1. Introduction
The assays of the activity of cytochromes P450 (P450s) in drug-metabolizing reactions are widely employed in pharmacological research. They constitute an ultimate part of the studies with newly developed drugs necessary for their approval for practical use [
1]. Determining the rate of P450-dependent reactions is among the most often performed enzyme assays in current biochemical practice. The most common methods for these studies are based on detecting the products of P450-dependent reactions with the LC-MS/MS technique. They are often used in a high-throughput setup necessary for scanning large series of drug candidates. However, LC-MS/MS methods are time-consuming, laborious, and require specific setups for each particular product being monitored. Therefore, developing a more universal and less resource-consuming method for high-throughput P450 activity assays would be highly beneficial. Our motivation for developing such a method is caused by our interest in high-throughput studies of correlations between the profile of drug metabolism and the composition of the P450 pool in the human liver. These studies are necessary for elaborating the concept of functional integration in the drug-metabolizing ensemble [
2].
In our search for a reliable, inexpensive, and versatile technique for high-throughput kinetic assays of drug metabolism, we turned our attention to an old-school approach based on the determination of formaldehyde (FA), which is formed in oxidative demethylation of drugs [3-4]. N- and O-demethylations constitute up to one-third of all reactions catalyzed by human P450 enzymes (see [
5] for examples). The most common approach for monitoring the P450-dependent formation of FA is a colorimetric technique based on the Nash method [
6] that uses the formation of diacetyldihydrolutidine, a heterocyclic compound absorbing in the blue and near-UV region, from formaldehyde, ammonium, and acetylacetone through the so-called Hantzsch reaction. Following the first publications with its use [7-8], this method became predominant in the early studies of P450 catalysis. However, due to its relatively low sensitivity, this technique was later superseded by HPLC- and LC-MS/MS-based techniques.
Nevertheless, the capabilities of methods based on formaldehyde detection are nowhere near exhausted. There is a series of new sensitive techniques for colorimetric and fluorometric detection of FA (see [9-10] for a review), which may be used for monitoring P450-dependent reactions. In this study, we probed several of these techniques and chose to go with a fluorometric approach based on the Hantzsch reaction with acetoacetanilide. Here we describe a sensitive and robust high-throughput method for monitoring P450-dependent demethylation reactions with the use of a liquid handling robot and fluorometric plate reader.
We also report the application of our new technique to re-evaluate the pathways of metabolism of ketamine by cytochrome P450 ensemble of the human liver. This drug is an NMDA receptor antagonist widely used as a dissociative anesthetic and antidepressant. Our interest in the metabolism of ketamine is inspired by the fact that this drug, besides being a typical example of a substrate of P450-dependent demethylation, is increasingly used as an antidepressant for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS) and alcohol use disorder (AUD) [11-12]. However, due to a narrow therapeutic index of ketamine used as an antidepressant, a better understanding of its metabolic pathways in alcohol-exposed patients is needed to further expand its use [
13].
The only FDA-approved ketamine-based medication for the treatment of AWS and other depressive disorders is Esketamine, a nasal spray containing S-ketamine, one of the two enantiomers of the drug [
14]. Therefore, in this study, we elected S-ketamine as a substrate of P450-dependent demethylation reactions. We studied its metabolism by ten recombinant human drug-metabolizing P450s. Our results make significant adjustments to the understanding of ketamine metabolism pathways. Besides confirming the role of CYP3A and CYP2B6 enzymes, they indicate a significant involvement of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19, which was initially underestimated.
We also studied ketamine demethylation by five different pooled preparations of human liver microsomes (HLM) including a preparation from ten chronic alcohol consumers. We observed dramatic differences in the kinetic parameters of this reaction across the HLM samples. Notably, the activity of the preparation from alcohol consumers was the highest of all HLM samples probed, and the shape of its substrate saturation profile (SSP) suggests an important difference from other HLM samples in the involvement of the individual P450 species.
In summary, our study introduces an efficient, robust, and inexpensive platform for high-throughput studies of drug metabolism by HLM samples, which is necessary for studying functional integration in the P450 ensemble. It also provides important new information on the pathways of metabolism of ketamine, a perspective antidepressant for use in AWS and AUD.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
Actoacetanilide was the product of the Tokyo Chemical Industry (Tokyo, Japan). S-Ketamine was obtained from Cayman Chemical Company (Ann Arbor, MI) as a certified reference material (CRM) solution in methanol (1 mg/ml). Prior to the use of this reagent, the methanol solvent was evaporated under the stream of argon gas and the chemical was re-dissolved in 0.1 M Hepes buffer pH 7.4 containing 60 mM KCl. The concentration of ketamine in the stock solution was determined from its absorbance at 265 nm using the extinction coefficient of 0.562 mM-1cm-1. (S)-norketamine hydrochloride and midazolam were purchased from Cayman Chemical Company (Ann Arbor, MI). Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides, NADP, Glucose-6-phosphate, and midazolam were the products of MilliporeSigma (Burlington, MA). All other reagents were of ACS grade and used without additional purification.
2.2. Microsomes containing recombinant human cytochromes P450
Most microsomal preparations containing individual P450 enzymes were the (Supersomes®, the products of BD Gentest, formerly a part of Corning Life Sciences (Tewksbury, MA). In the present study, we used the preparations containing CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2E1, CYP3A4, and CYP3A5. All those preparations contained human CPR and cytochrome b5 co-expressed. The preparation of insect cell microsomes containing human CYP2D6 along with human CPR and cytochrome b5 (Baculosomes®) was the product of Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, Massachusetts).
2.3. Pooled human liver microsomes
The pooled HLM preparation obtained from 10 donors (mixed gender) with a history of chronic alcohol exposure (lot FVT) was purchased from BioIVT Corporation (Baltimore, MD) and referred to here as HLM(FVT). We also studied three different preparations of pooled human liver microsomes from 50 donors (mixed gender) without a reported alcohol exposure history (the lots EGW, DNJ, and CDN). The sample referred to as HLM(Xen263) is the pulled preparation from 50 donors (mixed gender) supplied by XenoTech Corp (lot 2110263), which is also now a part of BioIVT Corp. The suppliers of the HLM preparations used in our studies, BioIvt Corporation and XenoTech Corp., have declared to adhere to the regulations of the Department of Health and Human Services for the protection of human subjects (45 CFR §46.116 and §46.117) and Good Clinical Practice (GLP), (ICH E6) in obtaining the samples of human tissues used for producing the preparations of human subcellular fractions available from these companies.
The concentrations of CPR in microsomal membranes, which were used to calculate apparent turnover numbers of the P450-dependent demethylation, we determined based on the rate of NADPH-dependent reduction of cytochrome c at 25 °C. The effective molar concentration of CPR was estimated using the turnover number of 3750 min
-1 [
15].
2.4. High-throughput assay of P450-dependent demethylation.
The process of development of this procedure is outlined in section 3.1 under Results. The final protocol of the high-throughput assay with the use of an OT-2 liquid handling robot (Opentrons Inc., Brooklyn, NY) and Cary Eclipse fluorometer equipped with a plate reader accessory (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) is described below.
