1. Introduction
There has been a disturbing increase in multi-resistant microorganisms worldwide over the past decade (1), presenting clinicians with major diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. This phenomenon has been associated with a rise in the failure of empirical antibiotic therapies (2) and in the delay before administration of an effective drug (3), increasing mortality rates (4). The rate of carbapenemase-resistant Pseudomonas spp. is currently >20% in Spain (1), mainly due to efflux pumps and porin losses. Lower mortality rates have been obtained with meropenem than with piperacillin/tazobactam in patients with ceftriaxone-resistant E coli or Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infection (5). This has fostered the administration of bactericide antibiotics other than piperacillin/tazobactam to treat Gram-negative bacteria such as P. aeruginosa, including ceftobiprole.Ceftobiprole medocaril (Cefto-M) is a broad-spectrum, fifth-generation cephalosporin against Gram-negative cocci and bacilli, ranging from methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) to ampicillin-susceptible Enterococcus faecalis and faecium and P. aeruginosa, and it is not affected by efflux pumps or porin losses (6). It has a spectrum of potential interest for the treatment of catheter-related bacteremia, endocarditis, or complicated urine infections. In an experimental study, the bactericide capacity of Cefto-M in biofilm was higher than that of linezolid, vancomycin, or daptomycin in infections caused by MRSA, methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA), or coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS) (7). It may therefore be useful to treat infections related to devices (intracardiac, cranial leads, etc.), prosthetic valves, endoprostheses, or osteosynthesis material. It has demonstrated a similar effectiveness to that of other antibiotics in skin and soft-tissue infections (8). Nevertheless, it has only been approved in Europe for the treatment of community-acquired (CAP) and nosocomial (NP) pneumoniae, excluding ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP).
Clinical trials are the gold standard for approving novel pharmaceutical products or therapies but can differ from actual clinical experience due to their strict eligibility criteria and optimal conditions. Real World Data can help to bridge this gap, thereby supporting and accelerating the incorporation of effective new therapies and technologies into routine clinical practice (9). With this background, this real-life study in Spain was designed to examine the routine administration of Cefto-M to patients with any type of infection in hospital or receiving outpatient parenteral antimicrobial therapy (OPAT), considering health and safety outcomes and mortality-related factors.
2. Results
2.1. Cohort description
The study included 249 individuals with a mean age of 66.6±15.4 years; 59.4% were male and 92.8% Caucasian, with a mean age-adjusted Charlson index of 4 (IQR 2-6); 49.4% had cardiovascular risk factors, mainly cardiovascular disease (31.3%), arterial hypertension (29.3%), and diabetes mellitus (28.1%); 20.9% were immunosuppressed, 14.1% had chronic kidney failure, and 11.6% chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (also see
Table 1). Infection origin was nosocomial/healthcare-related in 57% of patients. Cefto-M was administered in-hospital in 95.6% of patients (medical department in 80.4%) and as outpatient parenteral antimicrobial therapy in 4.4%. Sepsis was present in 26.5%, septic shock in 4.4%, and concomitant COVID-19 infection in 13.7%. The median number of foci was 1 (IQR: 1-1). The type of infection was respiratory in 55.8% (CAP in 24.1%, NP in 24.9%, and VAP in 2%); skin and soft-tissue infection (SSTI) in 21.7%; and bacteremia in 17.7% (catheter-related in 2.8% and no focus in 14.9%) (also see
Table 1).
2.2. Microbiological isolation
Microbiological isolates were obtained from 138 patients (55.4%) and were polymicrobial in 56 (40.6%). Among the isolates, 87 (35.3%) were Gram-positive cocci (GPC), 20 (22.9%) of which were coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS), including 13 (65%) that were methicillin-resistant; 46 (18.4%)
S. aureus, including 21 (45.6%) methicillin-susceptible
S. aureus (MSSA) and 24 (52.3%) methicillin-resistant
S. aureus (MRSA) isolates; 9 (10.3%) were Enterococcus spp., including 8 (88.9%)
E. faecalis and 1 (11.1%) ampicillin-susceptible
E. faecium isolates; 10 (11.5%) were
Streptococcus spp., including 5 (50%)
S. pneumoniae and 5 (50%)
streptococci of other species; 48 were Gram-negative bacilli (GNB), including 13 (26.5%) multi-susceptible
Enterobacteriaceae, 31 (64.7%) nonfermenting GNB (100%
P. aeruginosa), and 5 (10.2%) GNB of other species (
Hemophilus influenzae [
2],
Morganella spp. [
2], and
Moraxella spp. [
1]). Supplementary Table 1 lists the other variables.
All isolated microorganisms treated with Cefto-M were susceptible to this drug (3 MRSA, 3 MSSA, 1 enterococcus, 1 streptococcus, and 10 GNB, including 4
P. aeruginosa). Among GPC, 97.2% (n=35) were susceptible to vancomycin (100% of MRSA, 93.3% of MSSA, and 100% of both enterococci and streptococci). In terms of GNB susceptibility, 83.3% of
P. aeruginosa isolates were susceptible to meropenem, 40% to cefepime, and 70% to piperacillin/tazobactam (
Table 2).
2.3. Outcomes
The median (IQR) stay was 20 (13-32) days. Total Cefto-M dose per patient was 10.5 (7.5-15) g for 7 days (5-10), being administered in monotherapy to 134 patients (53.8%). It was prescribed as empirical antibiotic treatment in 67.9% of patients, being appropriate in 82.8% of these. It was first-line antibiotic in 74 (29.7%) patients and second-line or more in 176 (70.3%). It was administered for failure of previous antibiotic therapy in 33.7% of patients and after receiving microbiology results in 26.1%. The death of 54 patients (21.7%) during the 6-month follow up was directly attributable to infection in 28 (11.2%) patients, 17 (60.7%) of whom died during the first 14 days, 9 (32.1%) between days 15 and 28, and 2 (7.1%) between day 29 and 6 months. Readmission for the same reason was recorded in 15 patients (6%) and recurrence during the first month of follow-up in 3 (1.2%).
