Introduction
Intradialytic hypotension (IDH) is defined as symptomatic hypotension during hemodialysis (HD) and is associated with cardiovascular diseases, cerebrovascular disease, vascular access thrombosis, and all−cause mortality in patients undergoing HD [
1,
2]. In previous literature, IDH-induced organ damage has been explained by impaired organ perfusion [
1,
2]. However, unexpectedly, only a few studies have empirically ,examined IDH and organ perfusion. The major reason for the insufficient evidence regarding IDH and organ perfusion is the difficulty in measuring organ blood flow during HD. Organ blood flow measurement using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or positron emission tomography (PET) is challenging to apply because continuous and dynamic changes are difficult to detect in the patient’s condition during HD in real-time [
3,
4,
5]. Additionally, catheter-based organ blood flow measurements are difficult because of their high invasiveness [
5]. Therefore, the relationship between IDH and organ blood flow is still hypothetical and a significant challenge for researchers.
The clinical importance of measuring the regional tissue oxygen saturation (rSO
2) using near-infrared spectroscopy has recently gained great attention [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10]. Measurement of the rSO
2 is a real-time and non-invasive method for evaluating organ tissue oxygenation in various clinical settings [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10]. The rSO
2 is not a parameter directory that indicates organ blood flow but assesses the organ tissue oxygenation, which is calculated using the ratio of oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin in the targeted tissue. However, the rSO
2 reflects the organ blood flow because it is significantly associated with the organ blood flow measured using MRI and PET [
3,
4]. Therefore, the relatively straightforward measurement of rSO
2 enables us to assess organ blood flow in the patient’s condition during HD. We have previously focused on the hepatic and cerebral rSO
2 in patients undergoing HD and reported the clinical importance of their changes in different clinical situations related to HD treatment [
6,
7,
8,
9]. Interestingly, hepatic and cerebral rSO
2 appear not to change synchronously but asynchronously under various HD conditions (blood transfusion during HD, treatment of congestive heart failure with HD, and feeding during HD) [
11,
12,
13]. Currently, only a few studies have focused on IDH-induced changes in organ rSO
2 [
7,
10]. Moreover, no clinical research has concurrently detected IDH-induced changes in rSO
2 in multiple organs. Therefore, we aimed to investigate IDH-induced changes in hepatic and cerebral rSO
2 and explore the importance of the difference in the two rSO
2 changes.
Materials and Methods
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Review Board of the Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University (RIN15-104 and RINS19-HEN007) and complied with the Declaration of Helsinki (revised in Tokyo in 2004).
Study design and participants
This prospective cross-sectional study was conducted at the dialysis center of the Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University. Hepatic and cerebral rSO2 during HD were measured (once per patient) in the patients undergoing HD. Detailed information about the study’s protocol was provided to patients undergoing HD, and those who agreed to participate in this study and signed the written consent form were included. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (i) patients who agreed to participate in this study, and (ii) patients aged ˃ 20 years undergoing HD (ii). The following were the exclusion criteria: (i) ˂ 1 month after starting HD, (ii) patients with congestive heart failure and severe neurological disorders, (iii) patients who developed the lowest SBP within 1 h after HD initiation, and (iv) patients who received intradialytic feeding. Recruitment of the study’s participants was conducted between August 1, 2013 and December 31, 2019.
Measurement of rSO2
Hepatic and cerebral rSO
2 data during HD were measured by the INVOS 5100C oxygen saturation monitor (Covidien Japan, Tokyo, Japan), whose detailed measurement mechanisms have been previously described [
14]. Briefly, this measurement device is composed of a light-emitting diode that transmits two wavelengths (735 and 810 nm) of near-infrared light and two light detectors to measure oxygenated and deoxygenated Hb. rSO
2 is calculated based on the ratio of the signal strengths of the oxygenated Hb and the total Hb (oxygenated Hb + deoxygenated Hb) [
15,
16]. The light detector obtains two signals at two different depths: 30 and 40 mm depth as superficial and deep tissues, respectively. By analyzing these differences in the signals, rSO
2 of 20–30 mm from the body surface can be measured [
17,
18]. This measurement is conducted once every 5 seconds and recorded automatically. For the measurement of hepatic rSO
2, the sensor device was attached to the right intercostal area above the liver after the correct position was confirmed through ultrasonography. In contrast, the sensor device was attached to the patient’s forehead to measure cerebral rSO
2.
