Introduction
Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is a structural and lateral curvature of the spine with rotation that affects 1%–3% of children and occurs around puberty.1 Mild scoliosis is usually asymptomatic; however, it might result in back pain of musculoskeletal origin. Thus, screening for and early detection of AIS are the most important factors for early intervention and preventing deformity from progressing. After detecting AIS, the criterion standard to identify changes in the spine position remains radiography to determine Cobb angle, which will guide important treatment decisions such as surgery or bracing. From the radiography, we can also assess shoulder balance and trunk imbalance, which have been considered characteristics of the deformity in idiopathic scoliosis.2–4 Posture changes increase the risk of psychosocial complications (self-image, body image, mental health, and quality of life)5,6. However, patients with AIS may also be at increased risk for damage to health because of radiography, increasing the risks for developing leukemia or breast cancer, or a heritable defect higher than the baseline risk.7,8 Therefore, to decrease their exposure to X-ray radiation during follow-up of AIS, numerous studies have sought nonradiological methods for diagnosing body posture to reduce childhood exposure to X-ray radiation. For example, the ability of photogrammetry to detect the progression of scoliosis was estimated from the calculations of sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and accuracy at several cutoff points using Cobb angle progression as the criterion standard. However, the accuracy of these methods compared with radiography remains controversial.
Conventionally, state-of-the-art marker-based motion capture systems or markerless motion capture systems (e.g., MicroSoft Kinect) are used to assess posture.
14 However, they require specialized instrumentation (e.g., infrared cameras, reflective markers, and MicroSoft Kinect software) and take a long time to produce an accurate analysis. Nevertheless, a marker-based photogrammetric method for detecting AIS takes approximately half an hour. Meanwhile, machine learning and deep neural networks now permit motion capture using low-cost webcams or cell phones, increasing the accessibility of pose estimation in clinical settings.
15,16 There are several open-source pose estimation software packages to estimate human posture. MoveNet is best suited for determining the posture of a single person. This method focuses on the person closest to the center of the image and ignores any other people in the frame, effectively rejecting any background people. The model’s parameters are inferred using two massive datasets: the COCO Keypoint Dataset [
https://arxiv.org/abs/1405.0312] and the Active Dataset [
https://tfhub.dev/google/movenet/singlepose/thunder]. The COCO Keypoint Dataset contains images taken in a variety of settings with varying sizes and occlusions, and the Active Dataset consists of images of people exercising, stretching, or dancing, sampled from YouTube. In total, 51,500 images are used.
Unfortunately, open-source methods of pose estimation were not designed for clinical analysis. Moreover, pose estimation software used to estimate posture differ based on the data used to train them (including the camera viewpoints, the types of movements, and even the clothing worn by the users) and the key points they were designed to track. Hence, the models will differ in their ability to perform motion capture accurately and reliably, which is required to translate this technology for clinical use.
The purposes of the present study were to (1) quantify the pose estimation of patients with AIS from photographs using open-source software packages and (2) determine correlations between parameters determined by radiography and photography.
Materials and methods
The present study was approved by our institutional review board (Approval No. 2556; February 2022). Written informed consent was obtained from the parents or guardians of all participants included in the study.
2.1. Patient population
We examined the medical records of 12 consecutive eligible patients with AIS with major thoracolumbar/lumbar (TL/L) curves (Lenke Type 5C) or MT curves (Lenke Type 1A) who underwent posterior spinal fusion surgery between July 2022 and February 2023 at our university teaching hospital.
2.2. Radiographic parameters
The Lenke classification defines a major T/TL/L curve with nonstructural thoracic curves (Cobb angle <25° on a side bending radiograph). Standing whole spine posterior–anterior and lateral standing radiographs before surgery were evaluated by two surgeons (GG and TO). Coronal alignment was measured by clavicle angle (Cla-A), radiographic shoulder height (RSH), C7-central sacral vertical line (C7–CSVL), Cobb angle, and pelvic obliquity. Sagittal alignment was measured by trunk tilt angle (TTA)17, sagittal vertical axis (SVA), and T1 pelvic angle (TPA)18. Radiographic measurements were made by two board-certified spine surgeons (GG and TO) to determine the interobserver error. The mean values of their measurements were used to calculate an intraclass coefficient of 0.932, indicating that the interrater reliability was almost ideal.