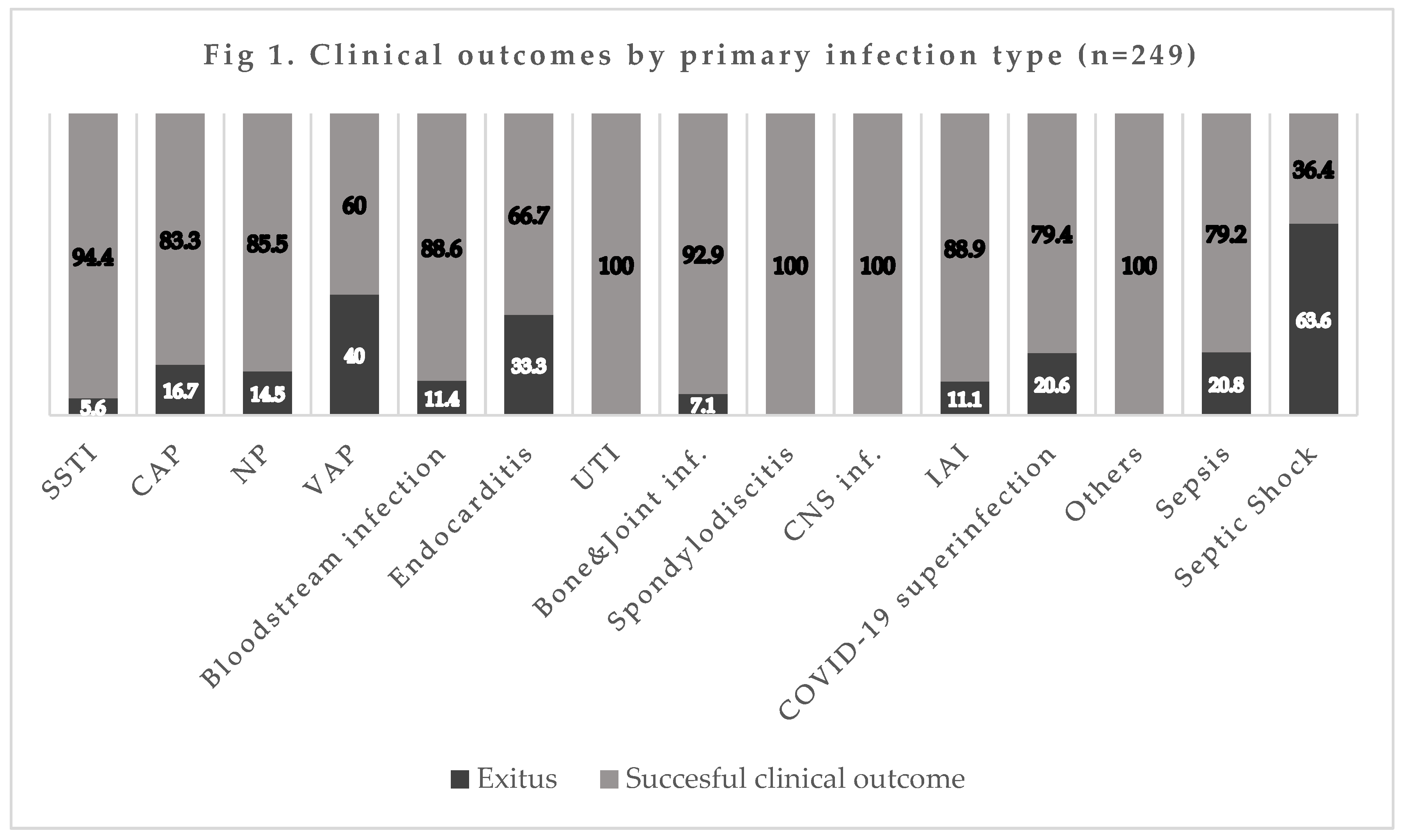
The mortality rate by infection type was 16.7% (10/60) for CAP, 14.5% (9/62) for NP, 40% (2/5) for VAP, 11.4% (5/44) for bacteremia, 5.6% (3/54) for SSTI, and 20% (7/34) for concomitant COVID-19 infection (also see
Figure 1).
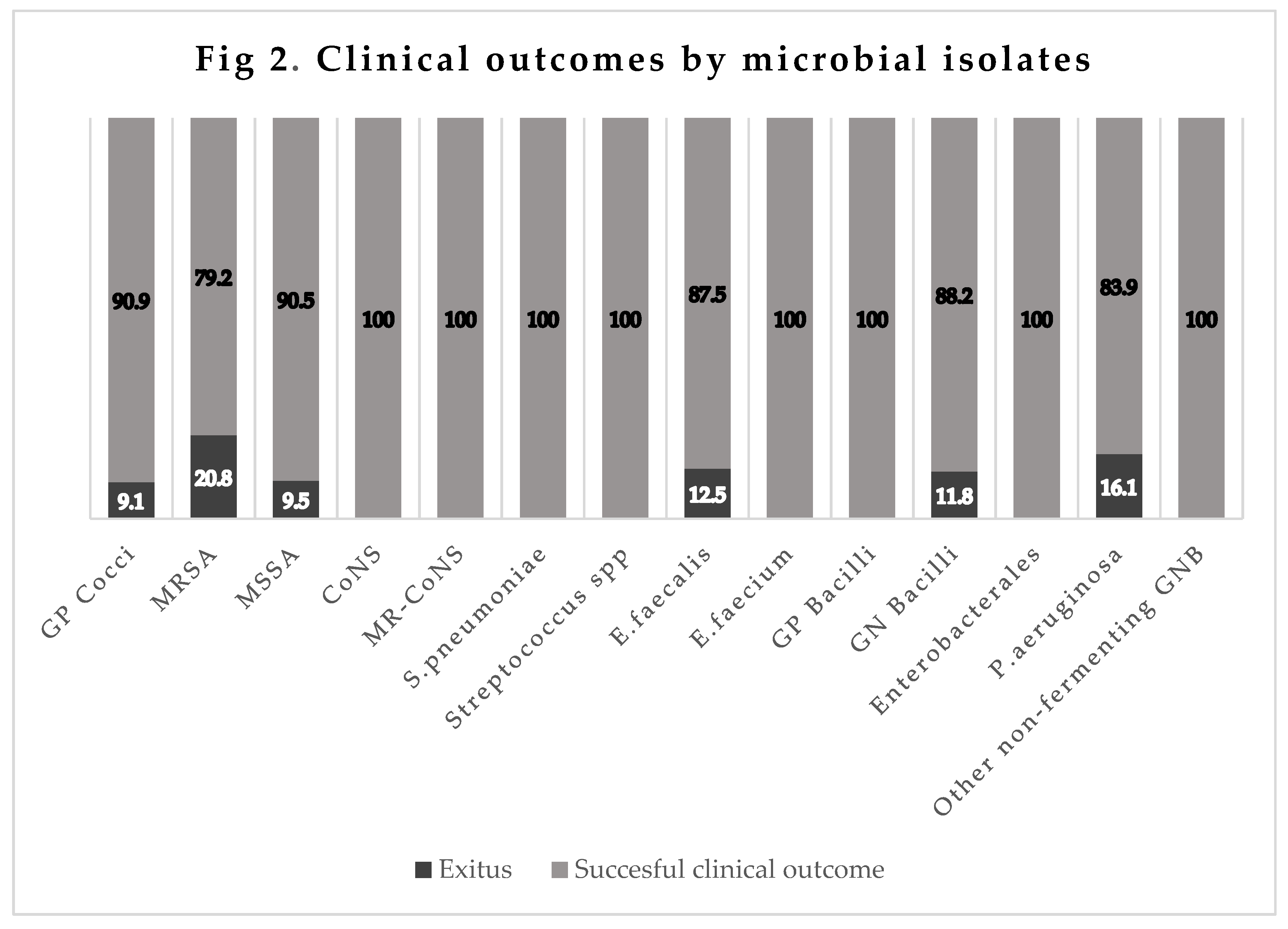
The mortality rate was 9.1% (8/88) for infections by GPC (MRSA 20.8% [5/24],
E. faecalis 12.5% [1/8], MSSA 9.5% [2/21], CNS-MR 0% [0/13],
Pneumococcus 0% [0/5],
E. faecium S-ampicillin 0% [0/1],
S. pneumoniae 0% [0/5], and
Streptococcus spp. 0% [0/5]). It was 11.8% (6/51) for infections by GNB (
P. aeruginosa 16.1% [5/31], multi-susceptibility
Enterobacteriaceae 0% [0/12], and other nonfermenting GNB 0% [0/2]), and 0% in infections by Gram-positive bacilli (0/1) (
Figure 2).
2.4. Adverse effects
No adverse effect was recorded in 96.4% of treated patients, a mild effect in 1.6% and a moderate effect in 1.6%. No patient abandoned treatment due to adverse effects; mild hypertransaminasemia was reported in 1.2%, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting in 0.8%, and skin rash in 0.4% (
Table 4).
2.5. Bi- and multivariate analyses of mortality-related factors
In the bivariate analysis, mortality was associated with higher age (76.7±13.3 vs. 65.3±15.2 yrs.; p=0.0001), ICU admission (28.6 vs. 2.1%; p= 0.001), cardiovascular risk factors (78.6 vs. 45.7%, p =0.001), underlying neurological disease (21.4 vs. 6.8%; p=0.019); immunodepression (35.7 vs. 19%; p= 0.04); sepsis/septic shock (57.1 vs. 27.6%; p=0.0001), VAP (7.1 vs. 1.4%, p=0.04), fewer days of Cefto-M treatment (6 [P25-P75: 3-8.5] vs. 7 [P25-P75: 5-10] days, p=0.029), and lower total dose (in mg) of Cefto-M (9 [4.5-12.75] vs. 10.5 [7.5-15], p=0.049). Hospitalization in a Department/Unit of Infectious Diseases emerged as a protective factor (24.9% vs. 7.1%; p=0.035).
In the multivariate analysis, factors associated with infection-related mortality were age (OR: 1.1 95% CI [1.04-1.16]), sepsis/septic shock (OR 2.94, 95% CI [1.01-8.54]), and ICU admission (OR 42.02, 95% CI [4.49-393.4]) (
Table 5).
2.6. Figures, Tables and Schemes
Table 1.
Epidemiological characteristics, comorbidities, and infection pathways.
Table 1.
Epidemiological characteristics, comorbidities, and infection pathways.
| |
Cohort N=249 |
| Age, mean (years), (± SD) |
66.6 (±15.4) |
| Charlson index, median (IQR) |
4 (2-6) |
Sex, n (%)
● Male
● Female |
148 (59.4)
101 (40.6) |
Ethnicity, n (%)
● Caucasian
● Latin
● African |
231 (92.8)
17 (6.8)
1 (0.4) |
Acquisition of the infection, n (%)
● Community-acquired infection
● Nosocomial/Nosohusial infection |
107 (43)
142 (57) |
Presence of Sepsis or Septic Shock, n (%)
● Sepsis
● Septic Shock |
66 (26.5)
11 (4.4) |
Inpatient department, n (%)
● Medical Services
● Intensive care
● Surgical Services
Outpatient antibiotic treatment, n (%) |
200 (80.4)
12 (6)
38 (15.2)
11 (4.4) |
| Coinfection with SARS-COV2 (COVID-19), n (%) |
34 (13.7) |
