1. Introduction
Loess is an Aeolian soil formed during the Quaternary geological period. It is widely distributed in northwestern China, where the Loess Plateau locates, covering an area of about 640,000 km
2 [
1]. Loess is a highly water-sensitive soil with large pores and unstable structures. The vertical joints and cracks are frequently developed in loess, which result to the collapse of loess under the condition of rainfall or irrigation [
2,
3,
4]. Various constructions and project applications in the Loess Plateau of China provide many development opportunities. However, it also brings many unprecedented geotechnical problems due to the special characteristics of loess [
5,
6]. The climate of Loess Plateau of China is continental is semi-arid [
7]. The drying or wetting effects due to climatic conditions can cause structural damage of loess, which in turn will produce cracks in soil.
There are different patterns of cracks in soils, among which cracks in networks or circle forms are more frequently observed. Interval parallel cracks, also called spacing cracks are more commonly observed in layered rocks and bar-like soils. The presence of cracks can significantly affect the behavior of soil, including soil volume variations, disintegration, permeability, residual shear and tensile strength etc. [
8,
9]. These changes will greatly reduce the mechanical properties of soils. Cracks related to desiccation also destroy soil integrity and provide preferential path for water infiltration, reducing the stability of slopes or hydraulic constructions [
10,
11,
12,
13]. Therefore, it is particularly important to explore the influencing factors and mechanisms of cracks related to drying in soils.
During drying, soils are prone to crack when the tensile stress of soils exceeds its tensile strength [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. In order to understand the cracking mechanism of soil during drying, the factors affecting the evolution of cracks were well studied. The mainly internal factors include physical properties and mineral composition of soils etc. [
19,
20]. The mainly external factors are layer thickness [
20,
21,
22], boundary conditions [
16,
23,
24], temperature [
22,
25,
26], relative humidity etc. [
18,
27,
28]. However, the in-depth study about the characteristics and mechanisms of spacing cracks are still inadequate.
Spacing cracks, a special case during drying of soils, are determined to be a series of parallel cracks at an interval distance. At present, the researches on spacing cracks are mainly concentrated on materials with high stiffness such as rocks or concretes. Wu et al., (1995) pointed that the spacing distribution must have three cracks at least [
29]. A series of theoretical results have been obtained. Tang et al., (2006) used RFPA software to model the development of spacing cracks in layered materials [
30]. Meanwhile, the development of cracks was observed by applying different principal stress ratios on layered materials. The results showed that the material usually breaks with parallel cracks under mechanical layer-parallel tensile forces. Under loads with different principal stress ratio, the cracks show a continuous transition from parallel to polygonal pattern. Xu et al. (1989) established a mechanical model of narrow and generalized spacing cracks from some typical geological phenomena [
31]. By applying the tensile strains to the boundary of model, three factors affecting the initiation of spacing cracks are derived. Bai et al. (2000) studied the phenomenon of spacing cracks and saturation mode in layered materials (sedimentary rocks, etc.) [
32]. During the cracking process, when the distances between two adjacent cracks reaches a certain value, more cracks cannot be formed even if the tensile strains keep increasing. The additional strain is used for widening the existing crack. This phenomenon can be defined as “crack saturation” [
33,
34].
There are many theories about spacing cracks especially in models such as shear lag models, stress transfer models, energy balance theory, etc. Comparing with experimentations, simulation is another efficient method to interpret the mechanisms of spacing cracks. Most of the modeling materials in researches are idealized materials by setting parameters. However, the experimental researches are relatively rare and spacing cracks in soils are less discussed in researches. The studies concentrating on the conditions of crack formation, the law of crack initiation and propagation, the microscopic mechanism etc. are still insufficient.
This research studied the characteristics and mechanism of spacing cracks in loess during drying. The remolded loess as a homogeneous geomaterial, which is appropriate to demonstrate the spacing cracking laws under the size effect. The evolution laws of spacing cracks are concluded by setting different dimensions of soil samples. The local displacement and strains of soils samples are obtained with Digital Image Correlation (DIC) method in order to reveal the cracking mechanisms of spacing cracks. Finally, the evolution of spacing cracks in loess during drying is performed based on the discrete element method. The influence of specimen dimension on characteristics of spacing crack are verified with the numerical modelling results.
2. Experimental materials and methods
2.1. Materials
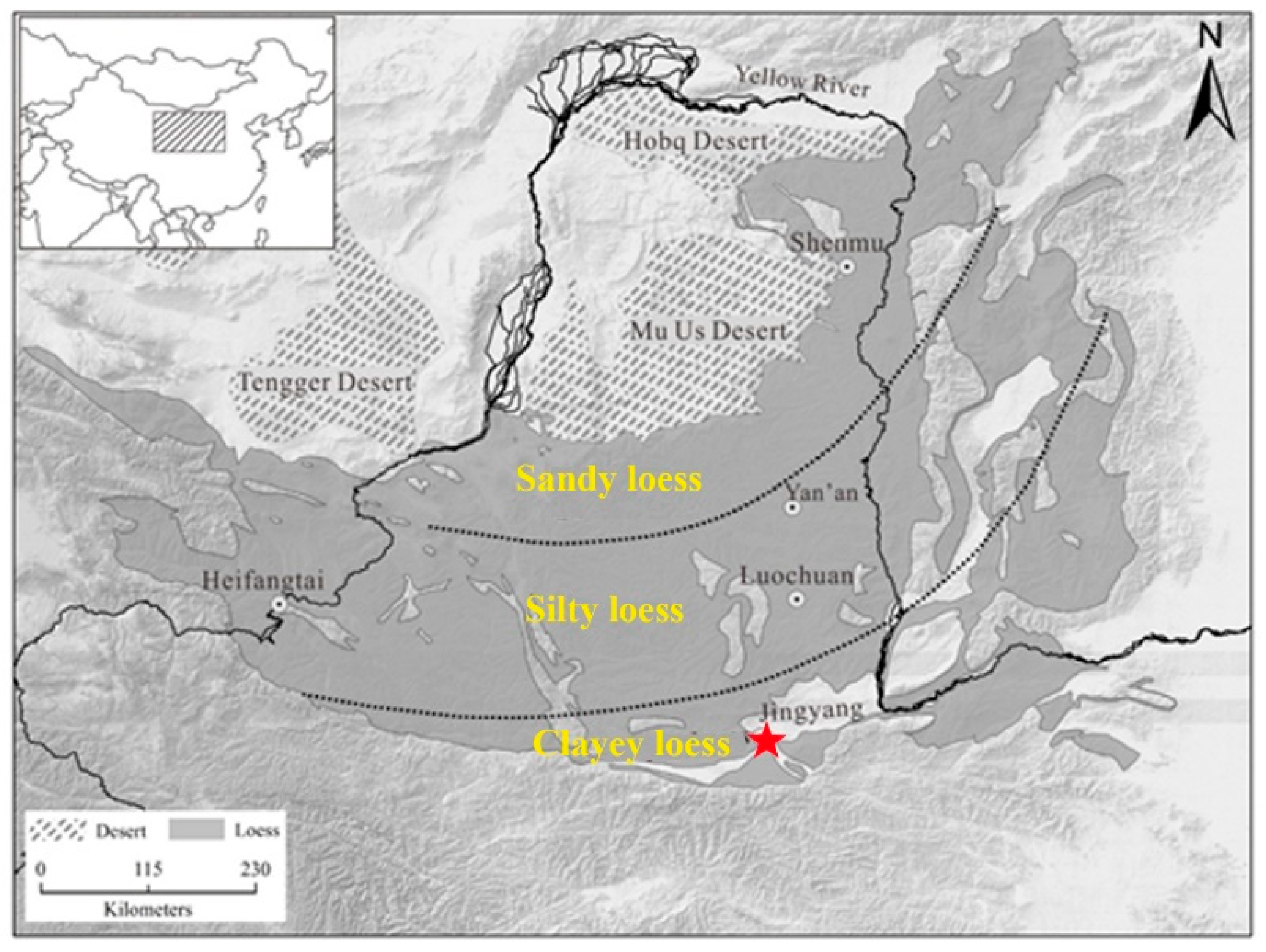
In this research, the loess was collected at the depth of 50 m in Jingyang, Shaanxi Province, which is Q4 loess (
Figure 1). Shaanxi Province is in the northwest of China, where the Chinese Loess Plateau locates. The materials source of loess is from Mu Us Desert. The physical properties and mineralogy of loess vary greatly in Chinese Loess Plateau. Loess particles with finer size and small density are prone to be transferred with longer distance. Therefore, loess can be classified as three types: clayey loess, silty loess and sandy loess [
1]. The soil used in this research is clayey loess.
Jingyang is located nearly in the center of Shaanxi Province. The climate in Jingyang is warm continental monsoon. The temperatures change dramatically in different season. Recently the impact of climate change is studied widely. A more intense, more frequent and longer lasing drought or rainfall has appeared in the last few years [
1].
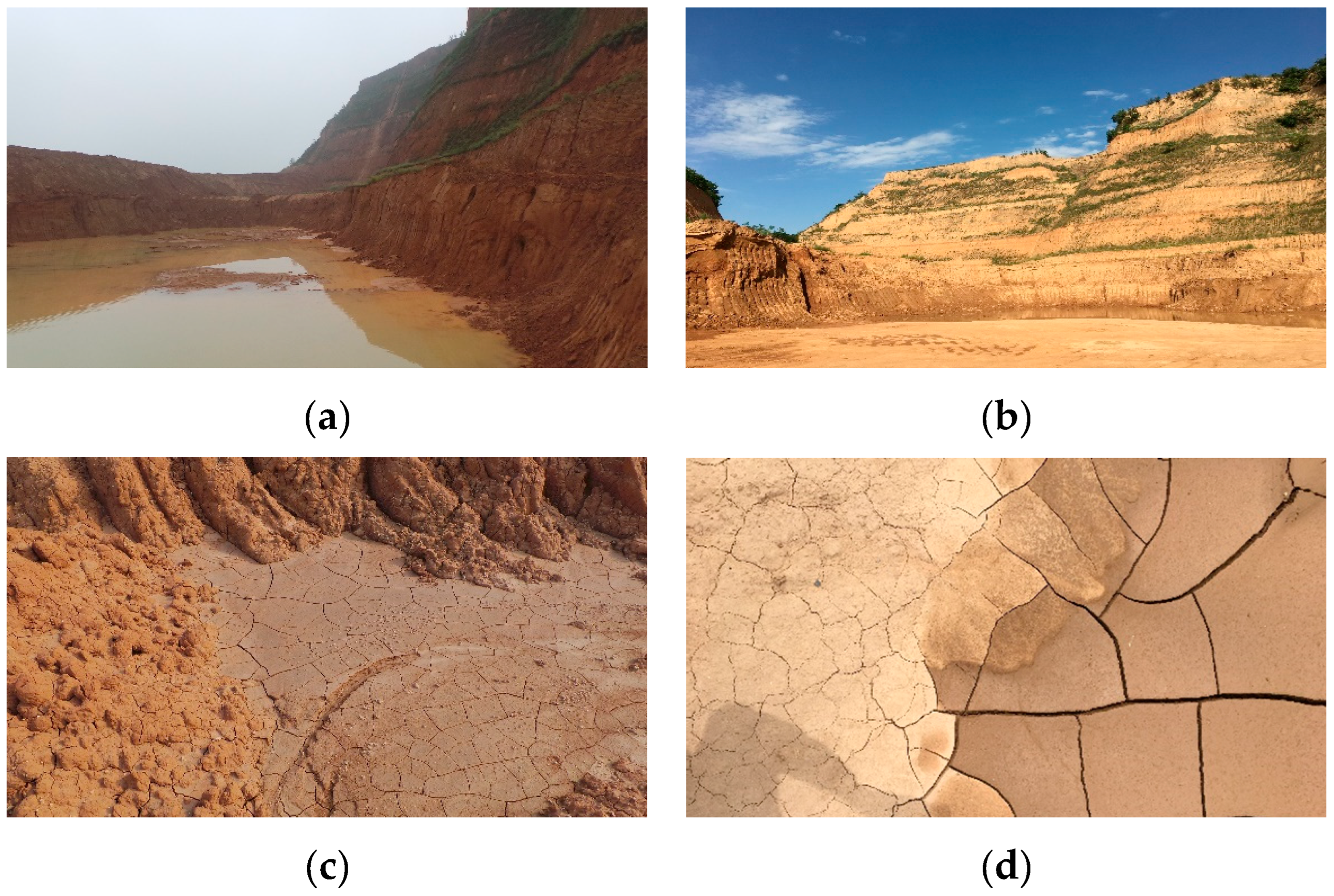
Figure 2a,b shows the same loess slopes under rainfall and drought conditions, respectively. The drought-induced cracks can be observed on the surface of the loess plateau beside the slope foot (
Figure 2c). The different scale of cracks due to inhomogeneous water evaporation can be observed in
Figure 2d.