Definition of IDH
In accordance with previous guidelines, IDH was defined as (i) intradialytic sudden decrease in SBP (> 20 mmHg) with IDH-related symptoms such as muscle cramps and loss of consciousness [
19] or (ii) intradialytic sudden decrease in SBP (> 30 mmHg) or MBP (> 10 mmHg) with IDH-related symptoms [
20].
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, or median and interquartile range. Statistical comparisons between the two groups were performed using the Student’s t-test. Correlations between the difference in the % changes in hepatic and cerebral rSO2 and clinical parameters in patients undergoing HD were evaluated using Pearson’s correlation or Spearman’s rank correlation for data with normal and skewed distribution, respectively. Multivariate linear regression analysis was performed to extract independent factors of the difference in the two rSO2 changes. All analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 26.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). P-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Patients’ Characteristics
Overall, 91 patients undergoing HD met this study’s criteria.
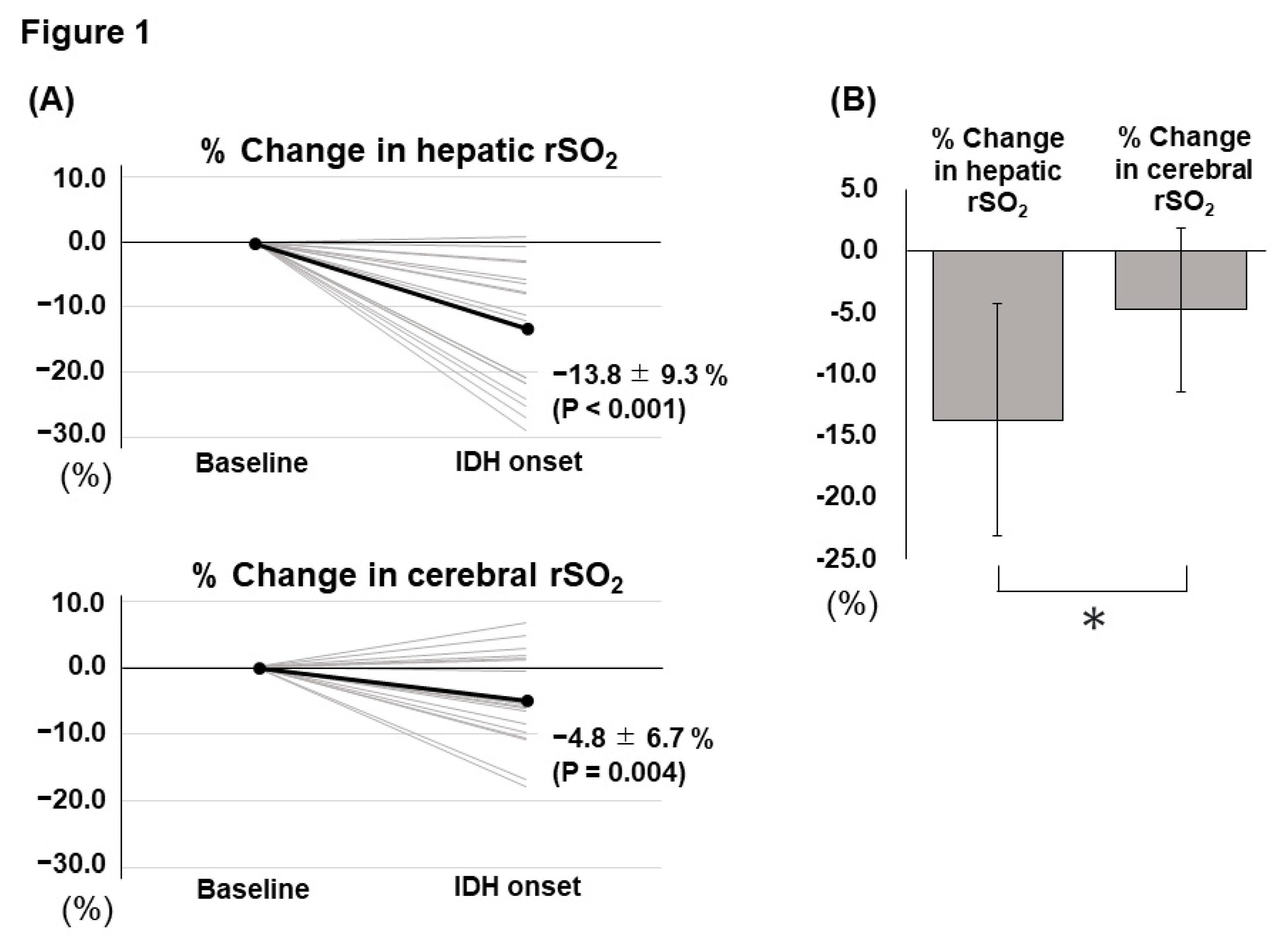
Table 1 shows the clinical characteristics of the patients. The patients’ age was 70.0 (63.0 – 76.0) years, 69 (76%) were male, and their mean body mass index was 22.4 (19.9 – 25.0) kg/m
