, China, 2007.
- Team, S.S.G.A. 1:50,000 Ecological Geology Map and report of Jiuzhaigou; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, X.; Xiao, Y.; Du, J.; TANG, Y.; XIAO, W.; ZHENG, X.; ZHANG, M. Tufa Landscapes in the Key Scenic Areas of the Jiuzhaigou Natural World Heritage Site: A ritical Review and Future Research Needs. Earth and Environment 2022, 50, 202–218. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, D.X.Y.X. Multiple stratigraphic classification and correlation of the Devonian- Triassic in the Jiuzhaigou area, Sichuan, and its sedimentary environment. Geology in China 2006, 33, 1013e–1022e. [Google Scholar]
- Xinlei, Z.; Ya, T.; Du Jie; Stefano, L.; Yao, X.; Qingxia, Y.; Hailiang, S.; Xue, Q. Enhanced soil erosion threatens fluvial tufa landscapes after an Ms. 7.0 earthquake in the Jiuzhaigou World Heritage Site, southwestern China. The Science of the total environment 2022, 848. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Xu, W.Y. Background and reflections on Dingxi earthquake of July 22, 2013. Nat Hazards 2014, 70, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.J. Is the Songpan-Ganzi terrane (central China) really underlain by oceanic crust? JOURNAL-GEOLOGICAL SOCIETY OF INDIA 2001, 57, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wen, X.; Shen, Z.; Chen, J. Oblique, high-angle, listric-reverse faulting and associated development of strain: The Wenchuan earthquake of May 12, 2008, Sichuan, China. Annu Rev Earth Pl Sc 2010, 38, 353–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Xiuling, W.; Hang, H.; Linjian, S.; Deqiang, Y.; Hao, W. The earthquake in Jiuzhaigou County of Northern Sichuan, China on August 8, 2017. Nat Hazards 2018, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Dong, F.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Q.; Li, Q.; Luo, Y. Characteristics of tufa output in Jiuzhaigou core heritage sites. In The 17th Annual Conference of Chinese Society for Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry, Hangzhou, China, 2019; pp 811-812.
- Lu, J.; Xiang, S.; Jiang, S.; Liu, C.; Zeng, F. Analysis of Soil Granularity at Dazhuka Country,Rikeze. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment 2008, 22, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Response of Stream Geomorphic Indices and Lacustrine Sediments to the Activity of Daqingshan Piedmont Fault. Master Degree Thesis Type, National Institute of Natural Hazards, MEMC, Beijing, China, 2021.
- Mao, X. Preliminary Study on Lacustrine Sediments at Diexi in the Upper Reach of the Minjiang River during the last deglaciation. Master Degree Thesis Type, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2011.
- Václav, S.; Pachnerová, B.K.; Jiří, Z.; Ivo, S.; Lenka, B. Gothic-Arch Calcite from Speleothems of the Bohemian Karst (Czech Republic): Its Occurrence, Microscopic Ultrastructure and Possible Mechanism of Growth. Minerals-Basel 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, B.; Sun, G.; Zhong, H.; LI, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; LI, X. Rare Earth Element Characteristics of Surface Sediments in the Fujian Coastal Area and their Implications for Provenance. Marine Geology Frontiers 2017, 33, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Xu, L. Geochemical Features of Rare Earth Elements in Sediments of the Chaohu Lake and its Environmental Implications. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology 2016, 36, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Yang, H.; Fan, H.; Xia, Y.; Meng, Q.; He, S.; Gong, X. Assessment of the Effect of Organic Matter on Rare Earth Elements and Yttrium Using the Zhijin Early Cambrian Phosphorite as an Example. Minerals 2022, 12, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibson, R.W. A Public Health Issue Related To Collateral Seismic Hazards: The Valley Fever Outbreak Triggered By The 1994 Northridge, California Earthquake. Surv Geophys 2002, 23, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhu, J.; Li, W.L.; Liang, J.T. Rainfall-triggered debris flows following the Wenchuan earthquake. B Eng Geol Environ 2009, 68, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudong, W.; Faqin, D.; Xueqin, Z.; Shiyong, S.; Qunwei, D.; Qiongfang, L.; Yaodong, L.; Pengcheng, M. The large dendritic fissures of travertine dam exposed by Jiuzhaigou earthquake, Sichuan, southwestern China. Int J Earth Sci 2018, 107, 2785–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugli, S.; Tang, Y.; Reghizzi, M.; Qiao, X.; Schreiber, B.C.; Deng, G. Seasonal Pattern In the High-Elevation Fluvial Travertine From the Jiuzhaigou National Nature Reserve, Sichuan, Southwestern China. J Sediment Res 2017, 87, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Wu, Y.; Huang, C.; Luo, M.; Chen, K. Grain size & elements composition characteristics and their lmplications for provenance of the late pleistocene loess in the upper reaches of the minjiang river china. Mountain Research 2019, 37, 488–498. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Zhong, N.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Ma, X.; Meng, Y.; Mao, X. Magnetostratigraphy and grain size record of the Xijiadian fluviolacustrine sediments in East China and its implied stepwise enhancement of the westerly circulation during the Eocene period. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2014, 119, 7442–7457. [Google Scholar]
- K., P.; H., T. The mechanics and geological implications of dust transport and deposition in deserts with particular reference to loess formation and dune sand diagenesis in the northern Negev, Israel. Geological Society, London, Special Publications 1987, 35, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu Huayu, A.Z. Comparison of Grain-size Distribution of Red Clay and Loess-paleosol Deposits in Chinese Loess Plateau. Acta Sedimentological Sinica 1999, 17, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Yu Xuefeng, Z.W.L.X. Grain size characteristics of the holocene peat sedmient in eastern Tibetan plateau and its paleo-clmiatic significance. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica 2006, 24, 64–869. [Google Scholar]
- Tang; Xian-Chun; Hui; Jie; Zeng; Lu; Yan; Li-Long; Zhang; Kai-Jun. Geochemistry of limestones deposited in various plate tectonic settings. Earth Science Reviews the International Geological Journal Bridging the Gap Between Research Articles & Textbooks 2017, 167, 27–46. [CrossRef]
Figure 2.
Sedimentation characteristics of the Sparking Lake dam: (a) scene of the Sparking Lake drying up after the earthquake; (b) schematic diagram of the profile of the Sparking Lake dam, where

hh1-4 = chronology sampling sites, I = laminated tufa, II = phytoclastic tufa, III = porous biological tufa and IV = Carbonaceous clastic layer; (c) tufa reef profile in the Sparking Lake [
28]; (d) profile of the dam on the rear of the Sparking Lake [
29].
Figure 2.
Sedimentation characteristics of the Sparking Lake dam: (a) scene of the Sparking Lake drying up after the earthquake; (b) schematic diagram of the profile of the Sparking Lake dam, where

hh1-4 = chronology sampling sites, I = laminated tufa, II = phytoclastic tufa, III = porous biological tufa and IV = Carbonaceous clastic layer; (c) tufa reef profile in the Sparking Lake [
28]; (d) profile of the dam on the rear of the Sparking Lake [
29].
Figure 3.
Jiuzhaigou particulate collection location map.
Figure 3.
Jiuzhaigou particulate collection location map.
Figure 4.
X-ray diffraction pattern of the particulate matter in Jiuzhaigou. HX = Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; HL = fluvial sediments in downstream Panda Lake; ZD = trestle way deposited particulate matter; BT = special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body.
Figure 4.
X-ray diffraction pattern of the particulate matter in Jiuzhaigou. HX = Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; HL = fluvial sediments in downstream Panda Lake; ZD = trestle way deposited particulate matter; BT = special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body.
Figure 5.
Grain size distribution curve of Jiuzhaigou: (a) special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; (b) Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; (c) fluvial sediments in downstream Panda Lake; (d) trestle way deposited particulate matter; I urban dust; (f) Ganzi loess.
