1. Introduction
Bone is the most common targeted site for metastatic cancer, especially in the advanced and later phase of cancer progression. Notably breast, prostate, and lung cancers, which exhibit the highest incidence rates [
1]. Bone metastases can severely impact patients' daily activities and quality of life due to severe pain and associated major complications. The protracted clinical course of bone metastasis poses significant challenges to treatment. As per a 2022 report published in the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database [
2], prostate cancer ranked sixth among the leading causes of cancer death among Taiwanese men, whereas breast cancer ranked second among the leading causes of cancer death among Taiwanese women. Diagnostic techniques for bone metastasis currently include bone scintigraphy (BS), X-ray imaging, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), while BS serving as the most cost-effective early screening method. BS can diagnose bone metastasis earlier than CT or X-ray does, within 3 to 6 months [
3].
Bone metastasis typically affects the central skeletal system and the proximal regions of the upper and lower limbs. The central skeletal system contains red bone marrow, which may contribute to the formation of bone metastasis due to its physiological characteristics [
4]. Physicians often perform a whole-body bone scan (WBBS) to diagnose the presence of bone metastasis.
99mTc-MDP is the radiopharmaceutical injected to patient’s vein, which can enter the bone cells and deposit with mineral components in four hours. Consequently, Tc-99m MDP tends to accumulate in areas of active bone formation in the affected region, resulting in localized increased radiopharmaceutical activity that appears as a "hot spot" on BS, allowing physicians to identify bone metastasis [
5]. However, BS may suffer from ambiguity owing to some impacts such as bone injury, arthritis, degenerative changes, and causes interpretation challenges. Inexperienced clinical physicians may struggle to make accurate judgments or even misinterpret images.
Bone scan index (BSI) is an image biomarker used to quantify the extent of bone metastasis in cancers [
6]. BSI is calculated as the ratio of "the number of bone lesions indicating bone metastasis" to "the number of regions with a high incidence of bone metastasis" [
7,
8,
9]. With the advent of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data, BSI calculation has become more objective, accurate, and diagnostically efficient. BSI's most attractive application is for monitoring treatment and prognosis, providing significant clinical value. Armstrong et al. from Duke University introduced the automated bone scan index (aBSI) as an objective imaging parameter [
10], which can evaluate the prognosis of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) patients undergoing systemic treatment in clinical trials. In [
11,
12], manual and automated BSI measurements were highly correlated (ρ= 0.80), and automated BSI scoring demonstrated reproducibility, eliminating the subjectivity of clinical judgment while retaining the same clinical significance as manual BSI scoring. Furthermore, some studies confirmed the utility of aBSI in mCRPC patients [
13,
14,
15], while other studies have begun to explore its application and refinement in other tumors [
16].
Generally, computer-assisted diagnosis (CAD) systems that utilize machine learning or neural network (NN) framework for calculating BSI on WBBS images can be divided into two parts: lesion segmentation and skeleton segmentation, which respectively reflect the numerator and denominator of the BSI value [
17,
18,
19,
20]. Recently, there have been numerous studies [
21,
22] and related patents [
23,
24,
25] on lesion segmentation using NN framework, however, the performance of the lesion pixel-wise segmentation has not been thoroughly and rigorously investigated. Similarly, research on skeleton segmentation using deep learning and NN models is also scarce in previous studies [
20,
26]. Despite mention of its skeleton segmentation approach in [
20], which lacks comparison with other NN models. Although [
26] compared its performance with U-Net, it still remained confined to traditional semantic segmentation network architectures. Thus, the field of skeleton segmentation using NN remains insufficiently explored. In this paper, we use different NN models for skeleton segmentation on WBBS images and investigate their results. Additionally, we have built a website platform for online skeleton segmentation of WBBS images, which provides effective skeleton segmentation data for further evaluation of BSI.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
In this retrospective study with the collaboration with the Department of Nuclear Medicine at China Medical University Hospital, 196 WBBS images of patients with prostate cancer were collected. Among the 196 patients, 110 patients had bone metastasis and 86 patients had no evidence of bone metastasis. We also collected 163 WBBS images of patients with breast cancer, all of them had bone metastasis. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) and the Hospital Research Ethics Committee (CMUH106-REC2-130) of China Medical University.
The radiopharmaceutical used for WBBS was Tc-99m MDP, and the imaging was performed 4 hours after the vein injection. A Gamma camera (Millennium MG, Infinia Hawkeye 4, or Discovery NM/CT 670 system; GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI, USA) was used for planar bone scanning, with a low-energy high-resolution or general-purpose collimator, a matrix size of 1024 × 256, a photon energy centered on the 140 keV peak, and a symmetric 20% energy window. The collected bone scan images were in DICOM format, with a spatial resolution of 1024 × 512 pixels (composed of anterior-posterior (AP) and posterior-anterior (PA) views), and the intensity information of each pixel was saved in 2-byte (uint16). The images were preprocessed using the dedicated GE Xeleris workstation (GE Medical Systems, Haifa, Israel; version 3.1) before being uploaded to PACS.
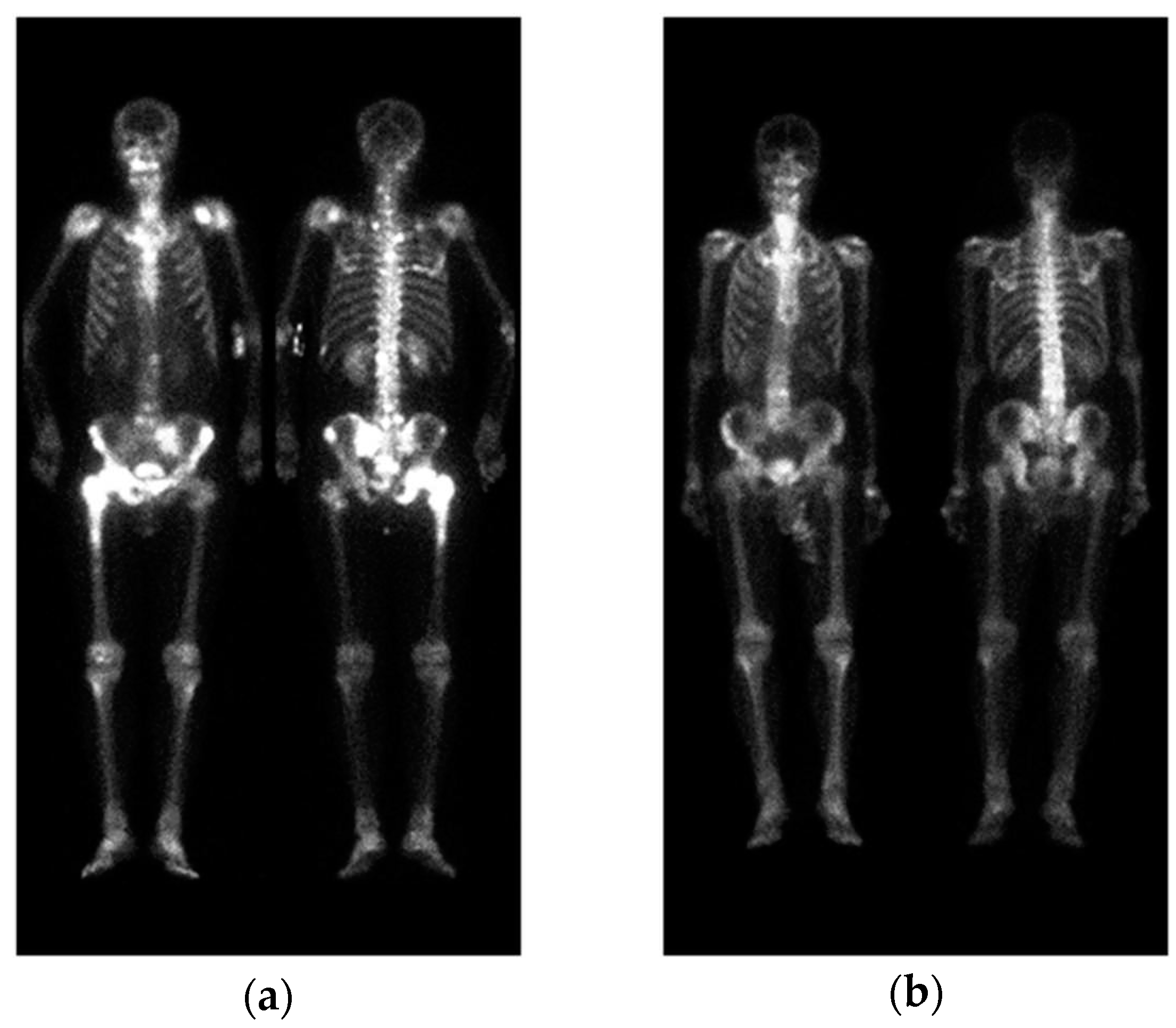
A standard WBBS image contains two views: anterior and posterior. The original DICOM images were first converted to PNG format after removing any identifiable information. Following the approach described in [22], pre-processing was performed by normalizing the image size and intensity. Afterwards, the anterior view and posterior view were cropped into a single image with a size of 950 × 512, without any scaling or geometric transformations, as shown in
Figure 1.