2. Twenty (22%) patients developed IDH in this study, and all those who developed IDH complained of muscle cramps as IDH-related symptoms. The values of hepatic and cerebral rSO
2 at baseline were 55.8 ± 15.3% and 50.2 ± 10.1%, respectively. In contrast, the hepatic and cerebral rSO
2 values at the lowest systolic blood pressure (SBP) were 53.8 ± 14.9% and 49.3 ± 9.7%, respectively. The percentage (%) changes were calculated as [(value at the lowest SBP - value before HD)/value before HD × 100]. % changes in hepatic and cerebral rSO
2 were -2.8 ± 11.3% and - 1.5 ± 6.4%, respectively. Furthermore, % changes in SBP and mean blood pressure (MBP) were -13.4 (-21.3 – -7.6) % and -9.0 (-20.4 – -5.0) %, respectively.
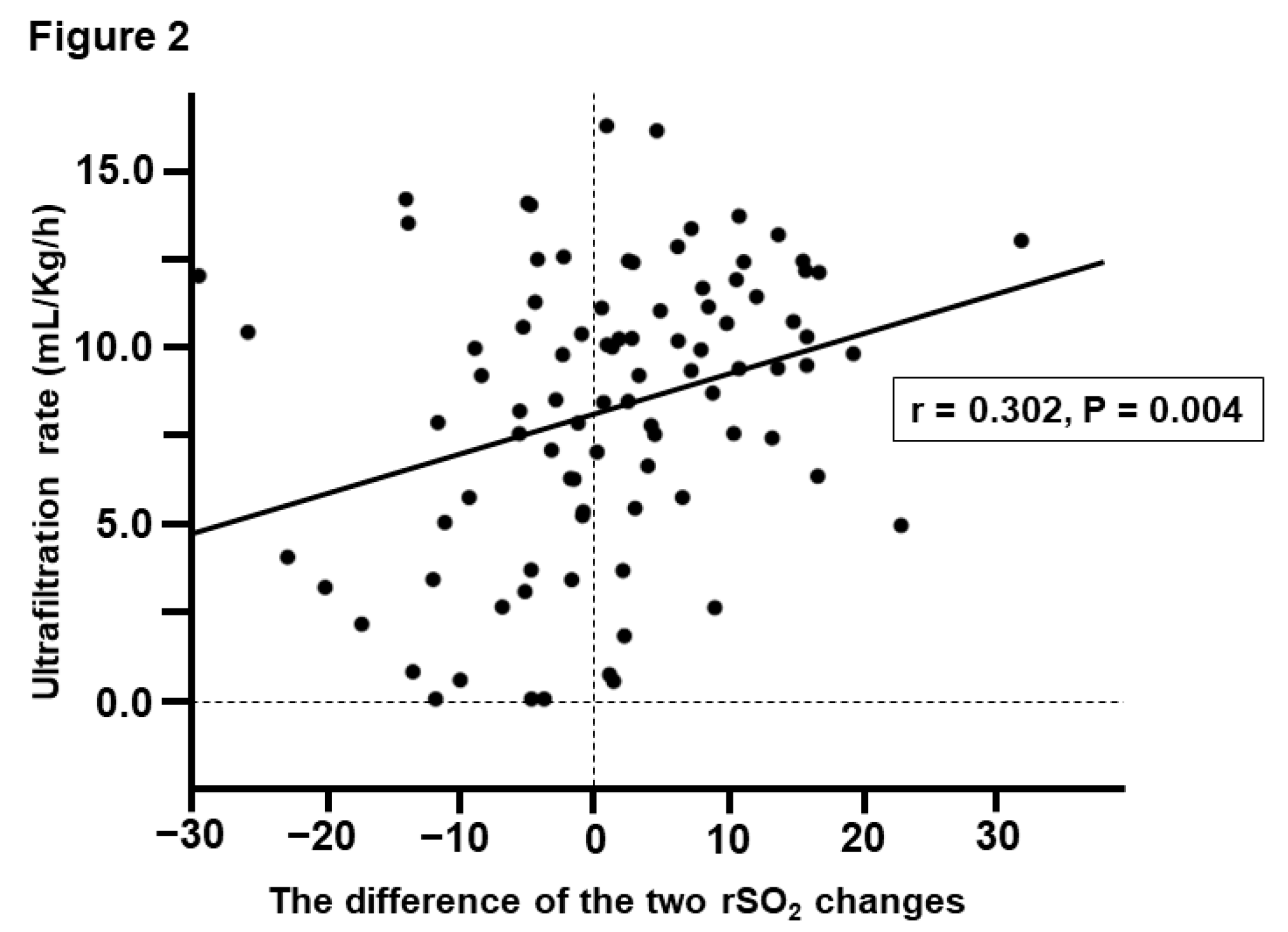
Factors associated with the difference in the two rSO2 changes
The clinical factors associated with the difference between the % change in cerebral and hepatic rSO
2 were investigated with univariate and multivariate analyses (
Table 3). Univariate analysis showed that ultrafiltration rate (UFR) (
P = 0.004) and IDH development (
P < 0.001) were significantly associated with the difference between the two rSO
2 changes. In contrast, multivariable linear regression analysis using these factors as explanatory variables showed that the difference in the two rSO
2 changes was significantly associated with UFR (
P = 0.010) and the development of IDH (
P < 0.001,
Figure 2).
Discussion
In this study, we explored the IDH-induced changes in hepatic and cerebral rSO2. Summarily, our findings showed that both hepatic and cerebral rSO2 significantly decreased in IDH development and that hepatic rSO2 was more largely decreased than cerebral rSO2 at the time of IDH onset. Additionally, the difference in the two rSO2 changes calculated using “% change in cerebral rSO2 - % change in hepatic rSO2” was significantly associated with UFR and the development of IDH. These results are considered to be important because only a few previous studies have examined IDH-related changes in rSO2.
As mentioned in the introduction section, rSO
2 reflects the organ blood flow [
3,
4]. In this regard, hepatic and cerebral rSO
2 indicate hepato-splanchnic and cerebral circulations, respectively [
3,
4,
21]. Our study result suggested that hepato-splanchnic and cerebral circulation decreased with IDH onset; this result was expected [
1,
2]. However, it was unexpected that hepato-splanchnic circulation decreases more largely than cerebral circulation with IDH onset. Why there is the difference between the changes in hepato−splanchnic circulation and cerebral circulation with the onset of IDH? The difference may be explained by the fact that each organs have different mechanisms for maintaining organ blood flow.