2.3. Photographic parameters
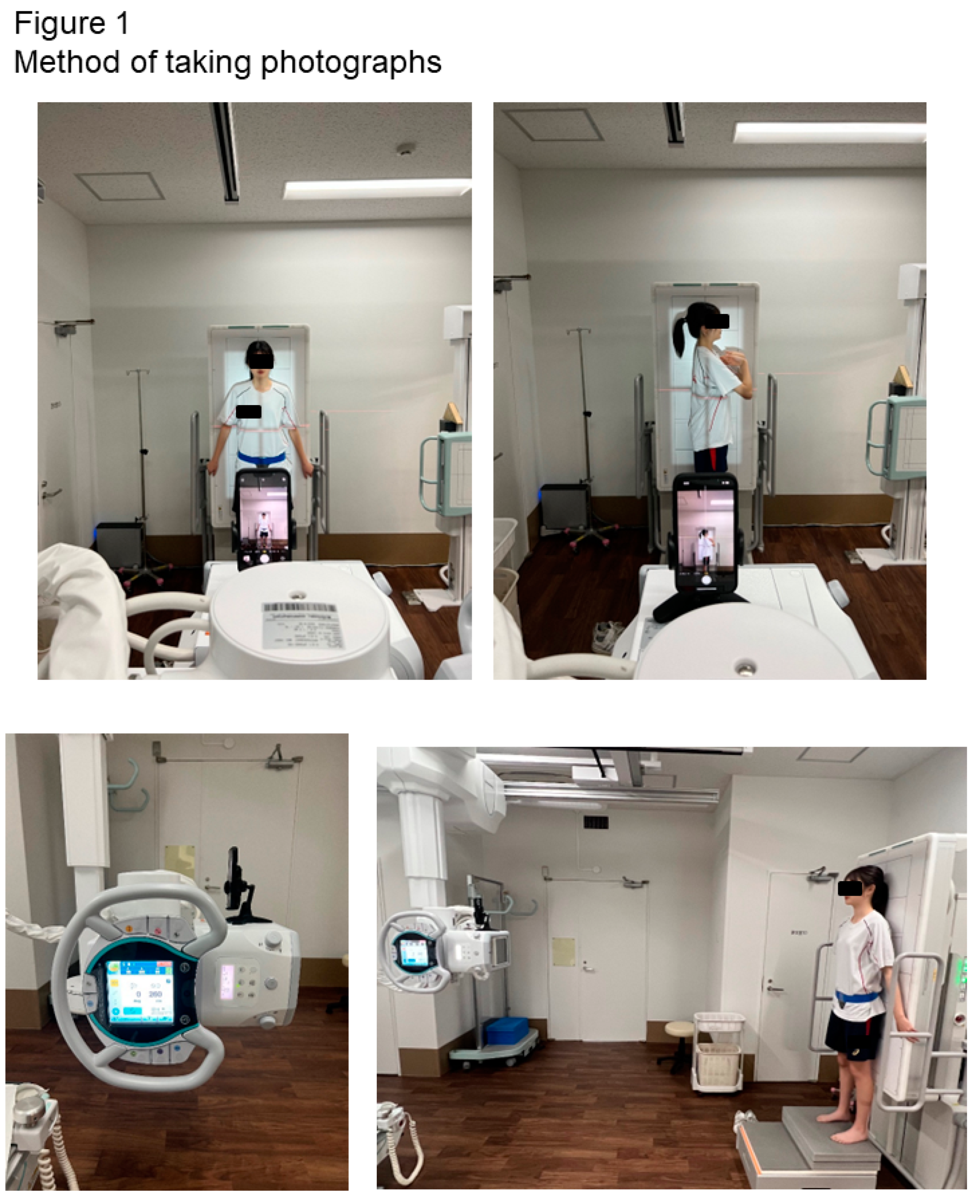
Photographs were taken using a tripod-mounted camera (iPhone 13Pro) on an X-ray tube head, without zoom, positioned at the same distance from the X-ray tube to the patient (
Figure 1).