| Comorbidities |
|
● Cardiovascular Risk Factors, n (%)
- Hypertension
- Dyslipidemia
- Obesity
- ≥ 2 Risk Factors |
123 (49.4)
73 (29.3)
11 (4.4)
1 (0.4)
38 (15.2) |
● Cardiovascular disease, n (%)
- Ischemic Heart Disease
- Heart Failure
- Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter
- Pacemaker Carrier
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy
- Other Conditions
- ≥ 2 Conditions |
78 (31.3)
26 (33.3)
9 (11.5)
15 (19.2)
1 (1.3)
1 (1.3)
9 (11.5)
17 (21.8) |
● Respiratory diseases, n (%)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
- Thromboembolic Pulmonary Vascular Disease (TPVD)
- Bronchiectasis
- Asthma
- Interstitial Lung Disease
- Other Conditions
- ≥ 2 Conditions |
74 (29.7)
29 (39.2)
9 (12.2)
4 (5.4)
8 (10.8)
4 (5.4)
3 (4.1)
6 (8.1)
11 (14.9) |
● Gastrointestinal and hepatic diseases, n (%)
- Chronic Liver Disease
- Liver Cirrhosis
- Peptic Ulcer Disease
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Liver Transplantation
- Other Conditions |
45 (18.1)
18 (40)
8 (17.8)
6 (13.3)
3 (6.7)
3 (6.7)
7 (15.6) |
| ● Chronic Kidney Disease, n (%) |
35 (14.1) |
| ● Active Solid Malignancy, n (%) |
20 (8) |
| ● Active Hematologic Malignancy, n (%) |
33 (13.3) |
● Metabolic disorders, n (%)
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Hypothyroidism
- Adrenal Insufficiency |
83 (33.3)
70 (84.3)
11 (13.3)
2 (2.4) |
| ● Neurological diseases, n (%) |
21 (8.4) |
| ● Stroke, n (%) |
14 (5.6) |
| ● Psychiatric conditions, n (%) |
9 (3.6) |
| ● Immunocompromised patients, n (%) |
52 (20.9) |
| ● Immunosuppressant drugs therapy, n (%) |
43 (17.3) |
| Infection Pathway |
|
● Bloodstream infection, n (%)
● Primary Bacteremia
● Catheter-associated Bloodstream Infection |
44 (17.7)
37 (14.9)
7 (2.8) |
| ● Infective Endocarditis, n (%) |
3 (1.2) |
● Respiratory Tract Infections, n (%)
- Nosocomial pneumonia
- Community-acquired pneumonia
- Ventilator-associated pneumonia |
139 (55.8)
62 (24.9)
60 (24.1)
5 (2) |
● Soft Tissue and Skin infection, n (%)
- Diabetic Foot Infection
- Cellulitis
- Soft Tissue Abscess
- Infected Pressure-Ulcer
- Surgical Wound Infection
- Myositis
- Other type |
54 (21.7)
20 (37)
10 (18.5)
7 (13)
7 (13)
6 (11.1)
2 (3.7)
2 (3.7) |
● Urinary Tract Infection, n (%)
- Complicated UTI (pyelonephritis)
- Non-complicated UTI
- Renal Abscess |
10 (4)
5 (50)
3 (30)
2 (20) |
● Central Nervous System infection, n (%)
- Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection
- Epidural Abscess
- Cerebral Abscess
- Meningitis |
8 (3.2)
3 (37.5)
2 (25)
2 (25)
1 (12.5) |
| ● Intra-abdominal infection, n (%) |
9 (3.6) |
● Bone and Joint infection, n (%)
- Prosthetic Joint Infection
- Osteomyelitis
- Infectious Tenosynovitis
- Septic Arthritis |
14 (5.6)
6 (42.9)
4 (28.6)
3 (21.4)
1 (7.1) |
| ● Spondylodiscitis, n (%) |
3 (1.2) |
| ● Other type of infection, n (%) |
4 (1.6) |
Table 2.
Susceptibility of microbial isolates.
Table 2.
Susceptibility of microbial isolates.