2.2. Region definition
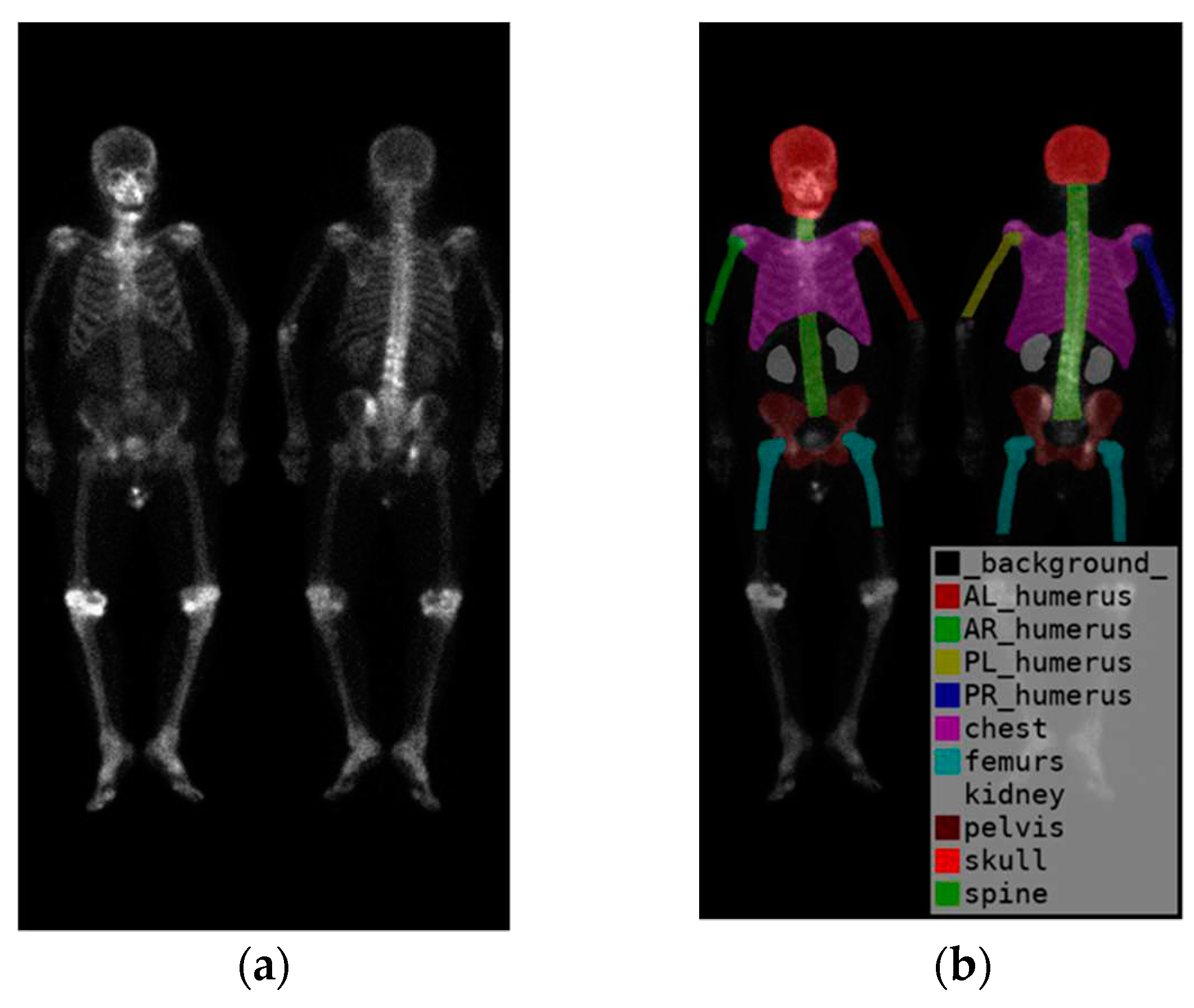
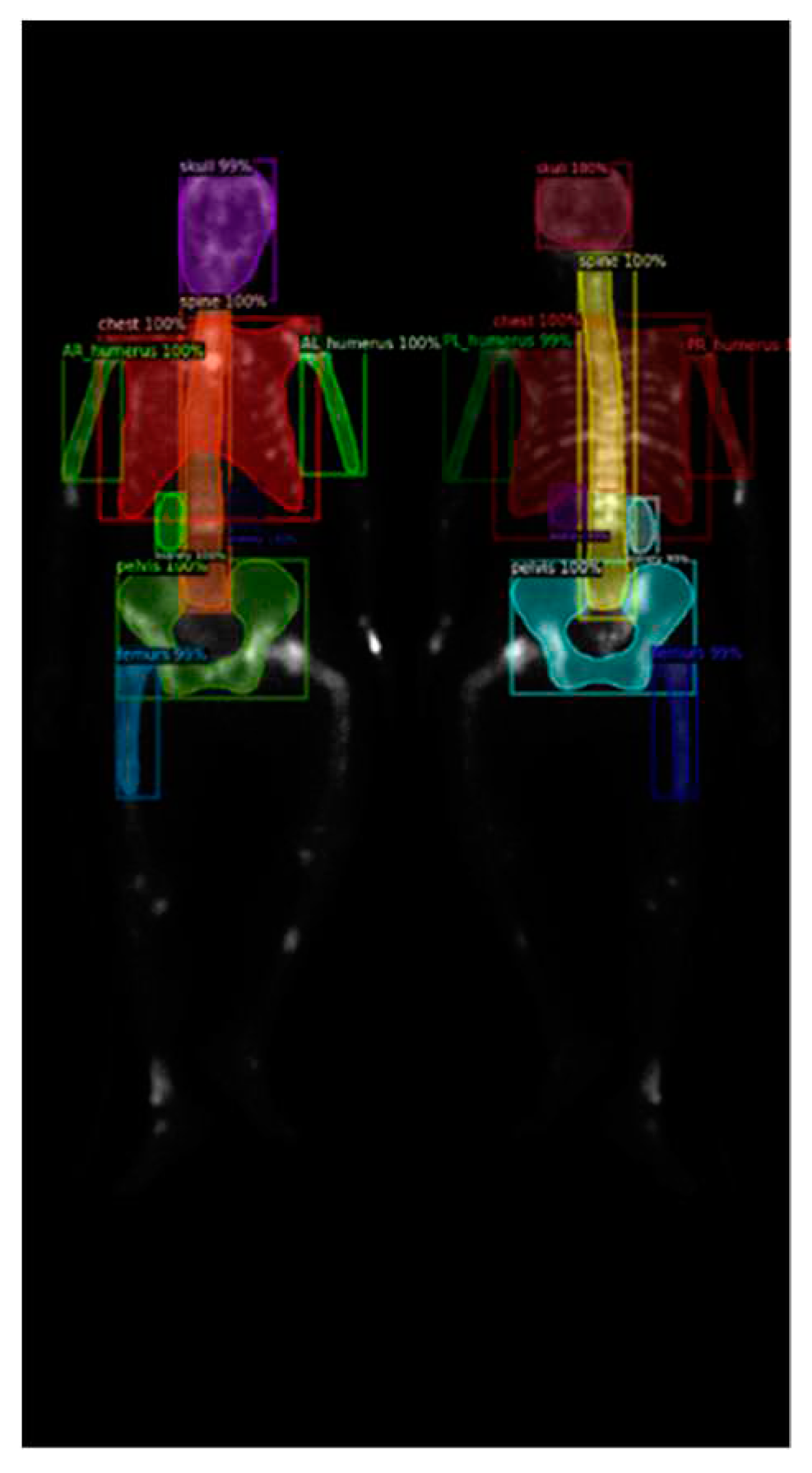
To identify the skeletal regions where bone metastases occur most frequently, we consulted with two experienced nuclear medicine physicians and established a set of standards. The standards require the approval of these two board-certified nuclear medicine physicians. The regions are the skull, spine, chest (including ribs, scapula, and clavicle), humerus (proximal to midshaft of the femurs), femurs (proximal to midshaft of the humerus), and pelvis.
The positions of the humerus on images differ significantly as show in
Figure 1. Different from only one category on femurs, we categorize humerus to four categories, i.e., the left and right humerus in the anterior and posterior views separately. The reason of doing so will be addressed in the discussion. Furthermore, Tc-99m MDP undergoes renal metabolism, which can result in the kidneys appearing as high signal areas. In some situation, the kidney will be misclassified to metastasis. To alleviate this problem, we created an extra category for kidneys to exclude the ambiguity.
In summary, there are in total 10 categories (
Figure 2), including the skull, spine, chest (including ribs, scapula, and clavicle), anterior right humerus(AR), anterior left humerus(AL), posterior right humerus(PR), posterior left humerus(PL), femurs (proximal to midshaft of the humerus), pelvis, and kidney.
2.3. Neural network architectures
Three different neural network architectures were tested, including Mask R-CNN, DoubleU-Net, and Deeplabv3 plus. We used similar hyperparameters on these three models to conduct experiments in order to compare their performances.