To assess photographic parameters, we used a human pose estimation algorithm based on deep learning [
https://www.nature.com/articles/nature14539], a computational technique that uses a set of example inputs and outputs to learn the parameters of a computational model, i.e., infer a function that maps arbitrary inputs to the intended outputs. We use an open-source model called MoveNet [
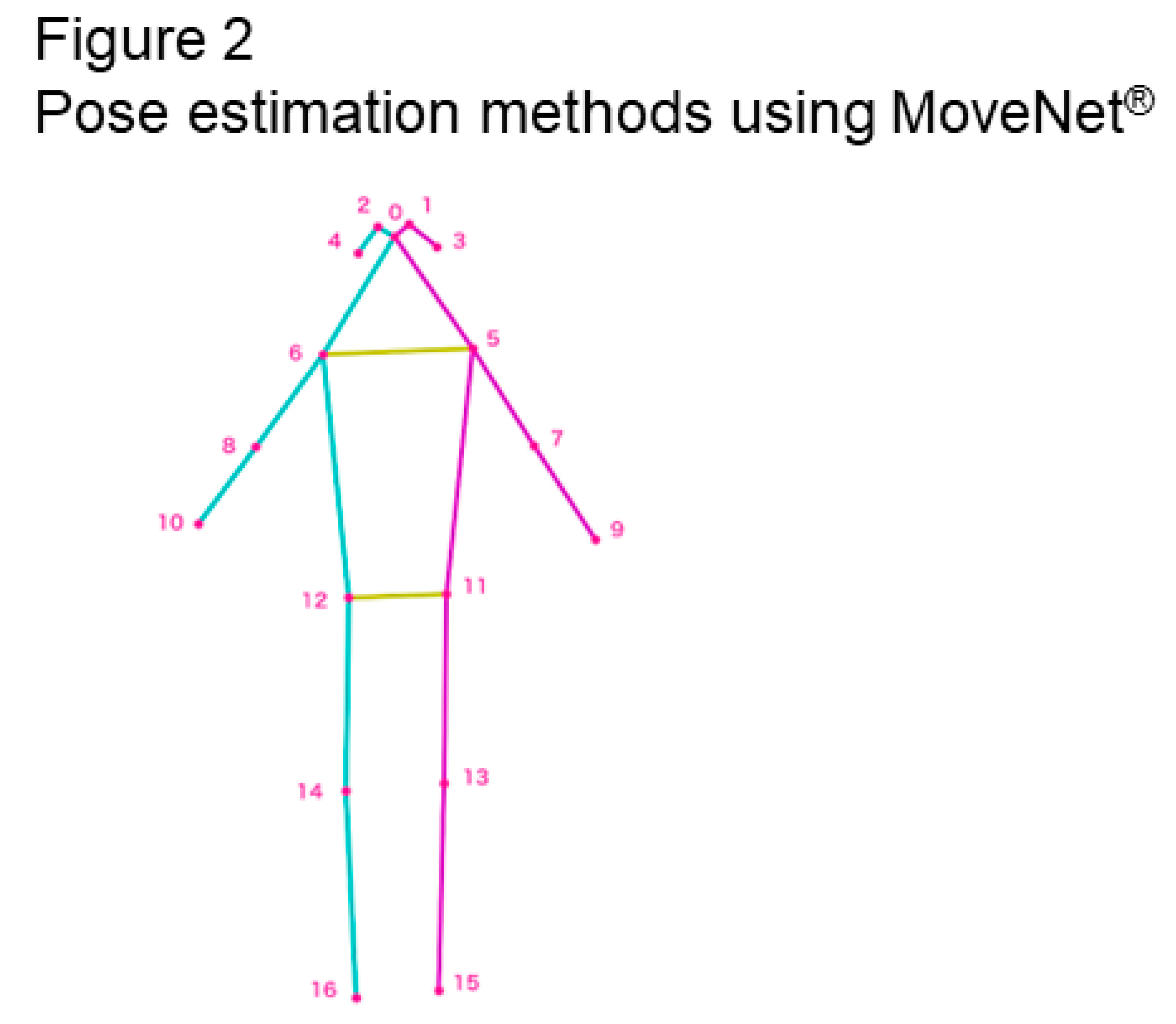
https://www.nature.com/articles/nature14539], which was specifically designed for movement and fitness activities. It takes RGB images as input and outputs the
x and
y coordinates of 17 points of body parts: the nose, left and right eyes, ears, shoulders, elbows, wrists, hips, knees, and ankles (
Figure 2 and
Figure 3). We used the 17 points to analyze posture and define parameters determined by photography (
Table 1 and
Table 2).