The ketamine metabolism experiments were conducted with a series of 12 ketamine stock solutions in the Incubation Buffer (0.1 M Hepes buffer pH 7.4 containing 60 mM KCl) with the concentration ranging from 0 to 2.8 mM prepared with serial dilution. This series of stock solutions provided the ketamine concentrations in the incubation mixture decreasing from 700 to 0 µM with a dilution factor of 1.73333 (≈√3). 2 ml plastic tubes with these solutions were placed in a 20-tube aluminum rack (20x1.5 ml tube rotor, Benchmark Scientific, Sayreville, NJ) positioned in location 8 of the OT-2 deck. Location 9 contained a 96-Well Deep Well Plate with 1 ml V-Bottom wells (Azotta Corp., Claymont, DE). The first row of this plate was filled with 500 µl of NADPH-generating system in each of the 8 wells. The NADPH-generating system contained 200 µM NADP, 2 mM glucose-6-phosphate, and 1 unit/ml of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in the Incubation Buffer. An empty 96-well plate (UltraCruz V-bottom black plate, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) was placed at position 7 of the OT2 deck. Positions 10 and 11 contained racks with 300µl and 20 µl pipet tips, respectively. The protocol of the OT-2 run starts with filling all wells of the incubation plate with 40 µl of the NADPH system using an 8-channel 300 µl pipette. It is followed by adding 20µl of ketamine solutions to the wells using a single-channel 20 µl pipette. The protocol of the OT-2 run was designed in such a way that the concentrations of ketamine in the wells on the plate were shuffled so that the order of the rows containing increasing concentration was 6 (0 µM ketamine), 12, 5, 11, 4, 10, 3, 9, 2, 8, 1, and 7 (700 µM in the incubation mixture). The OT-2-compatible protocol file is available from the authors on request.
The plate prepared as described above was placed into a heater-shaker module equipped with a PCR-plate adapter and placed in location 1 of the deck. Suspensions of microsomes were diluted to desired concentration (0.1 – 0.5 µM P450 for recombinant enzymes and 1 – 2 mg/ml for HLM samples) and placed into all eight wells of the first row of a PCR plate (96-well semi-skirted PCR plate, BrandTech Scientific Inc., Essex, CT ), 255 µl per well. The PCR plate was inserted into a pre-cooled PCR-plate cooling block (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) and placed at position 5 of the OT-2 deck. An Azzota deep-well plate placed in location 6 contained 0.4 ml of quenching solution in each well of the first row. The quenching solution is composed of 0.25 M acetoacetanilide and 1.5% acetic acid in ethanol. The second row of the same plate contained 0.6 ml of 7 M solution of ammonium acetate per well. A rack with 300µl pipette tips was inserted into the deck position 4. The protocol of the OT-2 run of the activity assay starts with pre-incubation of the reaction plate in the heater-shaker module set at 1200 rpm shaking and 37 °C. This setting of the heater resulted in the temperature of 29.5 – 31 °C in the incubation mixture stabilized after 10 min of pre-incubation. Subsequently, the robot starts the reaction by dispensing 20 µl of microsomal suspension per well with an 8-channel 300 µl pipet. The addition of microsomes to each row was followed by 20 sec shaking. After adding microsomes to the last row, the robot continues shaking at a constant temperature until reaching the desired incubation time (12 min). The reaction was then stopped by adding the quenching solution in the volume of 32 µl per well with an 8-channel 300 µl pipette. The addition of the reagent to each row was followed by shaking for 20 sec. The protocol then ends with adding 48 µl of the ammonium acetate solution per well with an 8-channel 300 µl pipette. The OT-2-compatible protocol file for this procedure is available from the authors on request.
The incubation plate treated as described above was then centrifuged at 3,800 rpm in a Beckman Allegra 6R centrifuge with a GH-3.8 swing-out rotor with multiwell-plate adapters. After 20 min of centrifugation, the plate was scanned with a Cary Eclipse fluorometer with a well-plate accessory. We acquired the spectra of excitation of fluorescence in the 300 – 440 nm region with emission at 468 nm and excitation and emission slits set at 10 and 20 nm, respectively. The fluorescence remains stable for approximately 40 min.
2.5. Methods of data analysis
All preparatory manipulations with the series of fluorescence spectra, their analysis, and the subsequent fitting of the titration traces were performed using our SpectraLab software [
16]. The latest version of the software package is freely available on the author’s website [
17].
The series of the excitation spectra were first sorted in the order of the increasing ketamine concentrations, smoothed with a 15-point window 3rd-order polynomial smoothing, and resampled to the 300 – 430 nm region with a 2 nm step. The amplitude of the spectra was corrected to take into account differences in the sensitivity of the plate reader between different wells of the 96-well plate. For this correction, we used a set of 96 correction factors obtained with a plate with all wells filled with 160 µl of a standard solution of a fluorescent dye (we used Cumarin-460 laser dye with excitation at 395 nm and emission at 468 nm).
The corrected set of fluorescence spectra was then subjected to a principal component analysis (PCA) combined with the approximation of the first three principal vectors with a combination of standard excitation spectra of 1 µM 3,5-di-N-phenylacetyl-1,4-dihydrolutidine (DPDL, the product of Hantzch reaction with acetoacetanilide), 1 µM NADPH and a prototypical spectrum of excitation of internal fluorescence of microsomes obtained with rat liver microsomes in the presence of AAA and acetic acid, but in the absence of ammonium acetate. The set of these fluorescence standards is available from the authors on request. The partitioning coefficients obtained from these approximations were then used by our software to resolve the fluorescence intensities of DPDL and NADPH in the wells. Since the concentration of NADPH in the wells was kept constant with the use of the NADPH-generating system, its fluorescence was used as an internal standard to correct for minor variations in the sensitivity of the plate reader due to possible differences in the level of the liquid between the wells (see section 3.1.2 for more details). After normalization, the set was subjected to PCA, and the approximations of the first two principal components with our set of fluorescence standards were used to determine the FA in the wells. The SpectraLab scripts for automatized data pre-pretreatment and analysis are available from the authors on request.
2.6. S-ketamine demethylation assays with LC-MS/MS technique.
Preparation on the well plates and their incubation were carried out with the use of an OT-2 robot following protocols similar to those described for FA detection. However, in this case, the AAA reagent in the quenching solution was replaced with 17.5 µM midazolam used as the internal standard. The addition of ammonium acetate was omitted.
Quantification of norketamine formed in N-demethylation of S-ketamine was performed using a Xevo-TQ-XS MS (Waters, Milford, MA), coupled with microflow M-Class UPLC. Acquity UPLC HSS T3 column (100 Å, 1.8 μm, 1 mm × 100 mm) was used for metabolite elution. The mass spectrometer was operated in multiple reaction monitoring mode using an electrospray ionization source. The LC parameters were set at a 50 μL/min flow rate with a 1 μL injection volume and a column temperature of 40 °C. Mobile phase A (water with 0.1% formic acid) and B (acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid) were used and the following gradient was applied: 70:30 from 0.0 to 0.9 minutes, shifting to 10:90 from 0.9 to 3.0 minutes, held at 10:90 from 3.0 to 5.5 minutes, shifting to 70:30 from 5.5 to 5.8 min, and remaining at 70:30 from 5.8 to 7.5 minutes. The mass spectrometer was set to the positive ion (ESI+) mode with a cone voltage of 35 V. The MRM transitions for norketamine and midazolam were m/z 224.1 → 207.1, 179.1, and 125.1 (collision energy (CE), 15 eV) and m/z 326.1 → 309.1, 291.1, and 244 (CE, 20 eV), respectively. For norketamine, an average of all three product ions was taken during data processing, whereas for midazolam, m/z 291.1 and 244 were chosen as the quantifier ions, and m/z 309.1 was used as a qualifier ion. Elution times for compounds were 2.4 min for norketamine and 4 min for midazolam. Quantification was accomplished using a linear regression fit to an external calibration curve prepared in tandem with samples. Peak integration and quantification were performed using Skyline 22.2 (University of Washington). Calibration curves of norketamine and midazolam (final concentrations, 1-1000 nM) prepared in a mixture of water: acetonitrile (30:70 v/v) were used for calculating metabolite concentrations in HLM incubations.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Developing a method for high-throughput assay of cytochrome P450-dependent demethylation reactions.