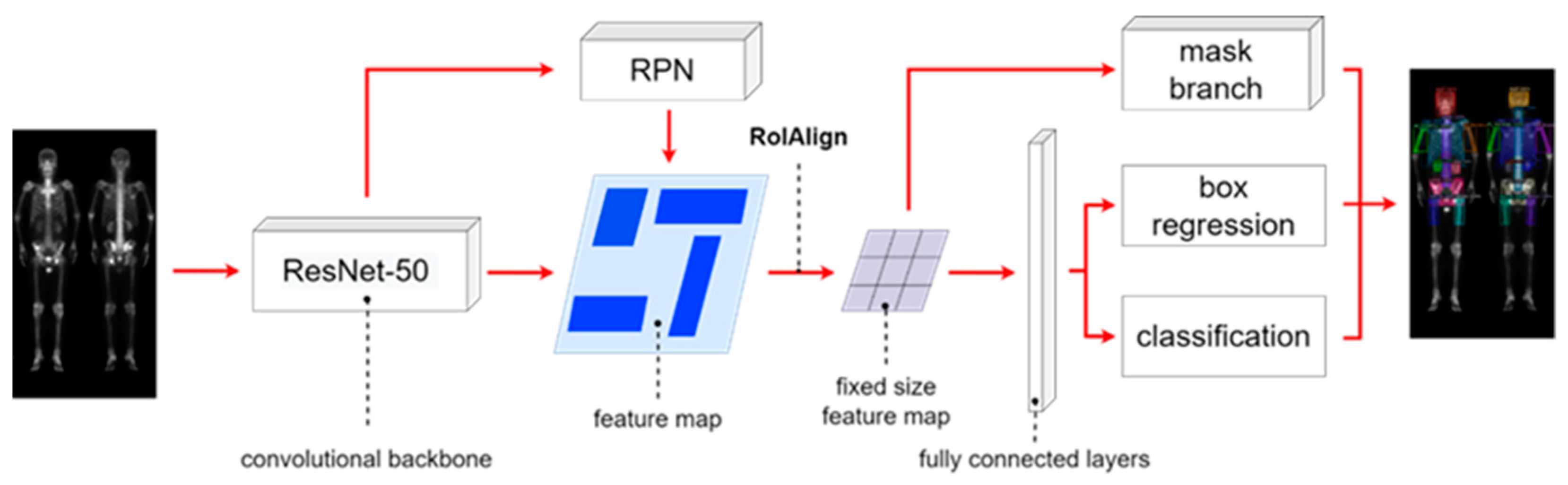
The Mask R-CNN architecture shown in
Figure 3 is composed of four main parts: backbone architecture, RPN, RoIAlign, and head architecture. We used ResNet-50 as the backbone. The hyperparameters hold to be same on learning rate of 0.005, batch size of 4, and 100 epochs.
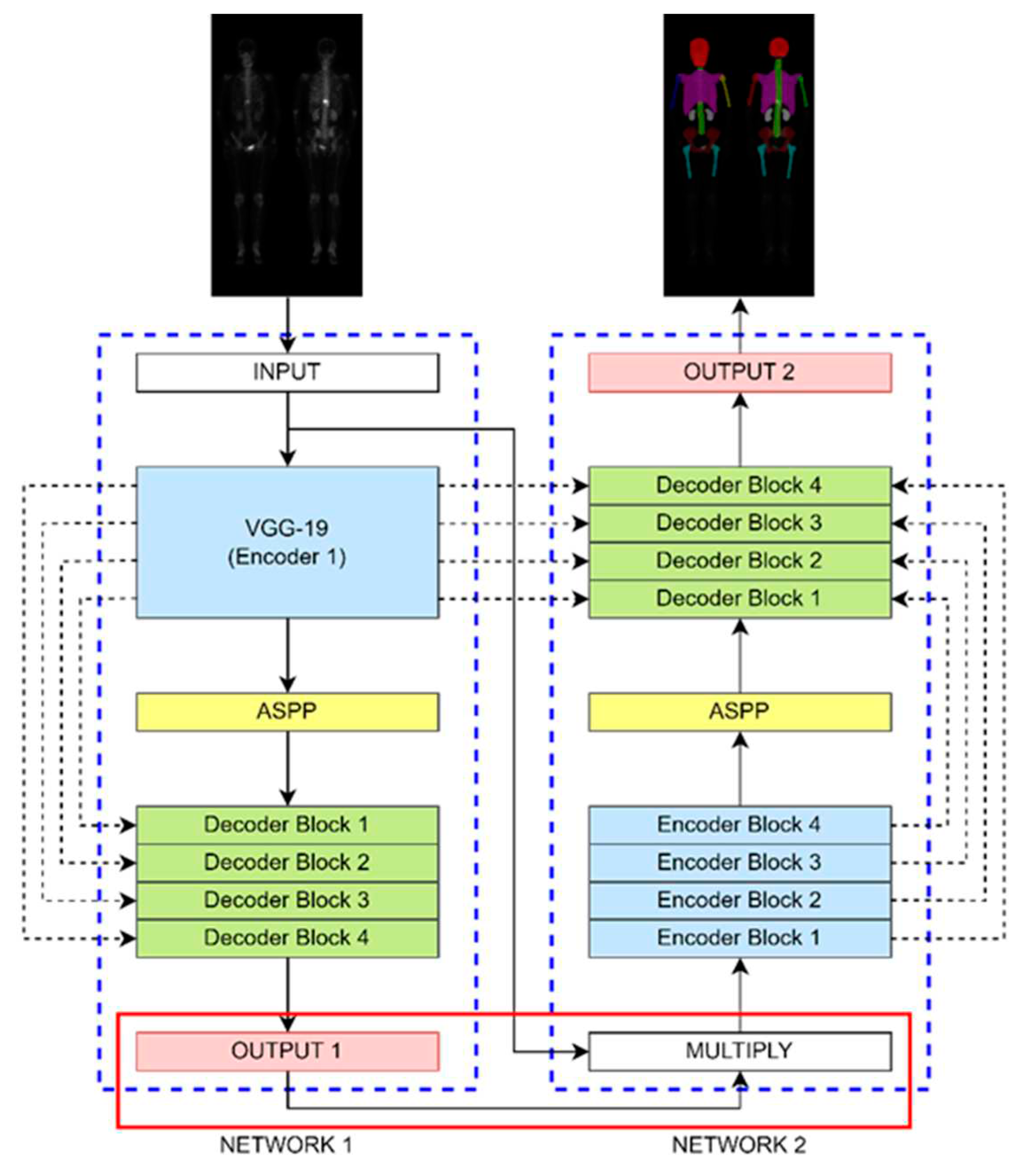
The DoubleU-Net architecture shown in
Figure 4 comprises two sub-networks, dilated convolution, spatial pyramid pooling, and an SE block. It was originally designed for binary classification, here we modified it to make multi-class classification. We changed the output layer of Network 1 to have a softmax activation function to enable multi-class classification. The hyperparameters were set to be learning rate of 0.0005, batch size of 4, and 200 epochs (without data augmentation) or 20 epochs (with data augmentation).
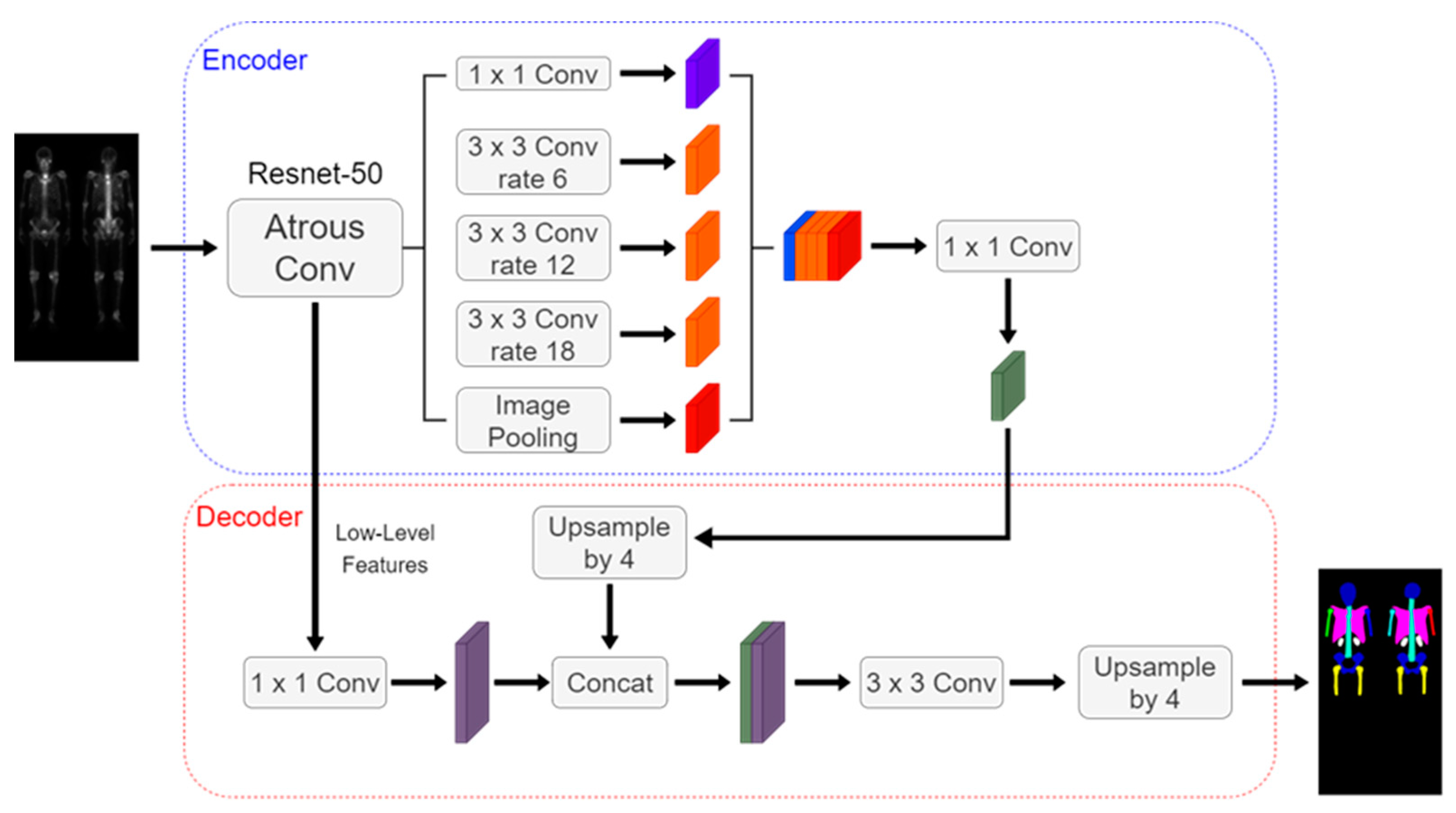
The Deeplabv3 plus architecture shown in
Figure 5 includes an encoder, decoder, dilated convolution, and depth-wise separable convolution. We used ResNet-50 as the encoder backbone. The hyperparameters were set to be learning rate of 0.0005, batch size of 4, and 200 epochs.