| Microorganisms, n (%) |
Cohort N=249 |
Vanco-S |
Cloxa-S |
Dapto-S |
Ceftobi-S |
Cefe-S |
Mero-S |
Pip/Taz-S |
Staphylococcus aureus
- MRSA
- MSSA
Enterococcus spp.
Streptococcus spp. |
46 (18.4)
24 (9.6)
21 (8.4)
10 (4)
10 (4) |
35 (97.2)
21 (100)
14 (93.3)
5 (100)
3 (100) |
14 (41.2)
0 (0)
14 (100)
NT
NT |
21 (67.7)
16 (80)
5 (45.5)
0 (0)
NT |
6 (100)
3 (100)
3 (100)
1 (100)
1 (100) |
|
|
|
GNB
Enterobacterales
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Haemophilus influenzae
|
51 (20.5)
13 (5.2)
31 (12.4)
2 (0.4) |
|
|
|
10 (100)
5 (100)
4 (100)
1 (100) |
4 (33.3)
1 (50)
2 (40)
1 (100) |
5 (83.3)
NT
5 (83.3)
NT |
16 (84.2)
6 (100)
7 (70)
NT |
EUCAST cutoff points
Staphylococci
Enterococci
Pneumococci
Cefepime: 1
Ceftobiprole: 0.5
Vancomycin: 2
Meropenem: 2
Enterobacteriaceae
Cefepime: 1
Ceftobiprole: 0.25
Meropenem: 2
Pseudomonas
Table 3.
Outcomes.
| |
N=249 |
| Total dose of ceftobiprole, median (IQR) |
10.5 (7.5-15) |
| Duration of antibiotic therapy, median (IQR) |
7 (5-10) |
Treatment regimen, n (%)
● Ceftobiprole Monotherapy
● Antibiotic combination
- Ceftobiprole + Daptomycin
- Ceftobiprole + Vancomycin
- Ceftobiprole + Linezolid
- Ceftobiprole + Dalbavancin
- Ceftobiprole + Clindamycin
- Ceftobiprole + Tigecycline
- Ceftobiprole + Cloxacillin
- Ceftobiprole + Ceftazidime
- Ceftobiprole + Ceftaroline
- Ceftobiprole + Ceftriaxone
- Ceftobiprole + Ceftazidime/Avibactam
- Ceftobiprole + Meropenem
- Ceftobiprole + Levofloxacin
- Ceftobiprole + Ciprofloxacin
- Ceftobiprole + Piperacillin/Tazobactam
- Ceftobiprole + Amikacin
- Ceftobiprole + Azithromycin
- Ceftobiprole + Metronidazole
- Ceftobiprole + Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole
- Ceftobiprole + Doxycycline
- Ceftobiprole + Fosfomycin
- Ceftobiprole + Antifungal agents
- Ceftobiprole + Antiviral agents |
134 (53.8)
115 (46.2)
27 (23.5)
4 (3.5)
8 (7)
1 (0.9)
2 (1.7)
4 (3.5)
3 (2.6)
1 (0.9)
2 (1.7)
2 (1.7)
2 (1.7)
9 (7.8)
10 (8.7)
4 (3.5)
2 (1.7)
6 (5.2)
10 (8.7)
13 (11.3)
7 (6.1)
2 (1.7)
1 (0.9)
6 (5.2)
2 (1.7) |
| Length of hospital stay, median (IQR) |
20 (13-32) |
Ceftobiprole as empirical treatment, n (%)
Appropriate empirical treatment, n (%) |
169 (67.9)
140 (82.8) |
Prescription of Ceftobiprole, n (%)
● As first-line treatment
● As second-line or more |
74 (29.7)
175 (70.3) |
Reason for switching to Ceftobiprole, n (%)
● Failure of previous antibiotic treatment
● Toxicity/adverse effects of previous antibiotic treatment
● Guided by microbiological results
● Other reasons (or combination of previous) |
84 (48)
3 (1.7)
65 (37.1)
23 (13.1) |
Recurrence and readmission, n (%)
● Recurrence of infection (in first month)
● Hospital readmission |
3 (1.2)
15 (6) |
Mortality, n (%)
● Total mortality
● Non-related-to-infection mortality
● Related-to-infection mortality |
54 (21.7)
26 (10.4)
28 (11.2) |
Related-to-infection mortality, n (%)
● 14-day mortality
● 28-day mortality
● 6-month mortality |
17 (60.7)
9 (32.1)
2 (7.1) |
Table 4.