3.1.1. Selecting the method for formaldehyde detection.
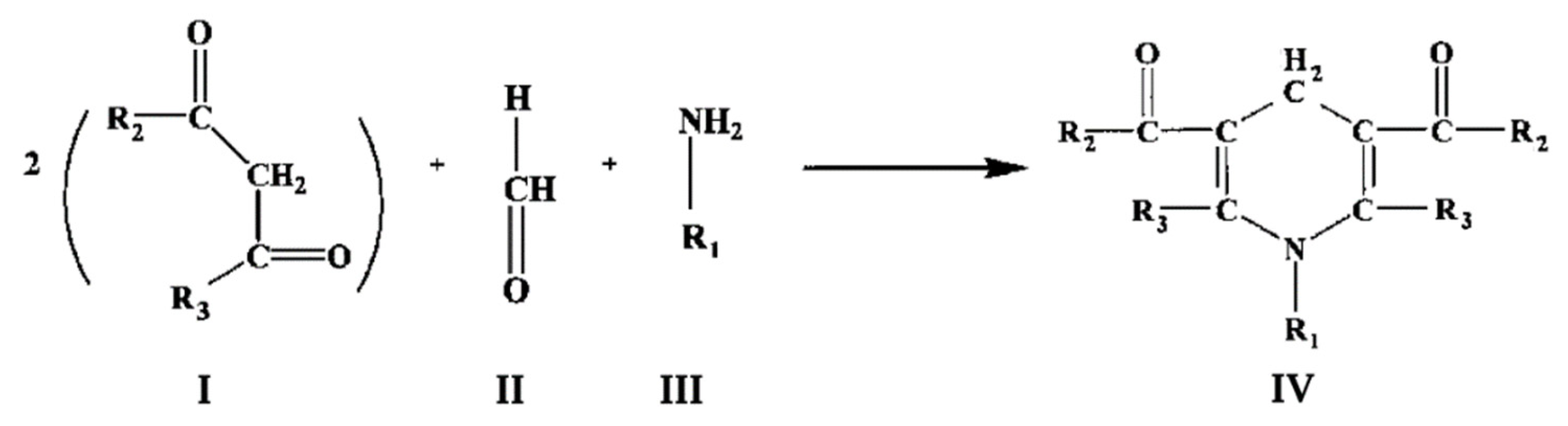
The most common method of detection of formaldehyde (FA) generated in P450-dependent demethylation reactions was developed in 1954 by Nash [
6]. It is based on the Hanzsch reaction, which is illustrated in
Figure 1. Here two molecules of a β-diketone (I) react with a molecule of formaldehyde (II) and a molecule of ammonia or alkylamine (III) to form a molecule of a heterocyclic compound, a derivative of dihydrolutidine (IV), which absorbs in the near-UV or blue region and exhibits fluorescence with the maximum at 460 – 510 nm depending of the nature of substituents R
1, R
2, and R
3:
The Nash method uses acetylacetone as β-diketone which interacts with FA and ammonia with the formation of 3,5-diacetyl-1,4-dihydrolutidine (DDA). This product is detected by the appearance of absorbance at 412 nm. The reaction requires prolonged incubation at a high temperature (60 °C). This method in its original implementation is the most frequently used technique for detecting formaldehyde formed in P450-dependent demethylation. This assay is very inexpensive and easy to perform. However, its sensitivity is limited by the relatively low extinction coefficient of DDA (7.7 mM
-1cm
-1 [
6]). In practice, reliable quantification of FA with Nash reagent and absorbance measurements requires concentrations higher than 20 µM. This low sensitivity undermines the utility of the method in the studies of P450-dependent reactions. Although the detection of DDA fluorescence allows for increasing the sensitivity of the method [
18], its fluorometric variant has been used only in one cytochrome P450-related study [
19].
Another method of detecting formaldehyde that is sometimes used in the P450 studies is a colorimetric determination of aldehydes with the purpald reagent (4-Amino-3-hydrazino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole) [20-21]. However, in our trials, the sensitivity of this method was found even lower than that of the Nash technique with fluorometric detection.
There are also several kits for fluorometric determination of formaldehyde available from such manufacturers as Abcam, AAT Bioquest, and Arbor Assays. They are based on the use of undisclosed reagents and are quite expensive (
$3 -
$5 per assay). Most of them are not designed for use in the P450 activity measurements. The only exception is the P450 Demethylation Fluorescent Activity Kit available from Arbor Assays (product K011-F1). Unfortunately, the documentation provided by the manufacturer does not include exact information on its sensitivity. We probed using this kit in the assays in the presence of rat liver microsomes and found its sensitivity to be around 10 µM FA, which is only slightly better than that of the Nash method (data not shown). This low sensitivity and the high price of the kit undermine its utility for the P450 studies – we found only one published paper with its use [
22].
Another commercial kit that we attempted to use is Amplite® Fluorimetric Formaldehyde Quantitation Kit from AAT Bioquest (catalog number 10057). We modified the protocol for the use with microsomal preparations and tested the method with the use of a conventional fluorometer with a 3x3 mm quartz cell. Although the sensitivity and reliability of this assay were better than that of the Arbor Assays kit, we held back from using it due to its high price.
There are also several new fluorometric techniques of FA detection developed in the recent decade [10,23-26]. However, these new methods use custom reagents, which are not commercially available. They have never been used for P450 activity detection in literature. To probe one of the most promising new methods, we synthesized the naphthalimide-based fluorescent probe RBNA introduced by Jiang and co-workers [
26]. Unfortunately, we found it extremely unstable and prone to spontaneous oxidation which prevents its practical use.
In our further search for a reliable, and low-cost method of FA detection adaptable to high-throughput applications, we turned back to fluorometric variants of the techniques based on the Hantzsch reaction. Probing the classical Nash method with the detection of DDA fluorescence, we found that, when used with a conventional fluorometer, it gives a sensitivity of around 10 µM FA, which is only slightly better than its implementation with the absorbance detection. In addition, this method requires a prolonged incubation of samples at 60 °C, which complicates its high-throughput implementation.
Besides acetylacetone used in the Nash method, there are several other commercially available β-diketones probed as reagents in fluorometric variants of the Hantzsch reaction [
27]. According to Li et al. [27-28], the best sensitivity is obtained with methyl acetoacetate (MeAA) and acetoacetanilide (AAA). The respective lutidine derivatives have the highest extinction coefficients and fluorescence quantum yields. We first tried the variant with MeAA and found it much more sensitive than the original Nash procedure. The variant of this method with a conventional fluorometer and a 3x3 mm quartz cell allows reliable detection of 1 µM FA in the presence of microsomal preparations. However, similar to the Nash method, the Hantzsch reaction with MeAA requires prolonged incubation at 60 °C, which complicates its high-throughput implementation because of evaporation from the wells and condensation of the liquid on the well-plate cover. This effect may unevenly affect the volume of the liquid in the wells and thus undermine reproducibility.
In contrast, the reaction with AAA requires only 20 min incubation at room temperature to be complete. Its sensitivity is even higher than that of the MeAA variant. Thus, we finally made our choice in favor of using the AAA-variant of the Hantzsch reaction in further elaboration of the FA-detection method. It is to note that the same chemistry is apparently used in the FA-detection kit ab272524 available from Abcam company, as well as the formerly available kit ab133084 from the same manufacturer [
29]. However, these kits are not optimized for use in enzyme activity assays with microsomes, and their high price bares large-scale implementation in research.
3.1.2. Elaborating a method for detecting cytochrome-P450 dependent generation of formaldehyde with the AAA reagent
Our work on developing an AAA-based assay procedure was based on the publication of Li and co-workers [
28]. According to these authors, the best sensitivity of the fluorometric assay with AAA, which is not readily soluble in water, is achieved in the presence of 30% ethanol. The optimal concentration of AAA recommended by Li et al. is 40 mM. In our optimization trials, we found that the ethanol concentration may be decreased to 20% without a loss of sensitivity, while the increase in the concentration of AAA to 50 mM decreases the incubation time needed. Following the recommendation of Li et al., we kept the concentration of ammonium acetate at 2.1 M.
Enzyme activity assays require the reaction to be quenched at the end of the incubation time. As a method of quenching, we selected acidification with acetic acid, which can be added along with the AAA reagent in ethanol solution. Since the optimal pH range for the Hantzch reaction is 7 – 7.8 [
28], the concentration of acetic acid must be adjusted to decrease the pH below 4, where no P450 activity is observed while allowing pH to return to neutral after the addition of ammonium acetate.