2.4. Image pre-processing
The input matrix size for Mask R-CNN was 950 × 512. For DoubleU-Net and Deeplabv3 plus, the input matrix size was adjusted to 960 × 512 by padding with zeros due to their restriction. The labels were saved in PNG format with integers ranging from 0 to 10.
Augmentation included rotations (-3॰, 0॰, 3॰) with step 1॰, scaling (0.9, 1, 1.1) with step 0.1, and brightness adjustments (0.8, 0.93, 1.06, 1.19, 1.32, 1.45, 1.58, 1.7 times). The augmented images had the same matrix size as the original images, resulting in a total rate of 63 times increase. The augmentations were only used in training.
2.5. Evaluations
In this study, the terms true positive (TP), false positive (FP), true negative (TN), and false negative (FN) were defined in pixel scale. The evaluation metrics used in the experiment were precision (Equation 1) and sensitivity (Equation 2), and the overall model evaluation was based on the F1 score (Equation 3).
3. Results
3.1. 10-fold Cross-Validation
In this study, validations on these three models used 10-fold cross-validation. Two datasets comprised 196 prostate cancer WBBS images and 163 breast cancer WBBS images, respectively. The ratio of training, validation, and test was set to be 8:1:1. The main goal of this experiment was to compare the performance differences among each network and to evaluate the impact of prostate and breast cancer WBBS images on network training. The hyperparameters used in the experiment were in
Table 1, and the results were depicted in
Table 2 and
Table 3. The qualitative results of bone segmentation were shown in
Figure 6 and
Figure 7.
We found that there was only a slight difference between these two datasets. The models performed better on the prostate cancer dataset compared to the breast cancer dataset, across all three networks. The reason might be due to the breast cancer BS images we collected were much serious on cancer progress than those images of the prostate cancers.
3.2. 10-fold Cross-validation with Data Augmentation
After the above experiments, we chose DoubleU-Net because it outperformed on F1-score. Following we fine-tuned the epoch to trade-off the training time and the performance. The images of training for prostate cancer and breast cancer were augmented 63 times by using rotation, scaling, and brightness adjustment described in methods. Again, the hyperparameters were in
Table 4, and the quantitative results of the 10-fold cross-validation were in
Table 5.
4. Discussion
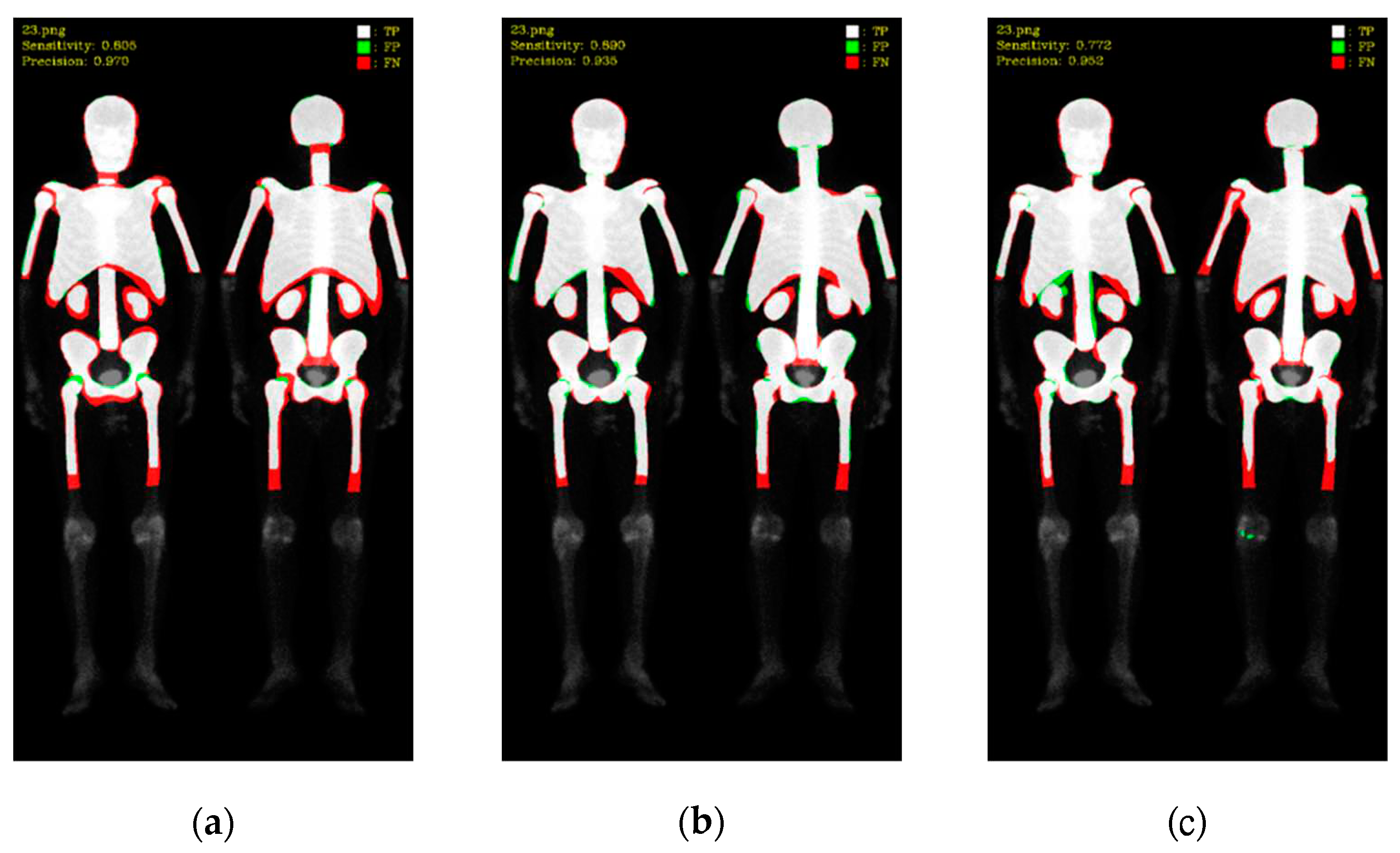
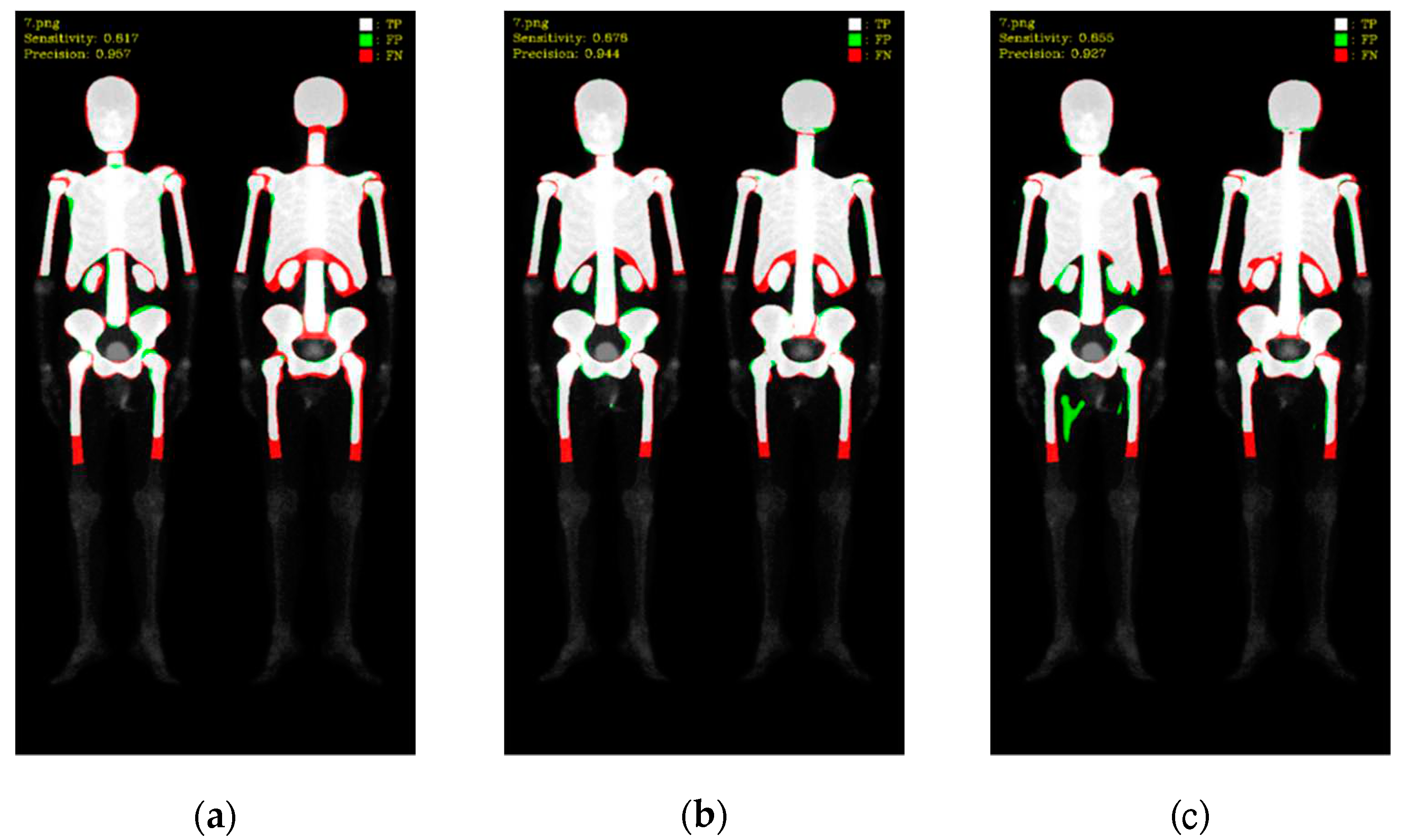
In this study, Mask R-CNN, DoubleU-Net, and DeeplabV3 plus were utilized for skeleton segmentation comparison on prostate cancer and breast cancer WBBS images. The quantitative results were investigated via 10-fold cross-validation. Based on the quantitative findings, Mask R-CNN exhibited higher precision than DoubleU-Net and DeeplabV3 plus in both datasets. On the other hand, DoubleU-Net demonstrated higher sensitivity than Mask R-CNN and DeeplabV3 plus. This indicated that Mask R-CNN had lower false positives (FP) during prediction, while DoubleU-Net had lower false negatives (FN).