The patient’s body is constantly exposed to hypovolemic stress due to ultrafiltration during HD [
1,
2]. Therefore, the body performs various compensatory functions to maintain the central circulation under this condition, including the activated sympathetic nervous system, arterial constriction, plasma refilling, and blood volume transfers from organs to the central circulation (described later) [
1,
2]. These compensatory mechanisms allow the patient’s body to maintain the central circulation (cardiac output) and prevent impaired organ perfusion [
1,
2]. In these mechanisms, hepato-splanchnic circulation particularly plays an important role [
1,
2]. The hepato-splanchnic circulation is known to be the reservoir that supplies blood volume to the central circulation under hypovolemic stress; this mechanism is known as the “De Jager–Krogh effect.” Hepato-splanchnic circulation has a very large capillary bed. In the absence of arterial constriction (not under hypovolemic stress), the pressure in the capillary bed is increased, and blood is pooled due to the stasis. However, in the presence of arterial constriction (under hypovolemic stress), the pressure in the capillary bed is decreased, supplying blood to the central circulation [
1,
2]. Specifically, the central circulation is constantly maintained on the basis of the self-sacrificing effect of hepato-splanchnic circulation, whereas the situation of cerebral circulation is greatly different. The brain has a mechanism that maintains cerebral blood flow even if systemic blood pressure fluctuates widely; this mechanism is known as “cerebral autoregulation” [
22,
23]. Cerebral blood flow is maintained by increasing cerebral vascular resistance when systemic blood pressure drops [
22,
23]. Classically, cerebral blood flow has been considered to be maintained at an MBP of 60−150 mmHg [
22,
23]. This range appears to be slightly different in patients undergoing HD; however, a recent study reported that the lower limit (i.e., not inducing cerebral ischemia) is an MBP of 74 mmHg [
10]. At least, cerebral circulation appears to be on the protected side under hypovolemic stress. When IDH develops due to triggers such as myocardial ischemia, hepato-splanchnic and cerebral circulation are negatively affected. In this case, hepato-splanchnic circulation would be greatly affected by its nature (self-sacrificing effect), whereas cerebral circulation would be minimally affected. This difference would have been indicated as the difference between hepatic and cerebral rSO
2 in this study. This study evaluated rSO
2 and not organ blood flow directly. However, we believe that there is no inconsistency considering previous reports.
This study is cross-sectional and cannot prove the causal relationships among parameters. However, it appears certain that the increased difference in the two rSO
2 changes is an “unfavorable sign” associated with IDH development. Interestingly, the difference in the two rSO
2 changes is also correlated with UFR. For clinicians, the optimization of UFR is a very important subject of discussion [
24]. High UFR (for example, > 13 mL/h/kg) is associated with not only IDH development but also patients’ mortality [
24,
25,
26,
27]. Therefore, the optimal UFR should be customized for each patient since it is influenced by the patient’s body size and background disease (particularly cardiac diseases) [
24]. In our study, we found a significant association between “the unfavorable sign” and UFR. This result provides us with an important suggestion indicating the importance of optimizing the UFR to prevent circulatory failure (IDH development). This clinical message may appear obvious to many clinicians. However, most evidence on UFR optimization is based on observational studies. Therefore, we explained the importance of optimizing the UFR in this study using the rSO
2 changes, which we measured.
This study has some limitations. First, there is a scope for further investigation regarding the relationship between rSO
2 and organ blood flow. However, rSO
2 remains the most promising method of assessing organ blood flow during HD at this time despite these concerns. Second, this cross-sectional method in our study should be emphasized. Specifically, we only found correlations between parameters; therefore, it is difficult to draw any causal conclusion. Furthermore, analysis of real-time changes during HD may provide more insight into the causal relationship between organ rSO
2 and IDH. Particularly, predicting IDH development using rSO
2 change would be an interesting research topic in the future. Third, the rSO
2 value may have been influenced by various dialysis conditions (dialysis setting, pre-dialysis feeding, medical history, medication, and various physiological factors) [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10].