Figure 5.
Grain size distribution curve of Jiuzhaigou: (a) special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; (b) Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; (c) fluvial sediments in downstream Panda Lake; (d) trestle way deposited particulate matter; I urban dust; (f) Ganzi loess.
Figure 6.
Morphology of Jiuzhaigou particulate matter under scanning electron microscopy: (a,b) special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; (c,d) trestle way deposited particulate matter; (e,f) Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; (g,h) fluvial sediments in downstream Panda Lake; (j) Ganzi loess.
Figure 6.
Morphology of Jiuzhaigou particulate matter under scanning electron microscopy: (a,b) special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; (c,d) trestle way deposited particulate matter; (e,f) Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; (g,h) fluvial sediments in downstream Panda Lake; (j) Ganzi loess.
Figure 7.
Distribution of rare earth elements in Jiuzhaigou by particulate matter. HY = collapsed limestone from mountains on both sides of Panda Lake; HL = fluvial sediments in downstream Panda Lake; HX = Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; BT = special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; ZD = trestle way deposited particulate matter.
Figure 7.
Distribution of rare earth elements in Jiuzhaigou by particulate matter. HY = collapsed limestone from mountains on both sides of Panda Lake; HL = fluvial sediments in downstream Panda Lake; HX = Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; BT = special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; ZD = trestle way deposited particulate matter.
Figure 8.
Pattern of the particulate matter deposition process in the mountains of the Jiuzhaigou earthquake: (a) seismogenic dust deposition schematic; (b) collapse of mountains on both sides of Panda Lake; (c) collapse of a mountain caused by the earthquake and the generated dust; (d) turbid water caused by particulate matter; (e) special interlayer formed in the dam body of Sparking Lake.
Figure 8.
Pattern of the particulate matter deposition process in the mountains of the Jiuzhaigou earthquake: (a) seismogenic dust deposition schematic; (b) collapse of mountains on both sides of Panda Lake; (c) collapse of a mountain caused by the earthquake and the generated dust; (d) turbid water caused by particulate matter; (e) special interlayer formed in the dam body of Sparking Lake.
Figure 9.
Evidence of the collapse of the Sparking Lake.
Figure 9.
Evidence of the collapse of the Sparking Lake.
Figure 10.
Grain size characteristics of Jiuzhaigou: (a) sediment grain size triangle illustration; (b) histogram of the percentage of each grain level. BT = special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; ZD = trestle way deposited particulate matter; HX = Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; HL = fluvial sediments in downstream Panda Lake; FC = urban dust; HT = Ganzi loess.
Figure 10.
Grain size characteristics of Jiuzhaigou: (a) sediment grain size triangle illustration; (b) histogram of the percentage of each grain level. BT = special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; ZD = trestle way deposited particulate matter; HX = Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; HL = fluvial sediments in downstream Panda Lake; FC = urban dust; HT = Ganzi loess.
Figure 11.
Grain size discriminant function diagram: (a) discriminant diagram for different deposition environments of particulate matter; (b) median–standard deviation scatter diagram; (c) median–kurtosis scatter diagram. BT = special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; ZD = trestle way deposited particulate matter; HX = Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; HL = fluvial sediments in downstream Panda Lake; FC = urban dust; HT = Ganzi loess.
Figure 11.
Grain size discriminant function diagram: (a) discriminant diagram for different deposition environments of particulate matter; (b) median–standard deviation scatter diagram; (c) median–kurtosis scatter diagram. BT = special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; ZD = trestle way deposited particulate matter; HX = Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; HL = fluvial sediments in downstream Panda Lake; FC = urban dust; HT = Ganzi loess.
Figure 12.