After optimization, we came to the following protocol: The incubation of microsomes with substrate and NADPH is performed in 80 µl of 0.1 M Hepes buffer, pH 7.4. The reaction is stopped by the addition of 32 µL of 0.25 M solution of AAA in ethanol containing 1.5% acetic acid. That results in 0.43% of acetic acid in the media and decreases its pH to 3.9. The subsequent addition of 48 µl of 7 M ammonium acetate alkalizes the media and brings its pH to 6.9, which is close to optimal for the Hantzsch reaction. The reaction is complete after 20 min of incubation at room temperature. This time is used to spin out the microsomes by centrifugation at 3,800 rpm in a Beckman Allegra 6R centrifuge with a GH-3.8 swing-out rotor. After 20 min of centrifugation, the fluorescence remains stable for approximately 40 min.
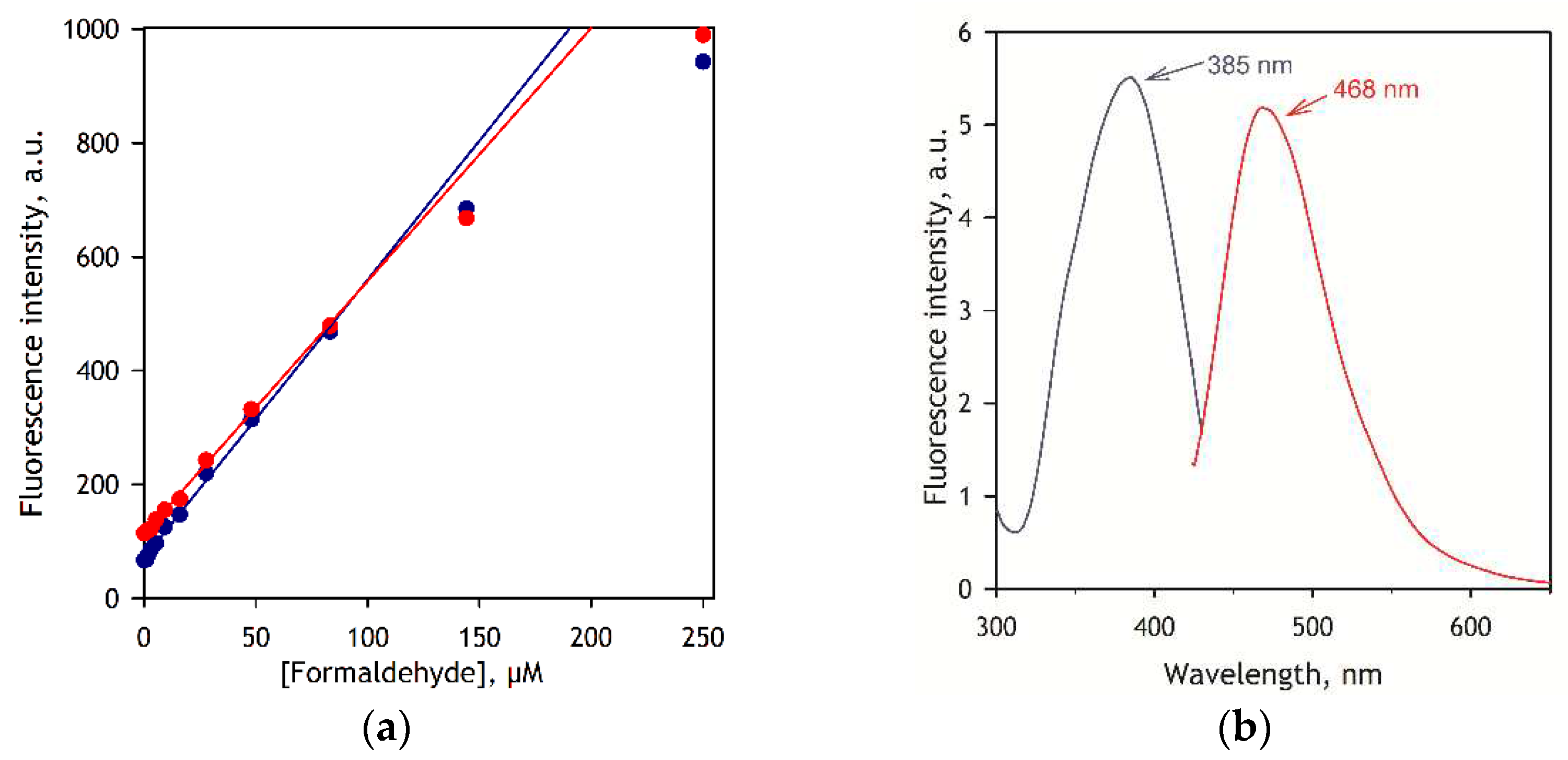
Calibration curves of the assay and the spectra of excitation and emission of DPDL are shown in
Figure 2. As seen from this figure, the dependence of the intensity of fluorescence on the concentration of FA remains linear up to 85 µl FA, after which point the slope starts to decrease.
As shown in
Figure 2 b, in the presence of microsomes the product of the Hantzsch reaction, 3,5-di-N-phenylacetyl-1,4-dihydrolutidine (DPDL), exhibits the maxima of excitation and emission at 385 and 468 nm, respectively. However, since the assays of P450-dependent demethylation require the presence of NADPH, which is also fluorescent at 468 nm, the best results are obtained with excitation at 395 nm, where the excitation of the NADPH fluorescence is negligible.
3.1.2. High-throughput implementation of the AAA method.
A high-throughput implementation of our assay requires the reaction to be carried out in multi-well plates, which are then scanned in a fluorescence plate reader. An important impediment in this setup is light scattering from the samples, which remains significant even after partial sedimentation of microsomes by centrifugation. The design of the plate readers, where the emission light is collected from the surface of the liquid, makes them much more sensitive to the scattering of excitation light than the conventional fluorometers, where the signal is collected through a wall of a rectangular glass cell. Furthermore, both the amplitude of the registered signal and its sensitivity to light scattering is highly dependent on the level of liquid in the wells. Even an insignificant variation in the volume of liquid may result in a considerable change in the intensity of the registered signal and the interference from light scattering. Because both the volume of liquid in the cell and light scattering by microsomal particles may differ between the wells, these effects cause considerable bias of the points and significantly decrease the accuracy of plate-reader-based assays. Our efforts in developing the high-throughput assay were directed towards minimizing these intervenient effects.
To minimize light scattering from the pellet on the bottom of the wells, we used black well plates with V-bottom, UltraCruz 96-well V-bottom Fluorescence Microplates from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. (Dallas, TX, USA). Probing the sensitivity of the registered signal to variations in the volume in the well, we found that a volume >150 µl per well is required to achieve minimal variations in the registered signal upon changes in the volume in ±10% limits. Thereafter, the sample volume of 160 µl was chosen for our protocol.
However, even after this optimization and careful tuning of the optics of our plate reader (Cary Eclipse fluorometer with a plate-reader accessory), the bias of the points in the assays carried out with registering fluorescence at one wavelength remained significant, especially at low concentrations of generated FA. To cope with these variations, we decided to register the spectra of excitation of the samples instead of measuring fluorescence at one wavelength. Furthermore, we saw a need to introduce an internal fluorescent standard used for the normalization of the spectra to compensate for possible variations in the sensitivity of light detection between the wells. As our assays require the presence of NADPH, which is also fluorescent at 468 nm, but differs from DPDL by the spectrum of excitation, we used the fluorescence of NADPH as a reference for normalizing the spectra while keeping the NADPH concentration constant with the use of NADPH-generating system.