Conclusion
Hepatic and cerebral rSO2 significantly decreased in IDH development and hepatic rSO2 was more largely decreased than cerebral rSO2 at IDH onset. Multivariable linear regression analysis showed that the difference between the % change in cerebral and hepatic rSO2 was significantly associated with IDH development and UFR. Therefore, larger-scale studies, including factor analysis, should be conducted to clarify this issue. Moreover, further large-scale studies are also required to accumulate data on rSO2 changes in IDH development.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.O; methodology, S.K., S.O., and K.I.; software, S.K., S.O., and K.I.; validation, S.K., S.O., and K.I.; formal analysis, S.K., S.O., and K.I.; investigation, S.K.; resources, S.O. and K.I.; data curation, S.K., S.O., K.I., S.M., Y.M., Y.U., K.H., and Y.M.; writing-original draft preparation, S.K.; writing−review and editing, S.K., S.O., and K.I.; visualization, S.K.; supervision, S.O.; project administration, S.O. and Y.M.
Funding
This work was partially supported by a grant from the Japanese Association of Dialysis Physicians [JADP Grant 2017-9, 2018-10] and JSPS KAKENHI [grant number. JP20K11534 to S.O. and JP21K16192 to K.I.].
Informed Consent Statement
This study was approved by the Review Board of the Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University (RIN15-104 and RINS19-HEN007) and complied with the Declaration of Helsinki (revised in Tokyo in 2004).
Data Availability Statement
All data analyzed during this study are available within the paper.
Acknowledgments
We thank all participants of this study and staff at the dialysis center at Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sars, B.; van der Sande, F. M.; Kooman, J. P. Intradialytic hypotension: mechanisms and outcome. Blood Purif. 2015, 49, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, P. B.; Mc Causland, F. R. Mechanisms, clinical implications, and treatment of intradialytic hypotension. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinder-Bos, H. A.; Elting, J. W. J.; Aries, M. J.; Garcia, D. V.; Willemsen, A. T.; van Laar, P. J.; Kuipers, J.; Krijnen, W. P.; Slart, R. H.; Luurtsema, G.; et al. Changes in cerebral oxygenation and cerebral blood flow during hemodialysis - A simultaneous near-infrared spectroscopy and positron emission tomography study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2020, 40, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderliesten, T.; De Vis, J. B.; Lemmers, P. M. A.; van Bel, F.; Benders, M. J. N. L.; Hendrikse, J.; Peterson, E. T. Simultaneous quantitative assessment of cerebral physiology using respiratory-calibrated MRI and near-infrared spectroscopy in healthy adults. NeuroImage. 2014, 85, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, S.; Sassaroli, A.; Tgavalekos, K. T.; Kornbluth, J. Cerebral blood flow and autoregulation: current measurement techniques and prospects for noninvasive optical methods. Neurophotonics. 2016, 3, 031411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ookawara, S.; Ito, K.; Sasabuchi, Y.; Miyahara, M.; Miyashita, T.; Takemi, N.; Nagamine, C.; Nakahara, S.; Horiuchi, Y.; Inose, N.; et al. Cerebral oxygenation and body mass index association with cognitive function in chronic kidney disease patients without dialysis: a longitudinal study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, T.; Ito, K.; Ookawara, S.; Shindo, M.; Uchida, T.; Kofuji, M.; Hayasaka, H.; Miyazawa, H.; Ueda, Y.; Hirai, K.; et al. Changes in tissue oxygenation in response to sudden intradialytic hypotension. J. Artif. Organs. 2020, 23, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Ookawara, S.; Ueda, Y.; Miyazawa, H.; Uchida, T.; Kofuji, M.; Hayasaka, H.; Minato, S.; Kaneko, S.; Mutsuyoshi, Y.; et al. Cerebral oxygenation improvement is associated with hemoglobin increase after hemodialysis initiation. Int. J. Artif. Organs. 2020, 43, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ookawara, S.; Ito, K.; Sasabuchi, Y.; Hayasaka, H.; Kofuji, M.; Uchida, T.; Horigome, K.; Imai, S.; Akikawa, T.; Wada, N.; et al. Associations of cerebral oxygenation with hemoglobin levels evaluated by near-infrared spectroscopy in hemodialysis patients. PLOS ONE. 2020, 15, e0236720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacEwen, C.; Sutherland, S.; Daly, J.; Pugh, C.; Tarassenko, L. Relationship between hypotension and cerebral ischemia during hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2511–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsuyoshi, Y.; Ito, K.; Ookawara, S.; Uchida, T.; Morishita, Y. Difference in cerebral and hepatic oxygenation in response to ultrafiltration in a hemodialysis patient with congestive heart failure. Cureus. 