Mortality risk factors: bivariate and multivariate analyses.
Table 4.
Mortality risk factors: bivariate and multivariate analyses.
| |
Non-survivor
N= 31 |
Survivor
N= 219 |
Bivariate
p* |
Multivariate
OR, 95% CI |
Epidemiological characteristics
● Age (± DS)
● Charlson index, median (IQR)
● Sex, n (%)
- Male
- Female
● Ethnicity n (%)
- Caucasian
- Latin
- African |
76.7 (±13.3)
4.5 (4-6.75)
20 (71.4)
8 (28.6)
27 (96.4)
1 (3.6)
0 (0) |
65.3 (±15.2)
4 (2-6)
128 (57.9)
93 (44.1)
204 (92.3)
16 (7.2)
1 (0.5) |
0.0001
0.253
0.17
0.718 |
1.1 (1.04-1.16)
|
Inpatient department, n (%)
● Medical Departments
- Infectious Diseases
- Internal Medicine
- Pneumology
- Intensive Care Unit
- Hematology
- Oncology
● Surgical Departments
OPAT, n (%) |
2(7.1)
9 (32.1)
2 (7.1)
8 (28.6)
1 (3.6)
2 (7.1)
2 (7.1)
2 (7.1) |
55 (24.9)
43 (19.5)
37 (16.7)
4 (1.8)
10 (4.5)
14 (6.3)
36 (16.3)
9 (4.1) |
0.035
0.12
0.27
0.001
0.25
0.27
0.27
0.36 |
0.19 (0.03-1.2)
42.02 (4.49-393.4) |
Comorbidities, n (%)
● Cardiovascular Risk Factors
● Cardiovascular Disease
● Lung Disease
● Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease
● Chronic Kidney Disease
● Active Solid Malignancy
● Hematological Malignancy
● Metabolic Disorder
● Neurological Disease
● Psychiatric Disorder
● Stroke
● Immunosuppression |
22 (78.6)
6 (21.4)
10 (35.7)
5 (17.9)
4 (14.3)
3 (10.7)
4 (14.3)
11 (39.3)
6 (21.4)
0 (0)
3 (10.7)
10 (35.7) |
101 (45.7)
72 (32.6)
64 (29)
40 (18.1)
31 (14)
17 (7.7)
29 (13.1)
72 (32.6)
15 (6.8)
9 (4.1)
11 (5)
42 (19) |
0.001
0.231
0.461
0.975
0.97
0.526
0.864
0.478
0.019
0.6
0.199
0.04 |
1.67 (0.49-5.62)
0.94(0-21-4.33)
1.81 (0.289-11.41)
1.21 (0.24-6.16)
2.59 (0.69-9.85)
2.03 (0.52-7.88) |
| COVID-19 superinfection |
7 (25) |
27 (12.2) |
0.063 |
2.08 (0.43-10.12) |
Number of infection pathways, median (IQR)
Pathway Infection, n (%)
● Bloodstream infection
● Infective endocarditis
● Community-acquired pneumonia
● Nosocomial pneumonia
● Ventilator-associated pneumonia
● Skin and Soft Tissue infection
● Urinary Tract infection
● Central Nervous System infection
● Intra-abdominal infection
● Bone and Joint infection
● Spondylodiscitis
● Other type of infection
● Sepsis or Shock |
1 (1-1)
5 (17.9)
1 (3.6)
10 (35.7)
9 (32.1)
2 (7.1)
3 (10.7)
0 (0)
0 (0)
1 (3.6)
1 (3.6)
0 (0)
0 (0)
16 (57.1) |
1 (1-1)
39 (17.6)
2 (0.9)
50 (22.6)
53 (24)
3 (1.4)
51 (23.1)
10 (4.5)
8 (3.6)
8 (3.6)
13 (5.9)
3 (1.4)
4 (1.8)
61 (27.6) |
0.945
0.978
0.223
0.127
0.347
0.04
0.135
0.251
0.306
0.99
0.617
0.535
0.473
0.0001 |
0.12 (0.004-3.89)
2.94 (1.01-8.54) |
Microbiology and acquisition of infection, n (%)
● Microbial isolation
- Monomicrobial infection
- Polymicrobial infection
● Setting of infection acquisition
- Community-acquired infection
- Nosocomial infection
- Nosohusial infection
● GPC
● MRSA
● MSSA
● CoNS
● Enterococcus faecalis
● Streptococcus pneumoniae
● GNB
● Pseudomonas aeruginosas
|
9 (32.1)
6 (21.4)
12 (42.9)
10 (35.7)
6 (21.4)
8 (28.6)
5 (17.9)
2 (7.1)
0 (0)
1 (3.6)
0 (0)
6 (21.4)
5 (17.9) |
84 (38)
50 (22.6)
95 (43)
90 (40.7)
36 (16.4)
80 (36.2)
19 (8.6)
19 (8.6)
20 (9)
7 (3.2)
5 (2.3)
45 (20.4)
26 (11.8) |
0.758
0.762
0.426
0.118
0.794
0.097
0.909
0.421
0.895
0.358 |
|
Antimicrobial Therapy
● Total dose of Ceftobiprole (mg), median (IQR)
● Length of Ceftobiprole therapy (days), median (IQR)
● Therapy regimen:
- Monotherapy, n (%)
- In combination, n (%)
● Prescription of Ceftobiprole:
- First-line, n (%)
- Rescue therapy, n (%)
● Empirical treatment, n (%) |
9 (4.5-12.75)
6 (3-8.5)
16 (57.1)
12 (42.9)
6 (21.4)
22 (78.6)
22 (78.6) |
10.5 (7.5-15)
7 (5-10)
118 (53.4)
103 (46.6)
68 (30.8)
153 (69.2)
146 (66.1) |
0.049
0.029
0.708
0.308
0.183 |
0.91 (0.73-1.12)
1.08 (0.82-1.4)
1.34 (0.4-4.49) |
Table 5.