In practice, the intensities of fluorescence of DPDL and NADPH in each well of the substrate titration series were resolved using the prototypical spectra of their excitation, as described in Materials and Methods. Then, the amplitudes of spectra in the series were normalized by the intensity of fluorescence of NADPH in each well divided by the averaged NADPH fluorescence in the series. This normalized series has been then used to determine the concentration of formaldehyde by approximating the spectra of excitation by a linear combination of the prototypical spectra of excitation of NADPH and DPDH. This procedure is described in more detail in Materials and Methods.
To automatize the assays, we used an Opentrons OT-2 liquid handling robot equipped with a heater-shaker module. We found that for optimal results, the reaction should be started by adding microsomal suspension (20 µl per well) to pre-heated well plates containing buffer solution with added substrate and NADPH-generating system (60 µl per well) and kept in the heater-shaker module. After incubation under shaking for a desired time, the reaction is stopped by AAA-containing stop solution (see above) in the volume of 32 µl per well. It is followed by the addition of 48 µl of 7 M solution of ammonium acetate. All additions are made with a 300 µl eight-channel automatic pipette. The plates were then centrifuged for 20 min at 3,800 rpm and subjected to scanning the spectra of excitation in 300 – 440 nm region (emission at 468 nm) with a fluorescence plate reader.
When developing the protocols for the OT-2 robot, we noticed that one of the sources of bias of points in titration traces is the tendency of the robot to acquire air bubbles in some tips as the pipette progresses across the well plate. This is especially noticeable when dispensing a viscous solution of ammonium acetate. This effect may cause an underdosing of liquid in a part of the plate. To make our assays less sensitive to these effects, we decided to “shuffle” the substrate concentrations in the wells, so that the first and the second half of the well plate (rows 1 – 6 and 7 – 12) both contain the wells with the lowest and highest substrate concentrations. In practice, the concentrations of substrate increasing from 0 to the maximal were placed in the rows taken in the following sequence: 6 (no substrate), 12, 5, 11, 4, 10, 3, 9, 2, 8, 1, and 7 (maximal concentration). As a result, possible underdosing in the second half of the plate results only in a saw-like bias, instead of causing systematic deviation of the points. This modification considerably increases the reproducibility of the assays.
3.2. Applying AAA-based technique to study ketamine demethylation by human cytochrome P450 species.
3.2.1. Setting up and validation of the AAA method as applied to ketamine demethylation.
For any single-time-point kinetic assay, a critical step is selecting the time of incubation, so that it lies on the linear part of the kinetic trace of the product formation. To this end, we studied the kinetics of S-ketamine demethylation by human liver microsomes (HLM). According to Yanagihara et al. [
30], the substrate saturation profiles of S-ketamine demethylation by HLM may be approximated with a combination of two Michaelis-Menten dependencies with
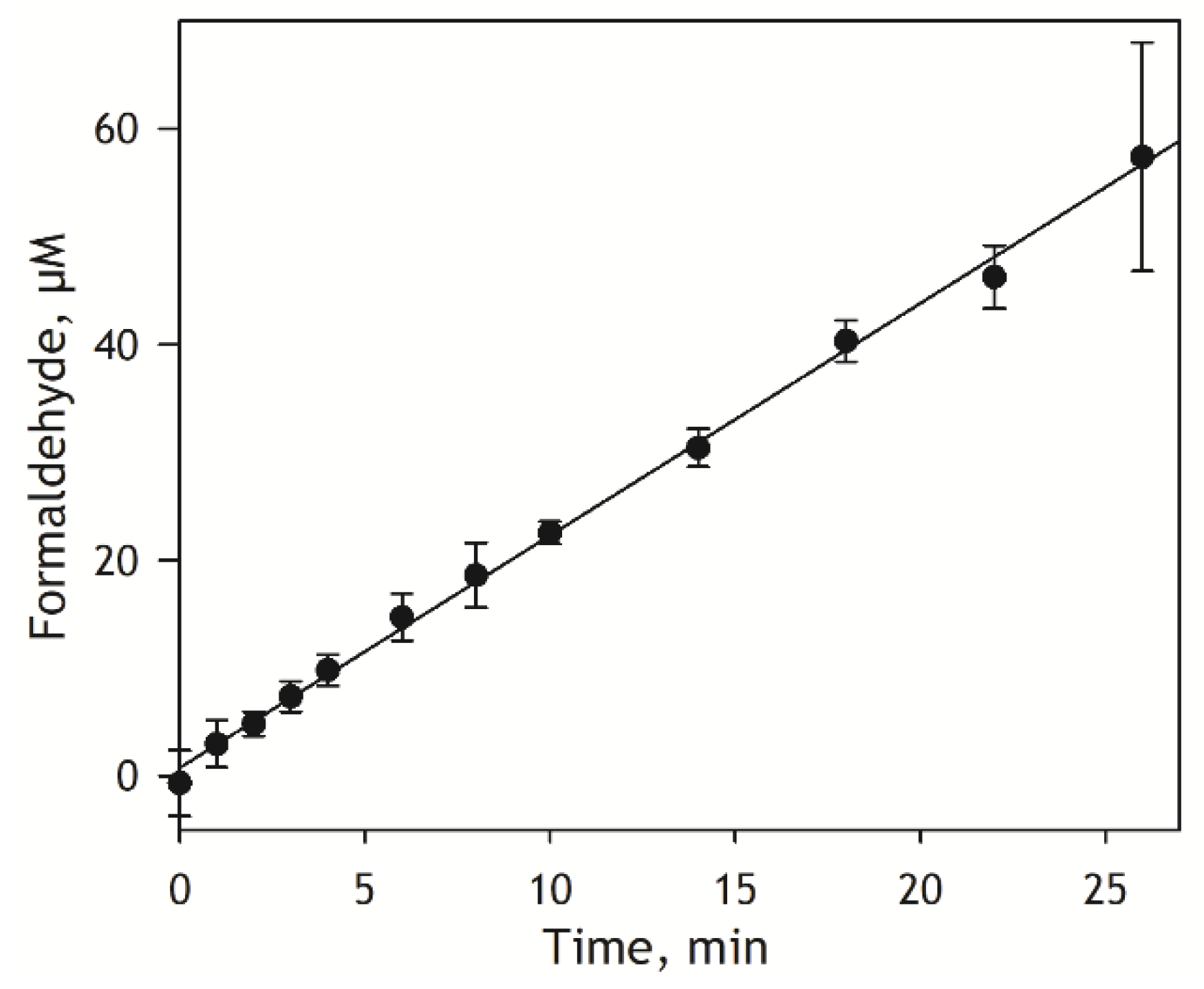
KM of 24 and 444 µM, respectively. Based on these estimates, for our kinetic assay, we selected the substrate concentration of 400 µM, which is close to KM of the low-affinity component. Kinetics of the generation of formaldehyde by pooled HLM preparation at 400 µM S-ketamine is shown in
Figure 3. As seen from this figure, the kinetic trace keeps its linearity for at least 25 minutes. Based on this result, for our subsequent experiments, we select the incubation time of 12 minutes, which lies in the middle of the initial linear part.
To probe and validate our assay further, we compared the results of studying S-ketamine metabolism by recombinant CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 enzymes by two different methods – i) the high-throughput FA-detection assay and ii) the detection of norketamine with LC-MS/MS. In these experiments performed with the use of an OT-2 robot, we divided the incubation multi-well plates into two parts of 4 columns. In the columns A-D the quenching solution contained AAA. These wells were complemented with ammonium acetate and analyzed with the fluorescence plate reader as usual. In the columns G-H, the AAA in the quenching solution was replaced with 17.5 µM midazolam, which we used as an internal standard. For these columns, the addition of ammonium acetate was omitted and the wells were analyzed with LC-MS/MS technique (see Materials and Methods).