2021, 13, e13023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minato, S.; Ookawara, S.; Ito, K.; Miyazawa, H.; Hayasaka, H.; Kofuji, M.; Uchida, T.; Morino, J.; Kaneko, S.; Yanai, K.; et al. Differences in cerebral and hepatic oxygenation in response to intradialytic blood transfusion in patients undergoing hemodialysis. J. Artif. Organs. 2019, 22, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, S. Does food ingestion during hemodialysis lead to change in hepatic oxygenation? Nefrologia 2022. (Online ahead of print). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, Y.; Ookawara, S.; Ito, K.; Sasabuchi, Y.; Hayasaka, H.; Kofuji, M.; Uchida, T.; Imai, S.; Kiryu, S.; Minato, S.; et al. Association between hepatic oxygenation on near-infrared spectroscopy and clinical factors in patients undergoing hemodialysis. PLOS ONE 2021, 16, e0259064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Mottola, L.; Quaresima, V. Principles, techniques, and limitations of near infrared spectroscopy. Can. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 29, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, J. D. Cerebral oxygenation monitoring: near-infrared spectroscopy. Expert Rev. Med. Devices. 2006, 3, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslehaty, H.; Krause-Titz, U.; Petridis, A. K.; Barth, H.; Mehdorn, H. M. Continuous measurement of cerebral oxygenation with near-infrared spectroscopy after spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage. ISRN Neurol. 2012, 2012, 907187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongo, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Okudera, H.; Hokama, M.; Nakagawa, F. Noninvasive cerebral optical spectroscopy: depth-resolved measurements of cerebral haemodynamics using indocyanine green. Neurol. Res. 1995, 17, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K/DOQI Workgroup. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 45 Supplement 3, S1-S153. [CrossRef]
- Hirakata, H.; Nitta, K.; Inaba, M.; Shoji, T.; Fujii, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Tabei, K.; Joki, N.; Hase, H.; Nishimura, M.; Ozaki, S.; et al. Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy guidelines for management of cardiovascular diseases in patients on chronic hemodialysis. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2012, 16, 387–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, D.; Chandler, B. Splanchnic circulation. BJA Educ. 2016, 16, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstead, W. M. Cerebral blood flow autoregulation and dysautoregulation. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2016, 34, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, O. B.; Strandgaard, S.; Edvinsson, L. Cerebral autoregulation. Cerebrovasc. Brain Metab. Rev. 1990, 2, 161–192. [Google Scholar]
- Kanbay, M.; Ertuglu, L. A.; Afsar, B.; Ozodogan, E.; Siriopol, D.; Covic, A.; Basile, C.; Ortiz, A. An update review of intradialytic hypotension: concept, risk factors, clinical implications and management. Clin. Kidney J. 2020, 13, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, R.; Bragg-Gresham, J. L.; Levin, N. W.; Twardowski, Z. J.; Wizemann, V.; Saito, A.; Kimata, N.; Gillespie, B. W.; Combe, C.; Bommer, J.; Akiba, T.; et al. Longer treatment time and slower ultrafiltration in hemodialysis: associations with reduced mortality in the DOPPS. Kidney Int. 2006, 69, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movilli, E.; Gaggia, P.; Zubani, R.; Camerini, C.; Vizzardi, V.; Parrinello, G.; Savoldi, S.; Fisher, M. S.; Londrino, F.; Cancarini, G. Association between high ultrafiltration rates and mortality in uraemic patients on regular haemodialysis. A 5-year prospective observational multicentre study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007; 22, 3547–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flythe, J. E.; Kimmel, S. E.; Brunelli, S. M. Rapid fluid removal during dialysis is associated with cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).