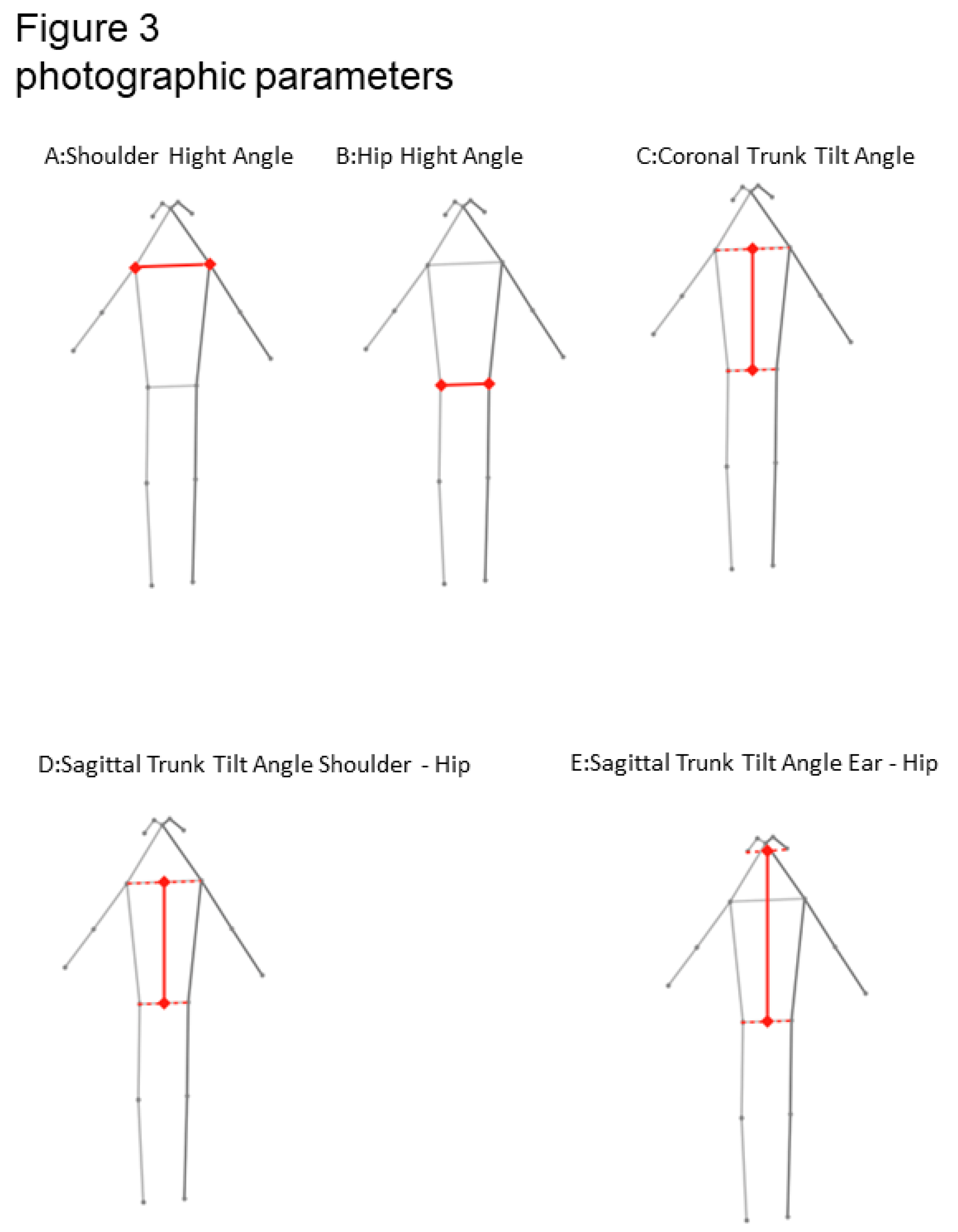
The shoulder height angle (SHA) was defined as the angle formed between the line connecting the left with the right point of the shoulder joint and the horizontal.
The hip height angle (HHA) was defined as the angle formed between the line connecting the left with the right point of the hip and the horizontal.
Sagittal trunk tilt angle_shoulder–hip (STTA_SH) was defined as the angle between the line connecting the middle point of each shoulder joint with the midpoint of each hip joint and the vertical.
Sagittal trunk tilt angle_ear–hip (STTA_EH) was defined as the angle between the line connecting the middle point of each ear with the midpoint of each hip joint and the vertical.
The coronal trunk tilt angle (CTTA) was defined as the angle between the line connecting the middle point of each shoulder joint with the midpoint of each hip joint and the vertical.
2.4. Statistical analysis
The parameters determined by radiography and photography were compared using Pearson correlation coefficients to investigate validity. Correlation coefficients from 0.00 to 0.25 were considered to indicate little to no relationship, from 0.25 to 0.50 fair, from 0.50 to 0.75 moderate-to-good, and above 0.75 good to excellent. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (p < 0.05).
Results
3.1. Overall data
We included data from 12 patients (67% female) eligible for the study (
Table 3). Their average age was 16.08 years (range 14 to 20 years), and their average BMI was 17.99.
They were categorized according to the Lenke classification: type 1A, 7 patients; type 5c, 5 patients.
3.2. Radiological parameters
Average radiological parameters for participants are summarized in
Table 4. In sagittal radiological parameters, the average TTA was –2.42° (range –6 to +3). The average SVA was –6.63 cm (range –77.06 to +52.04). The average TPA was 4.5° (range –13 to +21).