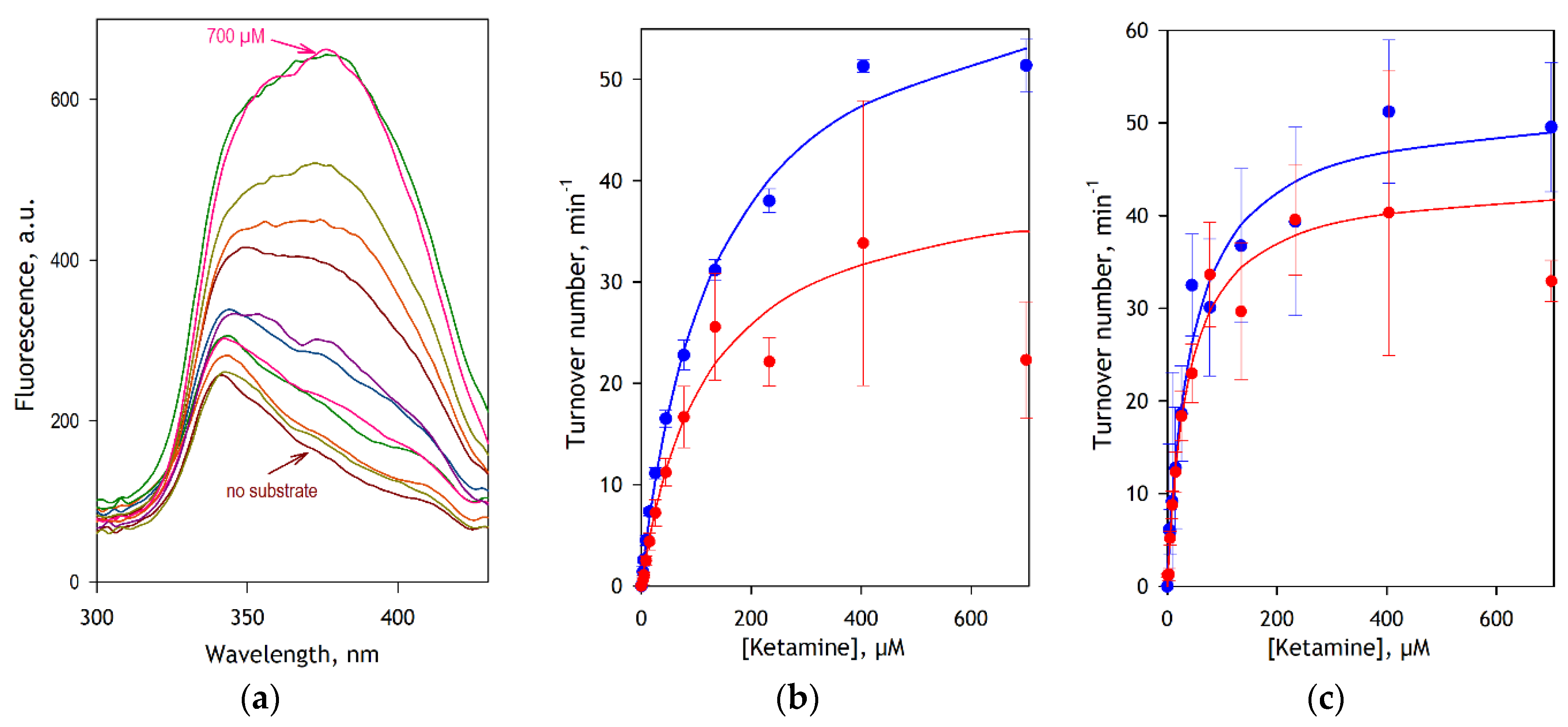
The results of these experiments are illustrated in
Figure 4. In this figure, panel
a exemplifies a series of fluorescence excitation spectra obtained in the assay with CYP3A4. As seen from this plot, these spectra feature a fairly invariant band of excitation of NADPH (λ
max=340 nm) overlapping peak of excitation of DPDL (λ
max=385 nm), which increases concomitantly with the increase in substrate concentration. The substrate saturation profiles obtained from the analysis of spectral series of this kind for CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 are shown in panels
a and
b in blue symbols. The data sets shown in red represent the result of LC-MS/MS assays. The results of fitting these traces to the Michaelis-Menten equation are compared in
Table 1.
Comparing the data sets obtained by the two methods presented in
Figure 4, it can be seen that the FA detection method is less prone to data scatter and provides better statistical reliability than the LC-MS/MS assay. The contrast between the two methods in their accuracy is particularly demonstrative in the case of CYP3A4 (
Figure 4b).
As seen from
Table 1, the
KM values for both CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 enzymes obtained by two different methods coincide up to the respective confidence intervals. At the same time, for both enzymes, the
Vmax values obtained from FA-detection assays are noticeably higher than the values obtained from the determination of the formed norketamine by LC-MS/MS. This difference, which is especially significant in the case of CYP3A4, may reveal further conversion of norketamine to its hydroxylated metabolites by these enzymes. It should be noted however that, while the ability of CYP2B6 to hydroxylate norketamine is already known [
31], no metabolism of norketamine by CYP3A4 has been reported so far.
3.2.2. Metabolism of ketamine by major human cytochrome P450 species
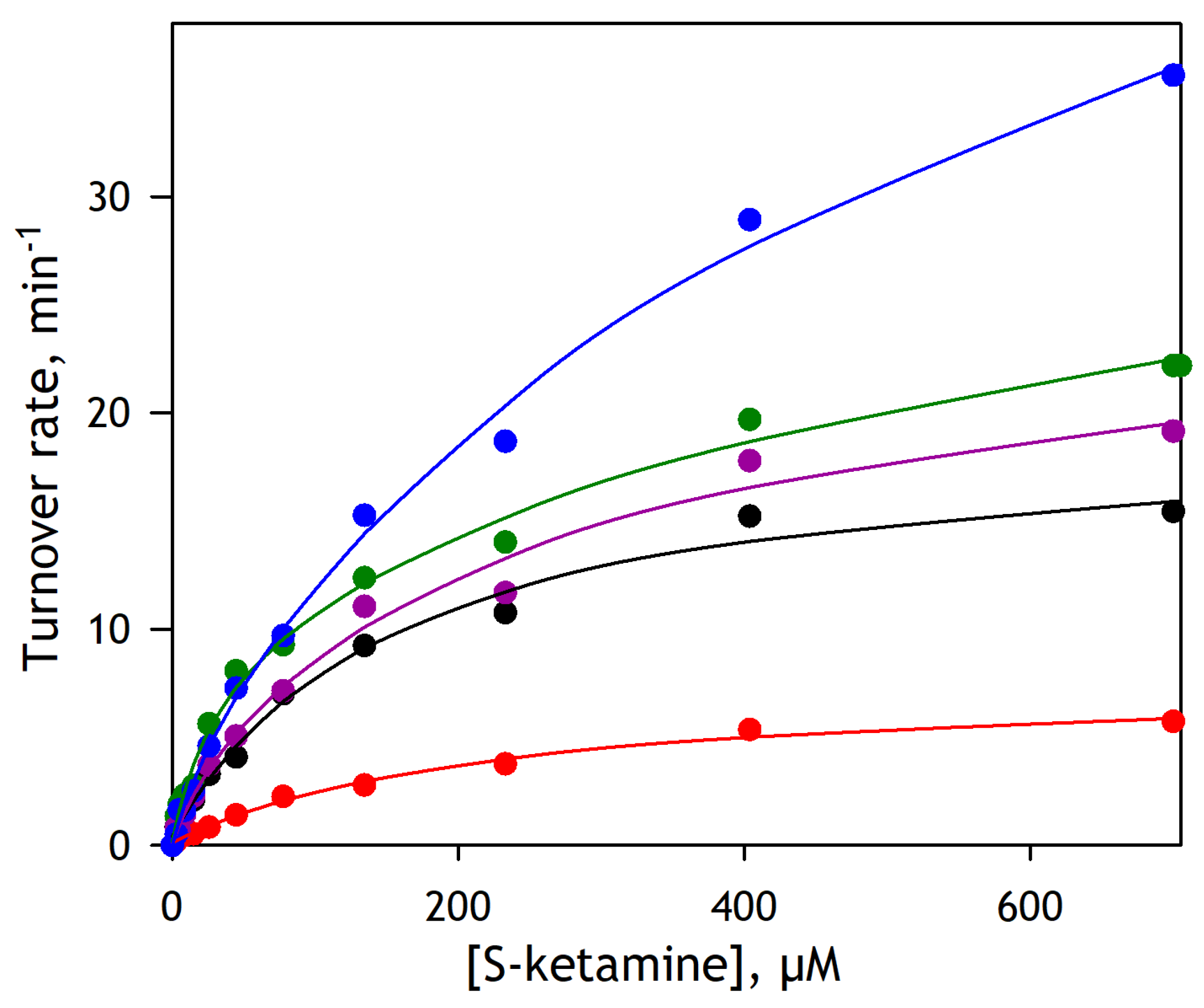
To better elucidate the involvement of the individual human P450 enzymes in ketamine metabolism, we used our novel high-throughput method to determine the kinetic parameters of S-ketamine demethylation by ten major cytochrome P450 species. In these studies, we used recombinant enzymes co-expressed with CPR and cytochrome b5 in the microsomes of insect cells. For all P450 species except CYP2D6, we used CYP-containing Supersomes® from Gentest Corporation, while for the latter enzyme, we used Baculosomes® Plus reagent from Thermo Fisher Scientific.