Scatter diagram of the characteristic parameters of rare earth elements: (a) Jiuzhaigou particulate matter Eu/Eu*-LREE/HREE scatter diagram; (b) Jiuzhaigou particulate matter Ce/Ce*-LREE/HREE scatter diagram; (c) Jiuzhaigou particulate matter LaN/SmN-GdN/YbN scatter diagram. HY = collapsed limestone from mountains on both sides of the Panda Lake; HX = Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; HL = fluvial sediments in downstream Panda Lake; BT = special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; ZD = trestle way deposited particulate matter.
Figure 12.
Scatter diagram of the characteristic parameters of rare earth elements: (a) Jiuzhaigou particulate matter Eu/Eu*-LREE/HREE scatter diagram; (b) Jiuzhaigou particulate matter Ce/Ce*-LREE/HREE scatter diagram; (c) Jiuzhaigou particulate matter LaN/SmN-GdN/YbN scatter diagram. HY = collapsed limestone from mountains on both sides of the Panda Lake; HX = Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; HL = fluvial sediments in downstream Panda Lake; BT = special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; ZD = trestle way deposited particulate matter.
Figure 13.
Eu/Eu* and Ce/Ce* ratios of particulate matter in Jiuzhaigou. HY = collapsed limestone from mountains on both sides of the Panda Lake; HX = Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; HL = fluvial sediments in the downstream Panda Lake; BT = special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; ZD = trestle way deposited particulate matter.
Figure 13.
Eu/Eu* and Ce/Ce* ratios of particulate matter in Jiuzhaigou. HY = collapsed limestone from mountains on both sides of the Panda Lake; HX = Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; HL = fluvial sediments in the downstream Panda Lake; BT = special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; ZD = trestle way deposited particulate matter.
Figure 14.
Rb, Sr, and Ba indicate the stability of particulate matter sources in Jiuzhaigou, bottom diagram reference from [
62]. (a) Rb-Sr-Ba triangles diagram indicative of continental margin marine sedimentary features of limestones. (b) Sr/Ba-Sr/Rb diagram indicates source stability of particulate matter in Jiuzhaigou. HY = collapsed limestone from mountains on both sides of the Panda Lake; HX = Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; HL = fluvial sediments in the downstream Panda Lake; BT = special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; ZD = trestle way deposited particulate matter.
Figure 14.
Rb, Sr, and Ba indicate the stability of particulate matter sources in Jiuzhaigou, bottom diagram reference from [
62]. (a) Rb-Sr-Ba triangles diagram indicative of continental margin marine sedimentary features of limestones. (b) Sr/Ba-Sr/Rb diagram indicates source stability of particulate matter in Jiuzhaigou. HY = collapsed limestone from mountains on both sides of the Panda Lake; HX = Sparking Lake lacustrine sediments; HL = fluvial sediments in the downstream Panda Lake; BT = special interlayer sediment of the Sparking Lake dam body; ZD = trestle way deposited particulate matter.
Table 1.
Percentage of the particulate matter minerals in Jiuzhaigou (wt.%).
Table 1.
Percentage of the particulate matter minerals in Jiuzhaigou (wt.%).
Sample
Number |
Calcite
(%) |
Quartz
(%) |
Muscovite
(%) |
Kaolinite
(%) |
Albite
(%) |
Dolomite
(%) |
Chlorite
(%) |
| BT-1 |
79.8 |
6.2 |
12.7 |
1.2 |
- |
- |
- |
| BT-2 |
80.3 |
6.3 |
10.6 |
2.9 |
- |
- |
- |
| BT-3 |
77.3 |
6.9 |
12.2 |
3.6 |
- |
- |
- |
| BT-4 |
78.0 |
7.4 |
9.6 |
4.9 |
- |
- |
- |
| HX |
95.1 |
3.1 |
- |
1.9 |
- |
- |
- |
| HL |
98.8 |
1.2 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| ZD |
49.7 |
18.8 |
13.5 |
4.3 |
5.8 |
7.9 |
- |
| HT |
1.0 |
44.2 |
32.5 |
4.4 |
14.7 |
0.6 |
2.5 |
Table 2.
Analysis results of rare earth elements and Rb, Sr, Ba in Jiuzhaigou particulate matter (ppm).