To better understand these results, we visualized the predictions, where white color represented TP, green color represented FP, and red color represented FN (as shown in
Figure 8 and
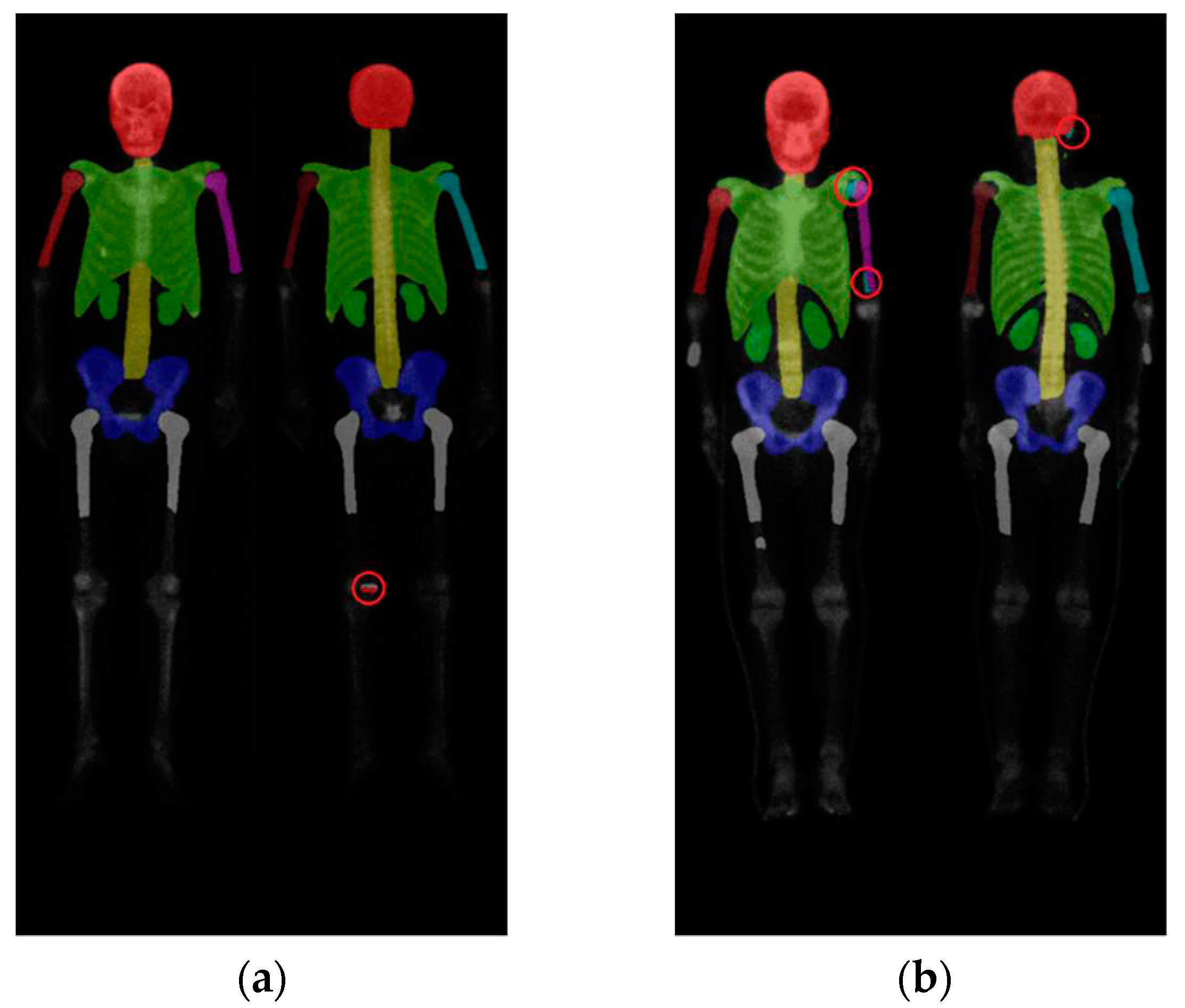
Figure 9). Mask R-CNN's predictions were slightly shifted inward compared to the ground truth (GT), resulting in more FN in the edge regions and only a few FP. DoubleU-Net's predictions were well aligned with the GT along the edges, resulting in significantly fewer FN but more in FP. DeeplabV3 plus exhibited irregularities along the edges compared to the other two models, leading to noticeable erroneous FP, resulting in an overall increase in FP.
These findings shed light on the performance of different models for skeleton segmentation, emphasizing the trade-off between FP and FN. Further improvements can be explored to address the limitations observed, particularly in the case of DeeplabV3 plus, to enhance its stability and accuracy.
Further investigation on Mask R-CNN results revealed an increase in false negatives (FN) when predicting smaller categories such as the humerus and kidneys, as shown in
Figure 10 (a). This result could be caused by the following reasons:
First, the insufficient brightness in the WBBS image may hinder feature detection. The brightness of WBBS images depends on the counts collected by the scintillation crystal, which can be influenced by factors such as patient thickness and radiopharmaceutical activity. In cases where the received counts are insufficient, resulting in inadequate image brightness, deep neural network models may struggle to make accurate judgments or even make errors. Adjusting the image brightness and conducting further tests can help alleviate this situation, as shown in
Figure 10 (b).
Second, abnormal patient positioning in the WBBS image could cause another issue. In a few instances, patient positioning in the WBBS image deviating to some extent from standard clinical positions. This deviation made challenges for CNN prediction, as shown in
Figure 11. The degree of deviation is closely related to the patient's clinical condition and is difficult to entirely avoid in clinical practice. While other previous studies might manually exclude misleading images to prevent such occurrences, however, this study aimed to maintain a dataset that reflects real clinical scenarios, thereby we did not exclude any case. To enhance the network's ability to predict WBBS images with unusual positioning, future considerations include employing hard negative mining techniques to improve the model's generalization capabilities.
Third, the model's insensitivity to features of small objects in WBBS images could also result in decreased performance. Quantitative results indicated relatively low precision for categories such as upper limbs, femurs, and kidneys, which correspond to smaller objects. This suggested Mask R-CNN facing certain difficulties in segmenting smaller regions.
These findings highlighted specific challenges encountered during the skeleton segmentation process, particularly related to image brightness, abnormal patient positioning, and the segmentation of smaller objects. Addressing these challenges could lead to improvements in the performance of the Mask R-CNN model in the future.
On the other hand, we observed that DeeplabV3 plus and DoubleU-Net had a tendency to mix categories, resulting in unstable performance. DoubleU-Net and DeeplabV3 plus did not exhibit the category missing issue observed in Mask R-CNN, but they experienced problems such as category confusion and masks appearing in unintended areas, with DeeplabV3 plus being particularly affected. The issue of category confusion during prediction in semantic segmentation network architectures was not explicitly mentioned in [20,26]. However, in our experiments, we did observe this problem.
Figure 12 (a) showed an incorrect segmentation in the knee area in a DoubleU-Net skeleton segmentation result, while
Figure 12 (b) depicted category confusion in the upper limbs and head in a DeeplabV3 plus skeleton segmentation result.