In coronal radiological parameters, the average Cobb was 42.75° (range 20 to 73). The average C7–CSVL was –7.16° (range –24.82 to +19.94). The average Cla-A was –1.75° (range –5 to +3).
The average RSH was –8.84° (range –22.54 to +15.54). The average pelvic obliquity was –0.0083° (range –4 to +3).
3.3. Photographic parameters
The average photographic parameters for the participants are summarized in
Table 5.
In sagittal photographic measurements, the average STTA_SH was –3.27° (range –6.53 to +0.67). The average STTA_EH was 0.003° (range –3.19 to +3.91).
In coronal photographic parameters, the average SHA was 0.080° (range –2.21 to +2.75). The average HHA was 0.45° (range –1.03 to +2.35). The average CTTA was –0.94° (range –2.99 to +1.40).
3.4. Correlations
The correlations between parameters determined by radiology and photography are summarized in
Table 6.
Table 6.
Correlation between photographic and photographic parameters.
Table 6.
Correlation between photographic and photographic parameters.
| Sagittal |
|
STTA_SH |
STTA_EH |
| SVA (mm) |
r |
0.54 |
0.53 |
| |
P |
0.070 |
0.079 |
| TPA (°) |
r |
0.39 |
0.47 |
| |
P |
0.21 |
0.12 |
| TTA |
r |
0.66 |
0.84 |
| |
P |
0.018* |
0.00070* |
| Cla-A |
r |
0.76 |
0.016 |
0.14 |
| |
P |
0.0041* |
0.96 |
0.66 |
| RSH |
r |
0.76 |
–0.030 |
0.14 |
| |
P |
0.0042* |
0.93 |
0.66 |
| C7–CSVL |
r |
0.15 |
0.49 |
0.67 |
| |
P |
0.64 |
0.10 |
0.017* |
| Pelvic Obliquity |
r |
–0.33 |
0.15 |
0.53 |
| |
P |
0.29 |
0.64 |
0.075 |
| Cobb |
r |
–0.033 |
–0.48 |
0.32 |
| |
P |
0.92 |
0.11 |
0.32 |
| Cobb, Cobb angle; C7–CSVL: C7–central sacral vertical line; Cla-A, clavicle angle; RSH, radiographic shoulder height; SHA, shoulder height angle; HHA, hip height angle; CTTA, coronal trunk tilt angle. *P < 0.05 |
3.4.1. Sagittal
There was a significant correlation between TTA and STTA_SH (
r = 0.66,
P = 0.018) and STTA_EH (
r = 0.84,
P < 0.00070). There were no significant correlations between SVA, TPA, and any other parameters determined by photography(
Figure 4 and
Figure 5).
3.4.2. Coronal
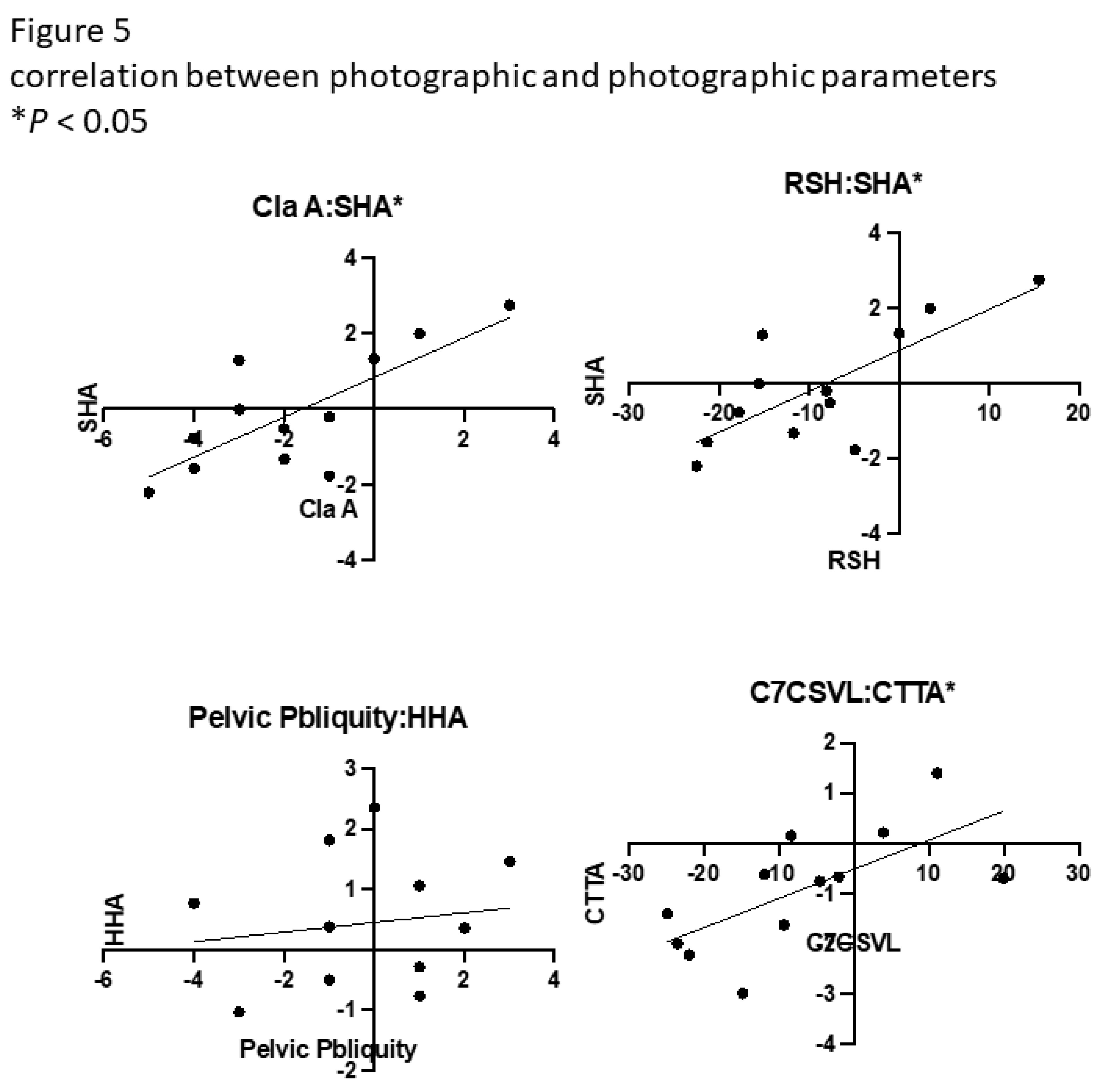
There was a significant correlation between Cla-A and SHA (
r = 0.76,
P = 0.0041), RSH and SHA (
r = 0.76,
P = 0.0042), and C7–CSVL and CTTA (
r = 0.67,
P = 0.017). There were no significant correlations between pelvic obliquity and Cobb angle and any other parameters determined by photography(
Figure 4 and
Figure 5).
Discussion
In the present study, we found a significantly positive correlation between alignment parameters determined by photography and alignment parameters determined by radiography. We found correlations between alignment parameters in the sagittal and coronal planes. These findings suggest that for patients with AIS sufficiently severe to require surgery, shoulder and trunk imbalances may be assessed from photography without exposure to X-ray radiation. To our knowledge, this is the first study to show the correlation between parameters determined by clinical photography using open-source pose estimation methods and parameters determined by conventional radiography in patients with AIS.