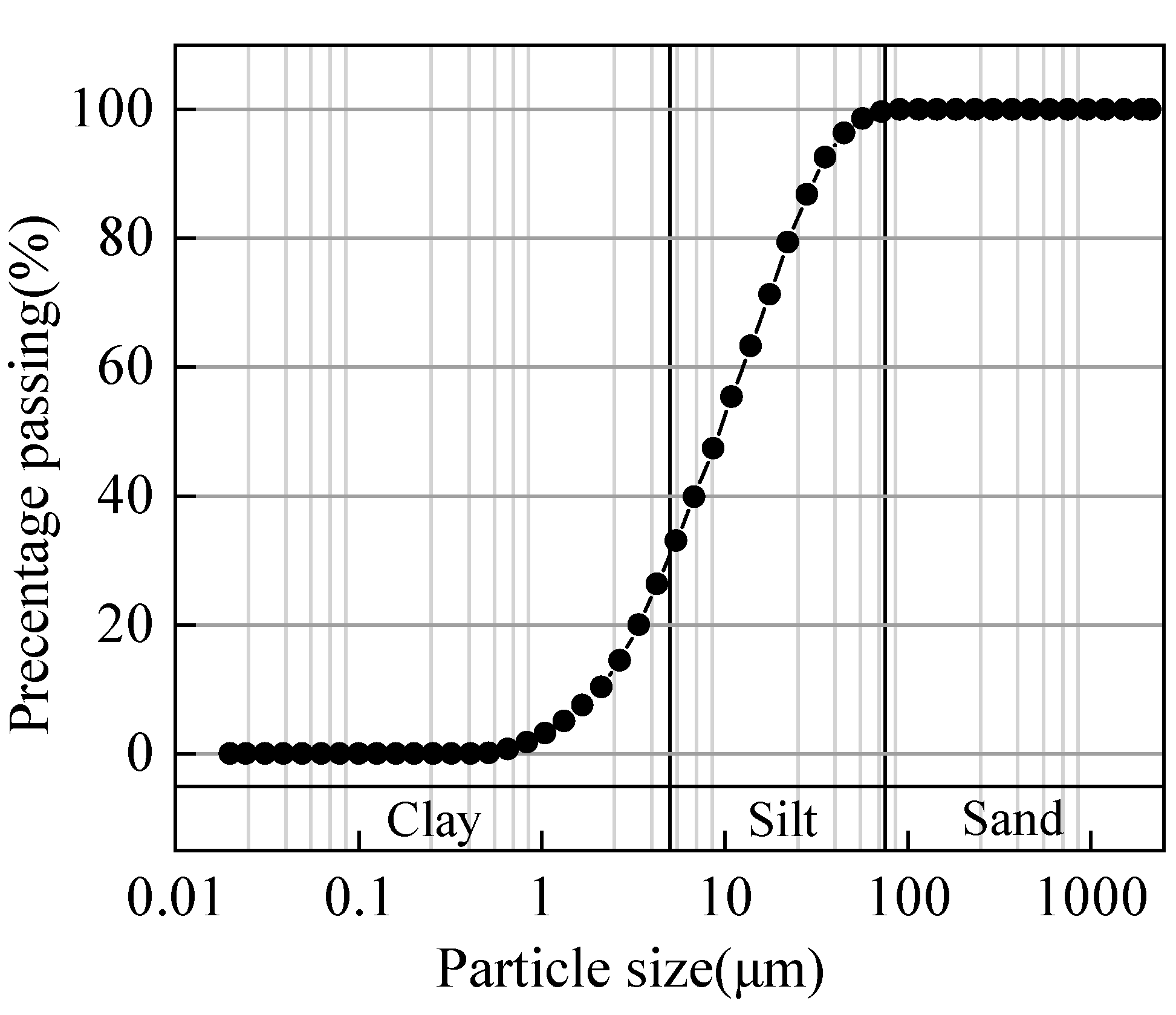
The particle size distribution curve of loess is shown in
Figure 3. The silt content and clay content of Jingyang loess is 82.7% and 17%, respectively. According to the Uniform Soil Classification System (ASTM 2021), it is classified as low plastic clay (CL). The physical properties of the loess are summarized in
Table 1. The soil sample used in this research is remolded loess. The initial water content of soil sample is 36%, which equals to its liquid limit. Before put into the plastic mold, the soil samples were placed in a sealed container for about 24h in order to reach a homogenous state.
2.2. Experimental set-ups
The confined drying tests were carried out in this research. The soil samples are with constant length and flexible height and width. The ratio of height and width are constant, which equals to 1. The dimensions of soils samples are 1×1×30 cm, 2×2×30 cm, 3×3×30 cm, 4×4×30 cm and 5×5×30 cm, respectively. Different volumes of soil samples were set for the purpose of exploring the size effect on characteristics of spacing cracks.
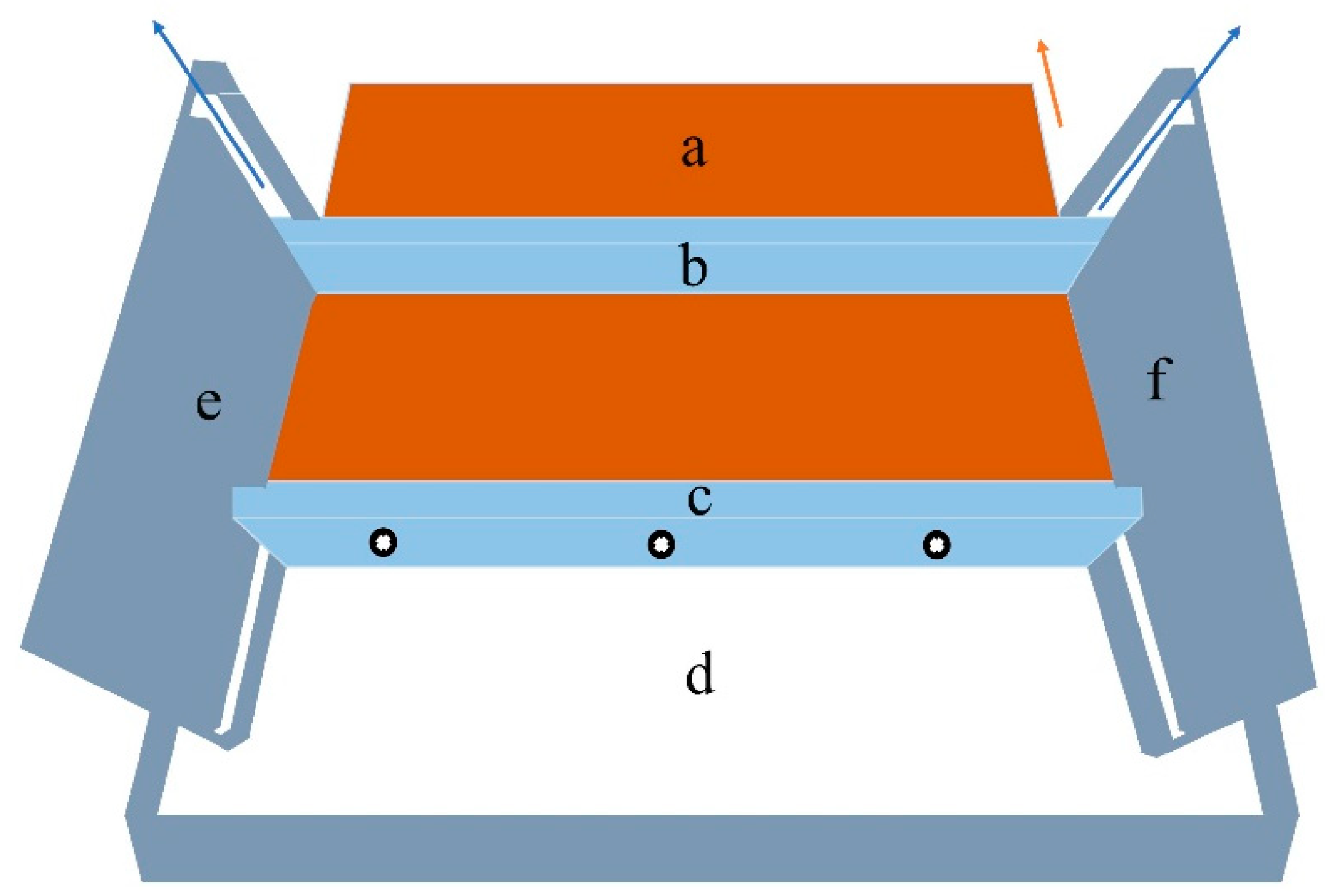
The schematic diagram of the soil sample mold is shown in
Figure 4. The mold is made in plexiglass with small friction. It provides boundary constrains for the samples. Support a, boundaries b and c are movable, of which vertical plate a is connected with horizontal plate c by three nails. The length of the mold is 30 cm, which is determined by two fixed plates e and f, which are sticked on support d. The blue vectors in
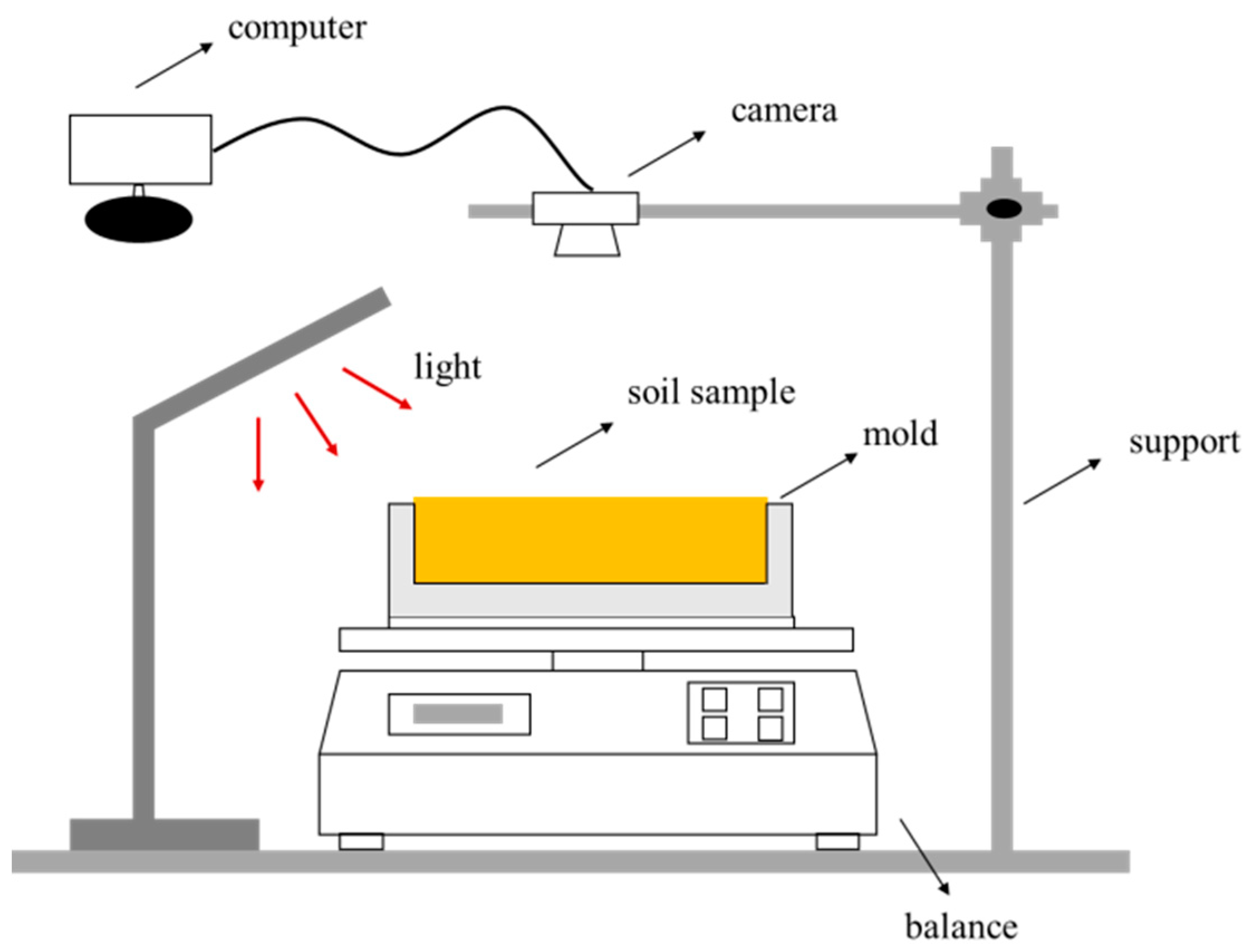
Figure 4 indicate the sliding direction of plates e and f. The position of plate a determines the width of soil samples. The height of plates b and c equals to the height of soils samples. Five sets of plates (b and c) with different height were made in order to change the height of the soil samples. Remolded loess samples were filled in this mold so that the soil samples with different dimensions were fabricated. The drying test set-up for the observation of spacing cracks is shown in
Figure 5. A high-speed camera is installed above the soil sample to record the evolution of spacing cracks on the surface at regular intervals. The lamp provides light source for the photos. Specimens and molds are placed on an electronic balance for recording the variations of soil water contents.