This problem stemmed from different network architectures. Mask R-CNN utilizes parallel branch networks to independently determine categories and select the appropriate masks based on individual region-of-interest (ROI). Consequently, different ROIs could be distinguished independently, and masks could also be treated as separate entities. In contrast, traditional fully convolutional network (FCN) architectures performed category and mask predictions simultaneously, leading to competition between different categories and masks. Additionally, due to the design of having one category per mask, FCN-based methods could not treat ROIs independently. Another critical factor was the use of the Sigmoid activation function and average binary cross-entropy loss in the branch networks, which mitigated the adverse effects of cross-category competition encountered in traditional FCN methods. This design yielded excellent instance segmentation results and avoids category overlap or confusion. From the experiments, Mask R-CNN demonstrated itself more suitable for skeleton segmentation in WBBS images compared to the other two network architectures.
The quantification results of the prostate cancer dataset slightly outperformed those of the breast cancer dataset, potentially due to differences in the composition of the two datasets. The prostate cancer dataset contained a larger number of images compared to the breast cancer dataset. With a larger training sample size, the network became more generalized and achieved better results. Moreover, the prostate cancer dataset contained 110 cases with bone metastasis and 86 cases without, while all 163 cases in the breast cancer dataset feature were bone metastasis. In the presence of bone metastasis, hotspots appeared in WBBS images, varying in number, size, and shape. These hotspots could potentially impact the neural network's learning process for skeletal structure. It is speculated that the breast cancer dataset, consisting entirely of images with bone metastasis, experiences greater interference, resulting in lower quantification results.
In the experiments involving data augmentation, it was observed that data augmentation contributed to a slight performance improvement. As the model already performed reasonably well without data augmentation, the addition of data augmentation only led to marginal performance gains. According to related literature [46], incorporating data augmentation helped reduce overfitting at higher learning rates, allowing the model to be trained for more epochs without sacrificing accuracy. Further experiments and investigations were warranted to explore the impact of data augmentation in more depth.
5. Conclusions
In this study we investigated three CNN models on bone segmentation of the WBBS images. We found that only one model was suitable for this goal, Mask R-CNN. The Double U-Net and Deeplabv3 + had a problem ‘category confusion’, which the human beings would never have. We used pixelwise scale to examine the model performance. The best performance we had ever made for Mask R-CNN was the precision, sensitivity and F1-score: 0.93, 0.87, 0.90 for prostate cancer dataset and 0.92, 0.86, 0.88 for breast cancer dataset, which was the average of 10-fold cross-validation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, DCC; methodology, DCC; software, PNY and YYC; validation, PNY and YYC; formal analysis DCC; investigation, YCL; resources, YCL and DCC; data curation, PNY and YYC; writing—original draft preparation, PNY; writing—review and editing, DCC; visualization, DCC; supervision, DCC; project administration, DCC; funding acquisition, DCC. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Science and Technology Council (NSTC), Taiwan, grant number MOST 111-2314-B-039-040.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) and the Hospital Research Ethics Committee (CMUH106-REC2-130) of China Medical University.
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived by IRB due to this is a retrospective study and only images were used without patient’s identification.
Acknowledgments
We thank to National Center for High-performance Computing (NCHC) for providing computational and storage resources.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix
According to the aforementioned research results, we established a skeleton segmentation website equipped with a deep learning framework, enabling clinical physicians to utilize website functions online to assist in calculating BSI and conducting clinical diagnoses, thereby achieving the purpose of the aforementioned research. This website has multiple functions that allow clinical physicians to upload images and perform simple post-processing on the images within the website. Finally, execute the skeleton segmentation deep learning model for skeleton segmentation. The public IP address of the website is 140.128.65.129, and login credentials are required (username: wbbsweb, password: wbbswebpass).
References
- Coleman, R. Metastatic bone disease: clinical features, pathophysiology and treatment strategies. Cancer treatment reviews 2001, 27(3), 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Insurance Research Database. Available online: https://www.mohw.gov.tw/cp-16-70314-1.html (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- O’Sullivan, G.J.; Carty, F.L.; Cronin, C.G. Imaging of bone metastasis: an update. World journal of radiology 2015, 7(8), 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, R.E. Clinical features of metastatic bone disease and risk of skeletal morbidity. Clinical cancer research 2006, 12(20), 6243–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, A.I.; et al. The bone scan. Seminars in nuclear medicine 2012, 42(1), 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbriaco, M.; et al. A new parameter for measuring metastatic bone involvement by prostate cancer: the Bone Scan Index. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 1998, 4(7), 1765–1772. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, E.R.; et al. Bone scan index: a quantitative treatment response biomarker for castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2012, 30(5), 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, A.; et al. Analytic validation of the automated bone scan index as an imaging biomarker to standardize quantitative changes in bone scans of patients with metastatic prostate cancer. Journal of Nuclear Medicine 2016, 57(1), 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Edenbrandt, L.; Mizokami, A. Bone scan index: a new biomarker of bone metastasis in patients with prostate cancer. International Journal of Urology 2017, 24(9), 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.J.; Nordle, O.; Morris, M. Assessing the Prognostic Value of the Automated Bone Scan Index for Prostate Cancer—Reply. JAMA oncology 2019, 5(2), 270–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmert, D.; et al. A novel automated platform for quantifying the extent of skeletal tumour involvement in prostate cancer patients using the Bone Scan Index. European urology 2012, 62(1), 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.; et al. A prospective study to evaluate the intra-individual reproducibility of bone scans for quantitative assessment in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. BMC Medical Imaging 2018, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.J.; et al. Phase 3 assessment of the automated bone scan index as a prognostic imaging biomarker of overall survival in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA oncology 2018, 4(7), 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, A.; et al. A preanalytic validation study of automated bone scan index: effect on accuracy and reproducibility due to the procedural variabilities in bone scan image acquisition. Journal of Nuclear Medicine 2016, 57(12), 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.; et al. Automated bone scan index as an imaging biomarker to predict overall survival in the Zometa European Study/SPCG11. European Urology Oncology 2021, 4(1), 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuestemann, J.; et al. Analysis of bone scans in various tumor entities using a deep-learning-based artificial neural network algorithm—evaluation of diagnostic performance. Cancers 2020, 12(9), 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, A.; Higashiyama, S.; Kawabe, J. Assessment of a software for semi-automatically calculating the bone scan index on bone scintigraphy scans. Clinical Imaging 2021, 78, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, M.; et al. Evaluation of a computer-assisted diagnosis system, BONENAVI version 2, for bone scintigraphy in cancer patients in a routine clinical setting. Annals of nuclear medicine 2015, 29, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, M.; et al. Evaluation of a revised version of computer-assisted diagnosis system, BONENAVI version 2.1.7, for bone scintigraphy in cancer patients. Annals of nuclear medicine 2015, 29, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, A.; et al. Correction to: Automated measurement of bone scan index from a whole-body bone scintigram. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery 2020, 15, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.C.; et al. Bone metastasis detection in the chest and pelvis from a whole-body bone scan using deep learning and a small dataset. Electronics 2021, 10(10), 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.C.; et al. Lesion-based bone metastasis detection in chest bone scintigraphy images of prostate cancer patients using pre-train, negative mining, and deep learning. Diagnostics 2021, 11(3), 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.C.; Liu, C.C.; Kao, C.H.; Hsieh, T.C. System of deep learning neural network in prostate cancer bone metastasis identification based on whole body bone scan images. U.S. Patent US11488303B2, 1 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, D.C.; Liu, C.C.; Kao, C.H.; Hsieh, T.C. System of deep learning neural network in prostate cancer bone metastasis identification based on whole body bone scan images. Taiwan Patent 202117742 / I709147, 1 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.S. Computer-Aided Bone Scan Assessment with Automated Lesion Detection and Quantitative Assessment of Bone Disease Burden Changes. U.S. Patent US20140105471, 7 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; et al. An end-to-end multi-task system of automatic lesion detection and anatomical localization in whole-body bone scintigraphy by deep learning. Bioinformatics 2023, 39(1), btac753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1703.06870v3. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, D.; Riegler, M.A.; Johansen, D.; Halvorsen, P.; Johansen, H.D. DoubleU-Net: A Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.04868. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.02611v3. [Google Scholar]
Figure 1.
Two WBBS, (a) has bone metastasis and (b) has no metastasis.
Figure 1.
Two WBBS, (a) has bone metastasis and (b) has no metastasis.
Figure 2.
(a) shows the original image, while (b) displays the ground truth of the bone metastasis-prone regions and 10 (+1 background) categories with different colors.
Figure 2.
(a) shows the original image, while (b) displays the ground truth of the bone metastasis-prone regions and 10 (+1 background) categories with different colors.
Figure 3.
The architecture of Mask R-CNN having multi-class classification.
Figure 3.
The architecture of Mask R-CNN having multi-class classification.
Figure 4.
The architecture of DoubleU-Net comprised of two sub-networks. To enable multi-class classification, we made a modification between the output of Network 1 and the input of Network 2.
Figure 4.
The architecture of DoubleU-Net comprised of two sub-networks. To enable multi-class classification, we made a modification between the output of Network 1 and the input of Network 2.
Figure 5.
The architecture of the DeeplabV3 plus using ResNet-50 as backbone.
Figure 5.
The architecture of the DeeplabV3 plus using ResNet-50 as backbone.