Table 2.
Analysis results of rare earth elements and Rb, Sr, Ba in Jiuzhaigou particulate matter (ppm).
| Sample |
HY-1 |
HY-2 |
HY-3 |
HL-1 |
HL-2 |
HX-1 |
HX-2 |
BT-1 |
BT-2 |
BT-3 |
BT-4 |
ZD-1 |
ZD-2 |
ZD-3 |
| La |
3.38 |
1.44 |
2.06 |
3.42 |
1.47 |
3.7 |
3.74 |
9.05 |
9.94 |
10.4 |
11.5 |
15.9 |
15.8 |
16.2 |
| Ce |
5.38 |
1.34 |
4.02 |
5.09 |
2.68 |
7.09 |
7.23 |
17.3 |
19.1 |
19.9 |
22 |
31.3 |
30.9 |
32 |
| Pr |
0.72 |
0.25 |
0.47 |
0.51 |
0.31 |
0.81 |
0.82 |
1.99 |
2.19 |
2.28 |
2.51 |
3.59 |
3.54 |
3.66 |
| Nd |
2.72 |
1 |
1.75 |
1.67 |
1.15 |
2.95 |
3.01 |
7.15 |
7.89 |
8.21 |
9.06 |
13.3 |
13.3 |
13.7 |
| Sm |
0.528 |
0.188 |
0.331 |
0.24 |
0.214 |
0.535 |
0.557 |
1.26 |
1.37 |
1.42 |
1.57 |
2.54 |
2.53 |
2.63 |
| Eu |
0.107 |
0.047 |
0.059 |
0.047 |
0.044 |
0.105 |
0.108 |
0.235 |
0.259 |
0.267 |
0.297 |
0.501 |
0.484 |
0.504 |
| Gd |
0.529 |
0.25 |
0.293 |
0.202 |
0.196 |
0.458 |
0.467 |
0.98 |
1.05 |
1.09 |
1.2 |
2.3 |
2.22 |
2.32 |
| Tb |
0.08 |
0.04 |
0.05 |
0.03 |
0.03 |
0.07 |
0.07 |
0.15 |
0.16 |
0.17 |
0.18 |
0.37 |
0.352 |
0.372 |
| Dy |
0.477 |
0.256 |
0.268 |
0.191 |
0.178 |
0.414 |
0.407 |
0.879 |
0.947 |
0.973 |
1.07 |
2.13 |
2.05 |
2.17 |
| Ho |
0.1 |
0.061 |
0.055 |
0.041 |
0.038 |
0.083 |
0.082 |
0.182 |
0.195 |
0.198 |
0.217 |
0.442 |
0.419 |
0.447 |
| Er |
0.29 |
0.18 |
0.16 |
0.12 |
0.11 |
0.24 |
0.24 |
0.54 |
0.57 |
0.59 |
0.64 |
1.26 |
1.18 |
1.27 |
| Tm |
0.042 |
0.027 |
0.023 |
0.018 |
0.018 |
0.038 |
0.037 |
0.085 |
0.09 |
0.093 |
0.101 |
0.197 |
0.186 |
0.195 |
| Yb |