Adverse drug effects.
Table 5.
Adverse drug effects.
| |
N = 249 |
| Total adverse effects, n (%) |
9 (3.6) |
Severity of adverse effects, n (%)
● Mild
● Moderate
● Severe |
4 (1.6)
4 (1.6)
1 (0.4) |
Adverse effects by symptoms, n (%)
● Acute kidney failure
● Elevated liver enzymes
● Gastrointestinal symptoms
● Urticaria-like cutaneous rash |
5 (2)
3 (1.2)
2 (0.8)
1 (0.4) |
Figure 1.
SSTI: Skin and Soft Tissue infection, CAP: Community-acquired pneumonia; NP: Nosocomial pneumonia; VAP: Ventilator-associated pneumonia; UTI: Urinary Tract infection; CNS: Central Nervous System; IAI: Intra-abdominal infection.
Figure 1.
SSTI: Skin and Soft Tissue infection, CAP: Community-acquired pneumonia; NP: Nosocomial pneumonia; VAP: Ventilator-associated pneumonia; UTI: Urinary Tract infection; CNS: Central Nervous System; IAI: Intra-abdominal infection.
Figure 2.
GP: Gram-Positive; MRSA: Methicilin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus; MSSA: Methicilin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus; CoNS: Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus spp; MR-CoNS: Methicilin-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus spp; GN: Gram-Negative; GNB: Gram-Negative Bacilli.
Figure 2.
GP: Gram-Positive; MRSA: Methicilin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus; MSSA: Methicilin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus; CoNS: Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus spp; MR-CoNS: Methicilin-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus spp; GN: Gram-Negative; GNB: Gram-Negative Bacilli.
3. Discussion
Patients in this real-life study were elderly and largely male and pluripathological, with a high comorbidity index and predominance of cardiovascular risk factors. Around one in five were immunodepressed, one in seven had kidney failure, and one in ten had COPD. More than half of infections were nosocomial or healthcare-related, and around 5% received outpatient antibiotic treatment. As in the case of other beta-lactams, the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of Cefto-M favor its infusion for 24 h, making it a potentially useful antibiotic for OPAT regimens in patients with infections by GPC, including MRSA and ampicillin-susceptible Enterococcus spp., and non-ESLB-producing GNB such as Pseudomonas spp. (15).
More than one-third of participants had sepsis/septic shock, and one-seventh were co-infected with SARS-COV2 (COVID-19). Septic shock has been described as an independent mortality risk factor, with an increase in risk of up to 12% for every hour in shock, regardless of the focus, isolate, type of poly-/mono-microbial infection, or presence/absence of bacteremia (16). A multicenter study of more than 5,000 individuals with septic shock reported a mortality rate of around 50% when the antibiotic treatment was appropriate and 89% when it was not (17). Coinfection with SARS-COV2 in critical patients with NP or VAP is known to worsen the prognosis, although it does not increase the rate of invasive fungal infection or change the type of microorganism isolated at respiratory level (18).
In the present study, only around half of the patients received Cefto-M for respiratory infection (half NP and half CAP), which is the sole indication for this antibiotic in Spain (19). One-fifth of patients were treated for skin/soft tissue infection and one-sixth for bacteremia. Cefto-M was effective against Enterococcus in a murine model of UTI (20) and has been proposed as a possible option in complicated UTI produced by Pseudomonas spp. (21). Three non-inferiority clinical trials in patients with skin and soft tissue infections reported no difference between Cefto-M and comparators in clinical or microbiological response or safety profile (22). Decisions of clinicians to prescribe Cefto-M to the remaining patients in this real-life study are supported by pharmacokinetic (23) and in vitro (24) studies and by a real-life study with a small sample size (25).
The total crude infection-related mortality in these patients was 11.2%, most frequently due to VAP (40%), followed by pneumonia with COVID-19 coinfection (20%), CAP requiring hospitalization (16.7%), NP (14.5%), bacteremia (11.4%), and skin/soft-tissue infections (5.6%). Among microorganisms, the highest mortality rates were for MRSA (20.8%) and P. aeruginosa (16.1%). The mortality rate was <1% in clinical trials of Cefto-M in patients with CAP. The difference with the present finding might be explained by their stricter eligibility criteria, with the exclusion of patients receiving an antibiotic for >24 h in the previous three days and those with aspiration pneumonia, viral respiratory infection, polymicrobial infection, or radiological or clinical suspicion of atypical pneumonia (26). In the trial in patients with NP, the total mortality rate was 16.7% and the infection-attributed rate was 5.9%. This major discrepancy with the present findings can again be attributed to the trial eligibility criteria, which excluded patients receiving systemic antibiotic treatment for >24 h in the previous two days and those with severe kidney failure or liver failure, evidence of infection with ceftazidime- or Cefto-M-resistant pathogens, and clinical circumstances potentially hampering the evaluation of effectiveness, e.g., sustained shock, active tuberculosis, pulmonary abscess or postobstructive pneumonia (27).
Only one patient (0.4%) had a severe complication, and the treatment was not withdrawn from any patient due to an adverse effect, similar to the findings of a single-center real-life study on the use of Cefto-M in 29 patients with infections in a third-level hospital (28).
Finally, the main factors related to mortality in this cohort of Cefto-M-treated patients were older age (the mean age of patients was 76.7 years), the presence of sepsis/septic shock, and ICU admission, which have all been independently related to higher infection-related mortality rates in previous studies (29).
The study is limited by its retrospective design and possible selection bias. Its strengths include its multicenter design, sample size (largest to date) and real-life nature, reflecting as faithfully as possible the utilization of Ceftobiprole-M in routine clinical practice in Spain.
4. Materials and Methods
Study design
This real-life, retrospective, multicenter, observational, and descriptive study on the use of Cefto-M included patients in hospital or receiving OPAT with nosocomial/nosohusial or community-acquired infections from 12 Spanish centers in six autonomous communities (Andalusia, Madrid, Cataluña, Valencia, Murcia, and Cantabria). The study period was from the time of the drug’s approval in 2021 to December 31, 2022. The study was approved by the Provincial Ethics Committee of Granada (ref: 0095-N-22), with no requirement for the informed consent of patients. All data were gathered in accordance with Spanish personal data protection legislation (Organic Law 3/2018 December 5) and the Helsinki declaration.