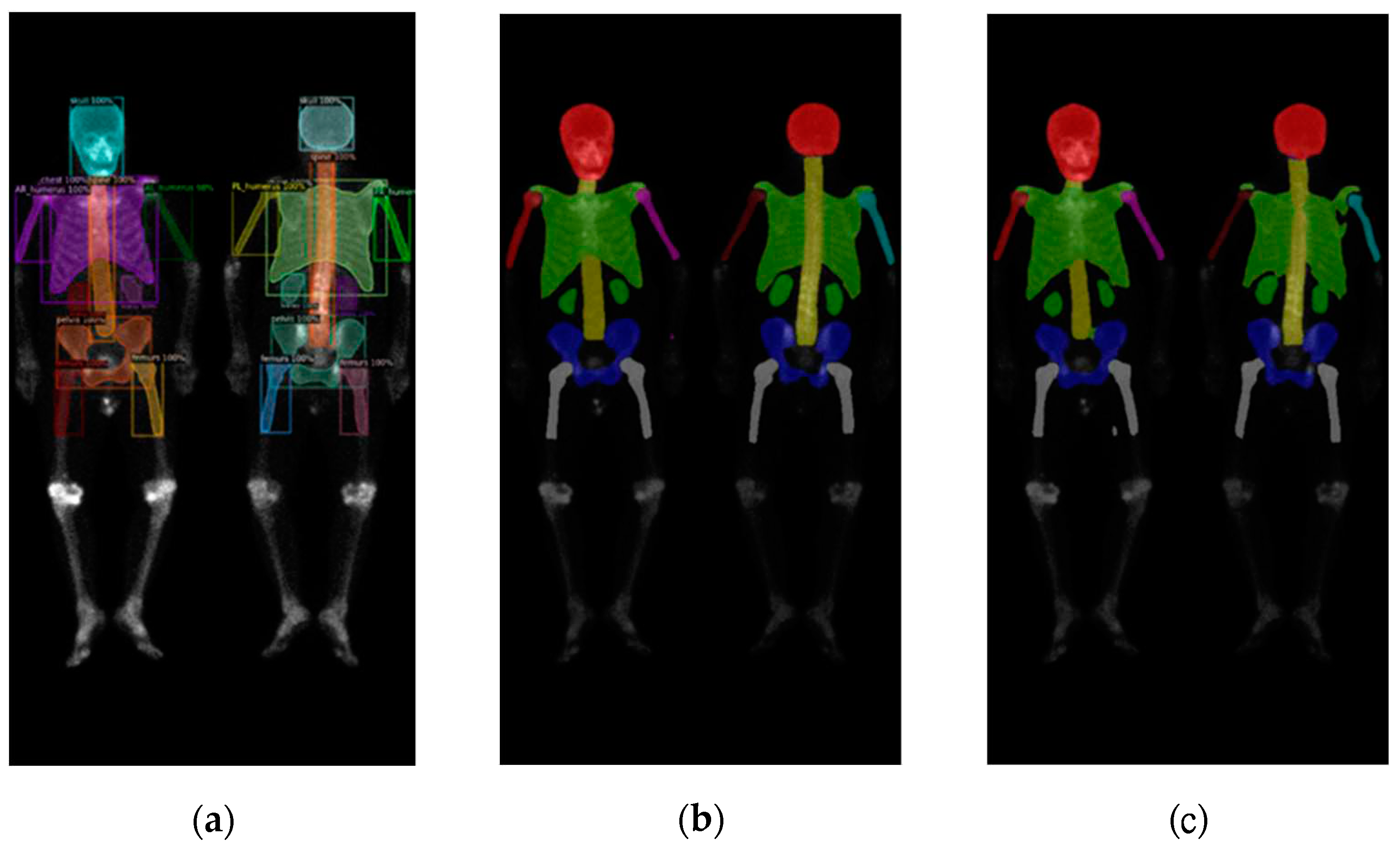
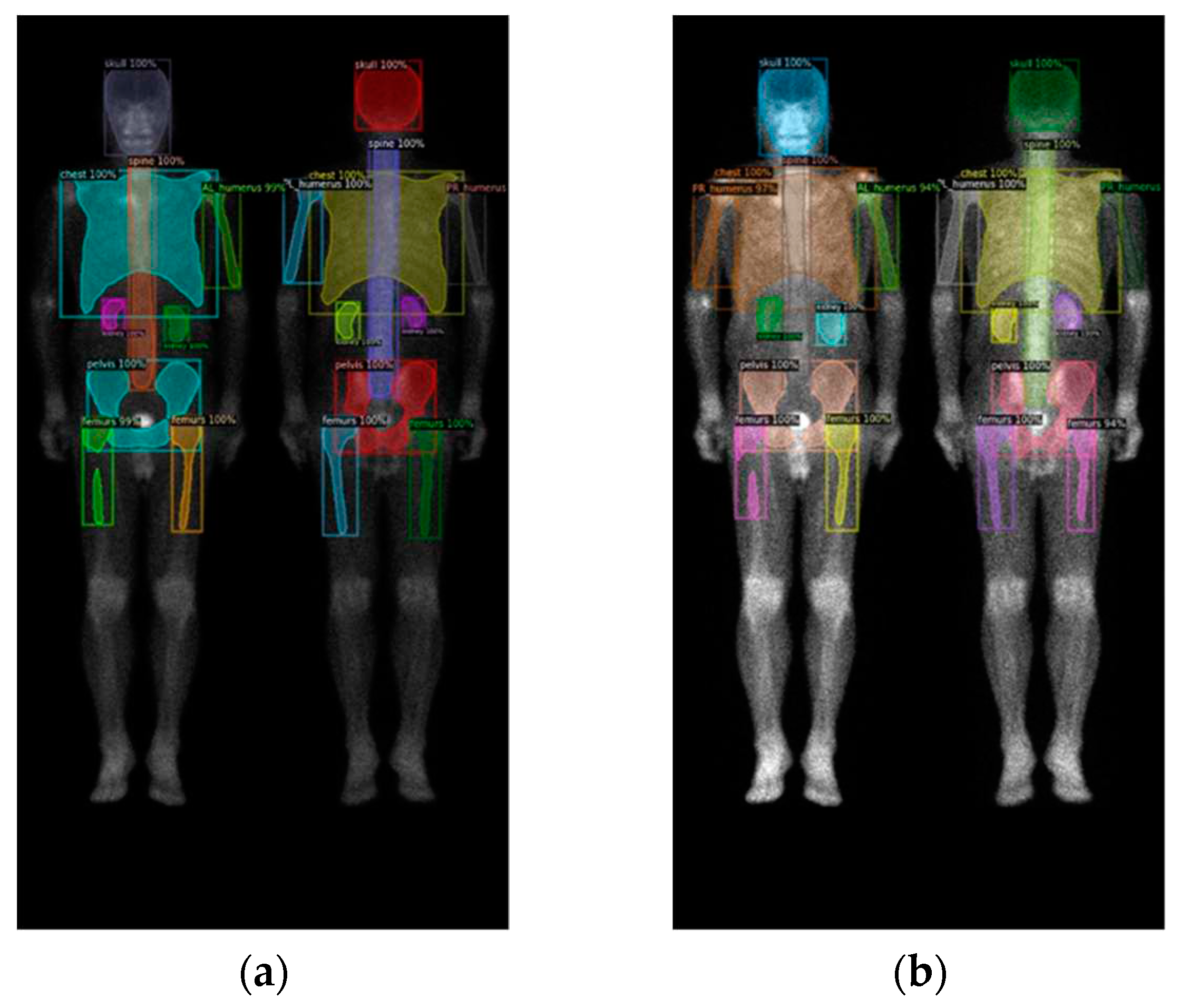
Figure 6.
The qualitative results of three models on prostate cancer WBBS images: (a) Mask R-CNN, (b) DoubleU-Net, and (c) DeeplabV3 plus.
Figure 6.
The qualitative results of three models on prostate cancer WBBS images: (a) Mask R-CNN, (b) DoubleU-Net, and (c) DeeplabV3 plus.