0.26 |
0.16 |
0.14 |
0.12 |
0.11 |
0.23 |
0.23 |
0.55 |
0.58 |
0.6 |
0.65 |
1.24 |
1.19 |
1.24 |
| Lu |
0.04 |
0.02 |
0.02 |
0.02 |
0.02 |
0.04 |
0.04 |
0.08 |
0.09 |
0.09 |
0.1 |
0.19 |
0.18 |
0.185 |
| Y |
3.86 |
3.27 |
1.81 |
1.58 |
1.49 |
2.47 |
2.46 |
5.49 |
5.79 |
5.98 |
6.52 |
13.4 |
12.8 |
13.6 |
| ΣREE |
14.65 |
5.26 |
9.69 |
11.71 |
6.57 |
16.76 |
17.0368 |
40.4262 |
44.43 |
46.2785 |
51.096 |
75.258 |
74.331 |
76.893 |
| LREE |
12.84 |
4.26 |
8.69 |
10.97 |
5.87 |
15.19 |
15.47 |
36.99 |
40.75 |
42.48 |
46.94 |
67.13 |
66.55 |
68.69 |
| HREE |
1.81 |
0.99 |
1 |
0.74 |
0.7 |
1.57 |
1.57 |
3.44 |
3.68 |
3.8 |
4.16 |
8.13 |
7.78 |
8.20 |
| LREE/HREE |
7.08 |
4.29 |
8.67 |
14.87 |
8.37 |
9.66 |
9.86 |
10.75 |
11.06 |
11.17 |
11.29 |
8.26 |
8.56 |
8.38 |
| LaN/YbN |
9.4 |
6.58 |
10.55 |
21.33 |
9.59 |
11.39 |
11.66 |
11.91 |
12.25 |
12.39 |
12.63 |
9.2 |
9.5 |
9.4 |
| Eu/Eu* |
0.62 |
0.66 |
0.58 |
0.66 |
0.65 |
0.65 |
0.65 |
0.65 |
0.66 |
0.66 |
0.66 |
0.63 |
0.62 |
0.62 |
| Ce/Ce* |
0.84 |
0.55 |
1 |
0.95 |
0.97 |
1.01 |
1.01 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1.02 |
1.01 |
1.01 |
| Rb |
8.39 |
1.17 |
1.01 |
4.34 |
4.34 |
11.9 |
12.0 |
28.1 |
32.1 |
31.3 |
34.2 |
56.9 |
54.6 |
55.2 |
| Sr |
231 |
818 |
1290 |
559 |
560 |
647 |
650 |
413 |
436 |
426 |
422 |
328 |
325.2 |
317.4 |
| Ba |
22 |
7.85 |
8.8 |
31.3 |
32.5 |
62.1 |
62.5 |
75.3 |
84 |
80.5 |
86.8 |
212 |
202 |
205.6 |
Table 3.
14C dating data of tufa in Sparkling Lake dam.
Table 3.
14C dating data of tufa in Sparkling Lake dam.