This descriptive study did not involve a pharmacological intervention. Treatments were always prescribed by attending physicians according to their clinical practice.
Inclusion criteria: age >17 years, receipt of Cefto-M as first-line or rescue treatment for ≥48 h (≥6 vials in patients with normal renal function, creatinine clearance-adjusted in patients with kidney failure); and ≥30 days of follow-up post-discharge or, in the case of patients with osteomyelitis o endocarditis, ≥ 6 months post-discharge.
Exclusion criteria: pregnancy, allergy to beta-lactams or any formulation excipient.
Variables and definitions
Age, sex, ethnicity, days of hospitalization (dates of admission and discharge); prescribing hospital department., age-adjusted Charlson index, comorbidities.
Infection type: bacteremia (complicated/non-complicated], endocarditis (definite/probable/suspected, native/early prosthetic/late prosthetic/on pacemaker, respiratory infection (upper tract/CAP/NP/VAP), urinary tract infection (UTI), central nervous system infection, spondylodiscitis, osteoarticular infection, intraabdominal infection, or other foci of infection. Infection origin: community or nosocomial/nosohusial/healthcare-related. Sepsis or septic shock. Monomicrobial/polymicrobial infection. Co-infection with SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19).
Cefto-M administration in monotherapy or combination therapy (for the same infection); empirical or targeted administration; first-line or rescue (due to poor response to previous antibiotherapy, microbiology results, or toxicity with previous antibiotherapy); days of administration and dose; and adverse events.
Previous antibiotic (for same infection) with treatment duration.
Microbiology: microorganism causing the infection and antibiogram according to EUCAST criteria (10).
Infection-related mortality at 14 and 28 days (at 6 months for endocarditis or osteomyelitis).
Readmission for the same reason during first month.
Relapse/recurrence of the infection.
Definitions.
- Nosocomial infection: onset >72 h after hospitalization.
- Nosohusial/nosocomial infection: healthcare-related (day hospital, residence, daycenter for elderly).
- The age-adjusted Charlson comorbidity index was used to estimate the 10-year life expectancy of patients as a function of their age and the presence of comorbidities at admission for the infectious episode (11).
- Sepsis/septic shock: refractory hypotension and end-organ perfusion dysfunction despite adequate fluid resuscitation (12).
- Immunodepression: congenital or acquired immunodeficiency or receipt of immunosuppressive treatment (13).
- Relapse/recurrence of the infection was defined by a second episode within three months (14).
- Adverse effect classification.
Mild: requires no antidote or treatment; brief hospitalization.
Moderate: requires treatment modification (e.g., dose adjustment, combination with another drug) but no interruption of drug administration; longer hospitalization or prescription of a specific treatment may be needed.
Severe: threatens the life of the patient and mandates interruption of drug administration and prescription of a specific treatment.
Lethal: can directly or indirectly contribute to the death of a patient.
Sample size
A sample size of around 250 individuals was estimated to be adequate to analyze the use of Cefto-M in routine clinical practice with a confidence interval of 95% and error of 5%. Information was obtained from the electronic records of the different Hospital Pharmacy Departments, gathering the number of patients administered the drug by type of infection. These data were introduced into an anonymized database in SPSS format, following national data protection legislation and the principles of the Helsinki declaration.
Statistical analysis
In a descriptive analysis, absolute and relative frequencies (%) were calculated for qualitative variables. Means with standard deviation were calculated for quantitative variables with normal distribution and medians with interquartile range (IQR) for those with non-normal distribution (Kolmogorov–Smirnov test).
In bivariate analyses of mortality-related factors, the chi-squared test was used to compare qualitative variables, the Student’s t-test for quantitative variables with normal distribution, and the Mann Whitney U test for those with non-normal distribution. Multivariate logistic regression analysis considered variables that were statistically significant in bivariate analysis or deemed relevant (i.e., chronic kidney failure, active hematological or solid organ neoplasia, coinfection by SARS-COV-2, rescue/first-line treatment).
Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the ethics committee of the coordinating center and was exempted from the need to obtain informed consent due to its retrospective design and large size. All data were gathered in accordance with Spanish personal data protection legislation.
5. Conclusions
Ceftobiprole-M is a safe antibiotic, with only half of prescriptions for patients with respiratory infection, mainly administered as rescue therapy in pluripathological patients with severe infections. The infection-attributable mortality was 11.2%, largely associated with higher age, presence of sepsis/septic shock, and ICU admission.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, CHT; methodology, CHT.; software, IPR, FJMN, LM, RM, OBP, VALM, MSL, PV, JLT, AAG, LMN, MM, MPRS; formal analysis, CHT, IPR; validation, IPR, FJMN, LM, RM, OBP, VALM, MSL, PV, JLT, AAG, LMN, MM, MPRS; formal analysis, CHT, IPR, DAG; investigation, CHT, IPR, DAG.; resources, IPR, DAG ; data curation, IPR, DAG.; writing—original draft preparation, CHT.; writing—review and editing, IPR, SS.; visualization, JMN, LM, RM, OBP, VALM, MSL, PV, JLT, AAG, LMN, MM, MPRS; supervision, SS.; project administration, CHT, IPR; funding acquisition, CHT. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Project received partial funding from the laboratory ADVANZ PHARMA Spain SLU, with central office in Calle suero de Quiñones 34-36 28002, Madrid, Spain.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Granada (CEIM/CEI of Granada); code: 0095-N-22.
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was exempted from the need to obtain due to its retrospective design and large size.
Data Availability Statement
The researchers confirm the accuracy and availability of the data used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Annual surveillance reports on antimicrobial resistance. EARS-Net. For 2019. Available online: https://antibiotic.ecdc.europa.eu/en.