Recently, the use of photography for clinical assessment has gradually become more widespread13,19–21. Because trunk asymmetry negatively impacts the body image perception and quality of life of patients with AIS, clinical photography is a relatively easy and inexpensive way to assess trunk deformities.19,22 However, surgeons lack agreement on the use of preoperative clinical photography to determine spinal deformity.23 Therefore, evaluations by clinical photography still require the placement of markers on anatomical landmarks or undressed patients to improve their accuracy.20,24 Assessment of AIS in patients using markers on anatomical landmarks is also attempted for use in medical examinations. Although this method showed a correlation with radiological measurements and good performance in detecting the progression of AIS, clinical application is still considered difficult because the method takes approximately half an hour per patient.13 By contrast, clinical photography with patients in an undressed state without markers is also being considered as a less time-consuming method. Shoulder balance determined by photography of undressed patients may be correlated with Cla-A.4 The waistline asymmetry and ratio of the back area determined by the photography of undressed patients may correlate with the Cobb angle. The waist region measurements of undressed patients can distinguish various curve patterns according to the Lenke classification and are considered a valid method for assessing torso asymmetry in patients with severe AIS.19,25
In these studies, not only were the images taken with patients undressed, but the landmarks were measured manually using software such as ImageJ, which is time-consuming and has an unacceptable interobserver error. Furthermore, clinical photographs have been shown to be useful in assessing cervical spine balance in the sagittal plane, but a manual method for measurement of landmarks was used.26 While clinical photography may be valuable, evaluations requiring markers or the patient in an undressed state are cumbersome to perform, which might explain their lack of widespread use.
One of the advantages of the present method is that patients can be readily photographed with a mobile device without having to undress. In the present study, we found an acceptable correlation between the radiological parameters and those determined by the photography of clothed patients using pose estimation, and the shoulder balance and trunk tilt can be evaluated while the patient is standing clothed. However, because the present study was conducted while patients wore a mask due to COVID-19, it was difficult to obtain accurate facial key points.