2.3. Digital Image Correlation (DIC) method
The Digital Image Correlation (DIC) method is used for analyzing local displacements and strains of the soil sample during the cracking process [
18,
35]. This method requires that the surface of the object is with different speckles for distinctions during calculation. Since the remolded loess is homogeneous, the surface of the specimen is sprayed with random speckles of different dimensions (
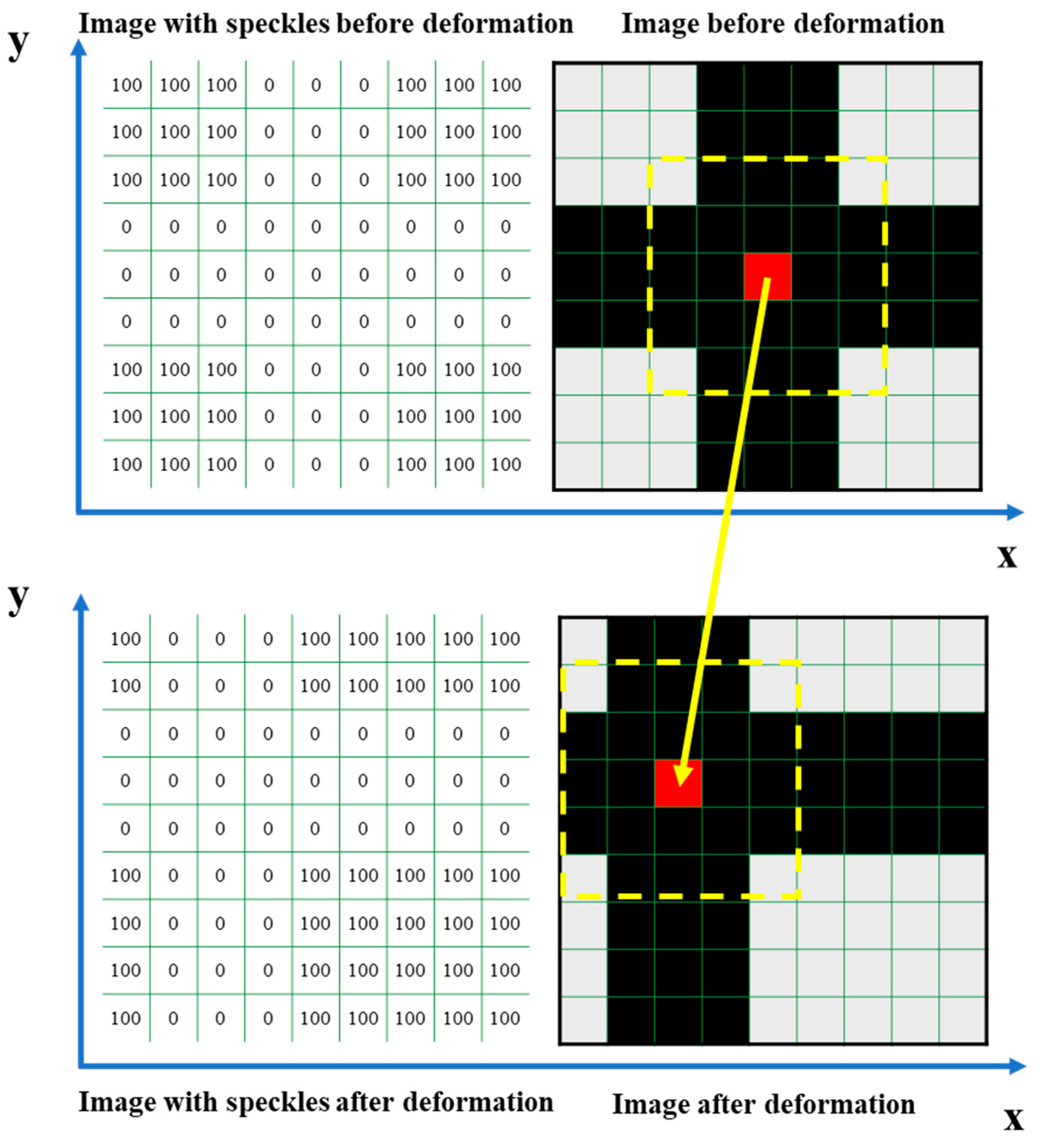
Figure 6). Different colors correspond to different pixels. A commercial software VIC-2D is used to calculate the local displacements and strains between the reference image (before deformation) and the deformed image. Finally, the local strains and displacements on the surface of the soil specimen are obtained.
With VIC-2D, 2 displacement components and 3 strain components can be obtained: U(mm)- longitudinal displacement along the x axis, V (mm)- transversal displacement along the y axis,
(%)- longitudinal strain along the x direction,
(%)- transversal strain along the y direction, and shear strain
(%). With these five components, the variations of local displacements and strains on the surface of the sample can be analyzed during drying process, allowing interpretations of the cracking mechanism. As an example,
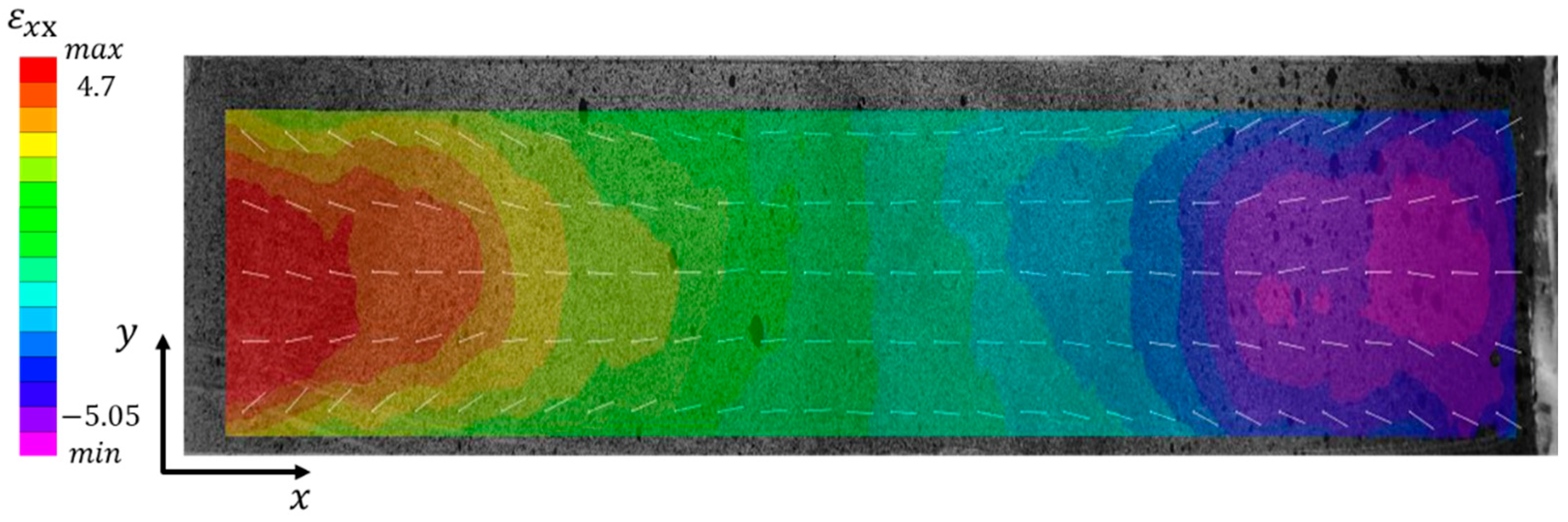
Figure 7 shows the result of longitudinal strain
of loess samples with the dimension of 5×5×30 cm at t = 25 h. The maximum
is 4.7% and the minimum
is -5.05%. The positive value represents tensile strain while the negative value represents compressive strain. The white vectors on the specimen surface show the global directions of local displacements.
2.4. Discrete Element Method based on MatDEM software
The numerical modelling in this research is realized with MatDEM, which is a discrete element simulation software based on Newton's second law developed by Nanjing University [
36]. In MatDEM, a discrete element model that couples the moisture field to the stress field is shown in
Figure 8a. Each unit shown in
Figure 8a is composed of soil particles, pores, and pore water. When the water evaporates, the water content of the surface unit gradually decreases and is lower than that of the adjacent unit. As a result of the hydraulic gradient, the water flows from the unit with higher water content to the unit with smaller water content.
The air entry value refers to the suction when the air begins to enter during the desaturation of the soil. When the water content is higher than that relates to the air entry value, the soil is saturated and the water flow obeys Darcy's law. The equation is as follows:
where
is the permeability coefficient;
A is the equivalent area of the permeation pathway, taking the average area of the two-element large circle, as shown in
Figure 8b;
is the difference between the water content of the two adjacent units;
presents their bulbar center spacing.
The mechanical properties of the soil also vary with the water content. At the microscopic scale, the connections between different units are correspondingly strengthened. If the strength of the connection is less than the tensile force caused by dry shrinkage, the connection will break. Herin, there will be no water migration between the two units. As the desiccation simulation progresses, the connections among units break one after the other. Therefore, many micro-cracks are generated in a certain direction to form a macroscopic crack. The numerical modeling of spacing cracks in loess samples with different dimensions were carried out with MatDEM.