The results of these experiments are summarized in
Table 2, where the P450 species are sorted in the order of decreasing intrinsic clearance (C
Lint=V
max/K
M) values. As seen from these data, in good agreement with the literature, the highest efficiency in ketamine demethylation is exhibited by CYP2B6. However, the KM value for this enzyme obtained in our study is considerably higher than the estimates reported by Protmann et al. [
31] (
Table 2) and Wang et al. (10.2 ± 0.6 µM, [
32]); it is more consistent with the estimate of 44.0 ± 0.6 µM obtained by Yanagihara et al. [
30]. Our
Vmax value is also more consistent with that reported in the above study.
The second efficient P450 species according to our analysis is CYP2C19, which has the highest affinity over all ten P450 isoforms studied here. This finding is notwithstanding the minor role in ketamine metabolism attributed to CYP2C19 by Yanagihara et al. [
30] and Hijazi and Boulieu [
33]. It is more consistent with the results of Protmann et al. [
31], where the activity of CYP2C19 with ketamine was classified as the third after CYP2B6 and CYP3A4.
The next two places in our list of ketamine metabolizers are occupied by two CYP3A enzymes. Although they exhibit quite similar parameters of S-ketamine demethylation, CYP3A4 is more efficient in this reaction due to its higher turnover number as compared to CYP3A5. Perhaps the most surprising finding is the relatively high efficiency of CYP2D6, which has the highest turnover number with S-ketamine over all P450 species under study. This is notwithstanding the presumed minor role of this enzyme in ketamine metabolism [
31,
33].
KM of 685 ± 124 µM in combination with the high turnover number exhibited by CYP2D6 allows us to hypothesize that this enzyme is the main P450 isoform responsible for the low-affinity component of ketamine SSPs (
KM >400 µM) observed in HLM [
30,
33]. Another unexpected observation is the very low turnover number exhibited by CYP2C9. The low efficiency observed with this enzyme makes its presumed role in ketamine demethylation negligible, along with that of CYP1A2, CYP2C8, and CYP2E1.
3.2.3. N-Demethylation of S-ketamine by human liver microsomes
To probe the potential involvement of the individual P450 species in ketamine demethylation by the P450 ensemble of the human liver, we studied substrate saturation profiles of S-ketamine demethylation by five different pooled HLM preparations. The results of these experiments are illustrated in
Figure 5. Of five HLM lots exemplified in this figure, the lots EGW, CDN, and DNJ are the INVITROCYP 150-Donor (mixed gender) HLM obtained from BioIVT Corp. The lot FVT is a pooled preparation from 10 mixed-gender donors under chronic alcohol exposure, which is obtained from the same supplier. Lot 2110263 designated hereafter as Xen263 is a pooled preparation from 50 donors (mixed gender) supplied by XenoTech Corp. The results of these experiments are illustrated in
Figure 5 and
Table 3. The rates of ketamine demethylation shown there are normalized on the concentration of CPR in HLM samples calculated from its activity in cytochrome c reduction (see Materials and methods) and thus expressed as mols of FA formed per minute per mole of CPR (min
-1).
The series of plots shown in
Figure 5 reveals a contrasting difference between different HLM samples in both the amplitude and the shape of the substrate saturation profiles of ketamine demethylation. Theoretically, these profiles may be considered as a combination of multiple Michaelis-Menten dependencies corresponding to the individual P450 species involved in the reaction. However, resolving more than two Michaelis-Menten components from a single titration curve is barely possible. In this view, we fitted the titration curves shown in
Figure 5 by a combination of two Michaelis-Menten equations to get a general idea of the possible involvement of individual P450s in ketamine metabolism. Parameters obtained from this fitting are shown in
Table 3.
Analyzing
Table 3, one can see that the HLM samples studied here may be divided into two groups. The SSPs of the preparations EGW and CDN that exhibit the lowest activity may be approximated with a single Michaelis-Menten equation with
KM values suggesting a predominate role of CYP3A enzymes with possible participation of some lower affinity enzyme, such as CYP1A2 or CYP2C9. In contrast, the SSPs of DNJ, Xen263, and FVT preparations reveal the participation of higher affinity enzymes, apparently CYP2B6 and CYP2C19, along with a very important low-affinity component, which is most likely associated with the involvement of CYP2D6. Notably, the FVT preparation obtained from the donors with chronic alcohol exposure has the highest activity with S-ketamine and exhibits the highest fraction of the low-affinity component over all five probed HLM samples.
4. Conclusion
In this study, we introduce and describe a reliable, inexpensive, and versatile method for high-throughput kinetic assays of drug metabolism based on fluorometric quantification of formaldehyde (FA) formed in cytochrome P450-dependent demethylation reactions. We describe the high-throughput implementation of this technique applicable for automatized assays of cytochrome P450-dependent drug metabolism in human liver microsomes. The new method provides an efficient tool for large-scale screening of the drug metabolism in individual HLM samples from individual donors. The method may considerably facilitate and streamline the routine studies of drug metabolism in the development of new pharmaceuticals. Furthermore, its combination with the toolset of proteomics offers a potent way for an in-depth analysis of correlations of the profile of drug metabolism with the composition of the drug-metabolizing ensemble, which is necessary for further elaboration of the concept of functional integration in human drug metabolism [
2,
34].
Application of our new method to the studies of the metabolism of ketamine allowed us to shed new light on the involvement of multiple cytochrome P450 species in the oxidative demethylation of this anesthetic and antidepressant, which is increasingly used in the treatment of AWS and AUD. Probing the kinetic parameters of ketamine demethylation by 10 major human P450s, we demonstrated that besides CYP2B6 and CYP3A enzymes, which were initially recognized as the primary metabolizers of ketamine, an important role is also played by CYP2C19, and CYP2D6, while the involvement of CYP2C9 suggested in the previous reports is insignificant.