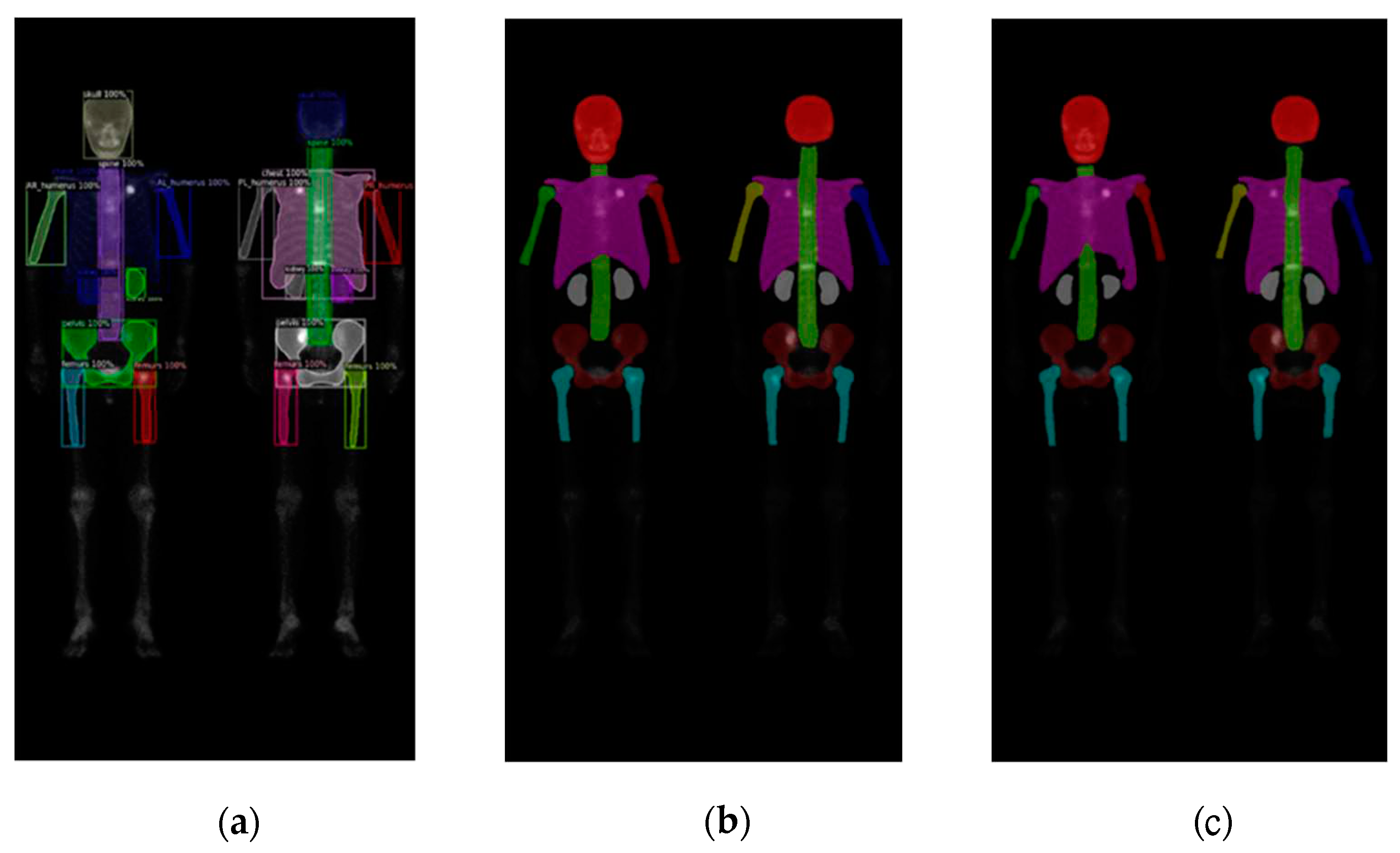
Figure 7.
The qualitative results of three models on breast cancer WBBS images: (a) Mask R-CNN, (b) DoubleU-Net, and (c) DeeplabV3 plus.
Figure 7.
The qualitative results of three models on breast cancer WBBS images: (a) Mask R-CNN, (b) DoubleU-Net, and (c) DeeplabV3 plus.
Figure 8.
Qualitative comparisons on three models: (a) Mask R-CNN, (b) DoubleU-Net, (c) DeeplabV3 plus. White: TP, red: FP, and green: FN.
Figure 8.
Qualitative comparisons on three models: (a) Mask R-CNN, (b) DoubleU-Net, (c) DeeplabV3 plus. White: TP, red: FP, and green: FN.
Figure 9.
Qualitative comparisons on three models: (a) Mask R-CNN, (b) DoubleU-Net, (c) DeeplabV3 plus.
Figure 9.
Qualitative comparisons on three models: (a) Mask R-CNN, (b) DoubleU-Net, (c) DeeplabV3 plus.
Figure 10.
(a) Original test segmentation result with missing right humerus in the frontal view. (b) Segmentation result after adjusting the brightness to 2.5 times and retest.
Figure 10.
(a) Original test segmentation result with missing right humerus in the frontal view. (b) Segmentation result after adjusting the brightness to 2.5 times and retest.
Figure 11.
A segmentation result showing the absence of the frontal and dorsal left femur due to abnormal patient position, while this abnormal position was rare and not existed in the training dataset.
Figure 11.
A segmentation result showing the absence of the frontal and dorsal left femur due to abnormal patient position, while this abnormal position was rare and not existed in the training dataset.
Figure 12.
(a) Segmentation result of DoubleU-Net with a segmentation error in the distal part of the leg. (b) Segmentation result of Deeplabv3 plus showing category confusion in the upper limbs and head region.
Figure 12.
(a) Segmentation result of DoubleU-Net with a segmentation error in the distal part of the leg. (b) Segmentation result of Deeplabv3 plus showing category confusion in the upper limbs and head region.
Table 1.
Hyperparameters used for the 10-fold cross-validation experiments with each neural network.
Table 1.
Hyperparameters used for the 10-fold cross-validation experiments with each neural network.
| Hyperparameters |
Mask R-CNN |
DoubleU-Net |
DeeplabV3 plus |
| Learning Rate |
0.005 |
0.0005 |
0.0005 |
| Batch Size |
4 |
4 |
4 |
| Epochs |
100 |
200 |
200 |
Table 2.
The comparing results of 10-fold cross-validation on prostate cancer WBBS image dataset.
Table 2.
The comparing results of 10-fold cross-validation on prostate cancer WBBS image dataset.
| Category |
Mask R-CNN |
DoubleU-Net |
DeeplabV3 plus |
| Precision |
Sensitivity |
Precision |
Sensitivity |
Precision |
Sensitivity |
| Skull |
97.22 |
94.43 |
96.05 |
96.13 |
95.34 |
95.91 |
| Spine |
93.90 |
88.62 |
91.16 |
91.30 |
89.94 |
89.79 |
| Chest |
95.33 |
93.58 |
94.83 |
94.52 |
93.61 |
93.87 |
| AR_humerus |
91.82 |
84.80 |
89.65 |
90.18 |
87.42 |
87.88 |
| AL_humerus |
92.46 |
85.30 |
89.76 |
90.12 |
87.94 |
89.02 |
| PR_humerus |
91.72 |
84.41 |
88.68 |
89.55 |
85.77 |
87.25 |
| PL_humerus |
89.94 |
82.01 |
87.89 |
88.78 |
87.50 |
83.64 |
| Pelvis |
92.32 |
88.26 |
90.76 |
90.83 |
90.99 |
87.84 |
| Femurs |
88.40 |
81.75 |
86.08 |
84.85 |
85.59 |
82.60 |
| Kidney |
86.13 |
79.23 |
82.45 |
82.73 |
80.15 |
81.87 |
| Average |
91.93 |
86.24 |
89.73 |
89.90 |
88.43 |
87.97 |
| Average (w/o kidney) |
92.57 |
87.02 |
90.54 |
90.70 |
89.34 |
88.64 |
Table 3.
The comparing results of 10-fold cross-validation on the breast cancer WBBS image dataset.
Table 3.
The comparing results of 10-fold cross-validation on the breast cancer WBBS image dataset.
| Category |
Mask_R-CNN |
DoubleU-Net |
DeeplabV3 plus |
| Precision |
Sensitivity |
Precision |
Sensitivity |
Precision |
Sensitivity |
| Skull |
97.24 |
94.23 |
96.18 |
95.88 |
95.91 |
93.24 |
| Spine |
93.20 |
88.61 |
91.15 |
90.68 |
90.56 |
87.76 |
| Chest |
95.17 |
93.48 |
94.10 |
94.32 |
92.78 |
93.40 |
| AR_humerus |
89.67 |
80.23 |
87.21 |
86.01 |
85.88 |
81.90 |
| AL_humerus |
89.07 |
81.20 |
86.44 |
84.97 |
87.15 |
80.26 |
| PR_humerus |
89.65 |
82.10 |
87.58 |
86.46 |
85.41 |
83.66 |
| PL_humerus |
88.28 |
80.08 |
87.34 |
86.39 |
86.62 |
81.92 |
| Pelvis |
92.22 |
88.27 |
90.86 |
90.24 |
91.34 |
87.54 |
| Femurs |
89.95 |
81.39 |
87.05 |
84.83 |
88.06 |
81.71 |
| Kidney |
87.21 |
80.71 |
84.37 |
83.74 |
83.91 |
77.59 |
| Average |
91.17 |
85.03 |
89.23 |
88.35 |
88.76 |
84.90 |
| Average (w/o Kidney) |
91.61 |
85.51 |
89.77 |
88.86 |
89.30 |
85.71 |
Table 4.
Hyperparameters for training DoubleU-Net.
Table 4.
Hyperparameters for training DoubleU-Net.
| Hyperparameters |
DoubleU-Net |
| Learning Rate |
0.0005 |
| Batch Size |
4 |
| Epochs |
20 |
Table 5.
Table 5. 10-fold cross-validation on DoubleU-Net, used augmentation.
Table 5.
Table 5. 10-fold cross-validation on DoubleU-Net, used augmentation.
| Fold Number |
Prostate |
Breast |
| Precision |
Sensitivity |
Precision |
Sensitivity |
| 1 |
86.67 |
96.05 |
83.95 |
94.84 |
| 2 |
87.01 |
94.92 |
86.18 |
95.26 |
| 3 |
91.22 |
91.33 |
81.14 |
96.05 |
| 4 |
93.01 |
91.37 |
81.87 |
96.32 |
| 5 |
85.69 |
94.85 |
84.35 |
96.18 |
| 6 |
94.18 |
89.28 |
96.23 |
76.73 |
| 7 |
96.10 |
86.81 |
95.64 |
85.26 |
| 8 |
93.43 |
88.31 |
95.37 |
84.49 |
| 9 |
92.99 |
87.74 |
95.57 |
85.51 |
| 10 |
93.89 |
88.12 |
94.97 |
89.19 |
| Average |
91.42 |
90.88 |
89.53 |
89.98 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).