3. Experimental results
3.1. Characteristics of spacing crack parameters in loess
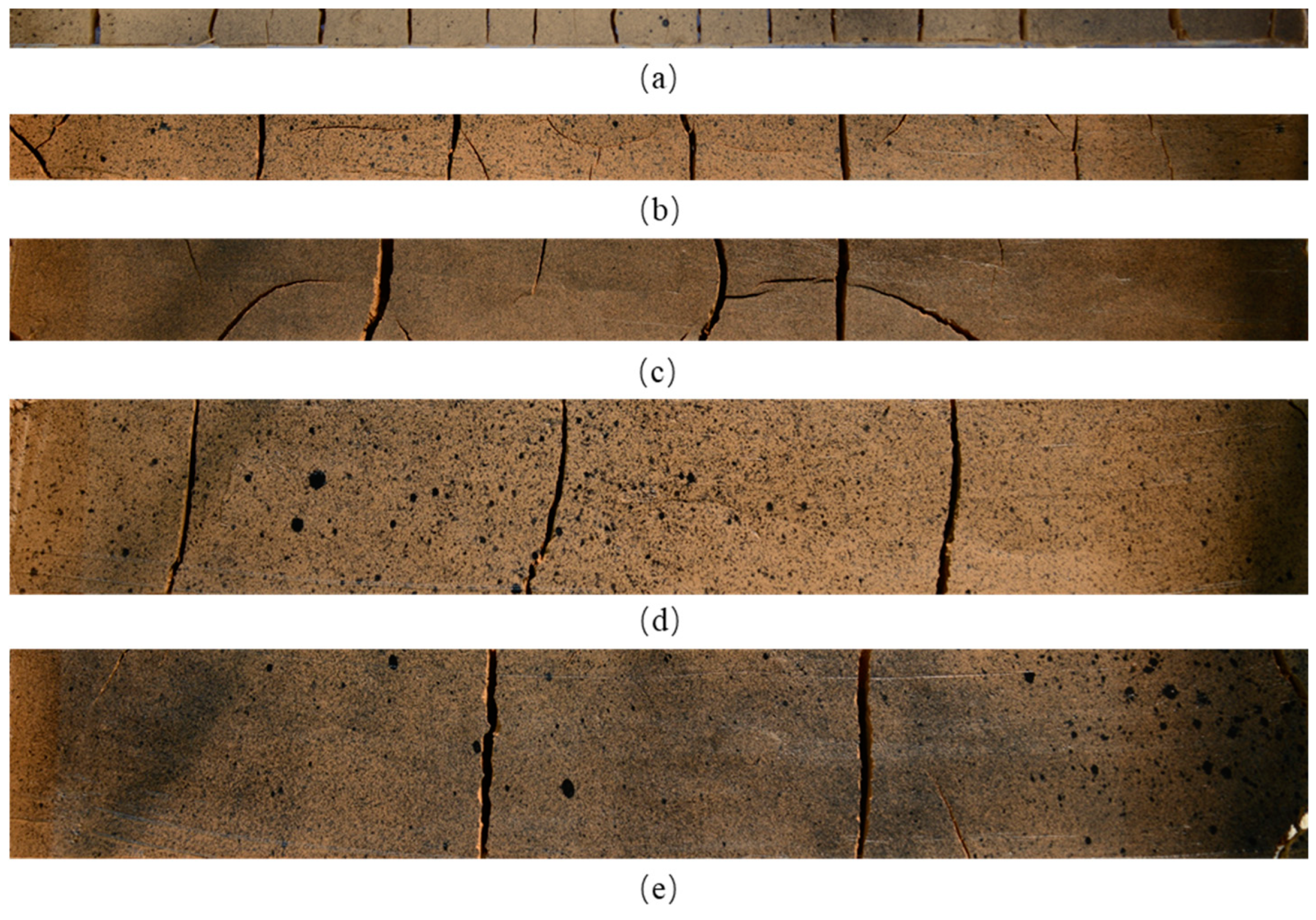
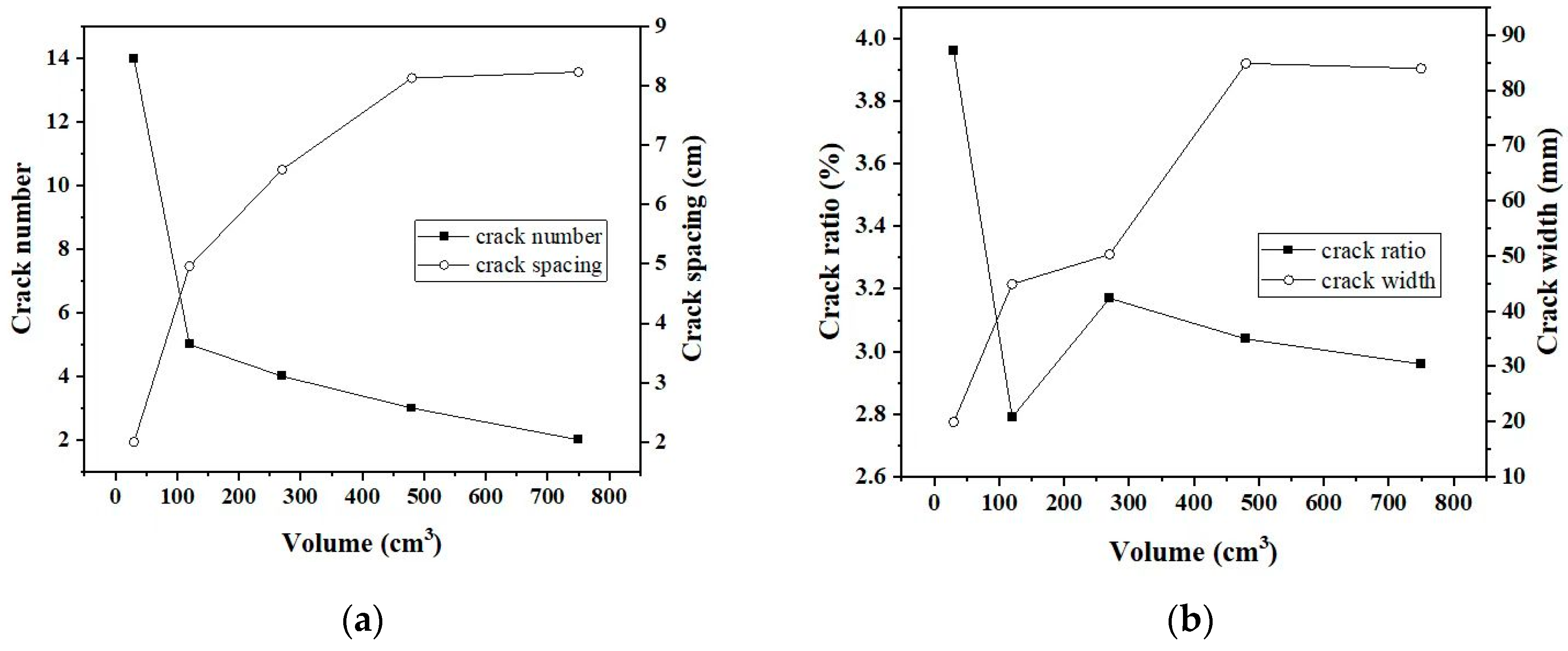
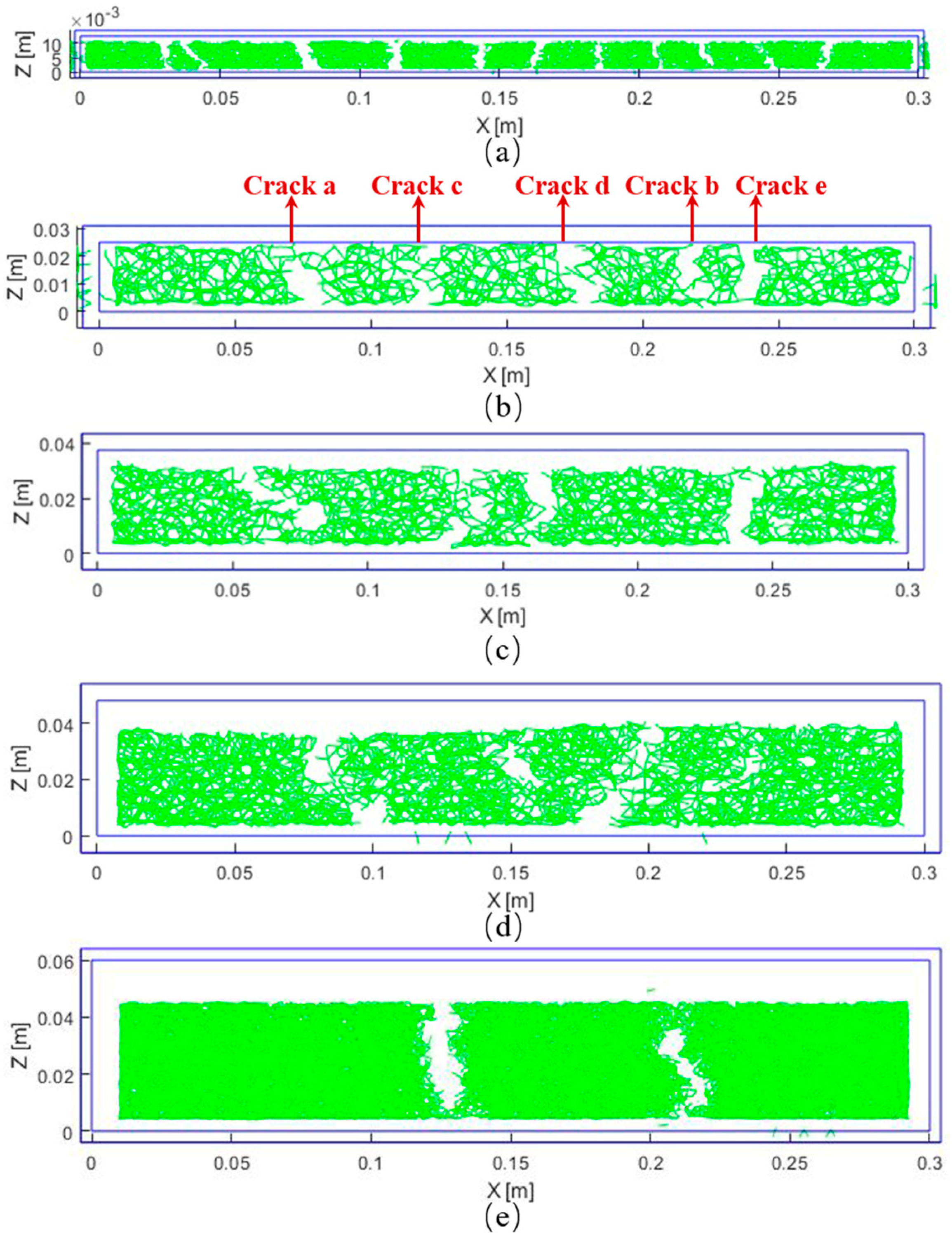
Figure 9 shows the final patterns of the spacing cracks of specimens with different dimensions. The number of cracks decreases as the specimen volume increases. At the end of drying tests, the variations of water contents and parameters of cracks, including the average width, the average spacing of the cracks, the cracking ratio, etc. of samples with different dimensions are analyzed (
Figure 10). The cracking ratio is calculated as
, where
is the surface of the cracks,
is the surface of the soil sample. The above parameters are calculated via PCAS, an image processing software developed by Nanjing University [
37]. The results of the spacing cracks parameters of different loess samples are presented in
Table 2.
The relationships between numbers of cracks, the average spacing of the cracks and the specimen volume are presented in
Figure 10a. It is obvious that as the volume of the specimen increases, the number of spacing cracks decreases. Since the length of the specimen is fixed at 30 cm, the average spacing of the cracks tends to increase with increasing volume. There is no much difference between the crack spacing of loess samples with the dimensions of 4×4×30 cm and 5×5×30 cm due to the small numbers of spacing cracks. The variation trend of cracking ratio and width of spacing cracks as a function of specimen volume is approximately the opposite (
Figure 10b). For specimen with the dimension of 1×1×30 cm, the crack ratio is the largest which equals to 4%, due to the relatively large cracking area. However, its average width of spacing cracks is the smallest, about 19.87 mm. Although the volume is the smallest, the number of cracks is the largest, reaching 14. For loess samples with smaller dimensions, spacing cracks are easily initiated comparing with soils samples with larger dimensions. The stresses between two adjacent cracks are continuously released. More cracks are generated and the width of the existing cracks is not able to increase. When the dimension of the soil sample increases to 2×2×30 cm, the number of cracks decreases greatly, with decreasing cracking ratio. When the dimension reaches 3×3×30 cm, the evolution tendency of the spacing crack is nearly stable. It is concluded that the dimensions of soil samples obviously influence the parameters of spacing cracks in loess.
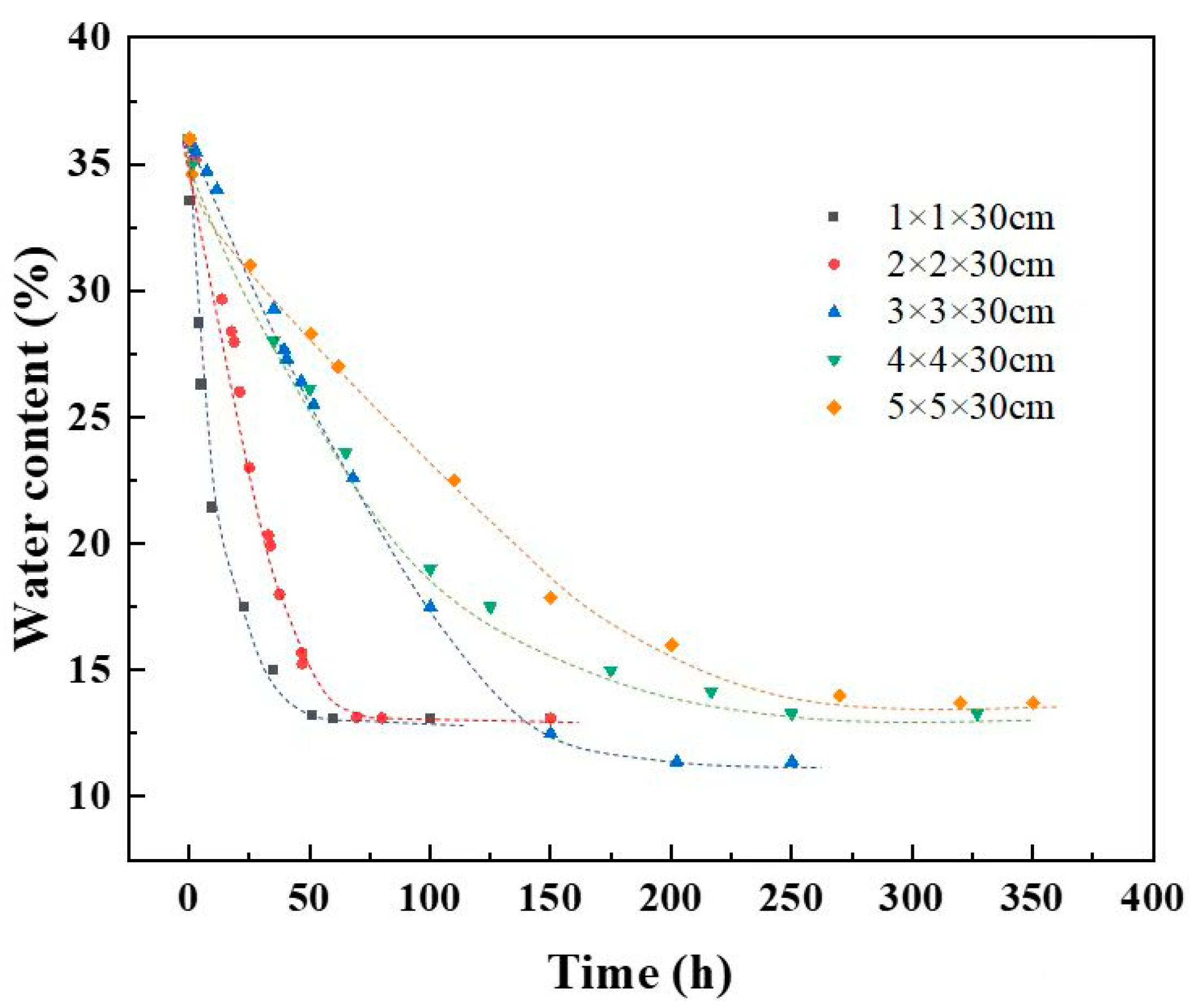
3.2. Variations of water contents in different samples
The characteristics of spacing cracks are affected by water content variations. The result of water content variations is shown in
Figure 11. Water content is an important factor related to the suction of soils. Their relationship is presented in Soil Water Characteristic Curve (SWCC) of soils [
35]. The water content of soil decreases, the matrix suction increases. Once the suction in soils exceeds the tensile strength of soil, cracks will generate. The overall water content variation trends of all the specimens are similar. The initial water contents of all specimens are 36%. At the beginning of desiccation, the water content decreases rapidly, then decreases gradually. At the end, the water content reaches a stable state, with a residual water content of about 13% - 15%. However, the evaporation rates are not the same for soil samples with different dimensions. The water content of the soil sample with small dimensions easily reaches stable. The water content gradient in the direction of thickness is greater as the size increases. The distances between the upper and lower interfaces, i.e., thickness of the soil samples, influences greatly the evaporation rates. Herein, the times for reaching the residual water content for samples with different dimensions are different. For the soil samples with larger dimensions, the time for the stabilization of water content is longer.