- Kollef, M.H. Inadequate antimicrobial treatment: an important determinant of outcome for hospitalized patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2000; 31 Suppl 4:S131-8. [CrossRef]
- Funk DJ, Parrillo JE, Kumar A. Sepsis and septic shock: a history. Crit Care Clin. 2009; 25: 83-101. [CrossRef]
- Micek ST, Hampton N, Kollef M. Risk Factors and Outcomes for Ineffective Empiric Treatment of Sepsis Caused by Gram-Negative Pathogens: Stratification by Onset of Infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017; 62: e01577-17. [CrossRef]
- Harris PNA, Tambyah PA, Lye DC, Mo Y, Lee TH, Yilmaz M, et al. Effect of Piperacillin-Tazobactam vs Meropenem on 30-Day Mortality for Patients with E coli or Klebsiella pneumoniae Bloodstream Infection and Ceftriaxone Resistance: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama 2018; 2018; 320: 984-994. [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo JL, Patel R. Ceftobiprole medocaril: a new generation beta-lactam. Drugs Today (Barc). 2008; 44: 801-25. [CrossRef]
- Abbanat D, Shang W, Amsler K, Santoro C, Baum E, Crespo-Carbone S et al. Evaluation of the in vitro activities of ceftobiprole and comparators in staphylococcal colony or microtitre plate biofilm assays. Int. J. Antimicrob Agents 2014; 43: 32-9. [CrossRef]
- Noel GJ, Strauss RS, Amsler K, Heep M, Pypstra R, Solomkin JS. Results of a double-blind, randomized trial of ceftobiprole treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections caused by gram-positive bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008; 52: 37-44. [CrossRef]
- Berger ML, Sox H, Willke RJ, Brixner DL, Eichler HG, Goettsch W. et al. Good practices for real-world data studies of treatment and/or comparative effectiveness: Recommendations from the joint ISPOR-ISPESpecial Task Force on real-world evidence in health care decision making. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2017; 26: 1033–1039. [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters. Version 13.0, 2023. Available online: http://www.eucast.org.
- Charlson ME, Charlson RE, Paterson JC, Marinopoulos SS, Briggs WM, Hollenberg JP. The Charlson comorbidity index is adapted to predict costs of chronic disease in primary care patients. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61:1234–40. [CrossRef]
- Cecconi M, Evans L, Levy M, Rhodes A. Sepsis and septic shock. 2018; 392: 75-87. [CrossRef]
- Ramirez JA, Musher DM, Evans SE, Dela Cruz C, Crothers KA, Hage CA, et al. Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Adults: A Consensus Statement Regarding Initial StrategiesChest. 2020; 158: 1896-1911. [CrossRef]
- Miguel Cisneros-Herreros J, Cobo-Reinoso J, Pujol-Rojo M, Rodríguez-Baño J, Salavert-Lletí M. Guía para el diagnóstico y tratamiento del paciente con bacteriemia. Guías de la Sociedad Española de Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica (SEIMC). Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2007; 25: 111–30. [CrossRef]
- López-Cortés LE, Herrera-Hidalgo L, Almadana V, Gil-Navarro MV; DOMUS OPAT Group. Ceftobiprole, a new option for multidrug resistant microorganisms in the outpatient antimicrobial therapy setting. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin (Engl Ed). 2022; 40: 399-400.
- Kumar A, Roberts D, Wood KE, Light B, Parrillo JE, Sharma S, Suppes R, Feinstein D, Zanotti S, Taiberg L, Gurka D, Kumar A, Cheang M. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2006; 34:1589-96. [CrossRef]
- Kumar A, Ellis P, Arabi Y, Roberts D, Light B, Parrillo JE et al. Initiation of inappropriate antimicrobial therapy results in a fivefold reduction of survival in human septic shock. Antimicrobial Therapy of Septic Shock Database Research Group. Chest. 2009; 136: 1237-1248. [CrossRef]
- Rouzé A, Martin-Loeches I, Povoa P, Makris D, Artigas A, Bouchereau M, et al. Relationship between SARS-CoV-2 infection and the incidence of ventilator-associated lower respiratory tract infections: a European multicenter cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2021; 47: 188-198. [CrossRef]
- Agencia española de medicamentos y productos sanitarios. CIMA. Ministerio de Sanidad. Gobierno de España. Available online: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/publico/home.html.
- Singh KV, Murray BE. Efficacy of ceftobiprole Medocaril against Enterococcus faecalis in a murine urinary tract infection model Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012; 56: 3457-60. [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M. Strategies for management of difficult to treat Gram-negative infections: focus on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infez Med. 2007; 15: 20-6.
- Lan SH, Lee HZ, Lai CC, Chang SP, Lu LC, Hung SH, et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of ceftobiprole in the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2022; 20: 95-102. [CrossRef]
- Barbour A, Schmidt S, Rout WR, Ben-David K, Burkhardt O, Derendorf H. Soft-tissue penetration of ceftobiprole in healthy volunteers determined by in vivo microdialysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemither 2009; 53: 2773-6. [CrossRef]
- Yin LY, Calhoun JH, Thomas JK, Shapiro S, Schmitt-Hoffmann A. Efficacies of ceftobiprole medocaril and comparators in a rabbit model of osteomyelitis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008; 52: 1618-22. [CrossRef]
- Zhanel GG, Kosar J, Baxter M, Dhami R, Borgia S, Irfan N, et al. Real-life experience with ceftobiprole in Canada: Results from the CLEAR (CanadianLEadership onAntimicrobialReal-life usage) registry. Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2021 Mar;24:335-339. [CrossRef]
- Nicholson SC, Welte T, File TM Jr, Strauss RS, Michiels B, Kaul P, et al. A randomised, double-blind trial comparing ceftobiprole medocaril with ceftriaxone with or without linezolid for the treatment of patients with community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalisation. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012; 39: 240-6. [CrossRef]
- Awad SS, Rodriguez AH, Chuang YC, Marjanek Z, Pareigis AJ, Reis G, Scheeren TW, Sánchez AS, Zhou X, Saulay M, Engelhardt M. A phase 3 randomized double-blind comparison of ceftobiprole medocaril versus ceftazidime plus linezolid for the treatment of hospital-acquired pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 2014; 59: 51-61. [CrossRef]
- Durante-Mangoni E, Andini R, Mazza MC, Sangiovanni F, Bertolino L, Ursi MP, Paradiso L, Karruli A, Esposito C, Murino P, Corcione A, Zampino R. Real-life experience with ceftobiprole in a tertiary-care hospital. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020; 22:386-390). [CrossRef]
- Taylor EH, Marson EJ, Elhadi M, Macleod KDM, Yu YC, Davids R, et al. Factors associated with mortality in patients with COVID-19 admitted to intensive care: a systematic review and meta-analysis Anaesthesia. 2021; 76: 1224-1232. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).