Although the use of photogrammetry cannot currently replace radiographs entirely, the amount of information from photography will increase with the progress of machine learning and deep neural networks. Pose estimation is commonly used in the field of kinematics. Although each pose estimation method has a different ability to measure kinematics, which dataset is better is still not well established. MoveNet has the lowest errors when measuring spatiotemporal gait parameters. In addition, there is a correlation between MoveNet and conventional marker-based optical motion capture.27 These findings indicate that this method of pose estimation has the potential to replace conventional methods. Pose estimation is expected to be a breakthrough method to increase the accuracy of evaluations using clinical photography and to decrease interobserver errors.
The present study demonstrated acceptable accuracy using widely available mobile devices. Accordingly, the use of mobile applications with pose estimation is being considered to assess posture, and several studies have found it to be helpful.28 Although pose estimation has received some recognition as a method to evaluate posture, its application to clinical evaluation remains controversial.15,29 While many nonradiographic methods to evaluate scoliosis have been proposed in recent decades,13 clinical photography using pose estimation had not yet been compared with radiography, the criterion standard. To our knowledge, no reports have mentioned its use in patients with AIS.
In the present study, we consider clinical photography using pose estimation. We believe that the present method has clinical utility in improving and promoting the screening and early detection of AIS because it is simple, uses popular mobile devices, avoids exposure of patients to X-ray radiation, and does not require clothed patients to wear markers.
The present study has some limitations. First, the small sample size (n = 12) in the present study restricted our ability to analyze parameters related to posture, and did not have sufficient power to compare those with various Lenke classifications. Future studies should ensure a larger sample size and a control group of children without AIS. Second, we only considered patients with cases of AIS that had required surgery. Therefore, in the present study, the average Cobb angle was 42.75°. Patients treated conservatively should also be considered. Third, we only analyzed pose estimation using MoveNet. In other open-source datasets, further clinically important parameters may be determined by photography. Further development of pose estimation may lead to more useful datasets.
Funding
We did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors for this research.
Acknowledgments
The manuscript submitted does not contain information about medical device(s)/drug(s). No relevant financial activities outside the submitted work.
IRB Statement
The study was approved by our institutional review board.
References
- Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Cheng JCY, Danielsson A, Morcuende JA. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Lancet Lond Engl. 2008 May;371(9623):1527–37. [CrossRef]
- Labelle H, Richards SB, Kleuver MD, Grivas TB, Luk KDK, Wong HK, et al. information statement by the scoliosis research society international task force. 2013; [CrossRef]
- Kuznia AL, Hernandez AK, Lee LU. Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Common Questions and Answers. 2020;101(1).
- Matamalas A, Bagó J, D’Agata E, Pellisé F. Reliability and validity study of measurements on digital photography to evaluate shoulder balance in idiopathic scoliosis. Scoliosis. 2014;9(1):23. [CrossRef]
- Freidel K, Petermann F, Reichel D, Steiner A, Warschburger P, Weiss HR. Quality of life in women with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2002 Feb;27(4):E87-91.
- Ohba T, Goto G, Tanaka N, Oda K, Katsu M, Takei H, et al. Upper Extremity Skeletal Muscle Mass Asymmetry Exacerbated by Shoulder Imbalance in Lenke1A Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 30;11(23):7117. [CrossRef]
- Goldberg MS, Mayo NE, Levy AR, Scott SC, Poîtras B. Adverse reproductive outcomes among women exposed to low levels of ionizing radiation from diagnostic radiography for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Epidemiol Camb Mass. 1998 May;9(3):271–8.
- Ovadia D, Bar-On E, Fragnière B, Rigo M, Dickman D, Leitner J, et al. Radiation-free quantitative assessment of scoliosis: a multi center prospective study. Eur Spine J. 2007 Jan 22;16(1):97–105. [CrossRef]
- Labecka MK, Plandowska M. Moiré topography as a screening and diagnostic tool—A systematic review. Kielbassa AM, editor. PLOS ONE. 2021 Dec 2;16(12):e0260858. [CrossRef]
- Yang S, Jones-Quaidoo SM, Eager M, Griffin JW, Reddi V, Novicoff W, et al. Right adolescent idiopathic thoracic curve (Lenke 1 A and B): does cost of instrumentation and implant density improve radiographic and cosmetic parameters? Eur Spine J. 2011 Jul;20(7):1039–47. [CrossRef]
- Aroeira RMC, Leal JS, Pertence AE de M, Casas EB de L, Greco M. Método não ionizante de rastreamento da escoliose idiopática do adolescente em escolares. Ciênc Saúde Coletiva. 2019 Feb;24(2):523–34.