3.3. Spacing cracking modes in loess
Generally, there are three modes in the cracking of soils: opening mode, sliding mode and tearing mode [
18,
35]. In this research, the first two cracking modes were observed in spacing cracks of loess.
3.2.1. Spacing cracks in opening mode
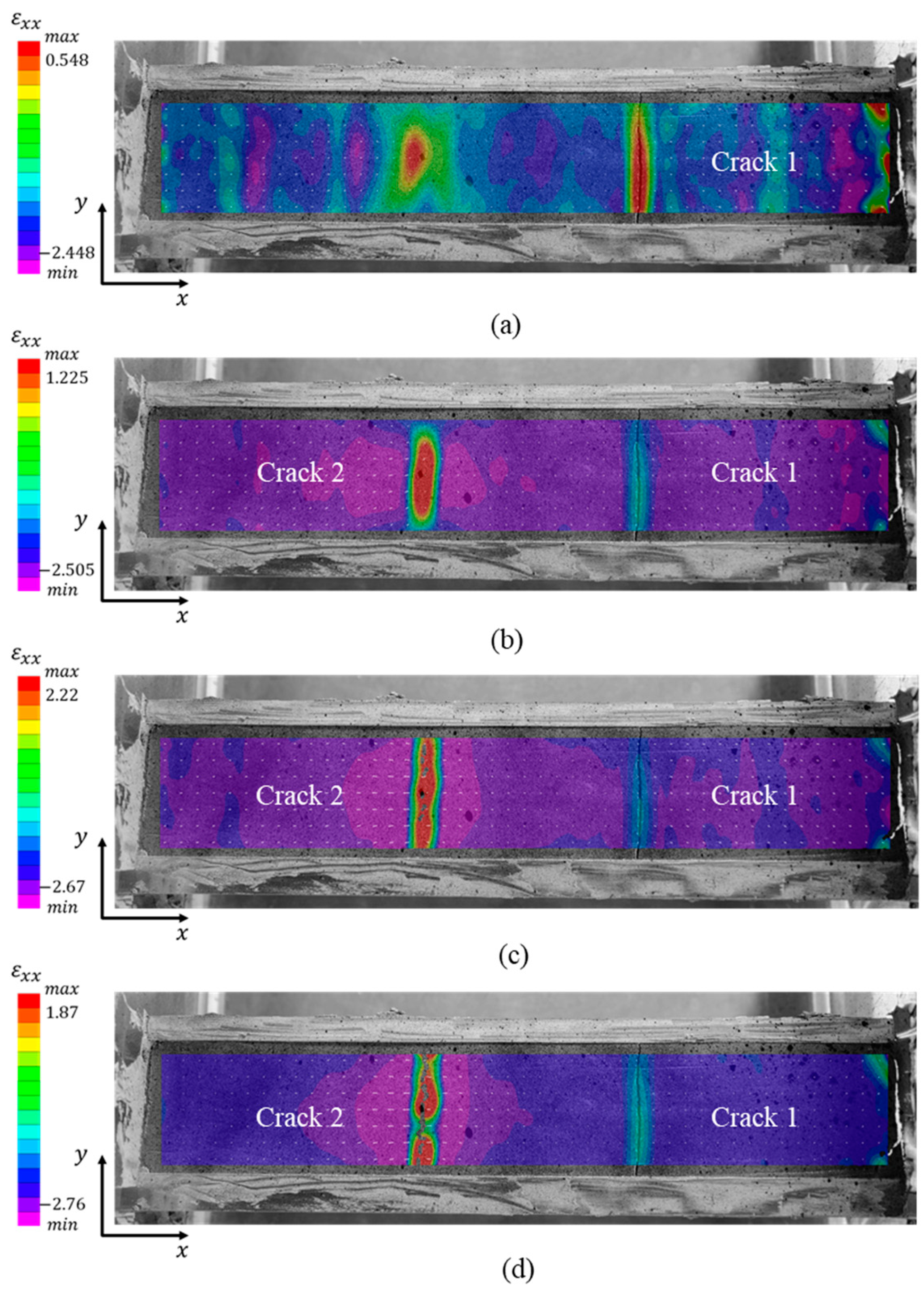
Taking the contour map of longitudinal strain
of loess samples with dimension of 5×5×30 cm as an example, the typical opening mode of the spacing crack is analyzed in
Figure 12, where two spacing cracks 1 and 2 were observed. Crack 1 was well developed and the evolution of crack 2 was analyzed. At t = 58 h,
in the area where crack 2 will generate are larger than that in the other areas (
Figure 12a).
around the upcoming crack 2 is positive, which indicated that the new crack is likely to initiate by tensile strains in this area. At t = 58.17 h, the maximum
increase from 0.548% to 1.225% (
Figure 12b). With increasing
, crack 2 initiated at t = 58.5 h (
Figure 12c). After about 10 mins, the maximum
decreases to 1.87%with the evolution of crack 2 (
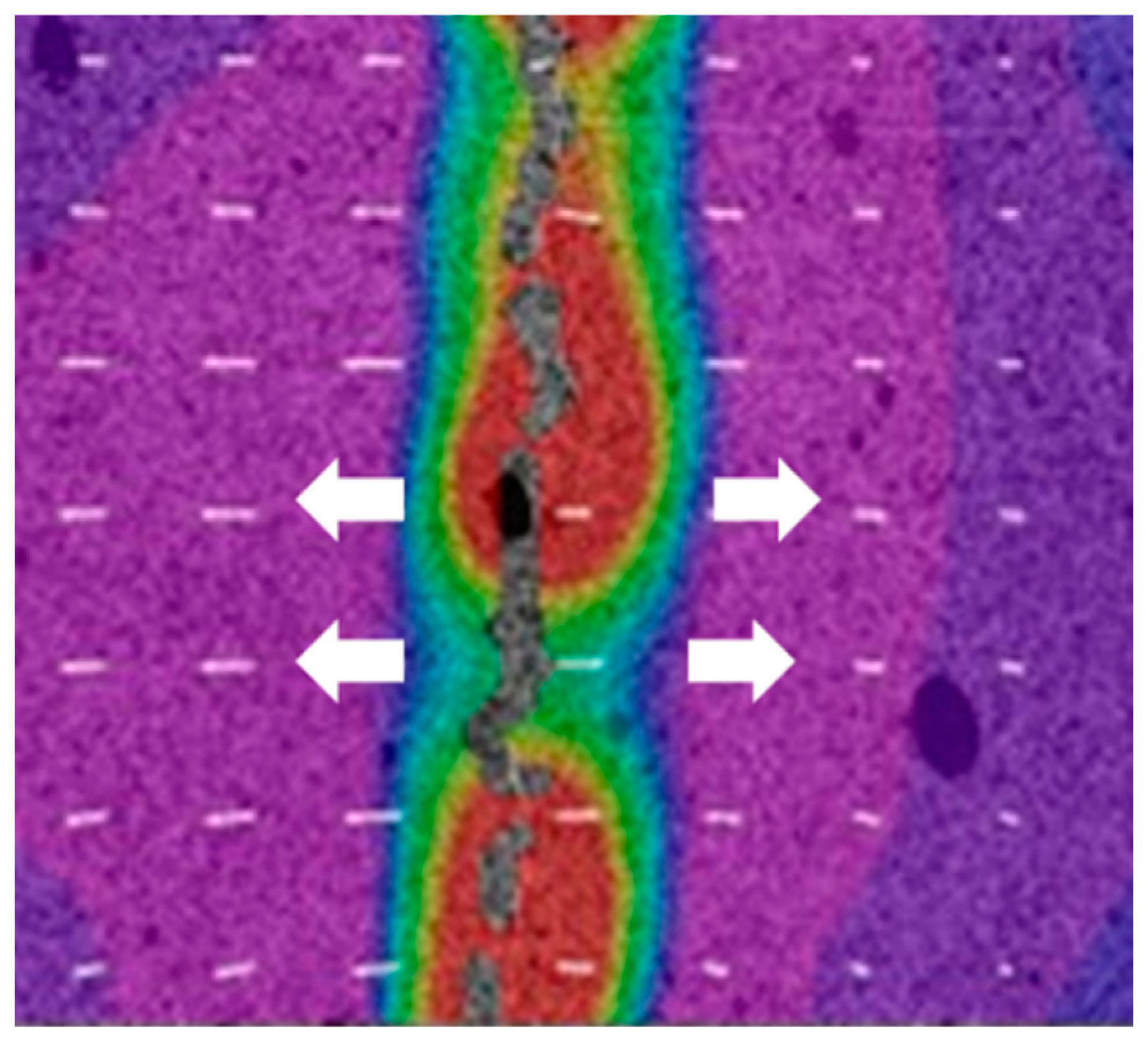
Figure 12d). Crack 2 penetrates the cross section of the sample. However, the width of crack 2 continuously increases under tensile strains until all the energy is released. It is obvious that the crack propagating direction is perpendicular to vectors according to
Figure 13. That means the reason of crack forming is tensile stress.