Studying the kinetics of ketamine demethylation by five pooled preparations of human liver microsomes, we observed dramatic differences in the kinetic parameters of this reaction between the HLM samples. Notably, the activity of the HLM preparation obtained from the donors with a history of chronic alcohol exposure was the highest of all HLM samples probed, and the shape of its substrate saturation profile (SSP) suggests an important difference from other HLM samples in the involvement of the individual P450 species. The apparent increase in the role of CYP2D6 and decrease in the CYP3A involvement in ketamine metabolism will be further probed in a large-scale study combining a newly developed activity assay with the toolset of proteomics. These studies are currently underway.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.R.D.; methodology, D.R.D. and B.P..; software, D.R.D..; formal analysis, D.R.D., N.D., K.A.G. and D.A.H.; investigation, N. D., D.R.D., D.A.H., K.A.G. and D.S.; writing – initial draft preparation, D.R.D., K. A. G .and D. A.H., writing – review and editing, D.R.D. and B.P.; funding acquisition, D.R.D. and B.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number R01AA030155. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within the article. The raw data sets used to generate the reported results are available from the authors upon a reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mak, K.K.; Epemolu, O.; Pichika, M.R. The role of DMPK science in improving pharmaceutical research and development efficiency. Drug Discovery Today 2022, 27, 705–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, D.R.; Prasad, B. Assembling the P450 puzzle: on the sources of nonadditivity in drug metabolism. Trends in Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guengerich, F.P. Common and uncommon cytochrome P450 reactions related to metabolism and chemical toxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 611–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, D.F.V. Human cytochromes P450 associated with the phase 1 metabolism of drugs and other xenobioties: A compilation of substrates and inhibitors of the CYP1, CYP2 and CYP3 families. Curr. Med. Chem. 2003, 10, 1955–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendic, S. Summary of information on human CYP enzymes: Human P450 metabolism data. Drug Metab. Reviews 2002, 34, 83–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, T. The colorimetric estimation of formaldehyde by means of the Hantzsch reaction. Biochem. J. 1953, 55, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heni, N. Decrease of cytochrome P450 after incubation with carbon tetrachloride in a NADPH regenerating system and partial conversion to cytochrome P-420. Experientia (Basel) 1971, 27, 777–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebert, D.W.; Robinson, J.R.; Kon, H. Further studies on genetically mediated differences in monooxygenase activities and spin state of cytochrome P-450 iron from rabbit rat and mouse liver. J. Biol. Chem. 1973, 248, 7637–7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hladová, M.; Martinka, J.; Rantuch, P.; Nečas, A. Review of Spectrophotometric Methods for Determination of Formaldehyde. Research Papers Faculty of Materials Science and Technology Slovak University of Technology 2019, 27, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, J.; Hu, L.-L.; Tan, Y.; Liu, S.-H.; Yin, J. Recent advances in formaldehyde-responsive fluorescent probes. Chinese Chemical Letters 2017, 28, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurth, K.P.; Jaworski, A.; Thomas, K.B.; Kirsch, W.B.; Rudoni, M.A.; Wohlfarth, K.M. The Reemergence of Ketamine for Treatment in Critically Ill Adults. Critical Care Medicine 2020, 48, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garel, N.; McAnulty, C.; Greenway, K.T.; Lesperance, P.; Miron, J.-P.; Rej, S.; Richard-Devantoy, S.; Jutras-Aswad, D. Efficacy of ketamine intervention to decrease alcohol use, cravings, and withdrawal symptoms in adults with problematic alcohol use or alcohol use disorder: A systematic review and comprehensive analysis of mechanism of actions. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2022, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, D.; Long, B.; Koyfman, A. The emergency medicine management of severe alcohol withdrawal. American Journal of Emergency Medicine 2017, 35, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryst, J.; Kawalec, P.; Pilc, A. Efficacy and safety of intranasal esketamine for the treatment of major depressive disorder. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2020, 21, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davydova, N.Y.; Dangi, B.; Maldonado, M.A.; Vavilov, N.E.; Zgoda, V.G.; Davydov, D.R. Toward a systems approach to cytochrome P450 ensemble: interactions of CYP2E1 with other P450 species and their impact on CYP1A2. Biochem. J. 2019, 476, 3661–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, D.R.; Deprez, E.; Hui Bon Hoa, G.; Knyushko, T.V.; Kuznetsova, G.P.; Koen, Y.M.; Archakov, A.I. High-pressure-induced transitions in microsomal cytochrome P450 2B4 in solution - evidence for conformational inhomogeneity in the oligomers. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1995, 320, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, D.R. SpectraLab Software. Available online: http://cyp3a4.chem.wsu.edu/spectralab.html (accessed on May 30).
- Rapoport, R.; Hanukoglu, I.; Sklan, D. A fluorimetric assay for hydrogen peroxide, suitable for NAD(P)H-dependent superoxide generating redox systems. Anal. Biochem. 1994, 218, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaori, S.; Yamazaki, H.; Suzuki, A.; Yamada, A.; Tani, H.; Kamidate, T.; Fujita, K.; Kamataki, T. Effects of cytochrome b(5) on drug oxidation activities of human cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3As: similarity of CYP3A5 with CYP3A4 but not CYP3A7. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, R.G.; Jacobsen, N.W. A New Sensitive and Specific Test for the Detection of Aldehydes: Formation of 6- Mercapto-3-substituted-s-triazolo[4,3-b]-tetrazines. J. Chem. Soc. D: Chem. Commun. 1970, 1970, 1719–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.-J.; Xu, J.-H.; Yin, Y.-C.; Wirth, N.; Ren, J.-M.; Zeng, B.-B.; Yu, H.-L. Rapid probing of the reactivity of P450 monooxygenases from the CYP116B subfamily using a substrate-based method. New Journal of Chemistry 2016, 40, 8928–8934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rensburg, G.J.; Bervoets, L.; Smit, N.J.; Wepener, V.; van Vuren, J. Biomarker Responses in the Freshwater Shrimp Caridina nilotica as Indicators of Persistent Pollutant Exposure. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 2020, 104, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Cheng, A.W.; Xia, X.K.; Liu, Y.F.; He, S.W.; Guo, X.; Sun, J.Y. Development of a facile and sensitive fluorimetric derivatization reagent for detecting formaldehyde. Analytical Methods 2016, 8, 2764–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, Z.M.; Wen, J.; Li, H.J.; Sun, S.G.; Xu, Y.Q. Imaging of formaldehyde in live cells and plants utilizing small molecular probes with large stokes shifts. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2018, 260, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Song, X.; Tang, Y.; Lin, W. A rapid and facile fluorimetric method for detecting formaldehyde. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2016, 222, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.R.; Hu, Q.; Chen, T.H.; Min, D.Y.; Yuan, H.Q.; Bao, G.M. Highly sensitive and rapid responsive fluorescence probe for determination of formaldehyde in seafood and in vivo imaging application. Spectrochimica Acta Part a-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2020, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sritharathikhum, P.; Oshima, M.; Motomizu, S. Development of novel detection reagent for simple and sensitive determination of trace amounts of formaldehyde and its application to flow injection spectrophotometric analysis. Analyt. Chim. Acta 2008, 612, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sritharathikhun, P.; Motomizu, S. Development of novel reagent for Hantzsch reaction for the determination of formaldehyde by spectrophotometry and fluorometry. Analyt. Sci. 2007, 23, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abcam. ab133084 – Formaldehyde Assay Kit. Available online: https://www.abcam.co.jp/ps/products/133/ab133084/documents/ab133084%20Formaldehyde%20Assay%20Kit%20protocol%20 (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Yanagihara, Y.; Kariya, S.; Ohtani, M.; Uchino, K.; Aoyama, T.; Yamamura, Y.; Iga, T. Involvement of CYP2B6 in N-demethylation of ketamine in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab. Disp. 2001, 29, 887–890. [Google Scholar]
- Portmann, S.; Kwan, H.Y.; Theurillat, R.; Schmitz, A.; Mevissen, M.; Thormann, W. Enantioselective capillary electrophoresis for identification and characterization of human cytochrome P450 enzymes which metabolize ketamine and norketamine in vitro. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7942–7948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.F.; Neiner, A.; Kharasch, E.D. Stereoselective Ketamine Metabolism by Genetic Variants of Cytochrome P450 CYP2B6 and Cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, Y.; Boulieu, R. Contribution of CYP3A4, CYP2B6, and CYP2C9 isoforms to N-demethylation of ketamine in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab. Disp. 2002, 30, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangi, B.; Davydova, N.Y.; Maldonado, M.A.; Ahire, D.; Prasad, B.; Davydov, D.R. Probing functional interactions between cytochromes P450 with principal component analysis of substrate saturation profiles and targeted proteomics. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).