- Trzcińska S, Kuszewski M, Koszela K. Analysis of Posture Parameters in Patients with Idiopathic Scoliosis with the Use of 3D Ultrasound Diagnostics-Preliminary Results. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr;19(8):4750. [CrossRef]
- Leal JS, Aroeira RMC, Gressler V, Greco M, Pertence AEustáquioM, Lamounier JA. Accuracy of photogrammetry for detecting adolescent idiopathic scoliosis progression. Spine J. 2019 Feb;19(2):321–9. [CrossRef]
- Clark RA, Mentiplay BF, Hough E, Pua YH. Three-dimensional cameras and skeleton pose tracking for physical function assessment: A review of uses, validity, current developments and Kinect alternatives. Gait Posture. 2019 Feb;68:193–200. [CrossRef]
- Hopkins BCB. Validity of PostureScreen Mobile® in the Measurement of Standing Posture. :41.
- Boland DM, Neufeld EV, Ruddell J, Dolezal BA, Cooper CB. Inter- and intra-rater agreement of static posture analysis using a mobile application. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28(12):3398–402. [CrossRef]
- Arima H, Yamato Y, Hasegawa T, Togawa D, Kobayashi S, Yasuda T, et al. Discrepancy Between Standing Posture and Sagittal Balance During Walking in Adult Spinal Deformity Patients. Spine. 2017 Jan 1;42(1):E25–30. [CrossRef]
- Protopsaltis T, Schwab F, Bronsard N, Smith JS, Klineberg E, Mundis G, et al. The T1 Pelvic Angle, a Novel Radiographic Measure of Global Sagittal Deformity, Accounts for Both Spinal Inclination and Pelvic Tilt and Correlates with Health-Related Quality of Life. J Bone Jt Surg. 2014 Oct 1;96(19):1631–40. [CrossRef]
- Bago J, Pizones J, Matamalas A, D’Agata E. Clinical photography in severe idiopathic scoliosis candidate for surgery: is it a useful tool to differentiate among Lenke patterns? Eur Spine J. 2019 Dec;28(12):3018–25. [CrossRef]
- Stolinski L, Kozinoga M, Czaprowski D, Tyrakowski M, Cerny P, Suzuki N, et al. Two-dimensional digital photography for child body posture evaluation: standardized technique, reliable parameters and normative data for age 7-10 years. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2017 Dec;12(1):38. [CrossRef]
- Yusuke Y, Hideki S, Sachiko K, Yuma S, Masaki I, Yasuhito T. Waistline asymmetry is most affects self-image in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Spine Res. 2022 Nov 20;13(11):1177–85.
- Heitz PH, Aubin-Fournier JF, Parent É, Fortin C. Test-retest reliability of posture measurements in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine J. 2018 Dec;18(12):2247–58. [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman SL, Cerpa M, Baum GR, Beauchamp EC, Sielatycki JA, Osorio J, et al. Surgeons lack of agreement on determining preoperative radiographic and clinical shoulder balance in adolescent and adult idiopathic scoliosis patients. Eur Spine J. 2021 Mar;30(3):661–7. [CrossRef]
- Penha PJ, Penha NLJ, De Carvalho BKG, Andrade RM, Schmitt ACB, João SMA. Posture Alignment of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Photogrammetry in Scoliosis School Screening. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2017 Jul;40(6):441–51. [CrossRef]
- Matamalas A, Bagó J, D´Agata E, Pellisé F. Validity and reliability of photographic measures to evaluate waistline asymmetry in idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2016 Oct;25(10):3170–9. [CrossRef]
- Jabbar KM, Gandomi F. The comparison of two corrective exercise approaches for hyperkyphosis and forward head posture: A quasi-experimental study. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2021 Jul 13;34(4):677–87. [CrossRef]
- Washabaugh EP, Shanmugam TA, Ranganathan R, Krishnan C. Comparing the accuracy of open-source pose estimation methods for measuring gait kinematics. Gait Posture. 2022 Sep;97:188–95. [CrossRef]
- Jo B, Kim S. Comparative Analysis of OpenPose, PoseNet, and MoveNet Models for Pose Estimation in Mobile Devices. Trait Signal. 2022 Feb 28;39(1):119–24. [CrossRef]
- Timurtaş E, Avcı EE, Mate K, Karabacak N, Polat MG, Demirbüken İ. A mobile application tool for standing posture analysis: development, validity, and reliability. Ir J Med Sci 1971 -. 2022 Oct;191(5):2123–31. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).