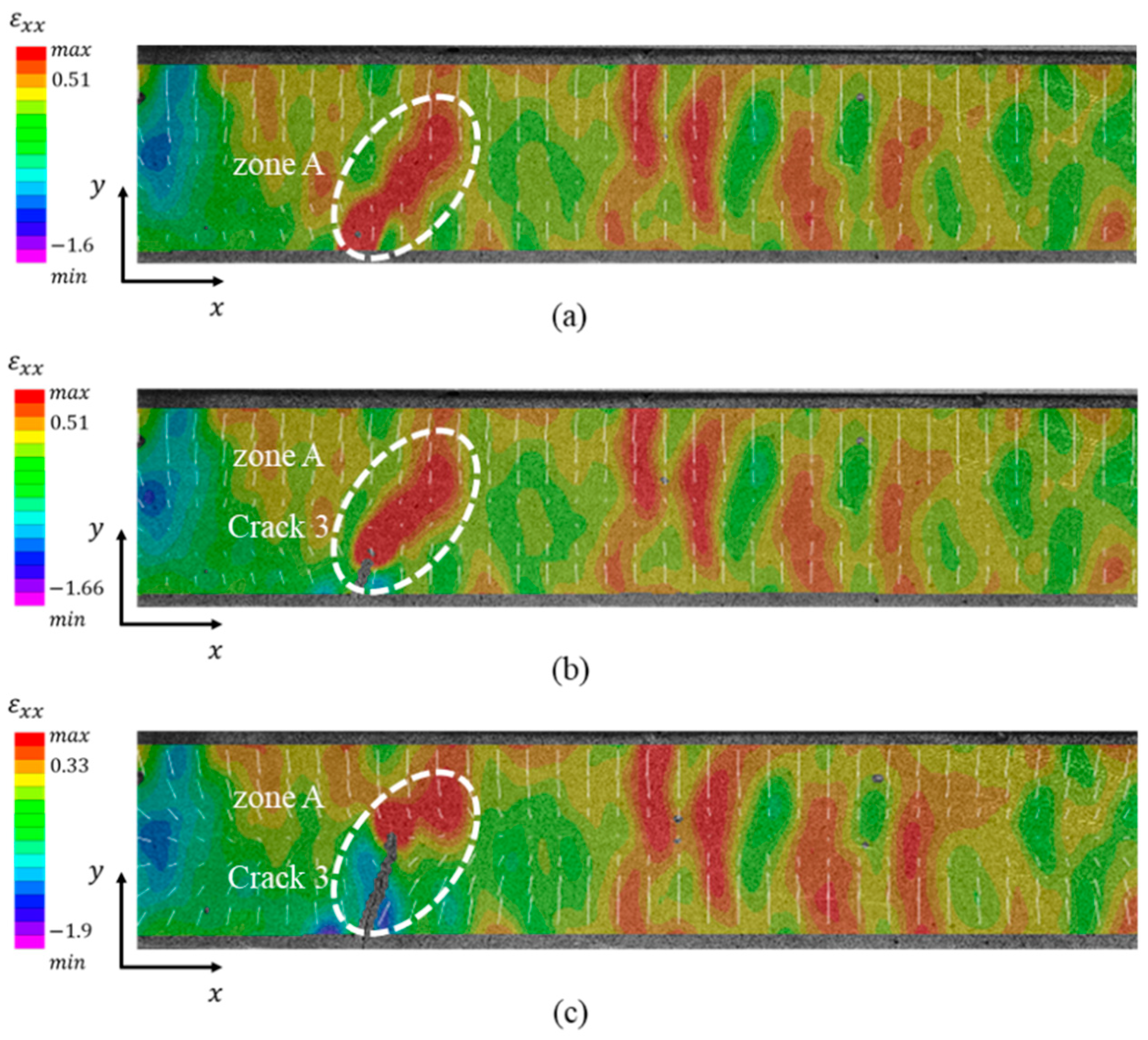
3.2.2. Spacing cracks in mixed opening-sliding mode
The mixed opening-sliding mode of spacing crack is also observed in the soil specimen with the dimension of 3×3×30 cm. The contour map of
of the specimen is presented in
Figure 14. At t = 8.67 h, the crack was not yet formed on the surface of the sample (
Figure 14a). The maximum
in zone A equals 0.51%. After 20 mins, crack 3 grows from the bottom of zone A.
on both sides of crack 3 decrease because the energy around crack 3 was released with the forming of the crack (
Figure 14b). However,
at the tip of crack 3 is still large, which remains 0.51%, indicating that crack 3 will continue to evolve following the distribution of tensile strains. At t = 9.33 h, crack 3 continues developing northeastern, and it has grown to about half the width of the specimen (
Figure 14c).
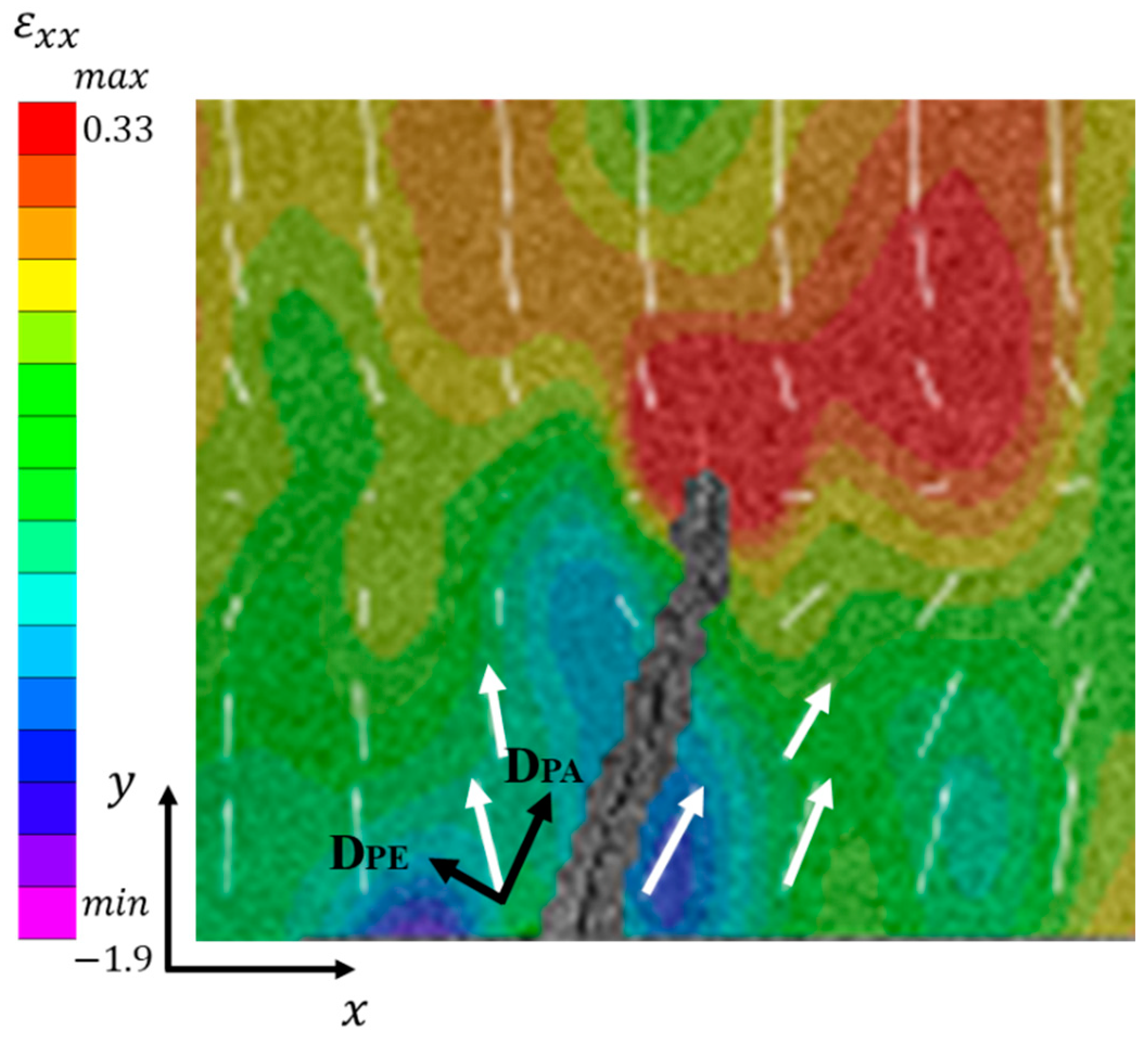
For the purpose of interpreting cracking modes of crack 3 in zone A, the white vectors presenting the local displacements of soils are decomposed in
Figure 15. The directions of local displacements on the left side of crack 3 is not parallel to the evolution direction of crack, with an angle about 30°. While on the right side of crack 3, the direction of local displacement is parallel to the direction of crack 3. The total displacement D can be decomposed into two components: D
PA which is parallel to the direction of crack 3 and D
PE which is perpendicular to the direction of crack 3. It is concluded that with D
PA, crack 3 evolves straightforward. Meanwhile, crack 3 is also submitted to tension due to D
PE. Crack 3 is in mixed opening-sliding mode.
3.3. Mechanism of spacing cracks in loess
With these 5 series of desiccation tests in loess, two characteristics can be concluded from the spacing cracks phenomenon.
3.3.1. The appearance order of spacing cracks
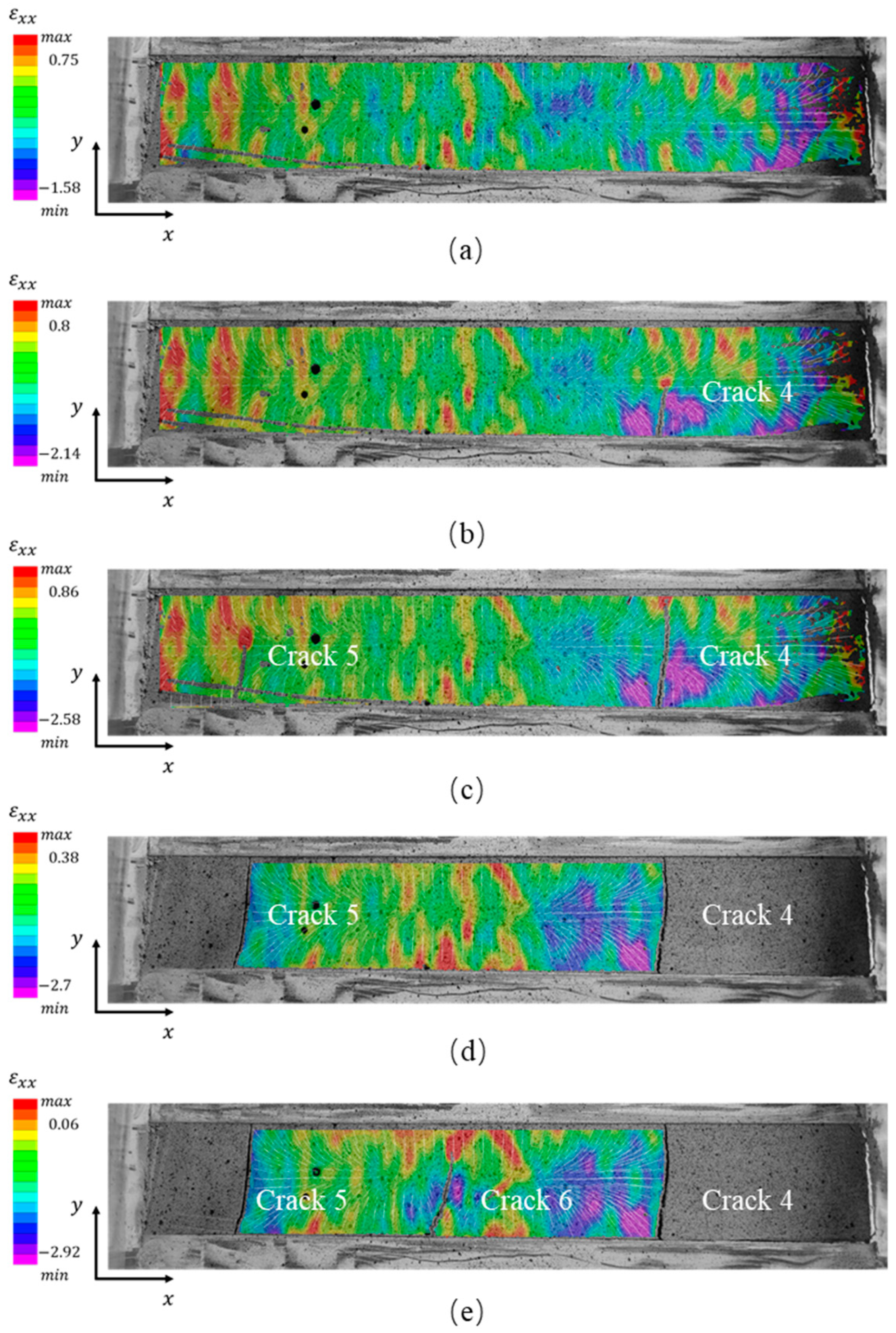
The first characteristic is that a new spacing crack is prone to appear between two existed spacing cracks. If the distances between two adjunct spacing cracks are larger, the possibility that a new crack between them are larger [
38]. The sample with the dimension of 4×4×30 cm is taken as an example (
Figure 16). In the beginning of desiccation, no crack was formed (
Figure 16a). When t = 13.33 h, crack 4 on the right bottom side of the soil sample can be observed with the maximum
of 0.8%. The maximum
concentrate at the tip of crack 4, indicating that crack 4 will continue to evolute upforwards (
Figure 16b). With increasing
, crack 5 gradually appeared on the left side of the soil sample of, which is approximately parallel to crack 4 (
Figure 16c). At t = 21 h, these two spacing cracks were well developed along the north direction. Meanwhile,
in the zone between these two cracks are relatively large which continues increasing afterwards. When the maximum
reach 0.38%, crack 6 initiated in the bottom of soil sample (
Figure 16d). After about 4.67 h, crack 6 evolves and finally inserts between the two existing spacing cracks 4 and 5 (
Figure 16e).