| Sample Number |
δ13C(IRMS,‰) |
Corrected age(cal BP) |
Average corrected age(2δ a BP) |
| hh1 |
-25.3 |
(412-315calBP)(54.1%)
(492-420calBP)(14.6%) |
1170±30 |
| hh2 |
-26.7 |
(1182-1050calBP)(87.5%)
(1030-999calBP)(7.2%)
(1220-1214calBP)(0.7%) |
1180±30 |
| hh3 |
-24.2 |
(1188-1063calBP)(74.5%)
(1258-1202calBP)(20.9%) |
1220±30 |
| hh4 |
-25.7 |
(412-315calBP)(54.1%)
(492-420calBP)(41.3%) |
350±30 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
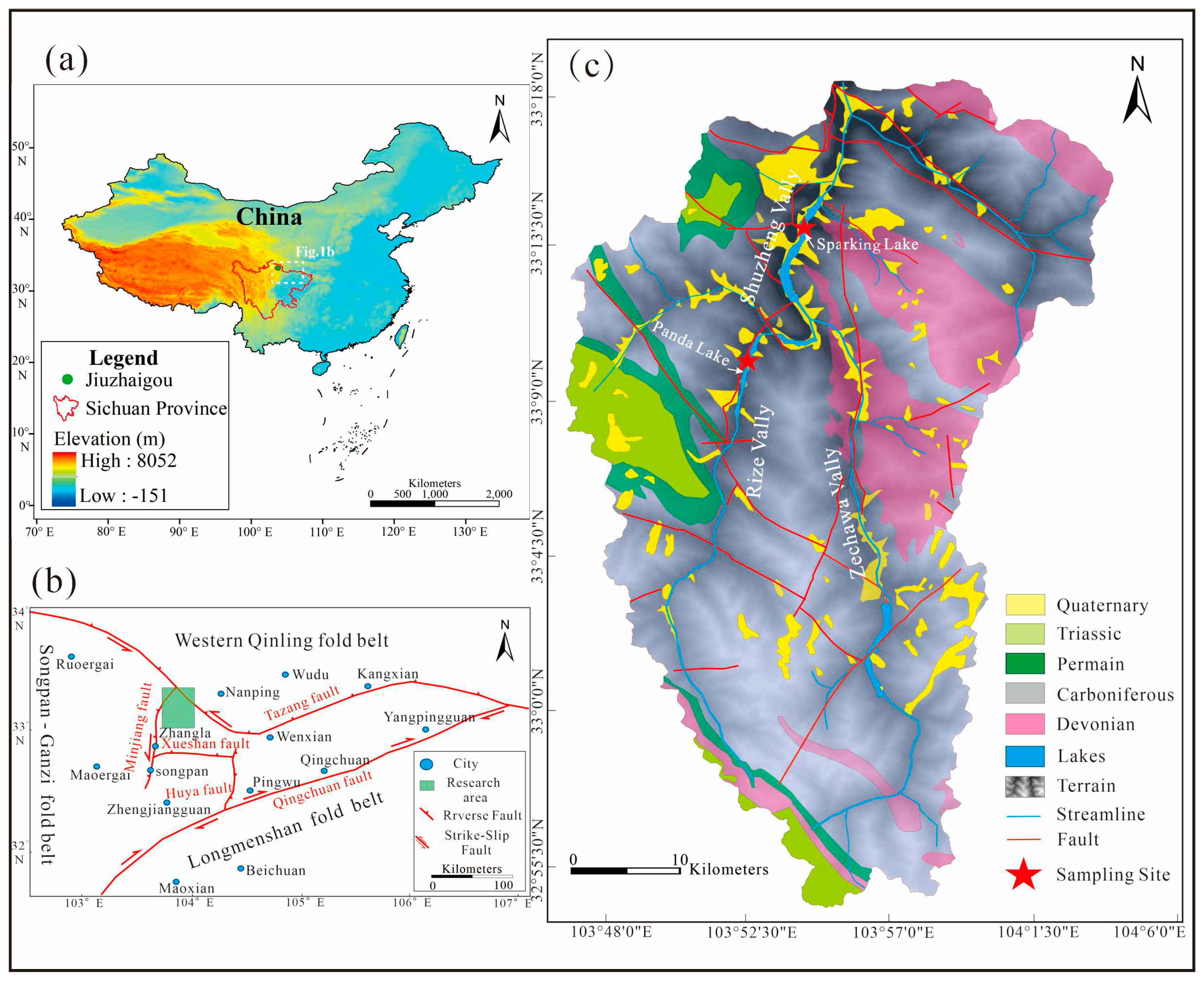
 hh1-4 = chronology sampling sites, I = laminated tufa, II = phytoclastic tufa, III = porous biological tufa and IV = Carbonaceous clastic layer; (c) tufa reef profile in the Sparking Lake [28]; (d) profile of the dam on the rear of the Sparking Lake [29].
hh1-4 = chronology sampling sites, I = laminated tufa, II = phytoclastic tufa, III = porous biological tufa and IV = Carbonaceous clastic layer; (c) tufa reef profile in the Sparking Lake [28]; (d) profile of the dam on the rear of the Sparking Lake [29].
 hh1-4 = chronology sampling sites, I = laminated tufa, II = phytoclastic tufa, III = porous biological tufa and IV = Carbonaceous clastic layer; (c) tufa reef profile in the Sparking Lake [28]; (d) profile of the dam on the rear of the Sparking Lake [29].
hh1-4 = chronology sampling sites, I = laminated tufa, II = phytoclastic tufa, III = porous biological tufa and IV = Carbonaceous clastic layer; (c) tufa reef profile in the Sparking Lake [28]; (d) profile of the dam on the rear of the Sparking Lake [29].