3.3.2. The saturation of spacing cracks
During desiccation, when the number of cracks reaches a certain value, the energy in the soil releases so that no more crack will generate. The number and the characteristics of existing cracks reach a stable state, which can be identified as "crack saturation". Since the number of spacing cracks is limited and the spacing cracks are more or less parallel in this study, the “crack saturation” phenomenon is more obvious. As we all know, energy is related to stress state in soils. In this study, the local suction distributions on the surface of soils sample are calculated with VG model for the purpose of interpreting the saturation of spacing cracks.
The distribution of water in the soil affects the distribution of suction, which result to the formation of cracks [
39,
40]. The distribution of water content in the specimen is calculated by the following equation 2:
where
is the local water content;
is the local void ratio correspondent to
;
is the saturation degree of soil.
In order to obtain
, the void ratio is obtained with the following equation 2. The relationship between void ratio and volumetric strains is as follows:
where
is the volumetric strains of soil;
is the initial void ratio, which can be deduced from the SWCC curve of loess [
35].
Therefore, the local void ratio on the surface of the soil sample can be calculated by the following equation 4:
where
is the local volumetric strains of soil, which can be calculated with VIC results [
41].
Combining equation 2 and 4, the local water content on the surface of soil sample can be deduced with the volumetric strains obtained with DIC method. Herein, the suctions can be obtained.
- 2.
Estimation of the local suction
With VG model, the local suctions of soil can be deduced:
where
is the volume water content;
is the saturated volumetric water content;
is the residual volumetric water content; s is the suction; m, n,
are the coefficients related to the types of soils.
and
can be determined by
Figure 11, the results of water contents variations.
The value of
is necessary for the calculation of
s. In order to obtaining
, the following equation 6 is adopted:
where w is the mass water content;
is the specific gravity of loess, equals to 2.69 [
35]; e is the void ratio.
- 3.
Interpretation of saturation of spacing cracks
The sample with the dimension of 4×4×30 cm is taken as an example to interpret the saturation of spacing cracks. The distribution of the local suctions of the loess is obtained based on the estimations of local water content (
Figure 17). Once the suction exceeds the tensile strength of the soil, the cracks will appear. At t = 12 h, crack 4 was formed and at the tip of it, the suction is relatively large, which indicates that crack 4 will evolve (
Figure 17a). At t = 14.67 h (
Figure 17b), crack 4 developed upwards and crack 5 appeared. Like the distributions of local strains, the suctions around crack 5 are relatively larger than the neighboring arears. About 20 mins later, the suctions in the middle of the two cracks 4 and 5 increase, which appears in red color (
Figure 17c). It can be predicted that a new crack may generate in this area. The new crack 6 appears when t = 21 h, which verifies that in the domains with large suctions, cracks are prone to initiate (
Figure 17d). It can be concluded that the initiation of cracks is related to the energy increase while the stable of cracks is result by the energy release. Therefore, when the energy between two cracks is not enough to support the development of a new crack, the crack will be in a stable state and the number of cracks will no longer change. In
Figure 16e, the maximum
between cracks 4 and 6, cracks 5 and 6 are just 0.06%. No more crack will appear due to the insufficient energy. The number of cracks in the samples with a dimension of 3×3×30 cm stabilized at 3 and will not increase during the afterwards desiccation process.
4. Numerical simulation results of spacing cracks in loess
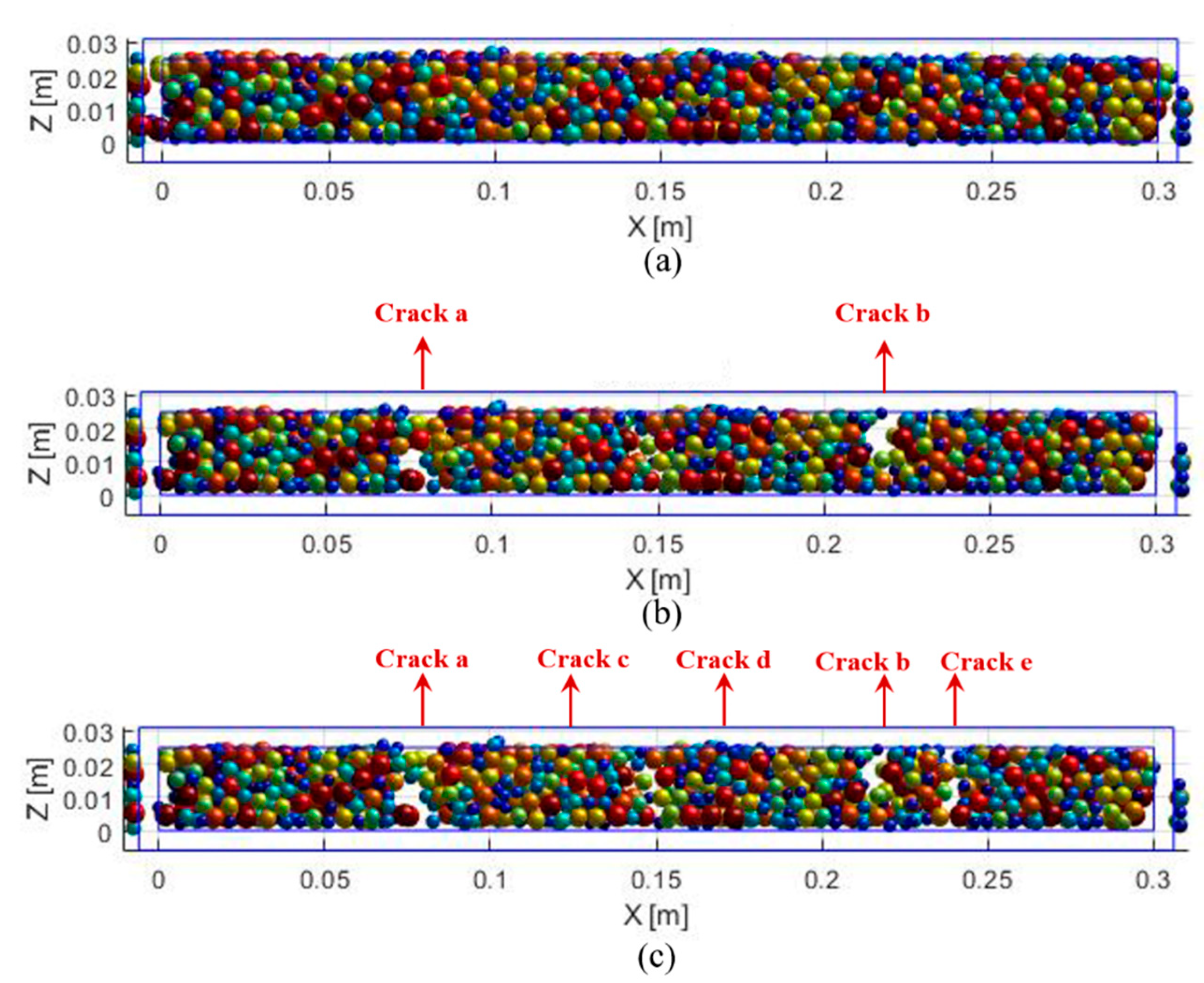
In order to verify the size effect on the characteristics of spacing cracks and to better illustrate the spacing cracking mechanism, the numerical simulations of specimens with different dimensions are carried out based on MatDEM software. In order to compare with experimental results, the initial water content of the model is set as 36%, which is the same as that in the experiments. The simulation results of spacing cracks from sideview with a dimension of 2×2×30 cm are presented in
Figure 18. The desiccation process with different water contents is simulated. At
w = 28%, the sample begins to shrink and no crack initiates (
Figure 18a). When
w decreased to 18%, the connections between the soil particles are broken. Two cracks
a and
b appear in the soil (
Figure 18b). Crack
c also initiates in the middle of the soil sample. With the decrease of water content, the well-developed cracks
a,
b and the ongoing-developed crack
c continue to evolve upwards. When
w = 13%, the fourth crack
e on the right side gradually develops. Finally, five cracks are formed in the soil samples with the dimension of 2×2×30 cm, which can be seen obviously in the micro-connection results (
Figure 19b). Although the locations of these 5 cracks are not exactly consistent with that in the experimental test, the number of the cracks is exactly the same (
Figure 18c). In addition, the appearance order of spacing cracks is identified in this numerical modelling example. Crack
c appears between cracks
a and
b verifies the “insertion phenomenon”.
The connection diagrams of soil samples with different dimensions at the end of desiccation are presented in
Figure 19, which represent the bonding forces between the particles. The green lines represent bonding between particles while the vides among them identify the bonding failures of soils. The number and positions of cracks of the specimen can be better observed in the micro-connection diagram. The number of cracks in different soil samples are 11, 5, 4, 3 and 2, respectively. The simulation results of crack numbers are nearly consistent with the experimental tests. Since the contact model in MatDEM is linear elastic, the simulation crack patterns are not exactly the same as those generated in experiments. Generally, the simulation results indeed reflect the size effect on the characteristics of the spacing cracks. The crack number is smaller in soil samples with larger dimension. Two important phenomena of “insertion of cracks”, “saturation of cracks” in spacing cracks are also observed in the simulation results.
5. Conclusions
This paper mainly explores the spacing crack characteristics of Jingyang loess considering specimen size. Free drying test of five samples with different size were carried out in order to record the evolution of spacing cracks. VIC-2D software is used to calculate the local displacements and strains of soil sample. The conclusions are as follows:
(1) The spacing cracks are observed in loess samples with different dimensions. The characteristics of spacing cracks are identified. They are generally developed along the width of the specimen, which are approximate parallel.
(2) The characteristics of spacing cracks are greatly influenced by the dimensions of soil samples. As the volume of specimen increases, the number of spacing cracks tends to decrease. Meanwhile, the increasing average spacing between cracks also increases. The crack width also increases with the increase of average spacing of the cracks. Once the volume of specimen reaches 270 cm3 (3 cm × 3 cm × 30 cm), the number of cracks doesn’t increase any more. The variations of crack ratio and the number of spacing cracks show the same tendency.
(3) Different mechanisms of spacing cracks in loess are interpreted in this research. Based on Digital Image Correlation (DIC) method, opening modes and mixed opening-sliding mode in spacing cracks are detected. In addition, two evolution laws about the spacing cracks are interpreted. The first law is that a new crack is prone to appear in the areas between two existed cracks. If the distances between two adjunct cracks are larger, the possibility that the new crack between them are larger. The second law is that, when the number of cracks reaches a certain value, the energy in the soil release so that no more crack will generate during the following desiccation. The number and the characteristics of existing cracks reach a stable state, which can be considered as "crack saturation".
(4) The numerical simulations were carried out on loess samples with different dimensions based on the discrete element method. The size effect on the characteristics of spacing cracks is verified and the spacing cracking mechanism is better illustrated. In discrete element models, the number of spacing cracks increases with the increasing soil volume, which is consistent with the experimental results. In addition, the characteristics of “insertion of cracks”, “saturation of cracks” in spacing cracks are also observed in the simulation results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W.; methodology, X.W.; software, YR.Z.; validation, YR.Z. and XY.C.; investigation, YR.Z. and XY.C.; resources, X.W.; data curation, YR.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, YR.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.W. and YR.Z.; supervision, X.W.; project administration, X.W.; funding acquisition, X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of Youth, grant number 42007278 and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, grant number xhj032021017-02.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article.
Acknowledgments
Ling. X. of School of Human Settlements and Civil Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University provided the experimental devices and aided with the field investigation. The authors would like to extend their deepest gratitude to him.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, T.S.; Ding, Z.L.; Guo, Z.T. Loess, Environment and Global Change; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire, E. Geological hazards in loess terrain, with particular reference to the loess regions of China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2011, 54, 231–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiao, F.; Li, X.; An, S. The Loess Plateau. In Multifunctional Land-Use Systems for Managing the Nexus of Environmental Resources. Zhang, L., Schwarzel, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tsunekawa, A.; Liu, G.; Yamanaka, N.; Du, S. [Ecological Research Monographs] Restoration and Development of the Degraded Loess Plateau, China. Climate of the Loess Plateau 2014, 2, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wu, Z.P.; Chen, H.; Shao, L.T.; Zhou, X.G.; Wang, S.H. Influence of dry-wet cycles on the strength behavior of basalt-fiber reinforced loess. Eng. Geol. 2022, 302, 106645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Peng, J.B.; Wang, Q.; Duan, Z.; Zhuang, J.Q. Loess landslides on the south Jingyang platform in Shaanxi Province, China. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2019, 52, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.M.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Victor, C.; Duan, M.D. Research on the rainfall-induced regional slope failures along the Yangtze River of Anhui, China. Landslides 2021, 18, 1801–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahlawi, H.; Kodikara, J.K. Laboratory experiments on desiccation cracking of thin soil layers. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2006, 24, 1641–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, H.; Hadrich, B.; Guiras, H. Evaporation, shrinkage and intrinsic permeability of unsaturated clayey soil: analytical modelling versus experimental data. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedifard, F.; Robinson, J.D.; AghaKouchak, A. Can protracted drought undermine the structural integrity of California’s earthen levees? J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2016, 142, 02516001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Xu, L.; Baudet, B.A.; Gao, C.Y.; Huang, C. The structure degradation of a silty loess induced by long-term water seepage. Eng. Geol. 2020, 272, 105634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.J.; Tang, C.S.; Yin, L.Y.; Xie, Y.H.; Shi, B. Applicability of Microbial Calcification Method for Sandy-Slope Surface Erosion Control. J. Mater. Civil Eng. 2019, 31, 04019250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Tang, C.S.; Cheng, Z.; Vahedifard, F.; Cheng, Q.; Shi, B. Desiccation cracking of soil subjected to different environmental relative humidity conditions. Eng. Geol. 2022, 297, 106536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corte, A.; Higashi, A. Experimental Research on Desiccation Cracks in Soil. Research Report, U.s.army Snow Ice & Permafrost Research Establishment. 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, P.H.; Graham, J.; Williams, D.J. Cracking in drying soils. Can. Geotech. J. 1992, 29, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péron, H.; Hueckel, T.; Laloui, L.; Hu, L. Fundamentals of desiccation cracking of fine-grained soils: experimental characterisation and mechanisms identification. Can. Geotech. J. 2009, 46, 1177–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.S.; Cui, Y.J.; Shi, B.; Tang, A.M.; Liu, C. Desiccation and cracking behaviour of clay layer from slurry state under wetting–drying cycles. Geoderma 2011, 166, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Hattab, M.; Taibi, S.; Bicalho, K.V.; Xu, L.; Fleureau, J.M. Crack development and coalescence process in drying clayey loess. Geomech. Eng. 2021, 25, 535–552. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.S.; Shi, B.; Liu, C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, B. Influencing factors of geometrical structure of surface shrinkage cracks in clayey soils. Eng. Geol. 2008, 101, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.; Kodikara, J.; Shannon, B. Salient factors controlling desiccation cracking of clay in laboratory experiments. Géotechnique 2013, 63, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahlawi, H.; Kodikara, J.K. Laboratory experiments on desiccation cracking of thin soil layers. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2006, 24, 1641–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.S.; Cui, Y.J.; Tang, A.M.; Shi, B. Experiment evidence on the temperature dependence of desiccation cracking behavior of clayey soils. Eng. Geol. 2010, 114, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmikantha, M.R.; Prat, P.C.; Ledesma, A. Experimental evidence of size effect in soil cracking. Can. Geotech. J. 2012, 49, 264–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmikantha, M.R.; Prat, P.C.; Ledesma, A. Boundary effects in the desiccation of soil layers with controlled environmental conditions. Geotech. Test. J. 2018, 41, 675–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, K.; Cerato, A.; Vahedifard, F.; Miller, G.A. Tensile Strength of Compacted Clays during Desiccation under Elevated Temperatures. Geotech. Test. J. 2021, 44, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, K.; Cerato, A.; Vahedifard, F.; Miller, G.A. A temperature-dependent model for tensile strength characteristic curve of unsaturated soils. Geomech. Energy Envir. 2021, 28, 100244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindle, E.M. Some factors affecting the development of Mud-Cracks. J. Geol. 1917, 25, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Li, L.; Chen, R.; Li, D.Q. Cracking and vertical preferential flow through landfill clay liners. Eng. Geol. 2016, 206, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Q.; Pollard, D.D. An experimental study of the relationship between joint spacing and layer thickness. J. Struct. Geol. 1995, 17, 887–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.A.; Zhang, Y.B.; Liang, Z.Z.; Xu, T.; Tham, L.G.; Lindqvist, P.A.; Kou, S.Q.; Liu, H.Y. Fracture spacing in layered materials and pattern transition from parallel to polygonal fractures. Phys. Rev. E. Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter. Phys. 2006, 73, 056120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.M. A study on formation conditions and mechanism of equal spacing fractures. Adv. Geosci. 1989, 1, 58–70. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, T.; Pollard, D.D. Fracture spacing in layered rocks: a new explanation based on the stress transition. J. Struct. Geol. 2000, 22, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Q.; Pollard, D.D. An experimental study of the relationship between joint spacing and layer thickness. J. Struct. Geol. 1995, 17, 887–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aveston, J.; Cooper, G.A.; Kelly, A. The Properties of Fiber Composites; Conf. Proc. Nat. Physical Lab., IPC Science and Technology Press: England, UK, 1971; pp. 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Bicalho, K.V.; Hajjar, A.E.; Taibi, S.; Hattab, M.; Fleureau, J.M. Experimental techniques for the study of the cracking mechanisms in drying clays. Geotech. Test. J. 2020, 44, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.C.; Liu, C.; Tang, C.S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Shi, B. Numerical Simulation of Desiccation Cracking in Clayey Soil Using a Multifield Coupling Discrete-Element Model. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2022, 148, 04021183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Dong, L.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhou, Y.R. Influence of soluble salt NaCl on cracking characteristics and mechanisms of loess. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.Y.; Tang, C.A.; Tang, S.B.; Cai, M.; Yu, Q. Study on the formation mode and mechanism of cracks on the surface of layered rock under uniaxial tension (in Chinese). Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2013, 32, 474–482. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Hattab, M.; Fleureau, J.M. Micro-macro-experimental study of two clayey materials on drying paths. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2013, 72, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.T. Etude expérimentale de la fissuration hydrique d’un sol argileux (in French); Univeristy of Lorraine: France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Hattab, M.; Bompard, P. Highlighting some mechanisms of crack formation and propagation in clays on drying path. Géotechnique 2016, 66, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Study area of Jingyang, Shaanxi Province, China.
Figure 1.
Study area of Jingyang, Shaanxi Province, China.
Figure 2.
Field and in situ investigations in Jingyang, Shaanxi Province: (a) loess slopes with accumulated water after rainfall (photo taken in October, 2022); (b) the same loess slopes with desiccation cracks (photo taken in Juin, 2022); (c) desiccation cracks on the surface of the platform; (d) different scale of cracks due to evaporation.
Figure 2.
Field and in situ investigations in Jingyang, Shaanxi Province: (a) loess slopes with accumulated water after rainfall (photo taken in October, 2022); (b) the same loess slopes with desiccation cracks (photo taken in Juin, 2022); (c) desiccation cracks on the surface of the platform; (d) different scale of cracks due to evaporation.
Figure 3.
Particle size distribution of Jingyang loess, China.
Figure 3.
Particle size distribution of Jingyang loess, China.
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of mold.
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of mold.
Figure 5.
Schematic drawing of the experimental set-up.
Figure 5.
Schematic drawing of the experimental set-up.
Figure 6.
Implementation of DIC analysis (pixel 100 = white, pixel 0 = black).
Figure 6.
Implementation of DIC analysis (pixel 100 = white, pixel 0 = black).
Figure 7.
The result of longitudinal strain of loess (with dimension of 5×5×30 cm).
Figure 7.
The result of longitudinal strain of loess (with dimension of 5×5×30 cm).
Figure 8.
Schematic presentation of DEM model used in MatDEM: (a) Multifield coupling discrete element model; (b) Schematic of water migration.
Figure 8.
Schematic presentation of DEM model used in MatDEM: (a) Multifield coupling discrete element model; (b) Schematic of water migration.
Figure 9.
Final patterns of spacing cracks of loess samples with different dimensions:(a) 1×1×30 cm; (b) 2×2×30 cm; (c) 3×3×30 cm; (d)4×4×30 cm; (e) 5×5×30 cm.
Figure 9.
Final patterns of spacing cracks of loess samples with different dimensions:(a) 1×1×30 cm; (b) 2×2×30 cm; (c) 3×3×30 cm; (d)4×4×30 cm; (e) 5×5×30 cm.
Figure 10.
The relationship between the parameters of spacing cracks versus volume of soil samples: (a) cracking ratio, crack width versus volume; (b) number of cracks, average crack spacing versus volume.
Figure 10.
The relationship between the parameters of spacing cracks versus volume of soil samples: (a) cracking ratio, crack width versus volume; (b) number of cracks, average crack spacing versus volume.
Figure 11.
Variations of water content of different specimens versus time.
Figure 11.
Variations of water content of different specimens versus time.
Figure 12.
Contour map of of loess samples with the dimension of 5×5× 30 cm at different times: (a) t = 58 h; (b) t = 58.17 h; (c) t = 58.5 h; (d) t = 58.67 h.
Figure 12.
Contour map of of loess samples with the dimension of 5×5× 30 cm at different times: (a) t = 58 h; (b) t = 58.17 h; (c) t = 58.5 h; (d) t = 58.67 h.
Figure 13.
Displacement vectors around crack 2 (t = 58.67 h).
Figure 13.
Displacement vectors around crack 2 (t = 58.67 h).
Figure 14.
Transversal strains of samples with the dimension of 3×3×30 cm at different times: (a) t = 8.67 h; (b) t = 9 h; (c) t = 9.33 h.
Figure 14.
Transversal strains of samples with the dimension of 3×3×30 cm at different times: (a) t = 8.67 h; (b) t = 9 h; (c) t = 9.33 h.
Figure 15.
Decomposition of displacement vectors around crack 3 in zone A (t = 9.33 h).
Figure 15.
Decomposition of displacement vectors around crack 3 in zone A (t = 9.33 h).
Figure 16.
The appearance order of spacing cracks of the soil sample with the dimension of 3×3×30 cm at different times: (a) t = 11 h; (b) t = 13.33 h; (c) t = 15 h; (d) t = 21 h; (e) t = 25.67 h.
Figure 16.
The appearance order of spacing cracks of the soil sample with the dimension of 3×3×30 cm at different times: (a) t = 11 h; (b) t = 13.33 h; (c) t = 15 h; (d) t = 21 h; (e) t = 25.67 h.
Figure 17.
Contour map of local suction distribution: (a) t = 12 h; (b) t = 14.67 h; (c) t = 15 h; (d) t = 25.67 h.
Figure 17.
Contour map of local suction distribution: (a) t = 12 h; (b) t = 14.67 h; (c) t = 15 h; (d) t = 25.67 h.
Figure 18.
Discrete element models of loess sample with the dimension of 2×2× 30 cm during drying: (a) w = 28%; (b) w = 18%; (c) w = 13%.
Figure 18.
Discrete element models of loess sample with the dimension of 2×2× 30 cm during drying: (a) w = 28%; (b) w = 18%; (c) w = 13%.
Figure 19.
Influence of sample size on crack pattern: (a) 1×1×30 cm; (b) 2×2×30 cm; (c) 3×3×30 cm; (d) 4×4×30 cm; (e) 5×5×30 cm.
Figure 19.
Influence of sample size on crack pattern: (a) 1×1×30 cm; (b) 2×2×30 cm; (c) 3×3×30 cm; (d) 4×4×30 cm; (e) 5×5×30 cm.
Table 1.
Physical properties of Jingyang loess.
Table 1.
Physical properties of Jingyang loess.
| Specific gravity |
Dry density
(g·cm-3) |
Liquid limit
(%)
|
Plastic limit
(%)
|
plasticity index
|
Granulometry (%) |
Sand content
(4.75-0.075 mm) |
Silt content
(0.075-0.002 mm) |
Clay content
(≤0.002 mm) |
| 2.69 |
1.57 |
35.6 |
17.1 |
18.5 |
0.3 |
82.7 |
17 |
Table 2.
Parameters of spacing cracks of loess samples with different size.
Table 2.
Parameters of spacing cracks of loess samples with different size.
| Dimension of soil samples |
1×1×30 cm |
2×2×30 cm |
3×3×30 cm |
4×4×30 cm |
5×5×30 cm |
| Volume of soil samples (cm3) |
30 |
120 |
270 |
480 |
750 |
| Number of spacing cracks |
14 |
5 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
| Cracking ratio R (%) |
3.96 |
2.79 |
3.17 |
3.04 |
2.96 |
| The average width of cracks (cm) |
1.987 |
4.488 |
5.025 |
8.487 |
8.392 |
| Average cracking spacing (cm) |
2 |
4.96 |
6.59 |
8.13 |
8.23 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).